Paraíba Politicians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Paraíba (
 According to the
According to the
Retrieved: March 29, 2012. The 2010 census also revealed the following figures relating
 Portuguese is the official and only language spoken in the state and thus the primary language taught in schools. Minor
Portuguese is the official and only language spoken in the state and thus the primary language taught in schools. Minor
 The
The
 Located in the municipality of Bayeux, from downtown João Pessoa,
Located in the municipality of Bayeux, from downtown João Pessoa,
 The BR-101 also the BR-230 are found in Paraíba . Several other roads also cross the state composing the complex net which is present all across the country.
The BR-101 also the BR-230 are found in Paraíba . Several other roads also cross the state composing the complex net which is present all across the country.
 In football, the main teams in the state are:
In football, the main teams in the state are:
Official Website
* List of cities in Brazil (all cities and municipalities) {{DEFAULTSORT:Paraiba States of Brazil *
Tupi Tupi may refer to:
* Tupi people of Brazil
* Tupi or Tupian languages, spoken in South America
** Tupi language, an extinct Tupian language spoken by the Tupi people
* Tupi oil field off the coast of Brazil
* Tupi Paulista, a Brazilian municipalit ...
: ''pa'ra a'íba''; ) is a state of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. It is located in the Brazilian Northeast
The Northeast Region of Brazil ( pt, Região Nordeste do Brasil; ) is one of the five official and political regions of the country according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Of Brazil's twenty-six states, it comprises n ...
, and it is bordered by Rio Grande do Norte
Rio Grande do Norte (, , ) is one of the states of Brazil. It is located in the northeastern region of the country, forming the northeasternmost tip of the South American continent. The name literally translates as "Great Northern River", ref ...
to the north, Ceará
Ceará (, pronounced locally as or ) is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northeastern part of the country, on the Atlantic coast. It is the eighth-largest Brazilian State by population and the 17th by area. It is also one of the ...
to the west, Pernambuco
Pernambuco () is a state of Brazil, located in the Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.6 million people as of 2020, making it seventh-most populous state of Brazil and with around 98,148 km², being the 19 ...
to the south and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
to the east. Paraíba is the third most densely populated state of the Northeast; João Pessoa, the sea-bordered state capital, and Campina Grande
Campina Grande is the second most populous Brazilian city in the State of Paraíba after João Pessoa, the capital. It is considered to be the most important city of the Northeastern Brazilian subregion called '' agreste''. It is considered one ...
, in the interior, rank among the fifteen-largest municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
in the Northeast of Brazil. The state is home to 1.9% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.9% of the Brazilian GDP.
Paraíba is most populated along the Atlantic coast, which extends as far as Ponta do Seixas
Ponta do Seixas (), also known as Cape Branco, is a cape on the Atlantic coast of Paraíba state, eastern Brazil, that forms the easternmost point of the American continents, roughly 8 km (5 mi) southeast of João Pessoa, the state ca ...
, the easternmost point of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. The state is a tourist and industrial hotspot; it is known for its cultural heritage, amenable climate and geographical features, ranging from the seaside beaches to the Borborema Plateau
The Borborema Plateau (Portuguese ''Planalto da Borborema'', also known as the ''Serra da Borborema'') is a plateau in northeastern Brazil which extends across the states of Pernambuco, Paraíba, and Rio Grande do Norte. The plateau is the northeas ...
. It is named after the Paraíba river.
Some of the most notable Brazilian writers and poets are from Paraíba like Augusto dos Anjos
Augusto de Carvalho Rodrigues dos Anjos (April 20, 1884 – November 12, 1914) was a Brazilian poet and professor. His poems speak mostly of sickness and death, and are considered the forerunners of Modernism in Brazil.
He is the patron of the f ...
, José Américo de Almeida, José Lins do Rego
José is a predominantly Spanish and Portuguese form of the given name Joseph. While spelled alike, this name is pronounced differently in each language: Spanish ; Portuguese (or ).
In French, the name ''José'', pronounced , is an old vernacul ...
, Ariano Suassuna
Ariano Vilar Suassuna (; 16 June 1927 – 23 July 2014) was a Brazilian playwright and author. He was the driving force behind the creation of the ''Movimento Armorial''. He founded the Student Theater at Federal University of Pernambuco.
Fou ...
and Pedro Américo
Pedro Américo de Figueiredo e Melo (29 April 1843 – 7 October 1905) was a Brazilian novelist, poet, scientist, art theorist, essayist, philosopher, politician and professor, but is best remembered as one of the most important academic painters ...
, the last being also known for his historical paintings.
History
In the mid-16th century, settlers fromSpain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, Olinda
Olinda () is a historic city in Pernambuco, Brazil, in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region. It is located on the country's northeastern Atlantic Ocean coast, in the Recife metropolitan area, Metropolitan Region of Recife, the state capi ...
and Itamaracá founded Filipéia de Nossa Senhora das Neves (today João Pessoa) at the mouth of the Paraíba do Norte River
The Paraíba do Norte River, mostly known as Paraíba River, is the most important watercourse of the state of Paraíba in northeastern Brazil. The river originates in the Borborema Plateau, and flows northeast to empty into the Atlantic Ocean, ...
.
The area soon proved perfect for sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
production, with the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, the Dutch and the Portuguese all constantly fighting to control the Paraíba region to grow the lucrative sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
in. The fortress of Santa Catarina, near João Pessoa, was built to protect the city from the Dutch, who soon became a threat to Portuguese supremacy in Brazil.
Geology
In late 1989 a team led bygemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, ...
prospector Heitor Dimas Barbosa uncovered what some consider to be the finest tourmaline
Tourmaline ( ) is a crystalline silicate mineral group in which boron is compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Tourmaline is a gemstone and can be found in a wide variety of colors.
The ...
crystals ever found in a small mountain range. A trace of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
gives the tourmalines a vivid turquoise
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrated phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula . It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone and ornamental stone for thousands of yea ...
color that had never been seen before in the gems, and is sometimes referred to as "neon".
The "neon" Paraíba tourmaline
Tourmaline ( ) is a crystalline silicate mineral group in which boron is compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Tourmaline is a gemstone and can be found in a wide variety of colors.
The ...
, a vivid blue and blue green, has also been found in other deposits close to the Batalha mine of Barbosa, and also in the neighboring state of Rio Grande do Norte. The bright colors of this tourmaline are due to the presence of copper. Around 2000, a similar copper-containing tourmaline was found in Nigeria, although the colors are not as vivid. Around 2005, crystals of copper-containing tourmaline were found in Mozambique.
Initially, the nomenclature for this tourmaline was "Paraíba tourmaline". Note the capitalization and the accent on the "i". In 2006, the LMHC (Laboratory Manual Harmonization Committee) agreed that "paraiba" should refer to a variety of tourmaline, and not indicate a geographic origin. Note "paraiba" is not capitalized, and does not have an accent on the "i". For more information on paraiba tourmaline, see article on tourmaline
Tourmaline ( ) is a crystalline silicate mineral group in which boron is compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium. Tourmaline is a gemstone and can be found in a wide variety of colors.
The ...
. The term "paraiba tourmaline" may now refer to gems found in Brazil, Nigeria, and Mozambique that contain copper and have the characteristic blue-green color.
Demographics
 According to the
According to the IBGE
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics ( pt, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística; IBGE) is the agency responsible for official collection of statistical, geographic, cartographic, geodetic and environmental information ...
census , there were 3,766,528 people residing in the state, with a population density of 66.7 inhabitants/km2.
Other numbers include: Urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
rate: 75.4% (2010), Population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
: 0.8% (1991–2000) and House
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condi ...
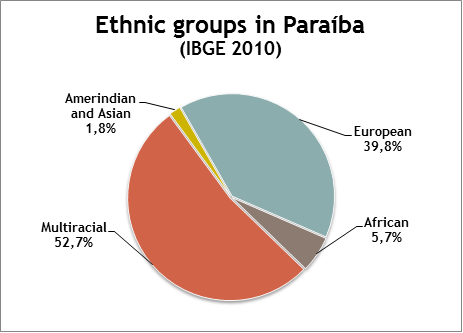
s: 987,000 (2006).IBGE Estados@ – ParaíbaRetrieved: March 29, 2012. The 2010 census also revealed the following figures relating
ethnicity
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
: 1,986,619 Brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model used ...
(Multiracial
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
) people (52.7%), 1,499,253 White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
(39.8%), 212,968 Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have o ...
(5.7%) and 67,636 (1.8%) people of Amerindian and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
n ancestry.
Among people of mixed ancestry the White, Amerindian and African altogether combination is the most prevalent one, followed by caboclo, mulato and zambo
Zambo ( or ) or Sambu is a racial term historically used in the Spanish Empire to refer to people of mixed Indigenous and African ancestry. Occasionally in the 21st century, the term is used in the Americas to refer to persons who are of mixe ...
.Largest cities
Religion
According to the 2010 census, the population of Paraíba is made up ofRoman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
s (76.96%), Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
s (15.16%), Spiritists (0.62%), Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ...
(0.47%), Brazilian Apostolic Catholics (0.22 %), Mormons
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into several ...
(0.11%), Orthodox Christians (0.05%), Candomblecists (0.035%), Umbanda (0.029%), Esoteric (0.023%), Jewish (0.017%), Eastern religious (0.014%), indigenous traditions ( 0.010%), spiritualists (0.004%), Islamic (0.002%), Hindus (0.002%) and Afro-Brazilian religious (0.001%), in addition to other religiosities. There were also those without religion (5.661%), including atheists (0.106%) and agnostics (0.046%); people with indeterminate religion and/or multiple belonging (0.154%); those who did not know (0.154%) and did not declare (0.016%).Statistics
*Vehicles
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), wate ...
: 432,337 (March/2007);
*Mobile phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link whil ...
s: 1.5 million (April/2007)
*Fixed line telephone
A landline (land line, land-line, main line, home phone, fixed-line, and wireline) is a telephone connection that uses metal wires or optical fiber telephone line for transmission, as distinguished from a mobile cellular network, which uses ...
s: 431 thousand (April/2007)
* Cities: 223 (2007).Education
 Portuguese is the official and only language spoken in the state and thus the primary language taught in schools. Minor
Portuguese is the official and only language spoken in the state and thus the primary language taught in schools. Minor dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of Linguistics, linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety (linguisti ...
al differences regarding other Brazilian varieties are mainly phonological (''Northeastern accent'').
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and Spanish are part of the official high school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper seconda ...
curriculum.
Educational institutions
* Universidade Federal da Paraíba (UFPB) (Federal University of Paraíba
Federal University of Paraíba ( pt, Universidade Federal da Paraíba, UFPB) is a public university whose main campus is located in the city of João Pessoa, Paraíba, Brazil. Along with Federal University of Campina Grande, they're the main u ...
);
* Universidade Federal de Campina Grande (UFCG) (Federal University of Campina Grande
The Federal University of Campina Grande ( pt, Universidade Federal de Campina Grande, UFCG) is a public university whose main campus is located in the city of Campina Grande, Paraíba, Brazil. Together with the Federal University of Paraíba, i ...
)
* Universidade Estadual da Paraíba (UEPB) (State University of Paraíba
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* '' State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our ...
);
* UNIPÊ (Centro Universitário de João Pessoa);
* Instituto de Educação Superior da Paraíba (IESP);
* Faculdade Maurício de Nassau (FMN) (Maurício de Nassau College);
* Instituto Federal de Educação Tecnológica (IFPB) ( Federal Institute of Technology of Paraiba);
* and many others.
Economy
 The
The service sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the second ...
is the largest component of GDP at 56.5%, followed by the industrial sector
In macroeconomics, the secondary sector of the economy is an economic sector in the three-sector theory that describes the role of manufacturing. It encompasses industries that produce a finished, usable product or are involved in construction ...
at 33.1%. Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
represents 10.4%, of GDP (2004). Paraíba exports: woven of cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
36.3%, footwear
Footwear refers to garments worn on the feet, which typically serves the purpose of protection against adversities of the environment such as wear from ground textures and temperature. Footwear in the manner of shoes therefore primarily serves th ...
es 20.1%, sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
and alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
10.8%, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
and crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
9.7%, sisal 7%, cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
6.6% (2002).
Share of the Brazilian economy: 0.8% (2004).
The Paraíba economy is largely based upon the making of shoe
A shoe is an item of footwear intended to protect and comfort the human foot. They are often worn with a sock. Shoes are also used as an item of decoration and fashion. The design of shoes has varied enormously through time and from culture t ...
s and other leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ...
products, the raising of cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
for beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quantity ...
, and sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
. Though historically sugarcane has dominated the Paraíba agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
sector, pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centuri ...
, corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
, and beans cultivation are also widespread. The other important economical sector in the state is tourism, especially the state urban and unspoilt beaches, ecotourism and festivals such as "carnaval" and "São João."Infrastructure
International Airport
 Located in the municipality of Bayeux, from downtown João Pessoa,
Located in the municipality of Bayeux, from downtown João Pessoa, Presidente Castro Pinto International Airport
Presidente Castro Pinto International Airport is the airport serving João Pessoa, Brazil located in the adjoining municipality of Santa Rita. The airport is named after João Pereira de Castro Pinto (1863-1944), a lawyer, writer and former Go ...
is currently undergoing expansion and remodeling work, which will raise the terminal's annual capacity to 860 thousand passengers.
The airport is well located in relation to obstacles because it covers an area roughly above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
and is sufficiently distant from urban areas or large real estate developments.
The surrounding area is sparsely populated, with large open spaces. The existing developments are industrial with some small weekend country houses. There is no rough terrain or tall buildings nearby creating obstacles for takeoffs and landings.
The airport also is blessed with excellent climatic conditions for air operations. Moreover, within its approach radius there are no obstacles that can hinder or create risk for local air traffic. Named for a past president (former name for governors) of Paraíba, Castro Pinto, the airport operates round the clock.
The current passenger terminal, built in an area of , has two levels, gardens and ample vehicle parking. It has all the expected amenities: arrival and departure lounges, a main concourse, check-in counters, baggage storage lockers, airline counters, snack bar/restaurant, tourist
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mo ...
information booth, car rental agencies, taxi
A taxi, also known as a taxicab or simply a cab, is a type of vehicle for hire with a driver, used by a single passenger or small group of passengers, often for a non-shared ride. A taxicab conveys passengers between locations of their choice ...
service and private parking.
Highways
 The BR-101 also the BR-230 are found in Paraíba . Several other roads also cross the state composing the complex net which is present all across the country.
The BR-101 also the BR-230 are found in Paraíba . Several other roads also cross the state composing the complex net which is present all across the country.
National Airport
Located in the interior of the state of Paraíba, in the city ofCampina Grande
Campina Grande is the second most populous Brazilian city in the State of Paraíba after João Pessoa, the capital. It is considered to be the most important city of the Northeastern Brazilian subregion called '' agreste''. It is considered one ...
, João Suassuna Airport was remodeled in 2003, receiving a new terminal with capacity of 250 thousand passengers a year.
The old building was demolished and on the site a new facility was built holding nine shops, the main concourse, arrival and departure lounges, VIP lounge, bathrooms, mezzanine and a diaper-changing area.
The terminal area was increased to . The boarding area has and the parking lot has spaces for 180 cars.
This expansion benefited the city both economically and from the standpoint of tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
. With the possibility for new flights, the air cargo movement will be able to grow, along with the number of tourists coming to attend the city's São João Festival.
A panel measuring in the front of the building carries a poem by the Paraíban writer Ariano Suassuna, in homage to his father, for whom the airport is named. Three more artworks are on permanent display in the passenger terminal.
Culture
Festa Junina (Saint John Festival)
Festa Junina was introduced to NortheasternBrazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
by the Portuguese for whom St John's day (also celebrated as Midsummer Day in several Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an countries), on the 24th of June, is one of the oldest celebrations of the year. Differently, of course, from what happens on the European Midsummer Day, the festivities in Brazil do not take place during the summer solstice
The summer solstice, also called the estival solstice or midsummer, occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the summer ...
but during the winter solstice
The winter solstice, also called the hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the winte ...
. The festivities traditionally begin after the 12th of June, on the eve of St Anthony's day, and last until the 29th, which is Saint Peter's day. During these fifteen days, there are bonfires
A bonfire is a large and controlled outdoor fire, used either for informal disposal of burnable waste material or as part of a celebration.
Etymology
The earliest recorded uses of the word date back to the late 15th century, with the Catho ...
, fireworks
Fireworks are a class of Explosive, low explosive Pyrotechnics, pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a l ...
, and folk dancing in the streets (step names are in French, which shows the mutual influences between court life and peasant culture in the 17th, 18th, and 19th-century Europe). Once exclusively a rural festival, today in Brazil, it is largely a city festival during which people joyfully and theatrically mimic peasant stereotypes and clichés in a spirit of jokes and good times. Typical refreshments and dishes are served. Like during Carnival, these festivities involve costume-wearing (in this case, peasant costumes), dancing, heavy drinking, and visual spectacles (fireworks display and folk dancing), such as what happens on Midsummer and St John's Day in Europe, and bonfires
A bonfire is a large and controlled outdoor fire, used either for informal disposal of burnable waste material or as part of a celebration.
Etymology
The earliest recorded uses of the word date back to the late 15th century, with the Catho ...
are a central part of these festivities in Brazil.
Carnival
The four-day period before Lent leading up to Ash Wednesday iscarnival
Carnival is a Catholic Christian festive season that occurs before the liturgical season of Lent. The main events typically occur during February or early March, during the period historically known as Shrovetide (or Pre-Lent). Carnival typi ...
time in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. Rich and poor alike forget their cares as they party in the streets.
Flag
The word ''nego'' on the state flag is Portuguese for "I deny" or "I refuse", referring to the events that led to the Brazilian Revolution of 1930. Due to Milk Coffee Politics in Brazil, thepresident
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
of the country always alternated between someone from the state of Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
and someone from the state of São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for 'Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaWC a ...
. In 1929, the incumbent president from São Paulo, Washington Luís, was supposed to support a politician from Minas Gerais as the next president, but he instead decided to nominate someone from São Paulo for the second time in a row, Júlio Prestes. The state governor of Paraíba, João Pessoa Cavalcânti de Albuquerque
João is the Portuguese equivalent of the given name John. The diminutive is Joãozinho and the feminine is Joana. It is widespread in Portuguese-speaking countries. Notable people with the name are enumerated in the sections below.
Kings
* ...
, refused to support the appointment of Júlio Prestes, and in 1930, Pessoa joined the alliance for the overthrow of the federal government. The revolution succeeded in toppling the Old Republic and installing Getúlio Vargas
Getúlio Dornelles Vargas (; 19 April 1882 – 24 August 1954) was a Brazilian lawyer and politician who served as the 14th and 17th president of Brazil, from 1930 to 1945 and from 1951 to 1954. Due to his long and controversial tenure as Brazi ...
—who was from neither Minas Gerais nor São Paulo—as the president of Brazil, however, João Pessoa was assassinated; there is still debate as to whether the motive behind his murder was personal, political, or both. Following these events, the word ''nego'' was added to the flag of Paraíba.
According to the official government site of the state of Paraíba, the red color stands for the blood of João Pessoa after his assassination, while the black color represents mourning.
Sports
 In football, the main teams in the state are:
In football, the main teams in the state are: Botafogo
Botafogo (local/standard alternative Brazilian Portuguese pronunciation: ) is a beachfront neighborhood (''bairro'') in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It is a mostly upper middle class and small commerce community, and is located between the hills of M ...
from João Pessoa, Campinense and Treze, both from Campina Grande
Campina Grande is the second most populous Brazilian city in the State of Paraíba after João Pessoa, the capital. It is considered to be the most important city of the Northeastern Brazilian subregion called '' agreste''. It is considered one ...
.Important figures and celebrities
Paraíba is home to some of the most noted Brazilian poets and writers such as Augusto dos Anjos (1884–1908), José Américo de Almeida (1887–1980), José Lins do Rego (1901–1957) and Pedro Américo (1843–1905) (mostly known for his historical paintings).See also
*Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
* Ingá Stone (Undeciphered petroglyph in Ingá municipality)
References
External links
Official Website
* List of cities in Brazil (all cities and municipalities) {{DEFAULTSORT:Paraiba States of Brazil *