Optic Neuritis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Optic neuritis describes any condition that causes inflammation of the
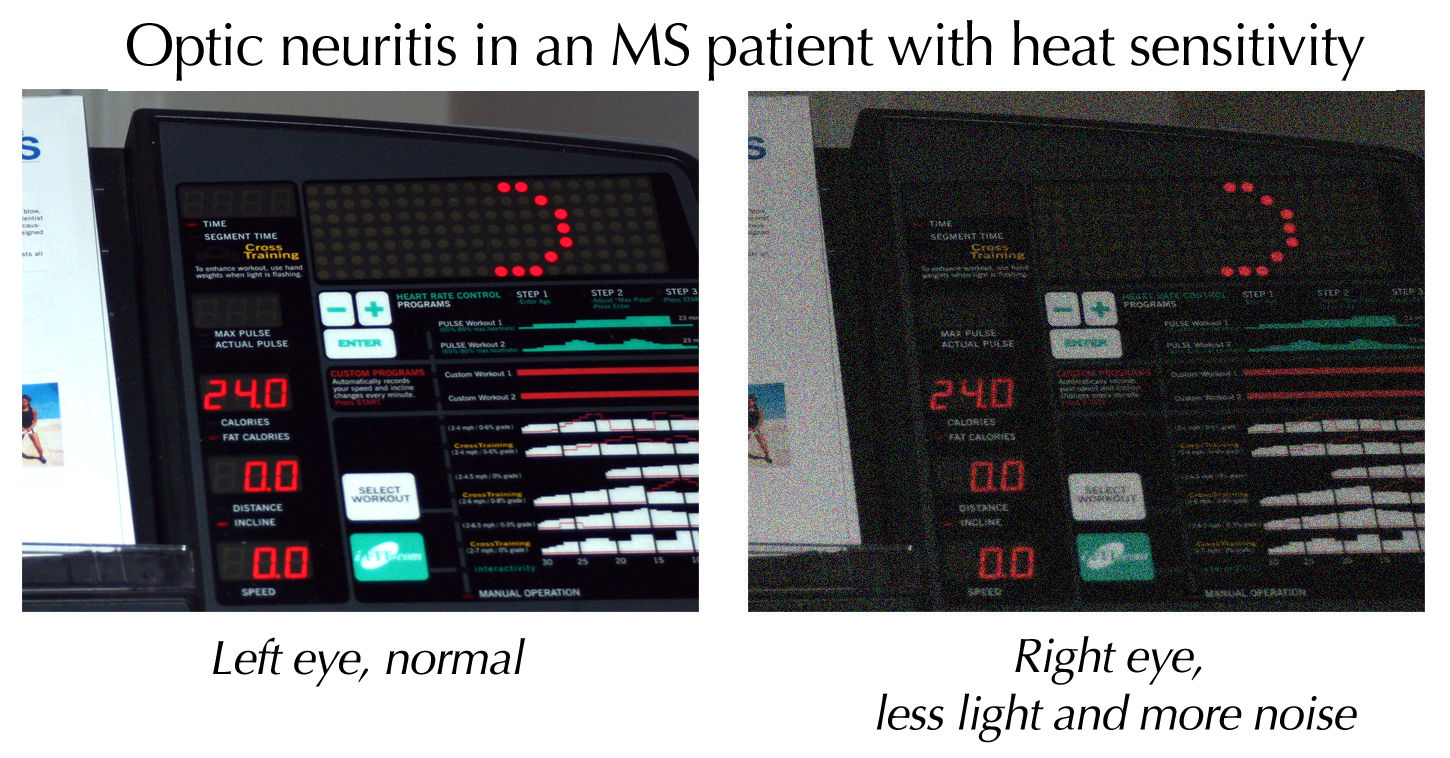 Major symptoms are sudden loss of vision (partial or complete), sudden blurred or "foggy" vision, and
Major symptoms are sudden loss of vision (partial or complete), sudden blurred or "foggy" vision, and
optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived fro ...
; it may be associated with demyelinating diseases
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency i ...
, or infectious or inflammatory processes.
It is also known as optic papillitis (when the head of the optic nerve is involved), neuroretinitis (when there is a combined involvement of the optic disc and surrounding retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
in the macular area) and retrobulbar neuritis (when the posterior part of the nerve is involved). Prelaminar optic neuritis describes involvement of the non-myelinated axons in the retina. It is most often associated with multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This d ...
, and it may lead to complete or partial loss of vision in one or both eyes. Other causes include:
# Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a mitochondrially inherited (transmitted from mother to offspring) degeneration of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and their axons that leads to an acute or subacute loss of central vision; it predomin ...
# Parainfectious optic neuritis (associated with viral infections
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Structural Characteristics
Basic structural characteristics, ...
such as measles, mumps, chickenpox, whooping cough
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis or the 100-day cough, is a highly contagious bacterial disease. Initial symptoms are usually similar to those of the common cold with a runny nose, fever, and mild cough, but these are followed by two or t ...
and glandular fever
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Structure
De ...
)
# Infectious optic neuritis (sinus related or associated with cat-scratch fever, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
, Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migran ...
and cryptococcal meningitis
Cryptococcosis is a potentially fatal mycosis, fungal infection of mainly the lungs, presenting as a pneumonia, and brain, where it appears as a meningitis. Cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, chest pain and fever are seen when the ...
in AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
patients
# Autoimmune causes (sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly a ...
, systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
, polyarteritis nodosa
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) is a systemic necrotizing inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis) affecting medium-sized muscular arteries, typically involving the arteries of the kidneys and other internal organs but generally sparing the lungs' ...
, MOG antibody disease
MOG antibody disease (MOGAD) or MOG antibody-associated encephalomyelitis (MOG-EM) is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. Serum anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies are present in up to half of patie ...
, granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), previously known as Wegener's granulomatosis (WG), is a rare long-term systemic disorder that involves the formation of granulomas and inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis). It is a form of vasculitis ...
)
# Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
# Low phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
levels
# Hyperkalaemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasi ...
Partial, transient vision loss (lasting less than one hour) can be an indication of early onset multiple sclerosis.
Signs and symptoms
 Major symptoms are sudden loss of vision (partial or complete), sudden blurred or "foggy" vision, and
Major symptoms are sudden loss of vision (partial or complete), sudden blurred or "foggy" vision, and pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
on movement of the affected eye. Early symptoms that require investigation include symptoms from multiple sclerosis (twitching, lack of coordination, slurred speech, frequent episodes of partial vision loss or blurred vision), episodes of "disturbed/blackened" rather than blurry indicate moderate stage and require immediate medical attention to prevent further loss of vision. Other early symptoms are reduced night vision, photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence of ...
and red eyes. Many patients with optic neuritis may lose some of their color vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
in the affected eye (especially red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondar ...
), with colors appearing subtly washed out compared to the other eye. Patients may also experience difficulties judging movement in depth, which can be particular troublesome during driving or sport (Pulfrich effect
The Pulfrich effect is a psychophysical percept wherein lateral motion of an object in the field of view is interpreted by the visual cortex as having a depth component, due to a relative difference in signal timings between the two eyes.
Overvie ...
). Likewise, transient worsening of vision with increase of body temperature (Uhthoff's phenomenon
Uhthoff's phenomenon (also known as Uhthoff's syndrome, Uhthoff's sign, and Uhthoff's symptom) is the worsening of neurologic symptoms in multiple sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinating diseases when the body is overheated. This may occur due to ...
) and glare disability are a frequent complaint. However, several case studies in children have demonstrated the absence of pain in more than half of cases (approximately 60%) in their pediatric study population, with the most common symptom reported simply as "blurriness." Other remarkable differences between the presentation of adult optic neuritis as compared to pediatric cases include more often unilateral optic neuritis in adults, while children much predominantly present with bilateral involvement.
On medical examination the head of the optic nerve can easily be visualized by a slit lamp
A slit lamp is an instrument consisting of a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine a thin sheet of light into the eye. It is used in conjunction with a biomicroscope. The lamp facilitates an examination of the anterior segme ...
with a high positive lens or by using direct ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part ...
; however, frequently there is no abnormal appearance of the nerve head in optic neuritis (in cases of retrobulbar optic neuritis), though it may be swollen in some patients (anterior papillitis or more extensive optic neuritis). In many cases, only one eye is affected, and patients may not be aware of the loss of color vision until they are asked to close or cover the healthy eye.
Cause
Theoptic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived fro ...
comprises axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action po ...
s that emerge from the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
of the eye and carry visual information to the primary visual nuclei, most of which is relayed to the occipital cortex
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head".
The occipital lobe is the vi ...
of the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
to be processed into vision. Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
of the optic nerve causes loss of vision, usually because of the swelling and destruction of the myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
sheath covering the optic nerve.
The most common cause is multiple sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This d ...
(MS) or ischemic optic neuropathy
Ischemic optic neuropathy (ION) is the loss of structure and function of a portion of the optic nerve due to obstruction of blood flow to the nerve (i.e. ischemia). Ischemic forms of optic neuropathy are typically classified as either anterior is ...
due to thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (t ...
or embolism
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule (fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas ( gas embolism), amniotic fluid (am ...
of the vessel that supplies the optic nerve. Up to 50% of patients with MS will develop an episode of optic neuritis, and 20-30% of the time optic neuritis is the presenting sign of MS. The presence of demyelinating white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution ...
lesions on brain MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
at the time of presentation of optic neuritis is the strongest predictor for developing clinically definite MS. Almost half of the patients with optic neuritis have white matter lesions consistent with multiple sclerosis.
Some other common causes of optic neuritis include infection (e.g. a tooth abscess in the upper jaw, syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, an ...
, Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migran ...
, herpes zoster
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. ...
), autoimmune disorder
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly ...
s (e.g. lupus, neurosarcoidosis
Neurosarcoidosis (sometimes shortened to neurosarcoid) refers to a type of sarcoidosis, a condition of unknown cause featuring granulomas in various tissues, in this type involving the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Neurosarcoidosi ...
, neuromyelitis optica
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord (myelitis). Episodes of ON and myelitis ...
), methanol poisoning
Methanol toxicity (also ''methanol poisoning'') is poisoning from methanol, characteristically via ingestion. Symptoms may include a decreased level of consciousness, poor or no coordination, hypothermia, vomiting, abdominal pain, and a specific s ...
, vitamin B12 deficiency, beriberi
Thiamine deficiency is a medical condition of low levels of thiamine (Vitamin B1). A severe and chronic form is known as beriberi. The two main types in adults are wet beriberi and dry beriberi. Wet beriberi affects the cardiovascular system, ...
, dysautonomia
Dysautonomia or autonomic dysfunction is a condition in which the autonomic nervous system (ANS) does not work properly. This may affect the functioning of the heart, bladder, intestines, sweat glands, pupils, and blood vessels. Dysautonomia ha ...
(i.e. autonomic nervous system dysfunction), and diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
, or an injury to the eye. In neuromyelitis optica higher AQP4 autoantibody
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
P ...
levels are associated with the occurrence of optic neuritis.
Less common causes are: papilledema
Papilledema or papilloedema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure due to any cause. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare.
In ...
, brain tumor
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and seconda ...
or abscess in the occipital region, cerebral trauma
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic b ...
or hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, v ...
, meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
, arachnoidal adhesions, sinus thrombosis, liver dysfunction
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the s ...
, or late stage kidney disease
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can ...
.
Demyelinating recurrent optic neuritis and non-demyelinating (CRION)
The repetition of an idiopathic optic neuritis is considered a distinct clinical condition, and when it shows demyelination, it has been found to be associated to anti- MOG and AQP4-negativeneuromyelitis optica
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord (myelitis). Episodes of ON and myelitis ...
.
When an inflammatory recurrent optic neuritis is not demyelinating, it is called chronic relapsing inflammatory optic neuropathy
Chronic relapsing inflammatory optic neuropathy (CRION) is a form of recurrent optic neuritis that is steroid responsive and dependent. Patients typically present with pain associated with visual loss. CRION is a clinical diagnosis of exclusion, ...
(CRION).
When it is anti-MOG related, it is demyelinating and it is considered inside the anti-MOG associated inflammatory demyelinating diseases.
Some reports point to the possibility to establish a difference via optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that uses low-coherence light to capture micrometer-resolution, two- and three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). It is used for medica ...
.
Treatment
In most MS-associated optic neuritis, visual function spontaneously improves over 2–3 months, and there is evidence thatcorticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
treatment does not affect the long term outcome. However, for optic neuritis that is not MS-associated (or atypical optic neuritis) the evidence is less clear and therefore the threshold for treatment with intravenous corticosteroids is lower. Intravenous corticosteroids also reduce the risk of developing MS in the following two years in patients with MRI lesions; but this effect disappears by the third year of follow up.
Paradoxically, oral administration of corticosteroids in this situation may lead to more recurrent attacks than in non-treated patients (though oral steroids are generally prescribed after the intravenous course, to wean the patient off the medication). This effect of corticosteroids seems to be limited to optic neuritis and has not been observed in other diseases treated with corticosteroids.
A Cochrane systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
studied the effect of corticosteroids for treating people with acute optic neuritis. Specific corticosteroids studied included intravenous and oral methylprednisone, and oral prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and ad ...
. The authors conclude that current evidence does not show a benefit of either intravenous or oral corticosteroids for rate of recovery of vision (in terms of visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, or visual fields). There are a number of reasons why this might be the case.
Epidemiology
Optic neuritis typically affects young adults ranging from 18–45 years of age, with a mean age of 30–35 years. There is a strong female predominance. The annual incidence is approximately 5/100,000, with a prevalence estimated to be 115/100,000.Society and culture
InCharles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
' ''Bleak House
''Bleak House'' is a novel by Charles Dickens, first published as a 20-episode serial between March 1852 and September 1853. The novel has many characters and several sub-plots, and is told partly by the novel's heroine, Esther Summerson, and ...
'', the main character, Esther Summerville, has a transient episode of visual loss, the symptoms of which are also seen in people who have optic neuritis. Legal historian William Searle Holdsworth
Sir William Searle Holdsworth (7 May 1871 – 2 January 1944) was an English legal historian and Vinerian Professor of English Law at Oxford University, amongst whose works is the 17-volume ''History of English Law''.
Biography
Holdsworth w ...
suggested that the events in ''Bleak House'' took place in 1827.
In an episode of ''Dr. Quinn, Medicine Woman
''Dr. Quinn, Medicine Woman'' is an American Western drama television series created and executive produced by Beth Sullivan and starring Jane Seymour, who plays Dr. Michaela Quinn, a physician who leaves Boston in search of adventure in the O ...
'' ("Season of Miracles", season five), Reverend Timothy Johnson is struck blind by optic neuritis on Christmas Day 1872. He remains blind for the duration of the series.
See also
*Optic neuropathy Optic neuropathy is damage to the optic nerve from any cause. The optic nerve is a bundle of millions of fibers in the retina that sends visual signals to the brain.
Damage and death of these nerve cells, or neurons, leads to characteristic featu ...
* Visual snow
Visual snow syndrome (VSS) is an uncommon neurological condition in which the primary symptom is that affected individuals see persistent flickering white, black, transparent, or coloured dots across the whole visual field. Other common symptom ...
References
External links
{{Headache Autoimmune diseases Disorders of optic nerve and visual pathways