Opal Kissing Bolin On The Cheek on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of

 Precious opal shows a variable interplay of internal colors, and though it is a mineraloid, it has an internal structure. At microscopic scales, precious opal is composed of silica spheres some in diameter in a hexagonal or cubic
Precious opal shows a variable interplay of internal colors, and though it is a mineraloid, it has an internal structure. At microscopic scales, precious opal is composed of silica spheres some in diameter in a hexagonal or cubic
 Besides the gemstone varieties that show a play of color, the other kinds of common opal include the milk opal, milky bluish to greenish (which can sometimes be of gemstone quality);
Besides the gemstone varieties that show a play of color, the other kinds of common opal include the milk opal, milky bluish to greenish (which can sometimes be of gemstone quality);
 Fire opal is a transparent to translucent opal, with warm body colors of yellow to orange to red. Although it does not usually show any play of color, occasionally a stone will exhibit bright green flashes. The most famous source of fire opals is the state of Querétaro in Mexico; these opals are commonly called Mexican fire opals. Fire opals that do not show a play of color are sometimes referred to as jelly opals. Mexican opals are sometimes cut in their rhyolitic host material if it is hard enough to allow cutting and polishing. This type of Mexican opal is referred to as a Cantera opal. Another type of opal from Mexico, referred to as Mexican water opal, is a colorless opal that exhibits either a bluish or golden internal sheen.
Girasol opal is a term sometimes mistakenly and improperly used to refer to fire opals, as well as a type of transparent to semitransparent type milky quartz from Madagascar which displays an asterism, or star effect when cut properly. However, the true girasol opal is a type of
Fire opal is a transparent to translucent opal, with warm body colors of yellow to orange to red. Although it does not usually show any play of color, occasionally a stone will exhibit bright green flashes. The most famous source of fire opals is the state of Querétaro in Mexico; these opals are commonly called Mexican fire opals. Fire opals that do not show a play of color are sometimes referred to as jelly opals. Mexican opals are sometimes cut in their rhyolitic host material if it is hard enough to allow cutting and polishing. This type of Mexican opal is referred to as a Cantera opal. Another type of opal from Mexico, referred to as Mexican water opal, is a colorless opal that exhibits either a bluish or golden internal sheen.
Girasol opal is a term sometimes mistakenly and improperly used to refer to fire opals, as well as a type of transparent to semitransparent type milky quartz from Madagascar which displays an asterism, or star effect when cut properly. However, the true girasol opal is a type of
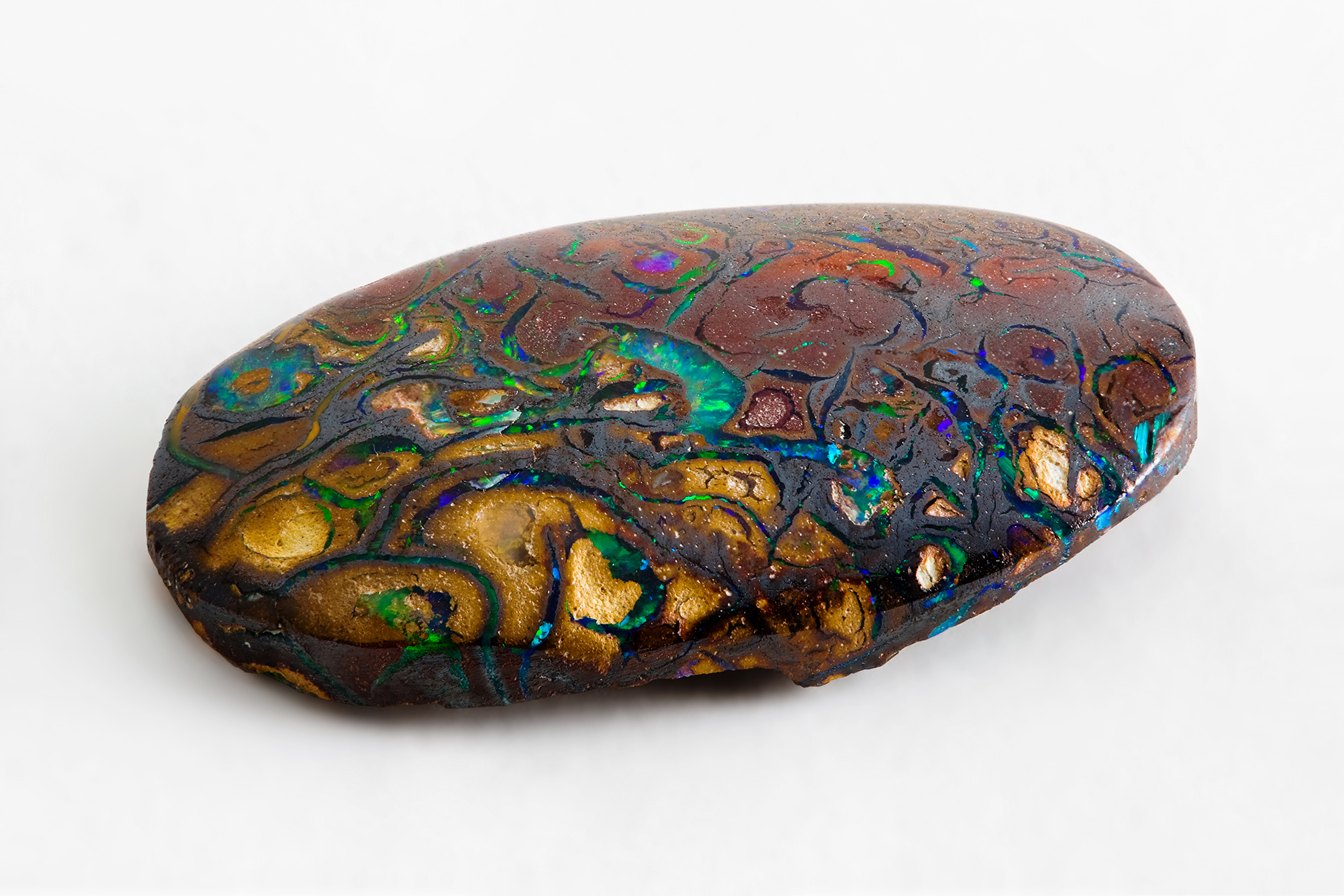
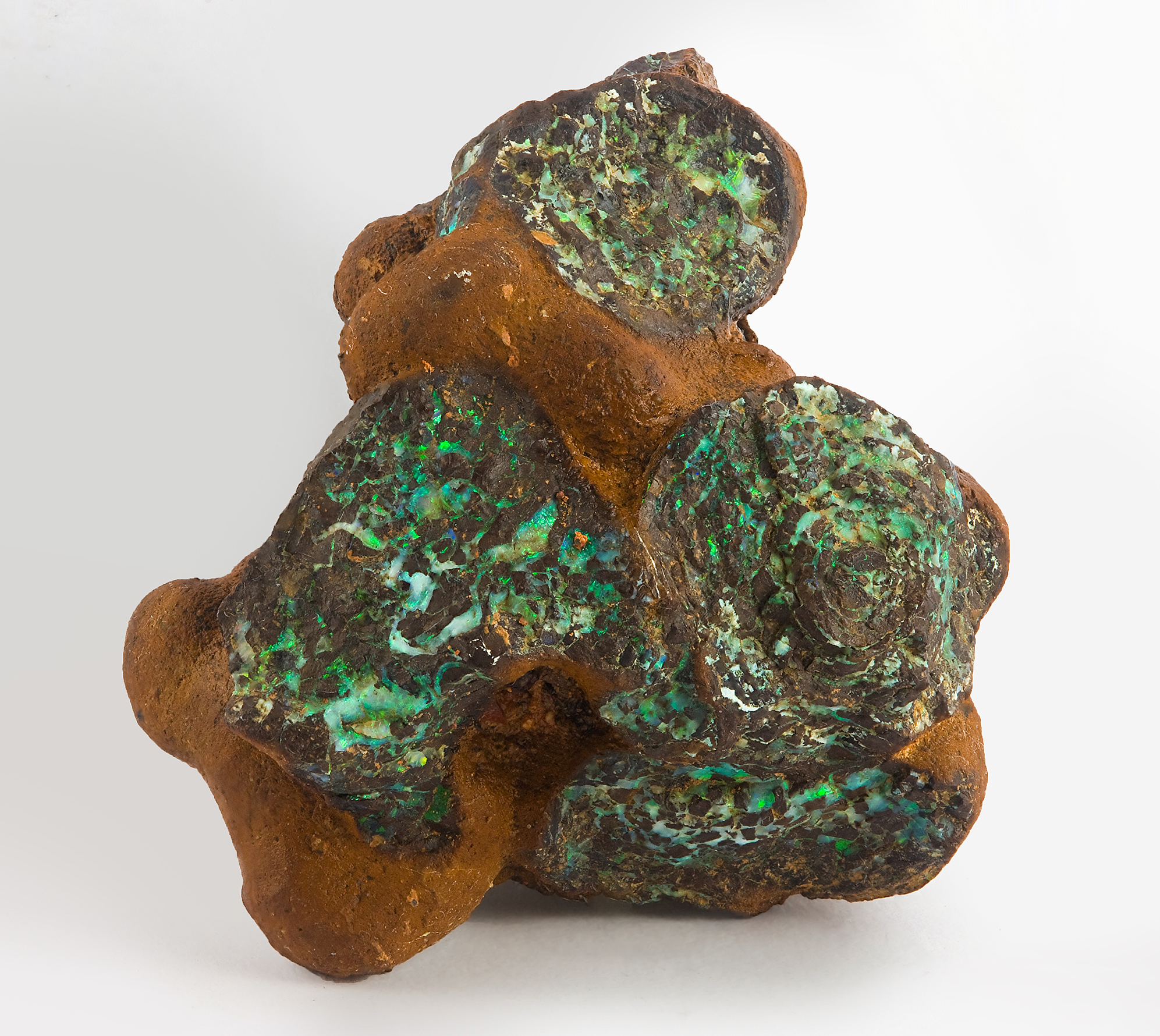
 The primary sources of opal are Australia and Ethiopia, but because of inconsistent and widely varying accountings of their respective levels of extraction, it is difficult to accurately state what proportion of the global supply of opal comes from either country.
Australian opal has been cited as accounting for 95–97% of the world's supply of precious opal, with the state of
The primary sources of opal are Australia and Ethiopia, but because of inconsistent and widely varying accountings of their respective levels of extraction, it is difficult to accurately state what proportion of the global supply of opal comes from either country.
Australian opal has been cited as accounting for 95–97% of the world's supply of precious opal, with the state of

 The Virgin Valley opal fields of Humboldt County in northern
The Virgin Valley opal fields of Humboldt County in northern
 Another source of white base opal or creamy opal in the United States is Spencer, Idaho. A high percentage of the opal found there occurs in thin layers.
Other significant deposits of precious opal around the world can be found in the Czech Republic, Canada, Slovakia, Hungary, Turkey, Indonesia, Brazil (in
Another source of white base opal or creamy opal in the United States is Spencer, Idaho. A high percentage of the opal found there occurs in thin layers.
Other significant deposits of precious opal around the world can be found in the Czech Republic, Canada, Slovakia, Hungary, Turkey, Indonesia, Brazil (in

 The lattice of spheres of opal that cause interference with light is several hundred times larger than the fundamental structure of crystalline silica. As a mineraloid, no
The lattice of spheres of opal that cause interference with light is several hundred times larger than the fundamental structure of crystalline silica. As a mineraloid, no
 Two broad categories of noncrystalline opals, sometimes just referred to as "opal-A" ("A" stands for "amorphous"), have been proposed. The first of these is opal-AG consisting of aggregated spheres of silica, with water filling the space in between. Precious opal and potch opal are generally varieties of this, the difference being in the regularity of the sizes of the spheres and their packing. The second "opal-A" is opal-AN or water-containing amorphous silica-glass.
Two broad categories of noncrystalline opals, sometimes just referred to as "opal-A" ("A" stands for "amorphous"), have been proposed. The first of these is opal-AG consisting of aggregated spheres of silica, with water filling the space in between. Precious opal and potch opal are generally varieties of this, the difference being in the regularity of the sizes of the spheres and their packing. The second "opal-A" is opal-AN or water-containing amorphous silica-glass.
Farlang opal Hist. References
Localities, anecdotes by
ICA's Opal Page
International Colored Stone Association
Opal Fossils from the South Australian Museum
Accessed 19 October 2016.
Opal Mineral data and specimen images
Mineralogy Database
Opalworld
Australian Opal Fields – Map of precious opal deposits {{Authority control Emblems of South Australia Glass in nature Hydrates National symbols of Australia Silica polymorphs
 Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
(SiO2·''n''H2O); its water content
Water content or moisture content is the quantity of water contained in a material, such as soil (called soil moisture), rock, ceramics, crops, or wood. Water content is used in a wide range of scientific and technical areas, and is expressed as ...
may range from 3 to 21% by weight, but is usually between 6 and 10%. Due to its amorphous property, it is classified as a mineraloid, unlike crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
line forms of silica, which are considered mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
s. It is deposited at a relatively low temperature and may occur in the fissure
A fissure is a long, narrow crack opening along the surface of Earth. The term is derived from the Latin word , which means 'cleft' or 'crack'. Fissures emerge in Earth's crust, on ice sheets and glaciers, and on volcanoes.
Ground fissure
...
s of almost any kind of rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
, being most commonly found with limonite, sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
, rhyolite, marl, and basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
.
The name ''opal'' is believed to be derived from the Sanskrit word (), which means 'jewel', and later the Greek derivative (), which means 'to see a change in color'.
There are two broad classes of opal: precious and common. Precious opal displays play-of-color ( iridescence); common opal does not. Play-of-color is defined as "a pseudo chromatic optical effect resulting in flashes of colored light from certain minerals, as they are turned in white light." The internal structure of precious opal causes it to diffract
Diffraction is defined as the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a s ...
light, resulting in play-of-color. Depending on the conditions in which it formed, opal may be transparent, translucent, or opaque, and the background color may be white, black, or nearly any color of the visual spectrum. Black opal is considered the rarest, while white, gray, and green opals are the most common.
Precious opal

 Precious opal shows a variable interplay of internal colors, and though it is a mineraloid, it has an internal structure. At microscopic scales, precious opal is composed of silica spheres some in diameter in a hexagonal or cubic
Precious opal shows a variable interplay of internal colors, and though it is a mineraloid, it has an internal structure. At microscopic scales, precious opal is composed of silica spheres some in diameter in a hexagonal or cubic close-packed
In geometry, close-packing of equal spheres is a dense arrangement of congruent spheres in an infinite, regular arrangement (or lattice). Carl Friedrich Gauss proved that the highest average density – that is, the greatest fraction of space occu ...
lattice
Lattice may refer to:
Arts and design
* Latticework, an ornamental criss-crossed framework, an arrangement of crossing laths or other thin strips of material
* Lattice (music), an organized grid model of pitch ratios
* Lattice (pastry), an orna ...
. It was shown by J. V. Sanders in the mid-1960s that these ordered silica spheres produce the internal colors by causing the interference
Interference is the act of interfering, invading, or poaching. Interference may also refer to:
Communications
* Interference (communication), anything which alters, modifies, or disrupts a message
* Adjacent-channel interference, caused by extr ...
and diffraction of light passing through the microstructure of the opal. The regularity of the sizes and the packing of these spheres is a prime determinant of the quality of precious opal. Where the distance between the regularly packed planes of spheres is around half the wavelength of a component of visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
, the light of that wavelength may be subject to diffraction from the grating
A grating is any regularly spaced collection of essentially identical, parallel, elongated elements. Gratings usually consist of a single set of elongated elements, but can consist of two sets, in which case the second set is usually perpendicul ...
created by the stacked planes. The colors that are observed are determined by the spacing between the planes and the orientation of planes with respect to the incident light. The process can be described by Bragg's law
In physics and chemistry , Bragg's law, Wulff–Bragg's condition or Laue–Bragg interference, a special case of Laue diffraction, gives the angles for coherent scattering of waves from a crystal lattice. It encompasses the superposition of wave ...
of diffraction.
Visible light cannot pass through large thicknesses of the opal. This is the basis of the optical band gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference ( ...
in a photonic crystal
A photonic crystal is an optical nanostructure in which the refractive index changes periodically. This affects the propagation of light in the same way that the structure of natural crystals gives rise to X-ray diffraction and that the atomic ...
. The notion that opals are photonic crystals for visible light was expressed in 1995 by Vasily Astratov's group. In addition, microfractures may be filled with secondary silica and form thin lamella
Lamella (plural lamellae) means a small plate or flake in Latin, and in English may refer to:
Biology
* Lamella (mycology), a papery rib beneath a mushroom cap
* Lamella (botany)
* Lamella (surface anatomy), a plate-like structure in an animal
...
e inside the opal during its formation. The term Opalescence is commonly used to describe this unique and beautiful phenomenon, which in gemology is termed play of color. In gemology, opalescence is applied to the hazy-milky-turbid
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids can ...
sheen of common or potch opal which does not show a play of color. Opalescence is a form of adularescence
Adularescence ( ) is an optical phenomenon that is produced in gemstones like moonstone. The optical effect is similar to labradorescence and aventurescence.
Description
The effect of adularescence, also commonly referred to as '' schiller'' ...
.
For gemstone use, most opal is cut and polished to form a cabochon
A cabochon (; ) is a gemstone that has been shaped and polished, as opposed to faceted. The resulting form is usually a convex (rounded) obverse with a flat reverse. Cabochon was the default method of preparing gemstones before gemstone cutt ...
. "Natural" opal refers to polished stones consisting wholly of precious opal. Opals too thin to produce a "Natural" opal may be combined with other materials to form "composite" gems. An opal doublet consists of a relatively thin layer of precious opal, backed by a layer of dark-colored material, most commonly ironstone, dark or black common opal (potch), onyx, or obsidian. The darker backing emphasizes the play of color and results in a more attractive display than a lighter potch. An opal triplet is similar to a doublet but has a third layer, a domed cap of clear quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical ...
or plastic on the top. The cap takes a high polish and acts as a protective layer for the opal. The top layer also acts as a magnifier, to emphasize the play of color of the opal beneath, which is often an inferior specimen or an extremely thin section of precious opal. Triplet opals tend to have a more artificial appearance and are not classed as precious gemstones, but rather "composite" gemstones. Jewelry applications of precious opal can be somewhat limited by opal's sensitivity to heat due primarily to its relatively high water content and predisposition to scratching. Combined with modern techniques of polishing, a doublet opal can produce a similar effect to Natural black or boulder opal at a fraction of the price. Doublet opal also has the added benefit of having genuine opal as the top visible and touchable layer, unlike triplet opals.
Common opal
 Besides the gemstone varieties that show a play of color, the other kinds of common opal include the milk opal, milky bluish to greenish (which can sometimes be of gemstone quality);
Besides the gemstone varieties that show a play of color, the other kinds of common opal include the milk opal, milky bluish to greenish (which can sometimes be of gemstone quality); resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on n ...
opal, which is honey-yellow with a resinous luster; wood opal, which is caused by the replacement of the organic material in wood with opal; menilite
Menilite is a greyish-brown form of the mineraloid opal. It is also known as ''liver opal'' or ''leberopal'' (German), due to its color. It is called menilite because it was first described from Ménilmontant (Paris), France, where it occurs as ...
, which is brown or grey; hyalite
Hyalite is a transparent form of opal with a glassy lustre. It may exhibit an internal play of colors if natural inclusions are present. It is also called Muller's glass, water opal, and jalite. Müller's glass is named after its discoverer, Fr ...
, a colorless glass-clear opal sometimes called Muller's glass; geyserite
Geyserite, or siliceous sinter, is a form of opaline silica that is often found as crusts or layers around hot springs and geysers. Botryoidal geyserite is known as fiorite. Geyserite is porous due to the silica enclosing many small cavities. S ...
, also called siliceous sinter
Geyserite, or siliceous sinter, is a form of opaline silica that is often found as crusts or layers around hot springs and geysers. Botryoidal geyserite is known as fiorite. Geyserite is porous due to the silica enclosing many small cavities. Si ...
, deposited around hot springs or geysers; and diatomaceous earth, the accumulations of diatom shells or tests. Common opal often displays a hazy-milky-turbid
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by large numbers of individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.
Fluids can ...
sheen from within the stone. In gemology
Gemology or gemmology is the science dealing with natural and artificial gemstone materials. It is a geoscience and a branch of mineralogy. Some jewelers (and many non-jewelers) are academically trained gemologists and are qualified to identif ...
, this optical effect is strictly defined as opalescence which is a form of adularescence.
Other varieties of opal
 Fire opal is a transparent to translucent opal, with warm body colors of yellow to orange to red. Although it does not usually show any play of color, occasionally a stone will exhibit bright green flashes. The most famous source of fire opals is the state of Querétaro in Mexico; these opals are commonly called Mexican fire opals. Fire opals that do not show a play of color are sometimes referred to as jelly opals. Mexican opals are sometimes cut in their rhyolitic host material if it is hard enough to allow cutting and polishing. This type of Mexican opal is referred to as a Cantera opal. Another type of opal from Mexico, referred to as Mexican water opal, is a colorless opal that exhibits either a bluish or golden internal sheen.
Girasol opal is a term sometimes mistakenly and improperly used to refer to fire opals, as well as a type of transparent to semitransparent type milky quartz from Madagascar which displays an asterism, or star effect when cut properly. However, the true girasol opal is a type of
Fire opal is a transparent to translucent opal, with warm body colors of yellow to orange to red. Although it does not usually show any play of color, occasionally a stone will exhibit bright green flashes. The most famous source of fire opals is the state of Querétaro in Mexico; these opals are commonly called Mexican fire opals. Fire opals that do not show a play of color are sometimes referred to as jelly opals. Mexican opals are sometimes cut in their rhyolitic host material if it is hard enough to allow cutting and polishing. This type of Mexican opal is referred to as a Cantera opal. Another type of opal from Mexico, referred to as Mexican water opal, is a colorless opal that exhibits either a bluish or golden internal sheen.
Girasol opal is a term sometimes mistakenly and improperly used to refer to fire opals, as well as a type of transparent to semitransparent type milky quartz from Madagascar which displays an asterism, or star effect when cut properly. However, the true girasol opal is a type of hyalite
Hyalite is a transparent form of opal with a glassy lustre. It may exhibit an internal play of colors if natural inclusions are present. It is also called Muller's glass, water opal, and jalite. Müller's glass is named after its discoverer, Fr ...
opal that exhibits a bluish glow or sheen that follows the light source around. It is not a play of color as seen in precious opal, but rather an effect from microscopic inclusions. It is also sometimes referred to as water opal, too, when it is from Mexico. The two most notable locations of this type of opal are Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
and Mexico.
Peruvian opal (also called blue opal) is a semi-opaque to opaque blue-green stone found in Peru, which is often cut to include the matrix in the more opaque stones. It does not display a play of color. Blue opal also comes from Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
and Idaho in the Owyhee region, as well as from Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
around the Virgin Valley
The Virgin Valley is a valley in northwest Arizona and southeast Nevada on the Virgin River. The Virgin River drains southwest Utah and southeast Nevada; parts of Arizona, especially the Arizona Strip region drain southwards into the Virgin River ...
.
Opal is also formed by diatoms. Diatoms are a form of algae that, when they die, often form layers at the bottoms of lakes, bays, or oceans. Their cell walls are made up of hydrated silicon dioxide which gives them structural coloration and therefore the appearance of tiny opals when viewed under a microscope. These cell walls or "tests" form the “grains” for the diatomaceous earth. This sedimentary rock is white, opaque, and chalky in texture. Diatomite has multiple industrial uses such as filtering or adsorbing since it has a fine particle size and very porous nature, and gardening to increase water absorption.
History
Opal was rare and very valuable in antiquity. In Europe, it was a gem prized by royalty. Until the opening of vast deposits in Australia in the 19th century the only known source was beyond the Roman frontier inSlovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
. Opal is the national gemstone of Australia.
Sources

 The primary sources of opal are Australia and Ethiopia, but because of inconsistent and widely varying accountings of their respective levels of extraction, it is difficult to accurately state what proportion of the global supply of opal comes from either country.
Australian opal has been cited as accounting for 95–97% of the world's supply of precious opal, with the state of
The primary sources of opal are Australia and Ethiopia, but because of inconsistent and widely varying accountings of their respective levels of extraction, it is difficult to accurately state what proportion of the global supply of opal comes from either country.
Australian opal has been cited as accounting for 95–97% of the world's supply of precious opal, with the state of South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
accounting for 80% of the world's supply. In 2012, Ethiopian opal production was estimated to be by the United States Geological Survey. USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, a ...
data from the same period (2012), reveals Australian opal production to be $41 million. Because of the units of measurement, it is not possible to directly compare Australian and Ethiopian opal production, but these data and others suggest that the traditional percentages given for Australian opal production may be overstated. Yet, the validity of data in the USGS report appears to conflict with that of Laurs et al. and Mesfin, who estimated the 2012 Ethiopian opal output (from Wegal Tena) to be only .
Australia
The town ofCoober Pedy
Coober Pedy () is a town in northern South Australia, north of Adelaide on the Stuart Highway. The town is sometimes referred to as the "opal capital of the world" because of the quantity of precious opals that are mined there. Coober Pedy is ...
in South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
is a major source of opal. The world's largest and most valuable gem opal " Olympic Australis" was found in August 1956 at the "Eight Mile" opal field in Coober Pedy. It weighs and is long, with a height of and a width of .
The Mintabie Opal Field in South Australia located about northwest of Coober Pedy has also produced large quantities of crystal opal and the rarer black opal. Over the years, it has been sold overseas incorrectly as Coober Pedy opal. The black opal is said to be some of the best examples found in Australia.
Andamooka in South Australia is also a major producer of matrix opal, crystal opal, and black opal. Another Australian town, Lightning Ridge
Lightning Ridge is a small outback town in north-western New South Wales, Australia. Part of Walgett Shire, Lightning Ridge is situated near the southern border of Queensland, about east of the Castlereagh Highway. The Lightning Ridge area i ...
in New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, is the main source of black opal, opal containing a predominantly dark background (dark gray to blue-black displaying the play of color), collected from the Griman Creek Formation
The Griman Creek Formation is a geological formation in northern New South Wales and southern Queensland, Australia whose strata date back to the Albian-Cenomanian of the Early-Late Cretaceous.Bell et al., 2019 It is most notable being a major so ...
. Boulder opal consists of concretion
A concretion is a hard, compact mass of matter formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles, and is found in sedimentary rock or soil. Concretions are often ovoid or spherical in shape, although irregular ...
s and fracture fillings in a dark siliceous ironstone
Ironstone is a sedimentary rock, either deposited directly as a ferruginous sediment or created by chemical replacement, that contains a substantial proportion of an iron ore compound from which iron (Fe) can be smelted commercially. Not to be con ...
matrix. It is found sporadically in western Queensland, from Kynuna in the north, to Yowah and Koroit
Koroit is a small rural town in western Victoria, Australia a few kilometres north of the Princes Highway, north-west of Warrnambool and west of Melbourne. It is in the Shire of Moyne local government area located amidst rolling green past ...
in the south. Its largest quantities are found around Jundah
Jundah is a rural town and locality in the Shire of Barcoo, Queensland, Australia. Jundah is the administrative centre of the Barcoo Shire local government area. In the , the locality of Jundah had a population of 106 people.
Geography
The t ...
and Quilpie
Quilpie ( ) is a rural town and locality in the Shire of Quilpie, Queensland, Australia. In the , Quilpie had a population of 595 people.
The town is the administrative centre of the Quilpie Shire local government area. The town of Toompine ...
in South West Queensland
South West Queensland is a remote region in the Australian state of Queensland which covers . The region lies to the south of Central West Queensland and west of the Darling Downs and includes the Maranoa district and parts of the Channel Coun ...
. Australia also has opalized fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
remains, including dinosaur bones in New South Wales and South Australia, and marine creatures in South Australia.
Ethiopia
It has been reported that Northern African opal was used to make tools as early as 4000 BC. The first published report of gem opal fromEthiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
appeared in 1994, with the discovery of precious opal in the Menz Gishe District, North Shewa Province. The opal, found mostly in the form of nodules, was of volcanic origin and was found predominantly within weathered layers of rhyolite. This Shewa Province opal was mostly dark brown in color and had a tendency to crack. These qualities made it unpopular in the gem trade. In 2008, a new opal deposit was found approximately 180 km north of Shewa Province, near the town of Wegel Tena, in Ethiopia's Wollo Province
Wollo ( Amharic: ወሎ) was a historical province of northern Ethiopia that overlayed part of the present day Amhara, Afar, and Tigray regions. During the Middle Ages this region was known as Bete Amhara and had Amhara kings. Bete Amhara ha ...
. The Wollo Province opal was different from the previous Ethiopian opal finds in that it more closely resembled the sedimentary opals of Australia and Brazil, with a light background and often vivid play-of-color. Wollo Province opal, more commonly referred to as "Welo" or "Wello" opal, has become the dominant Ethiopian opal in the gem trade.
Virgin Valley, Nevada
 The Virgin Valley opal fields of Humboldt County in northern
The Virgin Valley opal fields of Humboldt County in northern Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
produce a wide variety of precious black, crystal, white, fire, and lemon opal. The black fire opal is the official gemstone of Nevada. Most of the precious opal is partial wood replacement. The precious opal is hosted and found ''in situ
''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in ...
'' within a subsurface horizon or zone of bentonite
Bentonite () is an absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelling capacity than Ca-m ...
, which is considered a "lode" deposit. Opals which have weathered out of the ''in situ'' deposits are alluvial and considered placer deposit
In geology, a placer deposit or placer is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation from a specific source rock during sedimentary processes. The name is from the Spanish word ''placer'', meaning "alluvial sand". Placer mi ...
s. Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
-age opalised teeth, bones, fish, and a snake head have been found. Some of the opal has high water content and may desiccate and crack when dried. The largest producing mines of Virgin Valley have been the famous Rainbow Ridge, Royal Peacock, Bonanza, Opal Queen, and WRT Stonetree/Black Beauty mines. The largest unpolished black opal in the Smithsonian Institution, known as the "Roebling opal", came out of the tunneled portion of the Rainbow Ridge Mine in 1917, and weighs . The largest polished black opal in the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
comes from the Royal Peacock opal mine in the Virgin Valley, weighing , known as the "Black Peacock".
Mexico
Opal occurs in significant quantity and variety in central Mexico, wheremining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic ...
and production first originated in the state of Querétaro. In this region the opal deposits are located mainly in the mountain ranges of three municipalities: Colón, Tequisquiapan
Tequisquiapan (; Otomi: Ntʼe) is a town and municipality located in the southeast of the state of Querétaro in central Mexico. The center of the town has cobblestone streets, traditional rustic houses with wrought iron fixtures, balconies, and ...
and Ezequiel Montes
Ezequiel is a given name. Notable people with the name include:
People
*Ezequiel Adamovsky (born 1971), Argentine historian and political activist
* Ezequiel Alejo Carboni (born 1979), is an Argentine midfielder
* Ezequiel Andreoli (born 1978), ...
. During the 1960s through to the mid-1970s, the Querétaro mines were heavily mined. Today's opal miners report that it was much easier to find quality opals with a lot of fire and play of color back then, whereas today the gem-quality opals are very hard to come by and command hundreds of US dollars or more. They gave an orangey opaque lustre, which is called the "Mexican fire opal".
The oldest mine in Querétaro is Santa Maria del Iris. This mine was opened around 1870 and has been reopened at least 28 times since. At the moment there are about 100 mines in the regions around Querétaro, but most of them are now closed. The best quality of opals came from the mine Santa Maria del Iris, followed by La Hacienda la Esperanza, Fuentezuelas, La Carbonera, and La Trinidad. Important deposits in the state of Jalisco were not discovered until the late 1950s.
In 1957, Alfonso Ramirez (of Querétaro) accidentally discovered the first opal mine in Jalisco: La Unica, located on the outer area of the volcano of Tequila, near the Huitzicilapan farm in Magdalena. By 1960 there were around 500 known opal mines in this region alone. Other regions of the country that also produce opals (of lesser quality) are Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the pop ...
, which produces an opaque opal similar to the opals from Australia (some of these opals are carefully treated with heat to improve their colors so high-quality opals from this area may be suspect). There are also some small opal mines in Morelos, Durango, Chihuahua, Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
, Guanajuato, Puebla, Michoacán, and Estado de México
The State of Mexico ( es, Estado de México; ), officially just Mexico ( es, México), is one of the 32 federal entities of the United Mexican States. Commonly known as Edomex (from ) to distinguish it from the name of the whole country, it is ...
.
Other locations
Pedro II, Piauí
Pedro II, Piauí is a municipality in the state of Piauí in the Northeast region of Brazil.
The municipality contains part of the Serra da Ibiapaba Environmental Protection Area, created in 1996.
See also
*List of municipalities in Piauí
*P ...
), Honduras (more precisely in Erandique
Erandique is a municipality in the Lempira Department of Honduras.
Erandique is one of the several municipalities of the Lempira department. One has to travel on road CA11A from the city of Gracias passing by San Juan (del Caite). A second r ...
), Guatemala and Nicaragua.
In late 2008, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
announced it had discovered opal deposits on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
.
Synthetic opal
Opals of all varieties have been synthesized experimentally and commercially. The discovery of the ordered sphere structure of precious opal led to its synthesis by Pierre Gilson in 1974. The resulting material is distinguishable from natural opal by its regularity; under magnification, the patches of color are seen to be arranged in a "lizard skin" or "chicken wire" pattern. Furthermore, synthetic opals do notfluoresce
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, tha ...
under ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
light. Synthetics are also generally lower in density and are often highly porous.
Opals which have been created in a laboratory are often termed "lab-created opals", which, while classifiable as man-made and synthetic, are very different from their resin-based counterparts which are also considered man-made and synthetic. The term "synthetic" implies that a stone has been created to be chemically and structurally indistinguishable from a genuine one, and genuine opal contains no resins or polymers. The finest modern lab-created opals do not exhibit the lizard skin or columnar patterning of earlier lab-created varieties, and their patterns are non-directional. They can still be distinguished from genuine opals, however, by their lack of inclusions and the absence of any surrounding non-opal matrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** ''The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchis ...
. While many genuine opals are cut and polished without a matrix, the presence of irregularities in their play-of-color continues to mark them as distinct from even the best lab-created synthetics.
Other research in macroporous structures have yielded highly ordered materials that have similar optical properties to opals and have been used in cosmetics. Synthetic opals are also deeply investigated in photonics
Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. Though ...
for sensing and light management purposes.
Local atomic structure of opals

 The lattice of spheres of opal that cause interference with light is several hundred times larger than the fundamental structure of crystalline silica. As a mineraloid, no
The lattice of spheres of opal that cause interference with light is several hundred times larger than the fundamental structure of crystalline silica. As a mineraloid, no unit cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessaril ...
describes the structure of opal. Nevertheless, opals can be roughly divided into those that show no signs of crystalline order ( amorphous opal) and those that show signs of the beginning of crystalline order, commonly termed cryptocrystalline
Cryptocrystalline is a rock texture made up of such minute crystals that its crystalline nature is only vaguely revealed even microscopically in thin section by transmitted polarized light. Among the sedimentary rocks, chert and flint are crypt ...
or microcrystalline opal. Dehydration experiments and infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or function ...
have shown that most of the H2O in the formula of SiO2·''n''H2O of opals is present in the familiar form of clusters of molecular water. Isolated water molecules, and silanol
A silanol is a functional group in silicon chemistry with the connectivity Si–O–H. It is related to the hydroxy functional group (C–O–H) found in all alcohols. Silanols are often invoked as intermediates in organosilicon ch ...
s, structures such as SiOH, generally form a lesser proportion of the total and can reside near the surface or in defects inside the opal.
The structure of low-pressure polymorphs of anhydrous silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
consists of frameworks of fully corner bonded tetrahedra of SiO4. The higher temperature polymorphs of silica cristobalite
Cristobalite is a mineral polymorph of silica that is formed at very high temperatures. It has the same chemical formula as quartz, SiO2, but a distinct crystal structure. Both quartz and cristobalite are polymorphs with all the members of the ...
and tridymite
Tridymite is a high-temperature polymorph of silica and usually occurs as minute tabular white or colorless pseudo-hexagonal crystals, or scales, in cavities in felsic volcanic rocks. Its chemical formula is Si O2. Tridymite was first describe ...
are frequently the first to crystallize from amorphous anhydrous silica, and the local structures of microcrystalline opals also appear to be closer to that of cristobalite and tridymite than to quartz. The structures of tridymite and cristobalite are closely related and can be described as hexagonal
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A '' regular hexagon'' has ...
and cubic close-packed layers. It is therefore possible to have intermediate structures in which the layers are not regularly stacked.
Microcrystalline opal
Microcrystalline opal or ''Opal-CT'' has been interpreted as consisting of clusters of stackedcristobalite
Cristobalite is a mineral polymorph of silica that is formed at very high temperatures. It has the same chemical formula as quartz, SiO2, but a distinct crystal structure. Both quartz and cristobalite are polymorphs with all the members of the ...
and tridymite
Tridymite is a high-temperature polymorph of silica and usually occurs as minute tabular white or colorless pseudo-hexagonal crystals, or scales, in cavities in felsic volcanic rocks. Its chemical formula is Si O2. Tridymite was first describe ...
over very short length scales. The spheres of opal in microcrystalline opal are themselves made up of tiny nanocrystalline blades of cristobalite and tridymite. Microcrystalline opal has occasionally been further subdivided in the literature. Water content may be as high as 10 wt%. Opal-CT, also called ''lussatine'' or ''lussatite'', is interpreted as consisting of localized order of α-cristobalite with a lot of stacking disorder. Typical water content is about 1.5 wt%.
Noncrystalline opal
 Two broad categories of noncrystalline opals, sometimes just referred to as "opal-A" ("A" stands for "amorphous"), have been proposed. The first of these is opal-AG consisting of aggregated spheres of silica, with water filling the space in between. Precious opal and potch opal are generally varieties of this, the difference being in the regularity of the sizes of the spheres and their packing. The second "opal-A" is opal-AN or water-containing amorphous silica-glass.
Two broad categories of noncrystalline opals, sometimes just referred to as "opal-A" ("A" stands for "amorphous"), have been proposed. The first of these is opal-AG consisting of aggregated spheres of silica, with water filling the space in between. Precious opal and potch opal are generally varieties of this, the difference being in the regularity of the sizes of the spheres and their packing. The second "opal-A" is opal-AN or water-containing amorphous silica-glass. Hyalite
Hyalite is a transparent form of opal with a glassy lustre. It may exhibit an internal play of colors if natural inclusions are present. It is also called Muller's glass, water opal, and jalite. Müller's glass is named after its discoverer, Fr ...
is another name for this.
Noncrystalline silica in siliceous sediments is reported to gradually transform to opal-CT and then opal-C as a result of diagenesis
Diagenesis () is the process that describes physical and chemical changes in sediments first caused by water-rock interactions, microbial activity, and compaction after their deposition. Increased pressure and temperature only start to play a ...
, due to the increasing overburden pressure in sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
rocks, as some of the stacking disorder is removed.
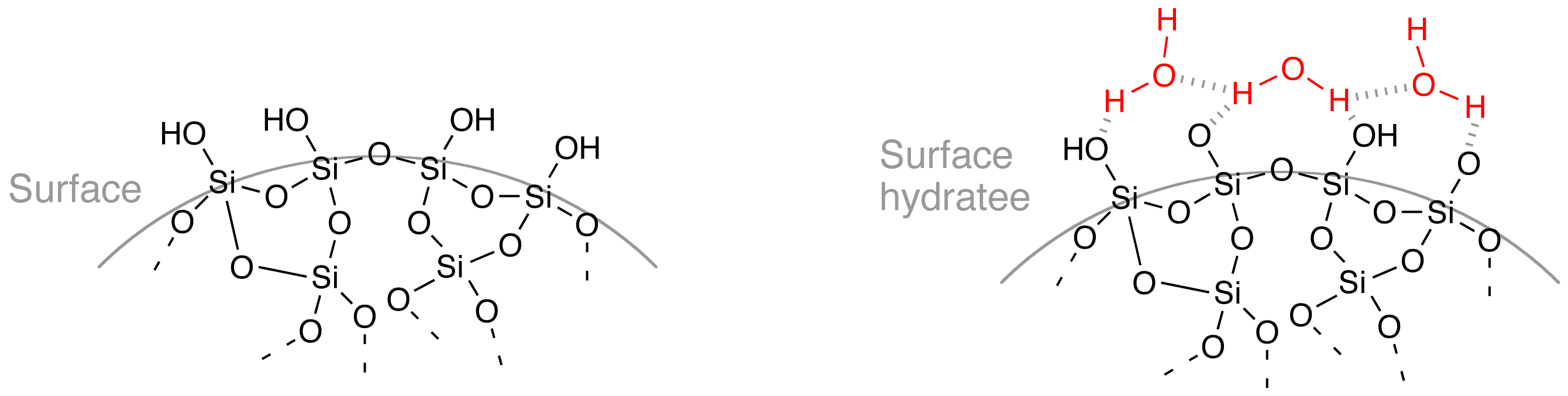
Opal surface chemical groups
The surface of opal in contact with water is covered bysiloxane
A siloxane is a functional group in organosilicon chemistry with the Si−O−Si linkage. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H(OSiH2)''n''OH and (OSiH2)n. Siloxanes also include branched compound ...
bonds (≡Si–O–Si≡) and silanol
A silanol is a functional group in silicon chemistry with the connectivity Si–O–H. It is related to the hydroxy functional group (C–O–H) found in all alcohols. Silanols are often invoked as intermediates in organosilicon ch ...
groups (≡Si–OH). This makes the opal surface very hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are ...
and capable of forming numerous hydrogen bonds.
Etymology
The word 'opal' is adapted from theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
term . The origin of this word in turn is a matter of debate, but most modern references suggest it is adapted from the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
word .
References to the gem are made by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
. It is suggested to have been adapted from Ops, the wife of Saturn, and goddess of fertility. The portion of Saturnalia devoted to Ops was "Opalia", similar to .
Another common claim that the term is adapted from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
word, . This word has two meanings, one is related to "seeing" and forms the basis of the English words like "opaque"; the other is "other" as in "alias" and "alter". It is claimed that combined these uses, meaning "to see a change in color". However, historians have noted the first appearances of do not occur until after the Romans had taken over the Greek states in 180 BC and they had previously used the term .
However, the argument for the Sanskrit origin is strong. The term first appears in Roman references around 250 BC, at a time when the opal was valued above all other gems. The opals were supplied by traders from the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
, who claimed the gems were being supplied from India. Before this, the stone was referred to by a variety of names, but these fell from use after 250 BC.
Historical superstitions
In the Middle Ages, opal was considered a stone that could provide great luck because it was believed to possess all the virtues of each gemstone whose color was represented in the color spectrum of the opal. It was also said to grant invisibility if wrapped in a fresh bay leaf and held in the hand. As a result, the opal was seen as the patron gemstone forthieves
Theft is the act of taking another person's property or services without that person's permission or consent with the intent to deprive the rightful owner of it. The word ''theft'' is also used as a synonym or informal shorthand term for some ...
during the medieval period
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. Following the publication of Sir Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels '' Ivanhoe'', '' Rob Roy ...
's ''Anne of Geierstein
''Anne of Geierstein, or The Maiden of the Mist'' (1829) is one of the Waverley novels by Sir Walter Scott. It is set in Central Europe, mainly in Switzerland, shortly after the Yorkist victory at the Battle of Tewkesbury (1471). It covers the p ...
'' in 1829, opal acquired a less auspicious reputation. In Scott's novel, the Baroness of Arnheim wears an opal talisman
A talisman is any object ascribed with religious or magical powers intended to protect, heal, or harm individuals for whom they are made. Talismans are often portable objects carried on someone in a variety of ways, but can also be installed perm ...
with supernatural powers. When a drop of holy water
Holy water is water that has been blessed by a member of the clergy or a religious figure, or derived from a well or spring considered holy. The use for cleansing prior to a baptism and spiritual cleansing is common in several religions, from ...
falls on the talisman, the opal turns into a colorless stone and the Baroness dies soon thereafter. Due to the popularity of Scott's novel, people began to associate opals with bad luck and death. Within a year of the publishing of Scott's novel in April 1829, the sale of opals in Europe dropped by 50%, and remained low for the next 20 years or so.
Even as recently as the beginning of the 20th century, it was believed that when a Russian saw an opal among other goods offered for sale, he or she should not buy anything more, as the opal was believed to embody the evil eye
The Evil Eye ( grc, ὀφθαλμὸς βάσκανος; grc-koi, ὀφθαλμὸς πονηρός; el, (κακό) μάτι; he, עַיִן הָרָע, ; Romanian: ''Deochi''; it, malocchio; es, mal de ojo; pt, mau-olhado, olho gordo; ar ...
.
Opal is considered the birthstone for people born in October.
Examples
* The Olympic Australis, the world's largest and most valuable gem opal, found inCoober Pedy
Coober Pedy () is a town in northern South Australia, north of Adelaide on the Stuart Highway. The town is sometimes referred to as the "opal capital of the world" because of the quantity of precious opals that are mined there. Coober Pedy is ...
* The Andamooka Opal, presented to Queen Elizabeth II, also known as the Queen's Opal
* The Addyman Plesiosaur from Andamooka, "the finest known opalised skeleton on Earth"
* The Burning of Troy, the now-lost opal presented to Joséphine de Beauharnais
Josephine may refer to:
People
* Josephine (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name)
* Josephine (singer), a Greek pop singer
Places
*Josephine, Texas, United States
*Mount Josephine (disambiguation)
* Josephine Cou ...
by Napoleon I of France and the first named opal
* The Flame Queen Opal
The Flame Queen Opal is perhaps the most famous of all opals. It is the best-known example of “eye-of-opal”, an eye-like effect created when opal in-fills a cavity.
The Flame Queen's flat central raised dome flashes red or gold depending on t ...
* The Halley's Comet Opal, the world's largest uncut black opal
* Although the clock faces above the information stand in Grand Central Terminal in New York City are often said to be opal, they are in fact opalescent glass
Opalescence refers to the optical phenomena displayed by the mineraloid gemstone opalopalescent. 2019. In Noah Webster's 1828 American Dictionary of the English Language. Retrieved January 7, 2019, from https://1828.mshaffer.com/d/word/opalesc ...
* The Roebling Opal, Smithsonian Institution
* The Galaxy Opal, listed as the "World's Largest Polished Opal" in the 1992 Guinness Book of Records
* The Rainbow Virgin, "the finest crystal opal specimen ever unearthed"
*The Sea of Opal, the largest black opal in the world
*The Fire of Australia, assumed to be "the finest uncut opal in existence"
*Beverly the Bug
Beverly the Bug is the first and only known opal with an insect inclusion. It contains "the exoskeleton of a nymphal insect belonging to the order Hemiptera and either the family Tettigarctidae or the Cicadidae".
It was found on Java in 2015. Gem ...
, the first known example of an opal with an insect inclusion
Inclusion or Include may refer to:
Sociology
* Social inclusion, aims to create an environment that supports equal opportunity for individuals and groups that form a society.
** Inclusion (disability rights), promotion of people with disabiliti ...
See also
*Biogenic silica
Biogenic silica (bSi), also referred to as opal, biogenic opal, or amorphous opaline silica, forms one of the most widespread biogenic minerals. For example, microscopic particles of silica called phytoliths can be found in grasses and other plant ...
*
*
* Labradorite
Labradorite (( Ca, Na)( Al, Si)4 O8) is a calcium-enriched feldspar mineral first identified in Labrador, Canada, which can display an iridescent effect (schiller).
Labradorite is an intermediate to calcic member of the plagioclase series. It ...
*
*
* ''Uncut Gems'' (2019 film)
References
Further reading
*External links
Farlang opal Hist. References
Localities, anecdotes by
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routle ...
, Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
, Georg Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Pawer or Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Emp ...
etc.
ICA's Opal Page
International Colored Stone Association
Opal Fossils from the South Australian Museum
Accessed 19 October 2016.
Opal Mineral data and specimen images
Mineralogy Database
Opalworld
Australian Opal Fields – Map of precious opal deposits {{Authority control Emblems of South Australia Glass in nature Hydrates National symbols of Australia Silica polymorphs