Paczków - Mury Obronne on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Paczków (german: Patschkau; szl, Paczkōw) is a town in
retrieved on April 21, 2009 Located in the southeastern outskirts of the historical province of
However, while the famous French Carcassonne is a 19th-century reconstruction, all historic buildings of Paczków are authentic. The old town and its medieval fortifications are listed as one of Poland's official national Historic Monuments (''
 Paczków was officially founded and granted
Paczków was officially founded and granted
It was granted the so-called Flemish rights, based on
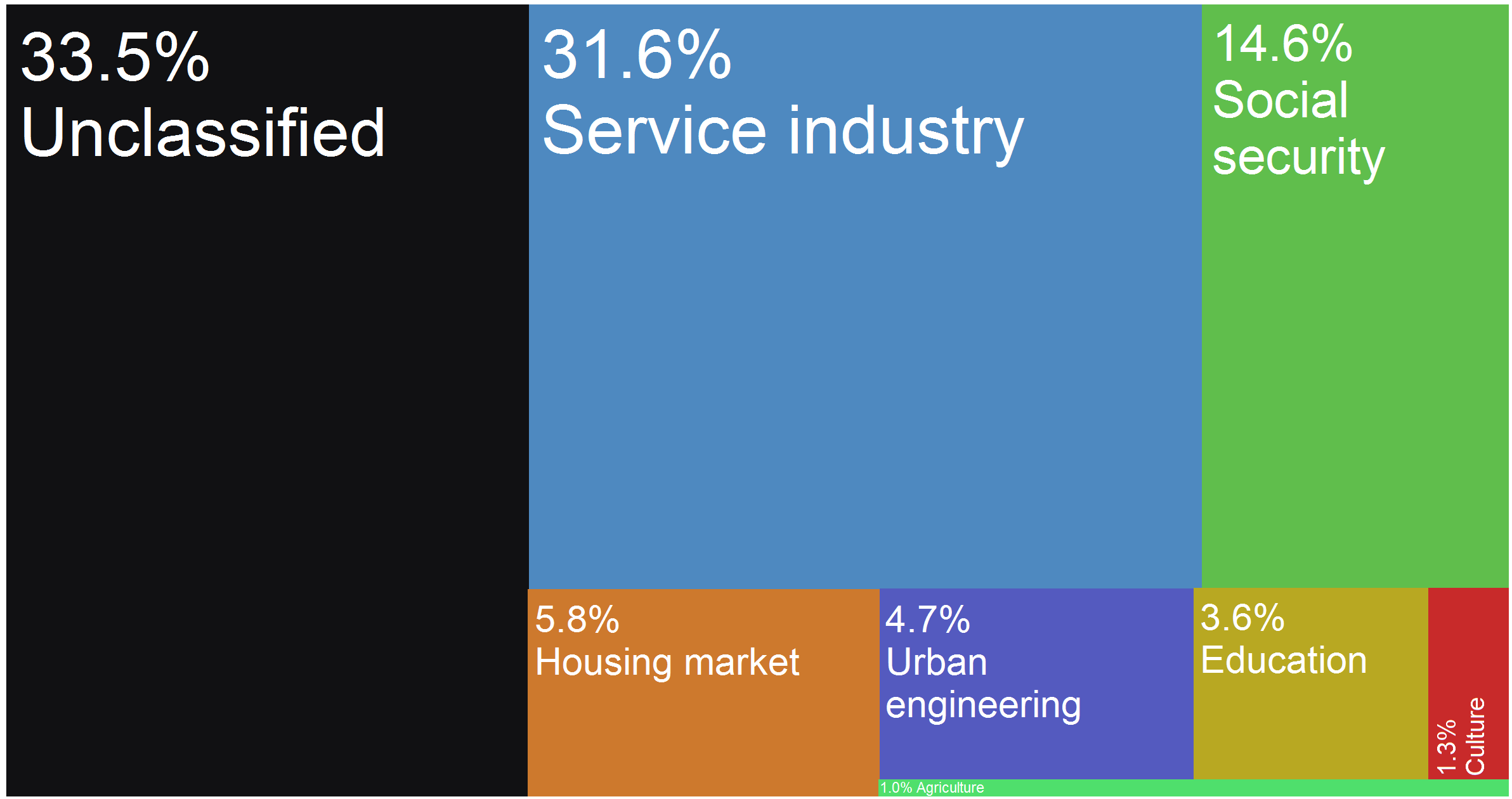 The characteristics of the town of Paczków's economic dependence is similar to that of the
The characteristics of the town of Paczków's economic dependence is similar to that of the
File:Kościół par. p.w. św. Jana Ewangelisty w Paczkowie..JPG, Town centre
File:2014 Paczków, Brama Kłodzka.JPG, Kłodzko Gate
File:Paczków - Katedra.JPG, Church of John the Evangelist
File:2014 Paczków, Rynek 22 i 23 (01).jpg, Historic townhouses
File:2014 Paczków Brama Wrocławska, 01.JPG, Wrocław Gate
File:Patschkau-Ring-2.jpg, Market square
File:Patschkau-evangKirche.jpg, Church of Our Lady of Perpetual Help
File:2014 Paczków, ul Wojska Polskiego 23 02.JPG, Executioner's house, 18th century
Official webpage of the town
Photo gallery of Paczkow
Jewish Community in Paczków
on Virtual Shtetl {{DEFAULTSORT:Paczkow Cities in Silesia Cities and towns in Opole Voivodeship Nysa County 13th-century establishments in Poland Populated places established in the 1250s Czech Republic–Poland border crossings
Nysa County
__NOTOC__
Nysa County ( pl, powiat nyski) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Opole Voivodeship, south-western Poland, on the Czech border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local ...
, Opole Voivodeship
Opole Voivodeship, or Opole Province ( pl, województwo opolskie ), is the smallest and least populated voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province's name derives from that of the region's capital and largest city, Opole. It is part of Upper S ...
, Poland, with 7,460 inhabitants (2019). It is one of the few towns in Europe in which medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
fortifications have been almost completely preserved.Gazeta Wyborcza. Piotr Walczak, Odwiedz polskie Carcassonne (Visit Polish Carcassonne)retrieved on April 21, 2009 Located in the southeastern outskirts of the historical province of
Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...
, along the medieval road from Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a s ...
to Klodzko Valley and Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
, Paczków is called "Polish Carcassonne
Carcassonne (, also , , ; ; la, Carcaso) is a French fortified city in the department of Aude, in the region of Occitanie. It is the prefecture of the department.
Inhabited since the Neolithic, Carcassonne is located in the plain of the ...
", thanks to its well-preserved medieval fortifications.Panorama of Polish cities. Silesian CarcassonneHowever, while the famous French Carcassonne is a 19th-century reconstruction, all historic buildings of Paczków are authentic. The old town and its medieval fortifications are listed as one of Poland's official national Historic Monuments (''
Pomnik historii
Historic Monument ( pl, pomnik historii) is one of several categories of objects of cultural heritage (in the singular, '' zabytek'') in Poland.
To be recognized as a Polish historic monument, an object must be declared such by the President ...
''), as designated November 13, 2012. Its listing is maintained by the National Heritage Board of Poland
The National Institute of Cultural Heritage of Poland ( pl, Narodowy Instytut Dziedzictwa NID) is a Polish governmental institution responsible for documenting cultural property and the intangible cultural heritage, as well as for supporting and ...
.
History
 Paczków was officially founded and granted
Paczków was officially founded and granted town rights
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the tradition ...
on March 8, 1254, when the Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
Bishop of Wrocław
Bishops of the (Breslau )Wrocław Bishopric, Prince-Bishopric (1290–1918), and Archdiocese (since 1930; see Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Wrocław for details).
Bishops
* 1000–? – John (Johannes)
* 1051–1062 – Hieronymus
* 1063–1072 ...
, Tomasz I gave permission to two Flemings
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.
"''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all inha ...
Henryk and Wilhelm, for the location of a new town Bogunów (mentioned under the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
ized name ''Bogunov'') to be settled by German immigrants. The new town was placed near the ancient village of Paczków and took its name, and henceforth, the name of the village was changed to Stary Paczków ("Old Paczków"). The name Paczków itself comes from the Old Polish
The Old Polish language ( pl, język staropolski, staropolszczyzna) was a period in the history of the Polish language between the 10th and the 16th centuries. It was followed by the Middle Polish language.
The sources for the study of the Old ...
male name Pakosław. Paczków, mentioned in medieval documents under the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
ized Old Polish names ''Paczkaw'' (''Liber fundationis episcopatus Vratislaviensis
Liber fundationis episcopatus Vratislaviensis ( pl, Księga uposażeń biskupstwa wrocławskiego, ''Book of endowments of the Bishopric of Wrocław'') is a Latin manuscript catalog of documents compiled in the later 13th or in the early 14th centu ...
'') and ''Patzkow'' (''Book of Henryków
The ''Book of Henryków'' ( pl, Księga henrykowska, la, Liber fundationis claustri Sanctae Mariae Virginis in Heinrichow) is a Latin chronicle of the Cistercian abbey in Henryków in Lower Silesia, Poland. Originally created as a registry of ...
''), quickly grew, becoming not only a market town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
, but also a stronghold
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, guarding southwestern borders of the ecclesiastical Duchy of Nysa
The Duchy of Nysa ( pl, Księstwo Nyskie, cs, Niské knížectví) or Duchy of Neisse (german: Herzogtum Neisse) was one of the duchies of Silesia with its capital at Nysa in Lower Silesia. Alongside the Duchy of Siewierz, it was the only eccle ...
of fragmented Poland
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in the early 12th ce ...
.History of Paczkow at portal paczkow infoIt was granted the so-called Flemish rights, based on
Magdeburg rights
Magdeburg rights (german: Magdeburger Recht; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within ...
. The new town received several privileges, such as the right to brew beer, and its early inhabitants were mostly craftsmen, such as bakers, butchers and shoemakers.
In the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur ...
and subsequent periods, Paczków shared the stormy fate of other towns of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
, with frequent disasters, such as hunger (1325), floods (1333, 1501, 1539, 1560, 1598, 1602), fires (1565, 1634), as well as epidemics - Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
(1349), and cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
(1603–1607, 1633). The town also suffered during the Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, European monarchs loyal to the Cat ...
, when it was captured by the Hussites
The Hussites ( cs, Husité or ''Kališníci''; "Chalice People") were a Czech proto-Protestant Christian movement that followed the teachings of reformer Jan Hus, who became the best known representative of the Bohemian Reformation.
The Hussit ...
on March 17, 1428. The period of religious wars did not end until the late 15th century, and only then did Paczków begin to flourish again. With the financial support of the dukes of Nysa
Nysa may refer to:
Greek Mythology
* Nysa (mythology) or Nyseion, the mountainous region or mount (various traditional locations), where nymphs raised the young god Dionysus
* Nysiads, nymphs of Mount Nysa who cared for and taught the infant ...
, new fortifications were constructed, with a wall
A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, shelter, or soundproofing; or, is decorative. There are many kinds of walls, including:
* Walls in buildings that form a fundamental part of the supe ...
and towers.
In 1526 Paczków, under the Germanized name ''Patschkau'', together with the Duchy of Nysa, passed under the suzerainty of the Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
n Habsburg dynasty
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. The town blossomed, as a major centre of trade, with several manufacturers of textiles. The end of prosperity came during the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (80 ...
, when warring armies destroyed Patschkau and adjacent areas. In 1742, after the Silesian Wars
The Silesian Wars (german: Schlesische Kriege, links=no) were three wars fought in the mid-18th century between Prussia (under King Frederick the Great) and Habsburg Austria (under Archduchess Maria Theresa) for control of the Central European ...
, Patschkau was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Re ...
, and it subsequently became part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in 1871. It was secularized
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses the ...
in 1810. The town was spared from serious destruction during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and II. During World War II, the Germans established five working parties (E158, E164, E274, E504, E534) of the Stalag VIII-B/344 prisoner-of-war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. P ...
in the town. In the final stages of the war, the town was captured by the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
in May 1945. Its German population was largely evacuated or expelled. After the war, following the Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement (german: Potsdamer Abkommen) was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union on 1 August 1945. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned th ...
, it became again part of Poland, and its Polish name was restored.
The town was repopulated by Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
settlers from war-devastated Central Poland and expellees from former eastern Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, mostly from areas of Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukraine ...
, Tarnopol
Ternópil ( uk, Тернопіль, Ternopil' ; pl, Tarnopol; yi, טאַרנאָפּל, Tarnopl, or ; he, טארנופול (טַרְנוֹפּוֹל), Tarnopol; german: Tarnopol) is a city in the west of Ukraine. Administratively, Ternopi ...
, and Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. Th ...
(current western Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
).
Monuments
Unlike nearby Nysa, World War II spared Paczków, and most of its monuments have been preserved. Called "The Polish Carcassonne" (or, before the town was reintegrated with Poland, "the Silesian Carcassonne"), as early as in the 15th century, it was surrounded by double ring ofdefensive wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
s. Initially, the fortifications were made of dirt and wood, but later they were replaced by mightier stone walls.
The first fortifications of Paczków were built in the mid-14th century upon the order of the Bishop of Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
, Przecław of Pogorzela. In the mid 15th century, Paczków had three gates
Gates is the plural of gate, a point of entry to a space which is enclosed by walls. It may also refer to:
People
* Gates (surname), various people with the last name
* Gates Brown (1939-2013), American Major League Baseball player
* Gates McFadde ...
- Wrocław Gate (''Brama Wrocławska'', eastern), Kłodzko Gate (''Brama Kłodzka'', western), and Zabkowice Slaskie Gate (''Brama Ząbkowicka'', southern). In the second half of the 16th century, the northern Nysa Gate (''Brama Nyska'') was added. Vertical, 9-metre walls made from stone still surround the historical centre of the town today. Altogether, the fortifications are around 1200 metres long, and apart from four gates, there originally were 24 wall tower
A fortified tower (also defensive tower or castle tower or, in context, just tower) is one of the defensive structures used in fortifications, such as castles, along with curtain walls. Castle towers can have a variety of different shapes and ful ...
s, out of which 19 have been preserved. Along the defensive walls, there was a moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
, which has been turned into a recreational park.
Besides its fortifications, Paczków is famous for renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
, and neoclassic tenement house
A tenement is a type of building shared by multiple dwellings, typically with flats or apartments on each floor and with shared entrance stairway access. They are common on the British Isles, particularly in Scotland. In the medieval Old Town, i ...
s, which surround the town square
A town square (or square, plaza, public square, city square, urban square, or ''piazza'') is an open public space, commonly found in the heart of a traditional town but not necessarily a true square, geometric square, used for community gathe ...
. The oldest of these buildings date back to around 1500, with the most visible being the so-called "House of the Executioner
An executioner, also known as a hangman or headsman, is an official who executes a sentence of capital punishment on a legally condemned person.
Scope and job
The executioner was usually presented with a warrant authorising or order ...
". Also, in the centre of Paczków, there is the town hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
, with a tower.
Another interesting monument of "Polish Carcassonne" is the Church of John the Evangelist, which is considered to be one of the most impressive fortified churches in Poland. Its construction began in 1350, and lasted for 30 years. The unique Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
church, which is made of stone and bricks displays a renaissance attic, and its mighty structure has been incorporated into the town's fortifications. The church stands out because of its immense size, and inside there are sculptures attributed to Wit Stwosz
Veit Stoss (also: ''Veit Stoß'' and ''Stuoss''; pl, Wit Stwosz; before 1450about 20 September 1533) was a leading German sculptor, mostly working with wood, whose career covered the transition between the late Gothic and the Northern Renaissa ...
. Next to the complex there is the so-called Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
well. According to a legend, a Tatar warrior (see Mongol invasion of Poland) was thrown into the well, after he had captured the daughter of a wealthy inhabitant of Paczków.
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Economy
 The characteristics of the town of Paczków's economic dependence is similar to that of the
The characteristics of the town of Paczków's economic dependence is similar to that of the Gmina Paczków
__NOTOC__
Gmina Paczków is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Nysa County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland, on the Czech Republic, Czech border. Its seat is the town of Paczków, which lies approximately west of Nysa, P ...
and the whole of the Opole Voivodeship
Opole Voivodeship, or Opole Province ( pl, województwo opolskie ), is the smallest and least populated voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province's name derives from that of the region's capital and largest city, Opole. It is part of Upper S ...
, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
. The gmina, under the local authority of the town has a total of 6193 ha used for agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
(80% of its land), with the main crop being canola
Close-up of canola blooms
Canola flower
Rapeseed oil is one of the oldest known vegetable oils. There are both edible and industrial forms produced from rapeseed, the seed of several cultivars of the plant family Brassicaceae. Historically, i ...
.
To the west of Paczków, the Paczkowski Lake, while predominantly performing the role of protecting the locality from flooding, is also home to a small fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
industry. Apart from food production, Paczków is home to numerous heavy industry
Heavy industry is an industry that involves one or more characteristics such as large and heavy products; large and heavy equipment and facilities (such as heavy equipment, large machine tools, huge buildings and large-scale infrastructure); o ...
complexes, including the "EMSTEEL" steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
plant by Robotnicza Street (''ul. Robotnicza'') and the "Pollena Paczków" chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
s manufacturing plant by Henryk Sienkiewicz Street (''ul. Henryka Sienkiewicza''). Withal, in 2015 the service industry (including manual labour) provided 31.6% (11.7 million złoty) to the city's budget.
Notable people
*Joseph Schröter
Joseph Schröter (14 March 1837 – 12 December 1894) was a noted German mycologist, doctor and scientist. He wrote several books and texts, and discovered and described many species of flora and fungi. He also spent around fifteen years, from 187 ...
(1837–1894), German scientist
* Lucyna Matuszna (born 1961), Polish female field hockey
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting ci ...
player
* Izabela Zatorska (born 1962), Polish retired female mountain runner
*Paweł Kukiz
Paweł Piotr Kukiz (born 24 June 1963) is a Polish politician, singer and actor. He is the leader of Kukiz'15, a non-partisan political alliance campaigning for single-member districts, and was a candidate in the 2015 presidential election, in whi ...
(born 1963), Polish politician, singer and actor
*Krzysztof Maksel
Krzysztof Maksel (born 4 July 1991) is a Polish professional racing cyclist. He rode at the 2015 UCI Track Cycling World Championships
The 2015 UCI Track Cycling World Championships were the World Championships for track cycling in 2015. They ...
(born 1991), Polish male cyclist
Twin towns – sister cities
See twin towns of Gmina Paczków.Gallery
References
External links
Official webpage of the town
Photo gallery of Paczkow
Jewish Community in Paczków
on Virtual Shtetl {{DEFAULTSORT:Paczkow Cities in Silesia Cities and towns in Opole Voivodeship Nysa County 13th-century establishments in Poland Populated places established in the 1250s Czech Republic–Poland border crossings