
Tesla Autopilot is a suite of
advanced driver-assistance system
An advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS) is any of a groups of electronic technologies that assist drivers in driving and parking functions. Through a safe human-machine interface, ADAS increase car and road safety. ADAS uses automated technol ...
(ADAS) features offered by
Tesla that amounts to
SAE International
SAE International, formerly named the Society of Automotive Engineers, is a United States-based, globally active professional association and standards developing organization for engineering professionals in various industries. SAE Internatio ...
Level 2 vehicle automation. Its features are
lane centering
In road-transport terminology, lane centering, also known as auto steer or autosteer, is an advanced driver-assistance system that keeps a road vehicle centered in the lane, relieving the driver of the task of steering. Lane centering is simil ...
,
traffic-aware cruise control, automatic lane changes, semi-autonomous navigation on limited access freeways,
self-parking, and the ability to summon the car from a garage or parking spot. With all of these features, the driver is responsible and the car requires constant supervision. The company claims the features reduce accidents caused by driver negligence and fatigue from long-term driving.
In October 2020,
Consumer Reports called Tesla Autopilot "a distant second" in driver assistance systems (behind
Cadillac's Super Cruise), although it was ranked first in the "Capabilities and Performance" and "Ease of Use" category.
Collisions and deaths involving Tesla cars with Autopilot engaged have drawn the attention of the press and government agencies. In late 2022, a class action suit was filed against Tesla for defrauding customers regarding Autopilot and Full Self-Driving.

As an upgrade to the capabilities of Autopilot, the company's stated intent is to offer full autonomous driving (SAE
Level 5) at a future time, acknowledging that technical and regulatory hurdles must be overcome to achieve this goal.
From 2016 through 2022,
Elon Musk
Elon Reeve Musk ( ; born June 28, 1971) is a business magnate and investor. He is the founder, CEO and chief engineer of SpaceX; angel investor, CEO and product architect of Tesla, Inc.; owner and CEO of Twitter, Inc.; founder of The ...
, Tesla’s CEO, has repeatedly made inaccurate predictions as to when Tesla would be able to achieve Level 5 autonomy. In 2019, some experts criticized Tesla vehicles' lack of
lidar, which is used by other companies working on autonomous driving.
In October 2020, Tesla started a Full Self-Driving (FSD) capability
program in the United States;
, Tesla has over 100,000 people in this program.
Some industry observers criticized Tesla's decision to use untrained consumers to validate the beta software as dangerous and irresponsible.
History
Elon Musk
Elon Reeve Musk ( ; born June 28, 1971) is a business magnate and investor. He is the founder, CEO and chief engineer of SpaceX; angel investor, CEO and product architect of Tesla, Inc.; owner and CEO of Twitter, Inc.; founder of The ...
first discussed the Tesla Autopilot system publicly in 2013, noting that "Autopilot is a good thing to have in planes, and we should have it in cars." Over the ensuing decade, Autopilot went through a series of hardware and software enhancements, gradually approaching the goal of full autonomy, which , remained a work in progress. Autopilot, as initially introduced in 2014, referred to
automatic parking and low-speed summoning on private property,
[ using sensor and computing hardware developed by Mobileye. By 2016, the Mobileye-based Autopilot had added ]automatic emergency braking
A collision avoidance system (CAS), also known as a pre-crash system, forward collision warning system, or collision mitigation system, is an advanced driver-assistance system designed to prevent or reduce the severity of a collision. In its ...
, adaptive cruise control
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is an available cruise control advanced driver-assistance system for road vehicles that automatically adjusts the vehicle speed to maintain a safe distance from vehicles ahead. As of 2019, it is also called by 20 un ...
, and lane centering
In road-transport terminology, lane centering, also known as auto steer or autosteer, is an advanced driver-assistance system that keeps a road vehicle centered in the lane, relieving the driver of the task of steering. Lane centering is simil ...
capabilities when Tesla and Mobileye dissolved their partnership that July. Enhanced Autopilot (EA) was announced later in 2016 as an extra-cost option that used a new hardware suite developed by Tesla;[ FSD beta testing started in October 2020.
]
Hardware 1 and Autopilot (Mobileye)
In October 2014, Tesla offered customers the ability to pre-purchase Autopilotself-driving
A self-driving car, also known as an autonomous car, driver-less car, or robotic car (robo-car), is a car that is capable of traveling without human input.Xie, S.; Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Ding, Z.; Arvin, F.,Distributed Motion Planning for S ...
.Mobileye
Mobileye Global Inc. is a company developing autonomous driving technologies and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) including cameras, computer chips and software. Mobileye was acquired by Intel in 2017 and went public again in 2022. Mobi ...
, but Mobileye ended the partnership in July 2016 because Tesla "was pushing the envelope in terms of safety".
Tesla cars manufactured after September 2014 had the initial hardware ( hardware version 1 or HW1) that supported Autopilot. The first Autopilot software release came in October 2015 as part of Tesla software version 7.0. Version 7.1 removed some features to discourage risky driving.
Version 8.0 processed radar signals to create a point cloud
Point or points may refer to:
Places
* Point, Lewis, a peninsula in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Point, Texas, a city in Rains County, Texas, United States
* Point, the NE tip and a ferry terminal of Lismore, Inner Hebrides, Scotland
* Poin ...
similar to lidar to help navigate in low visibility. In November 2016, Autopilot 8.0 was updated to encourage drivers to grip the steering wheel.
Hardware 2 and Enhanced Autopilot
In October 2016, Autopilot sensors and computing hardware transitioned to hardware version 2 (HW2) for new cars, the upgraded hardware collectively was called Autopilot 2.0 to distinguish it from the original Autopilot/HW1 vehicles. At the time it was launched, Autopilot 2.0 vehicles with HW2 actually had fewer features than HW1 vehicles; for example, HW2 vehicles were unable to be summoned in 2016.
Tesla also used the term Enhanced Autopilot (EA) to refer to planned capabilities that would be coming to HW2 vehicles; the signature EA feature announced in December 2016 was "Navigate on Autopilot", which allows machine-controlled driving on controlled-access highways from on-ramp to off-ramp, including the abilities to change lanes without driver input, transition from one freeway to another, and exit.The Verge
''The Verge'' is an American technology news website operated by Vox Media, publishing news, feature stories, guidebooks, product reviews, consumer electronics news, and podcasts.
The website launched on November 1, 2011, and uses Vox Media ...
'' reporter Andrew J. Hawkins called the beta "Navigate on Autopilot" system "the feature that could give Tesla an edge as it grows from niche company to global powerhouse". As initially released, "Navigate on Autopilot" would suggest lane changes, but could not change lanes until the suggestion had been confirmed by the driver through the turn signal stalk.
In March 2019, Tesla transitioned to hardware version 3 (HW3) for new cars. Completely automated lane changes without requiring driver confirmation using "Navigate on Autopilot" were added as an option in an April software update, although '' Consumer Reports'' called it "far less competent" than a human driver. To comply with the new United Nations Economic Commission for Europe
The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (ECE or UNECE) is one of the five regional commissions under the jurisdiction of the United Nations Economic and Social Council. It was established in order to promote economic cooperation and i ...
regulation related to automatically commanded steering function, Tesla provided an updated Autopilot in May, limited to Europe. In September, Tesla released software version 10 to Early Access Program (EAP) testers, citing improvements in driving visualization and automatic lane changes.
Full Self-Driving options
A video to demonstrate Full Self-Driving, the system designed to extend automated driving to local roads, was released by Elon Musk in November 2016; the main interior camera was arranged to show the person in the driver's seat does not touch the steering wheel or pedals during the demonstration. The video also shows perspectives from the vehicle's cameras and image recognition.
At the time, FSD was acknowledged to be "some way off in the future."[ The option to purchase the FSD upgrade to EA was removed from Tesla's website in October 2018; Elon Musk tweeted the upgrade was "causing too much confusion". Technology analyst Rob Enderle called the removal of the upgrade option "incredibly stupid", adding "don't release a system that doesn't work and make it hard to order." During a January 2019 earnings call, Elon Musk reiterated "full self-driving capability is there", referring to "Navigate on Autopilot", an EA feature limited to controlled-access highways.][ The EA option was replaced by FSD in 2019 without offering "Navigate on Autopilot"-like functionality for local roads; autosteer and traffic-aware cruise control were transferred to the basic Autopilot feature set, which was made standard on all new Teslas.][ and the FSD beta had expanded to approximately 160,000 testers in the United States and Canada by September. In November, the FSD beta was extended to all owners in North America that had purchased the option.][
]
Pricing
In 2016, the initial price of Autopilot (called "Enhanced Autopilot") was $5,000, and FSD was an add-on for $3,000. In April 2019, basic Autopilot was included in every Tesla car, and FSD was $5,000, growing to $10,000 in October 2020 and $15,000 in September 2022. As the price of FSD increased, the fraction of buyers who purchased it steadily declined, from an estimated 37% in 2019 to 22% in 2020 to 12% in 2021. Starting in 2021, the company offers a subscription for FSD for $199 per month or $99 per month if the customer has already purchased Enhanced Autopilot.
Team executive turnover
There has been high turnover in Autopilot lead roles. Some of the executives leaving were:
* 2015–2016: Sterling Anderson (Autopilot Director) left to start a competing company.
* 2017–2017: Chris Lattner
Christopher Arthur Lattner (born 1978) is an American software engineer, former Google and Tesla employee and co-founder of LLVM, Clang compiler, MLIR compiler infrastructure and the Swift programming language. , he is the co-founder and CEO ...
(Vice President of Autopilot Software) left after six months due to cultural fit issues.
* 2017–2018: Jim Keller (Vice President, Autopilot Hardware Engineering) left to join Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
.
* 2018–2022: Andrej Karpathy
Andrej Karpathy (born 23 October 1986) is a Slovakian-Canadian computer scientist who served as the director of artificial intelligence and Autopilot Vision at Tesla. He specializes in deep learning and computer vision.
Andrej Karpathy was bor ...
(Senior Director, Artificial Intelligence) left to revisit "long-term passions around technical work in AI, open source and education".
Full Self-Driving
Full Self-Driving (FSD) capability
Approach
Tesla's approach to try to achieve SAE Level 5 is to train a neural network using the behavior of hundreds of thousands of Tesla drivers using chiefly visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 te ...
cameras and information from components used for other purposes in the car (the coarse-grained two-dimensional maps used for navigation; the ultrasonic sensors used for parking, etc.)Waymo
Waymo LLC, formerly known as the Google self-driving car project, is an American autonomous driving technology company headquartered in Mountain View, California. It is a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc, the parent company of Google.
Waymo oper ...
and Cruise which train their neural networks using the behavior of highly trained drivers, and are additionally relying on highly detailed (centimeter-scale) three-dimensional maps and lidar in their autonomous vehicles.neural nets
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains.
An ANN is based on a collection of connected units ...
that can operate in reasonably sized computers in the car".
Predictions and deployment
In March 2015, speaking at an Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
conference, Musk stated:
:"I don't think we have to worry about autonomous cars because it's a sort of a narrow form of AI. It's not something I think is very difficult. To do autonomous driving that is to a degree much safer than a person, is much easier than people think." "...I almost view it like a solved problem."
In December 2015, Musk predicted "complete autonomy" by 2018. At the end of 2016, Tesla expected to demonstrate full autonomy by the end of 2017, and in April 2017, Musk predicted that in around two years, drivers would be able to sleep in their vehicle while it drives itself. In 2018 Tesla revised the date to demonstrate full autonomy to be by the end of 2019.
In February 2019, Musk stated that FSD would be "feature complete
A software release life cycle is the sum of the stages of development and maturity for a piece of computer software ranging from its initial development to its eventual release, and including updated versions of the released version to help impro ...
" by the end of 2019:
In 2019 and 2020, Tesla's order page for "Full Self-Driving Capability" stated:
:Coming later this year:
:* Recognize and respond to traffic lights and stop signs
:* Automatic driving on city streets.
In January 2020, Musk claimed the FSD software would be "feature complete" by the end of 2020, adding that feature complete "doesn't mean that features are working well". In August 2020, Musk stated that 200 software engineers, 100 hardware engineers and 500 " labelers" were working on Autopilot and FSD. In early 2021, Musk stated that Tesla would provide SAE Level 5 autonomy by the end of 2021. An email conversation between Tesla and the California Department of Motor Vehicles
The California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) is the state agency that registers motor vehicles and boats and issues driver licenses in the U.S. state of California. It regulates new car dealers (through the New Motor Vehicle Board), c ...
(DMV) retrieved via a Freedom of Information Act Freedom of Information Act may refer to the following legislations in different jurisdictions which mandate the national government to disclose certain data to the general public upon request:
* Freedom of Information Act 1982, the Australian act
* ...
request by PlainSite contradicts Musk's forward-looking statement.
Full Self-Driving beta
In October 2020, Tesla first released a beta version of its FSD software to early access program testers, a small group of users in the United States.[
]
Tesla Dojo
Dojo is an artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
(AI) neural network training supercomputer announced by Musk on Tesla's AI Day on August 19, 2021. It had previously been mentioned by Musk in April 2019teraflop
In computing, floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate mea ...
s of processing power",exaflop
In computing, floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate meas ...
million teraflopsof power".TOP500
The TOP500 project ranks and details the 500 most powerful non- distributed computer systems in the world. The project was started in 1993 and publishes an updated list of the supercomputers twice a year. The first of these updates always coinci ...
list, as they use vastly different architectures — Dojo computes with lower precision floating point numbers
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be r ...
to perform neural network training efficiently, and it is believed that the computer will have limited performance and applicability to more general applications.
Criticism
Tesla's self-driving strategy has been criticized as dangerous and obsolete as it was abandoned by other companies years ago. Most experts believe that Tesla's approach of trying to achieve autonomous vehicles by eschewing high-definition maps and lidar is not feasible.Brad Templeton
Brad Templeton (born June 1960 near Toronto) is a Canadian software developer, internet entrepreneur, online community pioneer, publisher of news, comedy, science fiction and e-books, writer, photographer, civil rights advocate, futurist, public s ...
has criticized Tesla's approach by arguing, "The no-map approach involves forgetting what was learned before and doing it all again." In a May 2021 study by Guidehouse Insights, Tesla was ranked last for both strategy and execution in the autonomous driving sector.Missy Cummings
__NOTOC__
Mary Louise "Missy" Cummings (born 1966) is an American academic who is a professor at Duke University and director of Duke's Humans and Autonomy Laboratory. She was one of the United States Navy, United States Navy's first female fight ...
''et al'' found three Tesla Model 3 cars exhibited "significant between and within vehicle variation on a number of metrics related to driver monitoring, alerting, and safe operation of the underlying autonomy... suggest ngthat the performance of the underlying artificial intelligence and computer vision systems was extremely variable."
In September 2021, legal scholars William Widen and Philip Koopman argued that Tesla's advertising of FSD as an SAE Level 2 system was misleading to "avoid regulatory oversight and permitting processes required of more highly automated vehicles".
Driving features
Tesla's Autopilot is classified as Level 2 under the SAE six levels (0 to 5) of vehicle automation.
Hardware
Summary
;Notes
Hardware 1
Vehicles manufactured after late September 2014 are equipped with a camera mounted at the top of the windshield, forward looking radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
in the lower grille and ultrasonic acoustic location
Acoustic location is the use of sound to determine the distance and direction of its source or reflector. Location can be done actively or passively, and can take place in gases (such as the atmosphere), liquids (such as water), and in solids (s ...
sensors in the front and rear bumpers that provide a 360-degree view around the car. The computer is the Mobileye EyeQ3. This equipment allows the Tesla Model S
The Tesla Model S is a battery-powered liftback car serving as the flagship model of Tesla, Inc. The Model S features a dual-motor, all-wheel drive layout, although earlier versions of the Model S featured a rear-motor and rear-wheel drive ...
to detect road signs, lane markings, obstacles, and other vehicles.
Auto lane change can be initiated by the driver turning on the lane changing signal when safe (due to the ultrasonic sensors' 16-foot limited range capability), and then the system completes the lane change.
Hardware 2
 HW2, included in vehicles manufactured after October 2016, includes an
HW2, included in vehicles manufactured after October 2016, includes an Nvidia
Nvidia CorporationOfficially written as NVIDIA and stylized in its logo as VIDIA with the lowercase "n" the same height as the uppercase "VIDIA"; formerly stylized as VIDIA with a large italicized lowercase "n" on products from the mid 1990s to ...
Drive PX 2 GPU for CUDA
CUDA (or Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) that allows software to use certain types of graphics processing units (GPUs) for general purpose processing, an approach ...
based GPGPU
General-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU, or less often GPGP) is the use of a graphics processing unit (GPU), which typically handles computation only for computer graphics, to perform computation in applications traditiona ...
computation.
Hardware 2.5
In August 2017, Tesla announced that HW2.5 included a secondary processor node to provide more computing power and additional wiring redundancy to slightly improve reliability; it also enabled dashcam
A dashboard camera or simply dashcam, also known as car digital video recorder (car DVR), driving recorder, or event data recorder (EDR), is an onboard camera that continuously records the view through a vehicle's front windscreen and sometimes ...
and "sentry mode" capabilities.
Hardware 3
According to Tesla's director of Artificial Intelligence Andrej Karpathy
Andrej Karpathy (born 23 October 1986) is a Slovakian-Canadian computer scientist who served as the director of artificial intelligence and Autopilot Vision at Tesla. He specializes in deep learning and computer vision.
Andrej Karpathy was bor ...
, Tesla had as of Q3 2018 trained large neural networks but they could not be deployed to Tesla vehicles built up to that time due to their insufficient computational resources. HW3 provides the necessary resources to run these neural networks.
HW3 includes a custom Tesla-designed system on a chip fabricated using a 14 nm process
The 14 nm process refers to the MOSFET technology node that is the successor to the 22nm (or 20nm) node. The 14nm was so named by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). Until about 2011, the node following 22nm was e ...
by Samsung. Jim Keller and Pete Bannon, among other architects, have led the project since February 2016. Tesla claimed that the new system processes 2,300 frames per second (fps), which is a 21× improvement over the 110 fps image processing capability of HW2.5.ARM Cortex-A72
The ARM Cortex-A72 is a central processing unit implementing the ARMv8-A 64-bit instruction set designed by ARM Holdings' Austin design centre. The Cortex-A72 is a 3-way decode out-of-order superscalar pipeline. It is available as SIP core to l ...
CPUs operating at 2.6 GHz, two Neural Network Accelerators operating at 2 GHz and a Mali GPU operating at 1 GHz.
Tesla Vision
 In late May 2021, Elon Musk posted to Twitter that "Pure Vision Autopilot" was starting to be implemented. The system, which Tesla brands "Tesla Vision", eliminates the forward-facing radar starting in May 2021 from the Autopilot hardware package on Model 3 and Model Y vehicles built for the North American market. For vehicles without the forward radar, temporary limitations were applied to certain features such as Autosteer, and other features (Smart Summon and Emergency Lane Departure Avoidance) were disabled, but Tesla promised to restore the features "in the weeks ahead ... via a series of over-the-air software updates".
In late May 2021, Elon Musk posted to Twitter that "Pure Vision Autopilot" was starting to be implemented. The system, which Tesla brands "Tesla Vision", eliminates the forward-facing radar starting in May 2021 from the Autopilot hardware package on Model 3 and Model Y vehicles built for the North American market. For vehicles without the forward radar, temporary limitations were applied to certain features such as Autosteer, and other features (Smart Summon and Emergency Lane Departure Avoidance) were disabled, but Tesla promised to restore the features "in the weeks ahead ... via a series of over-the-air software updates".Insurance Institute for Highway Safety
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) is a U.S. nonprofit organization funded by auto insurance companies, established in 1959 and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It works to reduce the number of motor vehicle traffic collisio ...
(IIHS) announced plans to delist the Model 3 as a Top Safety Pick+, but after further testing, both organizations restored those designations. Also, the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA ) is an agency of the U.S. federal government, part of the Department of Transportation. It describes its mission as "Save lives, prevent injuries, reduce vehicle-related crashes" rel ...
(NHTSA) rescinded the agency's check marks for forward collision warning, automatic emergency braking, lane departure warning, and dynamic brake support, applicable to Model 3 and Model Y vehicles built on or after April 27, 2021, but , those check marks have been restored.
In December 2021, the ''New York Times'' reported that Musk was the decision-maker behind the camera-only approach and had "repeatedly told members of the Autopilot team that humans could drive with only two eyes and that this meant cars should be able to drive with cameras alone." Several autonomous vehicle experts denounce the analogy.
Tesla announced in October 2022 they would remove ultrasonic sensors by 2023; vehicles without the ultrasonic sensors would be shipped without Autopark, Park Assist, Summon, and Smart Summon features initially. However, Tesla promised these features would be restored in the future through a software update.[
]
Comparisons
* In 2018, Consumer Reports rated Tesla Autopilot as second best out of four (Cadillac, Tesla, Nissan, Volvo) "partially automated driving systems".Insurance Institute for Highway Safety
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) is a U.S. nonprofit organization funded by auto insurance companies, established in 1959 and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It works to reduce the number of motor vehicle traffic collisio ...
compared Tesla, BMW, Mercedes and Volvo "advanced driver assistance systems" and stated that the Tesla Model 3
The Tesla Model 3 is a compact executive sedan that is battery powered and produced by Tesla. Limited production of the Model 3 began in mid-2017, with the first production vehicle rolling off the assembly line on July 7, 2017. The offici ...
experienced the fewest incidents of crossing over a lane line, touching a lane line, or disengaging.
* In February 2020, ''Car and Driver
''Car and Driver'' (''CD'' or ''C/D'') is an American automotive enthusiast magazine. In 2006 its total circulation was 1.23 million. It is owned by Hearst Magazines, who purchased prior owner Hachette Filipacchi Media U.S. in 2011. It was f ...
'' compared Cadillac Super Cruise, comma.ai and Autopilot. They called Autopilot "one of the best", highlighting its user interface and versatility, but criticizing it for swerving abruptly.
* In June 2020, Digital Trends
Digital Trends is a Portland, Oregon-based tech news, lifestyle, and information website that publishes news, reviews, guides, how-to articles, descriptive videos and podcasts about technology and consumer electronics products. With offices i ...
compared Cadillac Super Cruise self-driving and Tesla Autopilot. The conclusion: "Super Cruise is more advanced, while Autopilot is more comprehensive."
* In October 2020, the European New Car Assessment Program gave the Tesla Model 3 Autopilot a score of "moderate".
Safety statistics and concerns
Safety statistics
In 2016, data after 47 million miles of driving in Autopilot mode showed the probability of an accident was at least 50% lower when using Autopilot.
General concerns
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) criticized Tesla's lack of system safeguards in a fatal 2018 Autopilot crash in California, and for failing to foresee and prevent "predictable abuse" of Autopilot. Following this collective criticism amid increased regulatory scrutiny of ADAS systems, especially Tesla Autopilot, in June 2021, the NHTSA announced an order requiring automakers to report crashes involving vehicles equipped with ADAS features in the United States.
Driver monitoring
Drivers have been found sleeping at the wheel, driving under the influence of alcohol, and doing other inappropriate tasks with Autopilot engaged. Initially, Tesla decided against using driver monitoring options to limit such activities. It was not until late May 2021 that a new version of the OTA software turned on inside cameras for new Model 3 and Model Y (i.e. the first cars as part of the switch to Tesla Vision) to monitor drivers using Autopilot. Model S and Model X cars made before 2021 do not have an inside camera and therefore physically cannot offer such capabilities, although the refreshed versions are expected to have one. A review of the in-cabin camera-based monitoring system by Consumer Reports found that drivers could still use Autopilot even when looking away from the road or using their phones, and could also enable FSD beta software "with the camera covered."
Detecting stationary vehicles at speed
Autopilot may not detect stationary vehicles; the manual states: "Traffic-Aware Cruise Control cannot detect all objects and may not brake/decelerate for stationary vehicles, especially in situations when you are driving over and a vehicle you are following moves out of your driving path and a stationary vehicle or object is in front of you instead."
Dangerous and unexpected behavior
In a 2019 Bloomberg survey, hundreds of Tesla owners reported dangerous behaviors with Autopilot, such as phantom braking, veering out of lane, or failing to stop for road hazards. Autopilot users have also reported the software crashing and turning off suddenly, collisions with off ramp barriers, radar failures, unexpected swerving, tailgating, and uneven speed changes.
Ars Technica notes that the brake system tends to initiate later than some drivers expect. One driver claimed that Tesla's Autopilot failed to brake, resulting in collisions, but Tesla pointed out that the driver deactivated the cruise control of the car prior to the crash. The automatic emergency braking system also initiates sooner than some drivers expect. Tesla issued a recall of 11,728 vehicles due to a communication error that could lead to false forward-collision warnings or unexpected activations of the automatic emergency braking system. The error had been introduced by an October 2021 over-the-air firmware update, and was reversed by another over-the-air update the same month.
Ars Technica also noted that while lane
In road transport, a lane is part of a roadway that is designated to be used by a single line of vehicles to control and guide drivers and reduce traffic conflicts. Most public roads (highways) have at least two lanes, one for traffic in each ...
changes may be semi-automatic (if Autopilot is on, and the vehicle detects slow moving cars or if it is required to stay on route, the car may automatically change lanes without any driver input), the driver must show the car that he or she is paying attention by touching the steering wheel before the car makes the change. In 2019, ''Consumer Reports'' noted that Tesla's automatic lane-change feature is "far less competent than a human driver".
In October 2021, version 10.3 of the Full Self-Driving beta software was released with different driving profiles to control vehicle behavior, branded 'Chill', 'Average', and 'Assertive'; the 'Assertive' profile attracted negative coverage in January 2022 for advertising that it "may perform rolling stops" (passing through stop signs at up to 5.6 mph), frequent lane changes, and decrease the following distance. On February 1, after the NHTSA advised Tesla that failing to stop for a stop sign can increase the risk of a crash and threatened "immediate action" for "intentional design choices that are unsafe", Tesla recalled nearly 54,000 vehicles to disable the rolling stop behavior, removing the feature with an over-the-air software update.
Regulatory and legal actions
Regulation
A spokesman for the NHTSA said that "any autonomous vehicle would need to meet applicable federal motor vehicle safety standards" and the NHTSA "will have the appropriate policies and regulations in place to ensure the safety of this type of vehicles".
Court cases
Tesla's Autopilot was the subject of a class action suit
A class action, also known as a class-action lawsuit, class suit, or representative action, is a type of lawsuit where one of the parties is a group of people who are represented collectively by a member or members of that group. The class actio ...
brought in 2017 that claimed the second-generation Enhanced Autopilot system was "dangerously defective". The suit was settled in 2018; owners who in 2016 and 2017 paid to equip their cars with the updated Autopilot software were compensated between $20 and $280 for the delay in implementing Autopilot 2.0.
In 2020, a German court ruled in a lawsuit brought in 2019 by that Tesla had violated advertising regulations with its marketing of Autopilot. Upon appeal, that decision was reversed in 2021 by a higher court under the condition that Tesla clarify the capabilities of Autopilot on its website.
In July 2022, a German court awarded a plaintiff most of the that she had paid for a Model X, based in part on a technical report that demonstrated Autopilot did not reliably recognize obstacles and would unnecessarily activate its brakes, which could cause a "massive hazard" in cities; Tesla's lawyers argued unsuccessfully that Autopilot was not designed for city traffic.
In September 2022, a class action lawsuit was filed in the U.S. District Court (Northern California) alleging that "for years, Tesla has deceptively and misleading marketed its ADAS technology as autonomous driving technology under various names, including 'Autopilot,' 'Enhanced Autopilot,' and 'Full Self-Driving Capability'", adding that Tesla represented "that it was perpetually on the cusp of perfecting that technology and finally fulfilling its promise of producing a fully self-driving car", while "Tesla knew for years its statements regarding its ADAS technology were deceptive and misleading, but the company made them anyway."
False or misleading advertising
The Center for Auto Safety and Consumer Watchdog wrote to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in 2018, asking them to open an investigation into the marketing of Autopilot. The letter stated "the marketing and advertising practices of Tesla, combined with Elon Musk's public statements, have made it reasonable for Tesla owners to believe, and act on that belief, that a Tesla with Autopilot is an autonomous vehicle capable of 'self-driving. The groups renewed their appeal to the FTC and added the California DMV in 2019, noting that "Tesla continues to be the only automaker to describe its Level 2 vehicles as 'self-driving' and the name of its driver assistance suite of features, Autopilot, connotes full autonomy." U.S. Senators Ed Markey
Edward John Markey (born July 11, 1946) is an American lawyer, politician, and former Army reservist who has served as the junior United States senator from Massachusetts since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the U.S. representa ...
(D-MA) and Richard Blumenthal
Richard Blumenthal (; born February 13, 1946) is an American lawyer and politician who is the senior United States senator from Connecticut, a seat he has held since 2011. A member of the Democratic Party, he is one of the wealthiest members of ...
(D-CT) echoed these concerns to the FTC in 2021.
A 2019 IIHS study showed that the name "Autopilot" causes more drivers to misperceive behaviors such as texting or taking a nap to be safe, versus similar level 2 driver-assistance systems from other car companies. In 2020, UK safety experts called Tesla's Autopilot "especially misleading".
Tesla's use of the terms Autopilot and FSD were criticized in a May 2020 report published on ScienceDirect titled "Autonowashing: The Greenwashing of Vehicle Automation".
In 2021, following more than a dozen Autopilot crashes (some fatal), the U.S. Department of Justice started a criminal investigation to determine if Tesla misled consumers, investors, and regulators about Autopilot. The Securities and Exchange Commission also opened an independent civil probe into statements made by Tesla and its executives about Autopilot.
In July 2022, the California DMV filed two complaints with the state Office of Administrative Hearings that alleged Tesla "made or disseminated statements that are untrue or misleading, and not based on facts" relating to both "Autopilot and Full Self-Driving technologies". In August, Tesla requested a hearing to present its defense. In December 2022, a California state bill was signed into effect for 2023 that banned Tesla and other makers of cars with partial driver automation from using full self-driving language to advertise their products.
NHTSA investigations
According to a document released in June 2021, the NHTSA has initiated at least 30 investigations into Tesla crashes that were believed to involve the use of Autopilot, with some involving fatalities.
In August 2021, the NHTSA Office of Defects Investigation (ODI) opened a preliminary evaluation (PE 21-020) and released a list of eleven crashes involving Tesla vehicles striking stationary emergency vehicles; in each instance, NHTSA confirmed that Autopilot or Traffic Aware Cruise Control were active during the approach to the crashes. Of the eleven crashes, seven resulted in seventeen total injuries, and one resulted in one fatality. The scope of the planned evaluation of the Autopilot system specifically addressed the systems used to monitor and enforce driver engagement.The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large nati ...
'' also published an article detailing the surge in complaints to NHTSA over false positives to its automatic emergency-braking system. By May 2022, NHTSA had received 758 reports of unexpected braking when Autopilot was in use and requested that Tesla respond to questions by June 20, 2022.
Also in June 2022, NHTSA ODI upgraded PE 21-020 to an engineering analysis (EA 22-002), covering an estimated 830,000 Tesla vehicles sold between 2014 and 2022.[
SGO 2021-01 also applied to manufacturers of vehicles equipped with ADS (Levels 3 through 5); 25 ADS manufacturers reported 130 crashes in total over the same period, led by Waymo (62), Transdev Alternative Services (34), and Cruise LLC (23). In most cases, these crashes involved the ADS vehicle being struck from the rear; only one serious injury was reported, and 108 of the 130 crashes resulted in no injury.][ 85 were removed because other drivers were involved or there was insufficient data.][ It was found that in approximately of the remaining 106 crashes, the driver was not sufficiently responsive to the driving task, and approximately of the 106 resulted from operating Autopilot outside of limited-access highways, or when traction and weather conditions could interfere.][ Detailed telemetry existed for 43 of the 106 crashes; of these, data from 37 indicated the driver's hands were on the steering wheel in the last second prior to collision.][ Six incidents were added, making a total of sixteen accidents where a Tesla struck stationary emergency vehicle(s), including the August 2021 incident in Orlando.][ In these 16 incidents, NHTSA found that a majority resulted in forward collision warnings and approximately half resulted in automatic emergency braking.]
Notable crashes
Fatal crashes
, there have been nineteen verified fatalities from sixteen cases involving Tesla's Autopilot, though other deadly incidents involving suspected Autopilot use remain outstanding. Each of these incidents has received varying degrees of attention from news publications.
Handan, Hebei, China (January 20, 2016)
 On January 20, 2016, the driver of a Tesla Model S in Handan, Hebei, China, was killed when his car crashed into a stationary truck. The Tesla was following a car in the far left lane of a multi-lane highway; the car in front moved to the right lane to avoid a truck stopped on the left shoulder, and the Tesla, which the driver's father believes was in Autopilot mode, did not slow before colliding with the stopped truck.
On January 20, 2016, the driver of a Tesla Model S in Handan, Hebei, China, was killed when his car crashed into a stationary truck. The Tesla was following a car in the far left lane of a multi-lane highway; the car in front moved to the right lane to avoid a truck stopped on the left shoulder, and the Tesla, which the driver's father believes was in Autopilot mode, did not slow before colliding with the stopped truck.dashboard camera
A dashboard camera or simply dashcam, also known as car digital video recorder (car DVR), driving recorder, or event data recorder (EDR), is an onboard camera that continuously records the view through a vehicle's front windscreen and someti ...
, the stationary street sweeper on the left side of the expressway partially extended into the far left lane, and the driver did not appear to respond to the unexpected obstacle.
In September 2016, the media reported the driver's family had filed a lawsuit in July against the Tesla dealer who sold the car. The family's lawyer stated the suit was intended "to let the public know that self-driving technology has some defects. We are hoping Tesla when marketing its products, will be more cautious. Do not just use self-driving as a selling point for young people."telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", an ...
could not be retrieved remotely due to damage caused by the crash.SD card
Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.
The standard was introduced in August 1999 by joint efforts between SanDis ...
and was not able to be given to Tesla, who provided a decoding key to a third party for independent review. Tesla stated that "while the third-party appraisal is not yet complete, we have no reason to believe that Autopilot on this vehicle ever functioned other than as designed." Chinese media later reported that the family sent the information from that card to Tesla, which admitted autopilot was engaged two minutes before the crash. Tesla since then removed the term "Autopilot" from its Chinese website.
Williston, Florida, USA (May 7, 2016)

 On May 7, 2016, a Tesla driver was killed in a crash with an 18-wheel
On May 7, 2016, a Tesla driver was killed in a crash with an 18-wheel tractor-trailer
A semi-trailer truck, also known as a semitruck, (or semi, eighteen-wheeler, big rig, tractor-trailer or, by synecdoche, a semitrailer) is the combination of a tractor unit and one or more semi-trailers to carry freight. A semi-trailer a ...
in Williston, Florida
Williston is a city in Levy County, Florida, United States. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 2,768.
Histoy
The city was established before 1885 by J.M. Willis, who named it after himself.
Geography
Williston is located at (29.386 ...
. By late June 2016, the NHTSA opened a formal investigation into the fatal autonomous accident, working with the Florida Highway Patrol. According to the NHTSA, preliminary reports indicate the crash occurred when the tractor-trailer made a left turn in front of the 2015 Tesla Model S at an intersection on a non-controlled access highway, and the car failed to apply the brakes. The car continued to travel after passing under the truck's trailer.beltline
The Atlanta BeltLine (also Beltline or Belt Line) is a open and planned loop of multi-use trail and light rail transit system on a former railway corridor around the core of Atlanta, Georgia. The Atlanta BeltLine is designed to reconnect nei ...
, and caused fatal injuries to the driver. The NHTSA's preliminary evaluation was opened to examine the design and performance of any automated driving systems in use at the time of the crash, which involves a population of an estimated 25,000 Model S cars. On July 8, 2016, the NHTSA requested Tesla Inc. to hand over to the agency detailed information about the design, operation and testing of its Autopilot technology. The agency also requested details of all design changes and updates to Autopilot since its introduction, and Tesla's planned updates scheduled for the next four months.
According to Tesla, "neither autopilot nor the driver noticed the white side of the tractor-trailer against a brightly lit sky, so the brake was not applied." The car attempted to drive full speed under the trailer, "with the bottom of the trailer impacting the windshield of the Model S". Tesla also stated that this was Tesla's first known Autopilot-related death in over 130 million miles (208 million km) driven by its customers while Autopilot was activated. According to Tesla there is a fatality every 94 million miles (150 million km) among all type of vehicles in the U.S.
The NHTSA's preliminary evaluation was opened to examine the design and performance of any automated driving systems in use at the time of the crash, which involves a population of an estimated 25,000 Model S cars. On July 8, 2016, the NHTSA requested Tesla Inc. to hand over to the agency detailed information about the design, operation and testing of its Autopilot technology. The agency also requested details of all design changes and updates to Autopilot since its introduction, and Tesla's planned updates scheduled for the next four months.
According to Tesla, "neither autopilot nor the driver noticed the white side of the tractor-trailer against a brightly lit sky, so the brake was not applied." The car attempted to drive full speed under the trailer, "with the bottom of the trailer impacting the windshield of the Model S". Tesla also stated that this was Tesla's first known Autopilot-related death in over 130 million miles (208 million km) driven by its customers while Autopilot was activated. According to Tesla there is a fatality every 94 million miles (150 million km) among all type of vehicles in the U.S.Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. ne ...
that he could hear a ''Harry Potter'' movie playing in the crashed car, and said the car was driving so quickly that "he went so fast through my trailer I didn't see him. he film
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
was still playing when he died and snapped a telephone pole a quarter-mile down the road." According to the Florida Highway Patrol, they found in the wreckage an aftermarket portable DVD player. (It is not possible to watch videos on the Model S touchscreen
A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input ('touch panel') and output ('display') device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is ofte ...
display while the car is moving.
Mountain View, California, USA (March 23, 2018)
 On March 23, 2018, a second U.S. Autopilot fatality occurred in
On March 23, 2018, a second U.S. Autopilot fatality occurred in Mountain View, California
Mountain View is a city in Santa Clara County, California, United States. Named for its views of the Santa Cruz Mountains, it has a population of 82,376.
Mountain View was integral to the early history and growth of Silicon Valley, and is the ...
.Pacific Standard Time
The Pacific Time Zone (PT) is a time zone encompassing parts of western Canada, the western United States, and western Mexico. Places in this zone observe standard time by subtracting eight hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−08:00 ...
on southbound US 101
U.S. Route 101, or U.S. Highway 101 (US 101), is a north–south United States Numbered Highway that runs through the states of California, Oregon, and Washington, on the West Coast of the United States. It is also known as (The Royal Roa ...
at the carpool lane exit for southbound Highway 85, at a concrete barrier where the left-hand carpool lane offramp separates from 101. After the Model X crashed into the narrow concrete barrier, it was struck by two following vehicles, and then it caught on fire.
Both the NHTSA and NTSB began investigations into the March 2018 crash. Another driver of a Model S demonstrated that Autopilot appeared to be confused by the road surface marking
Road surface marking is any kind of device or material that is used on a road surface in order to convey official information; they are commonly placed with road marking machines (also referred to as road marking equipment or pavement marking eq ...
in April 2018. The gore ahead of the barrier is marked by diverging solid white lines (a vee-shape) and the Autosteer feature of the Model S appeared to mistakenly use the left-side white line instead of the right-side white line as the lane marking for the far left lane, which would have led the Model S into the same concrete barrier had the driver not taken control. ''Ars Technica'' concluded that "as Autopilot gets better, drivers could become increasingly complacent and pay less and less attention to the road."
 In a corporate blog post, Tesla noted the impact attenuator separating the offramp from US 101 had been previously crushed and not replaced prior to the Model X crash on March 23.
In a corporate blog post, Tesla noted the impact attenuator separating the offramp from US 101 had been previously crushed and not replaced prior to the Model X crash on March 23.impact attenuator
An impact attenuator, also known as a crash cushion, crash attenuator, or cowboy cushion, is a device intended to reduce the damage to structures, vehicles, and motorists resulting from a motor vehicle collision. Impact attenuators are designed to ...
and the vehicle fire after the collision, but after it was reported the driver had complained about the Autopilot functionality, the NTSB announced it would also investigate "all aspects of this crash including the driver's previous concerns about the autopilot". A NTSB spokesman stated the organization "is unhappy with the release of investigative information by Tesla". Elon Musk dismissed the criticism, tweeting that NTSB was "an advisory body" and that "Tesla releases critical crash data affecting public safety immediately & always will. To do otherwise would be unsafe." In response, NTSB removed Tesla as a party to the investigation on April 11.
NTSB released a preliminary report on June 7, 2018, which provided the recorded telemetry of the Model X and other factual details. Autopilot was engaged continuously for almost nineteen minutes prior to the crash. In the minute before the crash, the driver's hands were detected on the steering wheel for 34 seconds in total, but his hands were not detected for the six seconds immediately preceding the crash. Seven seconds before the crash, the Tesla began to steer to the left and was following a lead vehicle; four seconds before the crash, the Tesla was no longer following a lead vehicle; and during the three seconds before the crash, the Tesla's speed increased to . The driver was wearing a seatbelt and was pulled from the vehicle before it was engulfed in flames.California Highway Patrol
The California Highway Patrol (CHP) is a state law enforcement agency of the U.S. state of California. The CHP has primary patrol jurisdiction over all California highways and roads and streets outside city limits, and can exercise law enforcem ...
failed to report the collapsed attenuator to Caltrans as required. Caltrans was not aware of the damage until March 20, and the attenuator was not replaced until March 26 because a spare was not immediately available.distracted driving
Distracted driving is the act of driving while engaging in other activities which distract the driver's attention away from the road. Distractions are shown to compromise the safety of the driver, passengers, pedestrians, and people in other vehic ...
awareness and regulation. In addition, NTSB issued recommendations to manufacturers of portable electronic devices (to develop lock-out mechanisms to prevent driver-distracting functions) and to Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ' ...
(banning the nonemergency use of portable electronic devices while driving).
Kanagawa, Japan (April 29, 2018)
 On April 29, 2018, a Tesla Model X operating on Autopilot struck and killed a pedestrian in Kanagawa, Japan, after the driver had fallen asleep. According to a lawsuit filed against Tesla in federal court (N.D. Cal.) in April 2020, the Tesla Model X accelerated from after the vehicle in front of it changed lanes; it then crashed into a van, motorcycles, and pedestrians in the far right lane of the expressway, killing a 44-year-old man on the road directing traffic.
On April 29, 2018, a Tesla Model X operating on Autopilot struck and killed a pedestrian in Kanagawa, Japan, after the driver had fallen asleep. According to a lawsuit filed against Tesla in federal court (N.D. Cal.) in April 2020, the Tesla Model X accelerated from after the vehicle in front of it changed lanes; it then crashed into a van, motorcycles, and pedestrians in the far right lane of the expressway, killing a 44-year-old man on the road directing traffic.Japan Standard Time
, or , is the standard time zone in Japan, 9 hours ahead of UTC ( UTC+09:00). Japan does not observe daylight saving time, though its introduction has been debated on several occasions. During World War II, the time zone was often referred to ...
, shortly after entering the Tōmei Expressway
The is a national expressway on the island of Honshū in Japan. It is operated by Central Nippon Expressway Company. The expressway is designated as E1 under the "2016 Proposal for Realization of Expressway Numbering", because it parallels ...
.forum non-conveniens
''Forum non conveniens'' (Latin for "an inconvenient forum") (FNC) is a mostly common law legal doctrine through which a court acknowledges that another forum or court where the case might have been brought is a more appropriate Venue (law), venu ...
'' by Judge Susan van Keulen in September 2020 after Tesla said it would accept a case brought in Japan. The plaintiffs appealed the dismissal to the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals
The United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit (in case citations, 9th Cir.) is the U.S. federal court of appeals that has appellate jurisdiction over the U.S. district courts in the following federal judicial districts:
* District ...
in February 2021,
Delray Beach, Florida, USA (March 1, 2019)
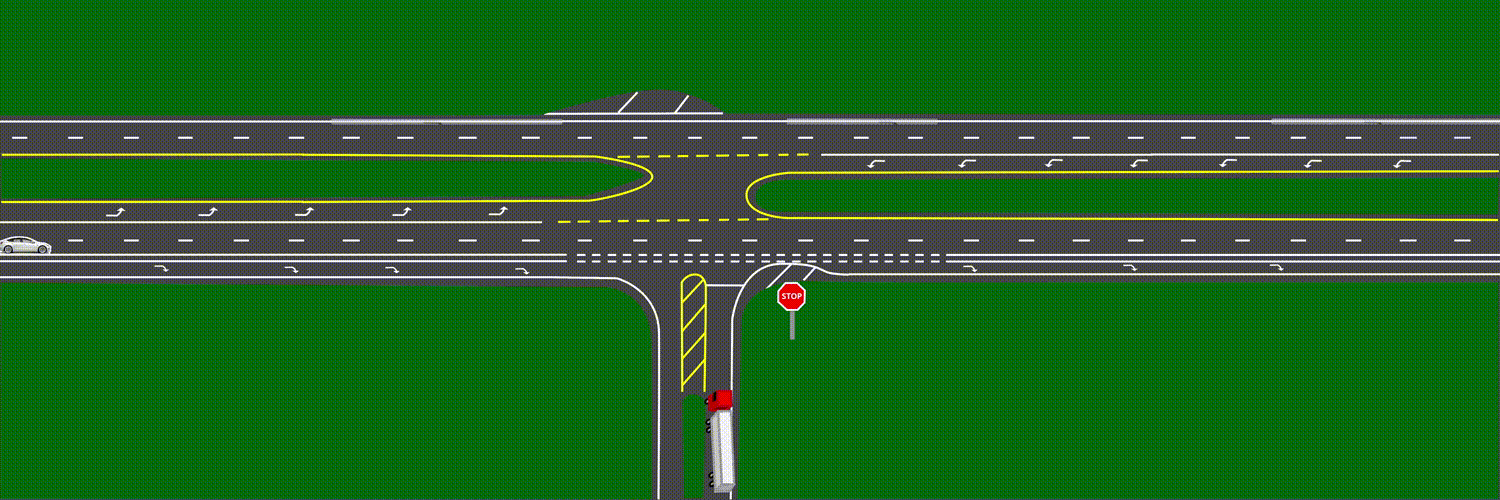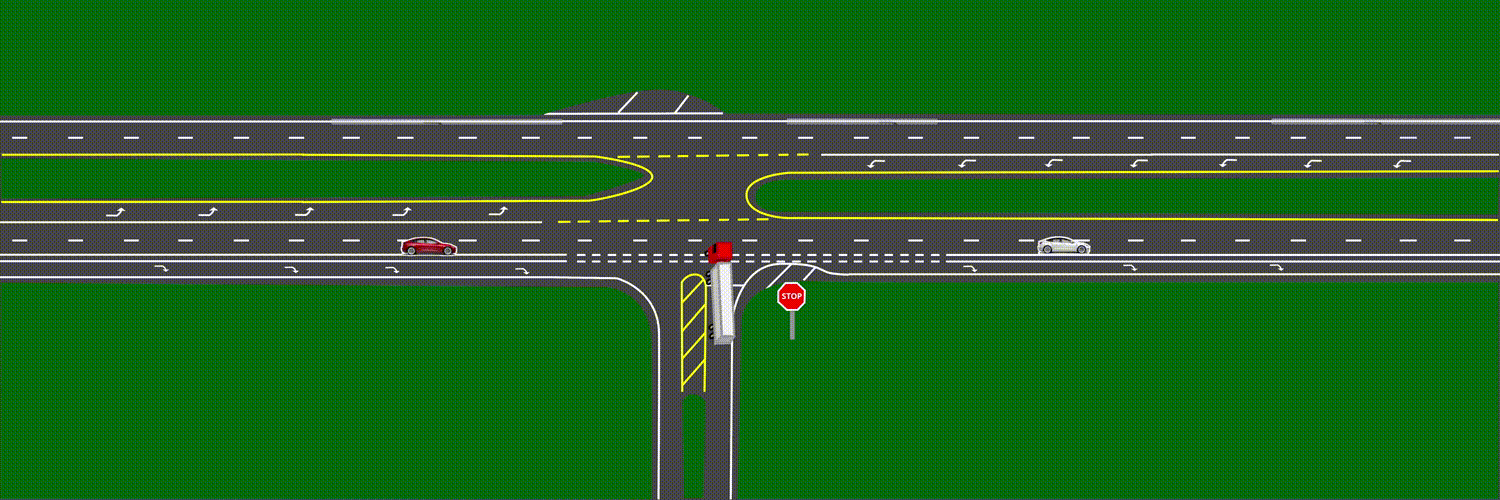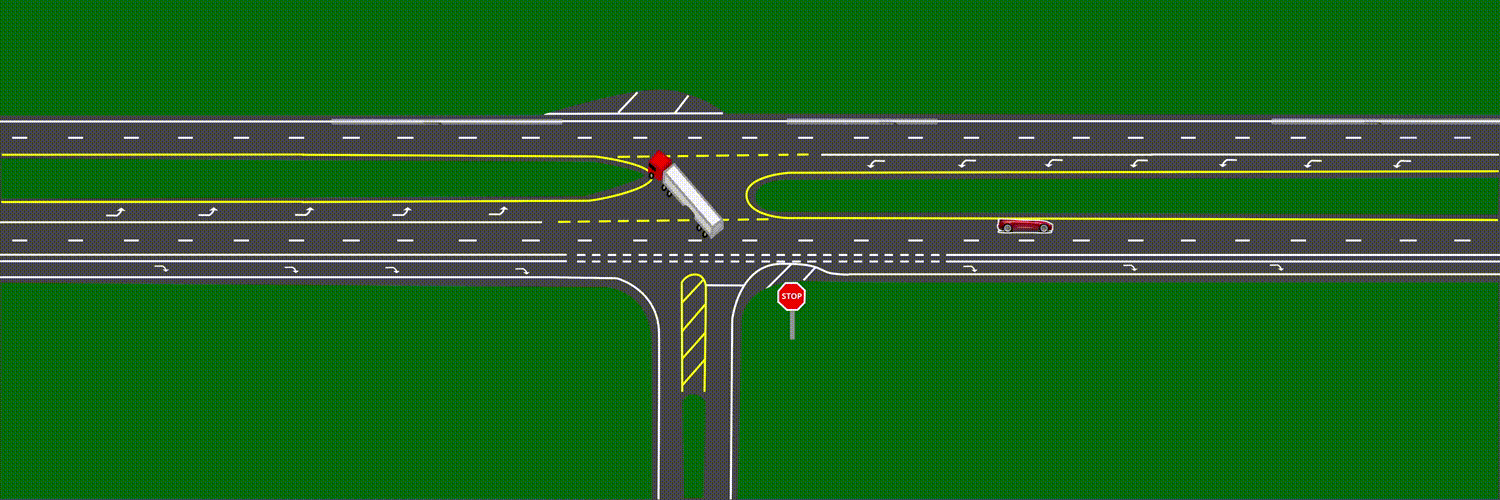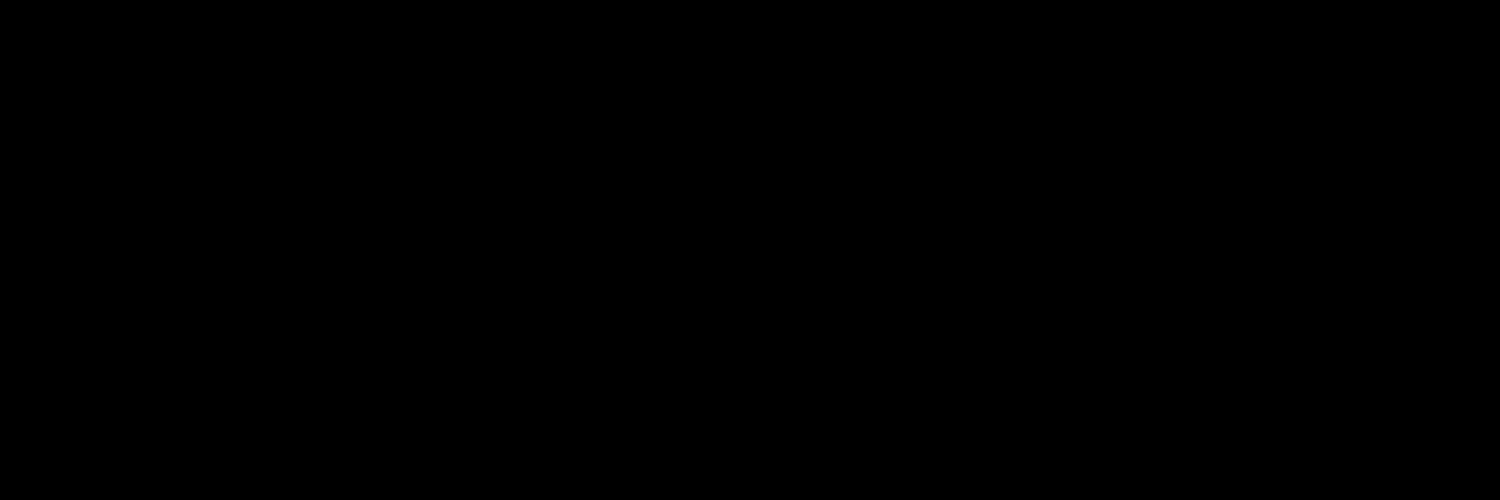 At approximately 6:17 a.m.
At approximately 6:17 a.m. Eastern Standard Time
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 U.S. states, states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and ...
on the morning of March 1, 2019, a Tesla Model 3 driving southbound on US 441
U.S. Route 441 (US 441) is a auxiliary route of U.S. Route 41. It extends from US 41 in Miami, Florida to US 25W in Rocky Top, Tennessee. Between its termini, US 441 travels through the states of Florida, Georgia, North ...
/ SR 7 in Delray Beach, Florida
Delray Beach is a city in Palm Beach County, Florida, Palm Beach County, Florida, United States. The population of Delray Beach as of April 1, 2020 was 66,846 according to the 2020 United States census, 2020 United States Census. Located 52 miles ...
, struck a semi-trailer truck
A semi-trailer truck, also known as a semitruck, (or semi, eighteen-wheeler, big rig, tractor-trailer or, by synecdoche, a semitrailer) is the combination of a tractor unit and one or more semi-trailers to carry freight. A semi-trailer ...
that was making a left-hand turn to northbound SR 7 out of a private driveway at Pero Family Farms; the Tesla underrode the trailer, and the force of the impact sheared off the greenhouse
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of Transparent ceramics, transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic condit ...
of the Model 3, resulting in the death of the Tesla driver. The driver of the Tesla had engaged Autopilot approximately 10 seconds before the collision and preliminary telemetry showed the vehicle did not detect the driver's hands on the wheel for the eight seconds immediately preceding the collision. The driver of the semi-trailer truck was not cited. Both the NHTSA and NTSB dispatched investigators to the scene.
According to telemetry recorded by the Tesla's restraint control module, the Tesla's cruise control was set to 12.3 seconds prior to the collision and Autopilot was engaged 9.9 seconds prior to the collision; at the moment of impact, the vehicle speed was . After the crash and underride, the Tesla continued southbound on SR 7 for approximately before coming to rest in the median between the northbound and southbound lanes.
Key Largo, Florida, USA (April 25, 2019)
While driving on Card Sound Road, a 2019 Model S ran through a stop sign and flashing red stop light at the T-intersection with County Road 905, then struck a parked Chevrolet Tahoe which then hit two pedestrians, killing one. A ''New York Times'' article later confirmed Autopilot was engaged at the time of the accident.
Fremont, California, USA (August 24, 2019)
In Fremont, California
Fremont is a city in Alameda County, California, United States. Located in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area, Bay Area, Fremont has a population of 230,504 as of 2020, making it the fourth List of cities and towns in the San Fra ...
on I-880, while driving north of Stevenson Boulevard, a Ford Explorer pickup was rear-ended by a Tesla Model 3 using Autopilot, causing the pickup's driver to lose control. The pickup overturned and a 15-year-old passenger in the Ford, who was not seat-belted, was jettisoned from the pickup and killed.[ The deceased's parents sued Tesla and claimed in their filing that "Autopilot contains defects and failed to react to traffic conditions." In response, a lawyer for Tesla noted the police had cited the driver of the Tesla for inattention and operating the car at an unsafe speed. The incident has not been investigated by the NHTSA.]
Cloverdale, Indiana, USA (December 29, 2019)
 An eastbound Tesla Model 3 rear-ended a fire truck parked along
An eastbound Tesla Model 3 rear-ended a fire truck parked along I-70
Interstate 70 (I-70) is a major east–west Interstate Highway in the United States that runs from I-15 near Cove Fort, Utah, to a park and ride lot just east of I-695 in Baltimore, Maryland, and is the fifth-longest Interstate in the co ...
near mile marker 38 in Putnam County, Indiana
Putnam County is a county located in the U.S. state of Indiana. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 37,963. The county seat is Greencastle. The county was named for Israel Putnam, a hero in the French and Indian War and a ...
at approximately 8 am;
Gardena, California, USA (December 29, 2019)
 Shortly before 12:39 a.m. on December 29, 2019, a westbound Tesla Model S exited the freeway section of SR 91, failed to stop for a red light, and crashed into the driver's side of Honda Civic in Gardena, California, killing the driver and passenger in the Civic and injuring the Tesla driver and passenger. The freeway section of SR 91 ends just east of the intersection of Artesia Blvd and Vermont Ave, and continues as Artesia. The Tesla was proceeding west on Artesia against the red light when it struck the Civic, which was turning left from Vermont onto Artesia. The occupants of the Tesla were taken to the hospital with non life-threatening injuries.
Shortly before 12:39 a.m. on December 29, 2019, a westbound Tesla Model S exited the freeway section of SR 91, failed to stop for a red light, and crashed into the driver's side of Honda Civic in Gardena, California, killing the driver and passenger in the Civic and injuring the Tesla driver and passenger. The freeway section of SR 91 ends just east of the intersection of Artesia Blvd and Vermont Ave, and continues as Artesia. The Tesla was proceeding west on Artesia against the red light when it struck the Civic, which was turning left from Vermont onto Artesia. The occupants of the Tesla were taken to the hospital with non life-threatening injuries.[ and later confirmed in January 2022 that Autopilot was engaged during the crash. The Tesla driver was charged in October 2021 with vehicular manslaughter in the ]Los Angeles Superior Court
The Superior Court of California, County of Los Angeles, is the California superior court with jurisdiction over Los Angeles County, which includes the city of Los Angeles. It is the largest single unified trial court in the United States.
The ...
. The families of the two killed also have filed separate civil lawsuits against the driver, for his negligence, and Tesla, for selling defective vehicles.
In May 2022, a Los Angeles County Superior Court
The Superior Court of California, County of Los Angeles, is the California superior court with jurisdiction over Los Angeles County, which includes the city of Los Angeles. It is the largest single unified trial court in the United States.
The ...
judge ordered the driver of the Tesla to stand trial on two counts of vehicular manslaughter
Vehicular homicide is a crime that involves the death of a person other than the driver as a result of either criminally negligent or murderous operation of a motor vehicle.
In cases of criminal negligence, the defendant is commonly charged ...
. Telemetry data indicated the driver had a hand on the steering wheel, but no brake inputs were detected in the six minutes preceding the crash, despite multiple signs at the end of the freeway warning drivers to slow down. The driver pleaded not guilty in June. The trial, scheduled for November 15, was postponed to February 2023.
Arendal, Norway (May 29, 2020)
 After being notified that some straps on his trailer had come loose, on May 29, 2020, at approximately 11:00 a.m., a solo truck driver parked a tractor-trailer on the hard shoulder of northbound E18, northeast of the Torsbuås tunnel exit, just outside
After being notified that some straps on his trailer had come loose, on May 29, 2020, at approximately 11:00 a.m., a solo truck driver parked a tractor-trailer on the hard shoulder of northbound E18, northeast of the Torsbuås tunnel exit, just outside Arendal
Arendal () is a List of municipalities of Norway, municipality in Agder counties of Norway, county in southeastern Norway. Arendal belongs to the Districts of Norway, region of Southern Norway, Sørlandet. The administrative centre of the munici ...
. Because of the restricted shoulder width, part of the truck was protruding into the right lane of E18.[ While fixing the loose strap that was securing the load, he was struck and killed by a northbound Tesla Model S.]warning triangle {{more citations needed, date=May 2021
A warning triangle is, together with warning lights, used in order to secure a traffic accident site. The legal rules in the individual states partly order a warning triangle to be brought in the vehicle (in ...
on the ground and he assumed the truck was abandoned.[ He then "heard a loud bang, and the car's windscreen cracked"; after pulling over to the shoulder, he walked back towards the parked truck and saw the truck driver's body.][
The Tesla's driver was charged with negligent homicide. Early in the trial, an expert witness testified that the car's computer indicated Autopilot was engaged at the time of the incident.][
The Accident Investigation Board Norway investigated the crash][
]
The Woodlands, Texas, USA (April 17, 2021)
 A Tesla Model S P100D crashed and caught fire in
A Tesla Model S P100D crashed and caught fire in The Woodlands, Texas
The Woodlands is a special-purpose district and census-designated place (CDP) in the U.S. state of Texas in the Houston–The Woodlands–Sugar Land metropolitan statistical area. The Woodlands is primarily located in Montgomery County, with por ...
, a suburb of Houston
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in ...
, at 11:25 p.m. CDT on April 17, 2021. According to a police spokesperson, the vehicle was traveling at a high speed and after failing to negotiate a curve, departed the roadway, crashed into a tree, and burst into flames; the resulting fire took four hours and more than of water to extinguish.earnings call An earnings call is a teleconference, or webcast, in which a public company discusses the financial results of a reporting period ("earnings guidance"). The name comes from earnings per share (EPS), the bottom line number in the income statement d ...
in April 2021, Tesla's vice president of vehicle engineering pushed back on the news coverage of the incident and added that Tesla representatives had studied the crash and reported the steering wheel was "deformed", which could indicate "someone was in the driver's seat at the time of the crash". The same Tesla officer noted a test car's adaptive cruise control
Adaptive cruise control (ACC) is an available cruise control advanced driver-assistance system for road vehicles that automatically adjusts the vehicle speed to maintain a safe distance from vehicles ahead. As of 2019, it is also called by 20 un ...
had accelerated the car to only at the crash site. The NTSB tested an exemplar car at the site and found that Autosteer was not available on that part of Hammock Dunes.
Fontana, California, USA (May 5, 2021)
At 2:35 a.m. PDT on May 5, 2021, a Tesla Model 3 crashed into an overturned tractor-trailer on the westbound Foothill Freeway
The Foothill Freeway is a freeway in the Los Angeles metropolitan area, California, running from the Sylmar district of Los Angeles east to Redlands. The western segment is signed as Interstate 210 (I-210) from its western end at I-5 to S ...
(I-210) in Fontana, California
Fontana is a city in San Bernardino County, California. Founded by Azariel Blanchard Miller in 1913, it remained essentially rural until World War II, when entrepreneur Henry J. Kaiser built a large steel mill in the area. It is now a regional h ...
. The driver of the Tesla was killed, and a man who had stopped to assist the driver of the truck was struck and injured by the Tesla. California Highway Patrol
The California Highway Patrol (CHP) is a state law enforcement agency of the U.S. state of California. The CHP has primary patrol jurisdiction over all California highways and roads and streets outside city limits, and can exercise law enforcem ...
(CHP) officials announced on May 13 that Autopilot "was engaged" prior to the crash, but added a day later that "a final determination as not beenmade as to what driving mode the Tesla was in or if it was a contributing factor to the crash". The CHP and NHTSA are investigating the crash.
Queens, New York, USA (July 26, 2021)
On July 26, 2021, just after midnight, a man was hit and killed by a driver in a Tesla Model Y SUV. The victim had parked his vehicle on the left shoulder of the westbound Long Island Expressway
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mensur ...
(I-495), just east of the College Point Boulevard exit in Flushing, Queens
Flushing is a neighborhood in the north-central portion of the New York City borough of Queens. The neighborhood is the fourth-largest central business district in New York City. Downtown Flushing is a major commercial and retail area, and the ...
, New York, to change a flat tire. The NHTSA later determined Autopilot was active during the collision and sent a team to further investigate.[
]
Evergreen, Colorado, USA (May 16, 2022)
In the evening of May 16, 2022, the driver of a Tesla Model 3 left Upper Bear Creek Road in Evergreen, Colorado and collided with a tree. After the car caught on fire, a passenger was able to exit, but the driver was unable to leave the car and died at the scene. Law enforcement suspect that the Tesla was operating in Autopilot.[
]
Mission Viejo, California, USA (May 17, 2022)
At 10:51 p.m. PDT on May 17, 2022, a pedestrian walking on southbound I-5
Interstate 5 (I-5) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the West Coast of the United States, running largely parallel to the Pacific coast of the contiguous U.S. from Mexico to Canada. It travels through the states of Californi ...
near Crown Valley Parkway in Mission Viejo, California
Mission Viejo ( ; corruption of ''Misión Vieja'', Spanish for "Old Mission") is a commuter city in the Saddleback Valley in Orange County, California, United States. Mission Viejo is considered one of the largest master-planned communities eve ...
was struck and killed by a driver operating a Tesla Model 3. After the driver of the Tesla parked the car and exited it to stand on the right shoulder of the freeway, an impaired driver crashed their car into the Tesla, and a third driver crashed into the two-car wreck, which was in a construction zone. Field report data confirmed the Tesla was operating in Autopilot.[
]
Gainesville, Florida, USA (July 6, 2022)
At approximately 2:00 p.m. Eastern Daylight Time, EDT on July 7, 2022, the driver of a Tesla Model S traveling southbound on Interstate 75 in Florida, I-75 exited at a rest area just south of Gainesville, Florida, near Paynes Prairie Preserve State Park, and smashed into the rear of a parked Walmart tractor-trailer. Both the driver and passenger of the Tesla, a married couple from Lompoc, California, were killed. A spokesperson for the Florida Highway Patrol noted "[The vehicle] came off the exit ramp to the rest area, continued south for a short period, and turned into an easterly direction and that's at what time we had the collision where the Tesla struck the rear of the tractor-trailer." The NHTSA confirmed it had sent an investigation team to the site. Data reported by Tesla under NHTSA SGO-2021-01 confirm that Autopilot was engaged during the crash.
Riverside, California, USA (July 7, 2022)
It was initially (and incorrectly) reported that at 4:47 a.m. Pacific Daylight Savings Time, PDT on July 7, 2022, a driver in a Tesla Model Y approached from behind, and then struck a motorcyclist on a Yamaha V-Star. Both vehicles were traveling eastbound in the high-occupancy vehicle lane of SR 91, west of Magnolia Avenue in Riverside, California. The motorcyclist was ejected from his vehicle and died at the scene, while the driver of the Tesla was uninjured after the Model Y went off the road. The driver of the Tesla was not arrested.
Subsequent CHP investigation showed the motorcyclist struck the dividing wall and fell off his motorcycle; the Tesla Model Y following behind struck the motorcycle (which was already lying on its side) but not the motorcyclist. Telemetry data from Tesla later confirmed the Model Y driver was using Autopilot.[
]
Draper, Utah, USA (July 24, 2022)
A motorcycle rider was struck from behind by a driver using Autopilot in a Tesla Model 3 on southbound Interstate 15 in Utah, Interstate 15 near 15000 S in Draper, Utah, at 1:09 a.m. Mountain Daylight Time, MDT on July 24, 2022. The collision threw the motorcycle rider from his Harley-Davidson to the ground, killing him. The driver told police he did not see the motorcyclist and he was using Autopilot at the time of the crash. Telemetric data submitted to NHTSA later confirmed his statements.[
Michael Brooks, the acting executive director of the Center for Auto Safety commented "It's pretty clear to me, and it should be to a lot of Tesla owners by now, this stuff isn't working properly and it's not going to live up to the expectations, and it is putting innocent people in danger on the roads ... Drivers are being lured into thinking this protects them and others on the roads, and it's just not working."]
Boca Raton, Florida, USA (August 26, 2022)
On August 26, 2022 at 2:11 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time, EDT, a motorcycle rider on a Kawasaki Vulcan was struck from behind by a driver in a Tesla Model 3 while both vehicles were traveling westbound on SW 18th Street approaching Boca Rio Road in Sandalfoot Cove, Florida, Sandalfoot Cove, a census-designated place in unincorporated Palm Beach County, just outside the city of Boca Raton, Florida. The motorcycle rider was thrown from her motorcycle into the windshield of the Tesla; the rider was transported to a hospital, where she later died from the injuries she sustained in the collision. The driver of the Tesla was suspected of driving under the influence of alcohol and/or prescription drugs.
The Palm Beach County Sheriff's Office later confirmed the driver of the Tesla was using Autopilot.[
It is the second fatal collision of 2022 in the United States where a Tesla operating with Autopilot struck a motorcycle from the rear; in both instances, the motorcyclist was killed. One theory is that because Tesla has shifted to exclusively visual sensors, the Autopilot logic to set the gap between the Tesla and a leading vehicle assumes the distance to a vehicle in front is inversely proportional to the spacing between that vehicle's taillights. Because motorcycle taillights are close-set, Tesla Autopilot may incorrectly assume the motorcycle is a distant car or truck.
]
Non-fatal crashes
Culver City, California, USA (January 22, 2018)
On January 22, 2018, a 2014 Tesla Model S crashed into a fire truck parked on the side of the Interstate 405 (California), I-405 freeway in Culver City, California, while traveling at a speed exceeding and the driver survived with no injuries. The driver told the Culver City Fire Department that he was using Autopilot. The fire truck and a California Highway Patrol vehicle were parked diagonally across the left emergency lane and high-occupancy vehicle lane of the southbound I-405, blocking off the scene of an earlier accident, with emergency lights flashing.
South Jordan, Utah, USA (May 11, 2018)
In the evening of May 11, 2018, a 2016 Tesla Model S with Autopilot engaged crashed into the rear of a fire truck that was stopped in the southbound lane at a red light in South Jordan, Utah, at the intersection of Utah State Route 154, SR-154 and Utah State Route 151, SR-151.
Moscow, Russia (August 10, 2019)
On the night of August 10, 2019, a Tesla Model 3 driving in the left-hand lane on the Moscow Ring Road in Moscow, Russia, crashed into a parked tow truck with a corner protruding into the lane and subsequently burst into flames. According to the driver, the vehicle was traveling at the speed limit of with Autopilot activated; he also claimed his hands were on the wheel, but was not paying attention at the time of the crash. All occupants were able to exit the vehicle before it caught on fire; they were transported to the hospital. Injuries included a broken leg (driver) and bruises (his children).
The force of the collision was enough to push the tow truck forward into the central dividing wall, as recorded by a surveillance camera. Passersby also captured several videos of the fire and explosions after the accident, these videos also show the tow truck that the Tesla crashed into had been moved, suggesting the explosions of the Model 3 happened later.
Chiayi, Taiwan (June 1, 2020)
Traffic cameras captured the moment when a Tesla Model 3 slammed into an overturned cargo truck in Taiwan on June 1, 2020.
Arlington Heights, Washington, USA (May 15, 2021)
A Tesla Model S crashed into a stopped Snohomish County, Washington, sheriff's patrol car at 6:40 p.m. PDT on May 15, 2021, shortly after the deputy parked it while responding to an earlier crash which had broken a utility pole near the intersection of Washington State Route 530, SR 530 and 103rd Ave NE in Arlington Heights, Washington. The patrol car was parked to partially block the roadway and protect the collision scene, and the patrol car's emergency vehicle lighting, overhead emergency lights were activated. Neither the deputy nor the driver of the Tesla were injured. The driver of the Tesla assumed his car would slow and move over on its own because it was in "Auto-Pilot mode".
Brea, California, USA (November 3, 2021)
The driver of a Tesla Model Y reported a crash to the NHTSA that occurred on November 3, 2021 while operating in FSD Beta. The incident was described as a "severe" crash after "the car by itself took control and forced itself into the incorrect lane" during a left turn. It is likely this is the first complaint filed with NHTSA that alleges FSD caused a crash; NHTSA requested further information from Tesla, but other details of the crash, such as the driver's identity and location of the crash, were not released.
See also
* Advanced driver-assistance systems
* Self-driving car
* Elon Musk's Crash Course
References
External links
*
* Video documentary.
{{Autonomous cars and enabling technologies
Advanced driver assistance systems
Automotive technology tradenames
Automotive accessories
Automotive technologies
Tesla, Inc., Autopilot
 Tesla Autopilot is a suite of
Tesla Autopilot is a suite of  As an upgrade to the capabilities of Autopilot, the company's stated intent is to offer full autonomous driving (SAE Level 5) at a future time, acknowledging that technical and regulatory hurdles must be overcome to achieve this goal. From 2016 through 2022,
As an upgrade to the capabilities of Autopilot, the company's stated intent is to offer full autonomous driving (SAE Level 5) at a future time, acknowledging that technical and regulatory hurdles must be overcome to achieve this goal. From 2016 through 2022,  HW2, included in vehicles manufactured after October 2016, includes an
HW2, included in vehicles manufactured after October 2016, includes an  On January 20, 2016, the driver of a Tesla Model S in Handan, Hebei, China, was killed when his car crashed into a stationary truck. The Tesla was following a car in the far left lane of a multi-lane highway; the car in front moved to the right lane to avoid a truck stopped on the left shoulder, and the Tesla, which the driver's father believes was in Autopilot mode, did not slow before colliding with the stopped truck. According to footage captured by a
On January 20, 2016, the driver of a Tesla Model S in Handan, Hebei, China, was killed when his car crashed into a stationary truck. The Tesla was following a car in the far left lane of a multi-lane highway; the car in front moved to the right lane to avoid a truck stopped on the left shoulder, and the Tesla, which the driver's father believes was in Autopilot mode, did not slow before colliding with the stopped truck. According to footage captured by a 
 On May 7, 2016, a Tesla driver was killed in a crash with an 18-wheel
On May 7, 2016, a Tesla driver was killed in a crash with an 18-wheel  The NHTSA's preliminary evaluation was opened to examine the design and performance of any automated driving systems in use at the time of the crash, which involves a population of an estimated 25,000 Model S cars. On July 8, 2016, the NHTSA requested Tesla Inc. to hand over to the agency detailed information about the design, operation and testing of its Autopilot technology. The agency also requested details of all design changes and updates to Autopilot since its introduction, and Tesla's planned updates scheduled for the next four months.
According to Tesla, "neither autopilot nor the driver noticed the white side of the tractor-trailer against a brightly lit sky, so the brake was not applied." The car attempted to drive full speed under the trailer, "with the bottom of the trailer impacting the windshield of the Model S". Tesla also stated that this was Tesla's first known Autopilot-related death in over 130 million miles (208 million km) driven by its customers while Autopilot was activated. According to Tesla there is a fatality every 94 million miles (150 million km) among all type of vehicles in the U.S. It is estimated that billions of miles will need to be traveled before Tesla Autopilot can claim to be safer than humans with statistical significance. Researchers say that Tesla and others need to release more data on the limitations and performance of automated driving systems if self-driving cars are to become safe and understood enough for mass-market use.
The truck's driver told the
The NHTSA's preliminary evaluation was opened to examine the design and performance of any automated driving systems in use at the time of the crash, which involves a population of an estimated 25,000 Model S cars. On July 8, 2016, the NHTSA requested Tesla Inc. to hand over to the agency detailed information about the design, operation and testing of its Autopilot technology. The agency also requested details of all design changes and updates to Autopilot since its introduction, and Tesla's planned updates scheduled for the next four months.
According to Tesla, "neither autopilot nor the driver noticed the white side of the tractor-trailer against a brightly lit sky, so the brake was not applied." The car attempted to drive full speed under the trailer, "with the bottom of the trailer impacting the windshield of the Model S". Tesla also stated that this was Tesla's first known Autopilot-related death in over 130 million miles (208 million km) driven by its customers while Autopilot was activated. According to Tesla there is a fatality every 94 million miles (150 million km) among all type of vehicles in the U.S. It is estimated that billions of miles will need to be traveled before Tesla Autopilot can claim to be safer than humans with statistical significance. Researchers say that Tesla and others need to release more data on the limitations and performance of automated driving systems if self-driving cars are to become safe and understood enough for mass-market use.
The truck's driver told the  On March 23, 2018, a second U.S. Autopilot fatality occurred in
On March 23, 2018, a second U.S. Autopilot fatality occurred in  In a corporate blog post, Tesla noted the impact attenuator separating the offramp from US 101 had been previously crushed and not replaced prior to the Model X crash on March 23. The post also stated that Autopilot was engaged at the time of the crash, and the driver's hands had not been detected manipulating the steering wheel for six seconds before the crash. Vehicle data showed the driver had five seconds and a "unobstructed view of the concrete divider, ... but the vehicle logs show that no action was taken." The NTSB investigation had been focused on the damaged
In a corporate blog post, Tesla noted the impact attenuator separating the offramp from US 101 had been previously crushed and not replaced prior to the Model X crash on March 23. The post also stated that Autopilot was engaged at the time of the crash, and the driver's hands had not been detected manipulating the steering wheel for six seconds before the crash. Vehicle data showed the driver had five seconds and a "unobstructed view of the concrete divider, ... but the vehicle logs show that no action was taken." The NTSB investigation had been focused on the damaged  On April 29, 2018, a Tesla Model X operating on Autopilot struck and killed a pedestrian in Kanagawa, Japan, after the driver had fallen asleep. According to a lawsuit filed against Tesla in federal court (N.D. Cal.) in April 2020, the Tesla Model X accelerated from after the vehicle in front of it changed lanes; it then crashed into a van, motorcycles, and pedestrians in the far right lane of the expressway, killing a 44-year-old man on the road directing traffic. The original complaint claims the accident occurred due to flaws in Tesla's Autopilot system, such as inadequate monitoring to detect inattentive drivers and an inability to handle traffic situations "that drivers will almost always certainly encounter". In addition, the original complaint claimed this is the first pedestrian fatality to result from the use of Autopilot.
According to vehicle data logs, the driver of the Tesla had engaged autopilot at 2:11 p.m.
On April 29, 2018, a Tesla Model X operating on Autopilot struck and killed a pedestrian in Kanagawa, Japan, after the driver had fallen asleep. According to a lawsuit filed against Tesla in federal court (N.D. Cal.) in April 2020, the Tesla Model X accelerated from after the vehicle in front of it changed lanes; it then crashed into a van, motorcycles, and pedestrians in the far right lane of the expressway, killing a 44-year-old man on the road directing traffic. The original complaint claims the accident occurred due to flaws in Tesla's Autopilot system, such as inadequate monitoring to detect inattentive drivers and an inability to handle traffic situations "that drivers will almost always certainly encounter". In addition, the original complaint claimed this is the first pedestrian fatality to result from the use of Autopilot.
According to vehicle data logs, the driver of the Tesla had engaged autopilot at 2:11 p.m.  At approximately 6:17 a.m.
At approximately 6:17 a.m.  An eastbound Tesla Model 3 rear-ended a fire truck parked along
An eastbound Tesla Model 3 rear-ended a fire truck parked along  Shortly before 12:39 a.m. on December 29, 2019, a westbound Tesla Model S exited the freeway section of SR 91, failed to stop for a red light, and crashed into the driver's side of Honda Civic in Gardena, California, killing the driver and passenger in the Civic and injuring the Tesla driver and passenger. The freeway section of SR 91 ends just east of the intersection of Artesia Blvd and Vermont Ave, and continues as Artesia. The Tesla was proceeding west on Artesia against the red light when it struck the Civic, which was turning left from Vermont onto Artesia. The occupants of the Tesla were taken to the hospital with non life-threatening injuries.
The NHTSA initiated an investigation of the crash, which was considered unusual for a two-vehicle collision, and later confirmed in January 2022 that Autopilot was engaged during the crash. The Tesla driver was charged in October 2021 with vehicular manslaughter in the
Shortly before 12:39 a.m. on December 29, 2019, a westbound Tesla Model S exited the freeway section of SR 91, failed to stop for a red light, and crashed into the driver's side of Honda Civic in Gardena, California, killing the driver and passenger in the Civic and injuring the Tesla driver and passenger. The freeway section of SR 91 ends just east of the intersection of Artesia Blvd and Vermont Ave, and continues as Artesia. The Tesla was proceeding west on Artesia against the red light when it struck the Civic, which was turning left from Vermont onto Artesia. The occupants of the Tesla were taken to the hospital with non life-threatening injuries.
The NHTSA initiated an investigation of the crash, which was considered unusual for a two-vehicle collision, and later confirmed in January 2022 that Autopilot was engaged during the crash. The Tesla driver was charged in October 2021 with vehicular manslaughter in the  After being notified that some straps on his trailer had come loose, on May 29, 2020, at approximately 11:00 a.m., a solo truck driver parked a tractor-trailer on the hard shoulder of northbound E18, northeast of the Torsbuås tunnel exit, just outside
After being notified that some straps on his trailer had come loose, on May 29, 2020, at approximately 11:00 a.m., a solo truck driver parked a tractor-trailer on the hard shoulder of northbound E18, northeast of the Torsbuås tunnel exit, just outside  A Tesla Model S P100D crashed and caught fire in
A Tesla Model S P100D crashed and caught fire in