Oligosaccharide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An oligosaccharide (; ) is a 
 ''N''-Linked glycosylation involves oligosaccharide attachment to asparagine via a beta linkage to the amine nitrogen of the side chain. The process of ''N''-linked glycosylation occurs cotranslationally, or concurrently while the proteins are being translated. Since it is added cotranslationally, it is believed that ''N''-linked glycosylation helps determine the folding of polypeptides due to the hydrophilic nature of sugars. All ''N''-linked oligosaccharides are pentasaccharides: five monosaccharides long.
In ''N''-glycosylation for eukaryotes, the oligosaccharide substrate is assembled right at the membrane of the endoplasmatic reticulum. For
''N''-Linked glycosylation involves oligosaccharide attachment to asparagine via a beta linkage to the amine nitrogen of the side chain. The process of ''N''-linked glycosylation occurs cotranslationally, or concurrently while the proteins are being translated. Since it is added cotranslationally, it is believed that ''N''-linked glycosylation helps determine the folding of polypeptides due to the hydrophilic nature of sugars. All ''N''-linked oligosaccharides are pentasaccharides: five monosaccharides long.
In ''N''-glycosylation for eukaryotes, the oligosaccharide substrate is assembled right at the membrane of the endoplasmatic reticulum. For
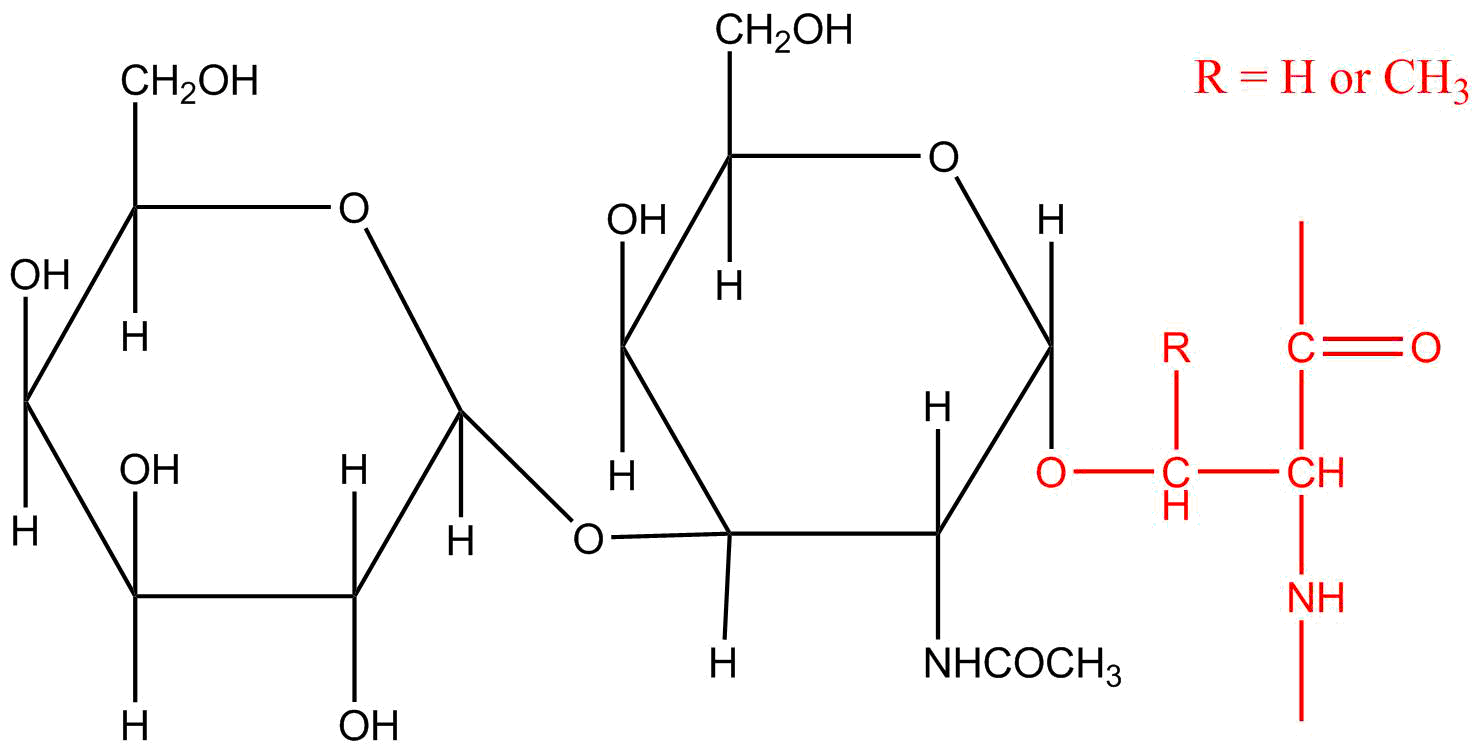 Oligosaccharides that participate in ''O''-linked glycosylation are attached to threonine or serine on the hydroxyl group of the side chain. ''O''-linked glycosylation occurs in the
Oligosaccharides that participate in ''O''-linked glycosylation are attached to threonine or serine on the hydroxyl group of the side chain. ''O''-linked glycosylation occurs in the
saccharide
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' m ...
polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
containing a small number (typically three to ten) of monosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
Chemically, monosaccharides are polyhy ...
s (simple sugars). Oligosaccharides can have many functions including cell recognition and cell adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as Cell_junction, cell junc ...
.
They are normally present as glycan
The terms glycans and polysaccharides are defined by IUPAC as synonyms meaning "compounds consisting of a large number of monosaccharides linked glycosidically". However, in practice the term glycan may also be used to refer to the carbohydrate ...
s: oligosaccharide chains are linked to lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s or to compatible amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
side chains in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, by ''N''- or ''O''- glycosidic bonds. ''N''-Linked oligosaccharides are always pentasaccharides attached to asparagine via a beta linkage to the amine nitrogen of the side chain.. Alternately, ''O''-linked oligosaccharides are generally attached to threonine or serine on the alcohol group of the side chain. Not all natural oligosaccharides occur as components of glycoproteins or glycolipids. Some, such as the raffinose series, occur as storage or transport carbohydrates
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ma ...
in plants. Others, such as maltodextrins or cellodextrins, result from the microbial breakdown of larger polysaccharides
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
such as starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
or cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
.
Glycosylation
In biology,glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not ...
is the process by which a carbohydrate is covalently attached to an organic molecule, creating structures such as glycoproteins and glycolipids.
''N''-Linked oligosaccharides
 ''N''-Linked glycosylation involves oligosaccharide attachment to asparagine via a beta linkage to the amine nitrogen of the side chain. The process of ''N''-linked glycosylation occurs cotranslationally, or concurrently while the proteins are being translated. Since it is added cotranslationally, it is believed that ''N''-linked glycosylation helps determine the folding of polypeptides due to the hydrophilic nature of sugars. All ''N''-linked oligosaccharides are pentasaccharides: five monosaccharides long.
In ''N''-glycosylation for eukaryotes, the oligosaccharide substrate is assembled right at the membrane of the endoplasmatic reticulum. For
''N''-Linked glycosylation involves oligosaccharide attachment to asparagine via a beta linkage to the amine nitrogen of the side chain. The process of ''N''-linked glycosylation occurs cotranslationally, or concurrently while the proteins are being translated. Since it is added cotranslationally, it is believed that ''N''-linked glycosylation helps determine the folding of polypeptides due to the hydrophilic nature of sugars. All ''N''-linked oligosaccharides are pentasaccharides: five monosaccharides long.
In ''N''-glycosylation for eukaryotes, the oligosaccharide substrate is assembled right at the membrane of the endoplasmatic reticulum. For prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s, this process occurs at the plasma membrane. In both cases, the acceptor substrate is an asparagine residue. The asparagine residue linked to an ''N''-linked oligosaccharide usually occurs in the sequence Asn-X-Ser/Thr, where X can be any amino acid except for proline, although it is rare to see Asp, Glu, Leu, or Trp in this position.
''O''-Linked oligosaccharides
 Oligosaccharides that participate in ''O''-linked glycosylation are attached to threonine or serine on the hydroxyl group of the side chain. ''O''-linked glycosylation occurs in the
Oligosaccharides that participate in ''O''-linked glycosylation are attached to threonine or serine on the hydroxyl group of the side chain. ''O''-linked glycosylation occurs in the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins ...
, where monosaccharide units are added to a complete polypeptide chain. Cell surface proteins and extracellular proteins are ''O''-glycosylated. Glycosylation sites in ''O''-linked oligosaccharides are determined by the secondary and tertiary structures of the polypeptide, which dictate where glycosyltransferases will add sugars.
Glycosylated biomolecules
Glycoproteins and glycolipids are by definition covalently bonded to carbohydrates. They are very abundant on the surface of the cell, and their interactions contribute to the overall stability of the cell.Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins have distinct Oligosaccharide structures which have significant effects on many of their properties, affecting critical functions such as antigenicity,solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a chemical substance, substance, the solute, to form a solution (chemistry), solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form su ...
, and resistance to proteases. Glycoproteins are relevant as cell-surface receptors, cell-adhesion molecules, immunoglobulins, and tumor antigens.
Glycolipids
Glycolipid
Glycolipids () are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the c ...
s are important for cell recognition, and are important for modulating the function of membrane proteins that act as receptors. Glycolipids are lipid molecules bound to oligosaccharides, generally present in the lipid bilayer. Additionally, they can serve as receptors for cellular recognition and cell signaling. The head of the oligosaccharide serves as a binding partner in receptor activity. The binding mechanisms of receptors to the oligosaccharides depends on the composition of the oligosaccharides that are exposed or presented above the surface of the membrane. There is great diversity in the binding mechanisms of glycolipids, which is what makes them such an important target for pathogens as a site for interaction and entrance. For example, the chaperone activity of glycolipids has been studied for its relevance to HIV infection.
Functions
Cell recognition
All cells are coated in either glycoproteins or glycolipids, both of which help determine cell types.Lectin
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar Moiety (chemistry), groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination (biology), agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates an ...
s, or proteins that bind carbohydrates, can recognize specific oligosaccharides and provide useful information for cell recognition based on oligosaccharide binding.
An important example of oligosaccharide cell recognition is the role of glycolipids in determining blood type
A blood type (also known as a blood group) is based on the presence and absence of antibody, antibodies and Heredity, inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycop ...
s. The various blood types are distinguished by the glycan modification present on the surface of blood cells. These can be visualized using mass spectrometry. The oligosaccharides found on the A, B, and H antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
occur on the non-reducing ends of the oligosaccharide. The H antigen (which indicates an O blood type) serves as a precursor for the A and B antigen. Therefore, a person with A blood type will have the A antigen and H antigen present on the glycolipids of the red blood cell plasma membrane. A person with B blood type will have the B and H antigen present. A person with AB blood type will have A, B, and H antigens present. And finally, a person with O blood type will only have the H antigen present. This means all blood types have the H antigen, which explains why the O blood type is known as the "universal donor".
Vesicles are directed by many ways, but the two main ways are:
# The sorting signals encoded in the amino acid sequence of the proteins.
# The Oligosaccharide attached to the protein.
The sorting signals are recognised by specific receptors that reside in the membranes or surface coats of budding vesicles, ensuring that the protein is transported to the appropriate destination.
Cell adhesion
Many cells produce specific carbohydrate-binding proteins known as lectins, which mediate cell adhesion with oligosaccharides. Selectins, a family of lectins, mediate certain cell–cell adhesion processes, including those of leukocytes to endothelial cells. In an immune response, endothelial cells can express certain selectins transiently in response to damage or injury to the cells. In response, a reciprocal selectin–oligosaccharide interaction will occur between the two molecules which allows the white blood cell to help eliminate the infection or damage. Protein-Carbohydrate bonding is often mediated byhydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently b ...
ing and van der Waals forces.
Dietary oligosaccharides
Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS), which are found in many vegetables, are short chains offructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
molecules. They differ from fructan
A fructan is a polymer of fructose molecules. Fructans with a short chain length are known as fructooligosaccharides. Fructans can be found in over 12% of the angiosperms including both monocots and dicotyledon, dicots such as agave, artichokes, a ...
s such as inulin
Inulins are a group of naturally occurring polysaccharides produced by many types of plants, industrially most often extracted from chicory. The inulins belong to a class of dietary fibers known as fructans. Inulin is used by some plants as a ...
, which as polysaccharides have a much higher degree of polymerization
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is the number of structural unit, monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule.
For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and the ''number-average'' degree of polymeriza ...
than FOS and other oligosaccharides, but like inulin and other fructans, they are considered soluble dietary fibre. Using fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) as fiber supplementations is shown to have an effect on glucose homeostasis quite similar to insulin. These (FOS) supplementations can be considered prebiotics which produce short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides (scFOS). Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) in particular are used to create a prebiotic effect for infants that are not being breastfed.
Galactooligosaccharides (GOS), which also occur naturally, consist of short chains of galactose molecules. Human milk is an example of this and contains oligosaccharides, known as human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), which are derived from lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from (Genitive case, gen. ), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ''-o ...
. These oligosaccharides have biological function in the development of the gut flora of infant
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
s. Examples include lacto-N-tetraose, lacto-N-neotetraose, and lacto-N-fucopentaose. These compounds cannot be digested in the human small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
, and instead pass through to the large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the Digestion, digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces befor ...
, where they promote the growth of '' Bifidobacteria'', which are beneficial to gut health.
HMOs can also protect infants by acting as decoy receptors against viral infection. HMOs accomplish this by mimicking viral receptors which draws the virus particles away from host cells. Experimentation has been done to determine how glycan-binding occurs between HMOs and many viruses such as influenza, rotavirus, human immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of th ...
(HIV), and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). The strategy HMOs employ could be used to create new antiviral drugs.
Mannan oligosaccharides (MOS) are widely used in animal feed to improve gastrointestinal health. They are normally obtained from the yeast cell walls of ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
''. Mannan oligosaccharides differ from other oligosaccharides in that they are not fermentable and their primary mode of action includes agglutination of type-1 fimbria pathogens and immunomodulation.
Sources
Oligosaccharides are a component of fibre from plant tissue. FOS and inulin are present inJerusalem artichoke
The Jerusalem artichoke (''Helianthus tuberosus''), also called sunroot, sunchoke, wild sunflower, topinambur, or earth apple, is a species of Helianthus, sunflower native to central North America. It is cultivated widely across the temperate z ...
, burdock, chicory, leeks, onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' , from Latin ), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus '' Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion which was classifie ...
s, and asparagus
Asparagus (''Asparagus officinalis'') is a perennial flowering plant species in the genus ''Asparagus (genus), Asparagus'' native to Eurasia. Widely cultivated as a vegetable crop, its young shoots are used as a spring vegetable.
Description ...
. Inulin is a significant part of the daily diet of most of the world's population. FOS can also be synthesized by enzymes of the fungus '' Aspergillus niger'' acting on sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
. GOS is naturally found in soybeans
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source of f ...
and can be synthesized from lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from (Genitive case, gen. ), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ''-o ...
. FOS, GOS, and inulin are also sold as nutritional supplements.
See also
* * *References
External links
* {{Authority control Nutrition Sugar substitutes Carbohydrate chemistry