Novgorod Operations Group on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, –í–µ–ª–∏–∫–∏–π –ù–æ–≤–≥–æ—Ä–æ–¥, t=Great Newtown, p=v ≤…™Ààl ≤ik ≤…™j Àànov…°…ôr…ôt), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and
 In 882, Rurik's successor, Oleg of Novgorod, conquered
In 882, Rurik's successor, Oleg of Novgorod, conquered
 In 1259, Mongol tax-collectors and census-takers arrived in the city, leading to political disturbances and forcing
In 1259, Mongol tax-collectors and census-takers arrived in the city, leading to political disturbances and forcing
 At the time of annexation, Novgorod became the third largest city under
At the time of annexation, Novgorod became the third largest city under
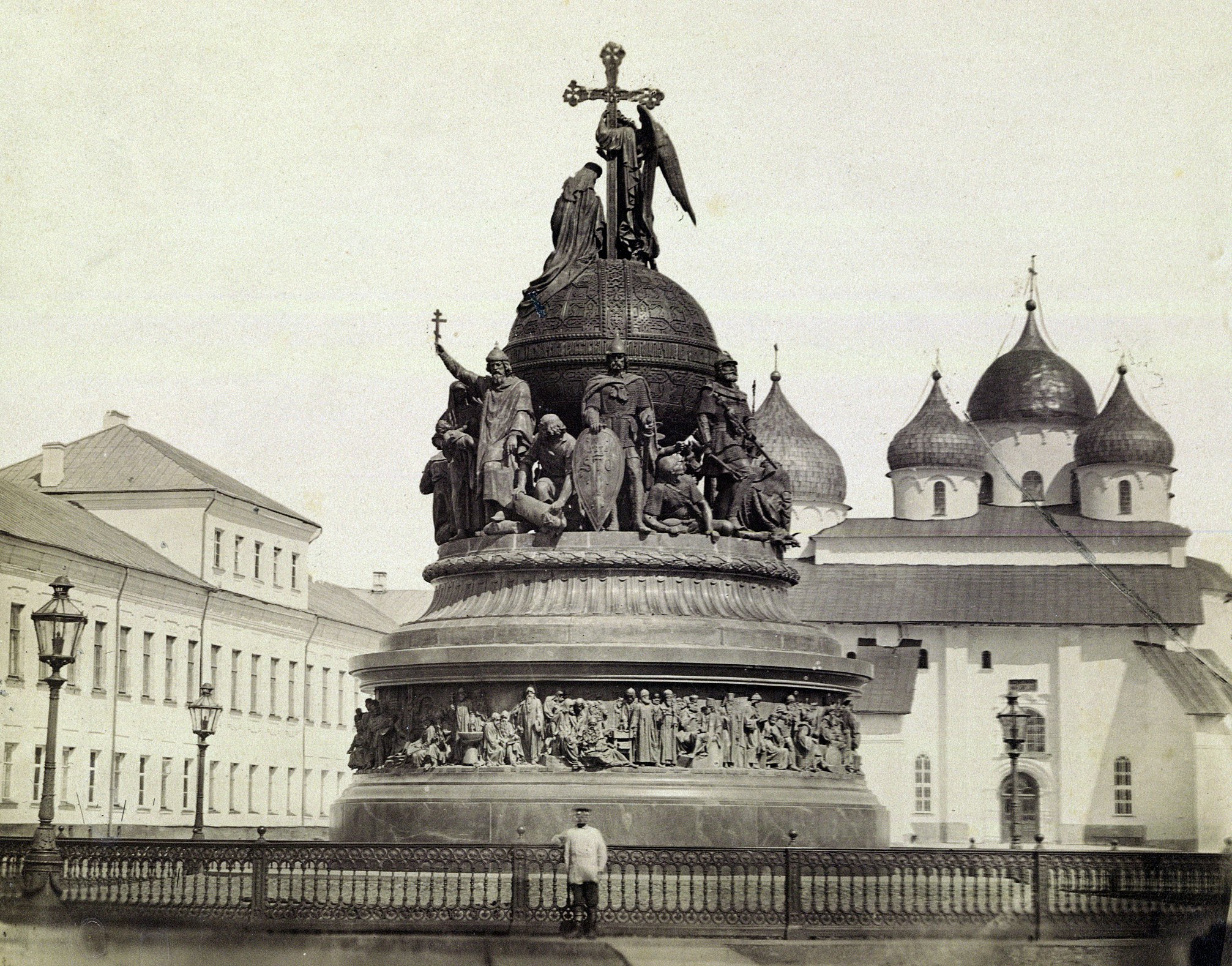 The city is known for the variety and age of its medieval monuments. The foremost among these is the St. Sophia Cathedral, built between 1045 and 1050 under the patronage of Vladimir Yaroslavich, the son of Yaroslav the Wise; Vladimir and his mother,
The city is known for the variety and age of its medieval monuments. The foremost among these is the St. Sophia Cathedral, built between 1045 and 1050 under the patronage of Vladimir Yaroslavich, the son of Yaroslav the Wise; Vladimir and his mother,  Outside the Kremlin walls, there are three large churches constructed during the reign of
Outside the Kremlin walls, there are three large churches constructed during the reign of
File:Nowgorod 2005 Millenium Monument.jpg, Bronze monument to the Millennium of Russia (1862)
File:Nowgorod 2005 w.jpg, Walls of the Novgorod Kremlin
File:VNovgorod WWIIMemoral 4211.JPG, War Memorial
File:Yaroslavovo Dvorische 01.jpg, View of the Yaroslav's Court
File:Novgorod - Oblast Duma and Administration.jpg, Government Building
 Novgorod has connections to Moscow (531 km) and St. Petersburg (189 km) by the federal highway M10. There are public buses to Saint Petersburg and other destinations.
The city has direct railway passenger connections with Moscow ( Leningradsky Rail Terminal, by night trains), St. Petersburg ( Moscow Rail Terminal and Vitebsk Rail Terminal, by suburban trains), Minsk ( Belarus) ( Minsk Passazhirsky railway station, by night trains) and Murmansk.
The city's former commercial airport Yurievo was decommissioned in 2006, and the area has now been redeveloped into a residential neighbourhood. The still existing Krechevitsy Airport does not serve any regular flights since mid-1990s although there is a plan to turn Krechevitsy into a new operational airport by 2025. The nearest international airport is St. Petersburg's Pulkovo, some north of the city.
Novgorod has connections to Moscow (531 km) and St. Petersburg (189 km) by the federal highway M10. There are public buses to Saint Petersburg and other destinations.
The city has direct railway passenger connections with Moscow ( Leningradsky Rail Terminal, by night trains), St. Petersburg ( Moscow Rail Terminal and Vitebsk Rail Terminal, by suburban trains), Minsk ( Belarus) ( Minsk Passazhirsky railway station, by night trains) and Murmansk.
The city's former commercial airport Yurievo was decommissioned in 2006, and the area has now been redeveloped into a residential neighbourhood. The still existing Krechevitsy Airport does not serve any regular flights since mid-1990s although there is a plan to turn Krechevitsy into a new operational airport by 2025. The nearest international airport is St. Petersburg's Pulkovo, some north of the city.
File:15 050528a.JPG, trolleybus Skoda-VMZ-14Tr
File:Novgorod - Trolleys and a bus at main station.jpg, Trolleybuses ZiU-9
File:Novgorod - Bus at main station 02.jpg, Bus
Official website of Veliky Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod City PortalVeliky Novgorod for touristsThe Faceted Palace of the Kremlin in Novgorod the Great site
* * * * {{Authority control Archaeological sites in Russia Rus' settlements Capitals of former nations Trading posts of the Hanseatic League Novgorodsky Uyezd World Heritage Sites in Russia
administrative centre
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, Lu ...
of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the Volkhov River just downstream from its outflow from Lake Ilmen
Lake Ilmen ( rus, –òÃÅ–ª—å–º–µ–Ω—å, p=Ààil ≤m ≤…™n ≤) is a large lake in the Novgorod Oblast of Russia. A historically important lake, it formed a vital part of the medieval trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks. The city of Novgorod - wh ...
and is situated on the M10 federal highway connecting Moscow and Saint Petersburg. UNESCO recognized Novgorod as a World Heritage Site in 1992. The city has a population of
At its peak during the 14th century, the city was the capital of the Novgorod Republic and was one of Europe's largest cities. The "Veliky" ("great") part was added to the city's name in 1999.
History
Early developments
The Sofia First Chronicle makes initial mention of it in 859, while the Novgorod First Chronicle first mentions it in 862, when it was purportedly already a major Baltics-to-Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
station on the trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks. The Charter of Veliky Novgorod recognizes 859 as the year when the city was first mentioned.Charter of Veliky Novgorod, Article 1 Novgorod is traditionally considered to be a cradle of Russian statehood.
The oldest archaeological excavations in the middle to late 20th century, however, have found cultural layers dating back to the late 10th century, the time of the Christianization of Rus' and a century after it was allegedly founded. Archaeological dating is fairly easy and accurate to within 15–25 years, as the streets were paved with wood, and most of the houses made of wood, allowing tree ring dating.
The Varangian name of the city or ( or ) is mentioned in Norse Sagas as existing at a yet earlier stage, but the correlation of this reference with the actual city is uncertain. Originally, referred to the stronghold, now only to the south of the center of the present-day city, Rurikovo Gorodische (named in comparatively modern times after the Varangian chieftain Rurik
Rurik (also Ryurik; orv, –Ý—é—Ä–∏–∫—ä, Rjurik≈≠, from Old Norse '' Hr√∏r√≠k Ä''; russian: –Ý—é—Ä–∏–∫; died 879); be, –Ý—É—Ä—ã–∫, Ruryk was a semi-legendary Varangian chieftain of the Rus' who in the year 862 was invited to reign in Novgoro ...
, who supposedly made it his "capital" around 860). Archaeological data suggests that the Gorodishche, the residence of the Knyaz
, or ( Old Church Slavonic: –ö–Ω—ß–∑—å) is a historical Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times of history and different ancient Slavic lands. It is usually translated into English as prince or duke, dependi ...
(prince), dates from the mid-9th century, whereas the town itself dates only from the end of the 10th century; hence the name Novgorod, "new city", from Old East Slavic
Old East Slavic (traditionally also Old Russian; be, старажытнаруская мова; russian: древнерусский язык; uk, давньоруська мова) was a language used during the 9th–15th centuries by East ...
and ( and ); the Old Norse term is a calque of an Old Russian
Old East Slavic (traditionally also Old Russian; be, старажытнаруская мова; russian: древнерусский язык; uk, давньоруська мова) was a language used during the 9th–15th centuries by East ...
word. First mention of this Norse etymology to the name of the city of Novgorod (and that of other cities within the territory of the then Kievan Rus') occurs in the 10th-century policy manual by Byzantine emperor Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Kar ...
.
Princely state within Kievan Rus'
 In 882, Rurik's successor, Oleg of Novgorod, conquered
In 882, Rurik's successor, Oleg of Novgorod, conquered Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
and founded the state of Kievan Rus'. Novgorod's size as well as its political, economic, and cultural influence made it the second most important city in Kievan Rus'. According to a custom, the elder son and heir of the ruling Kievan monarch was sent to rule Novgorod even as a minor. When the ruling monarch had no such son, Novgorod was governed by posadniks, such as the legendary Gostomysl, Dobrynya, Konstantin, and Ostromir.
Of all their princes, Novgorodians most cherished the memory of Yaroslav the Wise, who sat as Prince of Novgorod from 1010 to 1019, while his father, Vladimir the Great, was a prince in Kiev. Yaroslav promulgated the first written code of laws (later incorporated into Russkaya Pravda) among the Eastern Slavs and is said to have granted the city a number of freedoms or privileges, which they often referred to in later centuries as precedents in their relations with other princes. His son, Vladimir, sponsored construction of the great St. Sophia Cathedral, more accurately translated as the Cathedral of Holy Wisdom, which stands to this day.
Early foreign ties
In Norse sagas the city is mentioned as the capital of Gardariki. Many Viking kings and yarls came to Novgorod seeking refuge or employment, includingOlaf I of Norway
Olaf Tryggvason (960s – 9 September 1000) was King of Norway from 995 to 1000. He was the son of Tryggvi Olafsson, king of Viken (Vingulmark, and Rånrike), and, according to later sagas, the great-grandson of Harald Fairhair, first King of N ...
, Olaf II of Norway, Magnus I of Norway, and Harald Hardrada
Harald Sigurdsson (; – 25 September 1066), also known as Harald III of Norway and given the epithet ''Hardrada'' (; modern no, Hardråde, roughly translated as "stern counsel" or "hard ruler") in the sagas, was King of Norway from 1046 t ...
. No more than a few decades after the 1030 death and subsequent canonization
Canonization is the declaration of a deceased person as an officially recognized saint, specifically, the official act of a Christian communion declaring a person worthy of public veneration and entering their name in the canon catalogue of ...
of Olaf II of Norway, the city's community had erected in his memory Saint Olaf's Church in Novgorod
Saint Olaf's Church in Novgorod was a church for Varangians which existed from the 11th century until the 14th century in the Russian city of Novgorod.
The church was located in the permanent Varangian centre of trade in Novgorod's trading area ( ...
.
The Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the ...
town of Visby functioned as the leading trading center in the Baltic before the Hansa League. At Novgorod in 1080, Visby merchants established a trading post which they named Gutagard (also known as Gotenhof). Later, in the first half of the 13th century, merchants from northern Germany also established their own trading station in Novgorod, known as Peterhof. At about the same time, in 1229, German merchants at Novgorod were granted certain privileges, which made their position more secure.
Novgorod Republic
In 1136, the Novgorodians dismissed their prince Vsevolod Mstislavich. The year is seen as the traditional beginning of the Novgorod Republic. The city was able to invite and dismiss a number of princes over the next two centuries, but the princely office was never abolished and powerful princes, such asAlexander Nevsky
Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky (russian: Александр Ярославич Невский; ; 13 May 1221 – 14 November 1263) served as Prince of Novgorod (1236–40, 1241–56 and 1258–1259), Grand Prince of Kiev (1236–52) and Grand P ...
, could assert their will in the city regardless of what Novgorodians said. The city state controlled most of Europe's northeast, from lands east of today's Estonia to the Ural Mountains, making it one of the largest states in medieval Europe, although much of the territory north and east of Lakes Ladoga and Onega was sparsely populated and never organized politically.
One of the most important local figures in Novgorod was the , or mayor, an official elected by the public assembly (called the ) from among the city's boyars, or aristocracy. The , or "thousandman", originally the head of the town militia but later a commercial and judicial official, was also elected by the . Another important local official was the Archbishop of Novgorod who shared power with the boyars. Archbishops were elected by the or by the drawing of lots, and after their election, were sent to the metropolitan
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a typ ...
for consecration.
While a basic outline of the various officials and the can be drawn up, the city-state's exact political constitution remains unknown. The boyars and the archbishop ruled the city together, although where one official's power ended and another's began is uncertain. The prince, although his power was reduced from around the middle of the 12th century, was represented by his , or lieutenant, and still played important roles as a military commander, legislator and jurist. The exact composition of the , too, is uncertain, with some historians, such as Vasily Klyuchevsky, claiming it was democratic in nature, while later scholars, such as Marxists
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialectic ...
Valentin Ianin and Aleksandr Khoroshev, see it as a "sham democracy" controlled by the ruling elite.
In the 13th century, Novgorod, while not a member of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
, was the easternmost kontor, or entrepôt, of the league, being the source of enormous quantities of luxury (sable
The sable (''Martes zibellina'') is a species of marten, a small omnivorous mammal primarily inhabiting the forest environments of Russia, from the Ural Mountains throughout Siberia, and northern Mongolia. Its habitat also borders eastern Kaza ...
, ermine, fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelv ...
, marmot) and non-luxury furs (squirrel pelts).
Throughout the Middle Ages, the city thrived culturally. A large number of birch bark letters have been unearthed in excavations, perhaps suggesting widespread literacy. It was in Novgorod that the Novgorod Codex, the oldest Slavic book written north of Bulgaria, and the oldest inscription in a Finnic language ( Birch bark letter no. 292) were unearthed. Some of the most ancient Russian chronicles ( Novgorod First Chronicle) were written in the scriptorium of the archbishops who also promoted iconography and patronized church construction. The Novgorod merchant Sadko became a popular hero of Russian folklore.
Novgorod was never conquered by the Mongols during the Mongol invasion of Rus. The Mongol army turned back about from the city, not because of the city's strength, but probably because the Mongol commanders did not want to get bogged down in the marshlands surrounding the city. However, the grand princes of Moscow, who acted as tax collectors for the khans of the Golden Horde, did collect tribute in Novgorod, most notably Yury Danilovich and his brother, Ivan Kalita.
 In 1259, Mongol tax-collectors and census-takers arrived in the city, leading to political disturbances and forcing
In 1259, Mongol tax-collectors and census-takers arrived in the city, leading to political disturbances and forcing Alexander Nevsky
Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky (russian: Александр Ярославич Невский; ; 13 May 1221 – 14 November 1263) served as Prince of Novgorod (1236–40, 1241–56 and 1258–1259), Grand Prince of Kiev (1236–52) and Grand P ...
to punish a number of town officials (he cut off their noses) for defying him as Grand Prince of Vladimir (soon to be the khan's tax-collector in Russia) and his Mongol overlords. In the 14th century, raids by Novgorod pirates, or , sowed fear as far as Kazan and Astrakhan, assisting Novgorod in wars with the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
During the era of Old Rus' State, Novgorod was a trade hub at the northern end of both the Volga trade route and the "route from the Varangians to the Greeks
The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks was a medieval trade route that connected Scandinavia, Kievan Rus' and the Eastern Roman Empire. The route allowed merchants along its length to establish a direct prosperous trade with the Empir ...
" along the Dnieper river system. A vast array of goods were transported along these routes and exchanged with local Novgorod merchants and other traders. The farmers of Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the ...
retained the Saint Olof trading house well into the 12th century. Later German merchantmen also established tradinghouses in Novgorod. Scandinavian royalty would intermarry with Russian princes and princesses.
After the great schism, Novgorod struggled from the beginning of the 13th century against Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
, Danish, and German crusaders. During the Swedish-Novgorodian Wars, the Swedes invaded lands where some of the population had earlier paid tribute to Novgorod. The Germans had been trying to conquer the Baltic region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. ...
since the late 12th century. Novgorod went to war 26 times with Sweden and 11 times with the Livonian Brothers of the Sword. The German knights, along with Danish and Swedish feudal lords, launched a series of uncoordinated attacks in 1240–1242. Novgorodian sources mention that a Swedish army was defeated in the Battle of the Neva
The Battle of the Neva (russian: Невская битва, Nevskaya bitva; sv, slaget vid Neva; ) was fought between the Novgorod Republic and Karelians against History of Sweden (800–1521), Swedish, Kingdom of Norway (872–1397), Norwegian ...
in 1240. The Baltic German campaigns ended in failure after the Battle on the Ice in 1242. After the foundation of the castle of Viborg in 1293 the Swedes gained a foothold in Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, –ö–∞—Ä–µÃÅ–ª–∏—è, links=y, r=Kar√©lija, p=k…êÀàr ≤el ≤…™j…ô, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for ...
. On August 12, 1323, Sweden and Novgorod signed the Treaty of Nöteborg, regulating their border for the first time.
The city's downfall occurred partially as a result of its inability to feed its large population, making it dependent on the Vladimir-Suzdal region for grain. The main cities in the area, Moscow and Tver, used this dependence to gain control over Novgorod. Eventually Ivan III forcibly annexed the city to the Grand Duchy of Moscow
The Grand Duchy of Moscow, Muscovite Russia, Muscovite Rus' or Grand Principality of Moscow (russian: –í–µ–ª–∏–∫–æ–µ –∫–Ω—è–∂–µ—Å—Ç–≤–æ –ú–æ—Å–∫–æ–≤—Å–∫–æ–µ, Velikoye knyazhestvo Moskovskoye; also known in English simply as Muscovy from the Lati ...
in 1478. The was dissolved and a significant part of Novgorod's aristocracy, merchants and smaller landholding families was deported to central Russia. The Hanseatic League kontor was closed in 1494 and the goods stored there were seized by Muscovite forces.
Tsardom of Russia
 At the time of annexation, Novgorod became the third largest city under
At the time of annexation, Novgorod became the third largest city under Muscovy Muscovy is an alternative name for the Grand Duchy of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). It may also refer to:
*Muscovy Company, an English trading company chartered in 1555
*Muscovy duck (''Cairina moschata'') and Domest ...
and then the Tsardom of Russia (with 5,300 homesteads and 25–30 thousand inhabitants in the 1550s) and remained so until the famine of the 1560s and the Massacre of Novgorod in 1570. In the Massacre, Ivan the Terrible
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (russian: Ива́н Васи́льевич; 25 August 1530 – ), commonly known in English as Ivan the Terrible, was the grand prince of Moscow from 1533 to 1547 and the first Tsar of all Russia from 1547 to 1584.
Ivan ...
sacked the city, slaughtered thousands of its inhabitants, and deported the city's merchant elite and nobility to Moscow, Yaroslavl and elsewhere. The last decade of the 16th century was a comparatively favourable period for the city as Boris Godunov
Borís Fyodorovich Godunóv (; russian: Борис Фёдорович Годунов; 1552 ) ruled the Tsardom of Russia as ''de facto'' regent from c. 1585 to 1598 and then as the first non-Rurikid tsar from 1598 to 1605. After the end of his ...
restored trade privileges and raised the status of Novgorod bishop. The German trading post was reestablished in 1603. Even after the incorporation into the Russian state Novgorod land retained its distinct identity and institutions, including the customs policy and administrative division. Certain elective offices were quickly restored after having been abolished by Ivan III.
During the Time of Troubles, Novgorodians submitted to Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
troops led by Jacob De la Gardie in the summer of 1611. The city was restituted to Muscovy six years later by the Treaty of Stolbovo. The conflict led to further depopulation: the number of homesteads in the city decreased from 1158 in 1607 to only 493 in 1617, with the Sofia side described as 'deserted'. Novgorod only regained a measure of its former prosperity towards the end of the century, when such ambitious buildings as the Cathedral of the Sign and the Vyazhischi Monastery were constructed. The most famous of Muscovite patriarchs, Nikon, was active in Novgorod between 1648 and 1652. The Novgorod Land became one of the Old Believers' strongholds after the Schism
A schism ( , , or, less commonly, ) is a division between people, usually belonging to an organization, movement, or religious denomination. The word is most frequently applied to a split in what had previously been a single religious body, suc ...
. The city remained an important trade centre even though it was now eclipsed by Archangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ; rus, –ê—Ä—Ö–∞ÃÅ–Ω–≥–µ–ª—å—Å–∫, p=…êrÀàxan…° ≤…™l ≤sk), also known in English as Archangel and Archangelsk, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near i ...
, Novgorodian merchants were trading in the Baltic cities and Stockholm while Swedish merchants came to Novgorod where they had their own trading post since 1627. Novgorod continued to be a major centre of crafts which employed the majority of its population. There were more than 200 distinct professions in 16th century. Bells, cannons and other arms were produced in Novgorod; its silversmiths were famous for the skan'
A Skan' (Old Russian: —Å—ä–∫–∞–Ω—å, ''s''kan, which is in turn from the verb —Å—ä–∫–∞—Ç–∏, ''s''kati'', "twist", "twist into a single or a few strands") is the Russian counterpart of a filigree. It is a kind of jewelry art with a thin layer o ...
technique used for religious items and jewellery. Novgorod chests were in widespread use all across Russia, including the Tsar's household and the northern monasteries.
Russian Empire
In 1727, Novgorod was made the administrative center of Novgorod Governorate of the Russian Empire, which was detached from Saint Petersburg Governorate (see Administrative divisions of Russia in 1727–1728). This administrative division existed until 1927. Between 1927 and 1944, the city was a part ofLeningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast ( rus, –õ–µ–Ω–∏–Ω–≥—Ä–∞–¥—Å–∫–∞—è –æ–±–ª–∞—Å—Ç—å, Leningradskaya oblast‚Äô, l ≤…™n ≤…™nÀàgratsk…ôj…ô Ààobl…ôs ≤t ≤, , ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It was established on 1 August 1927, a ...
, and then became the administrative center of the newly formed Novgorod Oblast.
Modern era
On August 15, 1941, during World War II, the city was occupied by theGerman Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
. Its historic monuments were systematically obliterated. The Red Army liberated
Liberation or liberate may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Liberation'' (film series), a 1970–1971 series about the Great Patriotic War
* "Liberation" (''The Flash''), a TV episode
* "Liberation" (''K-9''), an episode
Gaming
* '' Liberati ...
the city on January 19, 1944. Out of 2,536 stone buildings, fewer than forty remained standing. After the war, thanks to plans laid down by Alexey Shchusev, the central part was gradually restored. In 1992, the chief monuments of the city and the surrounding area were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage Site list as the Historic Monuments of Novgorod and Surroundings. In 1999, the city was officially renamed Veliky Novgorod (literally, Great Novgorod), thus partly reverting to its medieval title "Lord Novgorod the Great". This reduced the temptation to confuse Veliky Novgorod with Nizhny Novgorod, a larger city the other side of Moscow which, between 1932 and 1990, had been renamed Gorky, in honour of Maxim Gorky.
Administrative and municipal status
Veliky Novgorod is the administrative center of the oblast and, within the framework of administrative divisions, it also serves as the administrative center ofNovgorodsky District
Novgorodsky District (russian: –ù–æ–≤–≥–æ—Ä–æ–¥—Å–∫–∏–π —Ä–∞–π–æ–Ω) is an administrativeLaw #559-OZ and municipalLaw #400-OZ district (raion), one of the twenty-one in Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is located in the southwest of the oblast and borde ...
, even though it is not a part of it.Law #559-OZ As an administrative division, it is incorporated separately as the city of oblast significance of Veliky Novgorod—an administrative unit with status equal to that of the districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
. As a municipal division, the city of oblast significance of Veliky Novgorod is incorporated as Veliky Novgorod Urban Okrug.Oblast Law #284-OZ
Sights
 The city is known for the variety and age of its medieval monuments. The foremost among these is the St. Sophia Cathedral, built between 1045 and 1050 under the patronage of Vladimir Yaroslavich, the son of Yaroslav the Wise; Vladimir and his mother,
The city is known for the variety and age of its medieval monuments. The foremost among these is the St. Sophia Cathedral, built between 1045 and 1050 under the patronage of Vladimir Yaroslavich, the son of Yaroslav the Wise; Vladimir and his mother, Anna Porphyrogenita
Anna Porphyrogenita ( grc-x-medieval, ·ºåŒΩŒΩŒ± ŒÝŒøœÅœÜœÖœÅŒøŒ≥ŒµŒΩŒΩŒÆœÑŒ∑, translit=Anna Porphyrogennƒìtƒì, rus, –ê–Ω–Ω–∞ –í–∏–∑–∞–Ω—Ç–∏–π—Å–∫–∞—è, uk, –ê–Ω–Ω–∞ –ü–æ—Ä—Ñ—ñ—Ä–æ–≥–µ–Ω–µ—Ç–∞; 13 March 963 ‚Äì 1011) was a Grand Princess consort ...
, are buried in the cathedral. It is one of the best preserved churches from the 11th century. It is also probably the oldest structure still in use in Russia and the first one to represent original features of Russian architecture (austere stone walls, five helmet-like domes). Its frescoes were painted in the 12th century originally on the orders of Bishop Nikita (died 1108) (the "porches" or side chapels were painted in 1144 under Archbishop Nifont) and renovated several times over the centuries, most recently in the nineteenth century. The cathedral features famous bronze gates, which now hang in the west entrance, allegedly made in Magdeburg in 1156 (other sources see them originating from Płock in Poland) and reportedly snatched by Novgorodians from the Swedish town of Sigtuna in 1187. More recent scholarship has determined that the gates were most likely purchased in the mid-15th century, apparently at the behest of Archbishop Euthymius II (1429–1458), a lover of Western art and architectural styles.
The Novgorod Kremlin, traditionally known as the ''Detinets'', also contains the oldest palace in Russia (the so-called Chamber of the Facets, 1433), which served as the main meeting hall of the archbishops; the oldest Russian bell tower (mid-15th century), and the oldest Russian clock tower (1673). The Palace of Facets, the bell tower, and the clock tower were originally built on the orders of Archbishop Euphimius II, although the clock tower collapsed in the 17th century and had to be rebuilt and much of the palace of Euphimius II is no longer standing. Among later structures, the most remarkable are a royal palace (1771) and a bronze monument to the Millennium of Russia, representing the most important figures from the country's history (unveiled in 1862).
Mstislav the Great
Mstislav I Vladimirovich Monomakh (Russian: –ú—Å—Ç–∏—Å–ª–∞–≤ –í–ª–∞–¥–∏–º–∏—Ä–æ–≤–∏—á –í–µ–ª–∏–∫–∏–π, uk, –ú—Å—Ç–∏—Å–ª–∞–≤ –í–æ–ª–æ–¥–∏–º–∏—Ä–æ–≤–∏—á –í–µ–ª–∏–∫–∏–π; February, 1076 – April 14, 1132), also known as Mstislav the Great, was t ...
. St. Nicholas Cathedral (1113–1123), containing frescoes of Mstislav's family, graces Yaroslav's Court (formerly the chief square of Novgorod). The Yuriev Monastery (one of the oldest in Russia, 1030) contains a tall, three-domed cathedral from 1119 (built by Mstislav's son, Vsevolod, and Kyurik, the head of the monastery). A similar three-domed cathedral (1117), probably designed by the same masters, stands in the Antoniev Monastery, built on the orders of Antony Antony may refer to:
* Antony (name), a masculine given name and a surname
* Antony, Belarus, a village in the Hrodna Voblast of Belarus
* Antony, Cornwall, a village in Cornwall, United Kingdom
** Antony House, Cornwall, United Kingdom
* Antony, ...
, the founder of that monastery.
There are now some fifty medieval and early modern churches scattered throughout the city and its surrounding areas. Some of them were blown up by the Nazis and subsequently restored. The most ancient pattern is represented by those dedicated to Saints Pyotr and Pavel (on the Swallow's Hill, 1185–1192), to Annunciation (in Myachino, 1179), to Assumption (on Volotovo Field, 1180s) and to St. Paraskeva-Piatnitsa (at Yaroslav's Court, 1207). The greatest masterpiece of early Novgorod architecture is the Savior church at Nereditsa (1198).
In the 13th century, tiny churches of the three-paddled design were in vogue. These are represented by a small chapel at the Peryn Monastery (1230s) and St. Nicholas' on the Lipnya Islet (1292, also notable for its 14th-century frescoes). The next century saw the development of two original church designs, one of them culminating in St Theodor's church (1360–1361, fine frescoes from 1380s), and another one leading to the Savior church on Ilyina street (1374, painted in 1378 by Feofan Grek
Theophanes the Greek (sometimes "Feofan Grek" from the russian: Феофан Грек, Greek: Θεοφάνης; c. 1340 Рc. 1410) was a Byzantine Greek artist and one of the greatest icon painters of Muscovite Russia, who influenced the 15t ...
). The Savior' church in Kovalevo (1345) was originally frescoed by Serbian masters, but the church was destroyed during the war. While the church has since been rebuilt, the frescoes have not been restored.
During the last century of the republican government, some new churches were consecrated to Saints Peter and Paul (on Slavna, 1367; in Kozhevniki, 1406), to Christ's Nativity (at the Cemetery, 1387), to St. John the Apostle's (1384), to the Twelve Apostles (1455), to St Demetrius (1467), to St. Simeon (1462), and other saints. Generally, they are not thought to be as innovative as the churches from the previous period. Several shrines from the 12th century (i.e., in Opoki) were demolished brick by brick and then reconstructed exactly as they used to be, several of them in the mid-fifteenth century, again under Archbishop Yevfimy II (Euthymius II), perhaps one of the greatest patrons of architecture in medieval Novgorod.
Novgorod's conquest by Ivan III in 1478 decisively changed the character of local architecture. Large commissions were thenceforth executed by Muscovite masters and patterned after cathedrals of Moscow Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, –ú–æ—Å–∫–æ–≤—Å–∫–∏–π –ö—Ä–µ–º–ª—å, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=Ààm…êÀàskofsk ≤…™j kr ≤eml ≤, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of the kremlins (R ...
: e.g., the Savior Cathedral of Khutyn Monastery (1515), the Cathedral of the Mother of God of the Sign (1688), the St. Nicholas Cathedral of Vyaschizhy Monastery (1685). Nevertheless, the styles of some parochial churches were still in keeping with local traditions: e.g., the churches of Myrrh-bearing Women (1510) and of Saints Boris and Gleb (1586).
In Vitoslavlitsy, along the Volkhov River and the Myachino Lake, close to the Yuriev Monastery, a museum of wooden architecture was established in 1964. Over twenty wooden buildings (churches, houses and mills) dating from the 14th to the 19th century were transported there from all around the Novgorod region.
11400 graves of the German 1st Luftwaffe Field Division
The 1st ''Luftwaffe'' Field Division (german: 1. Luftwaffen-Feld-Division) was an infantry division of the Luftwaffe branch of the Wehrmacht that fought in World War II. It was formed using surplus ground crew of the ''Luftwaffe'' and served on the ...
are found at the war cemetery in Novgorod. Also 1900 soldiers of the Spanish Blue Division are buried there.
Transportation
Intercity transport
 Novgorod has connections to Moscow (531 km) and St. Petersburg (189 km) by the federal highway M10. There are public buses to Saint Petersburg and other destinations.
The city has direct railway passenger connections with Moscow ( Leningradsky Rail Terminal, by night trains), St. Petersburg ( Moscow Rail Terminal and Vitebsk Rail Terminal, by suburban trains), Minsk ( Belarus) ( Minsk Passazhirsky railway station, by night trains) and Murmansk.
The city's former commercial airport Yurievo was decommissioned in 2006, and the area has now been redeveloped into a residential neighbourhood. The still existing Krechevitsy Airport does not serve any regular flights since mid-1990s although there is a plan to turn Krechevitsy into a new operational airport by 2025. The nearest international airport is St. Petersburg's Pulkovo, some north of the city.
Novgorod has connections to Moscow (531 km) and St. Petersburg (189 km) by the federal highway M10. There are public buses to Saint Petersburg and other destinations.
The city has direct railway passenger connections with Moscow ( Leningradsky Rail Terminal, by night trains), St. Petersburg ( Moscow Rail Terminal and Vitebsk Rail Terminal, by suburban trains), Minsk ( Belarus) ( Minsk Passazhirsky railway station, by night trains) and Murmansk.
The city's former commercial airport Yurievo was decommissioned in 2006, and the area has now been redeveloped into a residential neighbourhood. The still existing Krechevitsy Airport does not serve any regular flights since mid-1990s although there is a plan to turn Krechevitsy into a new operational airport by 2025. The nearest international airport is St. Petersburg's Pulkovo, some north of the city.
Local transportation
Local transportation consists of a network of buses and trolleybuses. The trolleybus network, which currently consists of five routes, started operating in 1995 and is the first trolley system opened in Russia after the fall of the Soviet Union.LiAZ-5256
LiAZ () is a bus manufacturing company located in Likino-Dulyovo, Russia. It is now a wholly owned subsidiary of GAZ. Specializes in designing and manufacturing buses large and extra large class (length 10.5 m and +).
Starting in 2015, th ...
Honours
A minor planet, 3799 Novgorod, discovered by the Soviet astronomerNikolai Stepanovich Chernykh
Nikolai Stepanovich Chernykh (russian: –ù–∏–∫–æ–ª–∞ÃÅ–π –°—Ç–µ–ø–∞ÃÅ–Ω–æ–≤–∏—á –ß–µ—Ä–Ω—ãÃÅ—Ö) (6 October 1931 ‚Äì 25 May 2004–ö–∞–∑–∞–∫–æ–≤–∞, –Ý.–ö. –ü–∞–º—è—Ç–∏ –ù–∏–∫–æ–ª–∞—è –°—Ç–µ–ø–∞–Ω–æ–≤–∏—á–∞ –ß–µ—Ä–Ω—ã—Ö'. –¢—Ä—É–¥—ã –ì–æ—Å—É–¥–∞—Ä—Å—Ç ...
in 1979, is named after the city.
Twin towns – sister cities
Veliky Novgorod istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Bielefeld, Germany
* Kohtla-Järve, Estonia
* Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
, Norway
* Nanterre, France
* Örebro, Sweden
* Rochester, New York, USA
* Uusikaupunki, Finland
* Watford, UK
* Zibo, China
See also
* Old Novgorod dialect *Novgorod uprising of 1650
The Novgorod uprising of 1650 (russian: –ù–æ–≤–≥–æ—Ä–æ–¥—Å–∫–æ–µ –≤–æ—Å—Å—Ç–∞–Ω–∏–µ 1650 –≥–æ–¥–∞) was an uprising in Novgorod, caused by the Russian government's bulk purchasing of grain (traded to Sweden) and the resulting increases in the price ...
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * *William Craft Brumfield. A History of Russian Architecture (Seattle: Univ. of Washington Press, 2004) *Peter Bogucki. Novgorod (in Lost Cities; 50 Discoveries in World Archaeology, edited by Paul G. Bahn: Barnes & Noble, Inc., 1997)External links
*Official website of Veliky Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod City Portal
* * * * {{Authority control Archaeological sites in Russia Rus' settlements Capitals of former nations Trading posts of the Hanseatic League Novgorodsky Uyezd World Heritage Sites in Russia