peace of Antalcidas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The King's Peace (387 BC) was a
The King's Peace (387 BC) was a
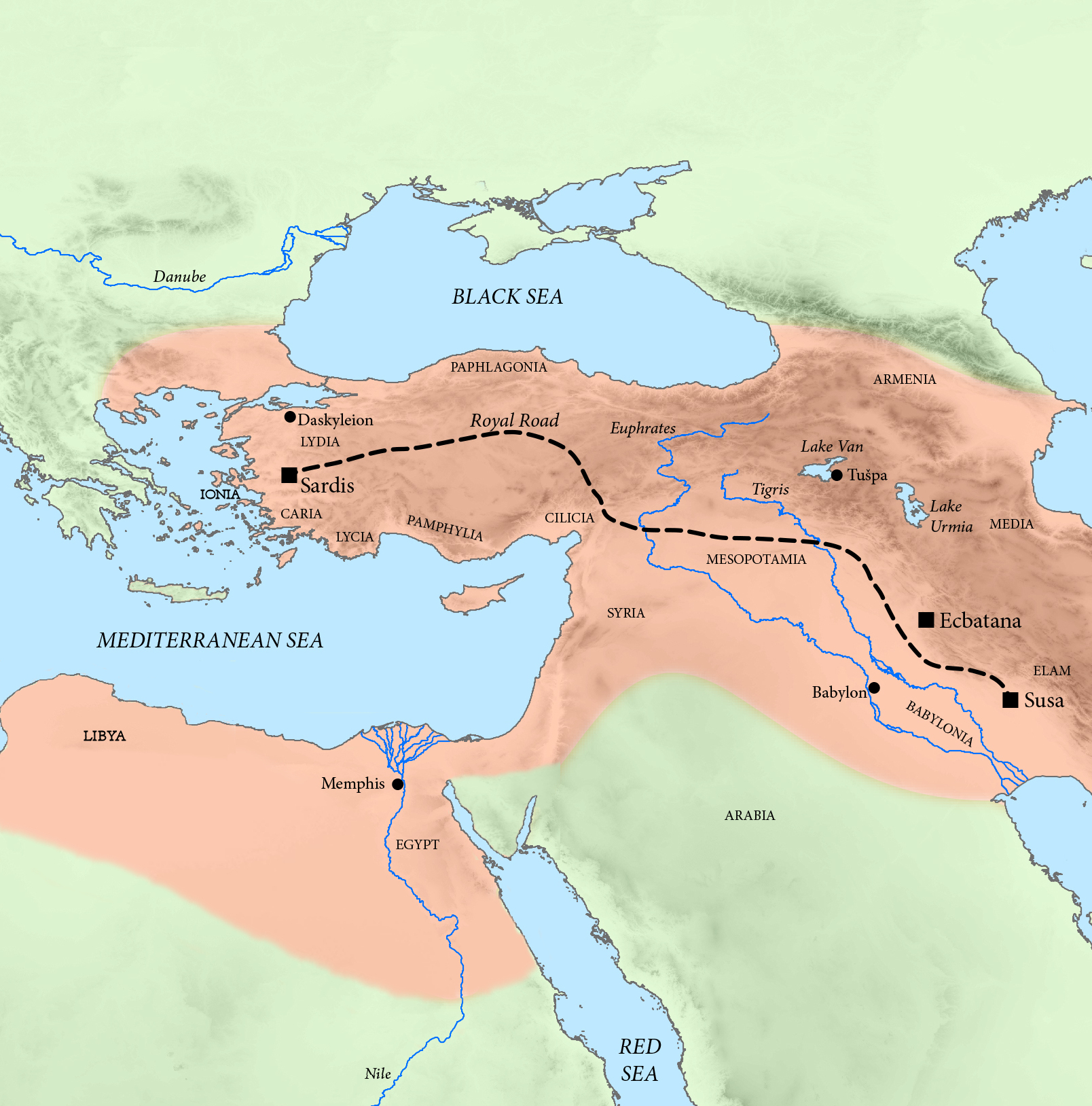 To bring the Athenians to the negotiating table, Antalcidas then moved his fleet of 90 ships to the Hellespont, where he could threaten the
To bring the Athenians to the negotiating table, Antalcidas then moved his fleet of 90 ships to the Hellespont, where he could threaten the
 The most notable feature of the King's Peace is the Persian influence it reflects. The Persian decree that established the terms of the peace, as recorded by
The most notable feature of the King's Peace is the Persian influence it reflects. The Persian decree that established the terms of the peace, as recorded by
 A second effect of this "most disgraceful event in Greek history", as
A second effect of this "most disgraceful event in Greek history", as
 The King's Peace (387 BC) was a
The King's Peace (387 BC) was a peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring ...
guaranteed by the Persian King Artaxerxes II
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and suc ...
that ended the Corinthian War
The Corinthian War (395–387 BC) was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The war was caused by dissatisfaction with ...
in ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
. The treaty is also known as the Peace of Antalcidas, after Antalcidas
Antalcidas ( grc-gre, Ἀνταλκίδας; died BC), son of Leon, was an ancient Greek soldier, politician, and diplomat from Sparta.
__NOTOC__
Life
Antalcidas came from a prominent family and was likely a relation by marriage to the Spa ...
, the Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
n diplomat who traveled to Susa to negotiate the terms of the treaty with the king of Achaemenid Persia
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
. The treaty was more commonly known in antiquity, however, as the King's Peace, a name that reflects the depth of Persian influence in the treaty, as Persian gold had driven the preceding war. The treaty was a form of Common Peace
The idea of the Common Peace (Κοινὴ Εἰρήνη, ''Koinē Eirēnē'') was one of the most influential concepts of 4th century BC Greek political thought, along with the idea of Panhellenism. The term described both the concept of a desirabl ...
, similar to the Thirty Years' Peace
The Thirty Years' Peace was a treaty signed between the ancient Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta in 446/445 BC. The treaty brought an end to the conflict commonly known as the First Peloponnesian War, which had been raging since c. 460 BC.
B ...
which ended the First Peloponnesian War
The First Peloponnesian War (460–445 BC) was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, Greece, Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Ancient Argos, ...
.
The end of the war
By 387 BC, the central front of the Corinthian War had shifted from the Greek mainland to the Aegean, where anAthenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
fleet under Thrasybulus
Thrasybulus (; grc-gre, Θρασύβουλος ; 440 – 388 BC) was an Athenian general and democratic leader. In 411 BC, in the wake of an oligarchic coup at Athens, the pro-democracy sailors at Samos elected him as a general, making him a ...
had successfully placed a number of cities across the Aegean under Athenian control, and was acting in collaboration with Evagoras, the king of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geo ...
. Since Evagoras was an enemy of Persia, and many of the Athenian gains threatened Persian interests, these developments prompted Artaxerxes to switch his support from Athens and her allies to Sparta. Antalcidas
Antalcidas ( grc-gre, Ἀνταλκίδας; died BC), son of Leon, was an ancient Greek soldier, politician, and diplomat from Sparta.
__NOTOC__
Life
Antalcidas came from a prominent family and was likely a relation by marriage to the Spa ...
, the commander of a Spartan fleet, was summoned to Susa, along with the satrap, Tiribazus
Tiribazus, Tiribazos or Teribazus (Old Iranian: ''Tīrībāzu'') (c.440 BC-370 BC) was an Achaemenid satrap of Western Armenia and later satrap of Lydia in western Anatolia.
Satrap of Western Armenia
He was highly regarded by the Persian King Ar ...
. There, the Spartans and Persians worked out the form of an agreement to end the war.
 To bring the Athenians to the negotiating table, Antalcidas then moved his fleet of 90 ships to the Hellespont, where he could threaten the
To bring the Athenians to the negotiating table, Antalcidas then moved his fleet of 90 ships to the Hellespont, where he could threaten the trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
s along which the Athenians imported grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
from the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
region. The Athenians, mindful of their disastrous defeat in 404 BC, when the Spartans had gained control of the Hellespont, agreed to negotiate, and Thebes, Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
, and Argos
Argos most often refers to:
* Argos, Peloponnese, a city in Argolis, Greece
** Ancient Argos, the ancient city
* Argos (retailer), a catalogue retailer operating in the United Kingdom and Ireland
Argos or ARGOS may also refer to:
Businesses
...
, unwilling to fight on without Athens, were also forced to negotiate. In a peace conference at Sparta, all the belligerents agreed to the terms laid down by Artaxerxes.
Terms of the peace
 The most notable feature of the King's Peace is the Persian influence it reflects. The Persian decree that established the terms of the peace, as recorded by
The most notable feature of the King's Peace is the Persian influence it reflects. The Persian decree that established the terms of the peace, as recorded by Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, wikt:Ξενοφῶν, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Anci ...
, clearly shows this:
Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian ...
and Cyprus were abandoned to the Persians, and the Athenians were compelled to cede their newly-won territories in the Aegean. Equally significantly, the insistence on autonomy put an end to a novel political experiment that had grown out of the war, the union of Argos and Corinth. In what the Greeks called '' sympoliteia'', the two cities had politically merged, granting all citizens joint citizenship
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
. They were forced to separate, and the Thebans were required to disband their Boeotia
Boeotia ( ), sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia ( el, Βοιωτία; modern: ; ancient: ), formerly known as Cadmeis, is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its ...
n league. Only Sparta's Peloponnesian League and helots
The helots (; el, εἵλωτες, ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their e ...
were overlooked, as the Spartans, who were responsible for administering the peace, had no wish to see the principle of independence applied there.
Effects
The single greatest effect of the Peace was the return of firm Persian control over Ionia and parts of the Aegean. Driven back from the Aegean shores by the Delian League during the 5th century, the Persians had been recovering their position since the later part of the Peloponnesian War, and were now strong enough to dictate terms to Greece. They would maintain this position of strength until the time ofAlexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
. As Mikhail Gasparov states in his book ''Greece for Entertainment'' ('' Занимательная Греция''), "Artaxerxes had succeeded where Xerxes had failed; the Persian King was giving orders in Greece like it was his, and without bringing in a single soldier at that." In short, the treaty placed Greece under Persian suzerainty.
 A second effect of this "most disgraceful event in Greek history", as
A second effect of this "most disgraceful event in Greek history", as Will Durant
William James Durant (; November 5, 1885 – November 7, 1981) was an American writer, historian, and philosopher. He became best known for his work '' The Story of Civilization'', which contains 11 volumes and details the history of eastern a ...
characterized it, was the establishment of Sparta in a formalized position at the top of a Greek political system enforced by the Great King. Using their mandate to protect and enforce the peace, the Spartans proceeded to launch a number of campaigns against ''poleis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
'' that they perceived as political threats. Near at hand, they forced the city of Mantinea
Mantineia (also Mantinea ; el, Μαντίνεια; also Koine Greek ''Antigoneia'') was a city in ancient Arcadia, Greece, which was the site of two significant battles in Classical Greek history.
In modern times it is a former municipality in ...
in Arcadia, to disband into its constituent villages.Simon Hornblower, in John Boardman, Jasper Griffin and Oswyn Murray, ''Greece and the Hellenistic World'' (Oxford)141. The largest intervention was a campaign in 382 BC to break up the federalist Chalcidian League
The Chalcidian League ( el, Κοινόν τῶν Χαλκιδέων, ''Koinon tōn Chalkideōn'', "League of the Chalcidians"), also referred to as the Olynthians or the Chalcidians in Thrace (, ''Chalkideis epi Thrakēs'') to distinguish them fr ...
in northeastern Greece, as violating the autonomy principle of the Great King's decree. On the way there, in 383 the Spartan commander Phoebidas Phoebidas ( el, Φοιβίδας) was a Spartan general who, in 382 BC, seized the Theban acropolis, thus giving Sparta control over Thebes. To punish his unauthorized action, Phoebidas was relieved of command. Nevertheless, the Spartans continued ...
, invited by a pro-Spartan faction, seized the Theban Kadmeia (the Theban acropolis) and left a Laconophile Laconophilia is love or admiration of Sparta and of the Spartan culture or constitution. The term derives from Laconia, the part of the Peloponnesus where the Spartans lived.
Admirers of the Spartans typically praise their valour and success in wa ...
oligarchy supported by a Spartan garrison; even the pro-Spartan Xenophon could only attribute the act to madness. The principle of autonomy proved to be a flexible tool in the hand of a hegemonic power.
The King's Peace was not successful in bringing peace to Greece. Pelopidas
Pelopidas (; grc-gre, Πελοπίδας; died 364 BC) was an important Theban statesman and general in Greece, instrumental in establishing the mid-fourth century Theban hegemony.
Biography
Athlete and warrior
Pelopidas was a member of a ...
and companions liberated Thebes in 379 by assassinating the Laconizing tyrants. After the campaign against Olynthus
Olynthus ( grc, Ὄλυνθος ''Olynthos'', named for the ὄλυνθος ''olunthos'', "the fruit of the wild fig tree") was an ancient city of Chalcidice, built mostly on two flat-topped hills 30–40m in height, in a fertile plain at the he ...
in 382, general fighting resumed with the revived Athenian naval confederacy and continued, with intermittent attempts to restore the peace, for much of the next two decades. The idea of a Common Peace
The idea of the Common Peace (Κοινὴ Εἰρήνη, ''Koinē Eirēnē'') was one of the most influential concepts of 4th century BC Greek political thought, along with the idea of Panhellenism. The term described both the concept of a desirabl ...
proved to be enduring, however, and numerous attempts would be made to establish one, with little more success than the original. By granting powers to Sparta that were sure to infuriate other states when used, the treaties sowed the seeds of their own demise, and a state of near-constant warfare continued to be the norm in Greece.
See also
*List of treaties
This list of treaties contains known agreements, pacts, peaces, and major contracts between states, armies, governments, and tribal groups.
Before 1200 CE
1200–1299
1300–1399
1400–1499
1500–1599
1600–1699
1700–1799
...
Notes
References
*Fine, John V.A. ''The Ancient Greeks: A Critical History'' (Harvard University Press, 1983) * {{Authority control 387 BC Wars involving ancient GreeceAntalcidas
Antalcidas ( grc-gre, Ἀνταλκίδας; died BC), son of Leon, was an ancient Greek soldier, politician, and diplomat from Sparta.
__NOTOC__
Life
Antalcidas came from a prominent family and was likely a relation by marriage to the Spa ...
Antalcidas
Antalcidas ( grc-gre, Ἀνταλκίδας; died BC), son of Leon, was an ancient Greek soldier, politician, and diplomat from Sparta.
__NOTOC__
Life
Antalcidas came from a prominent family and was likely a relation by marriage to the Spa ...
Corinthian War
4th-century BC treaties
Artaxerxes II