Organic Radical Battery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An organic radical battery (ORB) is a type of battery first developed in 2005. As of 2011, this type of battery was generally not available for the consumer, although their development at that time was considered to be approaching practical use. ORBs are potentially more environmentally friendly than conventional metal-based batteries, because they use organic radical polymers (flexible plastics) to provide electrical power instead of metals. ORBs are considered to be a high-power alternative to the

 The positive electrode uses the nitroxide - oxammonium cation redox pair to create an
The positive electrode uses the nitroxide - oxammonium cation redox pair to create an
 Free-radical polymerization as a synthetic approach has several drawbacks. The most relevant limitation is the fact that precursor polymer oxidation never proceeds to 100%. As a result, the synthesized PTMA has between 65% and 81% of the theoretically possible amount of nitroxide groups. The decreased number of nitroxide groups negatively impacts the charge capacity of the polymer and limits its efficacy in organic radical batteries. Not only are there fewer nitroxide groups present, but also side reactions between non-oxidized groups and oxammonium cations diminishes the redox reversibility of the compound.
The difficulties of free-radical polymerization of PTMA could be avoided if the oxidation step were not necessary. However, because nitroxide radicals would react with any carbon radicals formed during polymerization, use of a monomer with a nitroxide radical isn't practical.
Free-radical polymerization as a synthetic approach has several drawbacks. The most relevant limitation is the fact that precursor polymer oxidation never proceeds to 100%. As a result, the synthesized PTMA has between 65% and 81% of the theoretically possible amount of nitroxide groups. The decreased number of nitroxide groups negatively impacts the charge capacity of the polymer and limits its efficacy in organic radical batteries. Not only are there fewer nitroxide groups present, but also side reactions between non-oxidized groups and oxammonium cations diminishes the redox reversibility of the compound.
The difficulties of free-radical polymerization of PTMA could be avoided if the oxidation step were not necessary. However, because nitroxide radicals would react with any carbon radicals formed during polymerization, use of a monomer with a nitroxide radical isn't practical.
 RAFT-mediated polymerization of PTMA utilizes the same starting monomer as free-radical polymerization. Using the RAFT-mediated approach to polymerize 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl methacrylate (TMPM), the starting monomer, generates poly(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidnyl methacrylate) or PTMPM-RAFT. Direct oxidation of PTMPM-RAFT to PTMA is not practical, as direct oxidation causes side reactions involving the thiocaronylthiol end group of PTMPM-RAFT to react to form insoluble gel-like product. Rather, excess AIBN is used to remove the reactive terminus to form PTMPM, which can then be oxidized by meta-chloroperbenzoic acid to the desired PTMA.
Despite the promise of the RAFT-mediated polymerization, reported radical concentration was only 69 ± 4%.
RAFT-mediated polymerization of PTMA utilizes the same starting monomer as free-radical polymerization. Using the RAFT-mediated approach to polymerize 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl methacrylate (TMPM), the starting monomer, generates poly(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidnyl methacrylate) or PTMPM-RAFT. Direct oxidation of PTMPM-RAFT to PTMA is not practical, as direct oxidation causes side reactions involving the thiocaronylthiol end group of PTMPM-RAFT to react to form insoluble gel-like product. Rather, excess AIBN is used to remove the reactive terminus to form PTMPM, which can then be oxidized by meta-chloroperbenzoic acid to the desired PTMA.
Despite the promise of the RAFT-mediated polymerization, reported radical concentration was only 69 ± 4%.
 The following monomers (1-3) can be synthesized by
The following monomers (1-3) can be synthesized by 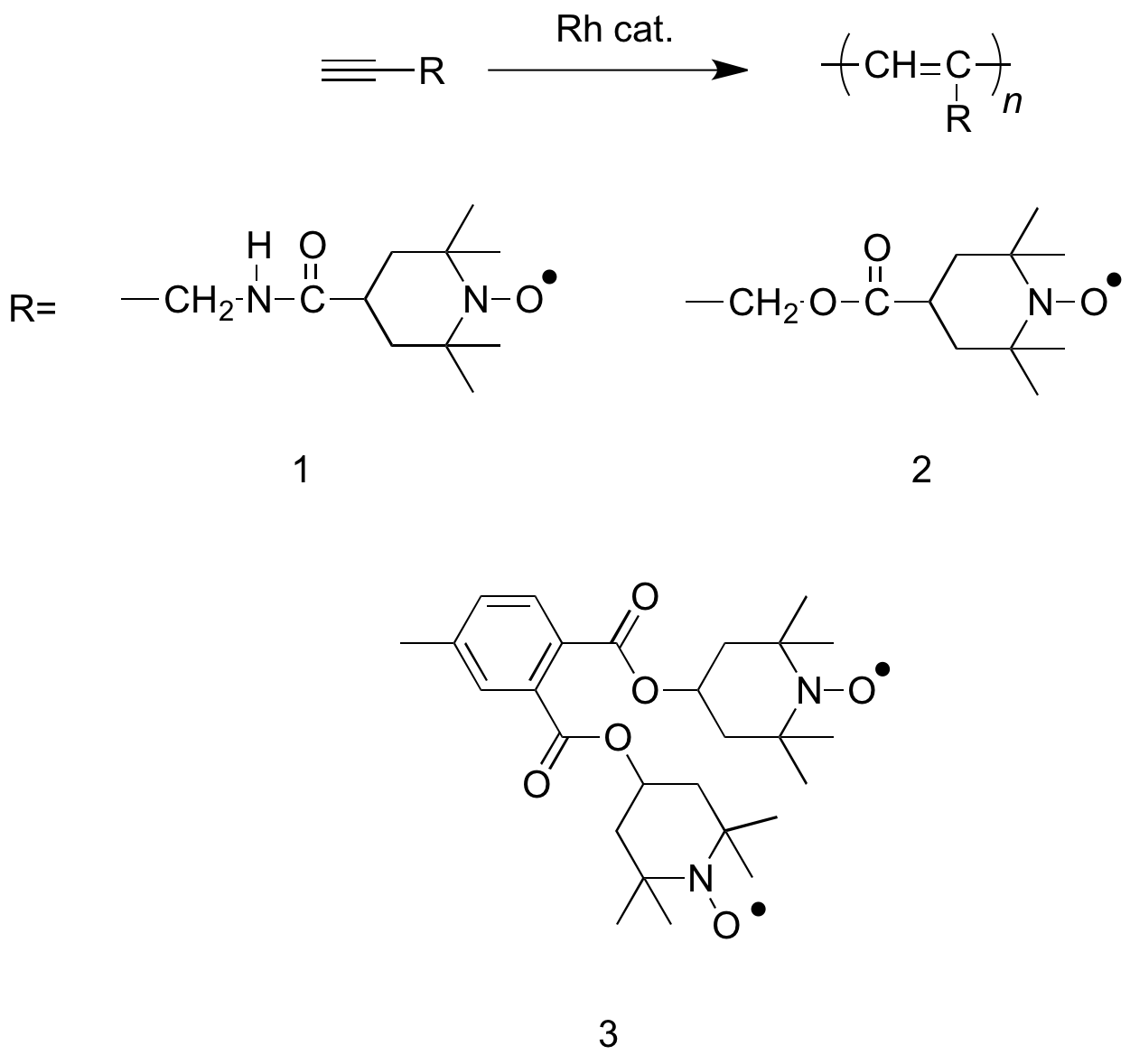 While use of a rhodium catalyst may be advantageous due to its high yield, use of a metal catalyst provides the additional challenge of having to separate the catalyst from the final product.
While use of a rhodium catalyst may be advantageous due to its high yield, use of a metal catalyst provides the additional challenge of having to separate the catalyst from the final product.
 Preparation of the monomer, 4-methacryloxyloxy-TEMPO can be accomplished by acylation of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO with methacryloyl chloride.
Preparation of the monomer, 4-methacryloxyloxy-TEMPO can be accomplished by acylation of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO with methacryloyl chloride.
 Polymerization using 1-methoxy-2-methyl-1trimethylsilyloxy-propene (MTS) as a catalyst proceeds rapidly at room temperature to form PTMA. Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) is used as an additional catalyst.
The following is a rationale for group-transfer polymerization.
Polymerization using 1-methoxy-2-methyl-1trimethylsilyloxy-propene (MTS) as a catalyst proceeds rapidly at room temperature to form PTMA. Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) is used as an additional catalyst.
The following is a rationale for group-transfer polymerization.

Li-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also sees ...
. Functional prototypes of the battery have been researched and developed by different research groups and corporations including the Japanese corporation NEC
is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It prov ...
.
The organic radical polymers used in ORBs are examples of stable radicals, which are stabilized by steric
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ...
and/or resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillatin ...
effects. For example, the nitroxide radical in ( 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl (TEMPO), the most common subunit used in ORBs, is a stable oxygen-centered molecular radical. Here, the radical is stabilized by delocalization of electrons from the nitrogen onto the oxygen. TEMPO radicals can be attached to polymer backbones to form poly(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl- piperidenyloxyl-4-yl methacrylate) (PTMA). PTMA-based ORBs have a charge-density slightly higher than that of conventional Li-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
, which should theoretically make it possible for an ORB to provide more charge than a Li-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also sees ...
of similar size and weight.
As of 2007, ORB research was being directed mostly towards Hybrid ORB/Li-ion batteries because organic radical polymers with appropriate electrical properties for the anode are difficult to synthesize.
Applications
As of 2015, ORBs were still under development and not in commercial use. Theoretically, ORBs could replaceLi-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
as more environmentally friendly batteries of similar or higher charge capacity and similar or shorter charge time. This would make ORBs well-suited for handheld electronic devices.
Organic radical batteries were first researched and developed by NEC in 2005 with the intent of being widely used to power tiny gadgets in the near future. They began with a size of 0.3 mm and an extremely quick charge time. Since the beginning of development, smart cards
A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card) is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) c ...
and RFID
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. When triggered by an electromag ...
tags were the main targets for ORB usage. NEC has also worked on a larger 0.7 mm battery which is thicker, but also has a high charge capacity of 5 mAh.
Given the fast redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction ...
chemistry of nitroxide radicals, ORBs have been shown useful in keeping a computer running momentarily following a power outage. Although the amount of additional time provided is short, it is adequate to allow a computer to backup any crucial data before completely shutting down.
Function
Radical polymer batteries rely on aredox reaction
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
of an organic radical
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ...
to generate an electrochemical potential
In electrochemistry, the electrochemical potential (ECP), ', is a thermodynamic measure of chemical potential that does not omit the energy contribution of electrostatics. Electrochemical potential is expressed in the unit of J/ mol.
Introductio ...
. The most studied example of such an organic radical redox reaction is that of nitroxide radicals, such as the one found on a molecule called (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian language, Italian, 'time'; plural ''tempos'', or ''tempi'' from the Italian plural) is the speed or pace of a given musical composition, piece. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an inst ...
, also known as TEMPO. A nitroxide radical can be oxidized to an oxammonium cation or reduced to a hydroxylamine anion.

 The positive electrode uses the nitroxide - oxammonium cation redox pair to create an
The positive electrode uses the nitroxide - oxammonium cation redox pair to create an electrochemical potential
In electrochemistry, the electrochemical potential (ECP), ', is a thermodynamic measure of chemical potential that does not omit the energy contribution of electrostatics. Electrochemical potential is expressed in the unit of J/ mol.
Introductio ...
, i.e. when the battery discharges the nitroxide radical is oxidized to the oxammonium cation and when the battery charges the oxammonium cation is reduced back to the nitroxide. The redox potentials for nitroxide show some variation and for the TEMPO
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian, 'time'; plural ''tempos'', or ''tempi'' from the Italian plural) is the speed or pace of a given piece. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (often ...
nitroxide for this redox pair has an oxidation potential of +0.87 V. The positive electrode often takes the shape of a gel made of organic radical solids and graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large ...
, permeated with electrolytes. Graphite is mixed with the polymer to increase the conductivity.Nishide, H.; Suga, T. The Electrochemical Society Interface 2005, No. Winter, 32–36
The negative electrode uses the nitroxide - hydroxylamine anion redox pair to create an electrochemical potential, i.e. when the battery discharges the nitroxide radical is reduced to the hydroxylamine anion and when the battery charges the hydroxylamine anion is oxidized back to the nitroxide. This half-reaction
A half reaction (or half-cell reaction) is either the oxidation or reduction reaction component of a redox reaction. A half reaction is obtained by considering the change in oxidation states of individual substances involved in the redox reaction. ...
has an oxidation potential of -0.11 V. Since this half-reaction
A half reaction (or half-cell reaction) is either the oxidation or reduction reaction component of a redox reaction. A half reaction is obtained by considering the change in oxidation states of individual substances involved in the redox reaction. ...
is not readily reversible as the half-reaction
A half reaction (or half-cell reaction) is either the oxidation or reduction reaction component of a redox reaction. A half reaction is obtained by considering the change in oxidation states of individual substances involved in the redox reaction. ...
at the positive electrode, several research groups have steered away from using pure organic radical batteries and instead use metal/ORB hybrid batteries usually consist of a radical polymer cathode and the same anode found in rechargeable Li-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
.Nishide, H.; Iwasa, S.; Pu, Y.-J.; Suga, T.; Nakahara, K.; Satoh, M. Electrochimica Acta 2004, 50 (2–3), 827–831. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2004.02.052
Much like a traditional battery such as a Li-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also sees ...
, an organic radical battery consists of a cathode and an anode that are separated by a porous film and submerged in an electrolyte. In a pure organic radical battery, both terminals are made of organic radical polymers (a p-type and an n-type polymer), while a metal/ORB hybrid battery usually has a radical polymer cathode and a Li-ion/graphite anode.
Synthesis of radical polymers
Several synthetic approaches have been utilized in the synthesis of polyradical species for use in organic radical batteries. The following methods have been used to synthesize poly(2,2,6,6- tetramethylpiperidinyloxy-4-yl methacrylate) (PTMA) and other nitroxide polymers.Free-radical polymerization
Initial attempts to synthesize PTMA involved synthesizing the polymer without radical functionality viafree radical polymerization
In polymer chemistry, free-radical polymerization (FRP) is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free-radical building blocks (repeat units). Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanis ...
. Once the polymer is synthesized, the nitroxide function can be introduced by oxidation.Bugnon, L.; Morton, C. J. H.; Novak, P.; Vetter, J.; Nesvadba, P. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19 (11), 2910–2914. doi: 10.1021/cm063052h
Several groups have described synthesis of PTMA (4) using free radical polymerization of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine methacrylate Methacrylates are derivatives of methacrylic acid.
* Methyl methacrylate
* Ethyl methacrylate
* Butyl methacrylate
* Hydroxyethyl methacrylate
* Glycidyl methacrylate
Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) is an ester of methacrylic acid and glycidol. Co ...
(2) with 2,2'-azobisiobutryonitrile ( AIBN) as a radical initiator. The monomer was prepared via 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinol (1) and methacryloyl chloride
Methacryloyl chloride is the acid chloride of methacrylic acid. It is used to manufacture polymers.
See also
* Acryloyl chloride
Acryloyl chloride, also known as 2-propenoyl chloride or acrylic acid chloride, is the organic compound with the fo ...
. The precursor neutral polymer (3) was oxidized to the stable radical polymer (4) by 3-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (mCPBA).Kurosaki, T.; Lee, K. W.; Okawara, M. J. Polym. Sci. A-1 Polym. Chem. 1972, 10 (11), 3295–3310. doi: 10.1002/pol.1972.170101116Nakahara, K.; Iwasa, S.; Satoh, M.; Morioka, Y.; Iriyama, J.; Suguro, M.; Hasegawa, E. Chemical Physics Letters 2002, 359 (5–6), 351–354. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2614(02)00705-4 Similar synthetic approaches have been proposed using 4-methacryloyloxy-N-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine as a monomer rather than 2,2,6,6- tetramethylpiperidine methacrylate.Kurosaki, T.; Takahashi, O.; Okawara, M. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1974, 12 (7), 1407–1420. doi: 10.1002/pol.1974.170120705
 Free-radical polymerization as a synthetic approach has several drawbacks. The most relevant limitation is the fact that precursor polymer oxidation never proceeds to 100%. As a result, the synthesized PTMA has between 65% and 81% of the theoretically possible amount of nitroxide groups. The decreased number of nitroxide groups negatively impacts the charge capacity of the polymer and limits its efficacy in organic radical batteries. Not only are there fewer nitroxide groups present, but also side reactions between non-oxidized groups and oxammonium cations diminishes the redox reversibility of the compound.
The difficulties of free-radical polymerization of PTMA could be avoided if the oxidation step were not necessary. However, because nitroxide radicals would react with any carbon radicals formed during polymerization, use of a monomer with a nitroxide radical isn't practical.
Free-radical polymerization as a synthetic approach has several drawbacks. The most relevant limitation is the fact that precursor polymer oxidation never proceeds to 100%. As a result, the synthesized PTMA has between 65% and 81% of the theoretically possible amount of nitroxide groups. The decreased number of nitroxide groups negatively impacts the charge capacity of the polymer and limits its efficacy in organic radical batteries. Not only are there fewer nitroxide groups present, but also side reactions between non-oxidized groups and oxammonium cations diminishes the redox reversibility of the compound.
The difficulties of free-radical polymerization of PTMA could be avoided if the oxidation step were not necessary. However, because nitroxide radicals would react with any carbon radicals formed during polymerization, use of a monomer with a nitroxide radical isn't practical.
RAFT-mediated polymerization
One of the more recent techniques identified to synthesis PTMA is a type of free radical polymerization known as reversibly addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) mediated polymerization.Rostro, L.; Baradwaj, A. G.; Boudouris, B. W. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5 (20), 9896–9901. doi: 10.1021/am403223s RAFT-mediated polymerization of PTMA utilizes the same starting monomer as free-radical polymerization. Using the RAFT-mediated approach to polymerize 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl methacrylate (TMPM), the starting monomer, generates poly(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidnyl methacrylate) or PTMPM-RAFT. Direct oxidation of PTMPM-RAFT to PTMA is not practical, as direct oxidation causes side reactions involving the thiocaronylthiol end group of PTMPM-RAFT to react to form insoluble gel-like product. Rather, excess AIBN is used to remove the reactive terminus to form PTMPM, which can then be oxidized by meta-chloroperbenzoic acid to the desired PTMA.
Despite the promise of the RAFT-mediated polymerization, reported radical concentration was only 69 ± 4%.
RAFT-mediated polymerization of PTMA utilizes the same starting monomer as free-radical polymerization. Using the RAFT-mediated approach to polymerize 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl methacrylate (TMPM), the starting monomer, generates poly(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidnyl methacrylate) or PTMPM-RAFT. Direct oxidation of PTMPM-RAFT to PTMA is not practical, as direct oxidation causes side reactions involving the thiocaronylthiol end group of PTMPM-RAFT to react to form insoluble gel-like product. Rather, excess AIBN is used to remove the reactive terminus to form PTMPM, which can then be oxidized by meta-chloroperbenzoic acid to the desired PTMA.
Despite the promise of the RAFT-mediated polymerization, reported radical concentration was only 69 ± 4%.
Rhodium catalyzed polymerization
Rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element with the symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isoto ...
-catalyzed polymerization of TEMPO
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian, 'time'; plural ''tempos'', or ''tempi'' from the Italian plural) is the speed or pace of a given piece. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (often ...
-bearing monomers avoids some of the challenges free-radical polymerization poses because an oxidation step to generate the radical is not needed.
The structure of (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine-1-yl)oxyl or TEMPO is shown below.
 The following monomers (1-3) can be synthesized by
The following monomers (1-3) can be synthesized by condensation reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a ...
between carboxyl groups with the amino
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent s ...
or hydroxyl group
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy g ...
of acetylene
Acetylene (systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure ...
derivatives and various TEMPO derivatives. Polymerization of the monomers is completed using a Rhodium catalyst (nbd)Rh+ 6-C6H5B−(C6H5)3Katsumata, T.; Satoh, M.; Wada, J.; Shiotsuki, M.; Sanda, F.; Masuda, T. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27 (15), 1206–1211. doi: 10.1002/marc.200600286 Rhodium catalyzed synthesis of TEMPO containing polymers has been performed with high quantitative yield.
 While use of a rhodium catalyst may be advantageous due to its high yield, use of a metal catalyst provides the additional challenge of having to separate the catalyst from the final product.
While use of a rhodium catalyst may be advantageous due to its high yield, use of a metal catalyst provides the additional challenge of having to separate the catalyst from the final product.
Anionic polymerization
Direct anionic polymerization of nitroxyl-containing monomers has also been used to synthesis PTMA. Anionic polymerization is not ideal because it must be carried using very strict procedures to avoid side reactions. Using 1,1-diphenylhexylllithium as an initiator of the reaction eliminates some side reactions by steric effects,Allgaier, J.; Finkelmann, H. Makromol. Chem., Rapid Commun. 1993, 14 (5), 267–271. doi: 10.1002/marc.1993.030140502 however, the procedures necessary are not amenable to large-scale synthesis.Group-transfer polymerization
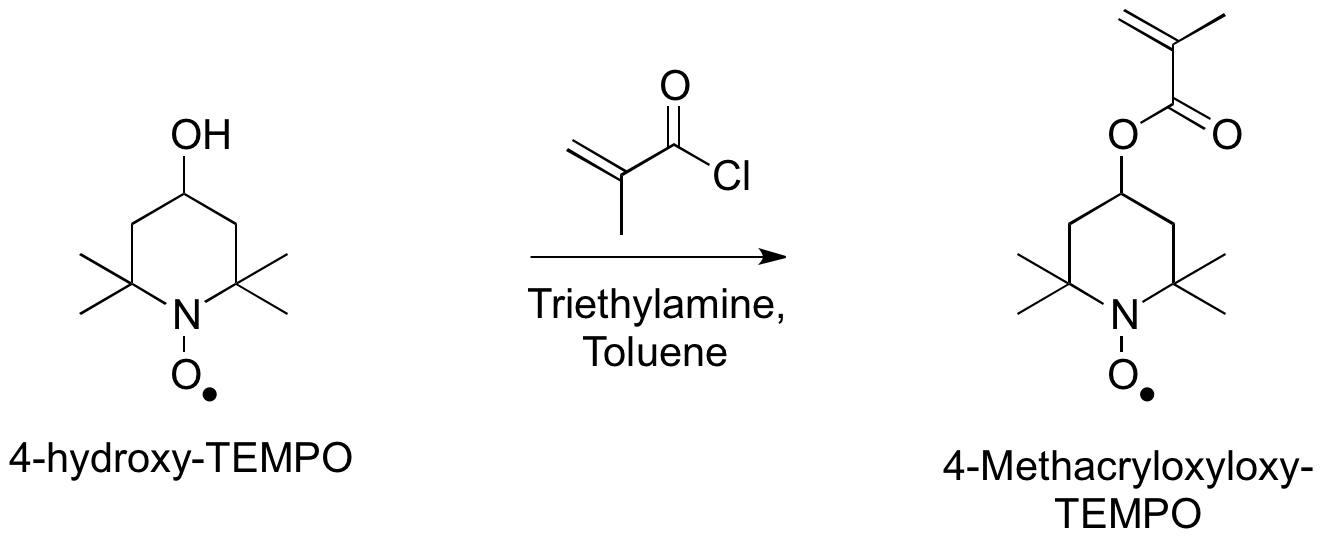
Group-transfer polymerization, like rhodium-catalyzed polymerization of PTMA, allows for polymerization of nitroxyl radical monomers. Unlike rhodium-catalyzed monomers, group-transfer polymerization utilizes silicon to catalyze the polymerization. Preparation of the monomer, 4-methacryloxyloxy-TEMPO can be accomplished by acylation of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO with methacryloyl chloride.
Preparation of the monomer, 4-methacryloxyloxy-TEMPO can be accomplished by acylation of 4-hydroxy-TEMPO with methacryloyl chloride.
 Polymerization using 1-methoxy-2-methyl-1trimethylsilyloxy-propene (MTS) as a catalyst proceeds rapidly at room temperature to form PTMA. Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) is used as an additional catalyst.
The following is a rationale for group-transfer polymerization.
Polymerization using 1-methoxy-2-methyl-1trimethylsilyloxy-propene (MTS) as a catalyst proceeds rapidly at room temperature to form PTMA. Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) is used as an additional catalyst.
The following is a rationale for group-transfer polymerization.

Advantages
Organic radical batteries are much more environmentally friendly thanLi-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
because ORBs do not contain any metals that pose the problem of proper disposal. ORBs are non-toxic and non-flammable and do not require additional care when handling. Burning nitroxide radical polymers yields carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen oxide without ash or odor.
While being environmentally friendly, they have properties that are otherwise comparable to Li-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
: ORBs have a theoretical capacity of 147 mA h g−1, which is slightly higher than that of Li-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
with 140 mA h g−1. ORBs also show comparable charge times and retain of charge-discharge capacity well, matching lithium-ion batteries at 75% of their initial charge after 500 cycles. Additionally, radical concentration in ORBs are stable enough at ambient conditions to remain unchanged for over a year.
ORBs are also more flexible than Li-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
, which would make them more adaptable to different design constraints, such as curved devices.
Disadvantages and difficulties faced in development
A major difficulty in the development of ORBs is difficulty of synthesizing an appropriate negative electrode. This disadvantage arises because theredox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction ...
reaction of the negative electrode is not fully reversible. Hybrid ORB/Li-ion batteries, in which the negative electrode is replaced by the one found in a Li-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also sees ...
, have been proposed as a compromise to overcome this difficulty.Nakahara, K.; Oyaizu, K.; Nishide, H. Chemistry Letters 2011, 40 (3), 222–227. doi:10.1246/cl.2011.222
Polymerization reactions of the stable radical-containing monomer have also proved to be an area of difficulty in development. The stable organic radicals that are crucial to the functioning of the battery are sometimes consumed in side-reactions of various polymerization reactions. A research group has, however, successfully synthesized a cross-linked organic radical polymer while only losing 0.4% of the organic radicals in synthesis of the polymer.
See also
*List of battery types
This list is a summary of notable electric battery types composed of one or more electrochemical cells. Three lists are provided in the table. The primary (non-rechargeable) and secondary (rechargeable) cell lists are lists of battery chemistry ...
References
{{reflist Rechargeable batteries