Oilfields Curling Club on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured
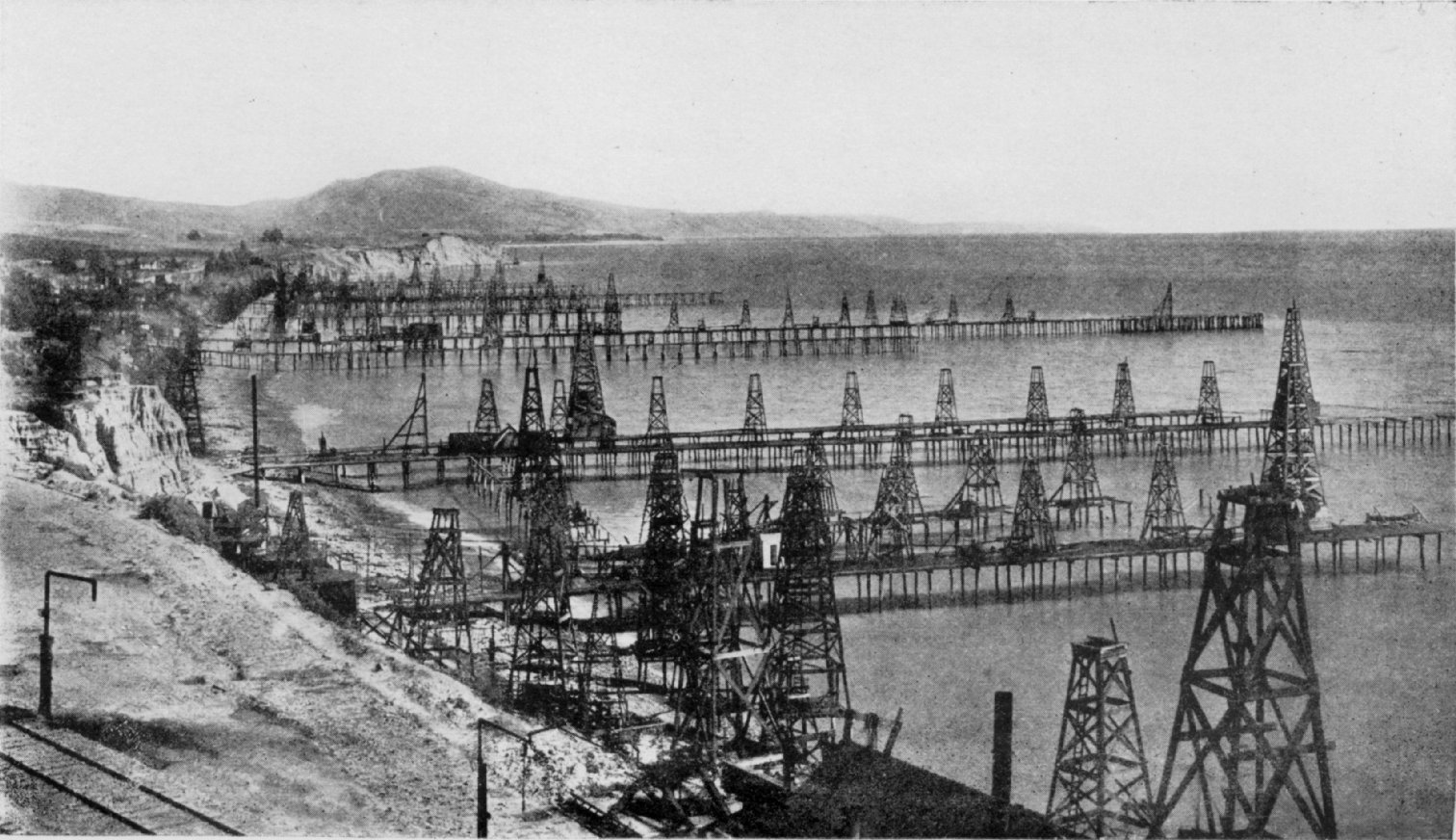

 An oil field is an area of accumulation of liquid oil underground in multiple (potentially linked) reservoirs, trapped as it rises by impermeable rock formations. In industrial terms, an oil field implies that there is economic benefit worthy of commercial attention. Oil fields themselves may extend up to several hundred kilometers across the surface, meaning that extraction efforts can be large and spread out across the area. In addition to extraction equipment, there may be exploratory wells probing the edges to find more reservoir area, pipelines to transport the oil elsewhere, and support facilities.
Oil fields can occur anywhere that the geology of the underlying rock allows, meaning that certain fields can be far away from civilization, including at sea. Creating an operation at an oil field can be a logistically complex undertaking, as it involves not only the equipment associated with
An oil field is an area of accumulation of liquid oil underground in multiple (potentially linked) reservoirs, trapped as it rises by impermeable rock formations. In industrial terms, an oil field implies that there is economic benefit worthy of commercial attention. Oil fields themselves may extend up to several hundred kilometers across the surface, meaning that extraction efforts can be large and spread out across the area. In addition to extraction equipment, there may be exploratory wells probing the edges to find more reservoir area, pipelines to transport the oil elsewhere, and support facilities.
Oil fields can occur anywhere that the geology of the underlying rock allows, meaning that certain fields can be far away from civilization, including at sea. Creating an operation at an oil field can be a logistically complex undertaking, as it involves not only the equipment associated with


 Natural gas originates by the same geological thermal cracking process that converts kerogen to petroleum. As a consequence, oil and natural gas are often found together. In common usage, deposits rich in oil are known as
Natural gas originates by the same geological thermal cracking process that converts kerogen to petroleum. As a consequence, oil and natural gas are often found together. In common usage, deposits rich in oil are known as
source rock, yellow: reservoir rock, green: cap rock, red: hydrocarbons">
File:Structural Trap (Anticlinal).svg, Structural trap within an Anticline
File:Structural Trap Fault.svg, Structural trap along a fault plane
File:StratigraphicTrap5.png, Structural-stratigraphic trap in a tilted block draped by mudstones
source rock, yellow: reservoir rock, green: cap rock, red: hydrocarbons">
File:StratigraphicTrap4.png, Stratigraphic trap under an unconformity
File:StratigraphicTrap2.png, Stratigraphic trap in a fossilized coral reef (yellow) sealed by mudstones (green)
File:StratigraphicTrap3-03.png, Stratigraphic trap around an evaporite (pink) salt dome
 Unconventional (oil & gas) reservoirs are accumulations where oil & gas phases are tightly bound to the rock fabric by strong capillary forces, requiring specialised measures for evaluation and
Unconventional (oil & gas) reservoirs are accumulations where oil & gas phases are tightly bound to the rock fabric by strong capillary forces, requiring specialised measures for evaluation and
Waterdrive
at
 A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formation
A rock formation is an isolated, scenic, or spectacular surface rock outcrop. Rock formations are usually the result of weathering and erosion sculpting the existing rock. The term ''rock formation'' can also refer to specific sediment ...
s.
Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence of high heat and pressure in the Earth's crust. Petroleum reservoirs are broadly classified as ''conventional'' and '' unconventional'' reservoirs. In conventional reservoirs, the naturally occurring hydrocarbons, such as crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
or natural gas, are trapped by overlying rock formations with lower permeability, while in unconventional reservoirs, the rocks have high porosity and low permeability, which keeps the hydrocarbons trapped in place, therefore not requiring a cap rock. Reservoirs are found using hydrocarbon exploration methods.
Oil field

 An oil field is an area of accumulation of liquid oil underground in multiple (potentially linked) reservoirs, trapped as it rises by impermeable rock formations. In industrial terms, an oil field implies that there is economic benefit worthy of commercial attention. Oil fields themselves may extend up to several hundred kilometers across the surface, meaning that extraction efforts can be large and spread out across the area. In addition to extraction equipment, there may be exploratory wells probing the edges to find more reservoir area, pipelines to transport the oil elsewhere, and support facilities.
Oil fields can occur anywhere that the geology of the underlying rock allows, meaning that certain fields can be far away from civilization, including at sea. Creating an operation at an oil field can be a logistically complex undertaking, as it involves not only the equipment associated with
An oil field is an area of accumulation of liquid oil underground in multiple (potentially linked) reservoirs, trapped as it rises by impermeable rock formations. In industrial terms, an oil field implies that there is economic benefit worthy of commercial attention. Oil fields themselves may extend up to several hundred kilometers across the surface, meaning that extraction efforts can be large and spread out across the area. In addition to extraction equipment, there may be exploratory wells probing the edges to find more reservoir area, pipelines to transport the oil elsewhere, and support facilities.
Oil fields can occur anywhere that the geology of the underlying rock allows, meaning that certain fields can be far away from civilization, including at sea. Creating an operation at an oil field can be a logistically complex undertaking, as it involves not only the equipment associated with extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pro ...
and transportation, but infrastructure such as roads and housing for workers. This infrastructure has to be designed with the lifespan of the oil field in mind, as production can last many years. Several companies, such as Hill International, Bechtel
Bechtel Corporation () is an American engineering, procurement, construction, and project management company founded in San Francisco, California, and headquartered in Reston, Virginia. , the ''Engineering News-Record'' ranked Bechtel as the sec ...
, Esso
Esso () is a trading name for ExxonMobil. Originally, the name was primarily used by its predecessor Standard Oil of New Jersey after the breakup of the original Standard Oil company in 1911. The company adopted the name "Esso" (the phonetic p ...
, Weatherford International, Schlumberger Limited, Baker Hughes
Baker Hughes Company, organized in Delaware and headquartered in Houston, is one of the world's largest oil field services companies. The company provides products and services for oil well drilling, formation evaluation, completion, productio ...
and Halliburton, have organizations that specialize in the large-scale construction of the infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
to support oil field exploitation.
The term "oilfield" can be used as a shorthand to refer to the entire petroleum industry. However, it is more accurate to divide the oil industry into three sectors: upstream ( crude oil production from wells and separation of water from oil), midstream ( pipeline and tanker
Tanker may refer to:
Transportation
* Tanker, a tank crewman (US)
* Tanker (ship), a ship designed to carry bulk liquids
** Chemical tanker, a type of tanker designed to transport chemicals in bulk
** Oil tanker, also known as a petroleum ta ...
transport of crude oil) and downstream (refining
{{Unreferenced, date=December 2009
Refining (also perhaps called by the mathematical term affining) is the process of purification of a (1) substance or a (2) form. The term is usually used of a natural resource that is almost in a usable form, b ...
of crude oil to products, marketing of refined products, and transportation to oil stations).
More than 65,000 oil fields are scattered around the globe, on land and offshore. The largest are the Ghawar Field in Saudi Arabia and the Burgan Field
The Burgan field is an oil field situated in the desert of southeastern Kuwait. Burgan field can also refer to the Greater Burgan—a group of three closely spaced fields, which includes Burgan field itself as well as the much smaller Magwa and ...
in Kuwait, with more than 66 to 104 billion barrels estimated in each. In the modern age, the location of oil fields with proven oil reserves is a key underlying factor in many geopolitical conflicts.
Gas field

 Natural gas originates by the same geological thermal cracking process that converts kerogen to petroleum. As a consequence, oil and natural gas are often found together. In common usage, deposits rich in oil are known as
Natural gas originates by the same geological thermal cracking process that converts kerogen to petroleum. As a consequence, oil and natural gas are often found together. In common usage, deposits rich in oil are known as oil field
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.
Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence ...
s, and deposits rich in natural gas are called natural gas fields.
In general, organic sediments buried in depths of 1,000 m to 6,000 m (at temperatures of 60 ° C to 150 °C) generate oil, while sediments buried deeper and at higher temperatures generate natural gas instead. The deeper the source, the "drier" the gas (that is, the smaller the proportion of condensate
Condensate may refer to:
* The liquid phase produced by the condensation of steam or any other gas
* The product of a chemical condensation reaction, other than water
* Natural-gas condensate, in the natural gas industry
* ''Condensate'' (album ...
s in the gas). Because both oil and natural gas are lighter than water, they tend to rise from their sources until they either seep to the surface or are trapped by a non-permeable stratigraphic trap. They can be extracted from the trap by drilling.
The largest natural gas field is South Pars/Asalouyeh gas field, which is shared between Iran and Qatar. The second largest natural gas field is the Urengoy gas field, and the third largest is the Yamburg gas field, both in Russia.
Like oil, natural gas is often found underwater in offshore gas fields such as the North Sea, Corrib Gas Field off Ireland, and near Sable Island. The technology to extract and transport offshore natural gas is different from land-based fields. It uses a few, very large offshore drilling rigs, due to the cost and logistical difficulties in working over water.
Rising gas prices in the early 21st century encouraged drillers to revisit fields that previously were not considered economically viable. For example, in 2008, McMoran Exploration passed a drilling depth of over 32,000 feet (9754 m) (the deepest test well in the history of gas production) at the Blackbeard site in the Gulf of Mexico. Exxon Mobil
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November 30, ...
's drill rig there had reached 30,000 feet by 2006, without finding gas, before it abandoned the site.
Formation
Crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
is found in all oil reservoirs formed in the Earth's crust from the remains of once-living things. Evidence indicates that millions of years of heat and pressure changed the remains of microscopic plant and animal into oil and natural gas.
Roy Nurmi, an interpretation adviser for Schlumberger
Schlumberger Limited (), doing business as SLB, is an oilfield services company. Schlumberger has four principal executive offices located in Paris, Houston, London, and The Hague.
Schlumberger is the world's largest offshore drilling compa ...
oil field services company, described the process as follows:
Plankton and algae, proteins and the life that's floating in the sea, as it dies, falls to the bottom, and these organisms are going to be the source of our oil and gas. When they're buried with the accumulating sediment and reach an adequate temperature, something above 50 to 70 °C they start to cook. This transformation, this change, changes them into the liquid hydrocarbons that move and migrate, will become our oil and gas reservoir.In addition to the aquatic environment, which is usually a sea but might also be a river, lake, coral reef, or algal mat, the formation of an oil or gas reservoir also requires a sedimentary basin that passes through four steps: * Deep burial under sand and mud * Pressure cooking * Hydrocarbon migration from the source to the reservoir rock * Trapping by impermeable rock Timing is also an important consideration; it is suggested that the Ohio River Valley could have had as much oil as the Middle East at one time, but that it escaped due to a lack of traps. The North Sea, on the other hand, endured millions of years of sea level changes that successfully resulted in the formation of more than 150 oilfields. Although the process is generally the same, various environmental factors lead to the creation of a wide variety of reservoirs. Reservoirs exist anywhere from the land surface to below the surface and are a variety of shapes, sizes, and ages. In recent years, igneous reservoirs have become an important new field of oil exploration, especially in trachyte and basalt formations. These two types of reservoirs differ in oil content and physical properties like
fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
connectivity, pore connectivity, and rock porosity.
Geology
Traps
Atrap
A trap is a mechanical device used to capture or restrain an animal for purposes such as hunting, pest control, or ecological research.
Trap or TRAP may also refer to:
Art and entertainment Films and television
* ''Trap'' (2015 film), Fil ...
forms when the buoyancy forces driving the upward migration of hydrocarbons through a permeable rock cannot overcome the capillary forces of a sealing medium. The timing of trap formation relative to that of petroleum generation and migration is crucial to ensuring a reservoir can form.
Petroleum geologists broadly classify traps into three categories that are based on their geological characteristics: the structural trap, the stratigraphic trap and the far less common hydrodynamic trap. The trapping mechanisms for many petroleum reservoirs have characteristics from several categories and can be known as a combination trap.
Traps are described as structural traps (in deformed strata such as folds and faults) or stratigraphic traps (in areas where rock types change, such as unconformities, pinch-outs and reefs). A trap is an essential component of a petroleum system.
Structural traps
Structural traps are formed as a result of changes in the structure of the subsurface due to processes such as folding and faulting, leading to the formation of domes, anticlines, and folds. Examples of this kind of trap are an anticline trap, a fault trap, and a salt dome trap (see salt dome). They are more easily delineated and more prospective than their stratigraphic counterparts, with the majority of the world's petroleum reserves being found in structural traps.Stratigraphic traps
Stratigraphic traps are formed as a result of lateral and vertical variations in the thickness, texture, porosity, orlithology
The lithology of a rock unit is a description of its physical characteristics visible at outcrop, in hand or core samples, or with low magnification microscopy. Physical characteristics include colour, texture, grain size, and composition. Lit ...
of the reservoir rock. Examples of this type of trap are an unconformity trap
An unconformity is a buried erosion surface, erosional or non-depositional surface separating two Rock (geology), rock masses or Stratum, strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer ...
, a lens trap
A lens is a transmissive optics, optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a #Compound lenses, compound lens consists of several simp ...
and a reef trap
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic component, abiotic processes—deposition (geology), deposition of ...
.
Hydrodynamic traps
Hydrodynamic traps are a far less common type of trap. They are caused by the differences in water pressure, that are associated with water flow, creating a tilt of the hydrocarbon-water contact.Seal / cap rock
The seal (also referred to as a cap rock) is a fundamental part of the trap that prevents hydrocarbons from further upward migration. A capillary seal is formed when thecapillary pressure In fluid statics, capillary pressure () is the pressure between two immiscible fluids in a thin tube (see capillary action), resulting from the interactions of forces between the fluids and solid walls of the tube. Capillary pressure can serve as bo ...
across the pore throats is greater than or equal to the buoyancy pressure of the migrating hydrocarbons. They do not allow fluids to migrate across them until their integrity is disrupted, causing them to leak. There are two types of capillary seal whose classifications are based on the preferential mechanism of leaking: the hydraulic seal and the membrane seal.
The membrane seal will leak whenever the pressure differential across the seal exceeds the threshold displacement pressure, allowing fluids to migrate through the pore spaces in the seal. It will leak just enough to bring the pressure differential below that of the displacement pressure and will reseal.
The hydraulic seal occurs in rocks that have a significantly higher displacement pressure such that the pressure required for tension fracturing is actually lower than the pressure required for fluid displacement – for example, in evaporites or very tight shales. The rock will fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displa ...
when the pore pressure is greater than both its minimum stress and its tensile strength then reseal when the pressure reduces and the fractures close.
Unconventional reservoirs
extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pro ...
.Unconventional reservoirs form in completely different ways to conventional reservoirs, the main difference being that they do not have "traps". This type of reservoir can be driven in a unique way as well, as buoyancy might not be the driving force for oil and gas accumulation in such reservoirs. This is analogous to saying that the oil which can be extracted forms ''within'' the source rock itself, as opposed to accumulating under a cap rock. Oil sands are an example of an unconventional oil reservoir.
Unconventional reservoirs and their associated unconventional oil are always changing in their definitions, as they encompass a broad spectrum of petroleum extraction and refinement techniques, as well as many different sources.
Due to how the oil is contained within the source rock, unconventional reservoirs require that the extracting entity function as a mining operation rather than drilling
Drilling is a cutting process where a drill bit is spun to cut a hole of circular cross-section in solid materials. The drill bit is usually a rotary cutting tool, often multi-point. The bit is pressed against the work-piece and rotated at ra ...
and pumping like a conventional reservoir. This has tradeoffs, with higher post-production costs associated with complete and clean extraction of oil being a factor of consideration for a company interested in pursuing a reservoir. Tailings are also left behind, increasing cleanup costs. Despite these tradeoffs, unconventional oil is being pursued at a higher rate due to the scarcity of conventional reservoirs around the world.
Estimating reserves
After the discovery of a reservoir, a petroleum engineer will seek to build a better picture of the accumulation. In a simple textbook example of a uniform reservoir, the first stage is to conduct a seismic survey to determine the possible size of the trap. Appraisal wells can be used to determine the location of oil-water contact and with it the height of the oil bearing sands. Often coupled with seismic data, it is possible to estimate the volume of an oil-bearing reservoir. The next step is to use information from appraisal wells to estimate the porosity of the rock. The porosity, or the percentage of the total volume that contains fluids rather than solid rock, is 20–35% or less. It can give information on the actual capacity. Laboratory testing can determine the characteristics of the reservoir fluids, particularly the expansion factor of the oil, or how much the oil expands when brought from the high pressure and high temperature of the reservoir to a "stock tank" at the surface. With such information, it is possible to estimate how many "stock tank"barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, ...
s of oil are located in the reservoir. Such oil is called the stock tank oil initially in place (STOIIP). As a result of studying factors such as the permeability of the rock (how easily fluids can flow through the rock) and possible drive mechanisms, it is possible to estimate the recovery factor, or what proportion of oil in place can be reasonably expected to be produced. The recovery factor is commonly 30–35%, giving a value for the recoverable resources.
The difficulty is that reservoirs are not uniform. They have variable porosities and permeabilities and may be compartmentalized, with fractures and faults breaking them up and complicating fluid flow. For this reason, computer modeling of economically viable reservoirs is often carried out. Geologists, geophysicist
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' som ...
s, and reservoir engineers
Reservoir engineering is a branch of petroleum engineering that applies scientific principles to the fluid flow through porous medium during the development and production of oil and gas reservoirs so as to obtain a high economic recovery. The wo ...
work together to build a model that allows simulation of the flow of fluids in the reservoir, leading to an improved estimate of the recoverable resources.
Reserves are only the part of those recoverable resources that will be developed through identified and approved development projects. Because the evaluation of "Reserves" has a direct impact on the company or the asset value, it usually follows a strict set of rules or guidelines (even though loopholes are commonly used by companies to inflate their own share price). The most common guidelines are the SPE PRMS guidelines, the SEC Rules, or the COGE Handbook. Government may also have their own systems, making it more complicated for investors to compare one company with another.
Production
To obtain the contents of the oil reservoir, it is usually necessary todrill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driverchuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to ...
into the Earth's crust, although surface oil seeps exist in some parts of the world, such as the La Brea tar pits
La Brea Tar Pits is an active paleontological research site in urban Los Angeles. Hancock Park was formed around a group of tar pits where natural asphalt (also called asphaltum, bitumen, or pitch; ''brea'' in Spanish) has seeped up from the gro ...
in California and numerous seeps in Trinidad. Factors that affect the quantity of recoverable hydrocarbons in a reservoir include the fluid distribution in the reservoir, initial volumes of fluids in place, reservoir pressure, fluid and rock properties, reservoir geometry, well type, well count, well placement, development concept, and operating philosophy.
Modern production includes thermal, gas injection, and chemical methods of extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pro ...
to enhance oil recovery.
Drive mechanisms
A virgin reservoir may be under sufficient pressure to push hydrocarbons to the surface. As the fluids are produced, the pressure will often decline, and production will falter. The reservoir may respond to the withdrawal of fluid in a way that tends to maintain the pressure. Artificial drive methods may be necessary.Solution-gas drive
This mechanism (also known as depletion drive) depends on the associated gas of the oil. The virgin reservoir may be entirely semi-liquid but will be expected to have gaseous hydrocarbons in solution due to the pressure. As the reservoir depletes, the pressure falls below thebubble point
In thermodynamics, the bubble point is the temperature (at a given pressure) where the first bubble of vapor is formed when heating a liquid consisting of two or more components.
Given that vapor will probably have a different composition tha ...
and the gas comes out of solution to form a gas cap at the top. This gas cap pushes down on the liquid helping to maintain pressure.
This occurs when the natural gas is in a cap below the oil. When the well is drilled the lowered pressure above means that the oil expands. As the pressure is reduced it reaches bubble point and subsequently the gas bubbles drive the oil to the surface. The bubbles then reach critical saturation and flow together as a single gas phase. Beyond this point and below this pressure the gas phase flows out more rapidly than the oil because of its lowered viscosity. More free gas is produced and eventually the energy source is depleted. In some cases depending on the geology the gas may migrate to the top of the oil and form a secondary gas cap.
Some energy may be supplied by water, gas in water, or compressed rock. These are usually minor contributions with respect to hydrocarbon expansion.
By properly managing the production rates, greater benefits can be had from solution-gas drives. Secondary recovery involves the injection of gas or water to maintain reservoir pressure. The gas/oil ratio and the oil production rate are stable until the reservoir pressure drops below the bubble point when critical gas saturation is reached. When the gas is exhausted, the gas/oil ratio and the oil rate drops, the reservoir pressure has been reduced, and the reservoir energy exhausted.
Gas cap drive
In reservoirs already having a gas cap (the virgin pressure is already below bubble point), the gas cap expands with the depletion of the reservoir, pushing down on the liquid sections applying extra pressure. This is present in the reservoir if there is more gas than can be dissolved in the reservoir. The gas will often migrate to the crest of the structure. It is compressed on top of the oil reserve, as the oil is produced the cap helps to push the oil out. Over time the gas cap moves down and infiltrates the oil and eventually the well will begin to produce more and more gas until it produces only gas. It is best to manage the gas cap effectively, that is, placing the oil wells such that the gas cap will not reach them until the maximum amount of oil is produced. Also a high production rate may cause the gas to migrate downward into the production interval. In this case, over time, the reservoir pressure depletion is not as steep as in the case of solution-based gas drive. In this case, the oil rate will not decline as steeply but will depend also on the placement of the well with respect to the gas cap. As with other drive mechanisms, water or gas injection can be used to maintain reservoir pressure. When a gas cap is coupled with water influx the recovery mechanism can be highly efficient.Aquifer (water) drive
Water (usually salty) may be present below the hydrocarbons. Water, as with all liquids, is compressible to a small degree. As the hydrocarbons are depleted, the reduction in pressure in the reservoir allows the water to expand slightly. Although this unit expansion is minute, if the aquifer is large enough this will translate into a large increase in volume, which will push up on the hydrocarbons, maintaining pressure. With a water-drive reservoir, the decline in reservoir pressure is very slight; in some cases, the reservoir pressure may remain unchanged. The gas/oil ratio also remains stable. The oil rate will remain fairly stable until the water reaches the well. In time, the water cut will increase and the well will be watered out.at
Schlumberger
Schlumberger Limited (), doing business as SLB, is an oilfield services company. Schlumberger has four principal executive offices located in Paris, Houston, London, and The Hague.
Schlumberger is the world's largest offshore drilling compa ...
Oilfield Glossary
The water may be present in an aquifer (but rarely one replenished with surface water). This water gradually replaces the volume of oil and gas that is produced out of the well, given that the production rate is equivalent to the aquifer activity. That is, the aquifer is being replenished from some natural water influx. If the water begins to be produced along with the oil, the recovery rate may become uneconomical owing to the higher lifting and water disposal costs.
Water and gas injection
If the natural drives are insufficient, as they very often are, then the pressure can be artificially maintained by injecting water into the aquifer or gas into the gas cap.Gravity drainage
The force of gravity will cause the oil to move downward of the gas and upward of the water. If vertical permeability exists then recovery rates may be even better.Gas and gas condensate reservoirs
These occur if the reservoir conditions allow the hydrocarbons to exist as a gas. Retrieval is a matter of gas expansion. Recovery from a closed reservoir (i.e., no water drive) is very good, especially if bottom hole pressure is reduced to a minimum (usually done with compressors at the wellhead). Any produced liquids are light-colored to colorless, with a gravity higher than 45 API. Gas cycling is the process where dry gas is injected and produced along with condensed liquid.See also
* Caprock *Drilling
Drilling is a cutting process where a drill bit is spun to cut a hole of circular cross-section in solid materials. The drill bit is usually a rotary cutting tool, often multi-point. The bit is pressed against the work-piece and rotated at ra ...
* Drilling fluid
* Drilling rig
* Drillship
*List of acronyms in oil and gas exploration and production
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
* List of natural gas fields
* List of oil fields
* List of oilfield service companies
* North Sea Oil
* Oilfield terminology
*Oil platform
An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platfor ...
*Oil well
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may ...
* OAPEC
*OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC, ) is a cartel of countries. Founded on 14 September 1960 in Baghdad by the first five members (Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela), it has, since 1965, been headquart ...
* Petroleum play
*Stranded gas reserve
Stranded gas is a natural gas field that has been discovered, but remains unusable for either physical or economic reasons. Gas found in an oil well is generally called associated gas rather than stranded gas but some flared gases from oil wel ...
* Subsea
*Underground hydrogen storage
Underground hydrogen storage is the practice of hydrogen storage in caverns, salt domes and depleted Oil field, oil/gas fields. Large quantities of gaseous hydrogen have been stored in caverns for many years. The storage of large quantities of hy ...
* Well stimulation
References