OV-10 Bronco Firing White Phosphorus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
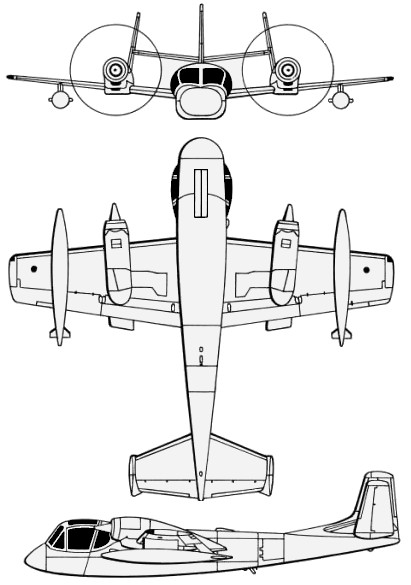
The Grumman OV-1 Mohawk is an armed military observation and attack aircraft that was designed for battlefield surveillance and light strike capabilities. It has a twin turboprop configuration, and carries two crew members in side-by-side seating. The Mohawk was intended to operate from short, unimproved runways in support of United States Army maneuver forces.
 The Mohawk began as a joint Army-Marine program through the then-Navy Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer), for an observation/attack plane that would outperform the Cessna L-19 Bird Dog. In June 1956, the Army issued Type Specification TS145, which called for the development and procurement of a two-seat, twin turboprop aircraft designed to operate from small, unimproved fields under all weather conditions. It would be faster, with greater firepower, and heavier armour than the Bird Dog, which had proved vulnerable during the Korean War. The Mohawk's mission would include observation,
The Mohawk began as a joint Army-Marine program through the then-Navy Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer), for an observation/attack plane that would outperform the Cessna L-19 Bird Dog. In June 1956, the Army issued Type Specification TS145, which called for the development and procurement of a two-seat, twin turboprop aircraft designed to operate from small, unimproved fields under all weather conditions. It would be faster, with greater firepower, and heavier armour than the Bird Dog, which had proved vulnerable during the Korean War. The Mohawk's mission would include observation,


 ;YAO-1 (YOV-1A): Initial prototypes (9 built).
;OV-1A (AO-1AF): Daylight observation variant (64 built).
;OV-1A - Pittsburgh Institute of Aeronautics: Fitted with two additional Westinghouse J34 jet engines. A non-flying, mixed-power, testbed, operated by the Pittsburgh Institute of Aeronautics (1 conversion).
;OV-1B (AO-1BF): SLAR variant (101 built).
;OV-1C (AO-1CF): IR reconnaissance variant (169 built).
;OV-1D: Consolidated sensor variant (37 new, 82 conversions).
;JOV-1A: OV-1As and OV-1Cs fitted with armament (59 conversions).
;RV-1C: Quick Look ELINT machines (two conversions).
;RV-1D: Quick Look II ELINT machine (31 conversions).
;EV-1E: Quick Look III ELINT machine (16 conversions).
;OV-1E: Prototype for unproduced modernized variant (1 built).
;YAO-1 (YOV-1A): Initial prototypes (9 built).
;OV-1A (AO-1AF): Daylight observation variant (64 built).
;OV-1A - Pittsburgh Institute of Aeronautics: Fitted with two additional Westinghouse J34 jet engines. A non-flying, mixed-power, testbed, operated by the Pittsburgh Institute of Aeronautics (1 conversion).
;OV-1B (AO-1BF): SLAR variant (101 built).
;OV-1C (AO-1CF): IR reconnaissance variant (169 built).
;OV-1D: Consolidated sensor variant (37 new, 82 conversions).
;JOV-1A: OV-1As and OV-1Cs fitted with armament (59 conversions).
;RV-1C: Quick Look ELINT machines (two conversions).
;RV-1D: Quick Look II ELINT machine (31 conversions).
;EV-1E: Quick Look III ELINT machine (16 conversions).
;OV-1E: Prototype for unproduced modernized variant (1 built).


 * 57-6539 – YOV-1A on display at the United States Army Aviation Museum in Fort Rucker, Alabama.
* 59-2633 – OV-1B on display at Cradle of Aviation Museum
* 60-3747 – OV-1C on display at the
* 57-6539 – YOV-1A on display at the United States Army Aviation Museum in Fort Rucker, Alabama.
* 59-2633 – OV-1B on display at Cradle of Aviation Museum
* 60-3747 – OV-1C on display at the  62-5880 – Texas Air Museum in Slaton, Texas has a modified OV-1D that was used by NASA that is on loan from the Museum of Naval Aviation.
* 62-5906 – Cockpit only on display at the Valiant Air Command Warbird Museum.
* 63-13128 - Military Aviation Preservation Society (MAPS) Air Museum (under restoration for museum display)
* 64-14247 – The United States Army's Tobyhanna Army Depot in Tobyhanna, Pennsylvania, has an OV-1B on display outside the main gate access control point.
* 64-14252 – The Mississippi Armed Forces Museum at Camp Shelby has an OV-1 on static display
* 67-15959 – The G-Star School of the Arts in West Palm Beach, Florida displays a static OV-1D
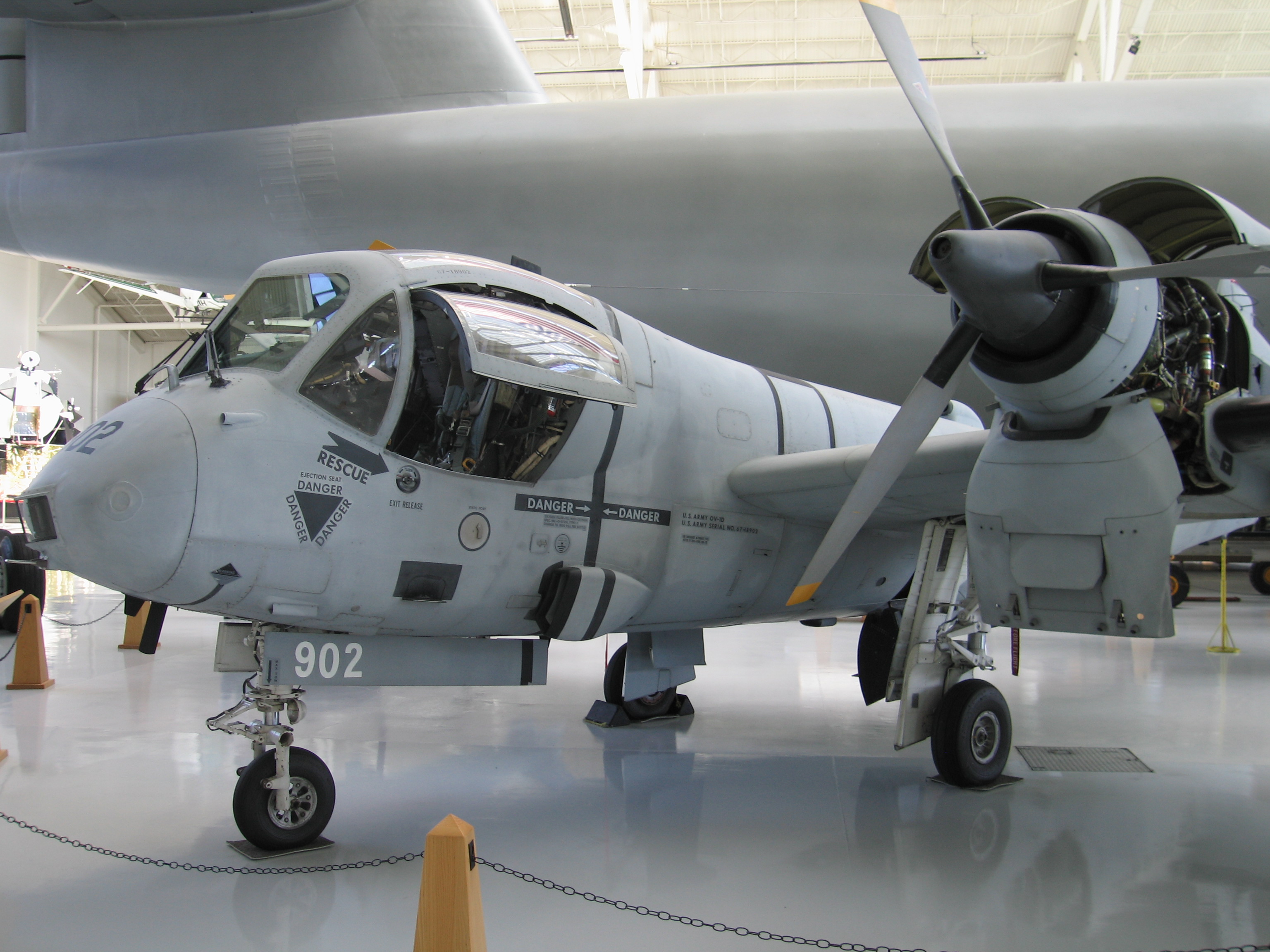
* 67-18902 – The
62-5880 – Texas Air Museum in Slaton, Texas has a modified OV-1D that was used by NASA that is on loan from the Museum of Naval Aviation.
* 62-5906 – Cockpit only on display at the Valiant Air Command Warbird Museum.
* 63-13128 - Military Aviation Preservation Society (MAPS) Air Museum (under restoration for museum display)
* 64-14247 – The United States Army's Tobyhanna Army Depot in Tobyhanna, Pennsylvania, has an OV-1B on display outside the main gate access control point.
* 64-14252 – The Mississippi Armed Forces Museum at Camp Shelby has an OV-1 on static display
* 67-15959 – The G-Star School of the Arts in West Palm Beach, Florida displays a static OV-1D
* 67-18902 – The
retrieved 2015-06-05 * AZO Plane Partners in current possession of the Air Zoo's OV-1D * OV-1D ex-Argentine Army Aviation, in the ''Aviación del Ejército Argentino'' Park Buenos Aires, Argentina * OV-1D Air Zoo Aerospace & Science Museum, Kalamzoo, Michigan
*
Mohawk as monument in the ''Aviación del Ejército Argentino'' Park
{{Authority control OV-001 Mohawk 1950s United States military reconnaissance aircraft Twin-turboprop tractor aircraft Mid-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1959 Triple-tail aircraft Aircraft with auxiliary jet engines Mixed-power aircraft
Development
 The Mohawk began as a joint Army-Marine program through the then-Navy Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer), for an observation/attack plane that would outperform the Cessna L-19 Bird Dog. In June 1956, the Army issued Type Specification TS145, which called for the development and procurement of a two-seat, twin turboprop aircraft designed to operate from small, unimproved fields under all weather conditions. It would be faster, with greater firepower, and heavier armour than the Bird Dog, which had proved vulnerable during the Korean War. The Mohawk's mission would include observation,
The Mohawk began as a joint Army-Marine program through the then-Navy Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer), for an observation/attack plane that would outperform the Cessna L-19 Bird Dog. In June 1956, the Army issued Type Specification TS145, which called for the development and procurement of a two-seat, twin turboprop aircraft designed to operate from small, unimproved fields under all weather conditions. It would be faster, with greater firepower, and heavier armour than the Bird Dog, which had proved vulnerable during the Korean War. The Mohawk's mission would include observation, artillery spotting
An artillery observer, artillery spotter or forward observer (FO) is responsible for directing artillery and mortar fire onto a target. It may be a ''forward air controller'' (FAC) for close air support (CAS) and spotter for naval gunfire sup ...
, air control, emergency resupply, naval target spotting, liaison, and radiological monitoring. The Navy specified that the aircraft must be capable of operating from small "jeep" escort class carriers (CVEs). The DoD selected Grumman Aircraft Corporation's G-134 design as the winner of the competition in 1957. Marine requirements contributed an unusual feature to the design. As originally proposed, the OF-1 could be fitted with water skis that would allow the aircraft to land at sea and taxi to island beaches at . Since the Marines were authorized to operate fixed-wing aircraft in the close air support
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and moveme ...
(CAS) role, the mockup also featured underwing pylons for rockets, bombs, and other stores.
The Air Force did not like the armament capability of the Mohawk and tried to get it removed, while the Marines did not want the Army's sophisticated sensors. However the Navy then opted to spend the allocated budget on a fleet oil tanker instead, so the Marines had to drop out of the program in September 1957. The Army continued with armed Mohawks and developed cargo pods that could be dropped from underwing hard points to resupply troops in emergencies.
The radar imaging capability of the Mohawk was to prove a significant advance in both peace and war. The Side-Looking Airborne Radar (SLAR) could look through foliage and map terrain, presenting the observer with a film image of the earth below only minutes after the area was scanned. In military operations, the image was split in two parts, one showing fixed terrain features, the other spotting moving targets.
The prototype (''YAO-1AF'') first flew on April 14, 1959. The OV-1 entered production in October 1959.
In mid-1961, the first Mohawks to serve with U.S. forces overseas were delivered to the 7th Army at Sandhofen Airfield
Sandhofen is a northern borough (''Stadtbezirk'') of Mannheim, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The US Army is present in Sandhofen with Coleman Airfield and Coleman Barracks. The US Army's only military prison in Europe is located on that base. All ...
near Mannheim, Germany. Before its formal acceptance, the camera-carrying AO-1AF was flown by Ralph Donnell on a tour of 29 European airfields to display it to the U.S. Army field commanders and potential European customers. In addition to their Vietnam and European service, SLAR-equipped Mohawks began operational missions in 1963 patrolling the Korean Demilitarized Zone. Germany and France showed early interest in the Mohawk, and Grumman actually signed a license production agreement with the French manufacturer Breguet Aviation in exchange for American rights to the Atlantic maritime patrol aircraft.
The very nature of the joint Army/Marine program had forced design compromises, such as ejection seats, that made the aircraft expensive and, sometimes, an openly resisted item in Army budgets. Orders for the OV-1 stopped in Fiscal 1964, and the controversy in the Pentagon over the armed Mohawk peaked with a 1965 directive that prohibited the Army from operating armed fixed-wing aircraft (See the Johnson-McConnell agreement of 1966). Operational success in Vietnam led to additional Mohawk orders in 1966, and by 1968, five surveillance companies were operating in Southeast Asia.
The last of the Mohawk versions to enter production was the OV-1D with more powerful T53-701 engines, improved avionics, and interchangeable mission pallets that made it possible to switch the aircraft from infrared to SLAR configuration in about an hour. The first four OV-1Ds were prototypes converted from earlier production airframes, and the first flew in 1969. These were followed by 37 new-build aircraft, the last of which was delivered in December 1970.
Over the years, the mission and the aircraft underwent many changes and roughly 380 were built over all variants. Mohawk variants included the JOV-1 rmed reconnaissance OV-1A, isual and photographic OV-1B isual, photographic, and side-looking radar (SLAR) pod the OV-1C isual, photographic, and infrared and the OV-1D (SLAR pod and bigger wings), OV-1E nlarged fuselage for more sensor operators or cargo EV-1E electronic intelligence installation">Signals intelligence#ELINT">electronic intelligence installationand RV-1E dvanced ELINT reconnaissance A four-engined Model 134E with tiltwings and tail ducted fan for control for VTOL was proposed to the Army but not built. Model 134R was a tandem cockpit version offered to meet the Light Armed Reconnaissance Aircraft (LARA) requirement, but the NA300 was chosen instead becoming the OV-10
The North American Rockwell OV-10 Bronco is an American twin-turboprop light attack and observation aircraft. It was developed in the 1960s as a special aircraft for counter-insurgency (COIN) combat, and one of its primary missions was as a forw ...
.
Operational history
United States Army
The U.S. Army flew the OV-1 operationally in the Vietnam War, with sixty-five lost to accidents, ground fire, and one shot down by a North Vietnamese fighter. In early 1968, while flying an OV-1 over South Vietnam, U.S. Army Captain Ken Lee shot down a MiG-17 “Fresco” fighter jet with his XM14 .50 in. (12.7 mm) caliber gun pods as well as two M159 unguided rocket pods, becoming the only Army Aviator to ever down a MiG. Due to the Key West Agreement, the Army tried to keep the shootdown a secret for fear that it would allow the USAF to transfer Mohawks to its inventory. Lee's kill was finally formally recognized by the Army in 2007. The Army also used the aircraft during Operation Desert Storm. Starting in 1972, theArmy National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG), in conjunction with the Air National Guard, is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States A ...
(ARNG) began to receive the Mohawk, with the ARNG eventually operating thirteen OV-1Bs, twenty-four OV-1Cs, and sixteen OV-1Ds serving with three aviation units in Georgia and Oregon. The Oregon Army National Guard Unit operating the Mohawk was located at McNary Field in Oregon, initially as the 1042nd Military Intelligence Company (Aerial Surveillance), then reflagged as the 641st Military Intelligence Battalion (CEWI)(Aerial Exploitation).
U.S. Army OV-1s were retired from Europe in 1992, from Korea in September 1996, and finally in the United States in 1996, superseded by newer systems, newer aircraft, and the evolution of reconnaissance satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications.
The ...
s. The OV-1 was primarily replaced by the EO-5C, a militarized version of the de Havilland Canada Dash 7 turboprop airliner equipped with a SLAR system, until the U.S. Air Force's Northrop Grumman E-8 Joint STARS
The Northrop Grumman E-8 Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System (Joint STARS) is a United States Air Force airborne ground surveillance, battle management and command and control aircraft. It tracks ground vehicles and some aircraft, col ...
(Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System) aircraft became fully operational.
As of 2011, Alliant Techsystems
Alliant Techsystems Inc. (ATK) was an American aerospace, defense, and sporting goods company with its headquarters in Arlington County, Virginia, in the United States. The company operated in 22 states, Puerto Rico, and other countries. ATK's ...
partnered with the Broadbay Group and Mohawk Technologies of Florida in a venture to return an armed, modernized version of the OV-1D to operational use as a counter-insurgency aircraft. A demonstrator was equipped with a FLIR Star Safire turret and a ventral, trainable M230 chain gun.
Argentine Army
The Argentine Army Aviation received twenty-three OV-1 in the 1990s. Ten were operational and the rest were used for spare parts. They became inactive and retired from use in 2015.Accidents and incidents
On 1 November 2019, a Grumman OV-1D Mohawk operated by Mohawk Airshows crashed at Witham Field,Stuart, Florida
Stuart is a city in and the seat of Martin County, Florida, United States. Located on Florida's Treasure Coast, Stuart is the largest of four incorporated municipalities in Martin County. The population is 17,425 according to the 2020 United State ...
, during the Stuart Air Show. The aircraft was destroyed and the pilot was killed. Its serial number was 68-15958.
Variants


 ;YAO-1 (YOV-1A): Initial prototypes (9 built).
;OV-1A (AO-1AF): Daylight observation variant (64 built).
;OV-1A - Pittsburgh Institute of Aeronautics: Fitted with two additional Westinghouse J34 jet engines. A non-flying, mixed-power, testbed, operated by the Pittsburgh Institute of Aeronautics (1 conversion).
;OV-1B (AO-1BF): SLAR variant (101 built).
;OV-1C (AO-1CF): IR reconnaissance variant (169 built).
;OV-1D: Consolidated sensor variant (37 new, 82 conversions).
;JOV-1A: OV-1As and OV-1Cs fitted with armament (59 conversions).
;RV-1C: Quick Look ELINT machines (two conversions).
;RV-1D: Quick Look II ELINT machine (31 conversions).
;EV-1E: Quick Look III ELINT machine (16 conversions).
;OV-1E: Prototype for unproduced modernized variant (1 built).
;YAO-1 (YOV-1A): Initial prototypes (9 built).
;OV-1A (AO-1AF): Daylight observation variant (64 built).
;OV-1A - Pittsburgh Institute of Aeronautics: Fitted with two additional Westinghouse J34 jet engines. A non-flying, mixed-power, testbed, operated by the Pittsburgh Institute of Aeronautics (1 conversion).
;OV-1B (AO-1BF): SLAR variant (101 built).
;OV-1C (AO-1CF): IR reconnaissance variant (169 built).
;OV-1D: Consolidated sensor variant (37 new, 82 conversions).
;JOV-1A: OV-1As and OV-1Cs fitted with armament (59 conversions).
;RV-1C: Quick Look ELINT machines (two conversions).
;RV-1D: Quick Look II ELINT machine (31 conversions).
;EV-1E: Quick Look III ELINT machine (16 conversions).
;OV-1E: Prototype for unproduced modernized variant (1 built).
Operators
; * Argentine Army Aviation ; * Israeli Air Force ; * United States Army *Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG), in conjunction with the Air National Guard, is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States A ...
Surviving aircraft


Airworthy
*59-2604 – OV-1A flown by the Planes of Fame Air Museum in Chino, California. *59-2631 –United States Military Air Power Museum
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two ...
in Jacksonville, FL has the only restored and flying OV-1B
*62-5874 – Flown by the Carolinas Aviation Museum at airshows.
*62-5889 – Cavanaugh Flight Museum flies one Mohawk
*62-5890 – Flown by the Carolinas Aviation Museum at airshows.
*64-14262 – American Wings Air Museum, Blaine, Minnesota.
*67-15959 – Operated by Mohawk Technologies and based at Palm Beach County Park Airport in Lantana, Florida.
*67-18899 – Operated by Mohawk Technologies and based at Palm Beach County Park Airport in Lantana, Florida.
*67-18923 – Operated by Mohawk Technologies and based at Palm Beach County Park Airport in Lantana, Florida.
*67-18924 – Operated by Mohawk Technologies and based at Palm Beach County Park Airport in Lantana, Florida.
*67-18926 – Owned by Paul Pefley, CEO of Mohawk Technologies, and based at Palm Beach County Park Airport in Lantana, Florida.
*68-15936 – American Wings Air Museum, Blaine, Minnesota.
*68-15946 – Operated by Mohawk Technologies and based at Palm Beach County Park Airport in Lantana, Florida.
*68-15947 – Located at Air Heritage Museum, Beaver County Airport
Beaver County Airport or is a county-owned public airport three miles northwest of Beaver Falls, in Beaver County, Pennsylvania.
Most U.S. airports use the same three-letter location identifier for the FAA and IATA, but Beaver County Airport i ...
, Pennsylvania. No longer owned by museum.
*69-17004 – Operated by Mohawk Technologies and based at Palm Beach County Park Airport in Lantana, Florida.
*69-17021 – American Wings Air Museum, Blaine, Minnesota.
Static display
 * 57-6539 – YOV-1A on display at the United States Army Aviation Museum in Fort Rucker, Alabama.
* 59-2633 – OV-1B on display at Cradle of Aviation Museum
* 60-3747 – OV-1C on display at the
* 57-6539 – YOV-1A on display at the United States Army Aviation Museum in Fort Rucker, Alabama.
* 59-2633 – OV-1B on display at Cradle of Aviation Museum
* 60-3747 – OV-1C on display at the 1st Cavalry Division Museum
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
in Fort Hood, Texas.
* 61-2724 – The Pima Air & Space Museum adjacent to Davis–Monthan Air Force Base in Tucson, Arizona lists an OV-1C Mohawk as a static display
* 62-5856 – The Wings of Eagles Discovery Center owns an OV-1C on static display among its collection
* 62-5860 – OV-1B on display at the United States Army Aviation Museum at Fort Rucker, Alabama.
* 62-5874 - Hickory Aviation Museum, Hickory, NC
* 62-5875 – Headquarters, 48th Infantry Brigade Combat Team
The 48th Infantry Brigade Combat Team (48th IBCT) ("Macon Volunteers") is a modular infantry brigade of the Georgia Army National Guard. One of the oldest units in U.S. Army history, the lineage of the 48th Infantry Brigade can be traced back ...
, (Georgia Army National Guard) in Macon, Georgia
Macon ( ), officially Macon–Bibb County, is a consolidated city-county in the U.S. state of Georgia. Situated near the fall line of the Ocmulgee River, it is located southeast of Atlanta and lies near the geographic center of the state of Geo ...
displays a static OV-1D as part of an outdoor exhibit
*  62-5880 – Texas Air Museum in Slaton, Texas has a modified OV-1D that was used by NASA that is on loan from the Museum of Naval Aviation.
* 62-5906 – Cockpit only on display at the Valiant Air Command Warbird Museum.
* 63-13128 - Military Aviation Preservation Society (MAPS) Air Museum (under restoration for museum display)
* 64-14247 – The United States Army's Tobyhanna Army Depot in Tobyhanna, Pennsylvania, has an OV-1B on display outside the main gate access control point.
* 64-14252 – The Mississippi Armed Forces Museum at Camp Shelby has an OV-1 on static display
* 67-15959 – The G-Star School of the Arts in West Palm Beach, Florida displays a static OV-1D
* 67-18902 – The
62-5880 – Texas Air Museum in Slaton, Texas has a modified OV-1D that was used by NASA that is on loan from the Museum of Naval Aviation.
* 62-5906 – Cockpit only on display at the Valiant Air Command Warbird Museum.
* 63-13128 - Military Aviation Preservation Society (MAPS) Air Museum (under restoration for museum display)
* 64-14247 – The United States Army's Tobyhanna Army Depot in Tobyhanna, Pennsylvania, has an OV-1B on display outside the main gate access control point.
* 64-14252 – The Mississippi Armed Forces Museum at Camp Shelby has an OV-1 on static display
* 67-15959 – The G-Star School of the Arts in West Palm Beach, Florida displays a static OV-1D
* 67-18902 – The Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum
The Evergreen Aviation & Space Museum is an aviation museum in McMinnville, Oregon. Its exhibits include the Hughes H-4 Hercules (''Spruce Goose'') and more than fifty military and civilian aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (drones), and spac ...
in McMinnville, Oregon displays a static OV-1D
* 67-18922 – Hunter Army Airfield
Hunter Army Airfield , located in Savannah, Georgia, United States, is a military airfield and subordinate installation to Fort Stewart located in Hinesville, Georgia.
Hunter features a runway that is 11,375 feet (3,468 m) long and an airc ...
in Savannah, Georgia displays a static OV-1D as part of an outdoor exhibit
* 67-18930 – Fort Huachuca
Fort Huachuca is a United States Army installation, established on 3 March 1877 as Camp Huachuca. The garrison is now under the command of the United States Army Installation Management Command. It is in Cochise County in southeast Arizona, appr ...
, Arizona maintains a static display of an OV-1 Mohawk
* 68-15932 – OV-1D c/n 136C, Argentine Army Aviation AE-021 – displayed at the Argentine Army Museum ( ''Museo Histórico del Ejército''), Buenos Aires, Argentina.
* 68-15939 – Was at McClain's Military Museum in Anderson, Indiana but now sits at "Vic's Antiques and Uniques" in Edinburgh, Indiana
* 69-16998 – The Valiant Air Command Warbird Museum at Space Coast Regional Airport in Titusville, Florida has a static OV-1 on display
* 69-17007 – The 1st Cavalry Division Museum at Fort Hood, Texas displays a static OV-1D as part of an outdoor exhibit
* 69-17010? – The United States Army Aviation Museum at Fort Rucker, Alabama displays a static OV-1D as part of the outdoor exhibit at the intersection of Red Cloud Avenue and Ruf Avenue
* 69-17022 - United States Army Garrison Humphreys, Republic of Korea, OV-1 Mohawk displayed outdoors at the intersection round-a-bout of Key Street & CPX Road
* The United States Army Intelligence and Security Command Headquarters Building at Fort Belvoir, Virginia displays a static OV-1DWhere Are They Now? MohawkStatusretrieved 2015-06-05 * AZO Plane Partners in current possession of the Air Zoo's OV-1D * OV-1D ex-Argentine Army Aviation, in the ''Aviación del Ejército Argentino'' Park Buenos Aires, Argentina * OV-1D Air Zoo Aerospace & Science Museum, Kalamzoo, Michigan
Specifications (OV-1D)

See also
References
;Notes ;Bibliography * *Further reading
;Printed sources * ;Online sources * * * *External links
*
Mohawk as monument in the ''Aviación del Ejército Argentino'' Park
{{Authority control OV-001 Mohawk 1950s United States military reconnaissance aircraft Twin-turboprop tractor aircraft Mid-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1959 Triple-tail aircraft Aircraft with auxiliary jet engines Mixed-power aircraft