Note-taking Software That Uses GTK on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Note-taking (sometimes written as notetaking or note taking) is the practice of recording information from different sources and platforms. By taking notes, the writer records the essence of the information, freeing their mind from having to recall everything. Notes are commonly drawn from a transient source, such as an oral discussion at a meeting, or a lecture (notes of a meeting are usually called
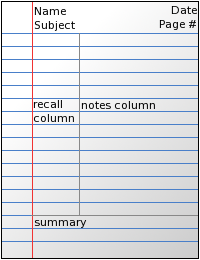 The Cornell Notes method of note-taking was developed by Walter Pauk of Cornell University and promoted in his bestselling 1974 book ''How to Study in College''. It is commonly used at universities today. The Cornell method consists of dividing a single page into three sections: a right-hand column for notes, a left-hand column for cues, and a strip at the bottom for a summary. Cues are key words or questions that help evoke key aspects of the topic. Cornell notes may be more effective for understanding concepts or producing readable notes, but studies have found that they had no significant effect on student performance.
The Cornell Notes method of note-taking was developed by Walter Pauk of Cornell University and promoted in his bestselling 1974 book ''How to Study in College''. It is commonly used at universities today. The Cornell method consists of dividing a single page into three sections: a right-hand column for notes, a left-hand column for cues, and a strip at the bottom for a summary. Cues are key words or questions that help evoke key aspects of the topic. Cornell notes may be more effective for understanding concepts or producing readable notes, but studies have found that they had no significant effect on student performance.
minutes
Minutes, also known as minutes of meeting (abbreviation MoM), protocols or, informally, notes, are the instant written record of a meeting or hearing. They typically describe the events of the meeting and may include a list of attendees, a state ...
), in which case the notes may be the only record of the event. Since the advent of writing and literacy, notes traditionally were almost always handwritten
Handwriting is the writing done with a writing instrument, such as a pen or pencil, in the hand. Handwriting includes both printing and cursive styles and is separate from formal calligraphy or typeface. Because each person's handwriting is u ...
(often in notebook
A notebook (also known as a notepad, writing pad, drawing pad, or legal pad) is a book or stack of paper pages that are often ruled and used for purposes such as note-taking, journaling or other writing, drawing, or scrapbooking.
History
...
s), but the advent of notetaking software has made digital notetaking possible and widespread. Note-taking is a foundational skill in personal knowledge management
Personal knowledge management (PKM) is a process of collecting information that a person uses to gather, classify, store, search, retrieve and share knowledge in their daily activities and the way in which these processes support work activitie ...
.
History
Note-taking has been an important part of human history and scientific development. The Ancient Greeks developed hypomnema, personal records on important subjects. In the Renaissance and early modern period, students learned to take notes in schools, academies and universities, often producing beautiful volumes that served as reference works after they finished their studies. In pre-digital times, people used many kinds of notebooks, including commonplace books, accounting waste books, andmarginalia
Marginalia (or apostils) are marks made in the margins of a book or other document. They may be scribbles, comments, glosses (annotations), critiques, doodles, drolleries, or illuminations.
Biblical manuscripts
Biblical manuscripts have ...
. Philosopher John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 – 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism ...
developed and published a popular indexing system which served as a model for commonplace books and inspired at least ten different published editions of commonplace book templates in Europe and the Americas as well as ''Bell's Common-Place Book, Form'd Generally upon the Principles Recommended and Practised by Mr Locke'' (London, 1770).
Cognitive psychology
Note-taking is a central aspect of a complex human behavior related to information management involving a range of underlying mental processes and their interactions with other cognitive functions.Piolat, A., Olive, T. & Kellogg, R. T. (2005). Cognitive effort during note-taking. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 19, 291–312. The person taking notes must acquire and filter the incoming sources, organize and restructure existing knowledge structures, comprehend and write down their explanation of the information, and ultimately store and integrate the freshly processed material. The result is a knowledge representation, and a memory storage. Studies comparing the performance of students who took handwritten notes to students who typed their notes found that students who took handwritten notes performed better on examinations, hypothetically due to the deeper processing of learned material through selective rephrasing instead of word-for-word transcription which is common when typing notes.Reasons for note-taking
Note-taking is an important skill forstudent
A student is a person enrolled in a school or other educational institution.
In the United Kingdom and most commonwealth countries, a "student" attends a secondary school or higher (e.g., college or university); those in primary or elementar ...
s, especially at the college level. In some contexts, such as college lectures, the main purpose of taking notes may be to implant the material in the mind, the written notes themselves being of secondary importance. Many studies have been able to show that note taking in college students has helped them become more engaged in the lecture and allowed them to better comprehend the material. Even when students fail to return to their notes and study them, they have shown higher test scores and better comprehension when they take notes versus not taking notes. The difference is even more significant when the notes are hand written and reworded rather than merely transcribed or typed.
Systems
Many different formats are used to structure information and make it easier to find and to understand later. The format of the initial record may often be informal and/or unstructured. One common format for such notes is shorthand, which can allow large amounts of information to be put on paper very quickly. Historically, note-taking was an analog process, written innotebook
A notebook (also known as a notepad, writing pad, drawing pad, or legal pad) is a book or stack of paper pages that are often ruled and used for purposes such as note-taking, journaling or other writing, drawing, or scrapbooking.
History
...
s, or other paper methods like Post-It notes. In the digital age, use of computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as C ...
s, tablet PCs and personal digital assistants (PDAs) is common.
The note taker usually has to work fast, and different note-taking styles and techniques try to make the best use of time. The average rate of speech is 2–3 words per second (which is 120-180 words per minute), but the average handwriting speed as only 0.2–0.3 words per second (which is 12-18 words per minute).
Regardless of the medium, note-taking can be broadly divided into linear and nonlinear methods, which can be combined.
Regardless of the system used, it can be best to focus on writing down the most important information first.
Linear note-taking
Linear note-taking is the process of recording information in the order in which you receive it. Linear notes are typically chronological outlines of a lecture or a text. Linear note taking is a common means of taking notes, however, the potential to just transcribe everything that is being said or on the presentation slide is quite high.Outlining
Outlining is a common note-taking system. Notes and thoughts are organized in a structured, logical manner, reducing the time needed to edit and review, allowing a lot of information to be digested in a short period of time. For classes that involve many formulas and graphs, like mathematics orchemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
, a system such as Cornell Notes may be better.
Outlines generally proceed down a page, using headings and bullets
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and con ...
to structure information. A common system consists of headings that use Roman numerals
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, eac ...
, letters of the alphabet, and Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals are the ten numerical digits: , , , , , , , , and . They are the most commonly used symbols to write Decimal, decimal numbers. They are also used for writing numbers in other systems such as octal, and for writing identifiers ...
at different levels. A typical structure would be:
:I. First main topic
::A. Subtopic
::# point 1
::# point 2
::#point 3
::B. Subtopic
::# point 1
::#point 2
::#point 3
:II. Second main topic
::A. Subtopic
::# point 1
::#point 2
::#point 3
::B. Subtopic
::# point 1
::#point 2
::#point 3
However, this sort of structure has limitations in non-digital form since it is difficult to go back and insert more information. Adaptive systems are used for paper-and-pen insertions, such as using the reverse side of the preceding page in a spiral notebook to make insertions. Or one can simply leave large spaces in between items, to enable more material to be inserted. (For information about application software that supports outlining, see :Outliners.)
Computerized note-taking, whether with a word processor, outliner software, or a digital notebook program, allows note-takers to revise easily and add more entries or rows to the outline.
Sentence method
Sentence note-taking is simply writing down each topic as a short, simple sentence. This method works well for fast-paced lesson where a lot of information is being covered. The note-taker records every new thought, fact, or topic on a separate line. All information is recorded but is not organized into major and minor topics. Notes can be numbered or set off with bullets showing where a new thought begins.Non-linear note-taking
Approaches to non-linear note-taking include clustering, concept mapping, Cornell Notes, idea mapping, instant replays,Ishikawa diagrams
Ishikawa diagrams (also called fishbone diagrams, herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams) are causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa that show the potential causes of a specific event.
Common uses of the Ishikawa diagram are product ...
, knowledge maps, learning maps, mind mapping, model maps, and the pyramid principle.
Charting
The charting method of note taking, which includes the drawing of tables sometimes called , is useful for subject matter that can be broken into categories, such as similarities, differences, date, event, impact, etc. Students may use charting to identify categories and draw a table prior to a lecture or may review and rewrite notes using the charting method.Mapping
Mapping uses spatial organization and diagrams to assemble information. Ideas are written in a node–link structure, with lines connecting ideas together. Mind maps are drawn in a tree structure from a central point, purpose, or goal in the center of the page and then branch outward to identify all the ideas connected to that goal. Colors, small graphics, and symbols are often used to help to visualize the information more easily. It is also used for planning and writing essays.Cornell Notes
 The Cornell Notes method of note-taking was developed by Walter Pauk of Cornell University and promoted in his bestselling 1974 book ''How to Study in College''. It is commonly used at universities today. The Cornell method consists of dividing a single page into three sections: a right-hand column for notes, a left-hand column for cues, and a strip at the bottom for a summary. Cues are key words or questions that help evoke key aspects of the topic. Cornell notes may be more effective for understanding concepts or producing readable notes, but studies have found that they had no significant effect on student performance.
The Cornell Notes method of note-taking was developed by Walter Pauk of Cornell University and promoted in his bestselling 1974 book ''How to Study in College''. It is commonly used at universities today. The Cornell method consists of dividing a single page into three sections: a right-hand column for notes, a left-hand column for cues, and a strip at the bottom for a summary. Cues are key words or questions that help evoke key aspects of the topic. Cornell notes may be more effective for understanding concepts or producing readable notes, but studies have found that they had no significant effect on student performance.
SQ3R
SQ3R ("Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review") is a method of taking notes from written material, though it might be better classified as a method of reading and gaining understanding. The reader skims the written material to produce a list of headings (Survey), which are then converted into questions (Question). The reader then considers the questions while reading to provide motivation for what is being covered (Read). The reader writes notes in sections headed by the questions (Recite), then writes a summary from memory and reviews the notes (Review). Research shows that students who use the SQ3R strategy retain more information and achieve higher test scores. An updated version called SQ4R, which adds a "Relate" step before "Review", has been used by some students since the early 1960s.Guided notes
Sometimes lecturers may provide handouts of guided notes, which provide a "map" of the lecture content with key points or ideas missing. Students then fill in missing items as the lecture progresses. Guided notes may assist students in following lectures and identifying the most important ideas from a lecture. This format provides students with a framework, yet requires active listening (as opposed to providing copies of presentation slides in their entirety), and promotes active engagement during lecture or independent reading. The student ends up with full and accurate notes for use as a study guide. Research suggests that guided notes improve student recording of critical points in lecture, as well as quiz scores on related content. In addition, an investigation carried out on students with learning problems showed that the use of the guided notes is an effective strategy to improve the performance of these students.Card file
A card file uses individual notes onindex card
An index card (or record card in British English and system cards in Australian English) consists of card stock (heavy paper) cut to a standard size, used for recording and storing small amounts of discrete data. A collection of such cards e ...
s (or their digital equivalent) that may be linked to each other through subject headings or other metadata
Metadata is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive metadata – the descriptive ...
such as numbers and tags.
Electronic note-taking methods
The growing ubiquity of laptops in universities and colleges has led to a rise in electronic note-taking. Many students write their notes in word processors or prepare digital hand-written notes using a graphics tablet or tablet computer and styli or digital pens, with the aid of note-taking software. Online applications are receiving growing attention from students who can forward notes using email, or otherwise make use of collaborative features in these applications and can also download the texts as a file on a local computer. It has also become common forlecturer
Lecturer is an List of academic ranks, academic rank within many universities, though the meaning of the term varies somewhat from country to country. It generally denotes an academic expert who is hired to teach on a full- or part-time basis. T ...
s to deliver lectures using these and similar technologies, including electronic whiteboards, especially at institutes of technology.
Online note-taking has created problems for teachers who must balance educational freedom
Freedom is understood as either having the ability to act or change without constraint or to possess the power and resources to fulfill one's purposes unhindered. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving on ...
with copyright and intellectual property concerns regarding course content.
Electronic note-taking may be less effective than traditional methods of note-taking. A study done by Pam A. Mueller of Princeton University and Daniel M. Oppenheimer of the University of California, Los Angeles showed that students who take notes digitally retain less information than students who take notes on paper, and the digital note-takers have more difficulty remembering what they've written. Electronic note-taking has created computer-aided distractions in class as multitasking on laptops is very easy to accomplish. However, this research only applies to typing notes on laptops, not writing on tablets.
Professional services
Professional note-takers provide access to information for people who cannot take their own notes, such as some deaf and hearing impaired people. They most frequently work incolleges
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offerin ...
and universities, but are also used in workplace meetings, appointments, conferences, and training sessions.
See also
* :Learning methods * Comparison of note-taking software ** List of concept- and mind-mapping software * Florilegium * Forgetting curve * Handwriting recognition * List of graphical methods * Memorandum * SketchnotingReferences
External links
* * {{Authority control Writing Educational psychology