|
Ponzo Illusion
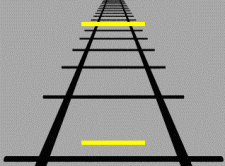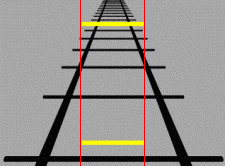
The Ponzo illusion is a geometrical-optical illusion that was first demonstrated by the Italian psychologist Mario Ponzo (1882–1960) in 1911. He suggested that the human mind judges an object's size based on its background. He showed this by drawing two identical lines across a pair of converging lines, similar to railway tracks. The upper line looks longer because we interpret the converging sides according to linear perspective as parallel lines receding into the distance. In this context, we interpret the upper line as though it were farther away, so we see it as longer – a farther object would have to be longer than a nearer one for both to produce retinal images of the same size. One of the explanations for the Ponzo illusion is the "perspective hypothesis", which states that the perspective feature in the figure is obviously produced by the converging lines ordinarily associated with distance, that is, the two oblique lines appear to converge toward the horizon or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponzo Illusion
The Ponzo illusion is a geometrical-optical illusion that was first demonstrated by the Italian psychologist Mario Ponzo (1882–1960) in 1911. He suggested that the human mind judges an object's size based on its background. He showed this by drawing two identical lines across a pair of converging lines, similar to railway tracks. The upper line looks longer because we interpret the converging sides according to linear perspective as parallel lines receding into the distance. In this context, we interpret the upper line as though it were farther away, so we see it as longer – a farther object would have to be longer than a nearer one for both to produce retinal images of the same size. One of the explanations for the Ponzo illusion is the "perspective hypothesis", which states that the perspective feature in the figure is obviously produced by the converging lines ordinarily associated with distance, that is, the two oblique lines appear to converge toward the horizon or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometrical-optical Illusion
Geometrical-optical illusions are visual illusions, also optical illusions, in which the geometrical properties of what is seen differ from those of the corresponding objects in the visual field. Geometrical properties In studying geometry one concentrates on the position of points and on the length, orientation and curvature of lines. Geometrical-optical illusions then relate in the first instance to object characteristics as defined by geometry. Though vision is three-dimensional, in many situations depth can be factored out and attention concentrated on a simple view of a two-dimensional tablet with its x and y co-ordinates.' Illusions are in visual space Whereas their counterparts in the observer's object space are public and have measurable properties, the illusions themselves are private to the observer's (human or animal) experience. Nevertheless, they are accessible to portrayal by verbal and other communication and even to measurement by psychophysics. A nulling technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mario Ponzo
Mario Ponzo (; June 23,1882 – January 9, 1960) was an Italian academic psychologist. He was also the Professor Emeritus of Psychology at the University of Rome as well as the Honorary President of the Italian Society of Psychology. He was born in Milan, Italy to a Piedmontese family. Academic career He went on to study medicine at the University of Turin while also studying psychology under Frederico Kiesow, receiving his degree in 1906. He was appointed docent in psychology in 1911 and worked under Kiesow for twenty-five years after his graduation, until he was asked to join the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Rome in 1931. There, he succeeded Sante De Sanctis as the chair of psychology and remained in the position until his retirement in 1952. After his retirement he worked as a non-staff professor for an additional five years, and was named Professor Emeritus in 1958. He was also involved in vocational guidance while he was in Rome and founded a school at the Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mind
The mind is the set of faculties responsible for all mental phenomena. Often the term is also identified with the phenomena themselves. These faculties include thought, imagination, memory, will, and sensation. They are responsible for various mental phenomena, like perception, pain experience, belief, desire, intention, and emotion. Various overlapping classifications of mental phenomena have been proposed. Important distinctions group them according to whether they are ''sensory'', ''propositional'', ''intentional'', ''conscious'', or ''occurrent''. Minds were traditionally understood as substances but it is more common in the contemporary perspective to conceive them as properties or capacities possessed by humans and higher animals. Various competing definitions of the exact nature of the mind or mentality have been proposed. ''Epistemic definitions'' focus on the privileged epistemic access the subject has to these states. ''Consciousness-based approaches'' give primacy to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
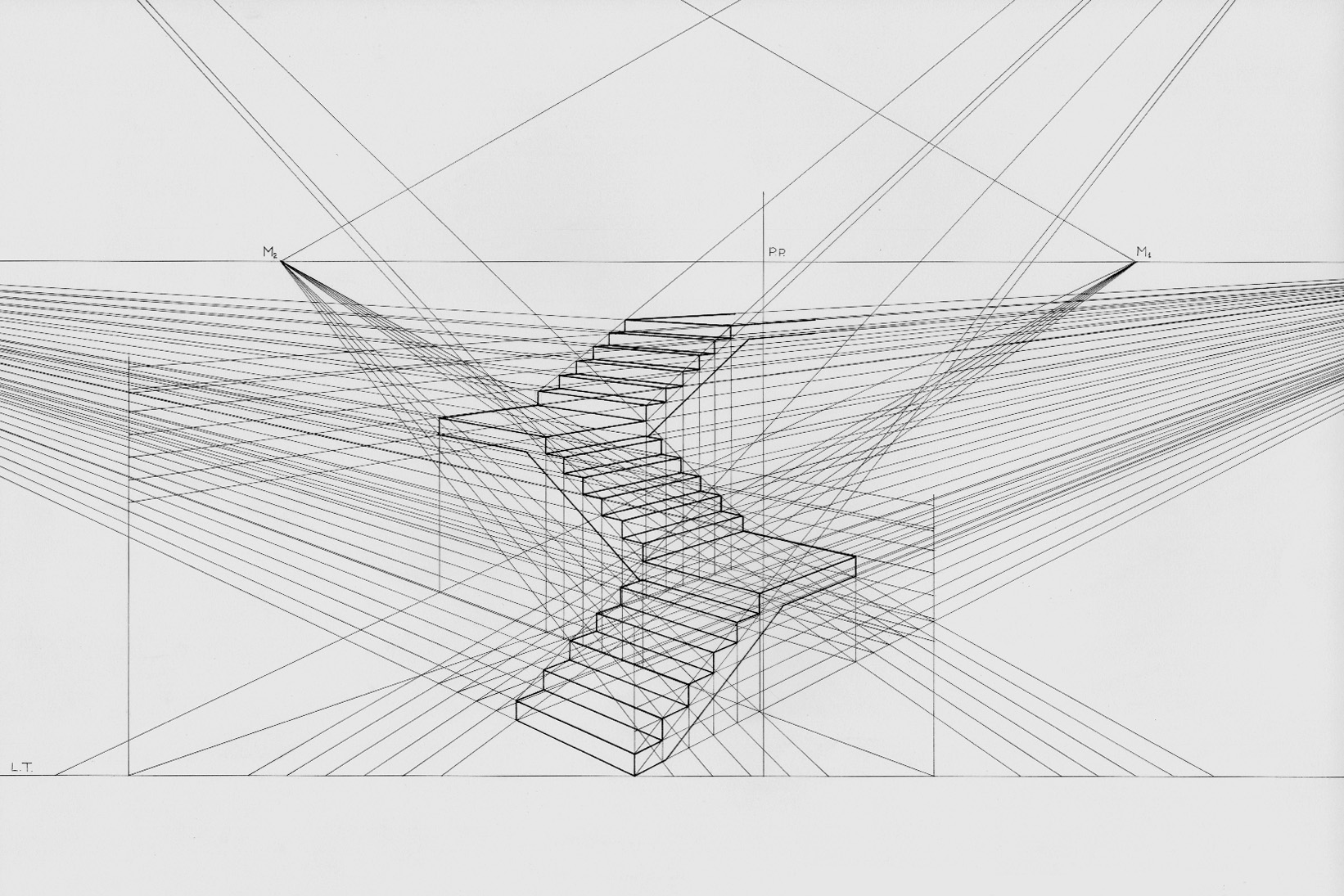
Linear Perspective
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspective Hypothesis
Perspective may refer to: Vision and mathematics * Perspectivity, the formation of an image in a picture plane of a scene viewed from a fixed point, and its modeling in geometry ** Perspective (graphical), representing the effects of visual perspective in graphic arts ** Aerial perspective, the effect the atmosphere has on the appearance of an object as it is viewed from a distance ** Perspective distortion (photography), the way that viewing a picture from the wrong position gives a perceived distortion ** Perspective (geometry), a relation between geometric figures ** Vue d'optique or perspective view, a genre of etching popular during the second half of the 18th century and into the 19th. Entertainment * ''Perspective'' (P-Model album), 1982 * ''Perspective'' (America album), 1984 * ''Perspective'' (Jason Becker album), 1996 * ''Perspective'' (Lawson album), 2016 * ''Perspective'', a 2010 album by Prague * Perspective (EP), an EP by Tesseract * ''Perspectives'' (album), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanishing Point
A vanishing point is a point on the image plane of a perspective drawing where the two-dimensional perspective projections of mutually parallel lines in three-dimensional space appear to converge. When the set of parallel lines is perpendicular to a picture plane, the construction is known as one-point perspective, and their vanishing point corresponds to the oculus, or "eye point", from which the image should be viewed for correct perspective geometry.Kirsti Andersen (2007) ''Geometry of an Art'', p. xxx, Springer, Traditional linear drawings use objects with one to three sets of parallels, defining one to three vanishing points. Italian humanist polymath and architect Leon Battista Alberti first introduced the concept in his treatise on perspective in art, '' De pictura'', written in 1435. Vector notation The vanishing point may also be referred to as the "direction point", as lines having the same directional vector, say ''D'', will have the same vanishing point. Mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Substitution
Sensory substitution is a change of the characteristics of one sensory modality into stimuli of another sensory modality. A sensory substitution system consists of three parts: a sensor, a coupling system, and a stimulator. The sensor records stimuli and gives them to a coupling system which interprets these signals and transmits them to a stimulator. In case the sensor obtains signals of a kind not originally available to the bearer it is a case of sensory augmentation. Sensory substitution concerns human perception and the plasticity of the human brain; and therefore, allows us to study these aspects of neuroscience more through neuroimaging. Sensory substitution systems may help people by restoring their ability to perceive certain defective sensory modality by using sensory information from a functioning sensory modality. History The idea of sensory substitution was introduced in the 1980s by Paul Bach-y-Rita as a means of using one sensory modality, mainly taction, to gai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |