P-TsOH on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''p''-Toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA or ''p''TsOH) or tosylic acid (TsOH) is an organic compound with the formula CH3 C6H4 SO3H. It is a white extremely hygroscopic solid that is soluble in water,
 In a famous and illustrative use of tosylate,
In a famous and illustrative use of tosylate,
alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
s, and other polar
Polar may refer to:
Geography
Polar may refer to:
* Geographical pole, either of two fixed points on the surface of a rotating body or planet, at 90 degrees from the equator, based on the axis around which a body rotates
* Polar climate, the c ...
organic solvents. The CH3C6H4SO2 group is known as the tosyl group and is often abbreviated as Ts or Tos. Most often, TsOH refers to the monohydrate, TsOH.H2O.
As with other aryl sulfonic acid
In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid (or sulphonic acid) refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula , where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is kn ...
s, TsOH is a strong organic acid
An organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are rel ...
. It is about one million times stronger than benzoic acid. It is one of the few strong acids that is solid and therefore is conveniently weighed and stored.
Preparation and uses
TsOH is prepared on an industrial scale by the sulfonation of toluene. Common impurities include benzenesulfonic acid and sulfuric acid. TsOH monohydrate contains an amount of water. To estimate the total moisture present as impurity, the Karl Fischer method is used. Impurities can be removed by recrystallization from its concentrated aqueous solution followed byazeotropic
An azeotrope () or a constant heating point mixture is a mixture of two or more liquids whose proportions cannot be altered or changed by simple distillation.Moore, Walter J. ''Physical Chemistry'', 3rd e Prentice-Hall 1962, pp. 140–142 This ...
drying with toluene.
TsOH finds use in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
as an "organic-soluble" strong acid. Examples of uses include:
* Acetalization of an aldehyde.
* Fischer–Speier esterification
* Transesterification reactions
Tosylates
Alkyl tosylates are alkylating agents because tosylate is electron-withdrawing as well as a good leaving group. Tosylate is a pseudohalide. Toluenesulfonate esters undergo nucleophilic attack orelimination
Elimination may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Elimination reaction, an organic reaction in which two functional groups split to form an organic product
*Bodily waste elimination, discharging feces, urine, or foreign substances from the bo ...
. Reduction of tosylate esters gives the hydrocarbon. Thus, tosylation followed by reduction allows for the deoxygenation of alcohols.
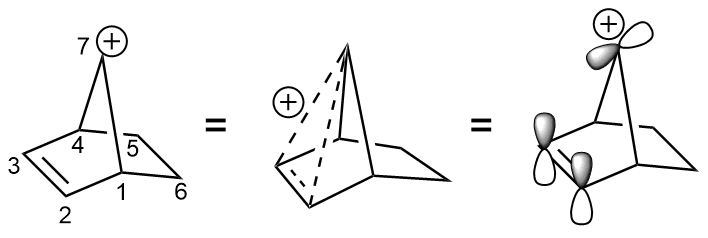
 In a famous and illustrative use of tosylate,
In a famous and illustrative use of tosylate, 2-norbornyl cation
In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation (or 2-bicyclo .2.1eptyl cation) describes one of the three carbocations formed from derivatives of norbornane. Though 1-norbornyl and 7-norbornyl cations have been studied, the most extensive studie ...
was displaced from the 7-norbornenyl tosylate. The elimination occurs 1011 times faster than the solvolysis of ''anti''-7-norbornyl ''p''-toluenesulfonate.
Tosylates are also protecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In many ...
for alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
s. They are prepared by combining the alcohol with 4-toluenesulfonyl chloride
4-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (''p''-toluenesulfonyl chloride, toluene-''p''-sulfonyl chloride) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2Cl. This white, malodorous solid is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. Abbreviated TsCl or ...
, usually in an aprotic solvent A polar aprotic solvent is a solvent that lacks an acidic proton and is polar. Such solvents lack hydroxyl and amine groups. In contrast to protic solvents, these solvents do not serve as proton donors in hydrogen bonding
In chemistry, a hydro ...
, often pyridine.
Reactions
* TsOH may be converted to ''p''-toluenesulfonic anhydride by heating with phosphorus pentoxide. * When heated with acid and water, TsOH undergoes hydrolysis to toluene: :CH3C6H4SO3H + H2O → C6H5CH3 + H2SO4 This reaction is general for arylsulfonic acid
In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid (or sulphonic acid) refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula , where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is kn ...
s.
See also
* Tosyl * Collidinium ''p''-toluenesulfonateReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Toluenesulfonic Acid, P- Benzenesulfonic acids Reagents for organic chemistry Acid catalysts Sulfonic acids P-Tosyl compounds