Olأ،h Gyأ¶rgy Elإ‘adأ،sa 8299 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 "Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and
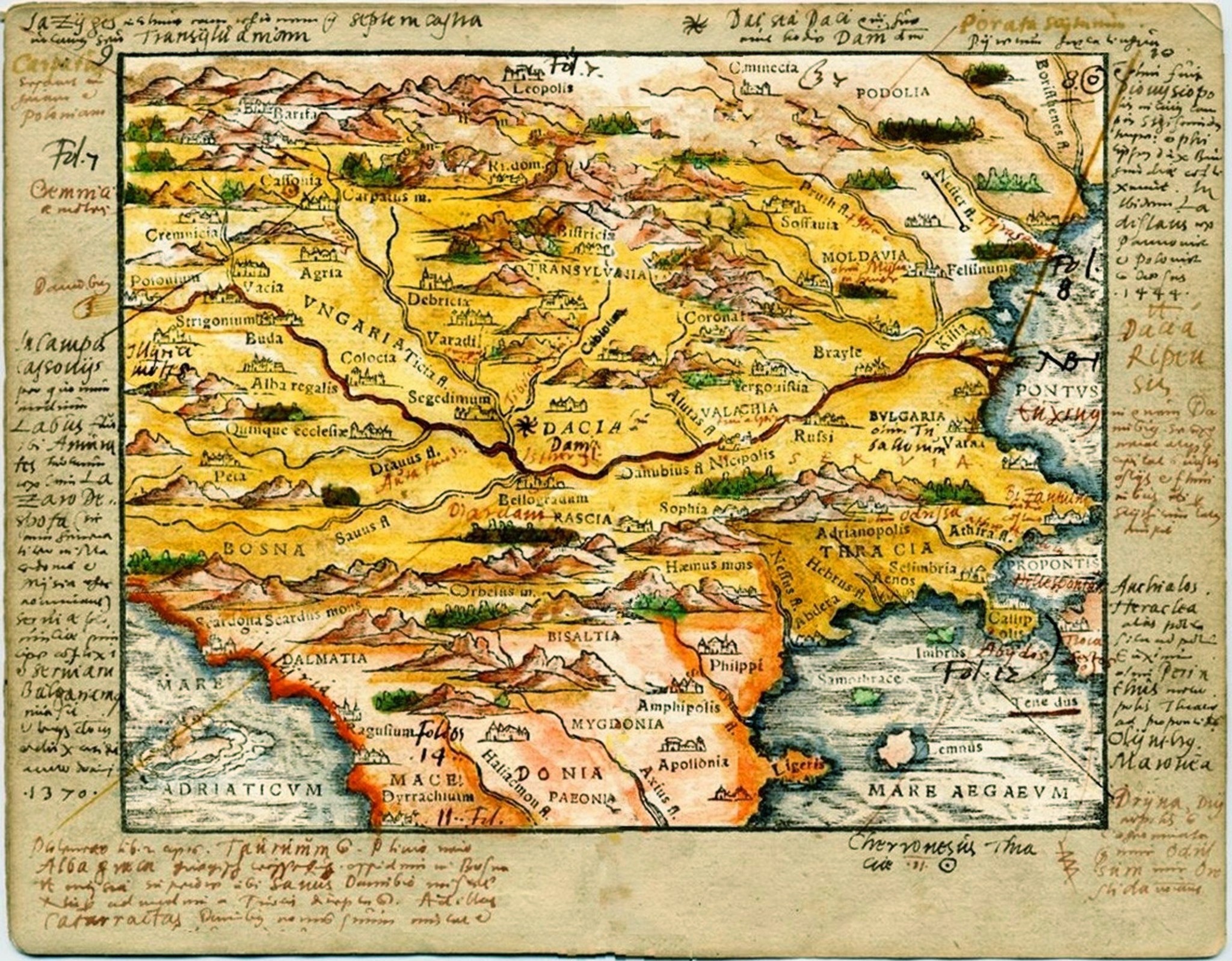
 The word ''Vlach''/''Wallachian'' (and other variants such as ''Vlah'', ''Valah'', ''Valach'', ''Voloh'', ''Blac'', ''olأ،h'', ''Vlas'', ''Ilac'', ''Ulah'', etc.) is etymologically derived from the ethnonym of a
The word ''Vlach''/''Wallachian'' (and other variants such as ''Vlah'', ''Valah'', ''Valach'', ''Voloh'', ''Blac'', ''olأ،h'', ''Vlas'', ''Ilac'', ''Ulah'', etc.) is etymologically derived from the ethnonym of a
Inheritance versus lexical borrowing: a case with decisive sound-change evidence
" ''Language Log,'' January 2009. ( Via both Germanic and Latin, the term started to signify "stranger, foreigner" also in the
Via both Germanic and Latin, the term started to signify "stranger, foreigner" also in the  During the early history of the
During the early history of the

 The ''Hellenic chronicle'' could possibly qualify to the first testimony of Vlachs in Pannonia and Eastern Europe during the time of Attila.
The ''Hellenic chronicle'' could possibly qualify to the first testimony of Vlachs in Pannonia and Eastern Europe during the time of Attila.
 The Russian
The Russian
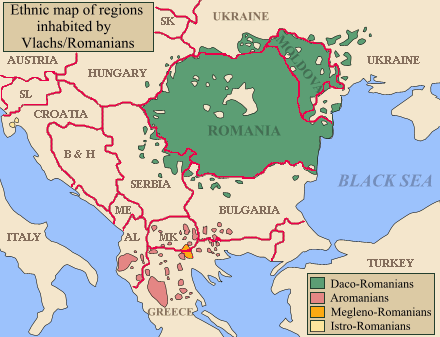
 In addition to the ethnic groups of Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, and
In addition to the ethnic groups of Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, and  *
*
File:Bosniangraves bosniska gravar februari 2007 stecak stecci3.jpg, Medieval necropolis in Radimlja,
/ref>
full text
Though focussed on the Vlachs of North Macedonia, has in-depth discussion of many topics, including the origins of the Vlachs, their status as a minority in various countries, their political use in various contexts, and so on. * Asterios I. Koukoudis, ''The Vlachs: Metropolis and Diaspora'', 2003, * * Th Capidan, Aromأ¢nii, Dialectul Aromأ¢n, ed2 خ•diturؤƒ Fundaإ£iei Culturale Aromأ¢ne, Bucureب™ti 2005
a photo-essay on the Valchs published by GEO magazine (France), 2010.
* Adina Berciu-Drؤƒghicescu, Aromأ¢ni, meglenoromأ¢ni, istroromأ¢ni : aspecte identitare إںi culturale, Editura Universitؤƒإ£ii din Bucureب™ti, 2012, * Octavian Ciobanu, "The Role of the Vlachs in the Bogomils' Expansion in the Balkans.", Journal of Balkan and Black Sea Studies, Year 4, Issue 7, December 2021, pp. 11–32.
ROMأ‚NII BALCANICI AROMأ‚NII
€”Maria Magiru about Aromanians {{in lang, Ro
Cultural appropriation of Vlachs' heritage
French Vlachs Association (in Vlach, EN and FR)
by Asterios Koukoudis
Vlachs' in Greece
(in Greek)
Consiliul A Tinirlor Armanj, Youth Aromanian community and their Projects
(in Vlach, EN and RO)
''Old Wallachia''
€”a short Czech film from 1955 depicting life of Vlachs in Czech Moravia Eastern Romance people Transhumant ethnic groups
 "Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
used from the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
until the Modern Era
The term modern period or modern era (sometimes also called modern history or modern times) is the period of history that succeeds the Middle Ages (which ended approximately 1500 AD). This terminology is a historical periodization that is applie ...
to designate mainly Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, romأ¢ni, ; dated exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Culture of Romania, Romanian culture and Cultural heritage, ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they l ...
but also Aromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armأ£nji, Rrأ£mأ£nji) are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Alba ...
, Megleno-Romanians
The Megleno-Romanians, also known as Meglenites ( ruq, Miglinits), Moglenite Vlachs or simply Vlachs ( ruq, Vlaب™), are a small Eastern Romance people, originally inhabiting seven villages in the Moglena region spanning the Pella and Kilkis reg ...
, Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( ruo, rumeri or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. However, due to se ...
and other Eastern Romance
The Eastern Romance languages are a group of Romance languages. Today, the group consists of the Daco-Romance subgroup, which comprises the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian), Aromanian language and two other related minor languages, Megleno-R ...
-speaking subgroups of Central and Eastern Europe
Central and Eastern Europe is a term encompassing the countries in the Baltics, Central Europe, Eastern Europe and Southeast Europe (mostly the Balkans), usually meaning former communist states from the Eastern Bloc and Warsaw Pact in Europe. ...
.
As a contemporary term, in the English language, the Vlachs are the Balkan Romance-speaking peoples who live south of the Danube in what are now southern Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipأ«ri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipأ«risأ«), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, ذ‘رٹذ»ذ³ذ°ر€ذ¸رڈ, Bاژlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
, northern Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Feder ...
, and eastern Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
as native ethnic groups, such as the Aromanians
The Aromanians ( rup, Armأ£nji, Rrأ£mأ£nji) are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Alba ...
, Megleno-Romanians
The Megleno-Romanians, also known as Meglenites ( ruq, Miglinits), Moglenite Vlachs or simply Vlachs ( ruq, Vlaب™), are a small Eastern Romance people, originally inhabiting seven villages in the Moglena region spanning the Pella and Kilkis reg ...
and the Timok Romanians. The term also became a synonym in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
for the social category of shepherds, and was also used for non-Romance-speaking peoples, in recent times in the western Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whol ...
derogatively. The term is also used to refer to the ethnographic group of Moravian Vlachs who speak a Slavic language but originate from Romanians.
"Vlachs" were initially identified and described during the 11th century by George Kedrenos. According to one origin theory, modern Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, romأ¢ni, ; dated exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Culture of Romania, Romanian culture and Cultural heritage, ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they l ...
, Moldovans and Aromanians originated from Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, خ”خ¬خ؛خ؟خ¹, خ”خ¬خ؟خ¹, خ”خ¬خ؛خ±خ¹) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
. According to some linguists and scholars, the Eastern Romance languages
The Eastern Romance languages are a group of Romance languages. Today, the group consists of the Daco-Romance subgroup, which comprises the Romanian language (Daco-Romanian), Aromanian language and two other related minor languages, Megleno-R ...
prove the survival of the Thraco-Romans in the lower Danube basin during the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
and western Balkan populations known as "Vlachs" also have had Romanized Illyrian origins.
Nowadays, Eastern Romance-speaking communities are estimated at 26–30 million people worldwide (including the Romanian diaspora and Moldovan diaspora).
Etymology and names
 The word ''Vlach''/''Wallachian'' (and other variants such as ''Vlah'', ''Valah'', ''Valach'', ''Voloh'', ''Blac'', ''olأ،h'', ''Vlas'', ''Ilac'', ''Ulah'', etc.) is etymologically derived from the ethnonym of a
The word ''Vlach''/''Wallachian'' (and other variants such as ''Vlah'', ''Valah'', ''Valach'', ''Voloh'', ''Blac'', ''olأ،h'', ''Vlas'', ''Ilac'', ''Ulah'', etc.) is etymologically derived from the ethnonym of a Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
tribe, adopted into Proto- Germanic ''* Walhaz'', which meant "stranger", from ''*Wolkؤپ-''Ringe, Don.Inheritance versus lexical borrowing: a case with decisive sound-change evidence
" ''Language Log,'' January 2009. (
Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caes ...
's la, Volcae, Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
and Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, خ د„خ؟خ»خµخ¼خ±ل؟–خ؟د‚, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's gr , Ouolkai).}), and in Poland ''Wإ‚ochy'' or in Hungary ''olasz'' became an exonym for Italians. The Slovenian term ''Lahi'' has also been used to designate Italians.
Historically, the term was used primarily for the Romanians. Testimonies from the 13th to 14th centuries show that, although in Europe (and beyond) they were called ''Vlachs'' or ''Wallachians'' (''olأ،h'' in Hungarian, ''Vlأ،choi'' (خ’خ»خ¬د‡خ؟خ¹) in Greek, ''Volأ³xi'' (ذ’ذ¾ذ»ذ¾جپر…ذ¸) in Russian, ''Walachen'' in German, ''Valacchi'' in Italian, ''Valaques'' in French, ''Valacos'' in Spanish), the Romanians used for themselves the endonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
"Rumأ¢n/Romأ¢n", from the Latin "Romanus" (in memory of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
). Vlachs are referred in late Byzantine documents as Bulgaro-Albano-Vlachs ("Bulgaralbanitoblahos"), or Serbo-Albano-Bulgaro-Vlachs Via both Germanic and Latin, the term started to signify "stranger, foreigner" also in the
Via both Germanic and Latin, the term started to signify "stranger, foreigner" also in the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, where it in its early form was used for Romance-speakers, but the term eventually took on the meaning of "shepherd, nomad". The Romance-speaking communities themselves, however, used the endonym "Romans". Term Vlach can denote various ethnic elements: ''"Slovak, Hungarian, Balkan, Transylvanian, Romanian, or even Albanian".'' According to historian Sima ؤ†irkoviؤ‡, the name "Vlach" in medieval sources has the same rank as the name "Greek", "Serb" or "Latin". During the early history of the
During the early history of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ذخ¸د‰خ¼خ±خ½خ¹خ؛خ® خ‘د…د„خ؟خ؛دپخ±د„خ؟دپخ¯خ±, Othإچmanikؤ“ Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in the Balkans, there was a military class of Vlachs in Serbia and Ottoman Macedonia, made up of Christians who served as auxiliary forces and had the same rights as Muslims, but their origin is not entirely clear. Some Greeks used "vlachos" as a pejorative term. In إ½umberak members of the Greek Catholic Church were called Vlachs, in Carniola
Carniola ( sl, Kranjska; , german: Krain; it, Carniola; hu, Krajna) is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region sti ...
residents of إ½umberak in general were Vlachs. In Posavina
Posavina ( sr-cyr, ذںذ¾رپذ°ذ²ذ¸ذ½ذ°) is a geographical region that stretches along the Sava river, encompassing only the inner areas of the Sava river basin, that are adjacent or near to the Sava river itself, namely catch region spanning from t ...
and Bihaؤ‡ area Muslims called Vlachs as Christians (both Orthodox and Catholics) while Catholics under that name consider Orthodox Christians. For residents of the Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
n islands population of immigrants (either Croats or Serbs) were called as Vlachs. The name Vlach in Dalmatia also has negative connotations as "newcomer", "peasant", "ignorant" while in Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eأ®stria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the larges ...
the ethnonym Vlach is used to make a distinction between the native Croats and newly settled Istro-Romanian old catholic Vlachs and Slavic population which was coming in the 15th and 16th century.
Romanian scholars have suggested that the term ''Vlach'' appeared for the first time in the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and was subsequently spread to the Germanic- and then Slavic-speaking worlds through the Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Norse people) were a North Germanic ethnolinguistic group of the Early Middle Ages, during which they spoke the Old Norse language. The language belongs to the North Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages and is the pre ...
(possibly by Varangians), who were in trade and military contact with Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, خ’د…خ¶خ¬خ½د„خ¹خ؟خ½) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
during the early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
(see also Blakumen
''Blakumen'' or ''Blأ¶kumenn'' were a people mentioned in Scandinavian sources dating from the 11th through 13th centuries. The name of their land, ''Blokumannaland'', has also been preserved. Victor Spinei, Florin Curta, Florin Pintescu and othe ...
).
Nowadays, the term ''Vlachs'' (also known under other names, such as "Koutsovlachs", "Tsintsars", "Karagouni", "Chobani", "Vlasi", etc.) is used in scholarship for the Romance-speaking communities in the Balkans, especially those in Greece, Albania and North Macedonia. In Serbia the term ''Vlach'' (Serbian ''Vlah'', plural ''Vlasi'') is also used to refer to Romanian speakers, especially those living in eastern Serbia. Aromanians themselves use the endonym "Armأ£n" (plural "Armأ£ni") or "Rأ£mأ£n" (plural "Rأ£mأ£ni"), etymologically from "Romanus", meaning "Roman". Megleno-Romanians designate themselves with the Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
form ''Vla'' (plural ''Vlaإ،'') in their own language.
Medieval usage

 The ''Hellenic chronicle'' could possibly qualify to the first testimony of Vlachs in Pannonia and Eastern Europe during the time of Attila.
The ''Hellenic chronicle'' could possibly qualify to the first testimony of Vlachs in Pannonia and Eastern Europe during the time of Attila.
6th century
What might be the earliest reference to the term “Vlach†comes from the 7th centuryByzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
historiographer Theophylact Simocatta, who mentions Blachernae
Blachernae ( gkm, خ’خ»خ±د‡خدپخ½خ±خ¹) was a suburb in the northwestern section of Constantinople, the capital city of the Byzantine Empire. It is the site of a water source and a number of prominent churches were built there, most notably the great ...
in connection with some historical data of the 6th century, during the reign of Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
Maurice.
8th century
First precise data about Vlachs are in connection with the Vlachs of the Rynchos river; the original document containing the information is from the Konstamonitou monastery.9th century
During the late 9th century theHungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation andآ ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
invaded the Carpathian Basin, where the province of Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
was inhabited by the "Slavs clavi
Clavus may refer to:
* Claudius Clavus (born 1388), 15th-century Danish cartographer
* ''Clavus'' (gastropod), a genus of snails in the family Drilliidae
* The Roman ''clavus'', a reddish-purple stripe on garments that distinguished members of the ...
Bulgarians ulgariiand Vlachs lachii and the shepherds of the Romans The "shepherds of the Romans" ( la, pastores Romanorum) were a population living in the Carpathian Basin at the time of the Hungarian conquest of the territory around 900, according to the ''Gesta Hungarorum'' and other medieval sources.
Hungary: ...
astores Romanorum (''sclauij, Bulgarij et Blachij, ac pastores romanorum'' —according to the '' Gesta Hungarorum'', written around 1200 by the anonymous chancellor of King Bأ©la III of Hungary.
10th century
Chroniclers John Skylitzes and George Kedrenos wrote that in 971, during battles between Romans (Byzantines) and Rus' people led by Sveinald (Sviatoslav I
; (943 – 26 March 972), also spelled Svyatoslav, was Grand Prince of Kiev famous for his persistent campaigns in the east and south, which precipitated the collapse of two great powers of Eastern Europe, Khazaria and the First Bulgarian Empire. H ...
), the dwellers of the north side of Danube came to Emperor John I Tzimiskes
John I Tzimiskes (; 925 – 10 January 976) was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general, he strengthened the Empire and expanded its borders during his short reign.
Background
John I Tzimiskes ...
and they handed over their fortresses and the Emperor sent troops to guard the fortresses. During those times, Northern part of Danube were dwelled by sedentary Vlachs and tribes of nomad Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peأ§enek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: ذںذµر‡ذµذ½ذµذ³(ذ¸), uk, ذںذµر‡ذµذ½ر–ذ³(ذ¸), hu, Besenyإ‘(k), gr, خ خ±د„خ¶خ¹خ½خ¬خ؛خ؟خ¹, خ خµد„دƒخµخ½خخ³خ؟خ¹, خ خ±د„خ¶خ¹خ½خ±خ؛خ¯د„خ±خ¹, ka, لƒلƒگلƒ ...
who lived in tents.
George Kedrenos mentioned about Vlachs in 976. The Vlachs were guides and guards of Roman (Byzantine) caravans in Balkans. Between Prespa and Kastoria they met and fought with a Bulgarian rebel named David. The Vlachs killed David in their first documented battle.
Mutahhar al-Maqdisi, "They say that in the Turkic neighbourhood there are the Khazars, Russians, Slavs, ''Waladj'', Alans, Greeks and many other peoples".
Ibn al-Nadؤ«m
Abإ« al-Faraj Muل¸¥ammad ibn Isل¸¥ؤپq al-Nadؤ«m ( ar, ط§ط¨ظˆ ط§ظ„ظپط±ط¬ ظ…طظ…ط¯ ط¨ظ† ط¥ط³طط§ظ‚ ط§ظ„ظ†ط¯ظٹظ…), also ibn Abؤ« Ya'qإ«b Isل¸¥ؤپq ibn Muل¸¥ammad ibn Isل¸¥ؤپq al-Warrؤپq, and commonly known by the ''nasab'' (patronymic) Ibn al-Nadؤ«m ...
published in 938 the work ''Kitؤپb al-Fihrist
The ''Kitؤپb al-Fihrist'' ( ar, ظƒطھط§ط¨ ط§ظ„ظپظ‡ط±ط³طھ) (''The Book Catalogue'') is a compendium of the knowledge and literature of tenth-century Islam compiled by Ibn Al-Nadim (c.998). It references approx. 10,000 books and 2,000 authors.''The ...
'' mentioning "Turks, Bulgars and Vlahs" (using ''Blagha'' for Vlachs)
11th century
Byzantine writer Kekaumenos, author of the '' Strategikon'' (1078), described a 1066 revolt against the emperor in Northern Greece led by Nicolitzas Delphinas and other Vlachs. The names ''Blakumen
''Blakumen'' or ''Blأ¶kumenn'' were a people mentioned in Scandinavian sources dating from the 11th through 13th centuries. The name of their land, ''Blokumannaland'', has also been preserved. Victor Spinei, Florin Curta, Florin Pintescu and othe ...
'' or ''Blأ¶kumenn'' is mentioned in Nordic sagas dating between the 11th–13th centuries, with respect to events that took place in either 1018 or 1019 somewhere at the northwestern part of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
and believed by some to be related to the ''Vlachs''.
In the Bulgarian state of the 11th and 12th century, Vlachs live in large numbers, and they were equals to the Bulgarian population.
12th century
 The Russian
The Russian Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, ذںذ¾ذ²ر£رپر‚رŒ ذ²ر€ذµذ¼ر§ذ½رŒذ½ر‹ر…رٹ ذ»ر£ر‚رٹ, translit=Povؤ›stؤ vremؤ™nؤnyxإ lؤ›tإ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
, written ca. 1113, wrote when the Volochi (Vlachs) attacked the Slavs of the Danube and settled among them and oppressed them, the Slavs departed and settled on the Vistula, under the name of Leshi. The Hungarians drove away the Vlachs and took the land and settled there.
Traveler Benjamin of Tudela
Benjamin of Tudela ( he, בض´ض¼× ض°×™ض¸×ض´×™×ں ×ض´×کض¼×•ض¼×“ض¶×œض¸×”, ; ar, ط¨ظ†ظٹط§ظ…ظٹظ† ط§ظ„طھط·ظٹظ„ظٹ ''Binyamin al-Tutayli''; Tudela, Kingdom of Navarre, 1130 Castile, 1173) was a medieval Jewish traveler who visited Europe, Asia, an ...
(1130–1173) of the Kingdom of Navarre
The Kingdom of Navarre (; , , , ), originally the Kingdom of Pamplona (), was a Basque kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, alongside the Atlantic Ocean between present-day Spain and France.
The medieval state took ...
was one of the first writers to use the word ''Vlachs'' for a Romance-speaking population.
Byzantine historian John Kinnamos described Leon Vatatzes' military expedition along the northern Danube, where Vatatzes mentioned the participation of Vlachs in battles with the Magyars (Hungarians) in 1166.
The uprising of brothers Asen and Peter was a revolt of Bulgarians and Vlachs living in the theme of Paristrion of the Byzantine Empire, caused by a tax increase. It began on 26 October 1185, the feast day of St. Demetrius of Thessaloniki, and ended with the creation of the Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1396. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II ...
, also known in its early history as the Empire of Bulgarians and Vlachs.
13th century
In 1213 an army of Romans (Vlachs), Transylvanian Saxons, andPechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peأ§enek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: ذںذµر‡ذµذ½ذµذ³(ذ¸), uk, ذںذµر‡ذµذ½ر–ذ³(ذ¸), hu, Besenyإ‘(k), gr, خ خ±د„خ¶خ¹خ½خ¬خ؛خ؟خ¹, خ خµد„دƒخµخ½خخ³خ؟خ¹, خ خ±د„خ¶خ¹خ½خ±خ؛خ¯د„خ±خ¹, ka, لƒلƒگلƒ ...
, led by Ioachim of Sibiu, attacked the Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ...
and Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian language, Russian Exonym and endonym, exonym ), were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confede ...
from Vidin. After this, all Hungarian battles in the Carpathian region were supported by Romance-speaking soldiers from Transylvania.
At the end of the 13th century, during the reign of Ladislaus the Cuman
Ladislaus IV ( hu, IV. (Kun) Lأ،szlأ³, hr, Ladislav IV. Kumanac, sk, Ladislav IV. Kumأ،nsky; 5 August 1262 – 10 July 1290), also known as Ladislaus the Cuman, was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1272 to 1290. His mother, Elizabeth, was ...
, Simon of Kأ©za wrote about the ''Blacki people
This is a list of characters from the anime and manga series ''Mazinger Z'', ''Great Mazinger'', ''Grendizer'', and ''Mazinkaiser'', as well as the ''Shin Mazinger Shougeki! Z Hen, Shin Mazinger'' reboot. It lists the main players of the plots a ...
'' and placed them in Pannonia with the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
. Archaeological discoveries indicate that Transylvania was gradually settled by the Magyars, and the last region defended by the Vlachs and Pechenegs (until 1200) was between the Olt River
The Olt (Romanian and Hungarian; german: Alt; la, Aluta or ', tr, Oltu, grc, ل¼Œخ»د…د„خ؟د‚ ''Alytos'') is a river in Romania. It is long, and its basin area is . It is the longest river flowing exclusively through Romania. Its average disch ...
and the Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The ...
.
Shortly after the fall of the Olt region, a church was built at the Cأ¢rب›a Monastery Cأ¢rب›a may refer to:
* Cأ¢rب›a, Harghita
Cأ¢rب›a (; hu, Csأkkarcfalva or ''Karcfalva'' ) is a commune in Romania, located in Harghita County. It lies in the Szأ©kely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania.
The commune is compo ...
and Catholic German-speaking settlers from Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhأ©nanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
and Mosel Valley (known as Transylvanian Saxons) began to settle in the Orthodox region. In the ''Diploma Andreanum
The ''Diploma Andreanum'', or ''Goldener Freibrief der Siebenbأ¼rger Sachsen'' (English: ''Golden Charter of the Transylvanian Saxons''), was issued by King Andrew II of Hungary in 1224, granting provisional autonomy to colonial Germans residing i ...
'' issued by King Andrew II of Hungary in 1224, ''"silva blacorum et bissenorum"'' was given to the settlers. The Orthodox Vlachs spread further northward along the Carpathians to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenskأ، republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
, and Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mأ¤hren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The me ...
and were granted autonomy under ''Ius Vlachonicum'' (Walachian law).
In 1285 Ladislaus the Cuman
Ladislaus IV ( hu, IV. (Kun) Lأ،szlأ³, hr, Ladislav IV. Kumanac, sk, Ladislav IV. Kumأ،nsky; 5 August 1262 – 10 July 1290), also known as Ladislaus the Cuman, was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1272 to 1290. His mother, Elizabeth, was ...
fought the Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
and Cumans, arriving with his troops at the in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Moldova River
The Moldova () is a river in Romania, in the historical region of Moldavia. It is a right tributary of the river Siret. The river rises from the Obcina Feredeu Mountains of Bukovina in Suceava County and joins the Siret in Cotu Vameب™, east of ...
. A town, Baia (near the said river), was documented in 1300 as settled by the Transylvanian Saxons (see also Foundation of Moldavia
The founding of Moldavia ( ro, Descؤƒlecatul Moldovei) began with the arrival of a Vlach (Romanian) voivode (military leader), Dragoب™, soon followed by his people from Maramureب™, then a voivodeship, to the region of the Moldova River. Drago ...
). In 1290 Ladislaus the Cuman was assassinated; the new Hungarian king allegedly drove voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the me ...
Radu Negru
Radu may refer to:
People
* Radu (given name), Romanian masculine given name
* Radu (surname), Romanian surname
* Rulers of Wallachia, see
* Prince Radu of Romania (born 1960), disputed pretender to the former Romanian throne
Other uses
* Radu ( ...
and his people across the Carpathians, where they formed Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, بڑara Romأ¢neascؤƒ, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and so ...
along with its first capital Cأ¢mpulung
Cأ¢mpulung (also spelled ''Cأ®mpulung'', , german: Langenau, Old Romanian ''Dlؤƒgopole'', ''ذ”ذ»رٹذ³ذ¾ذ؟ذ¾ذ»ذµ'' (from Middle Bulgarian)), or ''Cأ¢mpulung Muscel'', is a municipality in the Argeب™ County, Muntenia, Romania. It is situated among t ...
(see also Foundation of Wallachia
The founding of Wallachia ( ro, descؤƒlecatul بڑؤƒrii Romأ¢neب™ti), that is the establishment of the first independent Romanians, Romanian principality, was achieved at the beginning of the 14th century, through the unification of smaller politic ...
).
14th century
The biggest caravan shipment between Podvisoki inBosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and He ...
and Republic of Ragusa
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta it, La libertأ non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world"
, population_estimate = 90 000 in the XVI Century
, currency = ...
was recorded on 9 August 1428, where Vlachs transported 1500 modius
Modius may refer to:
* an Ancient Roman units of measurement#Dry measure, ancient Roman unit for dry measures, (8.73 L) roughly equivalent to a peck
* a Ancient Roman units of measurement#Area, medieval Roman unit for area, approximately 40 acres
...
of salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantitie ...
with 600 horses. In the 14th century royal charters include and some segregation policies declaring that ''"a Serb shall not marry a Vlach."'' Although this could be related to the term of the same origin, used for dependent shepherds of that time, like in the Duإ،an's Code, since the dependent population was encouraged to switch to agriculture, it being of more worth to the crown.
Toponymy
Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( ruo, rumeri or ) are a Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. However, due to se ...
who emerged during the Migration Period, other Vlachs could be found as far north as Poland, as far west as Moravia and Dalmatia. In search of better pasture, they were called ''Vlasi'' or ''Valaإ،i'' by the Slavs.
States mentioned in medieval chronicles were:
* ''Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, بڑara Romأ¢neascؤƒ, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and so ...
'' – between the Southern Carpathians and the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
('' إ¢ara Romأ¢neascؤƒ'' in Romanian); Bassarab-Wallachia ( Bassarab's Wallachia and Ungro-Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, بڑara Romأ¢neascؤƒ, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and so ...
or Wallachia Transalpina in administrative sources; Istro-Vlachia (Danubian Wallachia in Byzantine sources), and ''Velacia secunda'' on Spanish maps
* ''Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, ذ—ذµذ¼ذ»ر§ ذœذ¾ذ»ذ´ذ°ذ²رپذ؛ذ°ر§; el, ل¼©خ³خµخ¼خ؟خ½خ¯خ± د„ل؟†د‚ خœخ؟خ»خ´خ±خ²خ¯خ±د‚) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
'' – between the Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The ...
and the Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, ذ”ذ½ذµجپرپر‚ر€, links=1, Dnأ©str, ثˆdâپ؟ت²estr; ro, Nistru; grc, خ¤دچدپل¾±د‚, Tyrؤپs, ; la, Tyrؤپs, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and th ...
river (''Bogdano-Wallachia''; Bogdan's Wallachia, Moldo-Wallachia or ''Maurovlachia''; Black Wallachia, ''Moldovlachia'' or ''Rousso-Vlachia'' in Byzantine sources); ''Bogdan Iflak'' or Wallachia in Polish sources; ''L'otra Wallachia'' (the other Wallachia) in Genovese sources and ''Velacia tertia'' on Spanish maps
*''Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdأ©ly; german: Siebenbأ¼rgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
'' – between the Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The ...
and the Hungarian plain
The Great Hungarian Plain (also known as Alfأ¶ld or Great Alfأ¶ld, hu, Alfأ¶ld or ) is a plain occupying the majority of the modern territory of Hungary. It is the largest part of the wider Pannonian Plain. (However, the Great Hungarian plain ...
; ''Wallachia interior'' in administrative sources and ''Velacia prima'' on Spanish maps
*''Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1396. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II ...
'', between the Carpathians and the Balkan Mountains
The Balkan mountain range (, , known locally also as Stara planina) is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border betw ...
– ''Regnum Bulgarorum et Blachorum'' in documents by Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 J ...
*''Terra Prodnicorum'' (or Terra Brodnici), mentioned by Pope Honorius III in 1222. Vlachs led by Ploskanea supported the Tatars in the 1223 Battle of Kalka. Vlach lands near Galicia in the west, Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, ذ’ذ¾ذ»ذ¸جپذ½رŒ, Volyn' pl, Woإ‚yإ„, russian: ذ’ذ¾ذ»ر‹جپذ½رŒ, Volأ½nت¹, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. Th ...
in the north, Moldova in the south and the Bolohoveni lands in the east were conquered by Galicia.
*'' Bolokhoveni'' was Vlach land between Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
and the Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, ذ”ذ½ذµجپرپر‚ر€, links=1, Dnأ©str, ثˆdâپ؟ت²estr; ro, Nistru; grc, خ¤دچدپل¾±د‚, Tyrؤپs, ; la, Tyrؤپs, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and th ...
in Ukraine. Place names were Olohovets, Olshani, Voloschi and Vlodava, mentioned in 11th-to-13th-century Slavonic chronicles. It was conquered by Galicia.
Regions and places are:
 *
*White Wallachia
White Wallachia (Greek: خ‘دƒد€دپخ؟خ²خ»خ±د‡خ¯خ±, romanized: ''Asprovlachأa)'', sometimes referred to simply as Vlachia, Wallachia or Asen's Wallachia by Western sources, was a rarely used Byzantine term for the region between the Danube and the Bal ...
in Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, خœخ؟خ¹دƒخ¯خ±, Moisأa) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
Since Theophanes Confessor and Kedrenos, in : A.D. Xenopol, ''Istoria Romأ¢nilor din Dacia Traianؤƒ'', Nicolae Iorga, Teodor Capidan, C. Giurescu : ''Istoria Romأ¢nilor'', Petre بک. Nؤƒsturel ''Studii ب™i Materiale de Istorie Medie'', vol. XVI, 1998
*Great Wallachia
Great Vlachia or Great Wallachia ( rup, Vlأ£hia Mari; el, خœخµخ³خ¬خ»خ· خ’خ»خ±د‡خ¯خ±, Megأ،lؤ“ Vlachأa), also simply known as Vlachia ( rup, Vlأ£hia, link=no; el, link=no, خ’خ»خ±د‡خ¯خ±, Vlachأa), was a province and region in southeastern Thessa ...
(''خœخµخ³خ¬خ»خ· خ’خ»خ±د‡خ¯خ±''; ''Megأ،li vlahأa'') in Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, خکخµدƒدƒخ±خ»خ¯خ±, translit=Thessalأa, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
*Small Wallachia (''خœخ¹خ؛دپخ® خ’خ»خ±د‡خ¯خ±''; ''Mikrأ vlahأa'') in Aetolia
Aetolia ( el, خ‘ل¼°د„د‰خ»خ¯خ±, Aل¼°tإچlأa) is a mountainous region of Greece on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth, forming the eastern part of the modern regional units of Greece, regional unit of Aetolia-Acarnania.
Geography
The Achelous ...
, Acarnania
Acarnania ( el, ل¼ˆخ؛خ±دپخ½خ±خ½خ¯خ±) is a region of west-central Greece that lies along the Ionian Sea, west of Aetolia, with the Achelous River for a boundary, and north of the gulf of Calydon, which is the entrance to the Gulf of Corinth. Today i ...
, Dorida
Dorida ( el, خ”د‰دپخ¯خ´خ±) is a municipality in the Phocis regional unit, Central Greece, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Lidoriki. The municipality has an area of 998.893 km2.
Municipality
The municipality Dorida was forme ...
and Locrida
Locris (; el, label=Modern Greek, خ›خ؟خ؛دپخ¯خ´خ±, Lokrأda; grc, خ›خ؟خ؛دپخ¯د‚, Lokrأs) was a region of ancient Greece, the homeland of the Locrians, made up of three distinct districts.
Locrian tribe
The city of Locri in Calabria (Italy), ...
* Morlachia, in Lika
Lika () is a traditional region of Croatia proper, roughly bound by the Velebit mountain from the southwest and the Pljeإ،evica mountain from the northeast. On the north-west end Lika is bounded by Ogulin-Plaإ،ki basin, and on the south-east by ...
-Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
*Upper Valachia of Moscopole and Metsovon
Moscopole or Voskopoja ( sq, Voskopojأ«; rup, Moscopole, with several other variants; el, خœخ؟دƒد‡دŒد€خ؟خ»خ¹د‚, Moschopolis) is a village in Korأ§أ« County in southeastern Albania. During the 18th century, it was the cultural and commercial ...
(''خ†خ½د‰ خ’خ»خ±د‡خ¯خ±''; ''أپno Vlahأa'') in southern Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
, Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipأ«ri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipأ«risأ«), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
and Epirus
*''Stari Vlah'' ("the Old Vlach"), a region in southwestern Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
*Romanija
Romanija ( sr-cyrl, ذ ذ¾ذ¼ذ°ذ½ذ¸رکذ°) is a mountain, karst plateau, and geographical region in eastern Bosnia and Herzegovina, including numerous villages and towns, such as Pale, Sokolac, Rogatica and Han Pijesak. Its highest point is Veliki ...
mountain (''Romanija planina'') in eastern Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
*Vlaب™ca County
Vlaب™ca County is a former first-order administrative division of the Kingdom of Romania, in southern Muntenia, located between Bucharest and the Danube, which is now mostly the county of Giurgiu County, Giurgiu. The county seat was Giurgiu.
The c ...
, a former county of southern Wallachia (derived from Slavic ''Vlaإ،ka'')
* Greater Wallachia, an older name for the region of Muntenia, southeastern Romania
*Lesser Wallachia
Oltenia (, also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions, with the alternative Latin names ''Wallachia Minor'', ''Wallachia Alutana'', ''Wallachia Caesarea'' between 1718 and 1739) is a historical province and geographical region of Romania ...
, an older name for the region of Oltenia, southwestern Romania
*An Italian writer called the Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bأ،nsأ،g; sr, ذ‘ذ°ذ½ذ°ر‚, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
''Valachia citeriore'' ("Wallachia on this side") in 1550.
*''Valahia transalpina'', including Fؤƒgؤƒraب™ and Haب›eg
*Moravian Wallachia
Moravian Wallachia ( cs, Moravskأ© Valaإ،sko, or simply ''Valaإ،sko''; ro, Valahia Moravؤƒ) is a mountainous ethnoregion located in the easternmost part of Moravia in the Czech Republic, near the Slovak border, roughly centered on the cities Vs ...
( cz, Moravskأ© Valaإ،sko), in the Beskid Mountains
The Beskids or Beskid Mountains ( pl, Beskidy, cs, Beskydy, sk, Beskydy, rue, ذ‘ذµرپذ؛ذ¸ذ´ر‹ (''Beskydإ·''), ua, ذ‘ذµرپذ؛ذ¸ذ´ذ¸ (''Beskydy'')) are a series of mountain ranges in the Carpathian Mountains, Carpathians, stretching from the Czech ...
(Czech: Beskydy) of the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
.
Shepherd culture
As national states appeared in the area of the formerOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ذخ¸د‰خ¼خ±خ½خ¹خ؛خ® خ‘د…د„خ؟خ؛دپخ±د„خ؟دپخ¯خ±, Othإچmanikؤ“ Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, new state borders were developed that divided the summer and winter habitats of many of the transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower vall ...
groups. During the Middle Ages, many Vlachs were shepherds who drove their flocks through the mountains of Central and Eastern Europe. Vlach shepherds may be found as far north as southern Poland (Podhale) and the eastern Czech Republic (Moravia) by following the Carpathians, the Dinaric Alps in the west, the Pindus Mountains
The Pindus (also Pindos or Pindhos; el, خ خ¯خ½خ´خ؟د‚, Pأndos; sq, Pindet; rup, Pindu) is a mountain range located in Northern Greece and Southern Albania. It is roughly 160 km (100 miles) long, with a maximum elevation of 2,637 metres ...
in the south, and the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, ش؟ص¸ص¾ص¯ص،ص½صµص،ص¶ ص¬ص¥ص¼ص¶ص¥ض€,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz daؤںlarؤ±, pronounced
* rus, ذڑذ°ذ²ذ؛ذ°جپذ·رپذ؛ذ¸ذµ ذ³ذ¾جپر€ر‹, Kavkأ،zskiye gأ³ry, kةگfثˆkasثگkت²ةھje ثˆة،orة¨
* tr, Kafkas Daؤںla ...
in the east.
Some researchers, like Bogumil Hrabak
Bogumil Hrabak (Serbian Cyrillic: ذ‘ذ¾ذ³رƒذ¼ذ¸ذ» ذ¥ر€ذ°ذ±ذ°ذ؛; Zrenjanin, Serbia, Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, 11 January 1927 - Belgrade, Serbia, 12 December 2010) was a Serbian historian, university professor and pedagogue. With a pr ...
and Marian Wenzel
Marian Barbara Wenzel (December 18, 1932 – January 6, 2002) was a British artist and art historian. She dedicated most of her active career to research of Bosnian-Herzegovinian art and cultural history.
Education
Wenzel was born in 1932 in P ...
, theorized that the origins of Steؤ‡ci tombstones, which appeared in medieval Bosnia
This is the history of Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Middle Ages, between the ancient and Roman period and the Ottoman period.
Early Middle Ages
The western Balkans had been reconquered from "barbarians" by Byzantine Emperor Justinian (r. 52 ...
between 12th and 16th century, could be attributed to Vlach burial culture
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, plac ...
of Bosnia and Herzegovina of that times.
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
.
File:Vlachs transhumance in Western Balkans and some Vlach necropolises.jpg, Detailed map depicting Vlach transhumance in the Western Balkans, showcasing several examples of Vlach necropolises.
File:Rumanians in America.jpg, alt=, Romanian immigrants on Ellis Island in national dress
File:Raffet - Berger du Banat.jpg, alt=, Vlach shepherd of Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bأ،nsأ،g; sr, ذ‘ذ°ذ½ذ°ر‚, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
(Auguste Raffet
Denis Auguste Marie Raffet (2 March 180416 February 1860) was a French illustrator and lithographer. He was a student of Nicolas Toussaint Charlet, and was a retrospective painter of the Empire.
Biography
Raffet was born in Paris.
At an ...
, c. 1837)
Legacy
According to Ilona Czamaإ„ska ''"for several recent centuries the investigation of the Vlachian ethnogenesis was so much dominated by political issues that any progress in this respect was incredibly difficult."'' The transhumance of Vlachs, the heirs of Roman citizens, may be a key for solving the problem ofethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introdu ...
, but the problem is that many migrations were in multiple directions during the same time. These migrations were not just part of the Balkans and the Carpathians, they exist and in the Caucasus, the Adriatic islands
There are more than 1200 islands in the Adriatic Sea, 69 of which are inhabited. A recent study by the Institute of Oceanography in Split (2000) shows that there are 1246 islands: 79 large islands, 525 islets, and 642 ridges and rocks. The Italia ...
and possibly over the entire region of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. Because of this, our knowledge concerning primary migrations of the Vlachs and the ethnogenesis is more than modest.Ilona Czamaإ„ska; (2015) ''The Vlachs – several research problems'' p. 14; BALCANICA POSNANIENSIA XXII/1 IUS VALACHICUM I/ref>
See also
* Olأ،h (surname), Olأ،h *Morlachs
Morlachs ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Morlaci, ذœذ¾ر€ذ»ذ°ر†ذ¸ or , ; it, Morlacchi; ro, Morlaci) has been an exonym used for a rural Christian community in Herzegovina, Lika and the Dalmatian Hinterland. The term was initially used for a bilingual Vlach p ...
* Romania in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages in Romania started with the withdrawal of the Roman troops and administration from Dacia province in the 270s. In the next millennium a series of peoples, most of whom only controlled two or three of the nearly ten histor ...
* Statuta Valachorum
''Statuta Valachorum'' ("Vlach Statute(s)", sh, Vlaإ،ki statut(i)) was a decree issued by Emperor Ferdinand II of the Habsburg monarchy on 5 October 1630 that defined the rights of "Vlachs" (a term used for a community of mostly Orthodox refugees, ...
* Supplex Libellus Valachorum
''Supplex Libellus Valachorum Transsilvaniae'' (Latin for ''Petition of the Romanians of Transylvania'') is the name of two petitions sent by the leaders of the ethnic Romanians of Transylvania to the Holy Roman Emperor Leopold II, demanding equ ...
* Vlach (Ottoman social class)
* Vlach law
The Vlach law (, ro, legea romأ¢neascؤƒ, "Romanian law", or , "customs of the land", ) refers to the traditional Romanian common law as well as to various special laws and privileges enjoyed or enforced upon particularly pastoralist communities ...
* Vlachs in medieval Serbia
* Vlachs in the history of Croatia
* Vlachs in medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina
Vlachs in Bosnia and Herzegovina are a Balkans, Balkan population who descend from Romanization (cultural), Romanized Illyrians (Illyro-Romans), Thracians (Thraco-Romans) and other pre-Slavs, Slavic Romance language, Romance-speaking peoples and th ...
Notes
References
* G. Weigand, Die Aromunen, Bd.خ‘خ„-Bخ„, J. A. Barth (A.Meiner), Leipzig 1895–1894. * George Murnu, ''Istoria romأ¢nilor din Pind, Vlahia Mare 980–1259'' ("History of the Romanians of the Pindus, Greater Vlachia, 980–1259"), Bucharest, 1913 * Ilie Gherghel, Cأ¢teva consideraإ£iuni la cuprinsul noإ£iunii cuvأ¢ntului "Vlach". Bucuresti: Convorbiri Literare, (1920). *Theodor Capidan
Theodor Capidan (–September 1, 1953) was an Ottoman-born Romanian linguist. An ethnic Aromanian from the Macedonia region, he studied at Leipzig before teaching school at Thessaloniki. Following the creation of Greater Romania at the end ...
, ''Aromأ¢nii, dialectul aromأ¢n. Studiul lingvistic'' ("Aromanians, Aromanian dialect, Linguistic Study"), Bucharest, 1932
* A.Hأ¢ciu, Aromأ¢nii, Comerإ£. Industrie. Arte. Expasiune. Civiliytie, tip. Cartea Putnei, Focإںani 1936.
* Steriu T. Hagigogu, "''Romanus إںi valachus sau Ce este romanus, roman, romأ¢n, aromأ¢n, valah إںi vlah''", Bucharest, 1939
* خ¤. Winnifrith, The Vlachs. The History of a Balkan People, Duckworth 1987
* A. Koukoudis, Oi mitropoleis kai i diaspora ton Vlachon ajor Cities and Diaspora of the Vlachs publ. University Studio Press, Thessaloniki 1999.
* A. Keramopoulos, Ti einai oi koutsovlachoi hat are the Koutsovlachs? publ 2 University Studio Press, Thessaloniki 2000.
*
* Victor A. Friedman, "The Vlah Minority in Macedonia: Language, Identity, Dialectology, and Standardization" in ''Selected Papers in Slavic, Balkan, and Balkan Studies'', ed. Juhani Nuoluoto, ''et al.'' ''Slavica Helsingiensa'': 21, Helsinki: University of Helsinki. 2001. 26–50full text
Though focussed on the Vlachs of North Macedonia, has in-depth discussion of many topics, including the origins of the Vlachs, their status as a minority in various countries, their political use in various contexts, and so on. * Asterios I. Koukoudis, ''The Vlachs: Metropolis and Diaspora'', 2003, * * Th Capidan, Aromأ¢nii, Dialectul Aromأ¢n, ed2 خ•diturؤƒ Fundaإ£iei Culturale Aromأ¢ne, Bucureب™ti 2005
Further reading
* ''The Watchmen'', a documentary film by Alastair Kenneil and Tod Sedgwick (USA) 1971 describes life in the Vlach village of Samarina in Epiros, Northern Greece * John Kennedy Campbell, 'Honour Family and Patronage' A Study of Institutions and Moral Values in a Greek Mountain Community,Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
, 1974
* Gheorghe Bogdan, MEMORY, IDENTITY, TYPOLOGY: AN INTERDISCIPLINARY RECONSTRUCTION OF VLACH ETHNOHISTORY, B.A., University of British Columbia, 1992
* Franck Vogel
Franck Vogel (born 1977 in Strasbourg, France) is a French photographer specializing in social & environmental issues, journalist, speaker and documentary film director. He lives and works in Paris.
a photo-essay on the Valchs published by GEO magazine (France), 2010.
* Adina Berciu-Drؤƒghicescu, Aromأ¢ni, meglenoromأ¢ni, istroromأ¢ni : aspecte identitare إںi culturale, Editura Universitؤƒإ£ii din Bucureب™ti, 2012, * Octavian Ciobanu, "The Role of the Vlachs in the Bogomils' Expansion in the Balkans.", Journal of Balkan and Black Sea Studies, Year 4, Issue 7, December 2021, pp. 11–32.
External links
ROMأ‚NII BALCANICI AROMأ‚NII
€”Maria Magiru about Aromanians {{in lang, Ro
Cultural appropriation of Vlachs' heritage
French Vlachs Association (in Vlach, EN and FR)
by Asterios Koukoudis
Vlachs' in Greece
(in Greek)
Consiliul A Tinirlor Armanj, Youth Aromanian community and their Projects
(in Vlach, EN and RO)
''Old Wallachia''
€”a short Czech film from 1955 depicting life of Vlachs in Czech Moravia Eastern Romance people Transhumant ethnic groups