Niobium Capacitor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A niobium electrolytic capacitor (historically also ''Columbium capacitor'') is an electrolytic capacitor whose
A niobium electrolytic capacitor (historically also ''Columbium capacitor'') is an electrolytic capacitor whose
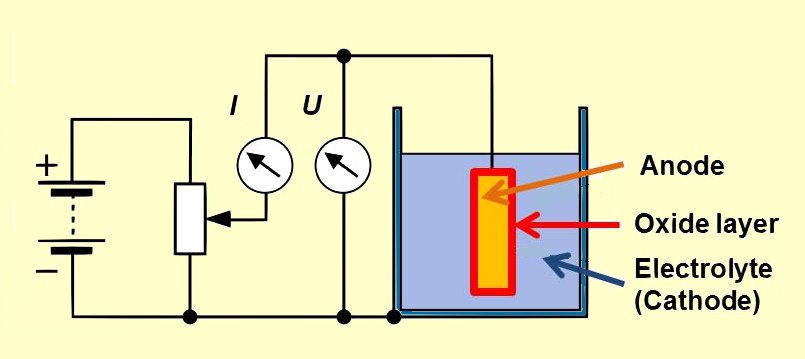 Niobium, similarly to tantalum and aluminum, is a so-called valve metal. Placing such a metal in contact with an
Niobium, similarly to tantalum and aluminum, is a so-called valve metal. Placing such a metal in contact with an  Every electrolytic capacitor can be thought of as a "plate capacitor" whose capacitance increases with the electrode area (A) and the dielectric
Every electrolytic capacitor can be thought of as a "plate capacitor" whose capacitance increases with the electrode area (A) and the dielectric
PDF
/ref> This very thin dielectric layer, combined with a sufficiently high dielectric strength, allows niobium electrolytic capacitors to achieve a high volumetric capacitance comparable to tantalum capacitors. The niobium anode material is manufactured from a powder sintered into a pellet with a rough surface structure intended to increase the electrode surface area A compared to a smooth surface with the same footprint. This increase in surface area can increase the capacitance by a factor of up to 200 for solid niobium electrolytic capacitors, depending on the rated voltage. The properties of the niobium pentoxide dielectric layer, compared with a tantalum pentoxide layer, are given in the following table:T. Kárník, AVX, Niobium oxide for capacitor manufacturing, Metal 2008, 2008-05-13 – 2008-05-15
PDF
/ref> The higher permittivity and lower breakdown voltage of niobium pentoxide relative to tantalum pentoxide results in niobium capacitors and tantalum capacitors having similar sizes for a given capacitance.
File:Niobium sintered pellet.png, The capacitor cell of a niobium electrolytic capacitor consist out of sintered niobium or niobium monoxide powder
File:Niobium sintered slug.png, Schematic representation of the structure of a sintered niobium electrolytic capacitor with solid electrolyte and the cathode contacting layers
File:Niobium-SMD-Chip.png, Construction of a typical SMD niobium electrolytic chip capacitor with solid electrolyte
A typical niobium capacitor is a chip capacitor and consists of niobium or
PDF
 A niobium electrolytic capacitor (historically also ''Columbium capacitor'') is an electrolytic capacitor whose
A niobium electrolytic capacitor (historically also ''Columbium capacitor'') is an electrolytic capacitor whose anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic ...
(+) is made of passivated niobium metal or niobium monoxide, on which an insulating niobium pentoxide
Niobium pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2 O5. A colorless, insoluble, and fairly unreactive solid, it is the most widespread precursor for other compounds and materials containing niobium. It is predominantly used in alloyi ...
layer acts as a dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
. A solid electrolyte on the surface of the oxide layer serves as the capacitor's cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in wh ...
(−).
Niobium capacitors are available in SMD packaging and compete with tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as ''tantalium'', it is named after Tantalus, a villain in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a very hard, ductile, lustrous, blue-gray transition metal that ...
chip capacitors in certain voltage and capacitance ratings. They are available with a solid manganese dioxide electrolyte.
Like most electrolytic capacitors, niobium capacitors are polarized components. Reverse voltages or ripple currents higher than specified tolerances can destroy the dielectric and thus the capacitor; the resulting short circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circui ...
can cause a fire or explosion in larger units.
Niobium capacitors were developed in the United States and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
in the 1960s. Since 2002 they have been commercially available in the West, taking advantage of the lower cost and better availability of niobium relative to tantalum.
Basic information
Niobium is a sister metal to tantalum. Niobium has a similar melting point (2744 °C) to tantalum and exhibits similar chemical properties. The materials and processes used to produce niobium-dielectric capacitors are essentially the same as for existing tantalum-dielectric capacitors. However, niobium as a raw material is much more abundant in nature than tantalum and is less expensive. The characteristics of niobium electrolytic capacitors and tantalum electrolytic capacitors are roughly comparable. Niobium electrolytic capacitors can be made with high purity niobium as the anode but the diffusion of oxygen from the dielectric (Nb2O5) into the niobium anode metal is very high, resulting in leakage current instability or even capacitor failures. There are two possible ways to reduce oxygen diffusion and improve leakage current stability – either by doping metallic niobium powders with nitride into passivated niobium nitride or usingniobium oxide Niobium oxide, sometimes called columbium oxide, may refer to:
* Niobium monoxide (niobium(II) oxide), NbO
* Niobium dioxide (niobium(IV) oxide), NbO2
* Niobium pentoxide (niobium(V) oxide), Nb2O5
In addition to the above, other distinct oxides ...
(NbO) as anode material. Niobium oxide is a hard ceramic material characterized by high metallic conductivity. Niobium oxide powder can be prepared in a similar structure to that of tantalum powder and can be processed in a similar way to produce capacitors. It also can be oxidized by anodic oxidation (anodizing
Anodizing is an electrolytic passivation process used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metal parts.
The process is called ''anodizing'' because the part to be treated forms the anode electrode of an electr ...
, forming) to generate the insulating dielectric layer. Thus two types of niobium electrolytic capacitors are marketed, those using a passivated niobium anode and those using a niobium oxide anode. Both types use niobium pentoxide
Niobium pentoxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Nb2 O5. A colorless, insoluble, and fairly unreactive solid, it is the most widespread precursor for other compounds and materials containing niobium. It is predominantly used in alloyi ...
(Nb2O5) as the dielectric layer.
Anodic oxidation
 Niobium, similarly to tantalum and aluminum, is a so-called valve metal. Placing such a metal in contact with an
Niobium, similarly to tantalum and aluminum, is a so-called valve metal. Placing such a metal in contact with an electrolytic
An electrolyte is a medium containing ions that is electrically conducting through the movement of those ions, but not conducting electrons. This includes most soluble salts, acids, and bases dissolved in a polar solvent, such as water. Upon di ...
bath and applying a positive voltage to it forms a layer of electrically insulating oxide whose thickness corresponds to the applied voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to ...
. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
in an electrolytic capacitor.
This property of niobium was known since the beginning of the 20th century. Although niobium is more abundant in nature and less expensive than tantalum, its high melting point of 2744 °C hindered the development of niobium electrolytic capacitors.
In the 1960s, the higher availability of niobium ore compared with tantalum ore prompted research into niobium electrolytic capacitors in the Soviet Union. Here they served the same purpose as tantalum capacitors in the West. With the collapse of the Iron Curtain, the technology became better-known in the West, with major capacitor manufacturers taking interest in the late 1990s. The materials and processes used to produce niobium capacitors are essentially the same as for tantalum capacitors. Rising tantalum prices in 2000 and 2001 encouraged the development of niobium electrolytic capacitors with manganese dioxide and polymer electrolytes, which have been available since 2002.
permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter ''ε'' (epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in ...
(ε), and decreases with the dielectric thickness (d).
:
The dielectric thickness of niobium electrolytic capacitors is very thin, in the range of nanometers per volt.J. Moore, Kemet, Nb capacitors compared to Ta capacitors a less costly alternativ/ref> This very thin dielectric layer, combined with a sufficiently high dielectric strength, allows niobium electrolytic capacitors to achieve a high volumetric capacitance comparable to tantalum capacitors. The niobium anode material is manufactured from a powder sintered into a pellet with a rough surface structure intended to increase the electrode surface area A compared to a smooth surface with the same footprint. This increase in surface area can increase the capacitance by a factor of up to 200 for solid niobium electrolytic capacitors, depending on the rated voltage. The properties of the niobium pentoxide dielectric layer, compared with a tantalum pentoxide layer, are given in the following table:T. Kárník, AVX, Niobium oxide for capacitor manufacturing, Metal 2008, 2008-05-13 – 2008-05-15
/ref> The higher permittivity and lower breakdown voltage of niobium pentoxide relative to tantalum pentoxide results in niobium capacitors and tantalum capacitors having similar sizes for a given capacitance.
Basic construction of solid niobium electrolytic capacitors
niobium oxide Niobium oxide, sometimes called columbium oxide, may refer to:
* Niobium monoxide (niobium(II) oxide), NbO
* Niobium dioxide (niobium(IV) oxide), NbO2
* Niobium pentoxide (niobium(V) oxide), Nb2O5
In addition to the above, other distinct oxides ...
powder pressed and sintered into a pellet as the anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic ...
of the capacitor, with the oxide layer of niobium
pentoxide as dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
, and a solid manganese dioxide electrolyte as the cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in wh ...
.
Comparison of niobium and tantalum electrolytic capacitor types
The combination of anode materials for niobium and tantalum electrolytic capacitors and the electrolytes used has formed a wide variety of capacitor types with different properties. An outline of the main characteristics of the different types is shown in the table below. Tantalum and niobium electrolytic capacitors with solid electrolyte as surface-mountable chip capacitors are mainly used in electronic devices in which little space is available or a low profile is required. They operate reliably over a wide temperature range without large parameter deviations.T. Zednicek, S. Sita, C. McCracken, W. A. Millman, J. Gill, AVX, Niobium Oxide Technology Roadmap, CARTS 200Comparison of electrical parameters of niobium and tantalum capacitor types
In order to compare the different characteristics of the different electrolytic chip capacitor types, specimens with the same dimensions and of comparable capacitance and voltage are compared in the following table. In such a comparison the values for ESR and ripple current load are the most important parameters for the use of electrolytic capacitors in modern electronic equipment. The lower the ESR the higher the ripple current per volume, thus the better the functionality of the capacitor in the circuit. (1) 100 μF/10 V, unless otherwise specified, (2) calculated for a capacitor 100 μF/10 V,History
The phenomenon that can electrochemically form an oxide layer on aluminum and metals like tantalum or niobium, blocking an electric current in one direction but allowing it to flow in the other direction, was discovered in 1875 by the French researcherEugène Ducretet
Eugene is a common male given name that comes from the Greek language, Greek εὐγενής (''eugenēs''), "noble", literally "well-born", from εὖ (''eu''), "well" and γένος (''genos''), "race, stock, kin".Karol Pollak) used this phenomenon for an idea of an polarized "Electric liquid capacitor with aluminum electrodes". In 1896 Pollak obtained a patent for the first electrolytic capacitor.
The first tantalum electrolytic capacitors with wound tantalum foils and non-solid electrolyte were developed in 1930 by Tansitor Electronics Inc., USA, and used for military purposes.
The development of solid electrolyte tantalum capacitors began in the early 1950s as a miniaturized, more reliable low-voltage support capacitor to complement the newly invented
 Niobium electrolytic capacitors as discrete components are not ideal capacitors, they have losses and parasitic inductive parts. All properties can be defined and specified by a series equivalent circuit composed out of an idealized capacitance and additional electrical components which model all losses and inductive parameters of a capacitor. In this series-equivalent circuit the electrical characteristics are defined by:
* ''C'', the capacitance of the capacitor
* ''R''leakage, the resistance representing the
Niobium electrolytic capacitors as discrete components are not ideal capacitors, they have losses and parasitic inductive parts. All properties can be defined and specified by a series equivalent circuit composed out of an idealized capacitance and additional electrical components which model all losses and inductive parameters of a capacitor. In this series-equivalent circuit the electrical characteristics are defined by:
* ''C'', the capacitance of the capacitor
* ''R''leakage, the resistance representing the
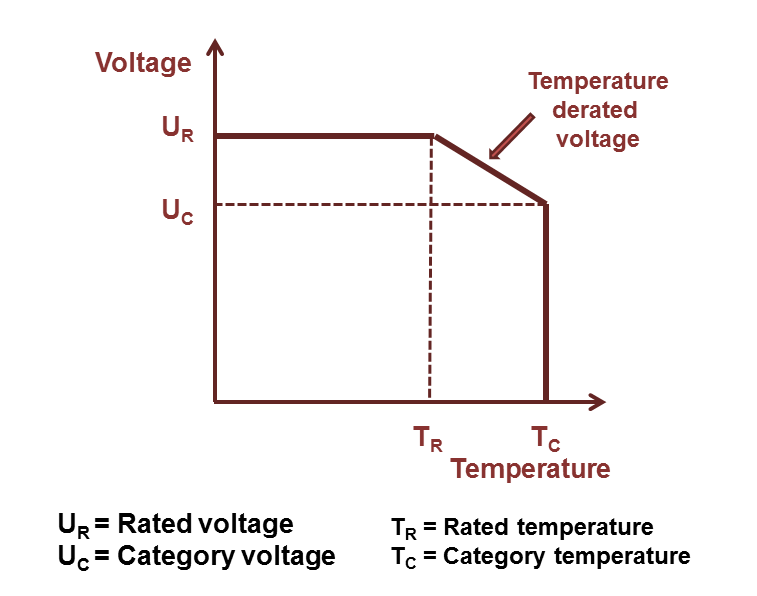 Referring to IEC/EN 60384-1 standard the allowed operating voltage for niobium capacitors is called "rated voltage UR " or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR (IEC/EN 60384-1).
The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture right (or above, on mobile devices).
Lower voltage applied may have positive influences for tantalum (and niobium) electrolytic capacitors. Lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.Ch. Reynolds, AVX, Technical Information, Reliability Management of Tantalum Capacitors
Referring to IEC/EN 60384-1 standard the allowed operating voltage for niobium capacitors is called "rated voltage UR " or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR (IEC/EN 60384-1).
The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture right (or above, on mobile devices).
Lower voltage applied may have positive influences for tantalum (and niobium) electrolytic capacitors. Lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.Ch. Reynolds, AVX, Technical Information, Reliability Management of Tantalum Capacitors
PDF
Applying a higher voltage than specified may destroy electrolytic capacitors.
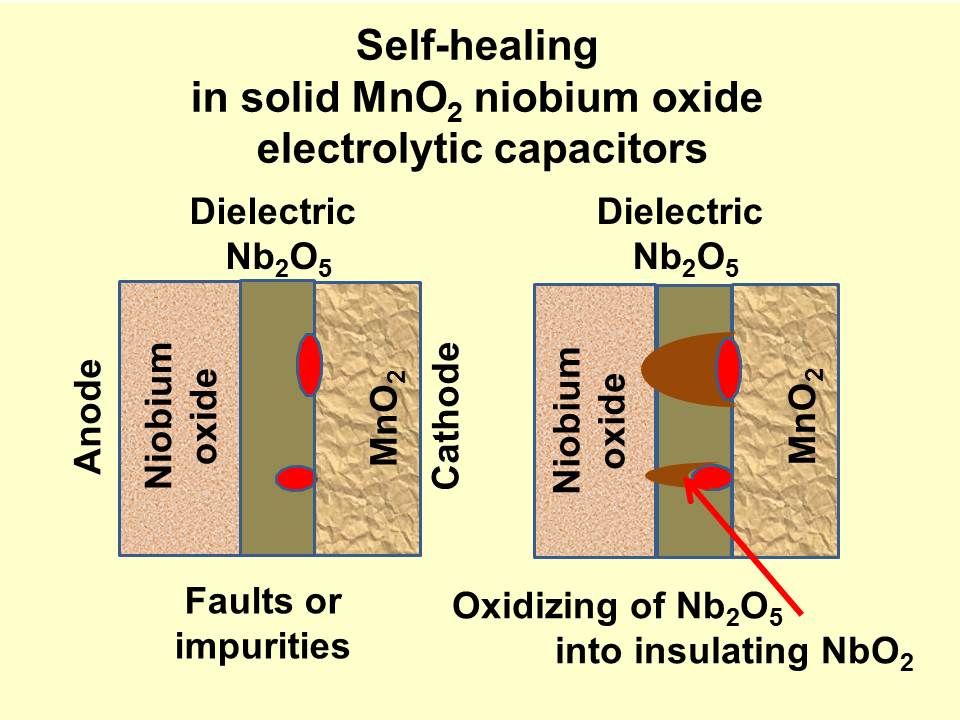 A rare failure in solid electrolytic capacitors is breakdown of the dielectric caused by faults or impurities. In niobium electrolytic capacitors the dielectric is niobium pentoxide (Nb2O5). Besides this pentoxide there is an additional niobium suboxide,
A rare failure in solid electrolytic capacitors is breakdown of the dielectric caused by faults or impurities. In niobium electrolytic capacitors the dielectric is niobium pentoxide (Nb2O5). Besides this pentoxide there is an additional niobium suboxide,
 Niobium capacitors are in general polarized components, with distinctly marked positive terminals. When subjected to reversed polarity (even briefly), the capacitor depolarizes and the dielectric oxide layer breaks down, which can cause it to fail even when later operated with correct polarity. If the failure is a short circuit (the most common occurrence), and current is not limited to a safe value, catastrophic thermal runaway may occur.
Niobium capacitors are in general polarized components, with distinctly marked positive terminals. When subjected to reversed polarity (even briefly), the capacitor depolarizes and the dielectric oxide layer breaks down, which can cause it to fail even when later operated with correct polarity. If the failure is a short circuit (the most common occurrence), and current is not limited to a safe value, catastrophic thermal runaway may occur.
G. Roos, Digi-Key, Niobium Capacitors Slow to Take Hold, 2012-11-20
/ref>
* D. Bach, Dissertation, 2009-06-05, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), EELS investigations of stoichiometric niobium oxides and niobium-based capacitor
* Ch. Schnitter: The taming of niobium. In: Bayer research, Bayer AG, 2004 (2007-02-11)
* Niobium Powder for Electrolytic Capacitor, JFE Technical Report No. 6 (October 2005
PDF
* Introduction to capacitor
Capacitors
transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
. The solution found by R. L. Taylor and H. E. Haring of the Bell Labs was based on experience with ceramics. They ground down tantalum to a powder, pressed this powder into a cylindrical form and then sintered the powder particles into a pellet ("slug") at high temperatures, between 1500 and 2000 °C, under vacuum conditions. These first sintered tantalum capacitors used a non-solid electrolyte not consistent with the concept of solid state electronics. 1952 a targeted search in the Bell Labs for a solid electrolyte by D. A. McLean and F. S. Power led to the invention of manganese dioxide as a solid electrolyte for a sintered tantalum capacitor.
Electrical characteristics
Series-equivalent circuit
leakage current
In electronics, leakage is the gradual transfer of electrical energy across a boundary normally viewed as insulating, such as the spontaneous discharge of a charged capacitor, magnetic coupling of a transformer with other components, or flow of cu ...
of the capacitor
* ''R''ESR, the equivalent series resistance
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series w ...
which summarizes all ohmic losses of the capacitor, usually abbreviated as "ESR"
* ''L''ESL, the equivalent series inductance
Equivalent series inductance (ESL) is an effective inductance that is used to describe the inductive part of the impedance of certain electrical components.
Overview
The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors and resistors tends to ...
which is the effective self-inductance of the capacitor, usually abbreviated as "ESL".
Using a series equivalent circuit instead of a parallel equivalent circuit is specified by IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; in French: ''Commission électrotechnique internationale'') is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and r ...
/EN 60384-1.
Capacitance standard values and tolerances
The electrical characteristics of niobium electrolytic capacitors depend on structure of the anode and the type of electrolyte. The capacitance value of the capacitor depends on measuring frequency and temperature. The rated capacitance value or nominal value is specified in the data sheets of the manufacturers and is symbolized CR CN. The standardized measuring condition for electrolytic capacitors is an AC measuring method with a frequency of 100/120 Hz. The AC measuring voltage shall not exceed 0,5 V AC- RMS. The percentage of allowed deviation of the measured capacitance from the rated value is called capacitance tolerance. Electrolytic capacitors are available in different tolerance series, whose values are specified in theE series E series may refer to:
* BMC E-series engine, a series of automobile engines
* Electronic E series of preferred numbers, a series of preferred values for electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, zener diodes
* Entwicklung seri ...
specified in IEC 60063. For abbreviated marking in tight spaces, a letter code for each tolerance is specified in IEC 60062.
* rated capacitance, E3 series, tolerance ±20%, letter code "M"
* rated capacitance, E6 series, tolerance ±20%, letter code "M"
* rated capacitance, E12 series, tolerance ±10%, letter code "K"
Rated and category voltage
 Referring to IEC/EN 60384-1 standard the allowed operating voltage for niobium capacitors is called "rated voltage UR " or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR (IEC/EN 60384-1).
The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture right (or above, on mobile devices).
Lower voltage applied may have positive influences for tantalum (and niobium) electrolytic capacitors. Lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.Ch. Reynolds, AVX, Technical Information, Reliability Management of Tantalum Capacitors
Referring to IEC/EN 60384-1 standard the allowed operating voltage for niobium capacitors is called "rated voltage UR " or "nominal voltage UN". The rated voltage UR is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously at any temperature within the rated temperature range TR (IEC/EN 60384-1).
The voltage proof of electrolytic capacitors decreases with increasing temperature. For some applications it is important to use a higher temperature range. Lowering the voltage applied at a higher temperature maintains safety margins. For some capacitor types therefore the IEC standard specifies a "temperature derated voltage" for a higher temperature, the "category voltage UC". The category voltage is the maximum DC voltage or peak pulse voltage that may be applied continuously to a capacitor at any temperature within the category temperature range TC. The relation between both voltages and temperatures is given in the picture right (or above, on mobile devices).
Lower voltage applied may have positive influences for tantalum (and niobium) electrolytic capacitors. Lowering the voltage applied increases the reliability and reduces the expected failure rate.Ch. Reynolds, AVX, Technical Information, Reliability Management of Tantalum CapacitorsApplying a higher voltage than specified may destroy electrolytic capacitors.
Surge Voltage
The surge voltage indicates the maximum peak voltage value that may be applied to electrolytic capacitors during their application for a limited number of cycles. The surge voltage is standardized in IEC/EN 60384-1. For niobium electrolytic capacitors the surge voltage shall be not higher than round 1.3 times of the rated voltage, rounded off to the nearest volt. The surge voltage applied to niobium capacitors may influence the capacitors failure rate.Reverse voltage
Like other electrolytic capacitors, niobium electrolytic capacitors are polarized and require the anode electrode voltage to be positive relative to the cathode voltage.Impedance, ESR and dissipation factor, ripple current , leakage current
General information to impedance, ESR, dissipation factor tan δ, ripple current, and leakage current see electrolytic capacitorReliability and life time
For general information on reliability and failure rate see electrolytic capacitor. The life time,service life
A product's service life is its period of use in service. Several related terms describe more precisely a product's life, from the point of manufacture, storage, and distribution, and eventual use.
Service life has been defined as "a product li ...
, load life or useful life of electrolytic capacitors is a special characteristic of non-solid electrolytic capacitors, especially non-solid aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Their liquid electrolyte can evaporate over time, leading to wear-out failures. Solid niobium capacitors with manganese dioxide electrolyte have no wear-out mechanism, so the constant failure rate lasts up to the point when all capacitors have failed. They don't have a life time specification like non-solid aluminum electrolytic capacitors.
However, solid polymer niobium electrolytic capacitors do have a life time specification. The electrolyte deteriorates by a thermal degradation mechanism of the conductive polymer. The electrical conductivity decreases, as a function of time, in agreement with a granular structure, in which aging is due to the shrinking of the conductive polymer grains. The life time of polymer electrolytic capacitors is specified in similar terms like non-solid e-caps but its life time calculation follows other rules leading to much longer operational life times.
Failure modes, self-healing mechanism and application rules
The different types of electrolytic capacitors show different behaviors in long-term stability, inherent failure modes and their self-healing mechanisms. Application rules for types with an inherent failure mode are specified to ensure capacitors high reliability and long life. A rare failure in solid electrolytic capacitors is breakdown of the dielectric caused by faults or impurities. In niobium electrolytic capacitors the dielectric is niobium pentoxide (Nb2O5). Besides this pentoxide there is an additional niobium suboxide,
A rare failure in solid electrolytic capacitors is breakdown of the dielectric caused by faults or impurities. In niobium electrolytic capacitors the dielectric is niobium pentoxide (Nb2O5). Besides this pentoxide there is an additional niobium suboxide, niobium dioxide
Niobium dioxide, is the chemical compound with the formula NbO2. It is a bluish-black non-stoichiometric solid with a composition range of NbO1.94-NbO2.09. It can be prepared by reducing Nb2O5 with H2 at 800–1350 °C. An alternative method ...
(NbO2). The NbO2 is a semi-conducting material with a higher conductivity than Nb2O5 but much lower than a short. In case of faults or impurities in the dielectric which evokes a partial dielectric breakdown the conducting channel would be effectively isolated by reduction of Nb2O5 into high ohmic NbO2 if energy is limited.
As more energy is applied to a faulty solid niobium eventually either the high ohmic NbO2 channel or the Nb2O5 dielectric breaks down and the capacitor exhibits a thermal runaway failure. In comparison to solid tantalum capacitors the thermal runaway of niobium anodes will occur at about three times higher power than of tantalum anodes. This gives a significant reduction (95%) of the ignition failure mode compared to solid tantalum capacitors.
The dielectric layer Nb2O5 of solid niobium electrolytic capacitors has a lower breakdown voltage proof than Ta2O5 in tantalum capacitors and therefore grows thicker per applied volt and so operates at lower field strength for a given voltage rating with the lower electrical stress the dielectric. In combination with niobium oxide anodes, which are more stable against oxygen diffusion that results in lower voltage derating rules compared with passivated niobium or tantalum anodes.
Additional information
Capacitor symbols
Electrolytic capacitor symbolsPolarity marking
 Niobium capacitors are in general polarized components, with distinctly marked positive terminals. When subjected to reversed polarity (even briefly), the capacitor depolarizes and the dielectric oxide layer breaks down, which can cause it to fail even when later operated with correct polarity. If the failure is a short circuit (the most common occurrence), and current is not limited to a safe value, catastrophic thermal runaway may occur.
Niobium capacitors are in general polarized components, with distinctly marked positive terminals. When subjected to reversed polarity (even briefly), the capacitor depolarizes and the dielectric oxide layer breaks down, which can cause it to fail even when later operated with correct polarity. If the failure is a short circuit (the most common occurrence), and current is not limited to a safe value, catastrophic thermal runaway may occur.
Standardization
The standardization for allelectrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
, electronic
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor
* ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device
*Electronic co ...
components and related technologies follows the rules given by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), a non-profit
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ...
, non-governmental international standards organization
A standards organization, standards body, standards developing organization (SDO), or standards setting organization (SSO) is an organization whose primary function is developing, coordinating, promulgating, revising, amending, reissuing, interpr ...
. The definition of the characteristics and the procedure of the test methods for capacitors for use in electronic equipment are set out in the generic specification:
* IEC 60384-1, Fixed capacitors for use in electronic equipment - Part 1: Generic specification
Until now (2014) no IEC detail specification for niobium electrolytic capacitors is available.
For electronics manufacturers in the United States the EIA Eia or EIA may refer to:
Medicine
* Enzyme immunoassay
* Equine infectious anemia
* Exercise-induced anaphylaxis
* Exercise-induced asthma
* External iliac artery
Transport
* Edmonton International Airport, in Alberta, Canada
* Erbil Internation ...
publish a standard for niobium and tantalum chip capacitors:
* EIA-717-A Surface Mount Niobium and Tantalum Capacitor Qualification Specification
Features
* Niobium capacitors serve as a replacement for tantalum capacitors * Niobium capacitors are available in SMD style, that makes them suitable for all portable electronic systems with flat design * Niobium capacitors have no inrush current limitation * Niobium capacitors are available with solid electrolyte for low ESR applications and stable electrical parameters * Niobium capacitors have a limited number of manufacturers (AVX and Vishay)/ref>
See also
*Types of capacitor
Capacitors are manufactured in many styles, forms, dimensions, and from a large variety of materials. They all contain at least two electrical conductors, called ''plates'', separated by an insulating layer ('' dielectric''). Capacitors are wi ...
References
Further reading
* R. P. Deshpande, Capacitors: Technology and Trends, {{ISBN, 1-25900731-6}* D. Bach, Dissertation, 2009-06-05, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), EELS investigations of stoichiometric niobium oxides and niobium-based capacitor
* Ch. Schnitter: The taming of niobium. In: Bayer research, Bayer AG, 2004 (2007-02-11)
* Niobium Powder for Electrolytic Capacitor, JFE Technical Report No. 6 (October 2005
* Introduction to capacitor
Capacitors