Pateros Creek Brewing Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pateros, officially the Municipality of Pateros ( tgl, Bayan ng Pateros), is the lone municipality of Metro Manila, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,643 people.
This municipality is famous for its duck-raising industry and especially for producing '' balut'', a Filipino delicacy, which is a boiled, fertilised duck egg. Pateros is also known for the production of red salty eggs and "''inutak''", a local rice cake. Moreover, the town is known for manufacturing of "''alfombra''", a locally-made footwear with a carpet-like fabric on its top surface. Pateros is bordered by the following highly urbanized cities of Pasig to the north, Makati to the west, and Taguig to the south.
Pateros is the smallest municipality both in population and in land area, in Metro Manila, but it is the second most densely populated at around 29,000 people per square kilometer after Manila.
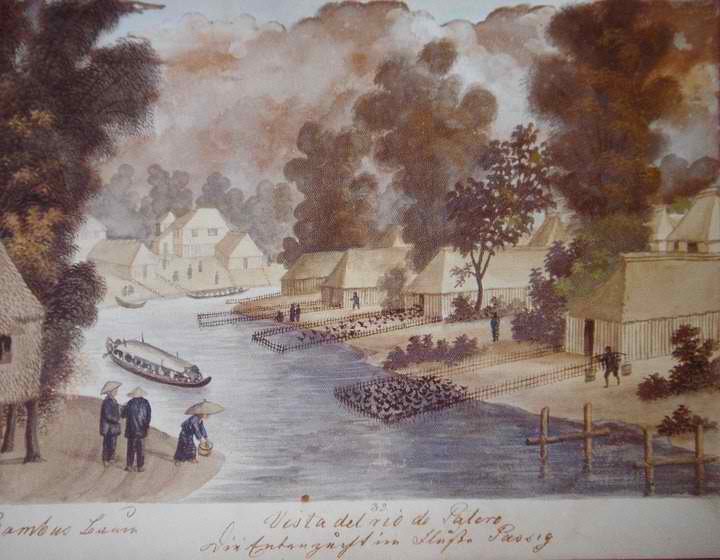 Before 1770, Pateros was only a ''barrio'' of Pasig until the Spanish Governor-General of the Philippines issued a decree making Pateros an independent municipality. The town was then composed of five barangays (villages): Aguho, San Roque, Santa Ana, Santo Rosario (Santo Rosario-Silangan and Santo Rosario-Kanluran), and Mamancat (now part of Fort Bonifacio).
Before 1770, Pateros was only a ''barrio'' of Pasig until the Spanish Governor-General of the Philippines issued a decree making Pateros an independent municipality. The town was then composed of five barangays (villages): Aguho, San Roque, Santa Ana, Santo Rosario (Santo Rosario-Silangan and Santo Rosario-Kanluran), and Mamancat (now part of Fort Bonifacio).
 During the
During the

SC wants Ft. Bonifacio land dispute settled amicably
'. Manila Bulletin. Pursuant to the decision, Pateros invited Makati to a council-to-council dialogue. This happened on October 8, 2009. Four meetings were held and at the fourth dialogue on November 23, 2009, a joint resolution was made stating that Makati is requesting a tripartite conference between Pateros, Taguig and Makati.Rosales, D. 2010, April. Update: Fort Bonifacio claim. ''Susi ng Pateros'', 1 & 4.
 As of 1818, the population was estimated at 3,840 Tagalog peoples. When Edmund Roberts visited in 1834, he estimated approximately 4,500 residents.
According to the town's 2005 land use classification report 91.62% of Pateros' land is classified as residential.
As of 1818, the population was estimated at 3,840 Tagalog peoples. When Edmund Roberts visited in 1834, he estimated approximately 4,500 residents.
According to the town's 2005 land use classification report 91.62% of Pateros' land is classified as residential.
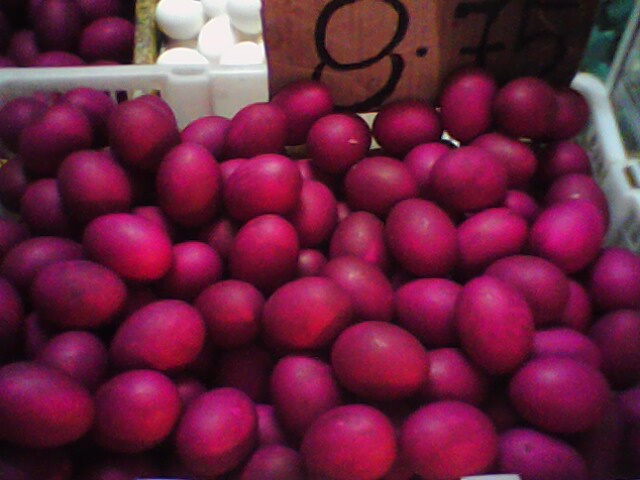 The town of Pateros is known for balut and had a duck raising industry. As early as 1834, Pateros has been raising and selling duck and maintaining a fishing industry. However, since the duck raising industry declined after the Pasig River, which is connected to the Pateros River too polluted around the 1970s or 1980s.
Vendors continues to sell balut in Pateros, taking advantage of the association of the food item to the town with duck eggs supplied from neighboring provinces in the Calabarzon region. While the duck raising industry in the town is now minimal, the local government is encouraging the growth of the balut industry. It gives tax exemptions to balut vendors in the town. As of 2017, the local government is encouraging the growth of other industries in Pateros such as business process outsourcing although the town's size, , remains a hindrance.
According to the town's 2005 classification report. 3.13% of its land area is classified as commercial, 0.39% industrial, and 0.88% agricultural.
The town of Pateros is known for balut and had a duck raising industry. As early as 1834, Pateros has been raising and selling duck and maintaining a fishing industry. However, since the duck raising industry declined after the Pasig River, which is connected to the Pateros River too polluted around the 1970s or 1980s.
Vendors continues to sell balut in Pateros, taking advantage of the association of the food item to the town with duck eggs supplied from neighboring provinces in the Calabarzon region. While the duck raising industry in the town is now minimal, the local government is encouraging the growth of the balut industry. It gives tax exemptions to balut vendors in the town. As of 2017, the local government is encouraging the growth of other industries in Pateros such as business process outsourcing although the town's size, , remains a hindrance.
According to the town's 2005 classification report. 3.13% of its land area is classified as commercial, 0.39% industrial, and 0.88% agricultural.
 *Pateros (
*Pateros (
 The following are the different Elementary and High schools in Pateros under Pateros School District of the Department of Education – Schools Division of Taguig and Pateros, a Community college recognized by Commission on Higher Education.
The following are the different Elementary and High schools in Pateros under Pateros School District of the Department of Education – Schools Division of Taguig and Pateros, a Community college recognized by Commission on Higher Education.
Municipality of Pateros official websiteMunicipality of Pateros official website
* {{Authority control Municipalities of Metro Manila Populated places established in 1770 1770 establishments in the Philippines
Etymology
The name ''Pateros'' is most likely derived from the duck-raising industry. TheTagalog
Tagalog may refer to:
Language
* Tagalog language, a language spoken in the Philippines
** Old Tagalog, an archaic form of the language
** Batangas Tagalog, a dialect of the language
* Tagalog script, the writing system historically used for Tagal ...
word (of Spanish origin) for "duck" is ''pato'' and ''pateros'', "duck-raisers". The early 19th-century U.S. diplomat Edmund Roberts used Duck-town, another name for Pateros, stating that he "never before saw so many ducks together" in one place. The duck reference is perfectly suited for Pateros, whose popular culinary specialty is a street food. called Balut (food), a fertilized developing duck embryo that is boiled and eaten from the shell. Several ''balutans'' like the famous El Patu at 425 F. Imson Street offer this unique cuisine as well as street merchants selling them on the side of the road.
History
Early Late History
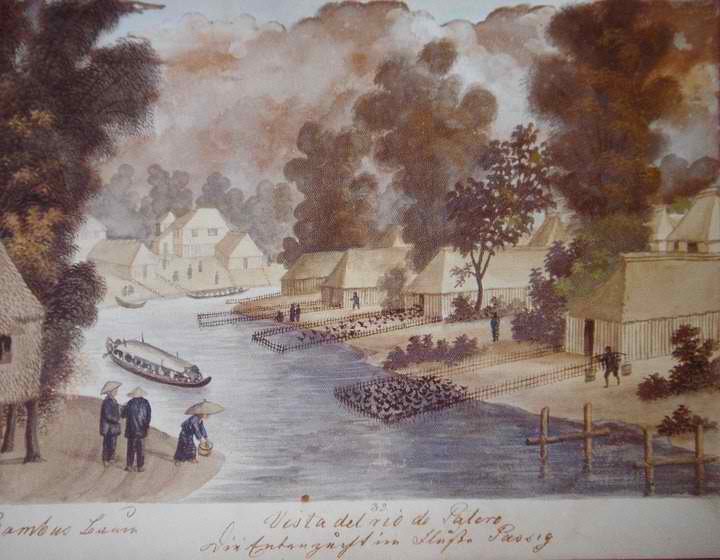 Before 1770, Pateros was only a ''barrio'' of Pasig until the Spanish Governor-General of the Philippines issued a decree making Pateros an independent municipality. The town was then composed of five barangays (villages): Aguho, San Roque, Santa Ana, Santo Rosario (Santo Rosario-Silangan and Santo Rosario-Kanluran), and Mamancat (now part of Fort Bonifacio).
Before 1770, Pateros was only a ''barrio'' of Pasig until the Spanish Governor-General of the Philippines issued a decree making Pateros an independent municipality. The town was then composed of five barangays (villages): Aguho, San Roque, Santa Ana, Santo Rosario (Santo Rosario-Silangan and Santo Rosario-Kanluran), and Mamancat (now part of Fort Bonifacio).
1899 Philippine-American War
 During the
During the Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
in March 1899, the first contingent of American Volunteers from Washington arrived in the town of Pateros. The American soldiers rallied and eventually won the battles to take control and establish a temporary camp. Throughout this period, American soldiers were able to experience the culture and livelihood of the citizens of Pateros. Having roast duck for meals during wartime and sending postcards of Pateros back to the United States of America. In 1900, a member of the American contingent, Lieutenant Charles Nosler, renamed the city of Ive's Landing in Washington State, USA, after the town of Pateros in the Philippines. Pateros in Washington State officially became an American city on May 1, 1913.
Inclusion to newly created province of Rizal
On March 29, 1900, Pateros, then a part of the province of Manila, became one of the towns in the newly created province ofRizal
Rizal, officially the Province of Rizal ( fil, Lalawigan ng Rizal), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region in Luzon. Its capital is the city of Antipolo. It is about east of Manila. The p ...
, by virtue of ''General Order No. 40, Act No. 137 of the Philippine Commission'', which was promulgated on June 11, 1901. Then on October 12, 1903, Act No. 942 united Pateros with Taguig and Muntinlupa into one municipality under Pateros. The municipality was renamed Taguig and Muntinlupa was separated from it on March 22, 1905, through Act No. 1308.
Executive Order No. 20 dated February 29, 1908, partitioned Pateros from Taguig, and the town regained independent status as a municipality on January 1, 1909, by Executive Order No. 36.
Incorporation to Metropolitan Manila
On November 7, 1975, Pateros became a part of the new Metropolitan Manila Area through Presidential Decree No. 824, which mandated by PresidentFerdinand Marcos
Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. ( , , ; September 11, 1917 – September 28, 1989) was a Filipino politician, lawyer, dictator, and kleptocrat who was the 10th president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. He ruled under martial ...
.
International partnership
On July 23, 2013, Mayor Jaime C. Medina visited the city of Pateros, Washington State, United States to sign the ''Sister City Memorandum of Understanding between the Municipality of Pateros, Metro Manila and Pateros City of Okanogan County, Washington State, USA''. According to Mayor Gail Howe, the two cities have not applied through Sister Cities International but the goals of promoting the culture and exchanges have turned the sisterhood into reality.Conversion to cityhood attempt
TheInauguration of Rodrigo Duterte
The inauguration of Rodrigo Duterte as the 16th president of the Philippines took place at around noon ( PHT) on Thursday, June 30, 2016 at the Rizal Ceremonial Hall of the Malacañang Palace in Manila. The oath of office was administered b ...
to presidency that took place on June 30, 2016, paved way to another attempt of the conversion of the town into a city and constituting into two congressional districts through the collaborative efforts of the municipal government of Pateros spearheaded by Mayor Miguel Ponce III and the most especially by the passage of a house bill sponsored by Pateros-Taguig Representative Arnel Cerafica.
Geography
Climate
Barangays
Pateros is politically subdivided into 10 barangays:
Boundary dispute
The municipal government of Pateros claims that its original land area was not its present land area of but including Fort Bonifacio, particularly theEmbo
Embo ( gd, Eurabol, IPA: �iaɾəpɔɫ̪ is a village in the Highland Council Area in Scotland and the former postal county of Sutherland, about north-northeast of Dornoch.
On 16 July 1988, Embo declared itself independent from the rest of the ...
barangays Comembo, Pembo, East Rembo, West Rembo, Cembo, South Cembo and Pitogo which are now part of the city of Makati and Bonifacio Global City
Bonifacio may refer to:
Places
* Bonifacio, Corse-du-Sud, a town in Corsica, France
* Strait of Bonifacio, separating Corsica from Sardinia
* Bonifacio, Misamis Occidental, a municipality in the Philippines
* Bonifacio Global City, a central bu ...
(known as Post Proper Northside and Post Proper Southside by Makati, and Mamancat, Masilang, San Nicolas, and Malapadnabato, former parts of Pateros) which was made part of Taguig, based on documents and official maps obtained by former Pateros Councilor Dominador Rosales from 30 libraries and offices including USA Library of Congress and USA Archives. One of those maps was the 1968 Land Classification Map of the Bureau of Land.Rosales, D. 2009, November. ''Sanhi ng pagliit ng Pateros. Susi ng Pateros'', 5.
Pateros' decrease in territory was accounted to a cadastral mapping in Metro Manila conducted in 1978. Pateros Mayor Nestor Ponce challenged the map through an objection letter dated June 23, 1978. But in January 1986, then President Ferdinand Marcos issued Proclamation No. 2475 which stated that Fort Bonifacio is situated in Makati and it is open for disposition. Because of that, a boundary dispute arose which moved Pateros to request a dialogue about that with then Municipal Council of Makati in 1990. Pateros also filed a complaint against Makati at the Makati Regional Trial Court in 1996 but the trial court dismissed the case for lack of jurisdiction. The case was brought to the Court of Appeals in 2003 but the case was also denied. The same case was also elevated to the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
in 2009 but it was denied again.
Supreme Court decision
Almost 2 decades later, the Supreme Court on June 16, 2009, per Antonio Eduardo B. Nachura denied Pateros' petition against Makati but ruled out that the boundary dispute should be settled amicably by their respective legislative bodies based on Section 118(d) of the Local Government Code.Panaligan, R. 2009, June 22.SC wants Ft. Bonifacio land dispute settled amicably
'. Manila Bulletin. Pursuant to the decision, Pateros invited Makati to a council-to-council dialogue. This happened on October 8, 2009. Four meetings were held and at the fourth dialogue on November 23, 2009, a joint resolution was made stating that Makati is requesting a tripartite conference between Pateros, Taguig and Makati.Rosales, D. 2010, April. Update: Fort Bonifacio claim. ''Susi ng Pateros'', 1 & 4.
Demographics
 As of 1818, the population was estimated at 3,840 Tagalog peoples. When Edmund Roberts visited in 1834, he estimated approximately 4,500 residents.
According to the town's 2005 land use classification report 91.62% of Pateros' land is classified as residential.
As of 1818, the population was estimated at 3,840 Tagalog peoples. When Edmund Roberts visited in 1834, he estimated approximately 4,500 residents.
According to the town's 2005 land use classification report 91.62% of Pateros' land is classified as residential.
Economy
 The town of Pateros is known for balut and had a duck raising industry. As early as 1834, Pateros has been raising and selling duck and maintaining a fishing industry. However, since the duck raising industry declined after the Pasig River, which is connected to the Pateros River too polluted around the 1970s or 1980s.
Vendors continues to sell balut in Pateros, taking advantage of the association of the food item to the town with duck eggs supplied from neighboring provinces in the Calabarzon region. While the duck raising industry in the town is now minimal, the local government is encouraging the growth of the balut industry. It gives tax exemptions to balut vendors in the town. As of 2017, the local government is encouraging the growth of other industries in Pateros such as business process outsourcing although the town's size, , remains a hindrance.
According to the town's 2005 classification report. 3.13% of its land area is classified as commercial, 0.39% industrial, and 0.88% agricultural.
The town of Pateros is known for balut and had a duck raising industry. As early as 1834, Pateros has been raising and selling duck and maintaining a fishing industry. However, since the duck raising industry declined after the Pasig River, which is connected to the Pateros River too polluted around the 1970s or 1980s.
Vendors continues to sell balut in Pateros, taking advantage of the association of the food item to the town with duck eggs supplied from neighboring provinces in the Calabarzon region. While the duck raising industry in the town is now minimal, the local government is encouraging the growth of the balut industry. It gives tax exemptions to balut vendors in the town. As of 2017, the local government is encouraging the growth of other industries in Pateros such as business process outsourcing although the town's size, , remains a hindrance.
According to the town's 2005 classification report. 3.13% of its land area is classified as commercial, 0.39% industrial, and 0.88% agricultural.
Government
Official seal
 *Pateros (
*Pateros (Mallard
The mallard () or wild duck (''Anas platyrhynchos'') is a dabbling duck that breeds throughout the temperate and subtropical Americas, Eurasia, and North Africa, and has been introduced to New Zealand, Australia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay, Arge ...
) Duck, symbolizes the duck-raising industry where town was known.
* Ten duck eggs represents the barangay which Pateros was politically subdivided; it also signifies the Balut industry of the town.
Education
 The following are the different Elementary and High schools in Pateros under Pateros School District of the Department of Education – Schools Division of Taguig and Pateros, a Community college recognized by Commission on Higher Education.
The following are the different Elementary and High schools in Pateros under Pateros School District of the Department of Education – Schools Division of Taguig and Pateros, a Community college recognized by Commission on Higher Education.
Secondary public schools
Secondary Institutions *Mayor Simplicio Manalo National High School *Maria Concepcion Cruz High School * Pateros National High SchoolTertiary
* Pateros Technological CollegePrivate schools
*APEC Schools
APEC Schools is a chain of private high schools based in the Philippines. It is one of subsidiary schools of IPO, the merger of the education businesses of Ayala Corporation and Yuchengco's House of Investments. APEC Schools currently has branches ...
- Pateros (Santo Rosario-Silangan)
* Pateros Catholic School
* Saint Genevieve School of Pateros
* Maranatha Christian Academy
* SEP Christian School Inc.
* Huckleberry Montessori School
Notable personalities
*Pelagia Mendoza y Gotianquin Pelagia Mendoza y Gotianquin (1867–1939) was the first female sculptor in the Philippines and was the first female student at the Escuela de Dibujo y Pintura (Drawing and Painting School).
Biography
Born in the Pateros district of Manila on 9 Jun ...
- first female sculptor in the Philippines and was the first female student at the Escuela de Dibujo y Pintura (Drawing and Painting School).
* Socrates Villegas - Archbishop of Lingayen-Dagupan, Former CBCP President
* Pete Lacaba
Jose Maria Flores Lacaba, popularly known as Pete Lacaba, is a Filipino screenwriter, editor, poet, journalist and translator.
Early life
Born in Misamis Oriental in 1945 to Jose Monreal Lacaba of Loon, Bohol and Fe Flores from Pateros, Rizal. H ...
- poet, writer and journalist
* Emmanuel Lacaba
Emmanuel Agapito Flores Lacaba (December 10, 1948 – March 18, 1976), popularly known as Eman Lacaba, was a Filipino writer, poet, essayist, playwright, short story writer, scriptwriter, songwriter and activist, often referred to as t ...
- poet, writer and activist
* Jimmy Santos Jimmy Santos may refer to:
* Jimmy Santos (singer), Afro-Uruguayan vocalist
* Jimmy Santos (actor)
Jaime Santos (born October 8, 1951), professionally known as Jimmy Santos, is a Filipino actor, comedian, TV host, and former professional basketb ...
- Filipino Actor, PBA Basketball Player, and TV Host, Eat Bulaga!
* Berting Labra
Berting Labra (born Roberto S. Labra; April 17, 1933 – February 10, 2009) was a Filipino child star and veteran actor equally adept in comedy and drama, in action flicks and musicals.
Personal life and career
Labra starred in ''Apat na Taga ...
- Actor, Side kick of FPJ
* Daisy Reyes - Beauty Queen, Actress
Sister cities
International and Local sister cities: ;Local * Taguig, Metro Manila * Pasig, Metro Manila ;International * Pateros, Washington, U.S.See also
* San Roque Parish Church *Santa Marta de Pateros
Santa Marta de Pateros is a title given to a 19th-century apparition of the biblical Saint Martha of Bethany in the town of Pateros, (formerly known as Aguho and a ''visita'' of Pasig) in Metro Manila, the Philippines.
Legend
Tradition recounts ...
References
External links
Municipality of Pateros official website
* {{Authority control Municipalities of Metro Manila Populated places established in 1770 1770 establishments in the Philippines