Nùng People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nùng (''pronounced as noong'' uːŋ are a

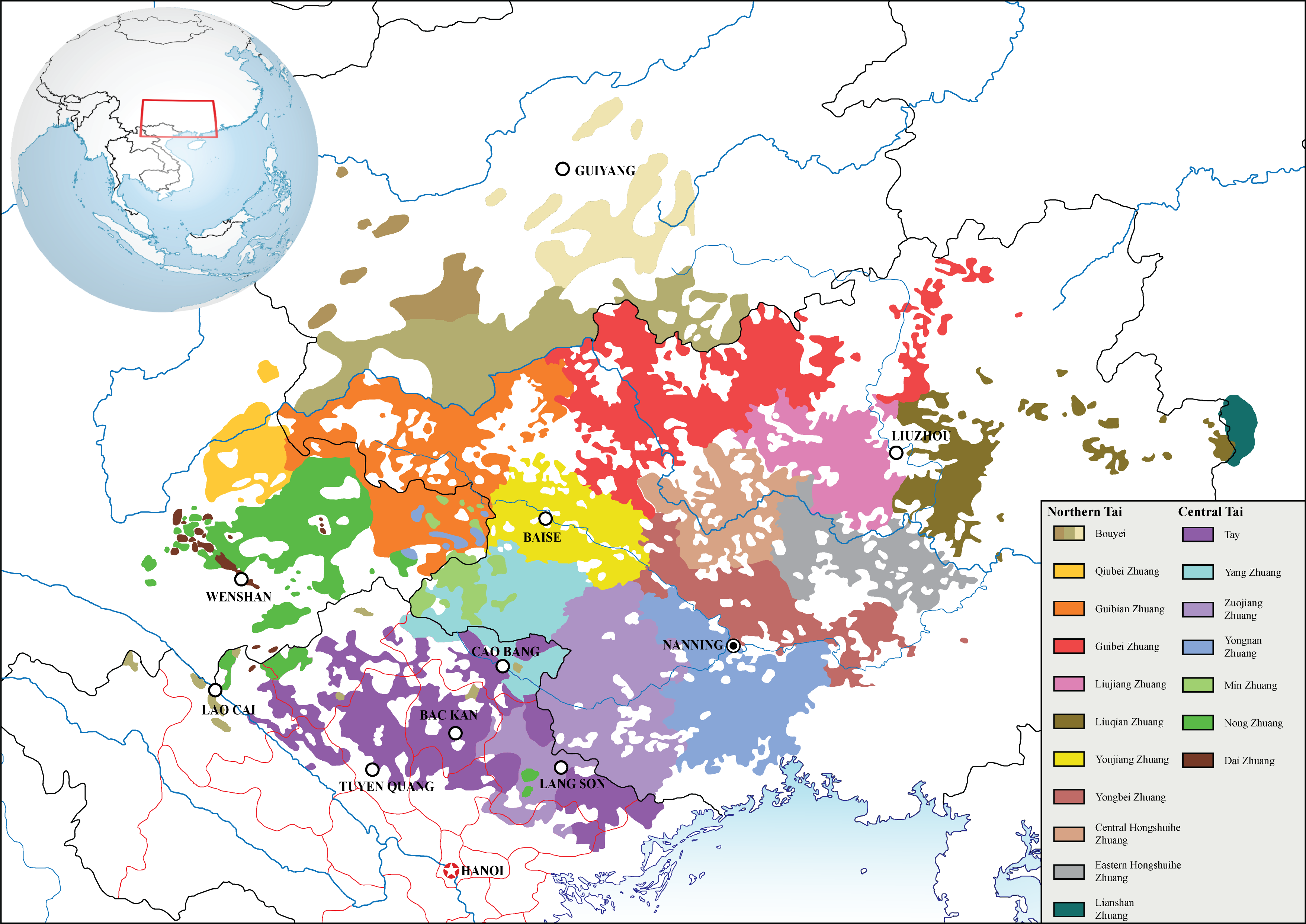 There are several subgroups among the Nùng: Nùng Xuồng, Nùng Giang, Nùng An, Nùng Phàn Slình, Nùng Lòi, Nùng Cháo, Nùng Quý Rỉn, Nùng Dín, Nùng Inh, Nùng Tùng Slìn etc.
Many of the Nùng's sub-group names correspond to the geographic regions of the Nùng homeland. Hoàng Nam (2008:11) lists the following Nùng subgroups.
*''Nùng Inh'': migrated from Long Ying
*''Nùng Phàn Slình'': migrated from Wan Cheng
**''Nùng Phàn Slình thua lài''
**''Nùng Phàn Slình cúm cọt''
*''Nùng An'': migrated from An Jie
*''Nùng Dín''
*''Nùng Lòi'': migrated from Xia Lei
*''Nùng Tùng Slìn'': migrated from Cong Shan
*''Nùng Quý Rỉn'': migrated from Gui Shun
*''Nùng Cháo'': migrated from Long Zhou
There are several subgroups among the Nùng: Nùng Xuồng, Nùng Giang, Nùng An, Nùng Phàn Slình, Nùng Lòi, Nùng Cháo, Nùng Quý Rỉn, Nùng Dín, Nùng Inh, Nùng Tùng Slìn etc.
Many of the Nùng's sub-group names correspond to the geographic regions of the Nùng homeland. Hoàng Nam (2008:11) lists the following Nùng subgroups.
*''Nùng Inh'': migrated from Long Ying
*''Nùng Phàn Slình'': migrated from Wan Cheng
**''Nùng Phàn Slình thua lài''
**''Nùng Phàn Slình cúm cọt''
*''Nùng An'': migrated from An Jie
*''Nùng Dín''
*''Nùng Lòi'': migrated from Xia Lei
*''Nùng Tùng Slìn'': migrated from Cong Shan
*''Nùng Quý Rỉn'': migrated from Gui Shun
*''Nùng Cháo'': migrated from Long Zhou
 The Zhuang, Nùng, and
The Zhuang, Nùng, and
 In 1041, Nong Zhigao and his mother seized Dangyouzhou (modern Jingxi,
In 1041, Nong Zhigao and his mother seized Dangyouzhou (modern Jingxi,
 The Nùng dominance became so pronounced that when
The Nùng dominance became so pronounced that when
Nùng People in Vietnam
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nung People Ethnic groups in Vietnam Tai peoples
Central Tai
The Central Tai languages include southern dialects of Zhuang, and various Nung and Tày dialects of northern Vietnam.
Central Tai languages differ from Northern Tai languages in that Central Tai distinguishes unaspirated and aspirated onset ...
-speaking ethnic group living primarily in northeastern Vietnam and southwestern Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
. The Nùng sometimes call themselves Tho, which literally means ''autochthonous
Autochthon, autochthons or autochthonous may refer to:
Fiction
* Autochthon (Atlantis), a character in Plato's myth of Atlantis
* Autochthons, characters in the novel ''The Divine Invasion'' by Philip K. Dick
* Autochthon, a Primordial in the ' ...
'' (indigenous or native to the land). Their ethnonym is often mingled with that of the Tày as Tày-Nùng. According to the Vietnam census, the population of the Nùng numbered about 856,412 by 1999, 968,800 by 2009, and 1,083,298 by 2019. They are the third largest Tai-speaking group, preceded by the Tày and the Thái ( Black Tai, White Tai and Red Tai groups), and sixth overall among national minority groups.
They are closely related to the Tày and the Zhuang. In China, the Nùng together with the Tày are classified as Zhuang people.
Subdivisions

 There are several subgroups among the Nùng: Nùng Xuồng, Nùng Giang, Nùng An, Nùng Phàn Slình, Nùng Lòi, Nùng Cháo, Nùng Quý Rỉn, Nùng Dín, Nùng Inh, Nùng Tùng Slìn etc.
Many of the Nùng's sub-group names correspond to the geographic regions of the Nùng homeland. Hoàng Nam (2008:11) lists the following Nùng subgroups.
*''Nùng Inh'': migrated from Long Ying
*''Nùng Phàn Slình'': migrated from Wan Cheng
**''Nùng Phàn Slình thua lài''
**''Nùng Phàn Slình cúm cọt''
*''Nùng An'': migrated from An Jie
*''Nùng Dín''
*''Nùng Lòi'': migrated from Xia Lei
*''Nùng Tùng Slìn'': migrated from Cong Shan
*''Nùng Quý Rỉn'': migrated from Gui Shun
*''Nùng Cháo'': migrated from Long Zhou
There are several subgroups among the Nùng: Nùng Xuồng, Nùng Giang, Nùng An, Nùng Phàn Slình, Nùng Lòi, Nùng Cháo, Nùng Quý Rỉn, Nùng Dín, Nùng Inh, Nùng Tùng Slìn etc.
Many of the Nùng's sub-group names correspond to the geographic regions of the Nùng homeland. Hoàng Nam (2008:11) lists the following Nùng subgroups.
*''Nùng Inh'': migrated from Long Ying
*''Nùng Phàn Slình'': migrated from Wan Cheng
**''Nùng Phàn Slình thua lài''
**''Nùng Phàn Slình cúm cọt''
*''Nùng An'': migrated from An Jie
*''Nùng Dín''
*''Nùng Lòi'': migrated from Xia Lei
*''Nùng Tùng Slìn'': migrated from Cong Shan
*''Nùng Quý Rỉn'': migrated from Gui Shun
*''Nùng Cháo'': migrated from Long Zhou
Relationship to the Zhuang and Tày
 The Zhuang, Nùng, and
The Zhuang, Nùng, and Tày people
The Tày people, also known as the Thô, T'o, Tai Tho, Ngan, Phen, Thu Lao, or Pa Di, are a Central Tai languages, Tai-speaking ethnic group who live in northern Vietnam. According to a 2009 census, there are 1.7 million Tày people living in Vi ...
are a cluster of Tai people
Tai peoples are the populations who speak (or formerly spoke) the Tai languages. There are a total of about 93 million people of Tai ancestry worldwide, with the largest ethnic groups being Dai, Thais, Isan, Tai Yai (Shan), Lao, Tai Ahom, an ...
s with very similar customs and dress known as the Rau peoples Rau, Laoz ( Zhuang: ), Liao ( Chinese: 僚人) or Lao peoples ( lo, ລາວລຸ່ມ),However, whether Lao belongs to the Lao group or Tày group is disputed. is an ethnic cluster covering Zhuang, Buyei, Tay– Nùng and other Northern Tai l ...
. In China, the Zhuang are today the largest non-Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive va ...
minority with around 14.5 million population in Guangxi Province
Guangxi (; ; alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam ( ...
alone. In Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, as of 1999, there were 933,653 Nùng people and 1,574,822 Tày people. Recently the Tày and Nùng have been referred to as a combined Tày-Nùng minority. However these ethnonyms are a recent phenomenon and did not exist until the modern age. According to Keith Taylor, the Vietnamese terms were "categories of French colonial knowledge" used to differentiate highlanders from lowlanders. The ethnic Zhuang was a product of the "ethnic identification project" pursued in 1950s China.
Many scholars of the Tai peoples consider the Zhuang and Nùng to be essentially the same people, a single ethnic group. During the early 11th century, ethnic identities and boundaries were more fluid than in the modern Sino-Vietnamese borderland. The Zhuang leader Nong Zhigao
Nong Zhigao (modern Zhuang language: ; , vi, Nùng Trí Cao, links=no) (1025–1055?) is a hero admired by the Nùng people of Vietnam, and Zhuang people, Zhuang people of China. His father Nong Quanfu was head of the local Zhuang people in Gu ...
was defeated in 1055 by the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
. Had he won, it's possible that he might have established a state under his own clan name, Nong. Instead, his people in China continued to be referred to as Zhuang, which in their own language means "cave", while in Vietnam they came to be known as Nùng. The majority ethnic group and now the largest minority, however, was and still is the same, the Zhuang/Nùng, who together number more than 15 million people. They are just recognized by different names in China and Vietnam. Nong Zhigao (V. Nùng Trí Cao) has sometimes been claimed by Vietnam as a Vietnamese native, but this is due to antagonism with modern China, while in previous times the Vietnamese sometimes saw him as primarily Chinese.
Like the Nùng, the Tày (originally Thô) would have been classified as Zhuang had they lived in China. However unlike the Nùng, the Tày are considered the most Vietnamized of all the Thai peoples in Vietnam and lacquered their teeth black like the Viets. The Tày and Nùng frequently intermarried, although the Tày seem to have been held in higher regard.
History
Rise of the Nùng
During the earlySong dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
, the Huang clan was left in charge of the You
In Modern English, ''you'' is the second-person pronoun. It is grammatically plural, and was historically used only for the dative case, but in most modern dialects is used for all cases and numbers.
History
''You'' comes from the Proto- ...
and Zuo rivers. The Wei had settled on the Song-Viet boarder. However the power of the Nong clan increased and began to upset Huang supremacy. By the early Song, they ruled over an area known as Temo, which stretched from modern Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture
Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture in southeastern Yunnan Province, People's Republic of China and the easternmost prefecture-level division of the province. It borders Baise, Guangxi to the east, Vietnam's ...
in the west to Jingxi in the east and Guangyuanzhou (Quảng Nguyên, now Cao Bằng
Cao Bằng () is a city in northern Vietnam. It is the capital and largest settlement of Cao Bằng Province. It is located on the bank of the Bằng Giang river, and is around away from the border with China's Guangxi region. According to the ...
province) in the south. Emperor Taizong of Song
Zhao Jiong (20 November 939 – 8 May 997), known as Zhao Guangyi from 960 to 977 and Zhao Kuangyi before 960, also known by his temple name Taizong after his death, was the second emperor of the Song dynasty of China. He reigned from 976 to h ...
(r. 976-997) bestowed special favors on Nong leadership, acknowledging that they had succeeded the Huang in the Zuo River region.
The first member of the Nong clan to gain official recognition was Nong Minfu Nong Minfu (, Vietnamese: ''Nùng Dân Phú''; 970s) was a Tai-speaking Rau chieftain who ruled over an area in what is today's Sino-Vietnamese borderland. He could have been Nong Quanfu's father. He was probably the leader of a confederation of ...
. It is not known when he was born, but a memorial in early 977 states that the "peaceful and generous" leader Nong Minfu of Guangyuanzhou had established himself over ten neighboring villages with the support of Southern Han
Southern Han (; 917–971), officially Han (), originally Yue (), was one of the ten kingdoms that existed during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was located on China's southern coast, controlling modern Guangdong and Guangxi. The ...
(907-971). Minfu had supported Duan Siping
Duan Siping (, IPA: ; Bai: Duainb six-pienp), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Dali, was a Chinese monarch and politician. He was the founding emperor of the Dali Kingdom. The Dali Kingdom would last until the Mongol conque ...
(r. 937–944) of the Dali Kingdom
The Dali Kingdom, also known as the Dali State (; Bai: Dablit Guaif), was a state situated in modern Yunnan province, China from 937 until 1253. In 1253, it was conquered by the Mongols but members of its former ruling dynasty continued to a ...
and was rewarded with titles. Duan rewarded another leader in Temo with the title ''buxie''. The Song bestowed the titles "minister of works" (''sigong'') and "grand master of splendid happiness bearing the golden pocket with purple trimming" (''jinzi guanglu daifu'') on Minfu. These titles were passed onto Minfu's son, Nong Quanfu
Nong Quanfu (, za, Nungz Cienzfuk; ?-1039), also recorded as Nùng Tồn Phúc ( vi, Nùng Tồn Phúc; ; Chữ Hán: ) was a Nùng/ Zhuang chieftain and zhou-level official of Guangyuan located in the modern-day Cao Bang in the 11th century AD ...
( za, Nungz Cienzfuk, vi, Nùng Tồn Phúc). He was also granted additional authority of Dangyouzhou (modern Jingxi, Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
). His younger brother, Nong Quanlu, controlled Wennaizhou (modern Na Rì District
NA, N.A., Na, nA or n/a may refer to:
Chemistry and physics
* Sodium, symbol Na, a chemical element
* Avogadro constant (''N''A)
* Nucleophilic addition, a type of reaction in organic chemistry
* Numerical aperture, a number that characterizes ...
). Such preferential treatment was viewed with anger in Đại Cồ Việt, which attacked a Song garrison in 1004 after it held a banquet for a Nong chieftain.
In 1005, a woman known as A Nong
A Nong (also A Nùng, zh, 阿儂; 1005–1055) was a Zhuang shamaness, matriarch and warrior. She was the mother of the warlord Nong Zhigao (1025–1055). Alongside her son, father, and husband, she led the Zhuang and Nùng minorities of the S ...
was born to a notable warrior chieftain who accepted titles from both the Song dynasty and the Early Lê dynasty
The Early Lê dynasty or the Former Lê dynasty ( vi, Nhà Tiền Lê; Hán Nôm: ; ) was a dynasty of Vietnam that existed from 980 to 1009. It followed the Đinh dynasty and was succeeded by the Lý dynasty. It comprised the reigns of thr ...
of Đại Cồ Việt. A Nong learned to spin and weave from her mother. At some point she was separated from the other girls and learned the ways of a shaman. She married Nong Quanfu and became his primary political adviser. Her brother, Nong Dangdao, inherited Wulezhou near Guangyuanzhou. She gave birth to Nong Zhigao
Nong Zhigao (modern Zhuang language: ; , vi, Nùng Trí Cao, links=no) (1025–1055?) is a hero admired by the Nùng people of Vietnam, and Zhuang people, Zhuang people of China. His father Nong Quanfu was head of the local Zhuang people in Gu ...
in 1025. A Nong induced Quanfu to kill his brother, the leader of the Cen clan, and take his lands. The Nong clan eventually controlled 14 major grottoes (''dong'') in comparison to only 5 for the Huang clan.
In 1035, Quanfu declared the founding of the Kingdom of Longevity (''Changsheng Guo'' 長生國) and took for himself the exalted title "Luminous and Sage Emperor" (''Zhaosheng Huangdi'' 昭聖皇帝) while A Nong became the "Enlightened and Virtuous Empress" (''Mingde Huanghou'' 明德皇后). Another source says he founded the ''Chang Qi Guo'' and styled himself the first king of Dali, ''Tu Dan Chao''. The local prefect of Tianzhou requested assistance from Yongzhou
Yongzhou, formerly known as Lingling, is a prefecture-level city in the south of Hunan province, People's Republic of China, located on the southern bank of the Xiang River, which is formed by the confluence of the Xiao and Xiang Rivers, and b ...
to deal with the rebellion, but officials there appear to have feared involvement and refused to offer aid. In 1039, the emperor of the Lý dynasty
The Lý dynasty ( vi, Nhà Lý, , chữ Nôm: 茹李, chữ Hán: 李朝, Hán Việt: ''Lý triều'') was a Vietnamese dynasty that existed from 1009 to 1225. It was established by Lý Công Uẩn when he overthrew the Early Lê dynasty an ...
, Lý Thái Tông
Lý Thái Tông ( chữ Hán: 李 太 宗; 29 July 1000 – 3 November 1054), personal name Lý Phật Mã, posthumously temple name Thái Tông, was the second monarch of the Lý dynasty, ruled Đại Việt from 1028 to 1054. He was consider ...
, invaded the newly found kingdom, captured Quanfu and four other male members of the Nong clan, and executed them. A Nong escaped with the 14-year old Zhigao into Song territory.
Nùng Trí Cao
 In 1041, Nong Zhigao and his mother seized Dangyouzhou (modern Jingxi,
In 1041, Nong Zhigao and his mother seized Dangyouzhou (modern Jingxi, Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
) and the Leihuo grotto settlement (modern Daxin County
Daxin County (, Standard Zhuang, Zhuang: ) is a county in the west of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. It is under the administration of Chongzuo city.
The southwest border of Daxin County is along Cao Bằng Province, Vietnam. The legal ...
). A Nong married a wealthy merchant but Zhigao murdered this man. A Nong married a third time to Nong Xiaqing, expanding their territory further into Temo. In 1042, Zhigao declared the founding the Kingdom of the Great Succession (''Dali Guo'' 大歷國, not to be confused with the Kingdom of Dali
The Dali Kingdom, also known as the Dali State (; Bai: Dablit Guaif), was a state situated in modern Yunnan province, China from 937 until 1253. In 1253, it was conquered by the Mongols but members of its former ruling dynasty continued to ...
大理). Đại Cồ Việt sent troops and captured him. He was held prisoner for a year before he was released with an honorary title and given control of Guangyuan, Leihuo, Ping'an, Pinpo, and Silang in return for a share of their natural resources, particularly gold. In 1048, Zhigao declared another state, the Kingdom of the Southern Heavens (''Nantian Guo''), and took a reign title, "Auspicious Circumstances" (''Jingrui''). He called the Viet court's actions criminal and that his territory would not be annexed by China. In the fall of 1049, Zhigao's forces pillaged Yongzhou. In 1050, Đại Cồ Việt launched an attack on Zhigao's stronghold and evicted him, sending him fleeing into Song territory.
Nong Zhigao approached the Song at Yongzhou for assistance but was denied an audience until he staged a military demonstration beneath the walls. He then presented substantial tribute (tame elephants and lumps of gold and silver) and petitioned the emperor. The prefect of Yongzhou, Chen Gong, never passed on the petition to court. However when the tribute reached the court, the Fiscal Commissioner Xiao Gu argued to the emperor that Zhigao should be granted title. The Song court refused because it considered Zhigao's service to be the right of Đại Cồ Việt. The military commander Yuan Yun was dispatched to attack Zhigao but instead he wanted to offer Zhigao protection, and returned to the capital with tribute, arguing for a change in policy.
Zhigao's followers set up shop and through the mineral wealth of his holdings formed close ties with Chinese traders, including jinshi
''Jinshi'' () was the highest and final degree in the imperial examination in Imperial China. The examination was usually taken in the imperial capital in the palace, and was also called the Metropolitan Exam. Recipients are sometimes referre ...
degree holders Huang Wei and Huang Shifu. He also recruited other Nong clan members such as Nong Zhizhong and Nong Jianhou. Under the influence of Huang Wei and A Nong, Zhigao decided to declare independence. In 1052, Zhigao proclaimed the establishment of the Kingdom of the Great South (''Danan Guo'') and granted himself the title of Benevolent and Kind Emperor (''Renhui Huangdi''). In the spring of 1052, Zhigao ordered the villages under his control to be burnt and led 5,000 subjects on the path to Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
. By summertime, he had taken Yongzhou and reached Guangzhou, where his 50,000 strong army became bogged down in a prolonged siege. Despite cutting off Guangzhou from water, the city was well stocked with provisions, and the defenders fought back with crossbow defenses. The district magistrate Xiao Zhu foiled a waterborne attack on Guangzhou by setting fire to their ships. After 57 days, Zhigao was forced to retreat as more Song reinforcements arrived. He held out at Yongzhou, defeating five Song commanders sent against him. The Song called in a veteran of the Song–Xia wars The Song–Xia wars () were a series of military conflicts fought by the Northern Song dynasty, Western Xia dynasty, and Liao dynasty from the late 10th century to early 12th century. Although sporadic conflicts would continue, the Northern Song lo ...
, Di Qing
Di Qing (1008–1057), formerly romanized as Ti Ch'ing, was a Chinese military general of the Northern Song dynasty.
Biography
Di Qing was born to a poor family in Xihe, Fenzhou (汾州西河; present-day Fenyang, Shanxi). He sported tattoos ...
, to assume command of the anti-rebel forces. He gathered 31,000 men and 32 generals, including Fanluo tribal cavalry from the northwest that "were able to ascend and descend mountains as though walking on level ground." Lý Thái Tông also offered to send 20,000 troops but the offer was refused out of fear that the troops would not leave afterwards.
One general, Chen Shu, attacked early with 8,000 men and suffered a defeat against the Zhuang forces. Di Qing executed him and 31 officers. He then marched his forces under cover of night and blocked the Kunlun Pass
Kunlun Pass () is mountain pass located 59 kilometers northeast of Nanning, Guangxi and traversed by . The altitude is around 300 m (1000 ft).
During the Second Sino-Japanese War, this pass was contended between the Japanese and the Chinese in t ...
east of Yongzhou. Zhigao attacked the Song forces in early 1054. The Zhuang wore bright crimson uniforms and fought in units of three armed with long shields that advanced "like fire." One man carried a shield while the other two hurled metal-tipped bamboo javelins. In the initial stages of battle, one Song commander was killed, and the Song army was momentarily forced to fall back. In the second engagement, the Zhuang forces could not withstand the Song infantry charges. The Song infantry hacked at the Zhuang shields with heavy swords and axes while the Fanluo cavalry attacked their wings, breaking their ranks. The Zhuang fled, suffering 5,341 casualties. Di Qing retook Yongzhou and executed the jinshi-holder Huang, two of Zhigao's family, and 57 officials. Zhigao and his remaining family fled to seek help from the Zhuang clans, but he was not well liked, and the Huang chieftain, Huang Shouling, refused to aid him. He also requested aid from the Viet court, which sent the tribal commander Võ Nhị to assist the rebels. A Nong and her son Nong Zhiguang, as well as Zhigao's sons Nong Jifeng and Nong Jizong, were caught at Temo in Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is ...
by Zhuang forces allied with the Song. They were executed. Zhigao failed to raise more troops in Dali.
According to official accounts, Nong Zhigao was executed by the ruler of Dali and his head presented to Song authorities. However popular accounts claim he fled further south into modern northern Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
, where his descendants thrive to this day. The Zhuang of Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture
Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture in southeastern Yunnan Province, People's Republic of China and the easternmost prefecture-level division of the province. It borders Baise, Guangxi to the east, Vietnam's ...
identify as survivors of Zhigao's rebel movement and other groups in Dali City
Dali City () is the county-level seat of the Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture in northwestern Yunnan. Dali City is administered through 12 township-level districts, two of which are also commonly referred to as Dali.
Xiaguan () formerly k ...
, Xishuangbana
Xishuangbanna, Sibsongbanna or Sipsong Panna ( Tham: , New Tai Lü script: ; ; th, สิบสองปันนา; lo, ສິບສອງພັນນາ; shn, သိပ်းသွင်ပၼ်းၼႃး; my, စစ်ဆောင်� ...
, and northern Thailand claim to be descended from Zhigao. Many Zhuang songs refer to him as "King Nong."
Migration
After the defeat of Nùng Trí Cao, Many of the Nùng rebels fled to Vietnam, concentrating aroundCao Bằng
Cao Bằng () is a city in northern Vietnam. It is the capital and largest settlement of Cao Bằng Province. It is located on the bank of the Bằng Giang river, and is around away from the border with China's Guangxi region. According to the ...
and Lạng Sơn
Lạng Sơn () is a city in far northern Vietnam, which is the capital of Lạng Sơn Province. It is accessible by road and rail from Hanoi, the Vietnamese capital, and it is the northernmost point on National Route 1.
History
Due to its ge ...
provinces and became known as the Nùng. Barlow (2005) suggests that many of the original 11th-century rebels who fled to Vietnam were absorbed by the related Tày peoples of the region.
With the end of the Song–Đại Việt war
The Song–Đại Việt war, also known as the Lý-Song War, was a military conflict between the Lý dynasty of Đại Việt and the Song dynasty of China between 1075 and 1077. The war was sparked by the shifting allegiances of tribal peoples ...
in 1078, the Nùng north of the border became more sinicized by accepting greater integration into the Chinese tributary system while the Tai-speaking people south of the border in Đại Việt
Đại Việt (, ; literally Great Việt), often known as Annam ( vi, An Nam, Chữ Hán: 安南), was a monarchy in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia from the 10th century AD to the early 19th century, centered around the region of present-day ...
remained in a patron-client relationship with the Viet court. These Tai-speaking communities lived in the mountainous areas of Việt Bắc Việt Bắc (''Northern Vietnam'') is a region of Vietnam north of Hanoi that served as the Việt Minh's base of support during the First Indochina War (1946–1954).
Việt Bắc is also called the capital of northernmost Vietnam because this a ...
and most of their interaction with Viets was through the Các Lái, Kinh (Vietnamese) merchants who had obtained government licenses for trade in the uplands in return for tribute to the court. Assimilation with broader society was not necessary unlike in China. The Viet court ruled the frontier region using a system similar to the Chinese Tusi
''Tusi'', often translated as "headmen" or "chieftains", were hereditary tribal leaders recognized as imperial officials by the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties of China, and the Later Lê and Nguyễn dynasties of Vietnam. They ruled certain et ...
known as thổ ty. Thổ ty officials who governed the frontier held hereditary positions and passed on their position from generation to generation. The thổ ty were ''de facto'' rulers and held absolute authority in their own areas. They paid tribute to both Chinese and Viet authorities. As late as the 19th century, imperial presence was not guaranteed. Central expansion and assertion of authority by the Nguyễn dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (chữ Nôm: 茹阮, vi, Nhà Nguyễn; chữ Hán: 阮朝, vi, Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1883. During its existence, ...
over these areas was often met by violent local opposition. Unlike the Chinese however, the Viets did offer princesses to the thổ ty to cement allegiances. Despite this, most Nùng communities were self ruled as late as 1953 when the Viet Minh
The Việt Minh (; abbreviated from , chữ Nôm and Hán tự: ; french: Ligue pour l'indépendance du Viêt Nam, ) was a national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1941. Also known as the Việt Minh Fro ...
took the Việt Bắc region.
As the strongest thổ ty, Nùng Trí Cao (C. Nong Zhigao) and his family members were deified by these communities. After the Lam Sơn uprising
The Lam Sơn uprising (; vi, Khởi nghĩa Lam Sơn; vi-hantu, 起義藍山) was a Vietnamese rebellion led by Lê Lợi in the province of Jiaozhi from 1418 to 1427 against the rule of Ming China. The success of the rebellion led to the es ...
which ended the Ming occupation, the Viet ruler Lê Lợi
Lê Lợi (, Chữ Hán: 黎利; c. 10 September 1384/1385 – 5 October 1433), also known by his temple name as Lê Thái Tổ (黎太祖) and by his pre-imperial title Bình Định vương (平定王; "Prince of Pacification"), was a Vietname ...
consolidated support from border communities by acknowledging a variety of local deities. It's suggested that a shrine to Nùng Trí Cao, the Great King of Kỳ Sầm Temple, was erected in the western outskirts of Cao Bằng
Cao Bằng () is a city in northern Vietnam. It is the capital and largest settlement of Cao Bằng Province. It is located on the bank of the Bằng Giang river, and is around away from the border with China's Guangxi region. According to the ...
in connection to the suppression of a rebel force by Lê forces in 1431. Worship of Nùng Trí Cao was widespread by the 19th century. In 1897, it was reported that local leaders had arranged the renovation of Kỳ Sầm Temple in conjunction with the Nùng clan. On the tenth day of the first lunar month a festival was held around the temple. Apparently "Han Chinese" from the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
flooded the region during the festival so that Quảng Nguyên "resembled nothing more than another region of China." Another festival focused on trade was held around the temple in the third lunar month during Thanh Minh (Qingming Festival
The Qingming festival or Ching Ming Festival, also known as Tomb-Sweeping Day in English (sometimes also called Chinese Memorial Day or Ancestors' Day), is a traditional Chinese festival observed by the Han Chinese of mainland China, Hong Ko ...
).
The Nùng, although lacking a leader of the stature of Nùng Trí Cao
Nong Zhigao (modern Zhuang language: ; , vi, Nùng Trí Cao, links=no) (1025–1055?) is a hero admired by the Nùng people of Vietnam, and Zhuang people of China. His father Nong Quanfu was head of the local Zhuang people in Guangyuan (廣� ...
, rose up in 1352, 1430, 1434.
In the 16th century the Zhuang from Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
and perhaps from southeast Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is ...
began migrating into Vietnam. This movement was accelerated by the cycle of disasters and political events of the seventeenth century which brought larger numbers of Chinese immigrants into the region, such as the fall of the Ming, the rebellion of Wu Sangui, the Qing occupation, and the Muslim revolts in Yunnan.This migration was a peaceful one which occurred family by family. French administrators later identified a number of Nùng clans in the course of their ethnographic surveys. These had incorporated Chinese place names in their clan names and indicated the place of their origin in China, such as the "Nùng Inh" clan from Long Ying in the southwest of Guangxi. Other names also reflected the locations from where they came, indicating that they were primarily from the immediate frontier region of the southwest of Guangxi. The Nùng became increasingly numerous in the region, and were spread out through a long stretch of the Vietnamese northern border from Lạng Sơn
Lạng Sơn () is a city in far northern Vietnam, which is the capital of Lạng Sơn Province. It is accessible by road and rail from Hanoi, the Vietnamese capital, and it is the northernmost point on National Route 1.
History
Due to its ge ...
to Cao Bằng
Cao Bằng () is a city in northern Vietnam. It is the capital and largest settlement of Cao Bằng Province. It is located on the bank of the Bằng Giang river, and is around away from the border with China's Guangxi region. According to the ...
. The Mạc dynasty
The Mạc dynasty ( vi, Nhà Mạc / ''Mạc triều''; Hán Nôm: 茹莫 / 莫 朝) (1527-1627), as known as House of Mạc ruled the whole of Đại Việt between 1527 and 1540 and the northern part of the country from 1540 until 1593, and ...
, a Vietnamese dynasty ruled over the Vietnamese northeast highlands, profited from the migration in that they were able to draw upon Nùng manpower for their own forces.
In 1833, Nông Văn Vân Nông Văn Vân (農文雲, ?–1835) was the leader of a peasant revolt in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge o ...
, a Nùng chieftain, led a rebellion against Vietnamese rule. He quickly took control of Cao Bằng
Cao Bằng () is a city in northern Vietnam. It is the capital and largest settlement of Cao Bằng Province. It is located on the bank of the Bằng Giang river, and is around away from the border with China's Guangxi region. According to the ...
, Tuyên Quang
Tuyên Quang () is a city in Vietnam, and is the capital of Tuyên Quang Province.
History
The French post at Tuyên Quang was defended for four months against 12,000 troops of the Yunnan Army and the Black Flag Army by two companies of the Fre ...
, Thái Nguyên
Thái Nguyên () is a city in Vietnam. It is the capital and largest city of Thái Nguyên Province. The city is listed as a first class city and is the ninth largest city in Vietnam. It has long been famous throughout Vietnam for its Tân Cư� ...
and Lạng Sơn
Lạng Sơn () is a city in far northern Vietnam, which is the capital of Lạng Sơn Province. It is accessible by road and rail from Hanoi, the Vietnamese capital, and it is the northernmost point on National Route 1.
History
Due to its ge ...
provinces, aiming to create a separate Tày-Nùng state in the northern region of Vietnam. His rising was eventually suppressed by the Nguyễn dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (chữ Nôm: 茹阮, vi, Nhà Nguyễn; chữ Hán: 阮朝, vi, Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1883. During its existence, ...
in 1835. In the 1860s, the Nùng sided with Sioung (Xiong), a self-proclaimed Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related to ...
king. Sioung's armies raided gold from Buddhist temples and seized large tracts of land from other people.
The period from the Taiping Rebellion
The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive rebellion and civil war that was waged in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Han, Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It lasted fr ...
(1850–64) to the early twentieth century was marked by continual waves of immigration by Zhuang/Nùng peoples from China into Vietnam. These waves were a result of the continuous drought of Guangxi which made the thinly occupied lands of northern Vietnam an attractive alternative habitation. The immigration process was generally a peaceful one as the Nùng purchased land from the "Tho" owners. The Nùng were superior to the Tho in cultivating wet rice and transformed poor lands, facilitating later migrations into adjoining areas. The repeated violent incursions of the Taiping era and the Black Flag occupation accelerated the outflow of Tho as the bands from China were largely Zhuang who favored the Nùng at the expense of the Tho. The Tho who remained became alienated from the Vietnamese government which could not offer protection and became clients of the Chinese and the Nùng.
Colonialism
Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen (; also known by several other names; 12 November 1866 – 12 March 1925)Singtao daily. Saturday edition. 23 October 2010. section A18. Sun Yat-sen Xinhai revolution 100th anniversary edition . was a Chinese politician who serve ...
wished to raise fighters in the region, he could recruit them from Nùng villages such as Na Cen and Na Mo, both on the Vietnamese side of the border. The French colonists saw this Nùng predominance as a threat, and found it convenient at that time to re-assert the primacy of the Vietnamese administrative system in the region. The French colonizers of the Tonkin Protectorate also saw the Nùng as potential converts to the colonial order and portrayed them as oppressed minorities who had suffered under Chinese and Viet rule. According to a 1908 military dispatch by Commandant LeBlond, they had been "subjugated and held ransom during many long centuries, sometimes by the one, sometimes by the other, the ùngrace has become flexible and is frequently able to ascertain the stronger eighbor to which it would turn instinctively. French domination appears soft to him and benevolent, compared with that of Annamites or the Chinese." During the Cần Vương movement
The Cần Vương (, Hán tự: , ) movement was a large-scale Vietnamese insurgency between 1885 and 1889 against French colonial rule. Its objective was to expel the French and install the Hàm Nghi Emperor as the leader of an independent V ...
to restore Viet independence, the Nùng showed little interest in supporting the lowland Kinh Viets against the French. Some of the upland peoples supported the Black Flag Army
The Black Flag Army (; , chữ Nôm: 軍旗𬹙) was a splinter remnant of a bandit group recruited largely from soldiers of ethnic Zhuang background, who crossed the border in 1865 from Guangxi, China into northern Vietnam, then during the Nguy ...
who fought against the French, while others sided with the French.
The French, however, perhaps having less choice, tended to support the Tho and other minorities, often undifferentiated as "Man" in their reports—usually a reference to Yao—as a counterweight against the Nùng. In 1908, for example, following an incident in which Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen (; also known by several other names; 12 November 1866 – 12 March 1925)Singtao daily. Saturday edition. 23 October 2010. section A18. Sun Yat-sen Xinhai revolution 100th anniversary edition . was a Chinese politician who serve ...
's mercenary Nùng warriors had killed several French officers, the French offered a bounty of eight dollars for each head brought in by the "Man". The bounty was paid 150 times.
When the Indochinese Communist Party
The Indochinese Communist Party (ICP), km, បក្សកុម្មុយនីស្តឥណ្ឌូចិន, lo, ອິນດູຈີນພັກກອມມູນິດ, zh, t=印度支那共產黨 was a political party which was t ...
was founded in 1930, its policy suggested upland peoples and minorities should be given full autonomy once the French colonial order was overthrown, however such policy was given little attention until 1941 when support from these communities became a strategic necessity. The Nùng assisted Ho Chi Minh
(: ; born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), commonly known as ('Uncle Hồ'), also known as ('President Hồ'), (' Old father of the people') and by other aliases, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and statesman. He served as Prime ...
in his activities. As a result of anti-French activities, temples of Nùng Trí Cao were destroyed. The French had more success with the Tai Dón people
White Tai (in Tai Dón, ꪼꪕꪒꪮꪙꫀ, ; in Thai language and Lao language Tai Khao; in Vietnamese language Tai Dón or Thái Trắng, in Chinese language Dai Duan) is an ethnic group of Laos, Vietnam and China. In Vietnam they are called ...
along the Lao-border, who established a regime known as Sip Song Chau Tai
The Sip Song Chau TaiOther spellings include: Sip Song Chau Thai, Sipsong Chuthai, Sipsong Chu Tai, Sip Song Chu Tai, Sipsongchuthai, Sip Song Chu Thai, Sipsong Chau Tai, Sip Song Chao Thai, Sipsong Chao Tai, Sipsongchutai, Sipsong Chao Thai. ("Tw ...
(''French:'' Pays Taï) under the control of collaborator Đèo Văn Long. When war broke out in 1946, groups of Thai, H’mong and Muong in the northwest sided with the French and against the Vietnamese and even provided battalions to fight with the French troops. But The Nùng and Tày supported the Viet Minh
The Việt Minh (; abbreviated from , chữ Nôm and Hán tự: ; french: Ligue pour l'indépendance du Viêt Nam, ) was a national independence coalition formed at Pác Bó by Hồ Chí Minh on 19 May 1941. Also known as the Việt Minh Fro ...
and provided the Vietnamese leader, Ho Chi Minh
(: ; born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), commonly known as ('Uncle Hồ'), also known as ('President Hồ'), (' Old father of the people') and by other aliases, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and statesman. He served as Prime ...
, with a safe base for his guerrilla armies. After defeating the French at Dien Bien Phu in 1954, the Viet Minh tried to win the allegiance of all of the northern ethnic minorities by creating two autonomous zones, Thai–Meo Autonomous Zone and Viet Bac Autonomous Zone respectively, allowing limited self-government within a “unified multi-national state”. During the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
, many Nùng fought alongside the North Vietnamese Army (NVA).
In 1954, several thousand Nùng Phàn Slình came to South Vietnam as refugees and settled in Lâm Đồng Province Lâm is a Vietnamese surname. The name is transliterated as Lin in Chinese and Im in Korean.
Lam is the anglicized variation of the surname Lâm.
Lam is also a commonly held surname of Cantonese speakers of Chinese descent. Large populations in ...
Nationalism
During theVietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
, Nùng villages in the Việt Bắc region received very little damage and avoided the devastation of upland communities in the Central Highlands. Although the Democratic Republic of Vietnam
North Vietnam, officially the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV; vi, Việt Nam Dân chủ Cộng hòa), was a socialist state supported by the Soviet Union (USSR) and the People's Republic of China (PRC) in Southeast Asia that existed f ...
supervised state-sponsored migration to upland areas, the north did not experience a massive influx of Kinh Viets, so the ethnic balance around the Nùng Trí Cao temples remained fairly consistent. However the Viet Bac Autonomous Zone in which the Nùng and Tày were most numerous was revoked by Lê Duẩn
Lê Duẩn (; 7 April 1907 – 10 July 1986) was a Vietnamese communist politician. He rose in the party hierarchy in the late 1950s and became General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam (VCP) at the 3rd Nat ...
and the government pursued a policy of forced assimilation of minorities into Vietnamese culture. All education was conducted in the Vietnamese language, traditional customs were discouraged or outlawed, and minority people were moved from their villages into government settlements. At the same time the government created ''“ New Economic Zones”'' along the Chinese border and in the Central Highlands. Frequently this involved taking the best land in order to resettle thousands of people from the overcrowded lowlands. As tension arose between Vietnam and China in 1975, Hanoi feared the loyalty of the Nùng and the Chinese-Vietnamese. After the Sino-Vietnamese War
The Sino-Vietnamese War (also known by #Names, other names) was a border war fought between China and Vietnam in early 1979. China launched an offensive in response to Vietnam's Cambodian–Vietnamese War, actions against the Khmer Rouge in 1 ...
, support for Nùng Trí Cao could be read as anti-Chinese, as he was mainly seen as a rebel against Chinese authority. Even so, during the 1980s, an estimated 250,000 ethnic Vietnamese were settled in the mountainous regions along the Chinese border, leading to a shortage of food in the region and much suffering.
Five temples dedicated to Nùng Trí Cao remained active into the 20th century. The keepers of the Kỳ Sầm Temple all bear the surname Nùng. Although a romanized script has been created for the Nùng language, worshipers of the temple prefer Chinese, similar to the Zhuang in China, and sometimes Vietnamese. In the 1990s, the '' Doi Moi program'' shifted the policy of ethnic affairs towards liberalization and preservation. Part of this was the appeal of creating tourist attractions and revenue. The Kỳ Sầm Temple was renovated sometime prior to 2001 to portray a more nationalistic image. The exterior and interior pillars of the temple have been retouched and the Chinese-character inscriptions at the front and Quốc ngữ inscriptions on the walls have been removed. References to "King Nùng" who had "raised high the banner proclaiming independence" have been replaced with floral patterns and pictures of horses, generic symbols associated with local heroes. A large sign indicates the temple as a historical landmark.
Culture
Economy
When the Nùng moved into Vietnam fromGuangxi
Guangxi (; ; Chinese postal romanization, alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the People's Republic ...
during the 12th and 13th centuries, they developed slash-and-burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a farming method that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. The downed vegeta ...
agriculture and worked on terraced hillsides, tending rice paddies
A paddy field is a flooded field of arable land used for growing semiaquatic crops, most notably rice and taro. It originates from the Neolithic rice-farming cultures of the Yangtze River basin in southern China, associated with pre-Aust ...
and using water wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets ...
s for irrigation. The Nùng engage in similar forms of agriculture today, using their gardens to grow a variety of vegetables, corn, peanuts, and fruits such as tangerines, persimmons, anise and other spices, and bamboo as cash crops. Nùng material culture is similar to other highlanders. They live on higher elevation with houses built with clay on stilts near rivers to avoid flooding. Like the Tày, they are known for silversmithing
A silversmith is a metalworker who crafts objects from silver. The terms ''silversmith'' and ''goldsmith'' are not exactly synonyms as the techniques, training, history, and guilds are or were largely the same but the end product may vary grea ...
, weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal th ...
, basketry
Basket weaving (also basketry or basket making) is the process of weaving or sewing pliable materials into three-dimensional artifacts, such as baskets, mats, mesh bags or even furniture. Craftspeople and artists specialized in making baskets ...
, papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a speciali ...
, and embroidery
Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on c ...
. Indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', m ...
, which represents faithfulness, is a popular choice of color for clothing. Typical motifs for embroidery are the sun, flowers, and stars.
Customs
Nùng society is patrilineal and grouped into clans denoted by the region in China they came from. In the past, men could marry outside the clan but women could only marry within the clan, however this practice has declined in the present day. Men could have multiple wives.Language
The Nùng language is part of theTai language family
The Tai or Zhuang–Tai languages ( th, ภาษาไท or , ISO 11940, transliteration: or ) are a branch of the Kra–Dai languages, Kra–Dai language family. The Tai languages include the most widely spoken of the Tai–Kadai languages, ...
. Its written script was developed around the 17th century. It is close to the Zhuang language
The Zhuang languages (; autonym: , pre-1982: , Sawndip: 話僮, from ''vah'', 'language' and ''Cuengh'', 'Zhuang'; ) are any of more than a dozen Tai languages spoken by the Zhuang people of Southern China in the province of Guangxi and adjac ...
.
Religion
Many Nùng practice anindigenous religion
Indigenous religions is a category used in the study of religion to demarcate the religious belief systems of communities described as being "indigenous". This category is often juxtaposed against others such as the "world religions" and "new re ...
with animistic
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, hum ...
, totemic
A totem (from oj, ᑑᑌᒼ, italics=no or ''doodem'') is a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people, such as a family, clan, lineage, or tribe, such as in the Anishinaabe clan system.
While ''the wo ...
and shamanic
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiri ...
features similarly to other Tai ethnic groups. In addition, Nùng religious practices are heavily invluenced by Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
and Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
. The Nùng worship Quan Âm (Guanyin
Guanyin () is a Bodhisattva associated with compassion. She is the East Asian representation of Avalokiteśvara ( sa, अवलोकितेश्वर) and has been adopted by other Eastern religions, including Chinese folk religion. She ...
) as the goddess of compassion and kindness.
Local religious services are led by a village shaman who oversees animal sacrifices and communication with the spiritual world. Nature spirits are known as the ''phi'' in Nùng cosmology. Ancestor worship is also practiced.
Notable people
* Chu Văn Tấn, a general of North Vietnam * Kim Đồng, fighter of theAugust Revolution
The August Revolution ( vi, Cách-mạng tháng Tám), also known as the August General Uprising (), was a revolution launched by the Việt Minh (League for the Independence of Vietnam) against the Empire of Vietnam and the Empire of Japan in ...
in 1945.
* Nong Quanfu
Nong Quanfu (, za, Nungz Cienzfuk; ?-1039), also recorded as Nùng Tồn Phúc ( vi, Nùng Tồn Phúc; ; Chữ Hán: ) was a Nùng/ Zhuang chieftain and zhou-level official of Guangyuan located in the modern-day Cao Bang in the 11th century AD ...
, a Nùng chieftain
* Nong Zhigao
Nong Zhigao (modern Zhuang language: ; , vi, Nùng Trí Cao, links=no) (1025–1055?) is a hero admired by the Nùng people of Vietnam, and Zhuang people, Zhuang people of China. His father Nong Quanfu was head of the local Zhuang people in Gu ...
, a Nùng chieftain
See also
*Zhuang people
The Zhuang (; ; za, Bouxcuengh, italic=yes; ) are a Tai-speaking ethnic group who mostly live in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region in Southern China. Some also live in the Yunnan, Guangdong, Guizhou, and Hunan provinces. They form one of ...
*Tay people
Tay may refer to:
People and languages
* Tay (name), including lists of people with the given name, surname and nickname
* Tay people, an ethnic group of Vietnam
** Tày language
*Atayal language, an Austronesian language spoken in Taiwan (ISO 63 ...
*Yue (state)
Yue (, Old Chinese: ''*''), also known as Yuyue (), was a state in ancient China which existed during the first millennium BC the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods of China's Zhou dynasty in the modern provinces of Zhejiang, Sha ...
*Wu (state)
Wu (; Old Chinese: ''*'') was one of the states during the Western Zhou dynasty and the Spring and Autumn period. It was also known as Gouwu ( /''*''/) or Gongwu ( /''*''/) from the pronunciation of the local language.
Wu was located at the ...
*Chu (state)
Chu, or Ch'u in Wade–Giles romanization, (, Hanyu Pinyin: Chǔ, Old Chinese: ''*s-r̥aʔ'') was a Zhou dynasty vassal state. Their first ruler was King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE. Chu was located in the south of the Zhou he ...
* Tai-Kadai languages
*Tai languages
The Tai or Zhuang–Tai languages ( th, ภาษาไท or , transliteration: or ) are a branch of the Kra–Dai language family. The Tai languages include the most widely spoken of the Tai–Kadai languages, including Standard Thai or Sia ...
* Xi'ou
* Luoyue
*Baiyue
The Baiyue (, ), Hundred Yue, or simply Yue (; ), were various ethnic groups who inhabited the regions of East China, South China and Northern Vietnam during the 1st millennium BC and 1st millennium AD. They were known for their short hair, ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * *Bibliography
* * * * * *Further reading
* Đoàn, Thiện Thuật. ''Tay-Nùng Language in the North Vietnam''. okyo? Instttute icfor the Study of Languages and Cultures of Asia and Africa, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies, 1996.External links
Nùng People in Vietnam
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nung People Ethnic groups in Vietnam Tai peoples