overhead contact system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit

 To achieve good high-speed current collection, it is necessary to keep the contact wire geometry within defined limits. This is usually achieved by supporting the contact wire from a second wire known as the ' (in the US & Canada) or ''catenary'' (in the UK). This wire approximates the natural path of a wire strung between two points, a catenary curve, thus the use of "catenary" to describe this wire or sometimes the whole system. This wire is attached to the contact wire at regular intervals by vertical wires known as "droppers" or "drop wires". It is supported regularly at structures, by a
To achieve good high-speed current collection, it is necessary to keep the contact wire geometry within defined limits. This is usually achieved by supporting the contact wire from a second wire known as the ' (in the US & Canada) or ''catenary'' (in the UK). This wire approximates the natural path of a wire strung between two points, a catenary curve, thus the use of "catenary" to describe this wire or sometimes the whole system. This wire is attached to the contact wire at regular intervals by vertical wires known as "droppers" or "drop wires". It is supported regularly at structures, by a

 An electrical circuit requires at least two conductors. Trams and railways use the overhead line as one side of the circuit and the steel rails as the other side of the circuit. For a trolleybus or a
An electrical circuit requires at least two conductors. Trams and railways use the overhead line as one side of the circuit and the steel rails as the other side of the circuit. For a trolleybus or a
 Catenary wires are kept in mechanical tension because the pantograph causes mechanical oscillations in the wire and the wave must travel faster than the train to avoid producing
Catenary wires are kept in mechanical tension because the pantograph causes mechanical oscillations in the wire and the wave must travel faster than the train to avoid producing
 To allow maintenance to the overhead line without having to turn off the entire system, the line is broken into electrically separated portions known as "sections". Sections often correspond with tension lengths. The transition from section to section is known as a "section break" and is set up so that the vehicle's pantograph is in continuous contact with one wire or the other.
For bow collectors and pantographs, this is done by having two contact wires run side by side over the length between 2 or 4 wire supports. A new one drops down and the old one rises up, allowing the pantograph to smoothly transfer from one to the other. The two wires do not touch (although the bow collector or pantograph is briefly in contact with both wires). In normal service, the two sections are electrically connected; depending on the system this might be an isolator, fixed contact or a Booster Transformer. The isolator allows the current to the section to be interrupted for maintenance.
On overhead wires designed for trolley poles, this is done by having a neutral section between the wires, requiring an insulator. The driver of the tram or trolleybus must temporarily reduce the power draw before the trolley pole passes through, to prevent arc damage to the insulator.
Pantograph-equipped locomotives must not run through a section break when one side is de-energized. The locomotive would become trapped, but as it passes the section break the pantograph briefly shorts the two catenary lines. If the opposite line is de-energized, this voltage transient may trip supply breakers. If the line is under maintenance, an injury may occur as the catenary is suddenly energized. Even if the catenary is properly grounded to protect the personnel, the
To allow maintenance to the overhead line without having to turn off the entire system, the line is broken into electrically separated portions known as "sections". Sections often correspond with tension lengths. The transition from section to section is known as a "section break" and is set up so that the vehicle's pantograph is in continuous contact with one wire or the other.
For bow collectors and pantographs, this is done by having two contact wires run side by side over the length between 2 or 4 wire supports. A new one drops down and the old one rises up, allowing the pantograph to smoothly transfer from one to the other. The two wires do not touch (although the bow collector or pantograph is briefly in contact with both wires). In normal service, the two sections are electrically connected; depending on the system this might be an isolator, fixed contact or a Booster Transformer. The isolator allows the current to the section to be interrupted for maintenance.
On overhead wires designed for trolley poles, this is done by having a neutral section between the wires, requiring an insulator. The driver of the tram or trolleybus must temporarily reduce the power draw before the trolley pole passes through, to prevent arc damage to the insulator.
Pantograph-equipped locomotives must not run through a section break when one side is de-energized. The locomotive would become trapped, but as it passes the section break the pantograph briefly shorts the two catenary lines. If the opposite line is de-energized, this voltage transient may trip supply breakers. If the line is under maintenance, an injury may occur as the catenary is suddenly energized. Even if the catenary is properly grounded to protect the personnel, the
 Sometimes on a larger electrified railway, tramway or trolleybus system, it is necessary to power different areas of track from different power grids, without guaranteeing synchronisation of the phases. Long lines may be connected to the country's national grid at various points and different phases. (Sometimes the sections are powered with different voltages or frequencies.) The grids may be synchronised on a normal basis, but events may interrupt synchronisation. This is not a problem for DC systems. AC systems have a particular safety implication in that the railway electrification system would act as a "Backdoor" connection between different parts, resulting in, amongst other things, a section of the grid de-energised for maintenance being re-energised from the railway substation creating danger.
For these reasons, Neutral sections are placed in the electrification between the sections fed from different points in a national grid, or different phases, or grids that are not synchronized. It is highly undesirable to connect synchronized grids. A simple section break is insufficient to guard against this as the pantograph briefly connects both sections.
In countries such as France, South Africa and the United Kingdom, a pair of permanent magnets beside the rails at either side of the neutral section operate a bogie-mounted transducer on the train which causes a large electrical circuit-breaker to open and close when the locomotive or the pantograph vehicle of a multiple unit passes over them. In the United Kingdom equipment similar to Automatic Warning System (AWS) is used, but with pairs of magnets placed the running rails (as opposed to the AWS magnets placed midway between the rails). Lineside signs on the approach to the neutral section warn the driver to shut off traction power and coast through the dead section.
A neutral section or phase break consists of two insulated breaks back-to-back with a short section of line that belongs to neither grid. Some systems increase the level of safety by the midpoint of the neutral section being earthed. The presence of the earthed section in the middle is to ensure that should the transducer controlled apparatus fail, and the driver also fail to shut off power, the energy in the arc struck by the pantograph as it passes to the neutral section is conducted to earth, operating substation circuit breakers, rather than the arc either bridging the insulators into a section made dead for maintenance, a section fed from a different phase, or setting up a Backdoor connection between different parts of the country's national grid.
Sometimes on a larger electrified railway, tramway or trolleybus system, it is necessary to power different areas of track from different power grids, without guaranteeing synchronisation of the phases. Long lines may be connected to the country's national grid at various points and different phases. (Sometimes the sections are powered with different voltages or frequencies.) The grids may be synchronised on a normal basis, but events may interrupt synchronisation. This is not a problem for DC systems. AC systems have a particular safety implication in that the railway electrification system would act as a "Backdoor" connection between different parts, resulting in, amongst other things, a section of the grid de-energised for maintenance being re-energised from the railway substation creating danger.
For these reasons, Neutral sections are placed in the electrification between the sections fed from different points in a national grid, or different phases, or grids that are not synchronized. It is highly undesirable to connect synchronized grids. A simple section break is insufficient to guard against this as the pantograph briefly connects both sections.
In countries such as France, South Africa and the United Kingdom, a pair of permanent magnets beside the rails at either side of the neutral section operate a bogie-mounted transducer on the train which causes a large electrical circuit-breaker to open and close when the locomotive or the pantograph vehicle of a multiple unit passes over them. In the United Kingdom equipment similar to Automatic Warning System (AWS) is used, but with pairs of magnets placed the running rails (as opposed to the AWS magnets placed midway between the rails). Lineside signs on the approach to the neutral section warn the driver to shut off traction power and coast through the dead section.
A neutral section or phase break consists of two insulated breaks back-to-back with a short section of line that belongs to neither grid. Some systems increase the level of safety by the midpoint of the neutral section being earthed. The presence of the earthed section in the middle is to ensure that should the transducer controlled apparatus fail, and the driver also fail to shut off power, the energy in the arc struck by the pantograph as it passes to the neutral section is conducted to earth, operating substation circuit breakers, rather than the arc either bridging the insulators into a section made dead for maintenance, a section fed from a different phase, or setting up a Backdoor connection between different parts of the country's national grid.
 On the
On the
 Occasionally gaps may be present in the overhead lines, when switching from one voltage to another or to provide clearance for ships at moveable bridges, as a cheaper alternative for moveable overhead power rails. Electric trains coast across the gaps. To prevent arcing, power must be switched off before reaching the gap and usually the pantograph would be lowered.
Occasionally gaps may be present in the overhead lines, when switching from one voltage to another or to provide clearance for ships at moveable bridges, as a cheaper alternative for moveable overhead power rails. Electric trains coast across the gaps. To prevent arcing, power must be switched off before reaching the gap and usually the pantograph would be lowered.
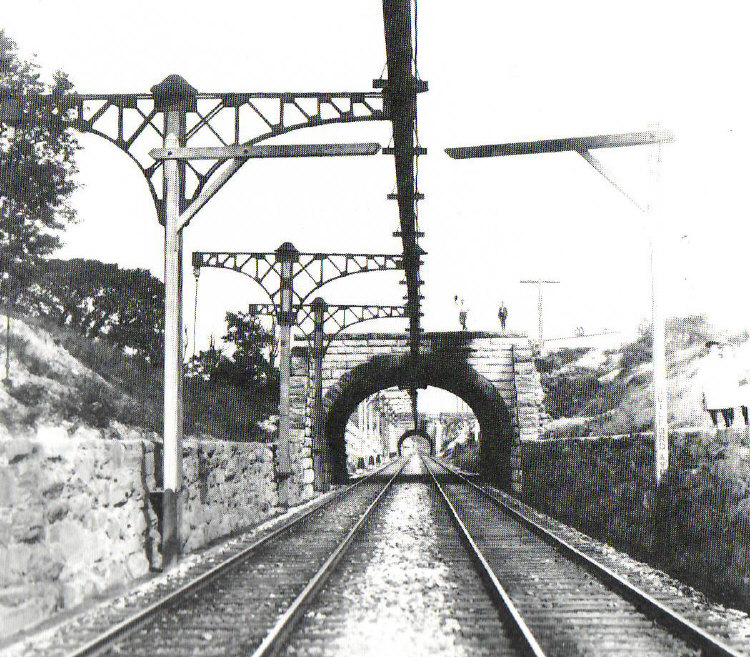 Given limited clearance such as in tunnels, the overhead wire may be replaced by a rigid overhead rail. An early example was in the tunnels of the Baltimore Belt Line, where a Π section bar (fabricated from three strips of iron and mounted on wood) was used, with the brass contact running inside the groove. When the overhead line was raised in the Simplon Tunnel to accommodate taller rolling stock, a rail was used. A rigid overhead rail may also be used in places where tensioning the wires is impractical, for example on moveable bridges.
In a movable bridge that uses a rigid overhead rail, there is a need to transition from the catenary wire system into an overhead conductor rail at the bridge portal (the last post before the movable bridge). For example, the power supply can be done through a catenary wire system near a swing bridge. The catenary wire typically comprises messenger wire (also called catenary wire) and a contact wire where it meets the pantograph. The messenger wire is terminated at the portal, while the contact wire runs into the overhead conductor rail profile at the transition end section before it is terminated at the portal. There is a gap between the overhead conductor rail at the transition end section and the overhead conductor rail that runs across the entire span of the swing bridge. The gap is required for the swing bridge to be opened and closed. To connect the conductor rails together when the bridge is closed, there is another conductor rail section called "rotary overlap" that is equipped with a motor. When the bridge is fully closed, the motor of the rotary overlap is operated to turn it from a tilted position into the horizontal position, connecting the conductor rails at the transition end section and the bridge together to supply power.
Short overhead conductor rails are installed at tram stops as for the
Given limited clearance such as in tunnels, the overhead wire may be replaced by a rigid overhead rail. An early example was in the tunnels of the Baltimore Belt Line, where a Π section bar (fabricated from three strips of iron and mounted on wood) was used, with the brass contact running inside the groove. When the overhead line was raised in the Simplon Tunnel to accommodate taller rolling stock, a rail was used. A rigid overhead rail may also be used in places where tensioning the wires is impractical, for example on moveable bridges.
In a movable bridge that uses a rigid overhead rail, there is a need to transition from the catenary wire system into an overhead conductor rail at the bridge portal (the last post before the movable bridge). For example, the power supply can be done through a catenary wire system near a swing bridge. The catenary wire typically comprises messenger wire (also called catenary wire) and a contact wire where it meets the pantograph. The messenger wire is terminated at the portal, while the contact wire runs into the overhead conductor rail profile at the transition end section before it is terminated at the portal. There is a gap between the overhead conductor rail at the transition end section and the overhead conductor rail that runs across the entire span of the swing bridge. The gap is required for the swing bridge to be opened and closed. To connect the conductor rails together when the bridge is closed, there is another conductor rail section called "rotary overlap" that is equipped with a motor. When the bridge is fully closed, the motor of the rotary overlap is operated to turn it from a tilted position into the horizontal position, connecting the conductor rails at the transition end section and the bridge together to supply power.
Short overhead conductor rails are installed at tram stops as for the

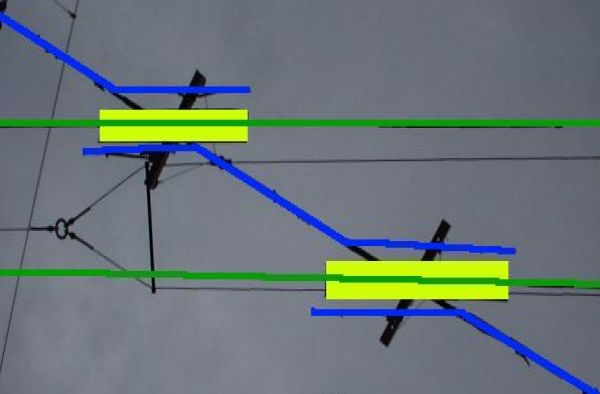 Trams draw their power from a single overhead wire at about 500 to 750 V. Trolleybuses draw from two overhead wires at a similar voltage, and at least one of the trolleybus wires must be insulated from tram wires. This is usually done by the trolleybus wires running continuously through the crossing, with the tram conductors a few centimetres lower. Close to the junction on each side, the tram wire turns into a solid bar running parallel to the trolleybus wires for about half a metre. Another bar similarly angled at its ends is hung between the trolleybus wires, electrically connected above to the tram wire. The tram's pantograph bridges the gap between the different conductors, providing it with a continuous pickup.
Where the tram wire crosses, the trolleybus wires are protected by an inverted trough of insulating material extending below.
Until 1946, a level crossing in
Trams draw their power from a single overhead wire at about 500 to 750 V. Trolleybuses draw from two overhead wires at a similar voltage, and at least one of the trolleybus wires must be insulated from tram wires. This is usually done by the trolleybus wires running continuously through the crossing, with the tram conductors a few centimetres lower. Close to the junction on each side, the tram wire turns into a solid bar running parallel to the trolleybus wires for about half a metre. Another bar similarly angled at its ends is hung between the trolleybus wires, electrically connected above to the tram wire. The tram's pantograph bridges the gap between the different conductors, providing it with a continuous pickup.
Where the tram wire crosses, the trolleybus wires are protected by an inverted trough of insulating material extending below.
Until 1946, a level crossing in
 Some railways used two or three overhead lines, usually to carry
Some railways used two or three overhead lines, usually to carry



 A catenary is a system of overhead wires used to supply electricity to a
A catenary is a system of overhead wires used to supply electricity to a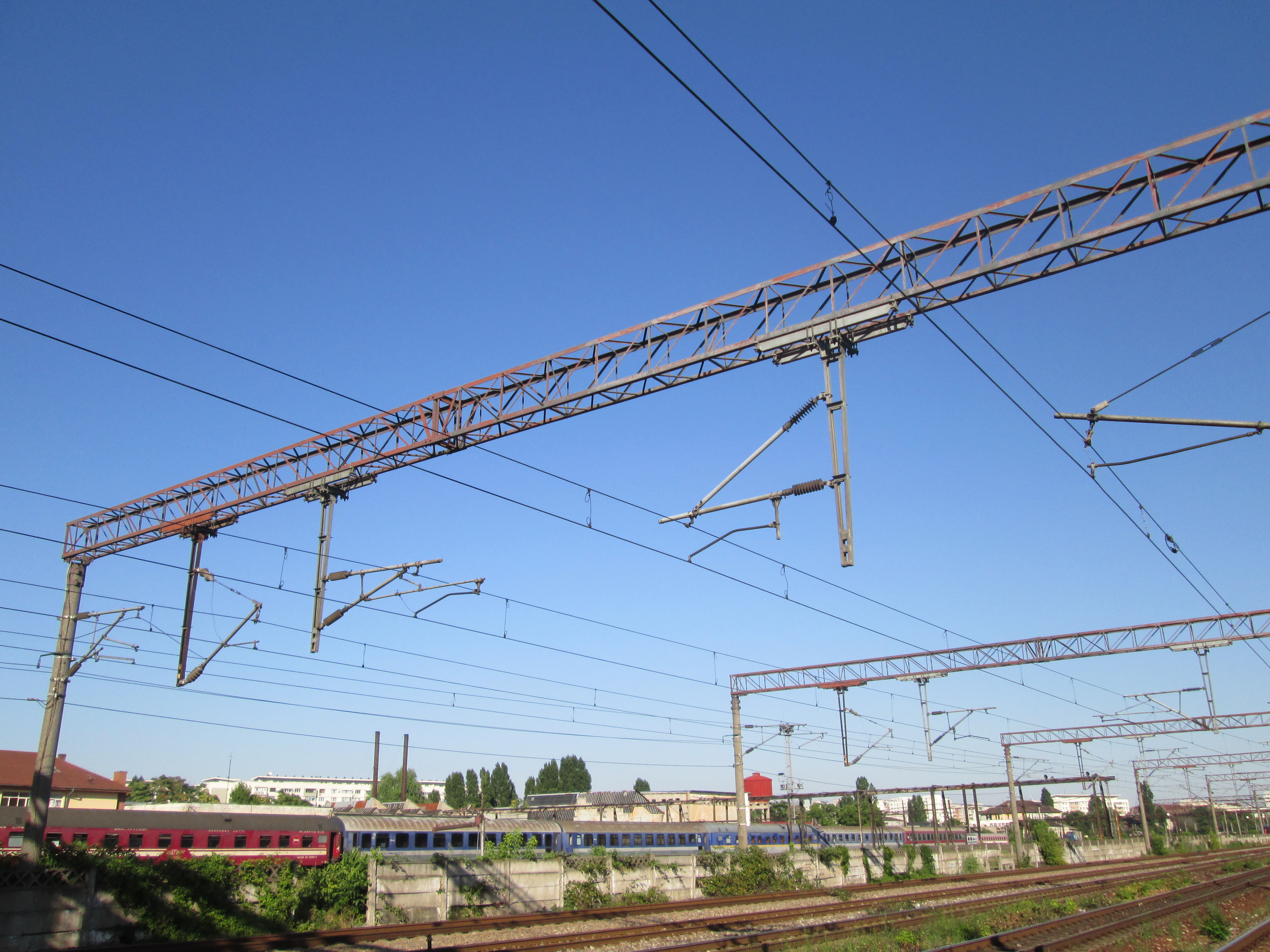  Unlike simple overhead wires, in which the uninsulated wire is attached by clamps to closely spaced crosswires supported by poles, catenary systems use at least two wires. The catenary or messenger wire is hung at a specific tension between line structures, and a second wire is held in tension by the messenger wire, attached to it at frequent intervals by clamps and connecting wires known as ''droppers''. The second wire is straight and level, parallel to the
Unlike simple overhead wires, in which the uninsulated wire is attached by clamps to closely spaced crosswires supported by poles, catenary systems use at least two wires. The catenary or messenger wire is hung at a specific tension between line structures, and a second wire is held in tension by the messenger wire, attached to it at frequent intervals by clamps and connecting wires known as ''droppers''. The second wire is straight and level, parallel to the
File:IMU 184.jpg, Overhead lines in Queensland, Australia
File:Overhead lines, Puidoux.jpg, Overhead lines on
 An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy
Electrical energy is energy related to forces on electrically charged particles and the movement of electrically charged particles (often electrons in wires, but not always). This energy is supplied by the combination of electric current and electr ...
to electric locomotives, trolleybuses or trams. It is known variously as:
* Overhead catenary
* Overhead contact system (OCS)
* Overhead equipment (OHE)
* Overhead line equipment (OLE or OHLE)
* Overhead lines (OHL)
* Overhead wiring (OHW)
* Traction wire
* Trolley wire
This article follows the International Union of Railways
The International Union of Railways (UIC, french: Union internationale des wikt:chemin de fer, chemins de fer) is an international rail transport industry body.
History
The railways of Europe originated as many separate concerns, and there wer ...
in using the generic term ''overhead line''.
An overhead line consists of one or more wires (or rails, particularly in tunnels) situated over rail tracks, raised to a high electrical potential by connection to feeder stations at regular intervals. The feeder stations are usually fed from a high-voltage electrical grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
.
Overview
Electric trains that collect their current from overhead lines use a device such as a pantograph, bow collector or trolley pole. It presses against the underside of the lowest overhead wire, the contact wire. Current collectors are electrically conductive and allow current to flow through to the train or tram and back to the feeder station through the steel wheels on one or both running rails. Non-electriclocomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
s (such as diesels) may pass along these tracks without affecting the overhead line, although there may be difficulties with overhead clearance
A structure gauge, also called the minimum clearance outline, is a diagram or physical structure that sets limits to the extent that bridges, tunnels and other infrastructure can encroach on rail vehicles. It specifies the height and width of pl ...
. Alternative electrical power transmission schemes for trains include third rail, ground-level power supply
Ground-level power supply, also known as surface current collection or, in French, ''alimentation par le sol'' ("feeding via the ground"), is a concept and group of technologies whereby electric vehicles collect electric power at ground level fro ...
, batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
and electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and James Clerk ...
.
Construction

 To achieve good high-speed current collection, it is necessary to keep the contact wire geometry within defined limits. This is usually achieved by supporting the contact wire from a second wire known as the ' (in the US & Canada) or ''catenary'' (in the UK). This wire approximates the natural path of a wire strung between two points, a catenary curve, thus the use of "catenary" to describe this wire or sometimes the whole system. This wire is attached to the contact wire at regular intervals by vertical wires known as "droppers" or "drop wires". It is supported regularly at structures, by a
To achieve good high-speed current collection, it is necessary to keep the contact wire geometry within defined limits. This is usually achieved by supporting the contact wire from a second wire known as the ' (in the US & Canada) or ''catenary'' (in the UK). This wire approximates the natural path of a wire strung between two points, a catenary curve, thus the use of "catenary" to describe this wire or sometimes the whole system. This wire is attached to the contact wire at regular intervals by vertical wires known as "droppers" or "drop wires". It is supported regularly at structures, by a pulley
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft that is designed to support movement and change of direction of a taut cable or belt, or transfer of power between the shaft and cable or belt. In the case of a pulley supported by a frame or shell that ...
, link or clamp. The whole system is then subjected to mechanical tension.
As the pantograph moves along under the contact wire, the carbon insert on top of the pantograph becomes worn with time. On straight track, the contact wire is zigzagged slightly to the left and right of the centre from each support to the next so that the insert wears evenly, thus preventing any notches. On curves, the "straight" wire between the supports causes the contact point to cross over the surface of the pantograph as the train travels around the curve. The movement of the contact wire across the head of the pantograph is called the "sweep".
The zigzagging of the overhead line is not required for trolley poles. For tramways, a contact wire without a messenger wire is used.
Depot areas tend to have only a single wire and are known as "simple equipment" or "trolley wire". When overhead line systems were first conceived, good current collection was possible only at low speeds, using a single wire. To enable higher speeds, two additional types of equipment were developed:
* Stitched equipment uses an additional wire at each support structure, terminated on either side of the messenger/catenary wire.
* Compound equipment uses a second support wire, known as the "auxiliary", between the messenger/catenary wire and the contact wire. Droppers support the auxiliary from the messenger wire, while additional droppers support the contact wire from the auxiliary. The auxiliary wire can be of a more conductive but less wear-resistant metal, increasing transmission efficiency.
Earlier dropper wires provided physical support of the contact wire without joining the catenary and contact wires electrically. Modern systems use current-carrying droppers, eliminating the need for separate wires.
The present transmission system originated about 100 years ago. A simpler system was proposed in the 1970s by the Pirelli Construction Company, consisting of a single wire embedded at each support for of its length in a clipped, extruded aluminum beam with the wire contact face exposed. A somewhat higher tension than used before clipping the beam yielded a deflected profile for the wire that could be easily handled at by a pneumatic servo pantograph with only 3 g acceleration.
Parallel overhead lines

 An electrical circuit requires at least two conductors. Trams and railways use the overhead line as one side of the circuit and the steel rails as the other side of the circuit. For a trolleybus or a
An electrical circuit requires at least two conductors. Trams and railways use the overhead line as one side of the circuit and the steel rails as the other side of the circuit. For a trolleybus or a trolleytruck
A trolleytruck (also known as a freight trolley or trolley truckIn the United Kingdom a ''trolley'' may refer to the hand operated wheeled vehicle called a ''hand truck'' in North America. In North American usage the term ''trolley truck'' may als ...
, no rails are available for the return current, as the vehicles use rubber tyres on the road surface. Trolleybuses use a second parallel overhead line for the return, and two trolley poles, one contacting each overhead wire. (Pantographs
A pantograph (, from their original use for copying writing) is a mechanical linkage connected in a manner based on parallelograms so that the movement of one pen, in tracing an image, produces identical movements in a second pen. If a line dr ...
are generally incompatible with parallel overhead lines.) The circuit is completed by using both wires. Parallel overhead wires are also used on the rare railways with three-phase AC railway electrification.
Types of wires
In the Soviet Union the following types of wires/cables were used. For the contact wire, cold drawn solid copper was used to ensure good conductivity. The wire is not round but has grooves at the sides to allow the hangers to attach to it. Sizes were (in cross-sectional area) 85, 100, or 150 mm2. To make the wire stronger, 0.04% tin might be added. The wire must resist the heat generated by arcing and thus such wires should never be spliced by thermal means. The messenger (or catenary) wire needs to be both strong and have good conductivity. They used multi-strand wires (or cables) with 19 strands in each cable (or wire). Copper, aluminum, and/or steel were used for the strands. All the 19 strands could be of the same metal or some strands could be of steel for strength with the remaining strands of aluminum or copper for conductivity. Another type looked like it had all copper wires but inside each wire was a steel core for strength. The steel strands were galvanized but for better corrosion protection they could be coated with an anti-corrosion substance. In Slovenia, where 3 kV system is in use, standard sizes for contact wire are 100 and 150 mm2. The catenary wire is made of copper or copper alloys of 70, 120 or 150 mm2. The smaller cross sections are made of 19 strands, whereas the bigger has 37 strands. Two standard configurations for main lines consist of two contact wires of 100 mm2 and one or two catenary wires of 120 mm2, totaling 320 or 440 mm2. Only one contact wire is often used for side tracks.Tensioning
 Catenary wires are kept in mechanical tension because the pantograph causes mechanical oscillations in the wire and the wave must travel faster than the train to avoid producing
Catenary wires are kept in mechanical tension because the pantograph causes mechanical oscillations in the wire and the wave must travel faster than the train to avoid producing standing wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect ...
s that would cause wire breakage. Tensioning the line makes waves travel faster, and also reduces sag from gravity.
For medium and high speeds, the wires are generally tensioned by weights or occasionally by hydraulic tensioners. Either method is known as "auto-tensioning" (AT) or "constant tension" and ensures that the tension is virtually independent of temperature. Tensions are typically between per wire. Where weights are used, they slide up and down on a rod or tube attached to the mast, to prevent them from swaying.
For low speeds and in tunnels where temperatures are constant, fixed termination (FT) equipment may be used, with the wires terminated directly on structures at each end of the overhead line. The tension is generally about . This type of equipment sags in hot conditions and is taut in cold conditions.
With AT, the continuous length of the overhead line is limited due to the change in the height of the weights as the overhead line expands and contracts with temperature changes. This movement is proportional to the distance between anchors. Tension length has a maximum. For most 25 kV OHL equipment in the UK, the maximum tension length is .
An additional issue with AT equipment is that, if balance weights are attached to both ends, the whole tension length is free to move along the track. To avoid this a midpoint anchor (MPA), close to the centre of the tension length, restricts movement of the messenger/catenary wire by anchoring it; the contact wire and its suspension hangers can move only within the constraints of the MPA. MPAs are sometimes fixed to low bridges, or otherwise anchored to vertical catenary poles or portal catenary supports. A tension length can be seen as a fixed centre point, with the two half-tension lengths expanding and contracting with temperature.
Most systems include a brake to stop the wires from unravelling completely if a wire breaks or tension is lost. German systems usually use a single large tensioning pulley (basically a ratchet
Ratchet may refer to:
Devices
* Ratchet (device), a mechanical device that allows movement in only one direction
* Ratchet, metonomic name for a socket wrench incorporating a ratcheting device
* Ratchet (instrument), a music instrument and a ...
mechanism) with a toothed rim, mounted on an arm hinged to the mast. Normally the downward pull of the weights and the reactive upward pull of the tensioned wires lift the pulley so its teeth are well clear of a stop on the mast. The pulley can turn freely while the weights move up or down as the wires contract or expand. If tension is lost the pulley falls back toward the mast, and one of its teeth jams against the stop. This stops further rotation, limits the damage, and keeps the undamaged part of the wire intact until it can be repaired. Other systems use various braking mechanisms, usually with multiple smaller pulleys in a block and tackle arrangement.
Breaks
Lines are divided into sections to limit the scope of an outage and to allow maintenance.Section break
 To allow maintenance to the overhead line without having to turn off the entire system, the line is broken into electrically separated portions known as "sections". Sections often correspond with tension lengths. The transition from section to section is known as a "section break" and is set up so that the vehicle's pantograph is in continuous contact with one wire or the other.
For bow collectors and pantographs, this is done by having two contact wires run side by side over the length between 2 or 4 wire supports. A new one drops down and the old one rises up, allowing the pantograph to smoothly transfer from one to the other. The two wires do not touch (although the bow collector or pantograph is briefly in contact with both wires). In normal service, the two sections are electrically connected; depending on the system this might be an isolator, fixed contact or a Booster Transformer. The isolator allows the current to the section to be interrupted for maintenance.
On overhead wires designed for trolley poles, this is done by having a neutral section between the wires, requiring an insulator. The driver of the tram or trolleybus must temporarily reduce the power draw before the trolley pole passes through, to prevent arc damage to the insulator.
Pantograph-equipped locomotives must not run through a section break when one side is de-energized. The locomotive would become trapped, but as it passes the section break the pantograph briefly shorts the two catenary lines. If the opposite line is de-energized, this voltage transient may trip supply breakers. If the line is under maintenance, an injury may occur as the catenary is suddenly energized. Even if the catenary is properly grounded to protect the personnel, the
To allow maintenance to the overhead line without having to turn off the entire system, the line is broken into electrically separated portions known as "sections". Sections often correspond with tension lengths. The transition from section to section is known as a "section break" and is set up so that the vehicle's pantograph is in continuous contact with one wire or the other.
For bow collectors and pantographs, this is done by having two contact wires run side by side over the length between 2 or 4 wire supports. A new one drops down and the old one rises up, allowing the pantograph to smoothly transfer from one to the other. The two wires do not touch (although the bow collector or pantograph is briefly in contact with both wires). In normal service, the two sections are electrically connected; depending on the system this might be an isolator, fixed contact or a Booster Transformer. The isolator allows the current to the section to be interrupted for maintenance.
On overhead wires designed for trolley poles, this is done by having a neutral section between the wires, requiring an insulator. The driver of the tram or trolleybus must temporarily reduce the power draw before the trolley pole passes through, to prevent arc damage to the insulator.
Pantograph-equipped locomotives must not run through a section break when one side is de-energized. The locomotive would become trapped, but as it passes the section break the pantograph briefly shorts the two catenary lines. If the opposite line is de-energized, this voltage transient may trip supply breakers. If the line is under maintenance, an injury may occur as the catenary is suddenly energized. Even if the catenary is properly grounded to protect the personnel, the arc
ARC may refer to:
Business
* Aircraft Radio Corporation, a major avionics manufacturer from the 1920s to the '50s
* Airlines Reporting Corporation, an airline-owned company that provides ticket distribution, reporting, and settlement services
* ...
generated across the pantograph can damage the pantograph, the catenary insulator or both.
Neutral section (phase break)
 On the
On the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named ...
, phase breaks were indicated by a position light signal face with all eight radial positions with lenses and no center light. When the phase break was active (the catenary sections out of phase), all lights were lit. The position light signal aspect was originally devised by the Pennsylvania Railroad and was continued by Amtrak and adopted by Metro North. Metal signs were hung from the catenary supports with the letters "PB" created by a pattern of drilled holes.
Dead section
A special category of phase break was developed in America, primarily by the Pennsylvania Railroad. Since its traction power network was centrally supplied and only segmented by abnormal conditions, normal phase breaks were generally not active. Phase breaks that were always activated were known as "Dead Sections": they were often used to separate power systems (for example, the Hell's Gate Bridge boundary between Amtrak and Metro North's electrifications) that would never be in-phase. Since a dead section is always dead, no special signal aspect was developed to warn drivers of its presence, and a metal sign with "DS" in drilled-hole letters was hung from the catenary supports.Gaps
Overhead conductor rails
 Given limited clearance such as in tunnels, the overhead wire may be replaced by a rigid overhead rail. An early example was in the tunnels of the Baltimore Belt Line, where a Π section bar (fabricated from three strips of iron and mounted on wood) was used, with the brass contact running inside the groove. When the overhead line was raised in the Simplon Tunnel to accommodate taller rolling stock, a rail was used. A rigid overhead rail may also be used in places where tensioning the wires is impractical, for example on moveable bridges.
In a movable bridge that uses a rigid overhead rail, there is a need to transition from the catenary wire system into an overhead conductor rail at the bridge portal (the last post before the movable bridge). For example, the power supply can be done through a catenary wire system near a swing bridge. The catenary wire typically comprises messenger wire (also called catenary wire) and a contact wire where it meets the pantograph. The messenger wire is terminated at the portal, while the contact wire runs into the overhead conductor rail profile at the transition end section before it is terminated at the portal. There is a gap between the overhead conductor rail at the transition end section and the overhead conductor rail that runs across the entire span of the swing bridge. The gap is required for the swing bridge to be opened and closed. To connect the conductor rails together when the bridge is closed, there is another conductor rail section called "rotary overlap" that is equipped with a motor. When the bridge is fully closed, the motor of the rotary overlap is operated to turn it from a tilted position into the horizontal position, connecting the conductor rails at the transition end section and the bridge together to supply power.
Short overhead conductor rails are installed at tram stops as for the
Given limited clearance such as in tunnels, the overhead wire may be replaced by a rigid overhead rail. An early example was in the tunnels of the Baltimore Belt Line, where a Π section bar (fabricated from three strips of iron and mounted on wood) was used, with the brass contact running inside the groove. When the overhead line was raised in the Simplon Tunnel to accommodate taller rolling stock, a rail was used. A rigid overhead rail may also be used in places where tensioning the wires is impractical, for example on moveable bridges.
In a movable bridge that uses a rigid overhead rail, there is a need to transition from the catenary wire system into an overhead conductor rail at the bridge portal (the last post before the movable bridge). For example, the power supply can be done through a catenary wire system near a swing bridge. The catenary wire typically comprises messenger wire (also called catenary wire) and a contact wire where it meets the pantograph. The messenger wire is terminated at the portal, while the contact wire runs into the overhead conductor rail profile at the transition end section before it is terminated at the portal. There is a gap between the overhead conductor rail at the transition end section and the overhead conductor rail that runs across the entire span of the swing bridge. The gap is required for the swing bridge to be opened and closed. To connect the conductor rails together when the bridge is closed, there is another conductor rail section called "rotary overlap" that is equipped with a motor. When the bridge is fully closed, the motor of the rotary overlap is operated to turn it from a tilted position into the horizontal position, connecting the conductor rails at the transition end section and the bridge together to supply power.
Short overhead conductor rails are installed at tram stops as for the Combino Supra
The Siemens Avenio is a low floor tram family produced by Siemens Mobility, a subsidiary of the German conglomerate Siemens. It is the successor to the Combino family. The first generation was sold as the Combino Supra , Combino MkII, or Combino ...
.
Crossings

 Trams draw their power from a single overhead wire at about 500 to 750 V. Trolleybuses draw from two overhead wires at a similar voltage, and at least one of the trolleybus wires must be insulated from tram wires. This is usually done by the trolleybus wires running continuously through the crossing, with the tram conductors a few centimetres lower. Close to the junction on each side, the tram wire turns into a solid bar running parallel to the trolleybus wires for about half a metre. Another bar similarly angled at its ends is hung between the trolleybus wires, electrically connected above to the tram wire. The tram's pantograph bridges the gap between the different conductors, providing it with a continuous pickup.
Where the tram wire crosses, the trolleybus wires are protected by an inverted trough of insulating material extending below.
Until 1946, a level crossing in
Trams draw their power from a single overhead wire at about 500 to 750 V. Trolleybuses draw from two overhead wires at a similar voltage, and at least one of the trolleybus wires must be insulated from tram wires. This is usually done by the trolleybus wires running continuously through the crossing, with the tram conductors a few centimetres lower. Close to the junction on each side, the tram wire turns into a solid bar running parallel to the trolleybus wires for about half a metre. Another bar similarly angled at its ends is hung between the trolleybus wires, electrically connected above to the tram wire. The tram's pantograph bridges the gap between the different conductors, providing it with a continuous pickup.
Where the tram wire crosses, the trolleybus wires are protected by an inverted trough of insulating material extending below.
Until 1946, a level crossing in Stockholm
Stockholm () is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, largest city of Sweden as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people liv ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
connected the railway south of Stockholm Central Station and a tramway. The tramway operated on 600-700 V DC and the railway on 15 kV AC
Railway electrification systems using at are used on transport railways in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Sweden, and Norway. The high voltage enables high power transmission with the lower frequency reducing the losses of the traction mo ...
. In the Swiss village of Oberentfelden, the Menziken–Aarau–Schöftland line operating at 750 V DC crosses the SBB line at 15 kV AC; there used to be a similar crossing between the two lines at Suhr but this was replaced by an underpass in 2010. Some crossings between tramway/light rail and railways are extant in Germany. In Zürich, Switzerland, VBZ trolleybus line 32 has a level crossing with the 1,200 V DC Uetliberg railway line; at many places, trolleybus lines cross the tramway. In some cities, trolleybuses and trams shared a positive (feed) wire. In such cases, a normal trolleybus frog can be used.
Alternatively, section breaks can be sited at the crossing point, so that the crossing is electrically dead.
Australia
Many cities had trams and trolleybuses using trolley poles. They used insulated crossovers, which required tram drivers to put the controller into neutral and coast through. Trolleybus drivers had to either lift off the accelerator or switch to auxiliary power. In Melbourne, Victoria, tram drivers put the controller into neutral and coast through section insulators, indicated by insulator markings between the rails. Melbourne has three level crossings between electrified suburban railways and tram lines. They have mechanical switching arrangements (changeover switch) to switch the 1500 V DC overhead of the railway and the 650 V DC of the trams, called a Tram Square. Proposals have been advanced to grade separate these crossings or divert the tram routes.Greece
Athens has two crossings of tram and trolleybus wires, at Vas. Amalias Avenue and Vas. Olgas Avenue, and at Ardittou Street and Athanasiou Diakou Street. They use the above-mentioned solution.Italy
In Rome, at the crossing between Viale Regina Margherita and Via Nomentana, tram and trolleybus lines cross: tram on Viale Regina Margherita and trolleybus on Via Nomentana. The crossing is orthogonal, therefore the typical arrangement was not available. In Milan, most tram lines cross its circular trolleybus line once or twice. Trolleybus and tram wires run parallel in streets such as viale Stelvio, viale Umbria and viale Tibaldi.Multiple overhead lines
 Some railways used two or three overhead lines, usually to carry
Some railways used two or three overhead lines, usually to carry three-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, Electric power transmission, transmission, and Electric power distribution, distribution. It is a type of polyphase system empl ...
current. This is used only on the Gornergrat Railway
The Gornergrat Railway (german: Gornergrat Bahn; GGB) is a mountain rack railway, located in the Swiss canton of Valais. It links the resort village of Zermatt, situated at above mean sea level, to the summit of the Gornergrat. The Gornergr ...
and Jungfrau Railway in Switzerland, the Petit train de la Rhune in France, and the Corcovado Rack Railway in Brazil. Until 1976, it was widely used in Italy. On these railways, the two conductors are used for two different phases of the three-phase AC, while the rail was used for the third phase. The neutral was not used.
Some three-phase AC railways used three overhead wires. These were an experimental railway line of Siemens in Berlin-Lichtenberg in 1898 (length 1.8 kilometres), the military railway between Marienfelde and Zossen between 1901 and 1904 (length 23.4 kilometres) and an 800-metre-long section of a coal railway near Cologne between 1940 and 1949.
On DC systems, bipolar overhead lines were sometimes used to avoid galvanic corrosion
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. A sim ...
of metallic parts near the railway, such as on the Chemin de fer de la Mure.
All systems with multiple overhead lines have a high risk of short circuits at switches and therefore tend to be impractical in use, especially when high voltages are used or when trains run through the points at high speed.
The Sihltal Zürich Uetliberg Bahn has two lines with different electrification. To be able to use different electric systems on shared tracks, the Sihltal line has its overhead wire right above the train, whilst the Uetliberg line has its overhead wire off to one side.
Overhead catenary


 A catenary is a system of overhead wires used to supply electricity to a
A catenary is a system of overhead wires used to supply electricity to a locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
, tram ( streetcar), or light rail vehicle that is equipped with a pantograph.
 Unlike simple overhead wires, in which the uninsulated wire is attached by clamps to closely spaced crosswires supported by poles, catenary systems use at least two wires. The catenary or messenger wire is hung at a specific tension between line structures, and a second wire is held in tension by the messenger wire, attached to it at frequent intervals by clamps and connecting wires known as ''droppers''. The second wire is straight and level, parallel to the
Unlike simple overhead wires, in which the uninsulated wire is attached by clamps to closely spaced crosswires supported by poles, catenary systems use at least two wires. The catenary or messenger wire is hung at a specific tension between line structures, and a second wire is held in tension by the messenger wire, attached to it at frequent intervals by clamps and connecting wires known as ''droppers''. The second wire is straight and level, parallel to the rail track
A railway track (British English and UIC terminology) or railroad track (American English), also known as permanent way or simply track, is the structure on a railway or railroad consisting of the rails, fasteners, railroad ties (sleepers, ...
, suspended over it as the roadway of a suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck (bridge), deck is hung below suspension wire rope, cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridg ...
is over water.
Catenary systems are suited to high-speed operations whereas simple wire systems, which are less expensive to build and maintain, are common on light rail or tram (streetcar) lines, especially on city streets. Such vehicles can be fitted with either a pantograph or trolley pole.
The Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston through Providence, New Haven, Stamford, New York City, Philadelphia, Wilmington, a ...
in the United States has catenary over the between Boston, Massachusetts and Washington, D.C. for Amtrak's inter-city
Inter-city rail services are express passenger train services that run services that connect cities over longer distances than commuter or regional trains.
There is no precise definition of inter-city rail; its meaning may vary from country ...
trains. Commuter rail agencies including MARC Marc or MARC may refer to:
People
* Marc (given name), people with the first name
* Marc (surname), people with the family name
Acronyms
* MARC standards, a data format used for library cataloging,
* MARC Train, a regional commuter rail system of ...
, SEPTA, NJ Transit, and Metro-North Railroad
Metro-North Railroad , trading as MTA Metro-North Railroad, is a suburban commuter rail service run by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA), a New York State public benefit corporations, public authority of the U.S. state of New Yor ...
utilize the catenary to provide local service.
In Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. ...
the interurban/light rail lines and the heavy rail
Various terms are used for passenger railway lines and equipment; the usage of these terms differs substantially between areas:
Rapid transit
A rapid transit system is an electric railway characterized by high speed (~) and rapid accelerati ...
line use the same overhead wires, due to a city ordinance intended to limit air pollution from the large number of steam trains that passed through Cleveland between the east coast and Chicago. Trains switched from steam to electric locomotives at the Collinwood railyards about east of Downtown and at Linndale
Linndale is the smallest village in Cuyahoga County, Ohio, United States. It is landlocked, surrounded by the city of Cleveland and the suburb of Brooklyn. According to the 2010 census, the village achieved the second highest growth rate in Cuya ...
on the west side. When Cleveland constructed its rapid transit (heavy rail) line between the airport, downtown, and beyond, it employed a similar catenary, using electrification equipment left over after railroads switched from steam to diesel. Light and heavy rail share trackage for about along the Cleveland Hopkins International Airport Red (heavy rail) line, Blue and Green interurban/light rail lines between Cleveland Union Terminal and just past East 55th Street station, where the lines separate.
Part of the Boston, Massachusetts Blue Line through the northeast suburbs uses overhead lines, as does the Green Line.
Height
The height of the overhead line can create hazards at level crossings, where it may be struck by road vehicles. Warning signs are placed on the approaches, advising drivers of the maximum safe height. The wiring in most countries is too low to allow double stack container trains. TheChannel Tunnel
The Channel Tunnel (french: Tunnel sous la Manche), also known as the Chunnel, is a railway tunnel that connects Folkestone (Kent, England, UK) with Coquelles ( Hauts-de-France, France) beneath the English Channel at the Strait of Dover. ...
has an extended height overhead line to accommodate double-height car and truck transporters. China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and India operate lines electrified with extra height wiring and pantographs to allow for double stack container trains.
Problems with overhead equipment
Overhead lines may be adversely affected by strong winds causing wires to swing. Power storms can knock the power out with lightning strikes on systems with overhead wires, stopping trains following a power surge. During cold or frosty weather, ice may coat overhead lines. This can result in poor electrical contact between the collector and the overhead line, resulting in electrical arcing and power surges. The installation of overhead lines may require reconstruction of bridges to provide safe electrical clearance. Overhead lines, like most electrified systems, require a greater capital expenditure when building the system than an equivalent non-electric system. While a conventional rail line requires only the grade, ballast, ties and rails, an overhead system also requires a complex system of support structures, lines, insulators, power-control systems and power lines, all of which require maintenance. This makes non-electrical systems more attractive in the short term, although electrical systems can pay for themselves eventually. Also, the added construction and maintenance cost-per-mile makes overhead systems less attractive on long-distance railways, such as those found in North America, where the distances between cities are typically far greater than in Europe. Such long lines require enormous investment in overhead line equipment, and major difficulties confront energizing long portions of overhead wire on a permanent basis, especially in areas where energy demand already outstrips supply. Many people consider overhead lines to be "visual pollution
Visual pollution is the study of secondary impacts of manmade interventions or visible deterioration and negative aesthetic quality of the natural and human-made landscapes around people. It refers to the impacts pollution has in impairing the q ...
", due to the many support structures and complicated system of wires and cables that fill the air. Such considerations have driven the move towards replacing overhead power and communications lines with buried cables where possible. The issue came to a head in the UK with the Great Western Main Line
The Great Western Main Line (GWML) is a main line railway in England that runs westwards from London Paddington to . It connects to other main lines such as those from Reading to Penzance and Swindon to Swansea. Opened in 1841, it was the or ...
electrification scheme, especially through the Goring Gap. A protest group with their own website has been formed.
The valuable copper conductor can also be subject to theft, as for example the Lahore-Khanewal line in Pakistan and the Gweru-Harare section of line in Zimbabwe.
History
The first tram with overhead lines was presented by Werner von Siemens at the 1881 International Exposition of Electricity in Paris: the installation was removed after that event. In October 1883, the first permanent tram service with overhead lines was on theMödling and Hinterbrühl Tram
Mödling and Hinterbrühl Tram or ''Mödling and Hinterbrühl Local Railway'' (German: ''Lokalbahn Mödling–Hinterbrühl'') was an electric tramway in Austria, running 4.5 km (2.8 mi) from Mödling to Hinterbrühl, in the southwest ...
in Austria. The trams had bipolar overhead lines, consisting of two U-pipes, in which the pantographs hung and ran like shuttles. From April to June 1882, Siemens had tested a similar system on his Electromote, an early precursor of the trolleybus.
Much simpler and more functional was an overhead wire in combination with a pantograph borne by the vehicle and pressed at the line from below. This system, for rail traffic with a unipolar line, was invented by Frank J. Sprague in 1888. From 1889 it was used at the Richmond Union Passenger Railway in Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
, pioneering electric traction.
Gallery
Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
File:Jungfraubahn with Eiger.jpg, Overhead lines (three-phase) on Jungfrau Railway, Switzerland
File:Overhead-lines-railway.JPG, Overhead lines in China
File:Overhead Line NW England.jpg, Overhead lines in NW England
File:Railway-electrification.jpg, Overhead lines in Denmark near Roskilde. For aesthetic reasons, the support structure is constructed from hollow COR-TEN steel
Weathering steel, often referred to by the genericised trademark COR-TEN steel and sometimes written without the hyphen as corten steel, is a group of steel alloys which were developed to eliminate the need for painting, and form a stable rus ...
masts.
File:Brussel Midi MS96.jpg, Brussels-South, overhead wires suspended across multiple tracks.
File:3rd rail to overhead wire transition zone on the Skokie Swift.jpg, Transition zone of third-rail to overhead-wire supply on Chicago's Yellow Line (the "Skokie Swift")
File:AMA 103 at Puhinui.jpg, Overhead lines in Auckland, New Zealand (25 kV AC)
File:NZR FP class Khandallah.jpg, Overhead lines in Wellington, New Zealand (1500 V DC)
File:LRT Station South Campus squared.jpg, Overhead lines on the Edmonton Capital Line
The Edmonton LRT Capital Line is a light rail transit line running from northeast Edmonton to the south. Operated by the Edmonton Transit Service, the line provides access to Downtown Edmonton and the University of Alberta. The Capital Line cur ...
.
File:Roofride kyiv.JPG, 3 kV DC overhead catenary in Kyiv.
File:Prittlewell railway station - geograph.org.uk - 918438.jpg, Prittlewell station, Southend-on-Sea. It was electrified in the 1950s.
Cholsey railway station, Oxfordshire (geograph 6944628).jpg, Cholsey railway station, Oxfordshire. It was electrified in the 2010s.
File:BR Class 308 1 EMU no. 308150, Cambridge, 11 April 1987.jpg, BR Class 308/1 EMU at Cambridge, April, 1987.
See also
* Electro-diesel locomotive *Gantry
A gantry is an overhead bridge-like structure supporting equipment such as a crane, signals, or cameras.
Devices and structures
*Gantry (medical), cylindrical scanner assembly used for medical 3D-imaging or treatment
*Gantry (transport), an over ...
* Insulator (electricity)
* Lineworker
* List of railway electrification systems
* Railway electrification system
A railway electrification system supplies electric power to railway trains and trams without an on-board prime mover or local fuel supply.
Electric railways use either electric locomotives (hauling passengers or freight in separate cars), ele ...
* Traction current pylon
A traction current pylon is a railroad pylon carrying at least one circuit for traction current. In Germany, traction current lines with two systems (4 conductor cables) typically have a single level arrangement of the conductor cables. For trac ...
* Utility pole
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
* {{Authority control Electric rail transport Tram technology Pylons Electric power infrastructure Electric power distribution