Overshoot (signal) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
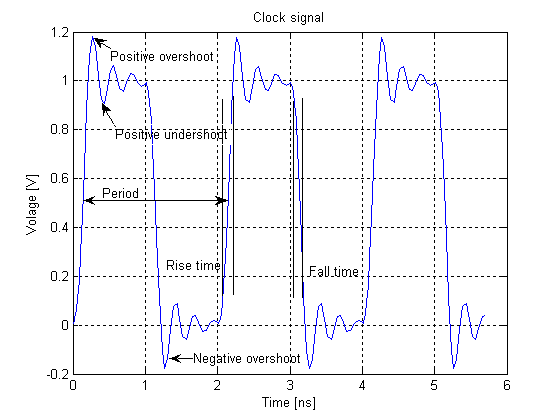 In electronics, ''overshoot'' refers to the transitory values of any parameter that exceeds its final (steady state) value during its transition from one value to another. An important application of the term is to the output signal of an amplifier.
''Usage'': Overshoot occurs when the transitory values exceed final value. When they are lower than the final value, the phenomenon is called ''"undershoot"''.
A
In electronics, ''overshoot'' refers to the transitory values of any parameter that exceeds its final (steady state) value during its transition from one value to another. An important application of the term is to the output signal of an amplifier.
''Usage'': Overshoot occurs when the transitory values exceed final value. When they are lower than the final value, the phenomenon is called ''"undershoot"''.
A
 In the approximation of functions, ''overshoot'' is one term describing quality of approximation. When a function such as a square wave is represented by a summation of terms, for example, a
In the approximation of functions, ''overshoot'' is one term describing quality of approximation. When a function such as a square wave is represented by a summation of terms, for example, a


 In
In
Percentage overshoot calculator
Transient response characteristics Classical control theory
 In
In signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
, control theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a ...
, electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
, and mathematics, overshoot is the occurrence of a signal or function exceeding its target. Undershoot is the same phenomenon in the opposite direction. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
s. It is often followed by ringing, and at times conflated with the latter.
Definition
Maximum overshoot is defined in Katsuhiko Ogata's ''Discrete-time control systems'' as "the maximum peak value of the response curve measured from the desired response of the system."Control theory
Incontrol theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a ...
, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value.
For a step input
Step(s) or STEP may refer to:
Common meanings
* Steps, making a staircase
* Walking
* Dance move
* Military step, or march
** Marching
Arts Films and television
* ''Steps'' (TV series), Hong Kong
* ''Step'' (film), US, 2017
Literature
* '' ...
, the ''percentage overshoot'' (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the ''overshoot'' is just the maximum value of the step response minus one. Also see the definition of ''overshoot'' in an electronics context.
For second-order systems, the percentage overshoot is a function of the damping ratio
Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation. Examples in ...
''ζ'' and is given by Modern Control Engineering (3rd Edition), Katsuhiko Ogata, page 153.
:
The damping ratio can also be found by
:
Electronics
 In electronics, ''overshoot'' refers to the transitory values of any parameter that exceeds its final (steady state) value during its transition from one value to another. An important application of the term is to the output signal of an amplifier.
''Usage'': Overshoot occurs when the transitory values exceed final value. When they are lower than the final value, the phenomenon is called ''"undershoot"''.
A
In electronics, ''overshoot'' refers to the transitory values of any parameter that exceeds its final (steady state) value during its transition from one value to another. An important application of the term is to the output signal of an amplifier.
''Usage'': Overshoot occurs when the transitory values exceed final value. When they are lower than the final value, the phenomenon is called ''"undershoot"''.
A circuit
Circuit may refer to:
Science and technology
Electrical engineering
* Electrical circuit, a complete electrical network with a closed-loop giving a return path for current
** Analog circuit, uses continuous signal levels
** Balanced circu ...
is designed to minimize rise time while containing distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio s ...
of the signal
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing' ...
within acceptable limits.
# Overshoot represents a distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio s ...
of the signal.
# In circuit design, the goals of minimizing overshoot and of decreasing circuit rise time can conflict.
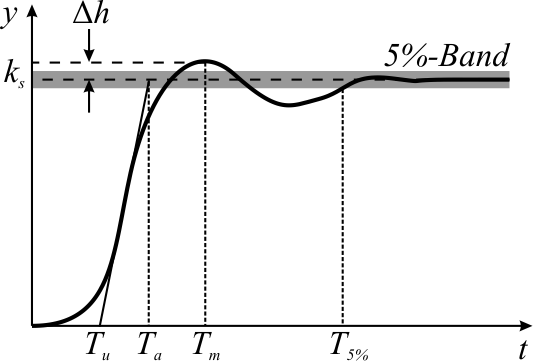
# The magnitude of overshoot depends on time through a phenomenon called ''" damping."'' See illustration under step response''.
# Overshoot often is associated with settling time, how long it takes for the output to reach steady state; see step response.
Also see the definition of ''overshoot'' in a control theory context.
Mathematics
Fourier series
A Fourier series () is a summation of harmonically related sinusoidal functions, also known as components or harmonics. The result of the summation is a periodic function whose functional form is determined by the choices of cycle length (or '' ...
or an expansion in orthogonal polynomials
In mathematics, an orthogonal polynomial sequence is a family of polynomials such that any two different polynomials in the sequence are orthogonal to each other under some inner product.
The most widely used orthogonal polynomials are the cl ...
, the approximation of the function by a truncated number of terms in the series can exhibit overshoot, undershoot and ringing. The more terms retained in the series, the less pronounced the departure of the approximation from the function it represents. However, though the period of the oscillations decreases, their amplitude does not;
this is known as the Gibbs phenomenon. For the Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
, this can be modeled by approximating a step function
In mathematics, a function on the real numbers is called a step function if it can be written as a finite linear combination of indicator functions of intervals. Informally speaking, a step function is a piecewise constant function having on ...
by the integral up to a certain frequency, which yields the sine integral. This can be interpreted as convolution with the sinc function; in signal processing terms, this is a low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
.
Signal processing

signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
, overshoot is when the output of a filter has a higher maximum value than the input, specifically for the step response, and frequently yields the related phenomenon of ringing artifacts
In signal processing, particularly digital image processing, ringing artifacts are artifacts that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "ec ...
.
This occurs for instance in using the sinc filter as an ideal ( brick-wall) low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
. The step response can be interpreted as the convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term ''convolution' ...
with the impulse response
In signal processing and control theory, the impulse response, or impulse response function (IRF), of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse (). More generally, an impulse response is the reac ...
, which is a sinc function.
The overshoot and undershoot can be understood in this way: kernels are generally normalized to have integral 1, so they send constant functions to constant functions otherwise they have gain
Gain or GAIN may refer to:
Science and technology
* Gain (electronics), an electronics and signal processing term
* Antenna gain
* Gain (laser), the amplification involved in laser emission
* Gain (projection screens)
* Information gain in d ...
. The value of a convolution at a point is a linear combination of the input signal, with coefficients (weights) the values of the kernel. If a kernel is non-negative, such as for a Gaussian kernel, then the value of the filtered signal will be a convex combination
In convex geometry and vector algebra, a convex combination is a linear combination of points (which can be vectors, scalars, or more generally points in an affine space) where all coefficients are non-negative and sum to 1. In other ...
of the input values (the coefficients (the kernel) integrate to 1, and are non-negative), and will thus fall between the minimum and maximum of the input signal{{snd it will not undershoot or overshoot. If, on the other hand, the kernel assumes negative values, such as the sinc function, then the value of the filtered signal will instead be an affine combination In mathematics, an affine combination of is a linear combination
: \sum_^ = \alpha_ x_ + \alpha_ x_ + \cdots +\alpha_ x_,
such that
:\sum_^ =1.
Here, can be elements ( vectors) of a vector space over a field , and the coefficients \alpha_ ...
of the input values, and may fall outside of the minimum and maximum of the input signal, resulting in undershoot and overshoot.
Overshoot is often undesirable, particularly if it causes clipping, but is sometimes desirable in image sharpening, due to increasing acutance
In photography, acutance describes a subjective perception of sharpness that is related to the edge contrast of an image. Acutance is related to the amplitude of the derivative of brightness with respect to space. Due to the nature of the huma ...
(perceived sharpness).
Related concepts
A closely related phenomenon is ringing, when, following overshoot, a signal then falls ''below'' its steady-state value, and then may bounce back above, taking some time to settle close to its steady-state value; this latter time is called the settle time. Inecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
, overshoot is the analogous concept, where a population exceeds the carrying capacity of a system.
See also
* Step response * Ringing (signal) * Settling time * Overmodulation *Integral windup
Integral windup, also known as integrator windup or reset windup, refers to the situation in a PID feedback controller where a large change in setpoint occurs (say a positive change) and the integral term accumulates a significant error during th ...
References and notes
External links
Percentage overshoot calculator
Transient response characteristics Classical control theory