The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden'';
lit. 'the North') are a geographical and
cultural region in
Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other g ...
and the
North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
. It includes the
sovereign states of
Denmark,
Finland,
Iceland,
Norway and
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
; the
autonomous territories
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy— ...
of the
Faroe Islands and
Greenland; and the autonomous region of
Åland.
The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life,
history, religion and
social structure. They have a long history of political unions and other close relations but do not form a singular entity today. The
Scandinavist movement sought to unite Denmark, Norway and Sweden into one country in the 19th century. With the
dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden (Norwegian independence), the
independence of Finland in the early 20th century and the
1944 Icelandic constitutional referendum
A constitutional referendum was held in Iceland between 20 and 23 May 1944. Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p961 The 1 December 1918 Danish–Icelandic Act of Union had granted Iceland independence ...
, this movement expanded into the modern organised Nordic cooperation. Since 1962, this cooperation has been based on the
Helsinki Treaty that sets the framework for the
Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
and the
Nordic Council of Ministers.
The Nordic countries cluster near the top in numerous metrics of national performance, including education, economic competitiveness, civil liberties, quality of life and human development. Each country has its own economic and social model, sometimes with large differences from its neighbours. Still, they share aspects of the
Nordic model
The Nordic model comprises the economic and social policies as well as typical cultural practices common to the Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden). This includes a comprehensive welfare state and multi-level coll ...
of economy and social structure to varying degrees. This includes a
mixed market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
combined with strong
labour unions
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ...
and a
universalist welfare sector financed by high taxes, enhancing individual autonomy and promoting
social mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given society ...
. There is a high degree of income redistribution, commitment to
private ownership
Private property is a legal designation for the ownership of property by non-governmental Legal personality, legal entities. Private property is distinguishable from public property and Personal property, personal property, which is owned by a s ...
and little social unrest.
North Germanic peoples
North Germanic peoples, commonly called Scandinavians, Nordic peoples and in a medieval context Norsemen, were a Germanic peoples, Germanic linguistic group originating from the Scandinavian Peninsula. They are identified by their cultural simila ...
, who comprise over three-quarters of the region's population, are the largest ethnic group, followed by the
Baltic Finnic Peoples, who comprise the majority in Finland; other ethnic groups are the
Greenlandic Inuit, the
Sami people
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise net ...
and recent immigrants and their descendants. Historically, the main religion in the region was
Norse paganism. This gave way first to
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
after the
Christianisation of Scandinavia. Then, following the
Protestant Reformation, the main religion became
Lutheran Christianity
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
, the
state religion
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular state, secular, is not n ...
of several Nordic countries.
Although the area is linguistically heterogeneous, with three unrelated language groups, the common linguistic heritage is one factor that makes up the Nordic identity. Most Nordic languages belong to
North Germanic languages,
Finno-Ugric languages and
Eskimo–Aleut languages
The Eskaleut (), Eskimo–Aleut or Inuit–Yupik–Unangan languages are a language family native to the northern portions of the North American continent and a small part of northeastern Asia. Languages in the family are indigenous to parts of w ...
.
Danish,
Norwegian and
Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
are considered
mutually intelligible
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as an ...
, and they are the working languages of the region's two political bodies.
Swedish is a mandatory subject in
Finnish schools and
Danish in Faroese and Greenlandic schools. Danish is also taught in schools in Iceland.
The combined area of the Nordic countries is . Uninhabitable icecaps and glaciers comprise about half of this area, mainly Greenland. In September 2021, the region had over 27 million people. Especially in English, ''
Scandinavia'' is sometimes used as a synonym for the Nordic countries. Still, that term more properly refers to the three monarchies of Denmark, Norway and Sweden. Geologically, the
Scandinavian Peninsula
The Scandinavian Peninsula ( sv, Skandinaviska halvön; no, Den skandinaviske halvøy (Bokmål) or nn, Den skandinaviske halvøya; fi, Skandinavian niemimaa) is a peninsula located in Northern Europe, which roughly comprises the mainlands ...
comprises the mainland of Norway and Sweden and the northernmost part of Finland.
Etymology and concept of the Nordic countries

The term ''Nordic countries'' found mainstream use after the advent of
Foreningen Norden. The term is
derived
Derive may refer to:
* Derive (computer algebra system), a commercial system made by Texas Instruments
* ''Dérive'' (magazine), an Austrian science magazine on urbanism
*Dérive, a psychogeographical concept
See also
*
*Derivation (disambiguatio ...
indirectly from the local term ''Norden'', used in the
Scandinavian languages, which means 'The North(ern lands)'.
Unlike ''the Nordic countries'', the term ''Norden'' is in the singular. The
demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
is ''nordbo'', literally meaning 'northern dweller'.
Similar or related regional terms include:
* ''
Scandinavia'' refers typically to the cultural and
linguistic group formed by
Denmark,
Norway and
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, or the
Scandinavian Peninsula
The Scandinavian Peninsula ( sv, Skandinaviska halvön; no, Den skandinaviske halvøy (Bokmål) or nn, Den skandinaviske halvøya; fi, Skandinavian niemimaa) is a peninsula located in Northern Europe, which roughly comprises the mainlands ...
, which is formed by mainland Norway and Sweden as well as the northwesternmost part of
Finland. Outside of the Nordic region the term ''Scandinavia'' is sometimes used as a synonym for the Nordic countries. First recorded use of the name by
Pliny the Elder about a "large, fertile island in the North" (possibly referring to
Scania).
* ''
Fennoscandia
__NOTOC__
Fennoscandia (Finnish language, Finnish, Swedish language, Swedish and no, Fennoskandia, nocat=1; russian: Фенноскандия, Fennoskandiya) or the Fennoscandian Peninsula is the geographical peninsula in Europe, which includes ...
'' refers to the area that includes the Scandinavian Peninsula, Finland,
Kola Peninsula and
Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, Каре́лия, links=y, r=Karélija, p=kɐˈrʲelʲɪjə, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for ...
. This term is mostly restricted to
geology, when speaking of the
Fennoscandian Shield.
*
Cap of the North consists of the provinces and counties of
Lapland
Lapland may refer to:
Places
*Lapland or Sápmi, an ethno-cultural region stretching over northern Fennoscandia (parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia)
**Lapland (Finland) (''Lappi''/''Lappland''), a Finnish region
*** Lapland (former pr ...
in Finland;
Finnmark,
Nordland
Nordland (; smj, Nordlánnda, sma, Nordlaante, sme, Nordlánda, en, Northland) is a county in Norway in the Northern Norway region, the least populous of all 11 counties, bordering Troms og Finnmark in the north, Trøndelag in the south, N ...
and
Troms in Norway; and
Lapland
Lapland may refer to:
Places
*Lapland or Sápmi, an ethno-cultural region stretching over northern Fennoscandia (parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia)
**Lapland (Finland) (''Lappi''/''Lappland''), a Finnish region
*** Lapland (former pr ...
and
Norrbotten in Sweden. This Arctic area is located around and north of the
Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at w ...
in the three Nordic European countries Norway, Sweden and Finland and the Kola Peninsula in Russia.
*
Barents Region is formed by the Cap of the North as well as the
Northern Ostrobothnia and
Kainuu
Kainuu ( sv, Kajanaland) is one of the 19 regions of Finland (''maakunta'' / ''landskap''). Kainuu borders the regions of North Ostrobothnia, North Savo and North Karelia. In the east, it also borders Russia (Republic of Karelia).
Culturally Kai ...
regions of Finland, Swedish provinces of
Lapland
Lapland may refer to:
Places
*Lapland or Sápmi, an ethno-cultural region stretching over northern Fennoscandia (parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia)
**Lapland (Finland) (''Lappi''/''Lappland''), a Finnish region
*** Lapland (former pr ...
,
Västerbotten and Norrbotten, Russian Oblasts of
Arkhangelsk and
Murmansk,
Nenets Autonomous Okrug, as well as the Republics of
Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, Каре́лия, links=y, r=Karélija, p=kɐˈrʲelʲɪjə, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for ...
and
Komi. This area cooperates through the
Barents Euro-Arctic Council
The Barents Euro-Arctic Council (BEAC) is the official body for inter-governmental co-operation in the Barents Region. It seeks solutions wherever and whenever the countries can achieve more together than by working on their own. Cooperation in the ...
and Barents Regional Council.
File:Scandinavian States.svg, Nordic countries (orange and red) and Scandinavian countries (red)
File:Barents-region.PNG, The Barents Region
File:Satellite image of Northern Europe.png, A satellite photograph of Northern Europe
List
Sovereign states
Associated territories and other areas
History
Timeline
Early history and Middle Ages


Little evidence remains in the Nordic countries of the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, or the Iron Age with the exception of a limited numbers of tools created from stone, bronze and iron, some jewelry and ornaments and stone burial cairns. However, one important collection that exists is a widespread and rich collection of stone drawings known as
petroglyphs. The
Goths, who originated in southern Scandinavia and would later divide into
Visigoths and
Ostrogoths, are known to have been one of the
Germanic people that would later relate to the
fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of
Medieval Europe. However, these acquired the
Latin culture of Rome.
The Nordic countries first came into more permanent contact with the rest of Europe during the
Viking Age. Southern Finland and northern parts of Sweden and Norway were areas where the Vikings mostly only traded and had raids, whilst the permanent settlements of Vikings in the Nordic region were in southern Norway and Sweden, Denmark and Faroes as well as parts of Iceland, Greenland and
Estonia. Christian Europe responded to the raids and conquest of Vikings with intensive missionary work. The missionaries wanted the new territories to be ruled by Christian kings who would help to strengthen the church. After conversion to Christianity in the 11th century, three northern kingdoms emerged in the region: Denmark, Norway and Sweden. Iceland first became a
commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
before it came under Norwegian rule in the early 13th century. There were several secular powers who aimed to bring Finland under their rule, but through the
Second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
and
Third Swedish Crusade in the latter part of 13th and through
the colonisation of some coastal areas of Finland with Christian Swedes, the Swedish rule was gradually established in the region.
During the
Middle Ages, increased trade meant that the Nordic countries became increasingly integrated into Europe and Nordic society became more
Continental. The monarchies strengthened their positions in the 12th and 13th centuries through imposing taxes on peasants and a class of nobles also emerged. By the Late Middle Ages, the whole of the Nordic region was politically united in the loose
Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and sv, Kalmarunionen; fi, Kalmarin unioni; la, Unio Calmariensis) was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden, that from 1397 to 1523 joined under ...
. Diverging interests and especially Sweden's dissatisfaction over the Danish dominance gave rise to a conflict that hampered the union from the 1430s onward until its final dissolution in 1523. After the dissolution Denmark and Norway, including Iceland, formed a personal union of the two kingdoms called
Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway (Danish and Norwegian: ) was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (including the then Norwegian overseas possessions: the Faroe I ...
whilst the successful period of
Vasa Kings began in Sweden and Finland. The
Lutheran Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
played a major role in the establishment of the early-modern states in Denmark–Norway and Sweden.
Early modern period and industrialization
Sweden was very successful during the
Thirty Years' War, while Denmark was a failure. Sweden saw an opportunity of a change of power in the region. Denmark–Norway had a threatening territory surrounding Sweden and the Sound Dues were a continuing irritation for the Swedes. In 1643, the
Swedish Privy Council determined Swedish territorial gain in an eventual war against Denmark–Norway to have good chances. Not long after this, Sweden invaded Denmark–Norway.
The war ended as foreseen with Swedish victory and with the
Treaty of Brömsebro in 1645 Denmark–Norway had to cede some of their territories, including Norwegian territories
Jemtland,
Herjedalen and
Idre and Serna, as well as the Danish
Baltic Sea islands of
Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the ...
and
Ösel. The Thirty Years' War thus began the
rise of Sweden as a great power, while it marked the start of decline for the Danish.
To some extent in the 16th century and certainly in the 17th, the Nordic region played a major role in European politics at the highest level. The struggle for dominion over the
Baltic Sea and its trading opportunities raged between Denmark–Norway and Sweden, which began to impact upon the neighboring nations. Sweden prevailed in the long term and became a major European power as it extended its reach into coastal tracts in modern-day Russia, Estonia, Latvia, and – following the Thirty Years' War – also into
Pomerania and other North German areas. Sweden also conquered vast areas from Denmark–Norway during the
Northern Wars in the middle of the 17th century. Sweden also had several conflicts with Russia over Finland and other eastern areas of the country and after the
Great Northern War (1700–1721) Sweden lost most of its territories outside the old Swedish border to Russia which then became the new major power in Northern Europe.
After the
Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815), the political map of the Nordic countries altered again. In 1809, Finland was conquered by
Russian Empire from Sweden in the
Finnish War, after which Finland became the autonomous
Grand Duchy of Finland. In turn, Sweden captured Norway from Denmark in 1814 in the
Swedish–Norwegian War and started a
Union between Sweden and Norway. Iceland, the Faroe Islands and Greenland, which had been re-colonised in the 18th century, became Danish. Population growth and industrialization brought change to the Nordic countries during the 19th century and new social classes steered political systems towards democracy. International politics and
nationalism also created the preconditions for the later
independence of Norway in 1905,
Finland in 1917 and
Iceland in 1944.
Late modern period and contemporary era
During the two world wars and the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, the five small Nordic states were forced into difficult balancing acts, but retained their independence and developed peaceful democracies. The Nordic states had been neutral during
World War I, but during
World War II they could no longer stand apart from world politics. The
Soviet Union attacked Finland in 1939 and Finland ceded territory following the
Winter War. In 1941, Finland launched a
retaliatory strike in conjunction with the German attack on the Soviet Union. However, more territory was lost and for many years to come Finnish foreign policy was based on
appeasing the Soviet Union, even though Finland was able to retain its democratic form of government.
Denmark and
Norway were occupied by Germany in 1940. The Allies responded by occupying Iceland, the Faroe Islands and Greenland.
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
managed to formally maintain its neutrality in the Axis/Allies conflict and avoided direct hostilities, but in practice it adapted to the wishes of the dominant power – first Germany, later the Allies. However, during the Winter War between Finland and Russia in 1939–1940, Sweden did support Finland and declared itself "non combatant" rather than neutral.
Compared with large parts of Europe, the Nordic region got off lightly during the World War II, which partially explains its strong post-war economic development. The
labour movement – both trade unions and political parties – was an important political presence throughout the Nordic countries in the 20th century. The big social democratic parties became dominant and after World War II the Nordic countries began to serve as a
model for the welfare state. Economically, the five Nordic countries were strongly dependent on foreign trade and so they positioned themselves alongside the big trading blocks. Denmark was the first to join
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
(EEC) in 1972 and after it became
European Union (EU) in 1993 Finland and Sweden also joined in 1995. Norway and Iceland are members of the
European Free Trade Association
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Europe, European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerlan ...
(EFTA). All the Nordic countries are however members of the
European Economic Area (EEA).
Geography


The Nordic countries and self-governing regions in alphabetic order – number of inhabitants (2018), area (km
2) and population density (people/km
2):
Denmark is by far the most densely populated country, whilst Sweden, Norway and Finland are low populated and similar to each other from this perspective. Iceland has both the lowest population and by far the lowest population density. But large areas in Finland, Norway and Sweden, like most of Iceland, are unpopulated. There are no such areas in Denmark. Denmark has a population density around continental average, higher than for instance France and Poland but lower when compared to the United Kingdom, Italy or Germany. Finland, Norway and Sweden has a population density that is a little lower than the United States, but higher than Canada. In round figures, Iceland's population density resembles Canada's.
Land and water area

This list includes
dependent territories
A dependent territory, dependent area, or dependency (sometimes referred as an external territory) is a territory that does not possess full political independence or sovereignty as a sovereign state, yet remains politically outside the controlli ...
within their
sovereign states (including uninhabited territories), but does not include claims on
Antarctica. EEZ+TIA is exclusive economic zone (EEZ) plus
total internal area (TIA) which includes land and internal waters.
Denmark

The Kingdom of Denmark includes the home-rule (''hjemmestyre'') territory of the
Faroe Islands and the self-rule (''selvstyre'') territory of
Greenland.
The Nordic countries have a combined area of around 3.5 million square kilometres and their geography is extremely varied. The area is so vast that it covers five
time zones. To the east the region borders Russia, and on the west the Canadian coastline can be seen from Greenland on a clear day. Even excluding Greenland and the Norwegian islands of
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
and
Jan Mayen, the remaining part of the Nordic countries covers around 1.3 million square kilometres. This is about the same area as France, Germany and Italy together. To the south, the countries neighbor the
Baltic states
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
, Poland, Germany and the United Kingdom, while to the north there is the
Arctic Ocean.
Notable natural features of the Nordic countries include the
Norwegian fjords, the
Archipelago Sea
The Archipelago Sea ( fi, Saaristomeri, sv, Skärgårdshavet) is a part of the Baltic Sea between the Gulf of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland and the Sea of Åland, within Finnish territorial waters. By some definitions it contains the largest ar ...
between Finland and Sweden, the
extensive volcanic and geothermal activity of Iceland, and Greenland, which is the largest island in the world. The southernmost point of the Nordic countries is
Gedser, on the island of
Falster
Falster () is an island in south-eastern Denmark with an area of and 43,398 inhabitants as of 1 January 2010. in Denmark. The northernmost point is
Kaffeklubben Island in Greenland, which is also the northernmost point of land on Earth. The largest cities and capitals of the Nordic countries are situated on the southern parts of the region, with the exception of
Reykjavík, the capital of Iceland.
Helsinki,
Oslo and
Stockholm
Stockholm () is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, largest city of Sweden as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people liv ...
are all close to the same latitude as the southernmost point of Greenland,
Egger Island (''Itilleq''): about
60°N
The 60th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
Although it lies approximately twice as far away from the Equator as ...
.
Topography
All of Denmark and most of Finland lie below 200 m and the topography of both is relatively flat. In Denmark,
moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
s and
tunnel valleys add some
relief to the landscape while in Finland the surroundings of lakes
Pielinen and
Päijänne display some moderate relief. The Finnish area just east of
Bothnian Bay stands out as the largest plain in the Nordic countries.
[ The ]Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway, whereas to the ...
dominate the landscape of Norway. The southern part of the Scandinavian Mountains is broader than the northern one and contains higher peaks. The southern part contains also a series of plateaux and gently undulating plains. The western parts of the mountains are cut by fjords, producing a dramatic landscape. The landscape of Sweden can be described as a mixture of that of Norway, Finland and Denmark. Except at the High Coast the coastal areas of Sweden form lowlands. Sweden has three highland areas, the South Swedish Highlands, the Scandinavian Mountains and the Norrland terrain which is the eastern continuation of the Scandinavian Mountains.[ The South Swedish Highland and the Norrland terrain are separated by the Central Swedish lowland. The topography of Iceland stands out among the Nordic countries for being a bowl-formed highland.]
Climate
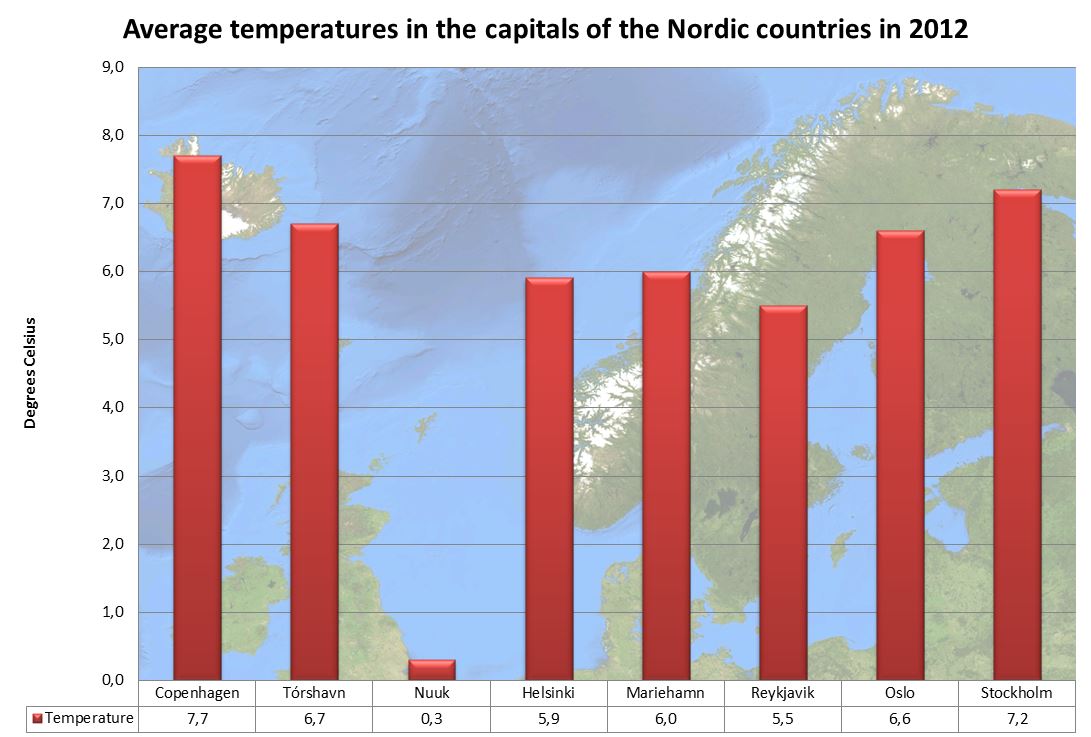 Despite their northern location, the Nordic countries generally have a mild climate compared with other countries that share globally the same latitudes. The climate in the Nordic countries is mainly influenced by their northern location, but remedied by the vicinity to the ocean and the
Despite their northern location, the Nordic countries generally have a mild climate compared with other countries that share globally the same latitudes. The climate in the Nordic countries is mainly influenced by their northern location, but remedied by the vicinity to the ocean and the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Current, North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida a ...
which brings warm ocean currents from the tip of Florida. Even far to the north, the winters can be quite mild, though north of the Polar Circle the climate zone is mostly subarctic with harsh winters and short summers. In Greenland and Svalbard the climate is polar. The sea has a heavy influence on the weather in the western coastal zones of Iceland, Norway, Denmark and Sweden. The precipitation is high and snow cover during winters is rare. Summers are generally cool.
The further away that one gets from the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf Stream the colder it gets during the winters. Finland, most of Sweden and the south-eastern part of Norway are influenced by the vast continent to the east which results in warm and long summers and clear and cold winters, often with snow. For example, Bergen at the west coast of Norway normally has a temperature above zero in February while Helsinki in Finland normally will have a temperature of 7–8 °C below zero during the same month.
Climatic conditions and quality of land have determined how land is used in the Nordic countries. In densely populated mainland Denmark there is hardly any wild nature left. Most of the scarce forests are plantations and nearly 60 per cent of Denmark's total area is cultivated or zoned as gardens or parks. On the other hand, in the other Nordic countries there is much wild nature left. Only between 0 and 9 per cent of the land in the other Nordic countries is cultivated. Around 17 per cent of the land area in Iceland is used for permanent meadows and pastures and both Finland, Norway as well as Sweden have large forest areas.
Politics
Political dimension and divisions
 The Nordic region has a political dimension in the joint official bodies called the
The Nordic region has a political dimension in the joint official bodies called the Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
and the Nordic Council of Ministers. The Helsinki Treaty, signed on 23 March 1962 entered into force on 1 July 1962 and is the political agreement which sets the framework for Nordic cooperation. 23 March is celebrated as the "Nordic Day" as the treaty is sometimes referred to as the constitution of the Nordic cooperation.
Several aspects of the common market as in the EU have been implemented decades before the EU implemented them. Intra-Nordic trade is not covered by the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG), but by local law. The Nordic countries have cooperated closely in the administrative and consular fields since the Nordic Passport Union was established and the Helsinki Treaty concluded. According to the Helsinki Treaty, public officials in the foreign services of any of the Nordic countries are to assist citizens
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
of another Nordic country if that country is not represented in the territory concerned.
Nordic Council and Nordic Council of Ministers
 Nordic cooperation is based on the Helsinki Treaty. Politically, Nordic countries do not form a separate entity, but they cooperate in the
Nordic cooperation is based on the Helsinki Treaty. Politically, Nordic countries do not form a separate entity, but they cooperate in the Nordic Council
The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomou ...
and the Nordic Council of Ministers. The council was established after World War II and its first concrete result was the introduction of a Nordic Passport Union in 1952. This resulted in a common labour market and free movement across borders without passports for the countries' citizens. In 1971, the Nordic Council of Ministers, an intergovernmental forum, was established to complement the council. The Nordic Council and the Council of Ministers have their headquarters in Copenhagen and various installations in each separate country, as well as many offices in neighbouring countries. The headquarters are located at Ved Stranden No. 18, close to Slotsholmen.
The Nordic Council consists of 87 representatives, elected from its members' parliaments and reflecting the relative representation of the political parties in those parliaments. It holds its main session in the autumn, while a so-called "theme session" is arranged in the spring. Each of the national delegations has its own secretariat in the national parliament. The autonomous territoriesGreenland, the Faroe Islands and Ålandalso have Nordic secretariats. The Council does not have any formal power on its own, but each government has to implement any decisions through its country's legislative assembly. With Denmark, Iceland, and Norway being members of NATO and Finland and Sweden being neutral, the Nordic Council has not been involved in any military cooperation. However, the Nordic foreign and security policy cooperation has become closer and over the past few years expanded its scope.
The Nordic Council of Ministers is responsible for inter-governmental cooperation. Prime ministers have ultimate responsibility, but this is usually delegated to the Minister for Nordic Cooperation and the Nordic Committee for Co-operation, which coordinates the day-to-day work. The autonomous territories have the same representation as states.
Nordic model
 The Nordic countries share an economic and social model, which involves the combination of a market economy with a welfare state financed with heavy taxes. The welfare states were largely developed by strong social democrat parties and in Finland with cooperation with the Agrarian League. Although the specifics differ between countries and there are ongoing political arguments, there is a strong consensus about keeping to the general concept.
A central theme in the Nordic model is the "universalist" welfare state aimed specifically at enhancing individual autonomy, promoting social mobility and ensuring the universal provision of basic human rights, as well as for stabilizing the economy. In this model welfare is not just aid to those who are in need of it, but a central part of the life of everybody: education is free, healthcare has zero or nominal fees in most cases, most children go to municipal day care, etc.
The Nordic model is distinguished from other types of welfare states by its emphasis on maximizing labour force participation, promoting gender equality, egalitarian and extensive benefit levels, the large magnitude of income redistribution and liberal use of expansionary fiscal policy. Trade unions are strong.
The model has been successful: the countries are among the wealthiest worldwide and there is little social unrest. In 2015, Save the Children ranked the Nordic countries as number 1–5 of countries where mothers and children fare the best (among 179 countries studied).
The Nordic countries share an economic and social model, which involves the combination of a market economy with a welfare state financed with heavy taxes. The welfare states were largely developed by strong social democrat parties and in Finland with cooperation with the Agrarian League. Although the specifics differ between countries and there are ongoing political arguments, there is a strong consensus about keeping to the general concept.
A central theme in the Nordic model is the "universalist" welfare state aimed specifically at enhancing individual autonomy, promoting social mobility and ensuring the universal provision of basic human rights, as well as for stabilizing the economy. In this model welfare is not just aid to those who are in need of it, but a central part of the life of everybody: education is free, healthcare has zero or nominal fees in most cases, most children go to municipal day care, etc.
The Nordic model is distinguished from other types of welfare states by its emphasis on maximizing labour force participation, promoting gender equality, egalitarian and extensive benefit levels, the large magnitude of income redistribution and liberal use of expansionary fiscal policy. Trade unions are strong.
The model has been successful: the countries are among the wealthiest worldwide and there is little social unrest. In 2015, Save the Children ranked the Nordic countries as number 1–5 of countries where mothers and children fare the best (among 179 countries studied).
Elections
 Nordic parliaments are all based on a one-chamber system. The Norwegian parliament, the
Nordic parliaments are all based on a one-chamber system. The Norwegian parliament, the Storting
The Storting ( no, Stortinget ) (lit. the Great Thing) is the supreme legislature of Norway, established in 1814 by the Constitution of Norway. It is located in Oslo. The unicameral parliament has 169 members and is elected every four years bas ...
, did actually function as two separate chambers until 2009 when dealing with certain issues. The Icelandic Althing, founded in 930 AD, is reputed to be the oldest working parliament in the world. However, it was dissolved for much of the first half of the 19th century. In Denmark, Iceland and Sweden elections are held at least once every four years. Finland, Åland and Norway have fixed four-year election periods. Elections in the Faroe Islands and Greenland follow the Danish system of elections. The Danish Folketing has 179 seats, including two seats each for the Faroe Islands and Greenland. The Finnish Eduskunta has 200 seats, including one seat for Åland. The Icelandic Althing has 63 seats, the Norwegian Storting 169 seats and the Swedish Riksdag
The Riksdag (, ; also sv, riksdagen or ''Sveriges riksdag'' ) is the legislature and the supreme decision-making body of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members (), elected proportionally and se ...
349 seats. The Faroese Løgting
The Løgting (pronounced ; da, Lagtinget) is the unicameral parliament of the Faroe Islands, an autonomous territory within the Danish Realm.
The name literally means "''Law Thing''"—that is, a law assembly—and derives from Old Norse ''l ...
has 32 seats, Greenland's Inatsisartut 31 seats and Åland's Lagtinget 30 seats.
Nordic citizens – and in the three member countries of the EU also EU citizens – living in another Nordic country are normally entitled to vote in local government elections after three months of residence, while other foreign citizens have to reside in the Nordic countries for three to four years before they are eligible to vote. In Denmark and the Faroe Islands, the percentage turn-out at elections is close to 90% per cent, but it is only about 67% in Åland and Finland. Men are more often elected to the national assembly compared to women. The biggest bias between the two sexes is seen in the Faroe Islands and Åland, while in Sweden men and women are close to being equally represented in the national assembly.
Nordic Passport Union
The Nordic Passport Union, created in 1954 and implemented on 1 May 1958, allows citizens of the Nordic countries: Denmark (Faroe Islands included since 1 January 1966, Greenland not included), Sweden, Norway (Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
, Bouvet Island and Queen Maud Land not included), Finland and Iceland (since 24 September 1965) to cross approved border districts without carrying and having their passport
A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that contains a person's identity. A person with a passport can travel to and from foreign countries more easily and access consular assistance. A passport certifies the personal ...
checked. Other citizens can also travel between the Nordic countries' borders without having their passport checked, but still have to carry some sort of approved travel identification documents. During the 2015 European migrant crisis
The 2015 European migrant crisis, also known internationally as the Syrian refugee crisis, was a period of significantly increased movement of refugees and migrants into Europe in 2015, when 1.3 million people came to the continent to request ...
, temporary border controls were set up between Denmark and Sweden to control the movement of refugees into Sweden.
Since 1996, these countries have been part of the larger EU directive Schengen Agreement area, comprising 30 countries in Europe. Border checkpoints have been removed within the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
and only a national ID card is required. Within the Nordic area any means of proving one's identity, e.g. a driving licence, is valid for Nordic citizens because of the Nordic Passport Union. When traveling to other countries than the Nordics, public officials in the foreign services of any of the Nordic countries are to assist citizens of another Nordic country if that country is not represented in the territory concerned, according to the Helsinki Treaty.
Since 25 March 2001, the Schengen acquis
The Community acquis or ''acquis communautaire'' (; ), sometimes called the EU acquis and often shortened to acquis, is the accumulated legislation, legal acts and court decisions that constitute the body of European Union law that came into b ...
has fully applied to the five countries of the Nordic Passport Union (except for the Faroe Islands). There are some areas in the Nordic Passport Union that give extra rights for Nordic citizens, not covered by Schengen, such as less paperwork if moving to a different Nordic country and fewer requirements for naturalisation.
European integration and international cooperation
The political cooperation between the Nordic countries has not led to a common policy or an agreement on the countries' memberships in the EU, Eurozone and NATO. Norway and Iceland are the only Nordic countries not members of the EU – both countries are instead members of EFTA. Finland and Sweden are the only Nordic countries not members of NATO. Denmark alone participates in both organizations. Only Finland is a member of the Eurozone. The Nordics are however all part of the European lex. The tasks and policies of the EU overlap with the Nordic Council significantly, e.g. the Schengen Agreement, Freedom of movement for workers in the European Union and Free Movement Directive partially supersedes the Nordic passport-free zone and the common Nordic labor market. The Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
covers all the Nordic countries, excluding the Faroe Island and Svalbard.
Additionally, certain areas of Nordic countries have special relationships with the EU. For example, Finland's autonomous island province Åland is not a part of the EU VAT zone.
In the EU, the Northern Dimension refers to external and cross-border policies covering the Nordic countries, the Baltic countries and Russia.
There is no explicit provision in the Treaty on European Union or Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union that takes Nordic cooperation into account. However, the Treaties provide that international agreements concluded by the Member States before they become members of the Union remain valid, even if they are contrary to the provisions of Union law. Each Member State must nonetheless take all necessary measures to eliminate any discrepancies as quickly as possible. Nordic cooperation can therefore in practice only be designed to the extent that it complies with Union law. Sweden and Finland issued a joint declaration when they joined the EU: "The Contracting Parties notes that Sweden ..and Finland, as members of the European Union, intend to continue their Nordic co-operation, both with each other and with other countries and territories, in full compliance with Community law and other provisions of the Maastricht Treaty."
Article 121 of the EEA-agreement states that "the provisions of the Agreement shall not preclude cooperation: (a) within the framework of the Nordic cooperation to the extent that such cooperation does not impair the good functioning of this Agreement".
Current leaders
All the Nordic countries are long-established parliamentary democracies. Denmark, Norway and Sweden have a political system of constitutional monarchy, in which a nonpolitical monarch acts as head of state and the '' de facto'' executive power is exercised by a cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
led by a prime minister. Margrethe II has reigned in Denmark as Queen Regnant and head of state since 14 January 1972, Carl XVI Gustaf
Carl XVI Gustaf (Carl Gustaf Folke Hubertus; born 30 April 1946) is King of Sweden. He ascended the throne on the death of his grandfather, Gustaf VI Adolf, on 15 September 1973.
He is the youngest child and only son of Prince Gustaf Adolf, Du ...
became King of Sweden on 15 September 1973 and King Harald V of Norway has reigned since 17 January 1991.
Finland and Iceland have been parliamentary republic
A parliamentary republic is a republic that operates under a parliamentary system of government where the executive branch (the government) derives its legitimacy from and is accountable to the legislature (the parliament). There are a number ...
s since their independence. Both countries are led by prime ministers, whilst the directly elected president acts mostly as a ceremonial head of state with some legislative power. Finland had a long tradition of having a strong presidential system, since in the beginning of its independence Prince Frederick Charles of Hesse was elected to the throne of Finland and Finland was to become a monarchy. This failed due to World War I and the fall of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
and so it was a compromise that Finland became a republic with a strong head of state. The President's powers were once so broad that it was said Finland was the only real monarchy in northern Europe. However, amendments passed in 1999 reduced his powers somewhat and the President now shares executive authority with the Prime Minister.
Margrethe II
Queen of Denmark
since 1972
File:Sauli Niinistö Senate of Poland 2015.JPG, Finland
Sauli Niinistö
Sauli Väinämö Niinistö (; born 24 August 1948) is a Finnish politician who has served as president of Finland since March 2012, the 12th person to hold that office.
A lawyer by education, Niinistö was Chairman of the National Coalition Part ...
President of Finland
The president of the Republic of Finland ( fi, Suomen tasavallan presidentti; sv, Republiken Finlands president) is the head of state of Finland. Under the Constitution of Finland, executive power is vested in the Finnish Government and the p ...
since 2012 election
This national electoral calendar for 2012 lists the national/ federal elections held in 2012 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
January
*3–4 January: ...
File:Guðni Th. Jóhannesson (2017-03-30).jpg, Iceland
Guðni Th. Jóhannesson
President of Iceland
since 2016 election
The following elections occurred in the year 2016.
Africa
Benin Republic
*2016 Beninese presidential election 6 March 2016
Cape Verde
* 2016 Cape Verdean presidential election 2 October 2016
Chad
* 2016 Chadian presidential election 10 A ...
File:Harald V of Norway in Slovenia in 2011 (crop).jpg, Norway
Harald V
King of Norway
since 1991
File:King Carl XVI Gustaf at National Day 2009 Cropped.png, Sweden
Carl XVI Gustaf
Carl XVI Gustaf (Carl Gustaf Folke Hubertus; born 30 April 1946) is King of Sweden. He ascended the throne on the death of his grandfather, Gustaf VI Adolf, on 15 September 1973.
He is the youngest child and only son of Prince Gustaf Adolf, Du ...
King of Sweden
since 1973
File:Mette Frederiksen 20120501.jpg, Denmark
Mette Frederiksen
Prime Minister of Denmark
since 2019 election
Frederiksen Cabinet
File:Prime Minister of Finland Sanna Marin 2019 (cropped).jpg, Finland
Sanna Marin
Prime Minister of Finland
since December 2019
Marin Cabinet
File:Katrín Jakobsdóttir at Göteborg Book Fair 2012 03 (cropped).jpg, Iceland
Katrín Jakobsdóttir
Prime Minister of Iceland
since 2017 election
Jakobsdóttir Cabinet
File:Jonas Gahr Støre - 25061469895 (cropped).jpg, Norway
Jonas Gahr Støre
Prime Minister of Norway
since 2021 election
Støre Cabinet
The Støre Cabinet is the incumbent government of the Kingdom of Norway, headed by Labour Party leader Jonas Gahr Støre as Prime Minister. The government was appointed by King Harald V on 14 October 2021, following the parliamentary election o ...
File:Ulf Kristersson in 2018 Swedish general election, 2018 (cropped).jpg, Sweden
Ulf Kristersson
Prime Minister of Sweden
since October 2022
File:Henrik Dam Kristensen (S) Danmarks delegation till Nordiska radet.jpg, Denmark
Henrik Dam Kristensen
Speaker of the Folketing
since 2019 election
File:2020-03-02_Matti_Vanhanen.jpg, Finland
Matti Vanhanen
Speaker of the Eduskunta
since 2022
File:Steingrimur J. Sigfusson, finansminister Island vid nordiskt finansministermote i Kopenhamn 2010-03-22 (2).jpg, Iceland
Steingrímur J. Sigfússon
Speaker of the Althing
since 2017 election
File:Masud Gharahkhani - Arbeiderpartiet.jpg, Norway
Masud Gharahkhani
Masud Gharahkhani ( fa, مسعود قرهخانی; born 22 September 1982) is a Norwegian politician who has served as the President of the Storting since 2021, and as an Member of the Storting for Buskerud since 2017 for the Labour Party.
Ea ...
President of the Storting
since 2021
File:Andreas Norlén in 2019.jpg, Sweden
Andreas Norlén
Speaker of the Riksdag
since 2018 election
The following elections are scheduled to occur in 2018. The National Democratic Institute also maintains a calendar of elections around the world.
Africa
*2018 Djiboutian parliamentary election 23 February 2018
*2018 Sierra Leonean general elect ...
File:20200612_Altinget_Jakob_Elleman_Jensen_750A4304-2_(cropped).jpg, Denmark
Jakob Ellemann-Jensen Chair of the Venstre
File:Riikkapurra.jpg, Finland
Riikka Purra Chair of the Finns Party
File:Logi_Már_Einarsson.jpg, Iceland
Logi Már Einarsson
Logi Már Einarsson (born 21 August 1964, in Akureyri) is an Icelandic politician and architect.
Early life and education
Logi grew up in Akureyri and took stúdentspróf from Menntaskólinn á Akureyri in 1985. He studied architecture at ...
Chair of the Social Democratic Alliance
File:Erna Solbergin Oct, 2014.jpg, Norway
Erna Solberg
Chair of the Conservative Party
File:Budgetpropositionen för_2022 (1 av 8) (cropped) (1).jpg, Sweden
Magdalena Andersson
Chair of the Social Democratic Party (Sweden)
Economy

 The Nordic economies are among the countries in the Western world with the best macroeconomic performance in the recent ten years. Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden have for example experienced constant and large excess exports in recent years. Iceland is the only country which has balance of payments deficits . At the same time, unemployment is low in most of the Nordic countries compared with the rest of Europe. As a result of the cyclical down-turn, the public balance is now in deficit, except for Norway. Over the past ten years, the Nordic countries had a noticeably larger increase in their gross domestic product (GDP) than the Eurozone. The only exceptions were Denmark and Åland which had a lower growth. Measured by GDP per capita, the Nordic countries have a higher income than the Eurozone countries. Norway's GDP per capita is as high as 80 per cent above the EA17 average and Norway is actually one of the countries with the highest standard of living in the world.
However, after the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and the following recession all the Nordic countries have been affected by the global crisis though to varying degrees. Iceland was most affected and had an economic crisis from 2008 to 2011, but GDP growth was also negative in all the other Nordic countries in 2008 and 2009. From 2009 most of the Nordic countries experienced growth again. The Nordic Council has set an objective for Nordic cooperation to achieve stable and sustainable economic growth, development of the
The Nordic economies are among the countries in the Western world with the best macroeconomic performance in the recent ten years. Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden have for example experienced constant and large excess exports in recent years. Iceland is the only country which has balance of payments deficits . At the same time, unemployment is low in most of the Nordic countries compared with the rest of Europe. As a result of the cyclical down-turn, the public balance is now in deficit, except for Norway. Over the past ten years, the Nordic countries had a noticeably larger increase in their gross domestic product (GDP) than the Eurozone. The only exceptions were Denmark and Åland which had a lower growth. Measured by GDP per capita, the Nordic countries have a higher income than the Eurozone countries. Norway's GDP per capita is as high as 80 per cent above the EA17 average and Norway is actually one of the countries with the highest standard of living in the world.
However, after the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and the following recession all the Nordic countries have been affected by the global crisis though to varying degrees. Iceland was most affected and had an economic crisis from 2008 to 2011, but GDP growth was also negative in all the other Nordic countries in 2008 and 2009. From 2009 most of the Nordic countries experienced growth again. The Nordic Council has set an objective for Nordic cooperation to achieve stable and sustainable economic growth, development of the Nordic welfare model
The Nordic model comprises the economic and social policies as well as typical cultural practices common to the Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden). This includes a comprehensive welfare state and multi-level co ...
, economic integration in the Nordic region and the promotion of joint Nordic interests at international level.
Private consumption
Consumption is the act of using resources to satisfy current needs and wants. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many o ...
has fallen during the crisis, but it gained pace again from 2010 onward. The decline was most profound in Denmark, Finland and Iceland. On the other hand, public consumption has experienced positive growth rates – except for Iceland since 2008 and Denmark since 2010. The general rise is due to the many fiscal initiatives made by the Nordic governments to support economic growth and the financial and business sectors. From 2006 Iceland has experienced a fall in gross capital formation. This is after many years with an Icelandic growth particularly driven by investments, which had more than tripled in the recent ten years. Iceland also holds a leading position compared to the other Nordic countries regarding growth in public consumption in the years from 2000 to 2008.
Recent years’ large balance-of-payments surplus in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden has reduced the countries’ foreign debt. In addition to a balance-of-payments surplus or deficit, the size of a country's foreign debt and foreign assets is affected by the exchange rate and the price of securities. Consequently, Finland's foreign debt increased noticeably when the price of technology shares increased drastically in the late 1990s due to a large proportion of these shares being owned by households, funds and companies abroad. In this way, these foreign owners held a greater claim on Finland. When share prices decreased drastically in 1999–2001 in the dot-com bubble, it also led to a marked decrease in Finland's net foreign debt. Iceland's foreign net debt accounts for close to five times of its GDP. This means that Iceland owes the surrounding world values corresponding to five times the country's total production. Sweden also had foreign debts by the end of 2010, but at a much smaller scale. In 2012, all Nordic countries had a surplus on the total balance of payments. Norway accounts for a substantial foreign exchange surplus, which is due to revenue from exports of oil and gas.
Industries
 Since the late 1990s, the Nordic manufacturing industry has accounted for a slightly declining proportion of the gross domestic product, with Norway being a distinct exception. In Norway, the manufacturing industry's proportion of GDP is still at a high level of around 35 per cent due to the large oil and natural gas sector. In the rest of the Nordic countries, the proportion lies between 15 and 20 per cent. Despite growing production, the manufacturing industry accounts for a decreasing proportion of total employment in the Nordic countries. Among the Nordic countries, Finland is today the number one Nordic industrial country, as the manufacturing industry in Finland accounts for the greatest proportion of the country's jobs, around 16 per cent. By way of comparison, in Denmark, Norway and Iceland it only accounts for less than 13 per cent of total employment.
The service sector has increased drastically in all Nordic countries in the last 15 years and today accounts for about three fourths of all employed persons. Denmark, Norway, Iceland, Sweden and Åland have the largest proportion of employed in the service sector, between 75 and more than 90 per cent of those employed, while the corresponding figure is 72 per cent in Finland and 70 per cent in Iceland. The service sector is a little smaller if its proportion of total gross domestic product is measured compared to the share of employment. In Norway, the service sector accounts for 57 per cent of GDP, in Iceland for 66 per cent, in Finland for 69 per cent, in Sweden for 72 per cent and in Denmark for 78 per cent. The service sector includes retail and wholesale trade, hotels, restaurants, transportation, communication, financial services, real estate sale, renting, business services and other services such as teaching and care of children, sick persons and the elderly – services which are typically rendered by the public sector in the Nordic countries.
Since the late 1990s, the Nordic manufacturing industry has accounted for a slightly declining proportion of the gross domestic product, with Norway being a distinct exception. In Norway, the manufacturing industry's proportion of GDP is still at a high level of around 35 per cent due to the large oil and natural gas sector. In the rest of the Nordic countries, the proportion lies between 15 and 20 per cent. Despite growing production, the manufacturing industry accounts for a decreasing proportion of total employment in the Nordic countries. Among the Nordic countries, Finland is today the number one Nordic industrial country, as the manufacturing industry in Finland accounts for the greatest proportion of the country's jobs, around 16 per cent. By way of comparison, in Denmark, Norway and Iceland it only accounts for less than 13 per cent of total employment.
The service sector has increased drastically in all Nordic countries in the last 15 years and today accounts for about three fourths of all employed persons. Denmark, Norway, Iceland, Sweden and Åland have the largest proportion of employed in the service sector, between 75 and more than 90 per cent of those employed, while the corresponding figure is 72 per cent in Finland and 70 per cent in Iceland. The service sector is a little smaller if its proportion of total gross domestic product is measured compared to the share of employment. In Norway, the service sector accounts for 57 per cent of GDP, in Iceland for 66 per cent, in Finland for 69 per cent, in Sweden for 72 per cent and in Denmark for 78 per cent. The service sector includes retail and wholesale trade, hotels, restaurants, transportation, communication, financial services, real estate sale, renting, business services and other services such as teaching and care of children, sick persons and the elderly – services which are typically rendered by the public sector in the Nordic countries.
Foreign investments
Iceland and Sweden have the highest rate of foreign direct investment, both with regards to foreign companies investing in Iceland and Sweden and Icelandic and Swedish companies investing abroad. However, in 2011 Denmark superseded Sweden regarding outward investments. Looking at a larger time span of ten years, most of the Nordic countries have experienced growth in both inward and outward investments.
However, Iceland has been in a league of its own in this area. Foreign investment from Iceland increased significantly and sharply especially from 2003 to 2007 from 16 to 123 per cent of GDP. The expansion of Icelandic companies into foreign markets was a rapid process. Strong pension funds provided capital for investments, and the privatization of the banking system made new sources of financing available for companies wishing to expand their operations. Also inward investment to Iceland increased sharply from 2003, but at a more moderate level compared with other Nordic countries. This pattern changed in 2007 with dramatic decreases in both outward and inward foreign direct investment.
Foreign and intra-Nordic trade
 Nordic cooperation is characterized largely by the international community and the global challenges and opportunities. The Nordic countries, which are relatively small, have historically and still are benefiting greatly by obtaining common use in cooperation with other countries and institutions. The Nordic economies are small and open and thus the countries are export-depending. Foreign trade constitutes an important part of the economic activity. Nordic foreign trade in goods, measured as the average of imports and exports, amounts to more than one fourth of GDP in the Nordic countries. All the Nordic countries except Finland had a surplus in their balance of trade in 2012 and every year since 1995 Denmark, Norway and Sweden have all had greater exports than imports.
The trade between the Nordic countries is especially considerable as about one fifth of the countries’ foreign trade is trade with other Nordic countries. The total population of the Nordic countries of around 26 million people makes them to a far greater extent dependent on each other with respect to exports and imports, compared to for example Germany with a population of 82 million people. Swedish exports to the other Nordic countries account for a considerably higher share than combined Swedish exports to Germany and France – despite the fact that the total population of Germany and France is 147 million people, while Denmark, Finland, Iceland and Norway only have a total population of 16 million. In 2012, around 23 per cent of the total exports from both Denmark and Sweden went to other Nordic countries. Other Nordic countries account for 16 per cent of Finnish exports, 13 per cent of Norwegian exports and 10 per cent of the total exports in Iceland.
In addition to the other Nordic countries, The EU is the largest trading partner for the Nordic countries. Especially important is trade with Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands. Outside of Europe, the United States is also a major trading partner. A common characteristic in the exports of the Nordic countries is a concentration on a few products. The exports of Greenland and the Faroe Islands are entirely dominated by fish and fish products, to a lesser extent in Iceland where aluminium exports also contribute significantly. Oil and gas are the predominant products exported by Norway and Finnish exports are dominated by wood, paper and paper products and telecommunication equipment. Danish and Swedish exports are more equally distributed on different products, with processed food, pharmaceuticals and chemical products as the major Danish export products and cars, wood, paper products and telecommunication equipment as predominant in Swedish exports. Germany is completely dominant when it comes to Nordic imports. However, the Nordic countries also have considerable imports from the Netherlands, China and Russia.
Nordic cooperation is characterized largely by the international community and the global challenges and opportunities. The Nordic countries, which are relatively small, have historically and still are benefiting greatly by obtaining common use in cooperation with other countries and institutions. The Nordic economies are small and open and thus the countries are export-depending. Foreign trade constitutes an important part of the economic activity. Nordic foreign trade in goods, measured as the average of imports and exports, amounts to more than one fourth of GDP in the Nordic countries. All the Nordic countries except Finland had a surplus in their balance of trade in 2012 and every year since 1995 Denmark, Norway and Sweden have all had greater exports than imports.
The trade between the Nordic countries is especially considerable as about one fifth of the countries’ foreign trade is trade with other Nordic countries. The total population of the Nordic countries of around 26 million people makes them to a far greater extent dependent on each other with respect to exports and imports, compared to for example Germany with a population of 82 million people. Swedish exports to the other Nordic countries account for a considerably higher share than combined Swedish exports to Germany and France – despite the fact that the total population of Germany and France is 147 million people, while Denmark, Finland, Iceland and Norway only have a total population of 16 million. In 2012, around 23 per cent of the total exports from both Denmark and Sweden went to other Nordic countries. Other Nordic countries account for 16 per cent of Finnish exports, 13 per cent of Norwegian exports and 10 per cent of the total exports in Iceland.
In addition to the other Nordic countries, The EU is the largest trading partner for the Nordic countries. Especially important is trade with Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands. Outside of Europe, the United States is also a major trading partner. A common characteristic in the exports of the Nordic countries is a concentration on a few products. The exports of Greenland and the Faroe Islands are entirely dominated by fish and fish products, to a lesser extent in Iceland where aluminium exports also contribute significantly. Oil and gas are the predominant products exported by Norway and Finnish exports are dominated by wood, paper and paper products and telecommunication equipment. Danish and Swedish exports are more equally distributed on different products, with processed food, pharmaceuticals and chemical products as the major Danish export products and cars, wood, paper products and telecommunication equipment as predominant in Swedish exports. Germany is completely dominant when it comes to Nordic imports. However, the Nordic countries also have considerable imports from the Netherlands, China and Russia.
Energy
 The Nordic region is one of the richest sources of energy in the world. Apart from the natural occurrence of fossil fuels such as oil and gas, the Nordic countries also have good infrastructure and technology to exploit renewable energy sources such as water, wind, bio-energy and geothermal heat. Especially Iceland and Norway, but also Finland and Sweden, have a significant production of electricity based on hydro power.
The Nordic region is one of the richest sources of energy in the world. Apart from the natural occurrence of fossil fuels such as oil and gas, the Nordic countries also have good infrastructure and technology to exploit renewable energy sources such as water, wind, bio-energy and geothermal heat. Especially Iceland and Norway, but also Finland and Sweden, have a significant production of electricity based on hydro power. Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth's crust which originates from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions. The high temperature and pres ...
production is the most important
source of energy in Iceland, whilst nuclear power is produced in both Finland and in Sweden. The indigenous production of energy in the Nordic countries has risen considerably over the last couple of decades – especially in Denmark and Norway due to oil deposits in the North Sea.
The most important energy sources in the Nordic countries measured in terms of energy supply in million toe (tonnes oil equivalent) are in order of importance: oil, solid fuels (e.g. coal and wood), nuclear power, hydro and geothermal power and solar energy and gas. In the EU, the most important source of energy is also oil, but gas comes in second. Hydro and geothermal power and other renewable sources of energy are major sources in the Nordic countries as compared to the EU countries. Particularly in Iceland and Norway, hydro and geothermal power constitute a major share of the overall energy supply. Denmark depends almost entirely on thermal power generated from coal, oil and gas. Iceland obtains a substantial part of its energy for heating from geothermal energy and depends almost entirely upon hydro-power resources for its production of electricity.
Tourism
The Nordic countries in order of popularity with tourists are Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Finland then Iceland.
Demographics
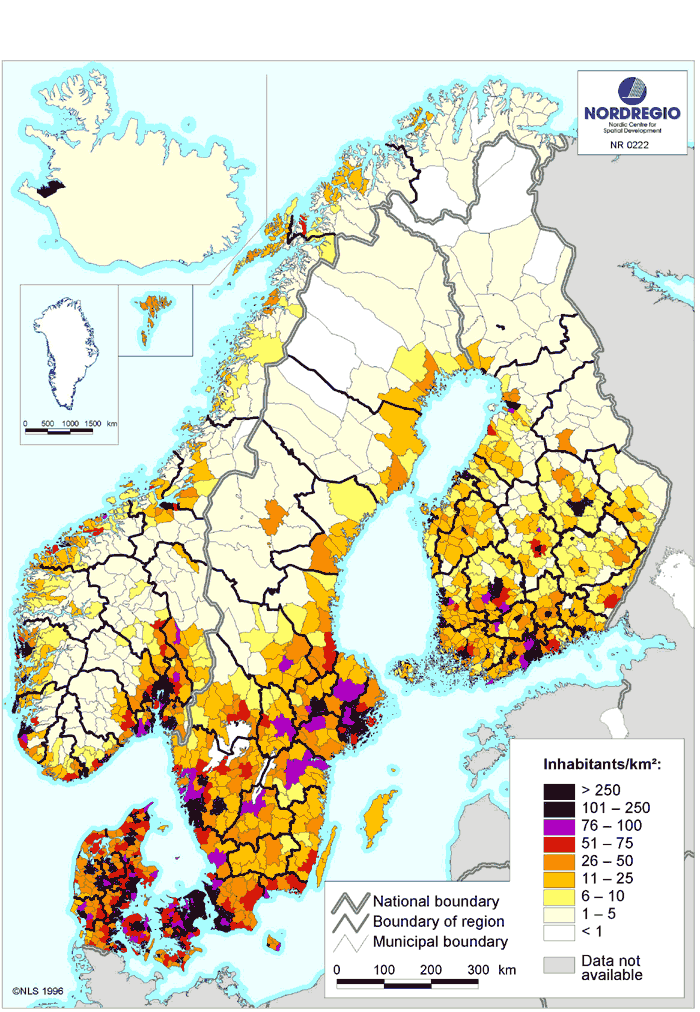 At the beginning of the 20th century, almost 12 million people lived in the Nordic countries. Today, the population has increased to 27 million people. The Nordic countries have one of the lowest population densities in the world. The low density is partly due to the fact that many parts of the Nordic countries are marginal areas, where nature puts limitations on settlement. In four out of five Nordic countries, around 20 per cent of the population is to be found in the vicinity of the respective capitals. In Iceland, this percentage is even higher, with more than 60 per cent of Icelanders residing at or nearby the capital city of Reykjavík.
At the beginning of the 20th century, almost 12 million people lived in the Nordic countries. Today, the population has increased to 27 million people. The Nordic countries have one of the lowest population densities in the world. The low density is partly due to the fact that many parts of the Nordic countries are marginal areas, where nature puts limitations on settlement. In four out of five Nordic countries, around 20 per cent of the population is to be found in the vicinity of the respective capitals. In Iceland, this percentage is even higher, with more than 60 per cent of Icelanders residing at or nearby the capital city of Reykjavík.
Languages
 Most of the Nordic languages belong to one of three linguistic families: North Germanic languages, Finno-Ugric languages and
Most of the Nordic languages belong to one of three linguistic families: North Germanic languages, Finno-Ugric languages and Eskimo–Aleut languages
The Eskaleut (), Eskimo–Aleut or Inuit–Yupik–Unangan languages are a language family native to the northern portions of the North American continent and a small part of northeastern Asia. Languages in the family are indigenous to parts of w ...
. Although the area is linguistically heterogeneous, with three unrelated language groups, the common linguistic heritage is one of the factors making up the Nordic identity.
Danish, Faroese, Icelandic, Norwegian and Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
belong to the North Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages. The languages have developed from a common Nordic language, but have moved away from each other during the past 1000 years. However, it is still possible for Danish, Norwegian and Swedish speakers to understand each other. These languages are taught in school throughout the Nordic countries: for example, Swedish is a mandatory subject in Finnish schools, whereas Danish is mandatory in Icelandic and Faroese schools. Approximately 5,3 per cent of population of Finland speak Swedish as their mother tongue.
In the Finnish-Sami group of the Finno-Ugric languages, Finnish is the most widely spoken language in the Nordic countries. However, other languages in this family are also spoken in the region. Various Sami languages
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise net ...
are spoken in northern Finland, Norway and Sweden. Karelian is spoken a little in Finland, the Kven language in Norway and Meänkieli or "Torne Valley Finnish" in Sweden. Finns are also the largest immigrant group in Sweden, around 4.46 per cent of the total population; and Finnish is an official minority language of Sweden.
Greenlandic or Kalaallisut belongs to the Inuit branch of the Eskimo-Aleut languages and is spoken in Greenland. The language is related to a number of languages spoken in northern Canada and Alaska. , the Greenland Home rule does not require Danish to be taught or the use of Danish for official purposes.
A number of other minority languages also exist in the region. German is spoken by a minority
Minority may refer to:
Politics
* Minority government, formed when a political party does not have a majority of overall seats in parliament
* Minority leader, in American politics, the floor leader of the second largest caucus in a legislative b ...
in Southern Jutland and their cultural and language rights are protected by the government. Finnish Kale
The Finnish Kale ( rom, Kàlo; sv, Kalé; fi, Kaale, also ''Suomen romanit'' — "Finnish Romani") are a group of the Romani people who live primarily in Finland and Sweden. Their main languages are Finnish, Swedish and Finnish Romani.
Histo ...
, Norwegian and Swedish Travellers and other Romani peoples of the Nordic countries have the right to maintain and develop their language and culture. Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
is also an official minority language in Sweden. Besides the so-called "natural" languages national variants of sign languages are used. The Icelandic Sign Language is derived from the Danish, while the Finnish Sign Language is developed on the basis of the Swedish variant. The right to use sign language is set in the Finnish Language Act and in Sweden the Swedish Sign Language is an official minority language.
File:North_germanic_languages.svg, The North Germanic languages in the Nordic countries
File:Finnic_languages_2.png, The Finnic languages in Northern Europe
Migration
In 2012, net migration had the greatest impact on the population increase in Sweden. That was also the case with Denmark, Finland, Åland and Norway. In the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Iceland, natural population increase had the greatest impact on the population change, but both Greenland and the Faroe Islands still had a slight decrease in the population due to a negative net migration in 2012.
A large proportion of the migration in the Nordic countries occurs between and among the countries themselves, largely as the result of the free labour market and liberal rules for the exchange of students in the Nordic countries. The trend has led to an increasing number of foreign citizens in the Nordic countries during the past few decades. In all the countries, the major part of the foreign citizens is non-Nordic. That is not the case for Greenland and the Faroe Islands, which have a high proportion of other Nordic citizens. Non-nationals range from 47 per cent of the total immigration in Iceland, to 89 per cent in Norway. In 2013 the largest proportions of non-nationals were in Norway and Denmark, where they account for 8.9 and 8.8 per cent of the population. The proportion
of non-nationals in the Finnish population is small compared to the other Nordic countries – 3.6 per cent in 2013 – but the proportion has risen significantly during and after the 1990s.
Sami people
 The
The Sami people
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise net ...
, also spelled Sámi or Saami, are a Finno-Ugric people who have their traditional settlement areas in northern Finland, Norway and Sweden and Western Russia. Most Sami live in Norway, followed by Sweden and Finland, while the fewest Sami live in Russia. Because the countries do not make an official record of who has the Sami identity or background, no one knows the exact number of the Sami people. The Sami are the only indigenous people of the Nordic countries excluding Greenland that are recognized and protected under the international conventions of indigenous peoples. They are hence the northernmost indigenous people of Europe. There are several Sami languages.
Traditionally, the Sami have plied a variety of livelihoods, including coastal fishing, fur trapping and sheep herding. However, the best known Sami livelihood is semi-nomadic reindeer herding. For traditional, environmental, cultural and political reasons, reindeer herding is legally reserved only for Sami people in certain regions of the Nordic countries. Nowadays, the Sami work in all sectors, in line with the non-Sami population, though the primary industries are still important culture bearers for the Sami people.
File:Share of total population in the Nordic countries in 2013.JPG, Share of total population of the Nordic countries by country in January 2013
File:Life expectancy at birth in the Nordic countries in 2012.JPG, Life expectancy at birth in the Nordic countries in 2012
File:Marriages and divorces in the Nordic countries in 2012.JPG, Marriages and divorces in the Nordic countries in 2012
File:Immigrants in the Nordic countries in 2012.JPG, Immigrants in the Nordic countries in 2012
Culture
 Nordic countries have historically been one of the most socially progressive cultures in the world and culture is one of the main components of cooperation between the Nordic countries. The policies of the Nordic countries with respect to cultural life, mass media and religion have many shared values and features in common. However, some differences may be pointed out and for instance cultural institutions arising from historical circumstances. In both Denmark and Sweden, there are cultural institutions with roots in the traditions of the royal courts. In these countries, national institutions formed the foundation of cultural life at an early stage while in Norway cultural institutions began to form later.
Iceland has the highest government expenditure on culture, a total of 3.3 per cent of its GDP in 2011. Denmark comes second with a total of 1.6 per cent of GDP in 2011. Sweden spend the least in 2011 with 1.1 per cent. Looking at per capita expenditure, Iceland again has the highest expenditure with Norway coming second. Greenland spends the third highest amount on culture and leisure per capita. In Iceland and Norway, expenditures have more than doubled since 2000. In the other Nordic countries, expenditures have gone up between 40 and 50 per cent in the same period.
Denmark has the most museums, a total of 274, but museums in Åland and Iceland have the most visitors, an average of 4 and 5 visits per inhabitant. Many theatres in the Nordic countries receive public funding. Theatre funding constitutes a major share of allocations within the cultural area in all the countries. All countries have national theatres, where plays, ballets and operas are performed. In addition to the national theatres, there are professional regional theatres, which are also supported by the state, counties or municipalities. Most countries also have a few private theatres and many amateur ensembles, which may be supported at least partially by municipalities, primarily.
Nordic Culture Fund, established in 1966, aims to support a broad spectrum of cultural cooperations between the Nordic countries. The Fund's ambition is to enable talented artists, both professionals and amateurs, to enrich each other via the cultural diversity that exists among the 26 million or more people of the Region. Its activities are based on an agreement between the Nordic countries, which came into force in 1967. The Fund receives its money in the form of an annual grant from the Nordic Council of Ministers.
Nordic countries have historically been one of the most socially progressive cultures in the world and culture is one of the main components of cooperation between the Nordic countries. The policies of the Nordic countries with respect to cultural life, mass media and religion have many shared values and features in common. However, some differences may be pointed out and for instance cultural institutions arising from historical circumstances. In both Denmark and Sweden, there are cultural institutions with roots in the traditions of the royal courts. In these countries, national institutions formed the foundation of cultural life at an early stage while in Norway cultural institutions began to form later.
Iceland has the highest government expenditure on culture, a total of 3.3 per cent of its GDP in 2011. Denmark comes second with a total of 1.6 per cent of GDP in 2011. Sweden spend the least in 2011 with 1.1 per cent. Looking at per capita expenditure, Iceland again has the highest expenditure with Norway coming second. Greenland spends the third highest amount on culture and leisure per capita. In Iceland and Norway, expenditures have more than doubled since 2000. In the other Nordic countries, expenditures have gone up between 40 and 50 per cent in the same period.
Denmark has the most museums, a total of 274, but museums in Åland and Iceland have the most visitors, an average of 4 and 5 visits per inhabitant. Many theatres in the Nordic countries receive public funding. Theatre funding constitutes a major share of allocations within the cultural area in all the countries. All countries have national theatres, where plays, ballets and operas are performed. In addition to the national theatres, there are professional regional theatres, which are also supported by the state, counties or municipalities. Most countries also have a few private theatres and many amateur ensembles, which may be supported at least partially by municipalities, primarily.
Nordic Culture Fund, established in 1966, aims to support a broad spectrum of cultural cooperations between the Nordic countries. The Fund's ambition is to enable talented artists, both professionals and amateurs, to enrich each other via the cultural diversity that exists among the 26 million or more people of the Region. Its activities are based on an agreement between the Nordic countries, which came into force in 1967. The Fund receives its money in the form of an annual grant from the Nordic Council of Ministers.
Music
 Nordic countries share certain traditions in music, many of which have diverged significantly. In folk music, Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and the Faroe Islands share many common aspects. Greenland's
Nordic countries share certain traditions in music, many of which have diverged significantly. In folk music, Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and the Faroe Islands share many common aspects. Greenland's Inuit culture
The Inuit are an indigenous people of the Arctic and subarctic regions of North America (parts of Alaska, Canada, and Greenland). The ancestors of the present-day Inuit are culturally related to Iñupiat (northern Alaska), and Yupik (Siberia and ...
has its own musical traditions, influenced by Scandinavian culture. Finland shares many cultural similarities with both the other Nordic countries as well as Estonia. The Sami have their own unique culture, with ties to the neighboring cultures.
Art music has a strong position in Nordic countries. Apart from state-owned opera houses, there are symphony orchestras in most major cities. The most prominent historical composers from Nordic countries are the Finn Jean Sibelius, the Dane Carl Nielsen and the Norwegian Edvard Grieg. Of contemporary composers, the Finns Magnus Lindberg, Kaija Saariaho and Esa-Pekka Salonen are among the most often performed in the world.
Rock and roll influences that came from the United States and United Kingdom were the start of the Nordic pop scene, but influences from the Nordic folk music can still be found today in popular music. Common characteristic in Nordic pop music is that it can often be either very lighthearted pop music or very dark metal. Some of the most well-known Nordic music groups include ABBA, Ace of Base, a-ha
A-ha (usually stylised as ''a-''h''a''; ) is a Norwegian synth-pop band formed in Oslo in 1982. Founded by Paul Waaktaar-Savoy (guitars and vocals), Magne Furuholmen (keyboards, guitars and vocals), and Morten Harket (lead vocals), the band ...
, Aqua, Björk
Björk Guðmundsdóttir ( , ; born 21 November 1965), known mononymously as Björk, is an Icelandic singer, songwriter, composer, record producer, and actress. Noted for her distinct three-octave vocal range and eccentric persona, she has de ...
, The Cardigans, Europe, Hanoi Rocks, Roxette
Roxette was a Swedish pop rock duo, consisting of Marie Fredriksson (vocals and keyboards) and Per Gessle (vocals and guitar). Formed in 1986, the duo became an international act in the late 1980s, when they released their breakthrough second a ...
, The Rasmus, Kaizers Orchestra and The Spotnicks. Sweden and Finland have possibly the largest music industries in the area, especially Sweden which is the largest exporter of pop music per capita and the third largest overall after the United States and the United Kingdom. Norway, Iceland and Denmark have all had successful domestic record industries for many years.
The Nordic metal scene is highly visible compared to other genres from the region. Many big names such as Amon Amarth
Amon Amarth () is a Swedish melodic death metal band from Tumba, formed in 1992. The band takes its name from the Sindarin name of Mount Doom, a volcano in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth. Their lyrics mostly deal with Viking mythology and hi ...
, Children of Bodom, In Flames
In Flames is a Swedish heavy metal band, formed by guitarist Jesper Strömblad in Gothenburg in 1990. Alongside At the Gates and Dark Tranquillity, In Flames pioneered the genres known as Swedish death metal and melodic death metal.
During t ...
, Meshuggah and Opeth
Opeth is a Swedish progressive metal/rock band from Stockholm, formed in 1990 by lead vocalist David Isberg. The group has been through several personnel changes, including the replacement of every original member; notably Isberg in 1992. Mikael ...
originate from the Nordic countries. Nordic metal bands have had a long and lasting influence on the metal subculture alongside their counterparts in the United Kingdom and the United States. The black metal
Black metal is an extreme metal, extreme subgenre of heavy metal music. Common traits include Tempo#Beats per minute, fast tempos, a Screaming (music)#Black metal, shrieking vocal style, heavily distorted Electric guitar, guitars played with t ...
genre was developed in Norway by bands such as Mayhem
Mayhem most commonly refers to:
* Mayhem (crime), a type of crime
Mayhem may also refer to:
People
* Monica Mayhem (born 1978), Australian pornographic actress
* Jason "Mayhem" Miller, American mixed martial arts fighter
* Mayhem Miller (dra ...
, Darkthrone
Darkthrone is a Norwegian extreme metal band from Kolbotn, Akershus. Formed in 1986 as a death metal band named Black Death, in 1991 Darkthrone embraced a black metal style influenced by Bathory and Celtic Frost and became one of the leadin ...
, Burzum
Burzum (; ) was a Norwegian music project founded by Varg Vikernes in 1991. Although Burzum never played live performances, it became a part of the early Norwegian black metal scene and is considered one of the most influential acts in black m ...
, Immortal and Emperor and the related genre of Viking metal was developed throughout the Nordic region by bands such as Bathory, Enslaved, Burzum, Emperor, Einherjer
Einherjer is a Viking metal band from Haugesund, Norway, founded in 1993. Some of the band's albums are heavily folk influenced, while others have a more traditional symphonic black metal sound. Their lyrics retell Norse legends, and each of th ...
, Moonsorrow and Amon Amarth.
Since 2000, the total sale of music has declined by almost 50 per cent in all the Nordic countries and at the same time the digital sale has increased (digital sales cover both downloads and streaming of music). In Denmark, Norway and Finland, the sale of digital music has increased by 400 per cent since 2006 and now amounts to 39, 27 and 25 per cent of the total sale in 2010/2011. In Denmark and Sweden, sales of digital music rose almost eight-fold in the same period and now represent 51 per cent of the total sale. In Iceland, digital sales still only represent three per cent of the total sale.
Literature

 The earliest written records from Scandinavia are
The earliest written records from Scandinavia are runic inscriptions
A runic inscription is an inscription made in one of the various runic alphabets. They generally contained practical information or memorials instead of magic or mythic stories. The body of runic inscriptions falls into the three categories of El ...
on memorial stones and other objects. Some of those contain allusions to Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period ...
and even short poems in alliterative verse. The best known example is the elaborate Rök runestone (c. 800) which alludes to legends from the migration age. The oldest of the Eddic poems are believed to have been composed in the 9th century, though they are only preserved in 13th-century manuscripts. They tell of the myths and heroic legends of Scandinavia. Skaldic poetry is mostly preserved in late manuscripts but was preserved orally from the 9th century onwards and also appears on runestones, such as the Karlevi Runestone
The Karlevi Runestone, designated as Öl 1 by Rundata, is commonly dated to the late 10th century and located near the Kalmarsund straight in Karlevi on the island of Öland, Sweden. It is one of the most notable and prominent runestones and const ...
. In Iceland the sagas of Icelanders are the best-known specimens of Icelandic literature. In Finland the most famous collection of folk poetry is by far the Kalevala, which is the national epic
A national epic is an epic poem or a literary work of epic scope which seeks or is believed to capture and express the essence or spirit of a particular nation—not necessarily a nation state, but at least an ethnic or linguistic group with as ...
of the country.
Nordic countries have produced important and influential literature. Henrik Ibsen
Henrik Johan Ibsen (; ; 20 March 1828 – 23 May 1906) was a Norwegian playwright and theatre director. As one of the founders of modernism in theatre, Ibsen is often referred to as "the father of realism" and one of the most influential playw ...
, a Norwegian playwright, was largely responsible for the popularity of modern realistic drama in Europe, with plays like '' The Wild Duck'' and '' A Doll's House''. His contemporary, Swedish novelist and playwright August Strindberg, was a forerunner of experimental forms such as expressionism
Expressionism is a modernist movement, initially in poetry and painting, originating in Northern Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. Its typical trait is to present the world solely from a subjective perspective, distorting it rad ...
, symbolism and surrealism
Surrealism is a cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists depicted unnerving, illogical scenes and developed techniques to allow the unconscious mind to express itself. Its aim was, according to l ...
. Nobel prizes for literature have been awarded to Selma Lagerlöf, Verner von Heidenstam, Karl Adolph Gjellerup
Karl Adolph Gjellerup (2 June 1857 – 11 October 1919) was a Danish poet and novelist who together with his compatriot Henrik Pontoppidan won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1917. He is associated with the Modern Breakthrough period of Scandin ...
, Henrik Pontoppidan, Knut Hamsun, Sigrid Undset, Erik Axel Karlfeldt, Frans Eemil Sillanpää, Johannes Vilhelm Jensen
Johannes Vilhelm Jensen (20 January 1873 – 25 November 1950) was a Danish author, known as one of the great Danish writers of the first half of 20th century. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1944 "for the rare strength and fert ...
, Pär Lagerkvist, Halldór Laxness
Halldór Kiljan Laxness (; born Halldór Guðjónsson; 23 April 1902 – 8 February 1998) was an Icelandic writer and winner of the 1955 Nobel Prize in Literature. He wrote novels, poetry, newspaper articles, essays, plays, travelogues and s ...
, Nelly Sachs, Eyvind Johnson, Harry Martinson and Tomas Tranströmer. World-famous Nordic children's book writers include Hans Christian Andersen
Hans Christian Andersen ( , ; 2 April 1805 – 4 August 1875) was a Danish author. Although a prolific writer of plays, travelogues, novels, and poems, he is best remembered for his literary fairy tales.
Andersen's fairy tales, consisti ...
, Tove Jansson and Astrid Lindgren
Astrid Anna Emilia Lindgren (; ; 14 November 1907 – 28 January 2002) was a Swedish writer of fiction and screenplays. She is best known for several children's book series, featuring Pippi Longstocking, Emil of Lönneberga, Karlsson-on- ...
.
Since 1962, the Nordic Council has awarded a literature prize once a year for a work of fiction written in one of the Nordic languages. Since its establishment, the prize has been won by 15 Swedish, 10 Danish, 10 Norwegian, 8 Finnish, 7 Icelandic, 2 Faroe and 1 Sami writers.
Nordic libraries function as information centres with a wide variety of services and access to all kinds of printed and electronic media. In the last twenty years, there has been an overall decline in stock and lending of books in public libraries. Despite the general decline in stock and loans, most of the Nordic countries have had an increase in the lending of other media than books. Since 2000, the stock of other media has increased between 30 and 85 per cent in the Nordic countries. The lending of books has at the same time decreased in all Nordic countries, a decline between 10 and 20 per cent.
Art
File:Interiør med ung læsende mand.jpg, Vilhelm Hammershøi
Vilhelm Hammershøi (), often anglicised as Vilhelm Hammershoi (15 May 186413 February 1916), was a Danish painter. He is known for his poetic, subdued portraits and interiors.Souren Melikian,Hammershoi's decade of brilliance, before banality set ...
(1864–1916)
'' Interior with Young Man Reading'', 1898
File:Tanssiaiskengat iso by Helena Schjerfbeck 1882.jpg, Helene Schjerfbeck
(1862–1946)
''Dancing Shoes'', 1882
File:Thorarinn thingvellir.jpg, Þórarinn B. Þorláksson
Þórarinn Benedikt Þorláksson (February 14, 1867 – July 10, 1924Kunst Index DanmarkThorarinn B. Thorlaksson URL last accessed August 13, 2007.) was one of Iceland's first contemporary painters, the first Icelander to exhibit paintings in ...
(1867–1924)
'' Þingvellir'', 1900
File:The Scream.jpg, Edvard Munch
Edvard Munch ( , ; 12 December 1863 – 23 January 1944) was a Norwegian painter. His best known work, ''The Scream'' (1893), has become one of Western art's most iconic images.
His childhood was overshadowed by illness, bereavement and the dr ...
(1863–1944)
'' The Scream'', 1893
File:Marine avec recif-August Strindberg-IMG 8230.JPG, August Strindberg
(1849–1912)
''Marine with rocks'', 1894
File:Didrikur a skarvanesi1.jpg, Díðrikur á Skarvanesi
Díðrikur á Skarvanesi also called Díðrikur í Kárastovu (25 July 1802 – 8 October 1865), was born in Dímun and was the first known painter in the Faroe Islands that art historians know of.
Díðrikiur á Skarvanesi was a bird painter. ...
(1802–1865)
''Birds'', 1800s
National symbols
 The Nordic countries, including the autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Åland, have a similar flag design, all based on the
The Nordic countries, including the autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Åland, have a similar flag design, all based on the Dannebrog
Dannebrog (until the mid-20th century often spelled Danebrog) may refer to:
Flags and orders
* The national Flag of Denmark
* Order of the Dannebrog ( da, Dannebrogordenen, links=no), a Royal Danish decoration
Places
* Dannebrog Island, an i ...
, the Danish flag. They display an off-centre cross with the intersection closer to the hoist – the " Nordic cross" or "Scandinavian cross"
See also
Associated
* Climate of the Nordic countries
* Comparison of the Nordic countries
* Subdivisions of the Nordic countries
The subdivisions of the Nordic countries are similar given the countries' shared culture and history.
Denmark
*Denmark proper
**5 regions ()
**98 municipalities ()
*2 autonomous insular overseas dependencies
**Faroe Islands
***6 regions
***30 ...
* Universal basic income in the Nordic countries
Universal basic income (Swedish: ''basinkomst'' or ''medborgarlön'') has been debated in the Nordic countries since the 1970s. It has mostly been seen as a radical and utopian proposal and not taken seriously by the big political parties. However ...
Others
* Baltic region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. ...
* Baltoscandia
* British Isles
* Nordic-Baltic Eight
* Nordic identity in Estonia
Notes
References
Further reading
* Clerc, Louis; Glover, Nikolas; Jordan, Paul, eds. ''Histories of Public Diplomacy and Nation Branding in the Nordic and Baltic Countries: Representing the Periphery'' (Leiden: Brill Nijhoff, 2015). 348 pp.
online review
* Elmgren, Ainur and Norbert Götz (eds.)
Theme issue "Power Investigation: The Political Culture of Nordic Self-Understanding"
''Journal of Contemporary European Studies'' 21 (2013) 3: 338–412.
* Götz, Norbert and Heidi Haggrén (eds.)
''Regional Cooperation and International Organizations: The Nordic Model in Transnational Alignment''
London: Routledge, 2009.
* Götz, Norbert and Carl Marklund (eds.)
''The Paradox of Openness: Transparency and Participation in Nordic Cultures of Consensus''
Leiden: Brill, 2015.
* Kjellberg, Anders (2022
''The Nordic Model of Industrial Relations''
Lund: Department of Sociology.
* Strang, Johan (ed.)
London: Routledge, 2016.
External links
Norden
website of the Nordic Council and Nordic Council of Ministers
Nordic Countries
railway map of the Nordic countries
Nordregio
European centre for research, education and documentation on spatial development, established by the Nordic Council of Ministers. Includes maps and graphs
Go Scandinavia
official website of the Scandinavian Tourist Boards in North America
Scandinavia House
the Nordic Center in New York, run by th
American-Scandinavian Foundation
vifanord
a digital library that provides scientific information on the Nordic and Baltic countries as well as the Baltic region as a whole
Nordic organization to promote sustainable development and growth in the region (archived 17 December 2009)
The Helsinki Treaty of 1962
nicknamed the constitution of the Nordic countries
{{Authority control
Nordic Council
Regions of Europe
Regions of North America
Geography of Northern Europe
Geography of North America
Germanic countries and territories
Cultural regions
 The term ''Nordic countries'' found mainstream use after the advent of Foreningen Norden. The term is
The term ''Nordic countries'' found mainstream use after the advent of Foreningen Norden. The term is 

 The Nordic countries and self-governing regions in alphabetic order – number of inhabitants (2018), area (km2) and population density (people/km2):
Denmark is by far the most densely populated country, whilst Sweden, Norway and Finland are low populated and similar to each other from this perspective. Iceland has both the lowest population and by far the lowest population density. But large areas in Finland, Norway and Sweden, like most of Iceland, are unpopulated. There are no such areas in Denmark. Denmark has a population density around continental average, higher than for instance France and Poland but lower when compared to the United Kingdom, Italy or Germany. Finland, Norway and Sweden has a population density that is a little lower than the United States, but higher than Canada. In round figures, Iceland's population density resembles Canada's.
The Nordic countries and self-governing regions in alphabetic order – number of inhabitants (2018), area (km2) and population density (people/km2):
Denmark is by far the most densely populated country, whilst Sweden, Norway and Finland are low populated and similar to each other from this perspective. Iceland has both the lowest population and by far the lowest population density. But large areas in Finland, Norway and Sweden, like most of Iceland, are unpopulated. There are no such areas in Denmark. Denmark has a population density around continental average, higher than for instance France and Poland but lower when compared to the United Kingdom, Italy or Germany. Finland, Norway and Sweden has a population density that is a little lower than the United States, but higher than Canada. In round figures, Iceland's population density resembles Canada's.
 This list includes
This list includes  Despite their northern location, the Nordic countries generally have a mild climate compared with other countries that share globally the same latitudes. The climate in the Nordic countries is mainly influenced by their northern location, but remedied by the vicinity to the ocean and the
Despite their northern location, the Nordic countries generally have a mild climate compared with other countries that share globally the same latitudes. The climate in the Nordic countries is mainly influenced by their northern location, but remedied by the vicinity to the ocean and the  The Nordic region has a political dimension in the joint official bodies called the
The Nordic region has a political dimension in the joint official bodies called the  Nordic cooperation is based on the Helsinki Treaty. Politically, Nordic countries do not form a separate entity, but they cooperate in the
Nordic cooperation is based on the Helsinki Treaty. Politically, Nordic countries do not form a separate entity, but they cooperate in the  The Nordic countries share an economic and social model, which involves the combination of a market economy with a welfare state financed with heavy taxes. The welfare states were largely developed by strong social democrat parties and in Finland with cooperation with the Agrarian League. Although the specifics differ between countries and there are ongoing political arguments, there is a strong consensus about keeping to the general concept.
A central theme in the Nordic model is the "universalist" welfare state aimed specifically at enhancing individual autonomy, promoting social mobility and ensuring the universal provision of basic human rights, as well as for stabilizing the economy. In this model welfare is not just aid to those who are in need of it, but a central part of the life of everybody: education is free, healthcare has zero or nominal fees in most cases, most children go to municipal day care, etc.
The Nordic model is distinguished from other types of welfare states by its emphasis on maximizing labour force participation, promoting gender equality, egalitarian and extensive benefit levels, the large magnitude of income redistribution and liberal use of expansionary fiscal policy. Trade unions are strong.
The model has been successful: the countries are among the wealthiest worldwide and there is little social unrest. In 2015, Save the Children ranked the Nordic countries as number 1–5 of countries where mothers and children fare the best (among 179 countries studied).
The Nordic countries share an economic and social model, which involves the combination of a market economy with a welfare state financed with heavy taxes. The welfare states were largely developed by strong social democrat parties and in Finland with cooperation with the Agrarian League. Although the specifics differ between countries and there are ongoing political arguments, there is a strong consensus about keeping to the general concept.
A central theme in the Nordic model is the "universalist" welfare state aimed specifically at enhancing individual autonomy, promoting social mobility and ensuring the universal provision of basic human rights, as well as for stabilizing the economy. In this model welfare is not just aid to those who are in need of it, but a central part of the life of everybody: education is free, healthcare has zero or nominal fees in most cases, most children go to municipal day care, etc.
The Nordic model is distinguished from other types of welfare states by its emphasis on maximizing labour force participation, promoting gender equality, egalitarian and extensive benefit levels, the large magnitude of income redistribution and liberal use of expansionary fiscal policy. Trade unions are strong.
The model has been successful: the countries are among the wealthiest worldwide and there is little social unrest. In 2015, Save the Children ranked the Nordic countries as number 1–5 of countries where mothers and children fare the best (among 179 countries studied).
 Nordic parliaments are all based on a one-chamber system. The Norwegian parliament, the
Nordic parliaments are all based on a one-chamber system. The Norwegian parliament, the 
 The Nordic region is one of the richest sources of energy in the world. Apart from the natural occurrence of fossil fuels such as oil and gas, the Nordic countries also have good infrastructure and technology to exploit renewable energy sources such as water, wind, bio-energy and geothermal heat. Especially Iceland and Norway, but also Finland and Sweden, have a significant production of electricity based on hydro power.
The Nordic region is one of the richest sources of energy in the world. Apart from the natural occurrence of fossil fuels such as oil and gas, the Nordic countries also have good infrastructure and technology to exploit renewable energy sources such as water, wind, bio-energy and geothermal heat. Especially Iceland and Norway, but also Finland and Sweden, have a significant production of electricity based on hydro power.  At the beginning of the 20th century, almost 12 million people lived in the Nordic countries. Today, the population has increased to 27 million people. The Nordic countries have one of the lowest population densities in the world. The low density is partly due to the fact that many parts of the Nordic countries are marginal areas, where nature puts limitations on settlement. In four out of five Nordic countries, around 20 per cent of the population is to be found in the vicinity of the respective capitals. In Iceland, this percentage is even higher, with more than 60 per cent of Icelanders residing at or nearby the capital city of Reykjavík.
During the past 100 years, the population growth has been strongest in Greenland, where the population has multiplied by almost five, from 12,000 to 56,000 people. In Iceland, the increase has gone from 78,000 to 322,000 people. The population on the Faroe Islands has more than tripled, from 15,000 to 48,000 people. The Swedish and Ålandic populations are the only ones that have not at least doubled. Since 1990, the total population in the Nordic countries has increased by more than 2.8 million people (12 per cent) – the most in Iceland (27 per cent) and in Norway and Åland by 19 and close to 18 per cent. Certain regions in Finland, Norway and Sweden have experienced a decline in the population due to urbanization, but at the national level all the Nordic countries have experienced growth. Compared to 2005, both the Faroe Islands and Greenland have experienced a minor decline in the population. Iceland has also experienced shorter periods with a declining population. The Danish population is expected to increase by 8 per cent until 2035, while Finland and Sweden expect an increase in the population of about 10 and almost 16 per cent respectively.
Life expectancy is rising in all the Nordic countries, though the levels vary greatly. Life expectancy for men in Greenland is 68.3 years (2011), compared to 80.8 years for men in Iceland. Women in the Faroe Islands and in Åland are expected to live the longest – more than 84 years. The population in the Nordic countries is getting older and according to the population projection for the Nordic countries as a whole, the share of the population above the age of 80 will reach 8.4 per cent in 2040, as compared to the 2013 level of 4.7 per cent. The share of population 80 years or older has increased from 1990 to 2013. The increase in the share of people above the age of 80 over the last 10 years is partly due to the fact that the death rate has fallen for almost all age groups and partly that the number of births has been low during the same period. In the next 25 years, the demographic dependency ratio is expected to have the strongest growth in Finland and Åland. According to the most recent population forecasts in Finland and Åland, in 2030 it is expected that people over 65 will make up 50 per cent of the adult population. Sweden and Denmark can look forward to a relatively modest increase in the next decades. Iceland and Norway seem to maintain their positions with the lowest proportions of elderly people in the Nordic countries.
At the beginning of the 20th century, almost 12 million people lived in the Nordic countries. Today, the population has increased to 27 million people. The Nordic countries have one of the lowest population densities in the world. The low density is partly due to the fact that many parts of the Nordic countries are marginal areas, where nature puts limitations on settlement. In four out of five Nordic countries, around 20 per cent of the population is to be found in the vicinity of the respective capitals. In Iceland, this percentage is even higher, with more than 60 per cent of Icelanders residing at or nearby the capital city of Reykjavík.
During the past 100 years, the population growth has been strongest in Greenland, where the population has multiplied by almost five, from 12,000 to 56,000 people. In Iceland, the increase has gone from 78,000 to 322,000 people. The population on the Faroe Islands has more than tripled, from 15,000 to 48,000 people. The Swedish and Ålandic populations are the only ones that have not at least doubled. Since 1990, the total population in the Nordic countries has increased by more than 2.8 million people (12 per cent) – the most in Iceland (27 per cent) and in Norway and Åland by 19 and close to 18 per cent. Certain regions in Finland, Norway and Sweden have experienced a decline in the population due to urbanization, but at the national level all the Nordic countries have experienced growth. Compared to 2005, both the Faroe Islands and Greenland have experienced a minor decline in the population. Iceland has also experienced shorter periods with a declining population. The Danish population is expected to increase by 8 per cent until 2035, while Finland and Sweden expect an increase in the population of about 10 and almost 16 per cent respectively.
Life expectancy is rising in all the Nordic countries, though the levels vary greatly. Life expectancy for men in Greenland is 68.3 years (2011), compared to 80.8 years for men in Iceland. Women in the Faroe Islands and in Åland are expected to live the longest – more than 84 years. The population in the Nordic countries is getting older and according to the population projection for the Nordic countries as a whole, the share of the population above the age of 80 will reach 8.4 per cent in 2040, as compared to the 2013 level of 4.7 per cent. The share of population 80 years or older has increased from 1990 to 2013. The increase in the share of people above the age of 80 over the last 10 years is partly due to the fact that the death rate has fallen for almost all age groups and partly that the number of births has been low during the same period. In the next 25 years, the demographic dependency ratio is expected to have the strongest growth in Finland and Åland. According to the most recent population forecasts in Finland and Åland, in 2030 it is expected that people over 65 will make up 50 per cent of the adult population. Sweden and Denmark can look forward to a relatively modest increase in the next decades. Iceland and Norway seem to maintain their positions with the lowest proportions of elderly people in the Nordic countries.
 Most of the Nordic languages belong to one of three linguistic families: North Germanic languages, Finno-Ugric languages and
Most of the Nordic languages belong to one of three linguistic families: North Germanic languages, Finno-Ugric languages and  The
The  Nordic countries have historically been one of the most socially progressive cultures in the world and culture is one of the main components of cooperation between the Nordic countries. The policies of the Nordic countries with respect to cultural life, mass media and religion have many shared values and features in common. However, some differences may be pointed out and for instance cultural institutions arising from historical circumstances. In both Denmark and Sweden, there are cultural institutions with roots in the traditions of the royal courts. In these countries, national institutions formed the foundation of cultural life at an early stage while in Norway cultural institutions began to form later.
Iceland has the highest government expenditure on culture, a total of 3.3 per cent of its GDP in 2011. Denmark comes second with a total of 1.6 per cent of GDP in 2011. Sweden spend the least in 2011 with 1.1 per cent. Looking at per capita expenditure, Iceland again has the highest expenditure with Norway coming second. Greenland spends the third highest amount on culture and leisure per capita. In Iceland and Norway, expenditures have more than doubled since 2000. In the other Nordic countries, expenditures have gone up between 40 and 50 per cent in the same period.
Denmark has the most museums, a total of 274, but museums in Åland and Iceland have the most visitors, an average of 4 and 5 visits per inhabitant. Many theatres in the Nordic countries receive public funding. Theatre funding constitutes a major share of allocations within the cultural area in all the countries. All countries have national theatres, where plays, ballets and operas are performed. In addition to the national theatres, there are professional regional theatres, which are also supported by the state, counties or municipalities. Most countries also have a few private theatres and many amateur ensembles, which may be supported at least partially by municipalities, primarily.
Nordic Culture Fund, established in 1966, aims to support a broad spectrum of cultural cooperations between the Nordic countries. The Fund's ambition is to enable talented artists, both professionals and amateurs, to enrich each other via the cultural diversity that exists among the 26 million or more people of the Region. Its activities are based on an agreement between the Nordic countries, which came into force in 1967. The Fund receives its money in the form of an annual grant from the Nordic Council of Ministers.
Nordic countries have historically been one of the most socially progressive cultures in the world and culture is one of the main components of cooperation between the Nordic countries. The policies of the Nordic countries with respect to cultural life, mass media and religion have many shared values and features in common. However, some differences may be pointed out and for instance cultural institutions arising from historical circumstances. In both Denmark and Sweden, there are cultural institutions with roots in the traditions of the royal courts. In these countries, national institutions formed the foundation of cultural life at an early stage while in Norway cultural institutions began to form later.
Iceland has the highest government expenditure on culture, a total of 3.3 per cent of its GDP in 2011. Denmark comes second with a total of 1.6 per cent of GDP in 2011. Sweden spend the least in 2011 with 1.1 per cent. Looking at per capita expenditure, Iceland again has the highest expenditure with Norway coming second. Greenland spends the third highest amount on culture and leisure per capita. In Iceland and Norway, expenditures have more than doubled since 2000. In the other Nordic countries, expenditures have gone up between 40 and 50 per cent in the same period.
Denmark has the most museums, a total of 274, but museums in Åland and Iceland have the most visitors, an average of 4 and 5 visits per inhabitant. Many theatres in the Nordic countries receive public funding. Theatre funding constitutes a major share of allocations within the cultural area in all the countries. All countries have national theatres, where plays, ballets and operas are performed. In addition to the national theatres, there are professional regional theatres, which are also supported by the state, counties or municipalities. Most countries also have a few private theatres and many amateur ensembles, which may be supported at least partially by municipalities, primarily.
Nordic Culture Fund, established in 1966, aims to support a broad spectrum of cultural cooperations between the Nordic countries. The Fund's ambition is to enable talented artists, both professionals and amateurs, to enrich each other via the cultural diversity that exists among the 26 million or more people of the Region. Its activities are based on an agreement between the Nordic countries, which came into force in 1967. The Fund receives its money in the form of an annual grant from the Nordic Council of Ministers.
 Nordic countries share certain traditions in music, many of which have diverged significantly. In folk music, Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and the Faroe Islands share many common aspects. Greenland's
Nordic countries share certain traditions in music, many of which have diverged significantly. In folk music, Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and the Faroe Islands share many common aspects. Greenland's 
 The earliest written records from Scandinavia are
The earliest written records from Scandinavia are