Outer Labia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
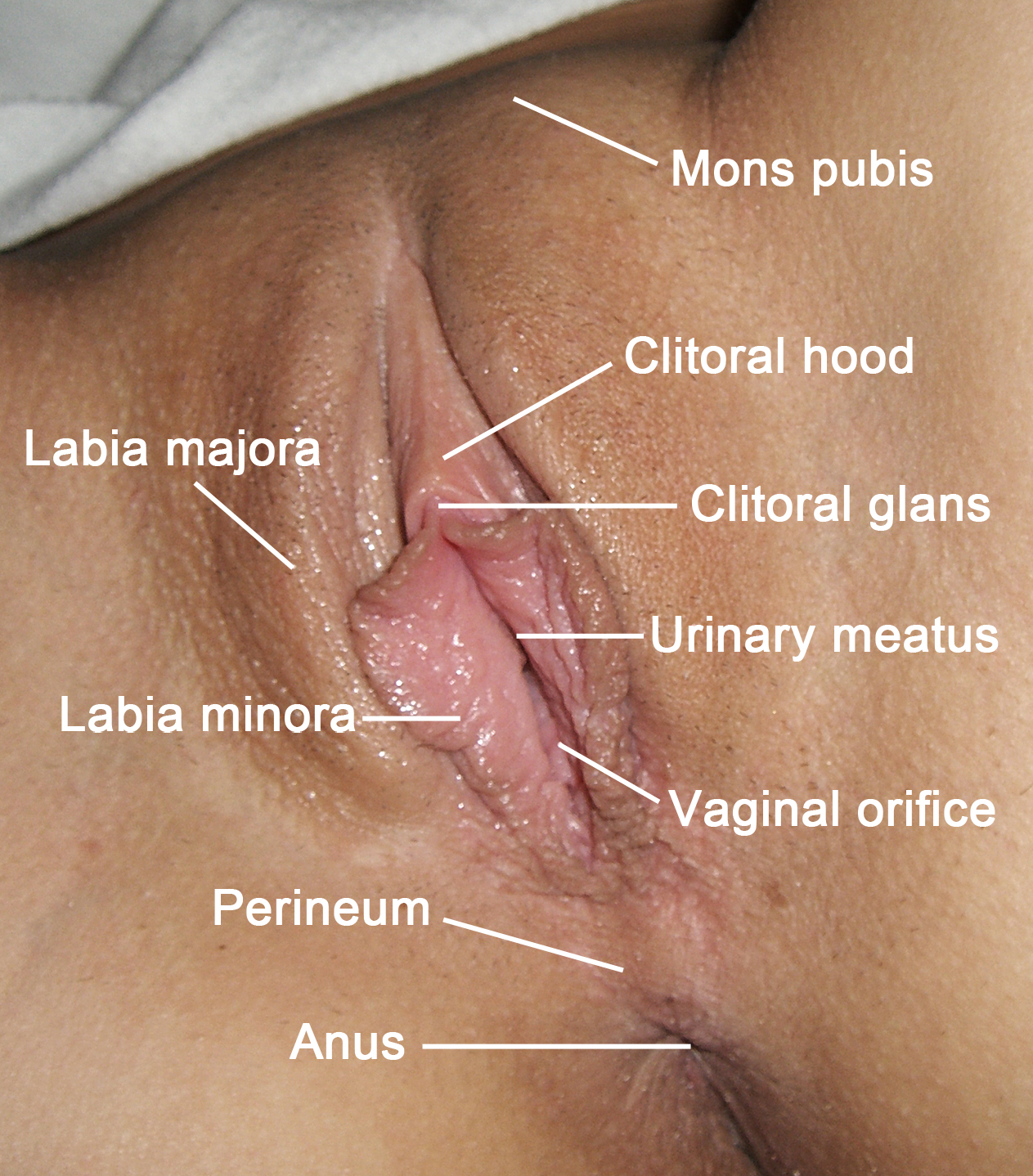 The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent
Labia Majora Medical Definition
{{DEFAULTSORT:Labia Majora Mammal female reproductive system de:Schamlippe#Die großen (äußeren) Schamlippen
 The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent longitudinal
Longitudinal is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
* Longitude
** Line of longitude, also called a meridian
* Longitudinal engine, an internal combustion engine in which the crankshaft is oriented along the long axis of the vehicle, ...
cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis
In human anatomy, and in mammals in general, the ''mons pubis'' or pubic mound (also known simply as the mons, and known specifically in females as the ''mons Venus'' or ''mons veneris'') is a rounded mass of fatty tissue found over the pubic symp ...
to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external sex organ, female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibu ...
.
The labia majora are homologous to the male scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum cont ...
.
Etymology
''Labia majora'' is theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
plural for big ("major") lips; the singular is ''labium majus.'' The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of female external genitals (vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external sex organ, female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, bulb of vestibu ...
)—labia majora and labia minora. Labia majora are commonly known as the outer lips, while labia minora (Latin for ''small lips''), which run alongside between them, are referred to as the inner lips. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the labia of female genitals were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.''
Embryology
Embryologically, they develop from labioscrotal folds. It means that they develop in the female foetus from the same previously sexually undifferentiated anatomical structure as thescrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum cont ...
, the sac of skin below the penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males do n ...
in males.
The same process of sex differentiation
Sexual differentiation is the process of development of the sex differences between males and females from an undifferentiated zygote. Sex-determination system, Sex determination is often distinct from sex differentiation; sex determination is the ...
concerns other male and female reproductive organs (see List of related male and female reproductive organs
This list of related male and female reproductive organs shows how the male and female reproductive organs and the development of the reproductive system are related, sharing a common developmental path. This makes them biological homologues. T ...
), with some organs of both sexes developing similar, yet not identical, structure and functions (like the gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sper ...
s - male testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testostero ...
s and female ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
, like male and female urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra con ...
s, erectile corpus cavernosum penis and prepuce in the penis ( foreskin) and the corpus cavernosum clitoridis
The corpus cavernosum of clitoris is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue of the clitoris in women. It is made of a sponge-like tissue that fills with blood during clitoral erection. This is homologous to the corpus cavernosum ...
in the clitoris and ( clitoral hood) and their frenula). But other male and female sex organs become absolutely different and unique, like the internal female genitalia.
The scrotum and labia majora develop to have both similarities and crucial differences. Like the scrotum, labia majora after puberty may become of a darker color than the skin outside them, and, similarly, also grow pubic hair on their external surface (the female genitals on accompanying photos are shaved to show their structure clearer). But, during sexual differentiation of the foetus, labioscrotal folds in the males normally fuse longitudinally in the middle, forming a sack for male gonads (testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testostero ...
s) to descend into it from the pelvis, while in the females these folds normally do not fuse, forming the two labia majora and the pudendal cleft
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval ...
between them. Female gonads (ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
) do not descend from the pelvis, thus the structure of labia majora may seem simpler (just fatty tissue covered with skin) and of lesser significance for functioning of the female body as a whole than the scrotum with testicles for males. The ridge or groove remaining of the fusion can be traced on the scrotum.
In some cases of intersex
Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical bina ...
with disorders of sex development
Disorders of sex development (DSDs), also known as differences in sex development, diverse sex development and variations in sex characteristics (VSC), are congenital conditions affecting the reproductive system, in which development of chromoso ...
male/female genitalia may look ambiguous for either gender with phallus too small for a typical penis yet too big for a clitoris, with external urethral opening in an atypical location, and with labia/scrotum fully or partially fused but without descended gonads in them. Undescended testicles, though, may also occur in otherwise generally healthy male infants.
Anatomy
The labia majora constitute the lateral boundaries of thepudendal cleft
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval ...
, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis
The clitoris ( or ) is a female sex organ present in mammals, ostriches and a limited number of other animals. In humans, the visible portion – the glans – is at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the ope ...
, the Hart's Line
The vulval vestibule (or vulvar vestibule or vestibule of vagina) is a part of the vulva between the labia minora into which the urinary meatus (urethral opening) and the vaginal opening open. Its edge is marked by Hart's line. It represents the ...
, and the vulval vestibule
The vulval vestibule (or vulvar vestibule or vestibule of vagina) is a part of the vulva between the labia minora into which the urinary meatus (urethral opening) and the vaginal opening open. Its edge is marked by Hart's line. It represents the ...
, which contains the external openings of the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra con ...
and the vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
. Each labium majus has two surfaces, an outer, pigmented and covered with strong, pubic hair
Pubic hair is terminal body hair that is found in the genital area of adolescent and adult humans. The hair is located on and around the sex organs and sometimes at the top of the inside of the thighs. In the pubic region around the pubis bon ...
; and an inner, smooth and beset with large sebaceous
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number ...
follicles. The labia majora are covered with squamous epithelium. Between the two there is a considerable quantity of areolar
Loose connective tissue, sometimes called areolar tissue, is a cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers. Its ground substance occupies more volume than the fibers do. It has a viscous to gel-like consistenc ...
tissue, fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers spec ...
, and a tissue resembling the dartos tunic
The dartos fascia or simply dartos is a layer of connective tissue found in the penile shaft, foreskin, scrotum and labia. The penile portion is referred to as the superficial fascia of penis or the subcutaneous tissue of penis, while the scrotal ...
of the scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum cont ...
, besides vessels, nerves, and glands
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Structure
De ...
. The labia majora are thicker in front, and form the anterior labial commissure where they meet below the mons pubis
In human anatomy, and in mammals in general, the ''mons pubis'' or pubic mound (also known simply as the mons, and known specifically in females as the ''mons Venus'' or ''mons veneris'') is a rounded mass of fatty tissue found over the pubic symp ...
. Posteriorly, they are not really joined, but appear to become lost in the neighboring integument, ending close to, and nearly parallel to, each other. Together with the connecting skin between them, they form another commissure the posterior labial commissure which is also the posterior boundary of the pudendum
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval ...
. The interval between the posterior commissure and the anus
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, d ...
, from 2.5 to 3 cm in length, constitutes the perineum. The anterior region of the perineum is known as the urogenital triangle
The urogenital triangle is the anterior part of the perineum. In female mammals, it contains the vagina and associated parts of the internal genitalia.
Structure
The urogenital triangle is the area bound by a triangle with one vertex at the pubi ...
which separates it from the anal region. Between the labia majora and the inner thigh
In human anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of bone ...
s are the labiocrural folds. Between the labia majora and labia minora are the interlabial sulci. Labia majora atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply t ...
after menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
.
Use in grafting
Thefat pad A fat pad (aka haversian gland) is a mass of closely packed fat cells surrounded by fibrous tissue septa.TheFreeDictionary > Fat padCiting: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. 2009 They may be extensively supplied with capillaries and nerve end ...
of the labia majora can be used as a graft, often as a so-called "Martius labial fat pad graft", and can be used, for example, in urethrolysis.
See also
* ''Femalia
''Femalia'' is a book of 32 full-color photographs of human vulvas, edited by Joani Blank and first published by Down There Press in 1993. A reprint edition was published by Last Gasp in 2011. The photographs were taken by Tee Corinne, Michael Per ...
''
* Labia pride
Labia pride (also termed labia liberation, vulvaversity and similar) is the promotion of a raised awareness of the appearance of female genitalia and the breaking of taboos surrounding the vulva, as carried out by feminist movements and advocacy g ...
References
External links
Labia Majora Medical Definition
{{DEFAULTSORT:Labia Majora Mammal female reproductive system de:Schamlippe#Die großen (äußeren) Schamlippen