)
, anthem =
( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type =
Sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
, subdivision_name =
Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date =
Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the Ha ...
, established_title2 =
Act of Abjuration
The Act of Abjuration ( nl, Plakkaat van Verlatinghe; es, Acta de Abjuración, lit=placard of abjuration) is the declaration of independence by many of the provinces of the Netherlands from the allegiance to Philip II of Spain, during the Dut ...
, established_date2 = 26 July 1581
, established_title3 =
Peace of Münster
The Peace of Münster was a treaty between the Lords States General of the Seven United Netherlands and the Spanish Crown, the terms of which were agreed on 30 January 1648. The treaty, parallelly negotiated to but not part of the Peace of We ...
, established_date3 = 30 January 1648
, established_title4 = Kingdom established
, established_date4 = 16 March 1815
, established_title5 =
Liberation Day
Liberation Day is a day, often a public holiday, that marks the liberation of a place, similar to an independence day. Liberation marks the date of either a revolution, as in Cuba, the fall of a dictatorship, as in Portugal, or the end of an oc ...
, established_date5 = 5 May 1945
, established_title6 =
Kingdom Charter
, established_date6 = 15 December 1954
, established_title7 =
Caribbean reorganisation
, established_date7 = 10 October 2010
, official_languages =
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, languages_type =
Regional language
*
A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area.
Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Lan ...
s
, languages_sub = yes
, languages =
, languages2_type = Recognised languages
, languages2_sub = yes
, languages2 =
, demonym = Dutch
, capital =
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
, largest_city = capital
, coordinates =
, admin_center =
The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
, admin_center_type = Government seat
, ethnic_groups =
, ethnic_groups_year = 2020
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, government_type =
Unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigroup ...
parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democracy, democratic government, governance of a sovereign state, state (or subordinate entity) where the Executive (government), executive derives its democratic legitimacy ...
constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
, leader_title1 =
Monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
, leader_name1 =
Willem-Alexander
Willem-Alexander (; Willem-Alexander Claus George Ferdinand; born ) is King of the Netherlands, having acceded to the throne following his mother's abdication in 2013.
Willem-Alexander was born in Utrecht as the oldest child of Princess Beatri ...
, leader_title2 =
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
, leader_name2 =
Mark Rutte
Mark Rutte (; born 14 February 1967) is a Dutch politician who has served as Prime Minister of the Netherlands since 2010 and Leader of the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) since 2006.
After a business career working for Unilever ...
, national_representation =
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adopts ...
, national_representation_type1 =
Netherlands constituency
, national_representation1 =
26 seats
, legislature =
States General The word States-General, or Estates-General, may refer to:
Currently in use
* Estates-General on the Situation and Future of the French Language in Quebec, the name of a commission set up by the government of Quebec on June 29, 2000
* States Genera ...
, upper_house =
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, lower_house =
House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
, area_km2 = 41850
, area_rank = 131st
, area_sq_mi = 16059
, percent_water = 18.41
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_ft =
, elevation_max_point =
Mount Scenery
Mount Scenery is an active volcano in the Caribbean Netherlands. Its lava dome forms the summit of the Saba island stratovolcano. At an elevation of , it is the highest point in both the Kingdom of the Netherlands, and, since the dissolution of th ...
, population_census = 16,655,799
, population_census_year = 2011
, population_estimate =
, population_estimate_rank = 67th
, population_estimate_year =
, population_density_km2 = 423
, population_density_sq_mi =
, population_density_rank = 16th
, GDP_PPP = $1.2 trillion
, GDP_PPP_year = 2022
, GDP_PPP_rank = 27th
, GDP_PPP_per_capita = $68,572
[
, GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 13th
, GDP_nominal = $1.01 trillion][
, GDP_nominal_year = 2022
, GDP_nominal_rank = 19th
, GDP_nominal_per_capita = $57,836][
, GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 13th
, Gini = 28.2
, Gini_year = 2020
, Gini_change = increase
, Gini_ref = ].nl
.nl is the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for the Netherlands. It is one of the most popular ccTLDs with over six million registered .nl domains .
When cwi.nl was registered by Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica on 1986-05-01, .nl ...
, .bq
.bq is designated—but not in use—as the Internet country code top-level domain ( ccTLD) for '' Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba'' (the Caribbean Netherlands) following the assignment on December 15, 2010, by the ISO 3166 Maintenance Agency ...
, drives_on=right
The Netherlands ( nl, Nederland ), informally Holland,Northwestern Europe
Northwestern Europe, or Northwest Europe, is a loosely defined subregion of Europe, overlapping Northern and Western Europe. The region can be defined both geographically and ethnographically.
Geographic definitions
Geographically, Northw ...
with overseas territories in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
. It is the largest of four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
. The Netherlands consists of twelve provinces
The Twelve Provinces is a term used in ancient Chinese histories to refer to territorial divisions during the reigns of the mythological emperors Yao and Shun of the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors.
Records in histories
The "Annals of the Fiv ...
; it borders Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
to the east, and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
to the south, with a North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
coastline to the north and west. It shares maritime borders with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, Germany and Belgium in the North Sea. The country's official language is Dutch, with West Frisian as a secondary official language in the province of Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
.Dutch Low Saxon
Dutch Low Saxon ( or ''Nederlaands Nedersaksies''; nl, Nederlands Nedersaksisch) are the Low Saxon dialects of the Low German language that are spoken in the northeastern Netherlands and are written there with local, unstandardised orthographi ...
and Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg (Netherlands), L ...
are recognised regional languages, while Dutch Sign Language
Dutch Sign Language ( nl, Nederlandse Gebarentaal or NGT; Sign Language of the Netherlands or SLN) is the predominant sign language used by deaf people in the Netherlands.
Although the same spoken Dutch language is used in the Netherlands and ...
, Sinte Romani
Sinte Romani (also known as Sintitikes, Manuš) is the variety of Romani spoken by the Sinti people in Germany, France, Austria, Belgium, the Netherlands, some parts of Northern Italy and other adjacent regions. Sinte Romani is characterized by ...
and Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
are recognised non-territorial languages.Papiamento
Papiamento () or Papiamentu (; nl, Papiaments) is a Portuguese-based creole language spoken in the Dutch Caribbean. It is the most widely spoken language on the Caribbean ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao), with official status in Arub ...
are official in the Caribbean territories.Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
, Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"N ...
, The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
and Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
. Amsterdam is the country's most populous city and the nominal capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
. The Hague holds the seat of the States General The word States-General, or Estates-General, may refer to:
Currently in use
* Estates-General on the Situation and Future of the French Language in Quebec, the name of a commission set up by the government of Quebec on June 29, 2000
* States Genera ...
, Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
and Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
. The Port of Rotterdam
The Port of Rotterdam is the largest seaport in Europe, and the world's largest seaport outside of East Asia, located in and near the city of Rotterdam, in the province of South Holland in the Netherlands. From 1962 until 2004, it was the List o ...
is the busiest seaport in Europe.Schiphol
Amsterdam Airport Schiphol , known informally as Schiphol Airport ( nl, Luchthaven Schiphol, ), is the main international airport of the Netherlands. It is located southwest of Amsterdam, in the municipality of Haarlemmermeer in the province ...
is the busiest airport in the Netherlands, and the third busiest in Europe. The Netherlands is a founding member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies ...
, G10, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
, OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
, and WTO
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
, as well as a part of the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
and the trilateral Benelux
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a politico-economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in western Europe: B ...
Union. It hosts several intergovernmental organisations
An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states an ...
and international court
International courts are formed by treaties between nations or under the authority of an international organization such as the United Nations and include ''ad hoc'' tribunals and permanent institutions but exclude any courts arising purely under n ...
s, many of which are centred in The Hague.
''Netherlands'' literally means "lower countries" in reference to its low elevation and flat topography, with only about 50% of its land exceeding above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, and nearly 26% falling below sea level.Dutch Golden Age
The Dutch Golden Age ( nl, Gouden Eeuw ) was a period in the history of the Netherlands, roughly spanning the era from 1588 (the birth of the Dutch Republic) to 1672 (the Rampjaar, "Disaster Year"), in which Dutch trade, science, and Dutch art, ...
. During this time, its trading companies, the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
and the Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company ( nl, Geoctrooieerde Westindische Compagnie, ''WIC'' or ''GWC''; ; en, Chartered West India Company) was a chartered company of Dutch merchants as well as foreign investors. Among its founders was Willem Usselincx ( ...
, established colonies and trading posts all over the world.
With a population of 17.7 million people, all living within a total area of —of which the land area is —the Netherlands is the 16th most densely populated country in the world and the second-most densely populated country in the European Union, with a density of . Nevertheless, it is the world's second-largest export
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is an ...
er of food and agricultural products by value, owing to its fertile soil
Soil fertility refers to the ability of soil to sustain agricultural plant growth, i.e. to provide plant habitat and result in sustained and consistent yields of high quality. , mild climate, intensive agriculture
Intensive agriculture, also known as intensive farming (as opposed to extensive farming), conventional, or industrial agriculture, is a type of agriculture, both of crop plants and of animals, with higher levels of input and output per unit of ag ...
, and inventiveness
The inventive step and non-obviousness reflect a general patentability requirement present in most patent laws, according to which an invention should be sufficiently inventive—i.e., non-obvious—in order to be patented. In other words, " henon ...
.parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democracy, democratic government, governance of a sovereign state, state (or subordinate entity) where the Executive (government), executive derives its democratic legitimacy ...
constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
with a unitary structure since 1848. The country has a tradition of pillarisation
Pillarisation (from the nl, verzuiling) is the politico-denominational segregation of a society into groups by religion and associated political beliefs. These societies were (and in some areas, still are) vertically divided into two or more gr ...
and a long record of social tolerance
Toleration is the allowing, permitting, or acceptance of an action, idea, object, or person which one dislikes or disagrees with. Political scientist Andrew R. Murphy explains that "We can improve our understanding by defining "toleration" as ...
, having legalised abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregn ...
, prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
and human euthanasia, along with maintaining a liberal drug policy
A drug policy is the policy regarding the control and regulation of psychoactive substances (commonly referred to as drugs), particularly those that are addictive or cause physical and mental dependence. While drug policies are generally implemen ...
. The Netherlands abolished the death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
in Civil Law in 1870, though it was not completely removed until a new constitution was approved in 1983. The Netherlands allowed women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ...
in 1919 and was the first country to legalise same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same Legal sex and gender, sex or gender. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 33 countries, with the most recent being ...
in 2001. Its mixed-market
A mixed economy is variously defined as an economic system blending elements of a market economy with elements of a planned economy, Market (economics), markets with state interventionism, or private enterprise with public enterprise. Common to ...
advanced economy has the twelfth-highest per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
globally. The Netherlands ranks among the highest in international indices of press freedom
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic media, especially published materials, should be considered a right to be exerci ...
, economic freedom
Economic freedom, or economic liberty, is the ability of people of a society to take economic actions. This is a term used in economic and policy debates as well as in the philosophy of economics. One approach to economic freedom comes from the l ...
, human development Human development may refer to:
* Development of the human body
* Developmental psychology
* Human development (economics)
* Human Development Index, an index used to rank countries by level of human development
* Human evolution, the prehistoric ...
and quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
, as well as happiness
Happiness, in the context of Mental health, mental or emotional states, is positive or Pleasure, pleasant emotions ranging from contentment to intense joy. Other forms include life satisfaction, well-being, subjective well-being, flourishin ...
.
Etymology
Netherlands and the Low Countries
The region called the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
(comprising Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
, the Netherlands and Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
) has the same toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
. Place names with ''Neder'', ''Nieder'', ''Nedre'', ''Nether'', ''Lage(r)'' or ''Low(er)'' (in Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, Engli ...
) and ''Bas'' or ''Inferior'' (in Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language fam ...
) are in use in low-lying places all over Europe. In the case of the Low Countries / Netherlands, the geographical location of the ''lower'' region has been more or less downstream and near the sea. The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
made a distinction between the Roman provinces of downstream Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippin ...
(nowadays part of Belgium and the Netherlands) and upstream Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesontio' ...
. The designation 'Low' returned in the 10th-century Duchy of Lower Lorraine
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as ''Lothier'' or ''Lottier'' , which covered much of the Low Countries.Dukes of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy (french: duc de Bourgogne) was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by France in 1477, and later by Holy Roman Emperors and Kings of Spain from the House of Habsburg ...
used the term ''les pays de par deçà'' ("the lands over here") for the Low Countries.Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
and the lower Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
in the late Middle Ages. From the mid-sixteenth century, the "Low Countries" and the "Netherlands" lost their original deictic meaning.
In most Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language fam ...
, the term "Low Countries" is officially used as the name for the Netherlands.
Holland and Dutch
The Netherlands is informally referred to as Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
in various languages, including Dutch and English. In other languages, Holland is the formal name for the Netherlands. Holland can also refer to a region within the Netherlands that consists of North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and South Holland
South Holland ( nl, Zuid-Holland ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.7 million as of October 2021 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely ...
. Formerly these were a single province, and earlier the County of Holland
The County of Holland was a State of the Holy Roman Empire and from 1433 part of the Burgundian Netherlands, from 1482 part of the Habsburg Netherlands and from 1581 onward the leading province of the Dutch Republic, of which it remained a part ...
, a remnant of the dissolved Frisian Kingdom
The Frisian Kingdom ( fy, Fryske Keninkryk), also known as Magna Frisia, is a modern name for the post-Roman Frisian realm in Western Europe in the period when it was at its largest (650–734). This dominion was ruled by kings and emerged in th ...
that also included parts of present-day Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
. Following the decline of the Duchy of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Neth ...
and the County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Ypr ...
, Holland became the most economically and politically important county in the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
region. The emphasis on Holland during the formation of the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
, the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Refo ...
, and the Anglo-Dutch Wars
The Anglo–Dutch Wars ( nl, Engels–Nederlandse Oorlogen) were a series of conflicts mainly fought between the Dutch Republic and England (later Great Britain) from mid-17th to late 18th century. The first three wars occurred in the second ...
in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, made Holland a ''pars pro toto
''Pars pro toto'' (, ), , is a figure of speech where the name of a ''portion'' of an object, place, or concept is used or taken to represent its entirety. It is distinct from a merism, which is a reference to a whole by an enumeration of parts; ...
'' for the entire country.
The term Dutch is used as the demonymic and adjectival form of the Netherlands in the English language. The origins of the word go back to Proto-Germanic ''*þiudiskaz'', Latinised into Theodiscus
' (in Medieval Latin, corresponding to Old English þēodisc, Old High German diutisc and other early Germanic reflexes of Proto-Germanic *þiudiskaz, meaning "popular" or "of the people") was a term used in the early Middle Ages to refer to ...
, meaning "popular" or "of the people"; akin to Old Dutch ''Dietsch'', Old High German ''duitsch'', and Old English ''þeodisc'', all meaning "(of) the common (Germanic) people". At first, the English language used (the contemporary form of) Dutch to refer to any or all speakers of West Germanic languages
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic languages, North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages, East Germanic ...
. Gradually its meaning shifted to the West Germanic people they had the most contact with, because of their geographical proximity and rivalry in trade and overseas territories.
History
Prehistory (before 800 BC)
 The prehistory of the area that is now the Netherlands was largely shaped by the sea and the rivers that constantly shifted the low-lying geography. The oldest human (
The prehistory of the area that is now the Netherlands was largely shaped by the sea and the rivers that constantly shifted the low-lying geography. The oldest human (Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
) traces, believed to be about 250,000 years old, were found in higher soils near Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
. At the end of the Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
, the nomadic
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
late Upper Palaeolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
Hamburg culture
The Hamburg culture or Hamburgian (15,500-13,100 BP) was a Late Upper Paleolithic culture of reindeer hunters in northwestern Europe during the last part of the Weichsel Glaciation beginning during the Bölling interstadial. Sites are found close ...
(13,000–10,000 BC) hunted reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspe ...
in the area, using spears. The later Ahrensburg culture
The Ahrensburg culture or Ahrensburgian (c. 12,900 to 11,700 BP) was a late Upper Paleolithic nomadic hunter culture (or technocomplex) in north-central Europe during the Younger Dryas, the last spell of cold at the end of the Weichsel glaciatio ...
(11,200–9,500 BC) used bow and arrow
The bow and arrow is a ranged weapon system consisting of an elastic launching device (bow) and long-shafted projectiles ( arrows). Humans used bows and arrows for hunting and aggression long before recorded history, and the practice was comm ...
. From Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
Maglemosian-like tribes (c. 8000 BC), the world's oldest canoe was found in Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nov ...
.
Indigenous late Mesolithic hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s from the Swifterbant culture The Swifterbant culture was a Subneolithic archaeological culture in the Netherlands, dated between 5300 BC and 3400 BC. Like the Ertebølle culture, the settlements were concentrated near water, in this case creeks, riverdunes and bogs along post-g ...
(c. 5600 BC), related to the southern Scandinavian Ertebølle culture
The Ertebølle culture (ca 5300 BCE – 3950 BCE) () is the name of a hunter-gatherer and fisher, pottery-making culture dating to the end of the Mesolithic period. The culture was concentrated in Southern Scandinavia. It is named after the ...
, were strongly linked to rivers and open water.[Louwe Kooijmans, L.P.,]
Trijntje van de Betuweroute, Jachtkampen uit de Steentijd te Hardinxveld-Giessendam
, 1998, ''Spiegel Historiael'' 33, pp. 423–428 Between 4800 and 4500 BC, the Swifterbant people started to adopt from the neighbouring Linear Pottery culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
the practice of animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starti ...
, and between 4300 and 4000 BC the practice of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
. The Funnelbeaker culture
The Funnel(-neck-)beaker culture, in short TRB or TBK (german: Trichter(-rand-)becherkultur, nl, Trechterbekercultuur; da, Tragtbægerkultur; ) was an archaeological culture in north-central Europe.
It developed as a technological merger of lo ...
(4300–2800 BC), related to the Swifterbant culture, erected the dolmens
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
, large stone grave monuments found in Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nov ...
. There was a quick and smooth transition from the Funnelbeaker farming culture to the pan-European Corded Ware
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a va ...
pastoralist culture (c. 2950 BC). In the southwest, the Seine-Oise-Marne culture — related to the Vlaardingen culture
Vlaardingen Culture was an archaeological culture on the border of the middle and late Neolithic era in what is now the coastal region in the west of the Netherlands. Archeologists found in 1958 in Vlaardingen, a city near Rotterdam, objects fr ...
(c. 2600 BC), an apparently more primitive culture of hunter-gatherers — survived well into the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period, until it too was succeeded by the Corded Ware culture.
The subsequent Bell Beaker culture
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from a ...
(2700–2100 BC) introduced metalwork in copper, gold and later bronze and opened international trade routes not seen before, reflected in copper artifacts. Finds of rare bronze objects suggest that Drenthe was a trading centre in the Bronze Age (2000–800 BC). The Bell Beaker culture developed locally into the Barbed-Wire Beaker culture (2100–1800 BC) and later the Elp culture
The Elp culture (c. 1800—800 BCE) is a Bronze Age archaeological culture of the Netherlands having earthenware pottery of low quality known as "Kümmerkeramik" (also "Grobkeramik") as a marker. The initial phase is characterized by tumuli (180 ...
(1800–800 BC), a Middle Bronze Age archaeological culture with earthenware
Earthenware is glazed or unglazed nonvitreous pottery that has normally been fired below . Basic earthenware, often called terracotta, absorbs liquids such as water. However, earthenware can be made impervious to liquids by coating it with a ce ...
low-quality pottery as a marker. The initial phase of the Elp culture was characterised by tumuli
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones buil ...
(1800–1200 BC). The subsequent phase was that of cremating the dead and placing their ashes in urns which were then buried in fields, following the customs of the Urnfield culture
The Urnfield culture ( 1300 BC – 750 BC) was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield tradition. The name comes from the custom of cremating the dead and p ...
(1200–800 BC). The southern region became dominated by the related Hilversum culture
The Hilversum culture is a prehistoric material culture found in middle Bronze Age in the region of the southern Netherlands and northern Belgium. It has been associated with the Wessex culture from the same period in southern England, and is one ...
(1800–800 BC), with apparently cultural ties with Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
of the previous Barbed-Wire Beaker culture.
Celts, Germanic tribes and Romans (800 BC–410 AD)
 From 800 BC onwards, the
From 800 BC onwards, the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
Celtic Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European Archaeological culture, culture of Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe ...
became influential, replacing the Hilversum culture
The Hilversum culture is a prehistoric material culture found in middle Bronze Age in the region of the southern Netherlands and northern Belgium. It has been associated with the Wessex culture from the same period in southern England, and is one ...
. Iron ore brought a measure of prosperity and was available throughout the country, including bog iron
Bog iron is a form of impure iron deposit that develops in bogs or swamps by the chemical or biochemical oxidation of iron carried in solution. In general, bog ores consist primarily of iron oxyhydroxides, commonly goethite (FeO(OH)).
Iron-bea ...
. Smiths travelled from settlement to settlement with bronze and iron, fabricating tools on demand. The King's grave of Oss (700 BC) was found in a burial mound, the largest of its kind in western Europe and containing an iron sword with an inlay of gold and coral.
The deteriorating climate in Scandinavia around 850 BC further deteriorated around 650 BC and might have triggered the migration of Germanic tribes from the North. By the time this migration was complete, around 250 BC, a few general cultural and linguistic groups had emerged.[de Vries, Jan W., Roland Willemyns and Peter Burger, ''Het verhaal van een taal'', Amsterdam: Prometheus, 2003, pp. 12, 21–27] The North Sea Germanic
North Sea Germanic, also known as Ingvaeonic , is a postulated grouping of the northern West Germanic languages that consists of Old Frisian, Old English, and Old Saxon, and their descendants.
Ingvaeonic is named after the Ingaevones, a West Ge ...
Ingaevones
The Ingaevones were a West Germanic cultural group living in the Northern Germania along the North Sea coast in the areas of Jutland, Holstein, and Frisia in classical antiquity. Tribes in this area included the Angles, Frisii, Chauci, Saxons, ...
inhabited the northern part of the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
. They would later develop into the Frisii
The Frisii were an ancient Germanic tribe living in the low-lying region between the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and the River Ems, and the presumed or possible ancestors of the modern-day ethnic Dutch.
The Frisii lived in the coastal area ...
and the early Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
.Weser-Rhine Germanic
Weser-Rhine Germanic is a proposed group of prehistoric West Germanic dialects which would have been both directly ancestral to Dutch, as well as being a notable substratum influencing West Central German dialects. The term was introduced by the G ...
(or Istvaeones
The Istaevones (also spelled Istvaeones) were a Germanic group of tribes living near the banks of the Rhine during the Roman Empire which reportedly shared a common culture and origin. The Istaevones were contrasted to neighbouring groups, the In ...
), extended along the middle Rhine and Weser
The Weser () is a river of Lower Saxony in north-west Germany. It begins at Hannoversch Münden through the confluence of the Werra and Fulda. It passes through the Hanseatic city of Bremen. Its mouth is further north against the ports of Bre ...
and inhabited the Low Countries south of the great rivers. This group consisted of tribes that would eventually develop into the Salian Franks
The Salian Franks, also called the Salians (Latin: ''Salii''; Greek: Σάλιοι, ''Salioi''), were a northwestern subgroup of the early Franks who appear in the historical record in the fourth and fifth centuries. They lived west of the Lowe ...
.Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defini ...
(c. 450 BC up to the Roman conquest) had expanded over a wide range, including the southern area of the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
. Some scholars have speculated that even a third ethnic identity and language, neither Germanic nor Celtic, survived in the Netherlands until the Roman period, the Iron Age Nordwestblock
The Nordwestblock (German, "Northwest Block") is a hypothetical Northwestern European cultural region that some scholars propose as a prehistoric culture in the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, northern France, and northwestern Germany, in an ar ...
culture,[Lendering, Jona]
"Germania Inferior"
, Livius.org. Retrieved 6 October 2011. that eventually was absorbed by the Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
to the south and the Germanic peoples from the east.
 The first author to describe the coast of
The first author to describe the coast of Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
and Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
was the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" a ...
Pytheas
Pytheas of Massalia (; Ancient Greek: Πυθέας ὁ Μασσαλιώτης ''Pythéas ho Massaliōtēs''; Latin: ''Pytheas Massiliensis''; born 350 BC, 320–306 BC) was a Greeks, Greek List of Graeco-Roman geographers, geographer, explor ...
, who noted in c. 325 BC that in these regions, "more people died in the struggle against water than in the struggle against men." During the Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homela ...
, the area south and west of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
was conquered by Roman forces under Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
from 57 BC to 53 BC.Menapii
The Menapii were a Belgic tribe dwelling near the North Sea, around present-day Cassel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name Attestations
They are mentioned as ''Menapii'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Orosius (early 5th c. AD), ...
and the Eburones
The Eburones (Greek: ) were a Gallic- Germanic tribe dwelling in the northeast of Gaul, in what is now the southern Netherlands, eastern Belgium and the German Rhineland, in the period immediately preceding the Roman conquest of the region. Thou ...
. The Rhine became fixed as Rome's northern frontier around 12 AD. Notable towns would arise along the Limes Germanicus
The (Latin for ''Germanic frontier'') is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier () fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsub ...
: Nijmegen
Nijmegen (;; Spanish and it, Nimega. Nijmeegs: ''Nimwèège'' ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and tenth largest of the Netherlands as a whole, located on the Waal river close to the German border. It is about 6 ...
and Voorburg
Voorburg is a town and former municipality in the west part of the province of South Holland, Netherlands. Together with Leidschendam and Stompwijk, it makes up the municipality Leidschendam-Voorburg. It has a population of about 39,000 people ...
. In the first part of Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, af ...
, the area south of the Limes became part of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippin ...
. The area to the north of the Rhine, inhabited by the Frisii, remained outside Roman rule (but not its presence and control), while the Germanic border tribes of the Batavi and Cananefates
The Cananefates, or Canninefates, Caninefates, or Canenefatae, meaning "leek masters", were a Germanic tribe, who lived in the Rhine delta, in western Batavia (later Betuwe), in the Roman province of ''Germania Inferior'' (now in the Dutch provi ...
served in the Roman cavalry
Roman cavalry (Latin: ''equites Romani'') refers to the horse-mounted forces of the Roman army throughout the Regal, Republican, and Imperial eras.
In the Regal era the Roman cavalry was a group of 300 soldiers called '' celeres'', tasked wit ...
. The Batavi rose against the Romans in the Batavian rebellion
The Revolt of the Batavi took place in the Roman province of Germania Inferior between AD 69 and 70. It was an uprising against the Roman Empire started by the Batavi, a small but militarily powerful Germanic tribe that inhabited Batavia, on th ...
of 69 AD but were eventually defeated. The Batavi later merged with other tribes into the confederation of the Salian Franks, whose identity emerged in the first half of the third century.[Previté-Orton, Charles, ''The Shorter Cambridge Medieval History'', vol. I, pp. 51–52, 151] Salian Franks appear in Roman texts as both allies and enemies. They were forced by the confederation of the Saxons from the east to move over the Rhine into Roman territory in the fourth century. From their new base in West Flanders
)
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of West Flanders.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van West-Vlaanderen.svg
, shield_size =
, image_map ...
and the Southwest Netherlands, they were raiding the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
. Roman forces pacified the region but did not expel the Franks, who continued to be feared at least until the time of Julian the Apostate
Julian ( la, Flavius Claudius Julianus; grc-gre, Ἰουλιανός ; 331 – 26 June 363) was Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplato ...
(358) when Salian Franks were allowed to settle as ''foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign stat ...
'' in Texandria
Texandria (also Toxiandria; later Toxandria, Taxandria), is a region mentioned in the 4th century AD and during the Middle Ages. It was situated in the southern part of the modern Netherlands and in the northern part of present-day Belgium, current ...
.Frisii
The Frisii were an ancient Germanic tribe living in the low-lying region between the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and the River Ems, and the presumed or possible ancestors of the modern-day ethnic Dutch.
The Frisii lived in the coastal area ...
disappeared as ''laeti
Laeti , the plural form of laetus , was a term used in the late Roman Empire to denote communities of ''barbari'' (" barbarians"), i.e. foreigners, or people from outside the Empire, permitted to settle on, and granted land in, imperial territory ...
'' in c. 296, leaving the coastal lands largely unpopulated for the next two centuries. However, recent excavations in Kennemerland
Kennemerland is a coastal region in the northwestern Netherlands, in the province of North Holland. It includes the sand dunes north of the North Sea Canal, as well as the dunes of Zuid-Kennemerland National Park.
History
Kennemerland gets its ...
show a clear indication of permanent habitation.
Early Middle Ages (411–1000)
 After the
After the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
government in the area collapsed, the Franks expanded their territories into numerous kingdoms. By the 490s, Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single kin ...
had conquered and united all these territories in the southern Netherlands in one Frankish kingdom
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
, and from there continued his conquests into Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
. During this expansion, Franks migrating to the south (modern territory of France and Walloon part of Belgium) eventually adopted the Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
of the local population.Old Frankish
Frankish ( reconstructed endonym: *), also known as Old Franconian or Old Frankish, was the West Germanic language spoken by the Franks from the 5th to 9th century.
After the Salian Franks settled in Roman Gaul, its speakers in Picardy an ...
, which by the ninth century had evolved into Old Low Franconian
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aroun ...
or Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aroun ...
. To the north of the Franks, climatic conditions improved, and during the
To the north of the Franks, climatic conditions improved, and during the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, the closely related Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ' ...
, Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nations ...
and Frisii
The Frisii were an ancient Germanic tribe living in the low-lying region between the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and the River Ems, and the presumed or possible ancestors of the modern-day ethnic Dutch.
The Frisii lived in the coastal area ...
settled the coastal land.England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and came to be known as Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
, but those who stayed would be referred to as Frisians
The Frisians are a Germanic ethnic group native to the coastal regions of the Netherlands and northwestern Germany. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany, ...
and their language as Frisian, named after the land that was once inhabited by Frisii.Frisian Kingdom
The Frisian Kingdom ( fy, Fryske Keninkryk), also known as Magna Frisia, is a modern name for the post-Roman Frisian realm in Western Europe in the period when it was at its largest (650–734). This dominion was ruled by kings and emerged in th ...
(650–734) under King Aldegisel
Aldegisel, Aldegisl, Aldgillis, Aldgisl, Aldgils or Eadgils (fl. c. 678) was the ruler of Frisia (as king or duke) in the late seventh century contemporarily with Dagobert II and a very obscure figure. All that is known of him is in relation to t ...
and King Redbad Radbod, Radbot, Ratbod, Ratpot, Redbod, Redbad, Radboud, Rapoto, or sometimes just Boddo, is a Germanic masculine given name that may refer to:
*Redbad, King of the Frisians (died 719)
*Radbod (prefect) (833–54), Frankish prefect
*Ratbod (archbis ...
emerged with Traiectum (Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
) as its centre of power,Dorestad
Dorestad (''Dorestat, Duristat'') was an early medieval emporium, located in the southeast of the province of Utrecht in the Netherlands, close to the modern-day town of Wijk bij Duurstede.
It flourished during the 8th to early 9th centuries, ...
was a flourishing trading place.Battle of the Boarn
The Battle of the Boarn ( fry, Slach oan de Boarn nl, Slag aan de Boorne) was an eighth century battle between the Franks and the Frisians near the mouth of the river Boarn in what is now the Dutch province of Friesland.
Battle
In 734 a Fran ...
, the Frisians were defeated after a series of wars. With the approval of the Franks, the Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
missionary Willibrord
Willibrord (; 658 – 7 November AD 739) was an Anglo-Saxon missionary and saint, known as the "Apostle to the Frisians" in the modern Netherlands. He became the first bishop of Utrecht and died at Echternach, Luxembourg.
Early life
His fathe ...
converted the Frisian people to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
. He established the Archdiocese of Utrecht and became the bishop of the Frisians. However, his successor Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of ...
was murdered by the Frisians in Dokkum
Dokkum is a Dutch fortified city in the municipality of Noardeast-Fryslân in the province of Friesland. It has 12,669 inhabitants (February 8, 2020). The fortifications of Dokkum are well preserved and are known as the ''bolwerken'' (bulwarks). ...
, in 754.
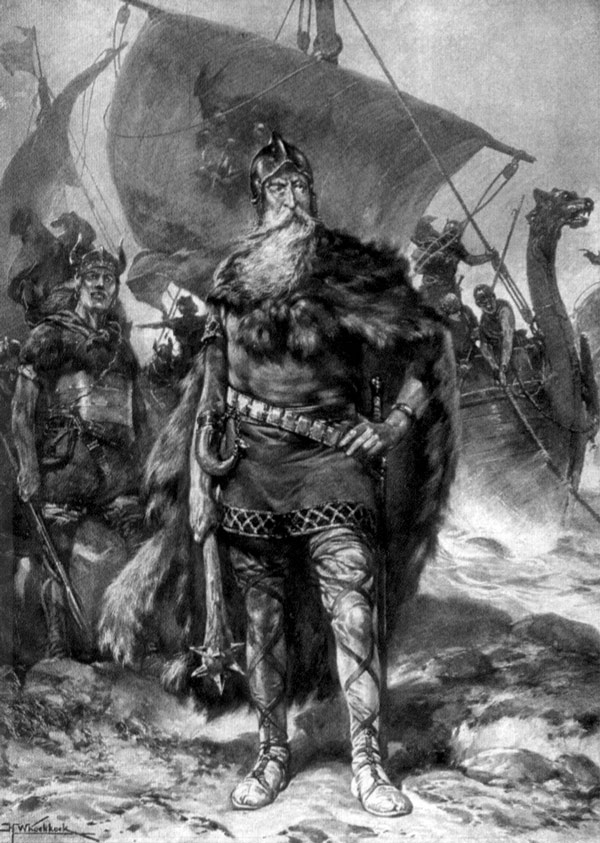 The Frankish
The Frankish Carolingian empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lom ...
modelled itself on the Roman Empire and controlled much of Western Europe. However, in 843, it was divided into three parts—East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
, Middle, and West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about ...
. Most of present-day Netherlands became part of Middle Francia
Middle Francia ( la, Francia media) was a short-lived Frankish kingdom which was created in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun after an intermittent civil war between the grandsons of Charlemagne resulted in division of the united empire. Middle Francia ...
, which was a weak kingdom and subject to numerous partitions and annexation attempts by its stronger neighbours. It comprised territories from Frisia
Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Ger ...
in the north to the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
in the south. Around 850, Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I (Dutch and Medieval Latin: ''Lotharius''; German: ''Lothar''; French: ''Lothaire''; Italian: ''Lotario'') (795 – 29 September 855) was emperor (817–855, co-ruling with his father until 840), and the governor of Bavar ...
of Middle Francia acknowledged the Viking Rorik of Dorestad
Rorik (''Roricus, Rorichus''; Old Norse ''HrœrekR'', c. 810 – c. 880) was a Danish Viking, who ruled over parts of Friesland between 841 and 873, conquering Dorestad and Utrecht in 850. Rorik swore allegiance to Louis the German in 873. He ...
as ruler of most of Frisia. When the kingdom of Middle Francia was partitioned in 855, the lands north of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
passed to Lothair II
Lothair II (835 – 8 August 869) was the king of Lotharingia from 855 until his death. He was the second son of Emperor Lothair I and Ermengarde of Tours. He was married to Teutberga (died 875), daughter of Boso the Elder.
Reign
For political ...
and subsequently were named Lotharingia
Lotharingia ( la, regnum Lotharii regnum Lothariense Lotharingia; french: Lotharingie; german: Reich des Lothar Lotharingien Mittelreich; nl, Lotharingen) was a short-lived medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. As a more durable ...
. After he died in 869, Lotharingia was partitioned, into Upper and Lower Lotharingia
The Duchy of Lower Lotharingia, also called Northern Lotharingia, Lower Lorraine or Northern Lorraine (and also referred to as ''Lothier'' or ''Lottier'' , the latter part comprising the Low Countries that technically became part of East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's Carolingian Empire, empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided t ...
in 870, although it was effectively under the control of Vikings, who raided the largely defenceless Frisian and Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
towns lying on the Frisian coast and along the rivers. Around 879, another Viking expedition led by Godfrid, Duke of Frisia
Godfrid, Godafrid, Gudfrid, or Gottfrid ( non, Guðfrið; murdered June 885) was a Danish Viking leader of the late ninth century. He had probably been with the Great Heathen Army, descended on the continent, and became a vassal of the emperor Cha ...
, raided the Frisian lands. The Viking raids made the sway of French and German lords in the area weak. Resistance to the Vikings, if any, came from local nobles, who gained in stature as a result, and that laid the basis for the disintegration of Lower Lotharingia into semi-independent states. One of these local nobles was Gerolf of Holland
Gerolf or Gerulf (c. 850 – 895/896) was the second count of this name who is attested in the area of Friesland (which also included Holland at the time). Gerolf's main area of power seems to have been in Kennemerland. Count Gerolf is often regard ...
, who assumed lordship in Frisia after he helped to assassinate Godfrid, and Viking rule came to an end.
High Middle Ages (1000–1384)
 The
The Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
(the successor state of East Francia and then Lotharingia) ruled much of the Low Countries in the 10th and 11th century but was not able to maintain political unity. Powerful local nobles turned their cities, counties and duchies into private kingdoms that felt little sense of obligation to the emperor. Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
, Hainaut, Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
, Gelre
The Duchy of Guelders ( nl, Gelre, french: Gueldre, german: Geldern) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in p ...
, Brabant Brabant is a traditional geographical region (or regions) in the Low Countries of Europe. It may refer to:
Place names in Europe
* London-Brabant Massif, a geological structure stretching from England to northern Germany
Belgium
* Province of Bra ...
, and Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
were in a state of almost continual war or paradoxically formed personal unions. The language and culture of most of the people who lived in the County of Holland were originally Frisia
Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Ger ...
n. As Frankish settlement progressed from Flanders and Brabant, the area quickly became Old Low Franconian
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aroun ...
(or Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch (Dutch: Oudnederlands) or Old Low Franconian (Dutch: Oudnederfrankisch) is the set of Franconian dialects (i.e. dialects that evolved from Frankish) spoken in the Low Countries during the Early Middle Ages, from aroun ...
). The rest of Frisia
Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Ger ...
in the north (now Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
and Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
) continued to maintain its independence and had its own institutions (collectively called the "Frisian freedom
Frisian freedom ( fy, Fryske frijheid; ; ) was the absence of feudalism and serfdom in Frisia, the area that was originally inhabited by the Frisians. Historical Frisia included the modern provinces of Friesland and Groningen, and the area of We ...
"), which resented the imposition of the feudal system.
Around 1000 AD, due to several agricultural developments, the economy started to develop at a fast pace, and the higher productivity allowed workers to farm more land or become tradesmen. Towns grew around monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
and castles
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
, and a mercantile middle class began to develop in these urban areas, especially in Flanders and later also Brabant. Wealthy cities started to buy certain privileges for themselves from the sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
. In practice, this meant that Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
and Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, became quasi-independent republics in their own right and would later develop into some of the most important cities and ports in Europe.
Around 1100 AD, farmers from Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
and Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
began draining and cultivating uninhabited swampy land in the western Netherlands, making the emergence of the County of Holland as the centre of power possible. The title of Count of Holland
The counts of Holland ruled over the County of Holland in the Low Countries between the 10th and the 16th century.
House of Holland
The first count of Holland, Dirk I, was the son or foster-son of Gerolf, Count in Frisia (Dijkstra suggests th ...
was fought over in the Hook and Cod Wars
The Hook and Cod wars ( nl, Hoekse en Kabeljauwse twisten) comprise a series of wars and battles in the County of Holland between 1350 and 1490. Most of these wars were fought over the title of count of Holland, but some have argued that the u ...
( nl, Hoekse en Kabeljauwse twisten) between 1350 and 1490. The Cod faction consisted of the more progressive cities, while the Hook faction consisted of the conservative noblemen. These noblemen invited Duke Philip the Good
Philip III (french: Philippe le Bon; nl, Filips de Goede; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) was Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonge ...
of Burgundy — who was also Count of Flanders — to conquer Holland.
Burgundian, Habsburg and Spanish Habsburg Netherlands (1384–1581)
Most of the Imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, Texa ...
and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
fiefs in what is now the Netherlands and Belgium were united in a personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
, in 1433. The House of Valois-Burgundy
The House of Valois-Burgundy (french: Maison de Valois-Bourgogne, nl, Huis van Valois-Bourgondië), or the Younger House of Burgundy, was a noble French family deriving from the royal House of Valois. It is distinct from the Capetian House of Bur ...
and their Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
heirs would rule the Low Countries in the period from 1384 to 1581. Before the Burgundian union, the Dutch identified themselves by the town they lived in or their local duchy or county. The Burgundian period is when the road to nationhood began. The new rulers defended Dutch trading interests, which then developed rapidly. The fleets of the County of Holland
The County of Holland was a State of the Holy Roman Empire and from 1433 part of the Burgundian Netherlands, from 1482 part of the Habsburg Netherlands and from 1581 onward the leading province of the Dutch Republic, of which it remained a part ...
defeated the fleets of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
several times. Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
grew and in the 15th century became the primary trading port in Europe for grain from the Baltic region
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries (or simply the Baltic Rim), and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. ...
. Amsterdam distributed grain to the major cities of Belgium, Northern France and England. This trade was vital because Holland could no longer produce enough grain to feed itself. Land drainage had caused the peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
of the former wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
s to reduce to a level that was too low for drainage to be maintained.
Under Habsburg Charles V Charles V may refer to:
* Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (1500–1558)
* Charles V of Naples (1661–1700), better known as Charles II of Spain
* Charles V of France (1338–1380), called the Wise
* Charles V, Duke of Lorraine (1643–1690)
* Infan ...
, ruler of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
and King of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, all fiefs in the current Netherlands region were united into the Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (Fre ...
, which also included most of present-day Belgium, Luxembourg, and some adjacent land in what is now France and Germany. In 1568, under Phillip II, the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Refo ...
between the Provinces and their Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
ruler began. The level of ferocity exhibited by both sides can be gleaned from a Dutch chronicler's report:
On more than one occasion men were seen hanging their own brothers, who had been taken prisoners in the enemy's ranks... A Spaniard had ceased to be human in their eyes. On one occasion, a surgeon at Veer cut the heart from a Spanish prisoner, nailed it on a vessel's prow, and invited the townsmen to come and fasten their teeth in it, which many did with savage satisfaction.
The Duke of Alba
Duke of Alba de Tormes ( es, Duque de Alba de Tormes), commonly known as Duke of Alba, is a title of Spanish nobility that is accompanied by the dignity of Grandee of Spain. In 1472, the title of ''Count of Alba de Tormes'', inherited by G ...
ruthlessly attempted to suppress the Protestant movement in the Netherlands. Netherlanders were "burned, strangled, beheaded, or buried alive" by his " Blood Council" and his Spanish soldiers. Severed heads and decapitated corpses were displayed along streets and roads to terrorise the population into submission. Alba boasted of having executed 18,600, but this figure does not include those who perished by war and famine.
The first great siege was Alba's effort to capture Haarlem
Haarlem (; predecessor of ''Harlem'' in English) is a city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is the capital of the province of North Holland. Haarlem is situated at the northern edge of the Randstad, one of the most populated metropoli ...
and thereby cut Holland in half. It dragged on from December 1572 to the next summer, when Haarlemers finally surrendered on 13 July upon the promise that the city would be spared from being sacked. It was a stipulation Don Fadrique was unable to honour, when his soldiers mutinied, angered over pay owed and the miserable conditions they endured during the long, cold months of the campaign. On 4 November 1576, Spanish tercio
A ''tercio'' (; Spanish for " third") was a military unit of the Spanish Army during the reign of the Spanish Habsburgs in the early modern period. The tercios were renowned for the effectiveness of their battlefield formations, forming the el ...
s seized Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, and subjected it to the worst pillage in the Netherlands' history. The citizens resisted but were overcome; seven thousand of them were killed; a thousand buildings were torched; men, women, and children were slaughtered by soldiers, who invoked the name of Spain's patron saint, ''¡Santiago! ¡España! ¡A sangre, a carne, a fuego, a sacco!'' (Saint James! Spain! To blood, to the flesh, to fire, to sack!)
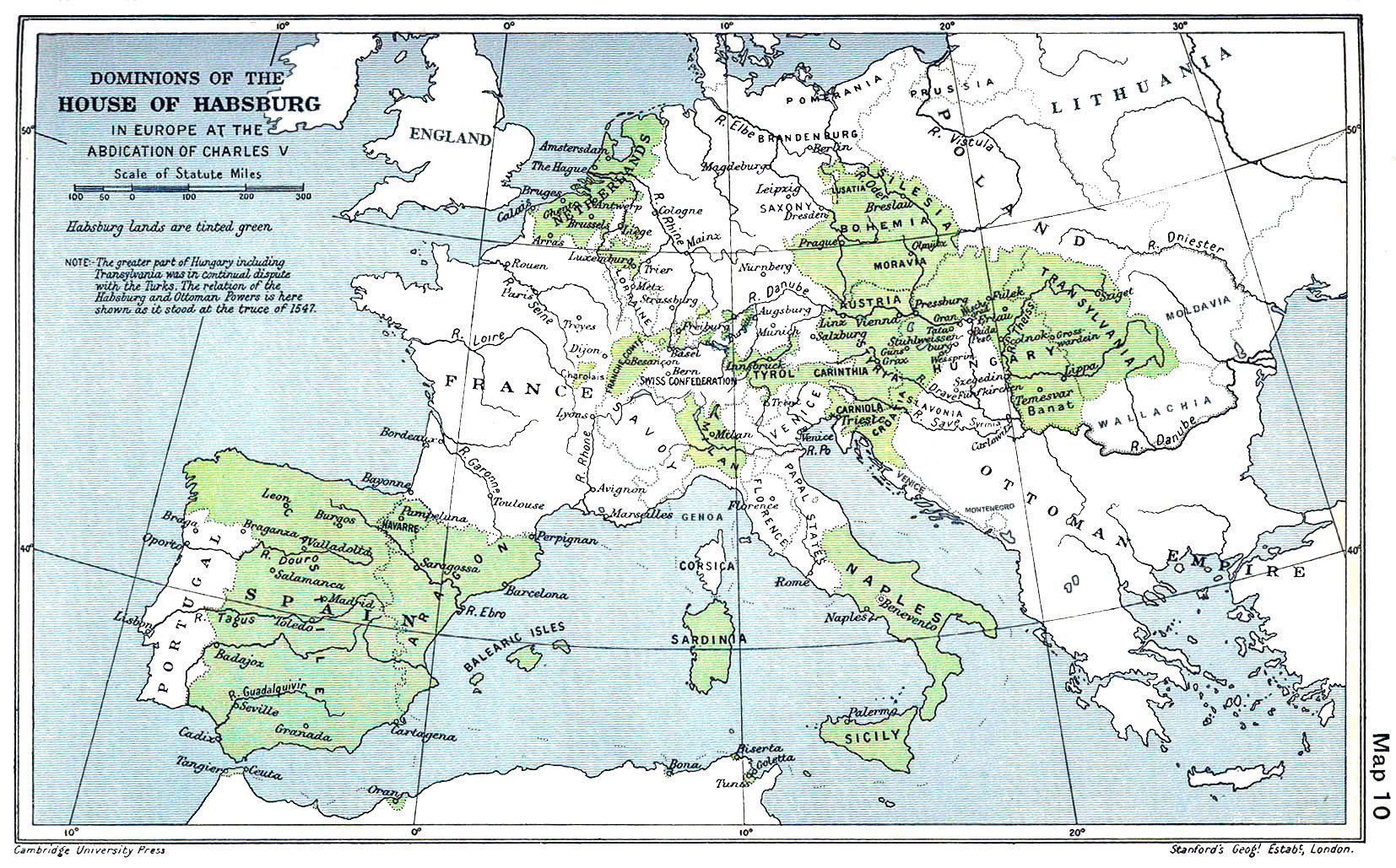
 Following the
Following the sack of Antwerp
The Sack of Antwerp, often known as the Spanish Fury at Antwerp, was an episode of the Eighty Years' War. It is the greatest massacre in the history of the Low Countries.
On 4 November 1576, mutinying Spain, Spanish tercios of the Army of Flande ...
, delegates from Catholic Brabant, Protestant Holland and Zeeland agreed, at Ghent, to join Utrecht and William the Silent in driving out all Spanish troops and forming a new government for the Netherlands. Don Juan of Austria, the new Spanish governor, was forced to concede initially, but within months returned to active hostilities. As the fighting restarted, the Dutch began to look for help from the Protestant Elizabeth I of England
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
, but she initially stood by her commitments to the Spanish in the Treaty of Bristol
The Convention of Nymegen (alt. spelling ''Nijmegen'' or ''Nymwegen'') was a treaty signed between England and Spain in 1573. The treaty pledged that the English government would cease support for raids on Spanish shipping in the West Indies and Ca ...
of 1574. The result was that when the next large-scale battle did occur at Gembloux
Gembloux (; wa, Djiblou; nl, Gembloers, ) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Namur, Belgium.
On 1 January 2006 the municipality had 21,964 inhabitants. The total area is 95.86 km², yielding a population dens ...
in 1578, the Spanish forces easily won the day, killing at least 10,000 rebels, with the Spanish suffering few losses. In light of the defeat at Gembloux, the southern states of the Seventeen Provinces (today in northern France and Belgium) distanced themselves from the rebels in the north with the 1579 Union of Arras
The Union of Arras (Dutch: ''Unie van Atrecht'', French: ''Union d'Arras'', Spanish: ''Unión de Arrás'') was an alliance between the County of Artois, the County of Hainaut and the city of Douai in the Habsburg Netherlands in early 1579 during ...
, which expressed their loyalty to Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
. Opposing them, the northern half of the Seventeen Provinces forged the Union of Utrecht
The Union of Utrecht ( nl, Unie van Utrecht) was a treaty signed on 23 January 1579 in Utrecht, Netherlands, unifying the northern provinces of the Netherlands, until then under the control of Habsburg Spain.
History
The Union of Utrecht is r ...
(also of 1579) in which they committed to support each other in their defence against the Spanish army. The Union of Utrecht is seen as the foundation of the modern Netherlands.
Spanish troops sacked Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
in 1579, killing over 10,000 civilians and thereby ensuring the rebellion continued. In 1581, the northern provinces adopted the Act of Abjuration
The Act of Abjuration ( nl, Plakkaat van Verlatinghe; es, Acta de Abjuración, lit=placard of abjuration) is the declaration of independence by many of the provinces of the Netherlands from the allegiance to Philip II of Spain, during the Dut ...
, the declaration of independence in which the provinces officially deposed Philip II as reigning monarch in the northern provinces. Against the rebels Philip could draw on the resources of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
, including in Iberia, Spanish America, Spanish Italy, and the Spanish Netherlands. Queen Elizabeth I of England sympathised with the Dutch struggle against England's Spanish rival and sent an army of 7,600 soldiers to aid the Dutch in their war with the Catholic Spanish. English forces under the Earl of Leicester and then Lord Willoughby faced the Spanish in the Netherlands under the Duke of Parma
The Duke of Parma and Piacenza () was the ruler of the Duchy of Parma and Piacenza, a historical state of Northern Italy, which existed between 1545 and 1802, and again from 1814 to 1859.
The Duke of Parma was also Duke of Piacenza, except ...
in a series of largely indecisive actions that tied down significant numbers of Spanish troops and bought time for the Dutch to reorganise their defences. The war continued until 1648, when Spain under King Philip IV Philip IV may refer to:
* Philip IV of Macedon (died 297 BC)
* Philip IV of France (1268–1314), Avignon Papacy
* Philip IV of Burgundy or Philip I of Castile (1478–1506)
* Philip IV, Count of Nassau-Weilburg (1542–1602)
* Philip IV of Spain ...
finally recognised the independence of the seven north-western provinces in the Peace of Münster
The Peace of Münster was a treaty between the Lords States General of the Seven United Netherlands and the Spanish Crown, the terms of which were agreed on 30 January 1648. The treaty, parallelly negotiated to but not part of the Peace of We ...
. Parts of the southern provinces became ''de facto'' colonies of the new republican-mercantile empire.
Dutch Republic (1581–1795)
 After declaring their independence, the provinces of
After declaring their independence, the provinces of Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
, Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
, Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
, Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
, Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
, Overijssel
Overijssel (, ; nds, Oaveriessel ; german: Oberyssel) is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the eastern part of the country. The province's name translates to "across the IJssel", from the perspective of the ...
, and Gelderland
Gelderland (), also known as Guelders () in English, is a province of the Netherlands, occupying the centre-east of the country. With a total area of of which is water, it is the largest province of the Netherlands by land area, and second by ...
formed a confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
. All these duchies, lordships and counties were autonomous and had their own government, the States-Provincial
The provincial council (, PS), also known as the States Provincial, is the provincial parliament and legislative assembly in each of the provinces of the Netherlands. It is elected for each province simultaneously once every four years and has ...
. The States General The word States-General, or Estates-General, may refer to:
Currently in use
* Estates-General on the Situation and Future of the French Language in Quebec, the name of a commission set up by the government of Quebec on June 29, 2000
* States Genera ...
, the confederal government, were seated in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
and consisted of representatives from each of the seven provinces. The sparsely populated region of Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nov ...
was part of the republic too, although it was not considered one of the provinces. Moreover, the Republic had come to occupy during the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Refo ...
a number of so-called Generality Lands
The Generality Lands, Lands of the Generality or Common Lands ( nl, Generaliteitslanden) were about one fifth of the territories of the United Provinces of the Netherlands, that were directly governed by the States-General. Unlike the seven pr ...
in Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, ...
, Brabant Brabant is a traditional geographical region (or regions) in the Low Countries of Europe. It may refer to:
Place names in Europe
* London-Brabant Massif, a geological structure stretching from England to northern Germany
Belgium
* Province of Bra ...
and Limburg
Limburg or Limbourg may refer to:
Regions
* Limburg (Belgium), a province since 1839 in the Flanders region of Belgium
* Limburg (Netherlands), a province since 1839 in the south of the Netherlands
* Diocese of Limburg, Roman Catholic Diocese in ...
. Their population was mainly Roman Catholic, and these areas did not have a governmental structure of their own and were used as a buffer zone between the Republic and the Spanish-controlled Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
.

 In the
In the Dutch Golden Age
The Dutch Golden Age ( nl, Gouden Eeuw ) was a period in the history of the Netherlands, roughly spanning the era from 1588 (the birth of the Dutch Republic) to 1672 (the Rampjaar, "Disaster Year"), in which Dutch trade, science, and Dutch art, ...
, spanning much of the 17th century, the Dutch Empire grew to become one of the major seafaring and economic powers, alongside Portugal, Spain, France and England. Science, military and art (especially painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ...
) were among the most acclaimed in the world. By 1650, the Dutch owned 16,000 merchant ships. The Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
and the Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company ( nl, Geoctrooieerde Westindische Compagnie, ''WIC'' or ''GWC''; ; en, Chartered West India Company) was a chartered company of Dutch merchants as well as foreign investors. Among its founders was Willem Usselincx ( ...
established colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
and trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to tr ...
s all over the world, including ruling the western parts of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
between 1624–1662 and 1664–1667. The Dutch settlement in North America began with the founding of New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
on the southern part of Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
in 1614. In South Africa, the Dutch settled the Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British Empire, British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when i ...
in 1652. Dutch colonies in South America were established along the many rivers in the fertile Guyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
plains, among them Colony of Surinam (now Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
). In Asia, the Dutch established the Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which ...
(now Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
), and the only western trading post in Japan, Dejima
, in the 17th century also called Tsukishima ( 築島, "built island"), was an artificial island off Nagasaki, Japan that served as a trading post for the Portuguese (1570–1639) and subsequently the Dutch (1641–1854). For 220 years, it ...
.
During the period of Proto-industrialisation
Proto-industrialization is the regional development, alongside commercial agriculture, of rural handicraft production for external markets.
The term was introduced in the early 1970s by economic historians who argued that such developments in par ...
, the empire received 50% of textiles and 80% of silks import from the India's Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, chiefly from its most developed region known as Bengal Subah
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Ben ...
.Om Prakash
Om Prakash (born Om Prakash Chibber 19 December 1919 – 21 February 1998) was an Indian film actor. He was born in Jammu as Om Prakash Chibber and went on to become a well-known character actor of Bollywood. His most well-known movies are Nam ...
,
Empire, Mughal
, ''History of World Trade Since 1450'', edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference USA, 2006, pp. 237–240, ''World History in Context''. Retrieved 3 August 2017capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, priva ...
country in the world. In early modern Europe, it had the wealthiest trading city (Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
) and the first full-time stock exchange
A stock exchange, securities exchange, or bourse is an exchange where stockbrokers and traders can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock, bonds and other financial instruments. Stock exchanges may also provide facilities for th ...
. The inventiveness of the traders led to insurance and retirement funds as well as phenomena such as the boom-bust cycle
Business cycles are intervals of expansion followed by recession in economic activity. These changes have implications for the welfare of the broad population as well as for private institutions. Typically business cycles are measured by examini ...
, the world's first asset-inflation bubble, the tulip mania
Tulip mania ( nl, tulpenmanie) was a period during the Dutch Golden Age when contract prices for some bulbs of the recently introduced and fashionable tulip reached extraordinarily high levels. The major acceleration started in 1634 and then ...
of 1636–1637, and the world's first bear raid
A bear raid is a type of stock market strategy, where a trader (or group of traders) attempts to force down the price of a stock to cover a short position. The name is derived from the common use of
''bear'' or ''bearish'' in the language of mar ...
er, Isaac le Maire, who forced prices down by dumping stock and then buying it back at a discount. In 1672 – known in Dutch history as the Rampjaar
In Dutch history, the year 1672 is referred to as the nl, Rampjaar, label=none (Disaster Year). In May 1672, following the outbreak of the Franco-Dutch War and its peripheral conflict the Third Anglo-Dutch War, France, supported by Münster an ...
(Disaster Year) – the Dutch Republic was at war with France, England and three German Bishoprics simultaneously. At sea, it could successfully prevent the English and French navies from entering the western shores. On land, however, it was almost taken over internally by the advancing French and German armies coming from the east. It managed to turn the tide by inundating parts of Holland but could never recover to its former glory again and went into a state of a general decline in the 18th century, with economic competition from England and long-standing rivalries between the two main factions in Dutch society, the republican ''Staatsgezinden'' and the supporters of the stadtholder
In the Low Countries, ''stadtholder'' ( nl, stadhouder ) was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and H ...
the ''Prinsgezinden'' as main political faction
A political faction is a group of individuals that share a common political purpose but differs in some respect to the rest of the entity. A faction within a group or political party may include fragmented sub-factions, "parties within a party," ...
s.
Batavian Republic and Kingdom (1795–1890)
With the armed support of revolutionary France
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, Dutch republicans
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
proclaimed the Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic ( nl, Bataafse Republiek; french: République Batave) was the successor state to the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 and ended on 5 June 1806, with the accession of Louis Bona ...
, modelled after the French Republic
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and rendering the Netherlands a unitary state
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only th ...
on 19 January 1795. The stadtholder
In the Low Countries, ''stadtholder'' ( nl, stadhouder ) was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and H ...
William V of Orange
William V (Willem Batavus; 8 March 1748 – 9 April 1806) was a prince of Orange and the last stadtholder of the Dutch Republic. He went into exile to London in 1795. He was furthermore ruler of the Principality of Orange-Nassau until his death in ...
had fled to England. But from 1806 to 1810, the Kingdom of Holland
The Kingdom of Holland ( nl, Holland (contemporary), (modern); french: Royaume de Hollande) was created by Napoleon Bonaparte, overthrowing the Batavian Republic in March 1806 in order to better control the Netherlands. Since becoming Emperor ...
was set up by Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
as a puppet kingdom governed by his brother Louis Bonaparte
Louis Napoléon Bonaparte (born Luigi Buonaparte; 2 September 1778 – 25 July 1846) was a younger brother of Napoleon I, Emperor of the French. He was a monarch in his own right from 1806 to 1810, ruling over the Kingdom of Holland (a French cl ...
to control the Netherlands more effectively. However, King Louis Bonaparte tried to serve Dutch interests instead of his brother's, and he was forced to abdicate on 1 July 1810. The Emperor sent in an army and the Netherlands became part of the French Empire until the autumn of 1813 when Napoleon was defeated in the Battle of Leipzig
The Battle of Leipzig (french: Bataille de Leipsick; german: Völkerschlacht bei Leipzig, ); sv, Slaget vid Leipzig), also known as the Battle of the Nations (french: Bataille des Nations; russian: Битва народов, translit=Bitva ...
.
 William Frederick, son of the last stadtholder, returned to the Netherlands in 1813 and proclaimed himself Sovereign Prince of the Netherlands. Two years later, the
William Frederick, son of the last stadtholder, returned to the Netherlands in 1813 and proclaimed himself Sovereign Prince of the Netherlands. Two years later, the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
added the southern Netherlands to the north to create a strong country on the northern border of France. William Frederick raised this United Netherlands to the status of a kingdom and proclaimed himself as King William I in 1815. In addition, William became hereditary Grand Duke of Luxembourg
The Grand Duke of Luxembourg ( lb, Groussherzog vu Lëtzebuerg, french: Grand-duc de Luxembourg, german: Großherzog von Luxemburg) is the monarchical head of state of Luxembourg. Luxembourg has been a grand duchy since 15 March 1815, when it w ...
in exchange for his German possessions. However, the Southern Netherlands had been culturally separate from the north since 1581, and rebelled
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
. The south gained independence in 1830 as Belgium (recognised by the Northern Netherlands in 1839 as the Kingdom of the Netherlands was created by decree), while the personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
between Luxembourg and the Netherlands was severed in 1890, when William III William III or William the Third may refer to:
Kings
* William III of Sicily (c. 1186–c. 1198)
* William III of England and Ireland or William III of Orange or William II of Scotland (1650–1702)
* William III of the Netherlands and Luxembourg ...
died with no surviving male heirs. Ascendancy laws prevented his daughter Queen Wilhelmina
Wilhelmina (; Wilhelmina Helena Pauline Maria; 31 August 1880 – 28 November 1962) was Queen of the Netherlands
The monarchy of the Netherlands is a constitutional monarchy. As such, the role and position of the monarch are governed by the ...
from becoming the next Grand Duchess.
The Belgian Revolution at home and the Java War
The Java War ( jv, ꦥꦼꦫꦁꦗꦮ) or Diponegoro War () was fought in central Java from 1825 to 1830, between the colonial Dutch Empire and native Javanese rebels. The war started as a rebellion led by Prince Diponegoro, a leading member ...
in the Dutch East Indies brought the Netherlands to the brink of bankruptcy. However, the Cultivation System
The Cultivation System ( nl, cultuurstelsel) was a Dutch government policy from 1830–1870 for its Dutch East Indies colony (now Indonesia). Requiring a portion of agricultural production to be devoted to export crops, it is referred to by Indon ...
was introduced in 1830; in the Dutch East Indies, 20% of village land had to be devoted to government crops for export. The policy brought the Dutch enormous wealth and made the colony self-sufficient.
The Netherlands abolished slavery in its colonies in 1863. Enslaved people in Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
would be fully free only in 1873, since the law stipulated that there was to be a mandatory 10-year transition.
World wars and beyond (1890–present)
 The Netherlands was able to remain neutral during
The Netherlands was able to remain neutral during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, in part because the import of goods through the Netherlands proved essential to German survival until the blockade by the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
in 1916.[Abbenhuis, Maartje M. (2006]
The Art of Staying Neutral
Amsterdam University Press, . That changed in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, when Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
invaded the Netherlands on 10 May 1940. The Rotterdam Blitz
Rotterdam was subjected to heavy aerial bombardment by the ''Luftwaffe'' during the German invasion of the Netherlands in World War II. The objective was to support the German troops fighting in the city, break Dutch resistance and force the Du ...
forced the main element of the Dutch army to surrender four days later. During the occupation, over 100,000 Dutch Jews
The history of the Jews in the Netherlands began largely in the 16th century when they began to settle in Amsterdam and other cities. It has continued to the present. During the occupation of the Netherlands by Nazi Germany in May 1940, the ...
were rounded up and transported to Nazi extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
s; only a few of them survived. Dutch workers were conscripted for forced labour in Germany, civilians who resisted were killed in reprisal for attacks on German soldiers, and the countryside was plundered for food. Although there were thousands of Dutch who risked their lives by hiding Jews from the Germans, over 20,000 Dutch fascists joined the Waffen SS, fighting on the Eastern Front. Political collaborators were members of the fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
NSB, the only legal political party in the occupied Netherlands. On 8 December 1941, the Dutch government-in-exile
The Dutch government-in-exile ( nl, Nederlandse regering in ballingschap), also known as the London Cabinet ( nl, Londens kabinet), was the government in exile of the Netherlands, supervised by Queen Wilhelmina, that fled to London after the Germ ...
in London declared war on Japan, but could not prevent the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies (Indonesia). In 1944–45, the First Canadian Army
The First Canadian Army (french: 1reArmée canadienne) was a field army and a formation of the Canadian Army in World War II in which most Canadian elements serving in North-West Europe were assigned. It served on the Western Front from July 1944 ...
, which included Canadian, British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
troops, was responsible for liberating much of the Netherlands. Soon after VE Day
Victory in Europe Day is the day celebrating the formal acceptance by the Allies of World War II of Germany's unconditional surrender of its armed forces on Tuesday, 8 May 1945, marking the official end of World War II in Europe in the Easter ...
, the Dutch fought a colonial war against the new Republic of Indonesia.
 In 1954, the
In 1954, the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands
The Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands (in Dutch: ''Statuut voor het Koninkrijk der Nederlanden''; in Papiamentu: ''Statuut di Reino Hulandes'') is a legal instrument that sets out the political relationship between the four countries tha ...
reformed the political structure of the Netherlands, which was a result of international pressure to carry out decolonisation
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on separatism, in ...
. The Dutch colonies of Surinam and Curaçao and Dependencies
The Colony of Curaçao and Dependencies ( nl, Kolonie Curaçao en onderhorigheden; pap, Kolonia di Kòrsou i dependensianan) was a Dutch colony in the Caribbean Sea from 1815 until 1828 and from 1845 until 1954. Between 1936 and 1948, the area wa ...
and the European country all became countries within the Kingdom, on a basis of equality. Indonesia had declared its independence in August 1945 (recognised in 1949), and thus was never part of the reformed Kingdom. Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
followed in 1975. After the war, the Netherlands left behind an era of neutrality and gained closer ties with neighbouring states. The Netherlands was one of the founding members of Benelux
The Benelux Union ( nl, Benelux Unie; french: Union Benelux; lb, Benelux-Unioun), also known as simply Benelux, is a politico-economic union and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighboring states in western Europe: B ...
and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
. In the 1950's, the Netherlands became one of the six founding countries of the European Communities
The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom), and the ...
, following the 1952 establishment of the European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was a European organization created after World War II to regulate the coal and steel industries. It was formally established in 1951 by the Treaty of Paris, signed by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembo ...
, and subsequent 1958 creations of the European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
and European Atomic Energy Community
The European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom) is an international organisation established by the Euratom Treaty on 25 March 1957 with the original purpose of creating a specialist market for nuclear power in Europe, by developing nucl ...
.European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
.population density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopul ...
prompted some 500,000 Dutch people
The Dutch (Dutch: ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Netherlands. They share a common history and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Arub ...
to leave the country after the war. The 1960s and 1970s were a time of great social and cultural change, such as rapid de-pillarisation
Pillarisation (from the nl, verzuiling) is the politico-denominational segregation of a society into groups by religion and associated political beliefs. These societies were (and in some areas, still are) vertically divided into two or more gr ...
characterised by the decay of the old divisions along political and religious lines. Students and other youth rejected traditional mores and pushed for change in matters such as women's rights
Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, ...
, sexuality
Human sexuality is the way people experience and express themselves sexually. This involves biological, psychological, physical, erotic, emotional, social, or spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied ...
, disarmament
Disarmament is the act of reducing, limiting, or abolishing weapons. Disarmament generally refers to a country's military or specific type of weaponry. Disarmament is often taken to mean total elimination of weapons of mass destruction, such as n ...
and environmental issues
Environmental issues are effects of human activity on the biophysical environment, most often of which are harmful effects that cause environmental degradation. Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment on t ...
. In 2002 the euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
was introduced as fiat money
Fiat money (from la, fiat, "let it be done") is a type of currency that is not backed by any commodity such as gold or silver. It is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tender. Throughout history, fiat money was sometime ...
, and in 2010 the Netherlands Antilles
nl, In vrijheid verenigd"Unified by freedom"
, national_anthem =
, common_languages = Dutch English Papiamento
, demonym = Netherlands Antillean
, capital = Willemstad
, year_start = 1954
, year_end = 2010
, date_start = 15 December
, ...
was dissolved. Referendums were held on each island to determine their future status. As a result, the islands of Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC i ...
, Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius (, ), also known locally as Statia (), is an island in the Caribbean. It is a special municipality (officially " public body") of the Netherlands.
The island lies in the northern Leeward Islands portion of the West Indies, so ...
and Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), L ...
(the BES islands) were to obtain closer ties with the Netherlands. This led to the incorporation of these three islands into the country of the Netherlands as '' special municipalities'' upon the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles. The special municipalities are collectively known as the Caribbean Netherlands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographics ...
.
In recent times, much of the Netherlands has seen a reclamation of land
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamat ...
from what were once waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary b ...
s.
Geography
 According to the Central Bureau of Statistics, the European Netherlands has a total area of , including water bodies; and a land area of . The
According to the Central Bureau of Statistics, the European Netherlands has a total area of , including water bodies; and a land area of . The Caribbean Netherlands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographics ...
has a total area of It lies between latitudes
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
50° and 54° N, and longitudes 3° and 8° E.
The Netherlands is geographically very low relative to sea level and is considered a flat country, with about 26% of its areaabove sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. The European part of the country is for the most part flat, with the exception of foothills in the far southeast, up to a height of no more than 321 metres, and some low hill ranges in the central parts. Most of the areas below sea level are caused by peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
extraction or achieved through land reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamati ...
. Since the late 16th century, large polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are:
# Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed
# Flood plains s ...
areas are preserved through elaborate drainage systems that include dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes, ...
, canals and pumping stations. Nearly 17% of the country's land area is reclaimed from the sea and from lakes.
Much of the country was originally formed by the estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
of three large European rivers: the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
(''Rijn''), the Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
(''Maas'') and the Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corr ...
(''Schelde''), as well as their tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage b ...
. The south-western part of the Netherlands is to this day a river delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition (geology), deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, res ...
of these three rivers, the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt delta.
The European Netherlands is divided into north and south parts by the Rhine, the Waal
WAAL (99.1 FM "The Whale") is a commercial radio station licensed to Binghamton, New York. It airs a classic rock radio format and is owned by Townsquare Media. WAAL is the oldest FM radio station in the Binghamton metropolitan area. It is an ...
, its main tributary branch, and the Meuse. In the past, these rivers functioned as a natural barrier between fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an Lord, overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a for ...
doms and hence historically created a cultural divide, as is evident in some phonetic traits that are recognisable on either side of what the Dutch call their "Great Rivers" (''de Grote Rivieren''). Another significant branch of the Rhine, the IJssel
The IJssel (; nds-nl, Iessel(t) ) is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer (before the 1932 completion of the Afsluitdijk known as the Zuiderzee), a North Sea natural harbour ...
river, discharges into Lake IJssel
The IJsselmeer (; fy, Iselmar, nds-nl, Iesselmeer), also known as Lake IJssel in English, is a closed off inland bay in the central Netherlands bordering the Provinces of the Netherlands, provinces of Flevoland, North Holland and Friesland. It ...
, the former Zuiderzee
The Zuiderzee or Zuider Zee (; old spelling ''Zuyderzee'' or ''Zuyder Zee'') was a shallow bay of the North Sea in the northwest of the Netherlands, extending about 100 km (60 miles) inland and at most 50 km (30 miles) wide, with an o ...
('southern sea'). Just like the previous, this river forms a linguistic divide: people to the northeast of this river speak Dutch Low Saxon
Dutch Low Saxon ( or ''Nederlaands Nedersaksies''; nl, Nederlands Nedersaksisch) are the Low Saxon dialects of the Low German language that are spoken in the northeastern Netherlands and are written there with local, unstandardised orthographi ...
dialects (except for the province of Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
, which has its own language).[Welschen, Ad: Course ''Dutch Society and Culture'', International School for Humanities and Social Studies ISHSS, Universiteit van Amsterdam, 2000–2005.]
Geology
The modern Netherlands formed as a result of the interplay of the four main rivers (Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
, Schelde
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to ...
and IJssel
The IJssel (; nds-nl, Iessel(t) ) is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer (before the 1932 completion of the Afsluitdijk known as the Zuiderzee), a North Sea natural harbour ...
) and the influence of the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
. The Netherlands is mostly composed of deltaic
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or (more rare ...
, coast
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in n ...
al and eolian derived sediments during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
glacial
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
and interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene in ...
periods.
Almost the entire west Netherlands is composed of the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
-Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
river estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
, but human intervention greatly modified the natural processes at work. Most of the western Netherlands is below sea level due to the human process of turning standing bodies of water into usable land, a polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are:
# Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed
# Flood plains s ...
.
In the east of the Netherlands, remains are found of the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
, which ended approximately ten thousand years ago. As the continental ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Las ...
moved in from the north, it pushed moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
forward. The ice sheet halted as it covered the eastern half of the Netherlands. After the ice age ended, the moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
remained in the form of a long hill-line. The cities of Arnhem
Arnhem ( or ; german: Arnheim; South Guelderish: ''Èrnem'') is a city and municipality situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands about 55 km south east of Utrecht. It is the capital of the province of Gelderland, located on both banks of ...
and Nijmegen
Nijmegen (;; Spanish and it, Nimega. Nijmeegs: ''Nimwèège'' ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and tenth largest of the Netherlands as a whole, located on the Waal river close to the German border. It is about 6 ...
are built upon these hills.
Floods
 Over the centuries, the Dutch coastline has changed considerably as a result of natural disasters and human intervention.
On 14 December 1287,
Over the centuries, the Dutch coastline has changed considerably as a result of natural disasters and human intervention.
On 14 December 1287, St. Lucia's flood
North Holland, 1st-10th century
St. Lucia's flood (Sint-Luciavloed) was a storm tide that affected the Netherlands and Northern Germany on 13/14 December 1287 ( OS), St. Lucia Day and the day after, killing approximately 50,000 to 80,000 peo ...
affected the Netherlands and Germany, killing more than 50,000 people in one of the most destructive floods in recorded history. The St. Elizabeth flood
The St. Elizabeth's flood of 1421 was a flooding of the Grote Hollandse Waard, an area in what is now the Netherlands. It takes its name from the feast day of Saint Elisabeth of Hungary which was formerly 19 November.
It ranks 20th on the list of ...
of 1421 and the mismanagement in its aftermath destroyed a newly reclaimed polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are:
# Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed
# Flood plains s ...
, replacing it with the ''Biesbosch
De Biesbosch National Park is one of the largest national parks of the Netherlands and one of the last extensive areas of freshwater tidal wetlands in Northwestern Europe. The Biesbosch ('forest of sedges' or 'rushwoods') consists of a large n ...
'' tidal floodplains in the south-centre. The huge North Sea flood of early February 1953 caused the collapse of several dikes in the south-west of the Netherlands; more than 1,800 people drowned in the flood. The Dutch government subsequently instituted a large-scale programme, the "Delta Works
The Delta Works ( nl, Deltawerken) is a series of construction projects in the southwest of the Netherlands to protect a large area of land around the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta from the sea. Constructed between 1954 and 1997, the works con ...
", to protect the country against future flooding, which was completed over a period of more than thirty years.
 The impact of disasters was, to an extent, increased through human activity. Relatively high-lying
The impact of disasters was, to an extent, increased through human activity. Relatively high-lying swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
land was drained to be used as farmland. The drainage caused the fertile peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
to contract and ground levels to drop, upon which groundwater levels were lowered to compensate for the drop in ground level, causing the underlying peat to contract further. Additionally, until the 19th-century peat was mined, dried, and used for fuel, further exacerbating the problem. Centuries of extensive and poorly controlled peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
extraction lowered an already low land surface by several metres. Even in flooded areas, peat extraction continued through turf dredging.
Because of the flooding, farming was difficult, which encouraged foreign trade, the result of which was that the Dutch were involved in world affairs since the early 14th/15th century.
 To guard against floods, a series of defences against the water were contrived. In the first millennium AD, villages and farmhouses were built on hills called ''
To guard against floods, a series of defences against the water were contrived. In the first millennium AD, villages and farmhouses were built on hills called ''terp
A ''terp'', also known as a ''wierde, woerd, warf, warft, werf, werve, wurt'' or ''værft'', is an artificial dwelling mound found on the North European Plain that has been created to provide safe ground during storm surges, high tides an ...
s''. Later, these terps were connected by dikes. In the 12th century, local government agencies called ''"waterschappen
In the Netherlands, a water board, water council or water authority ( nl, waterschap or heemraadschap) is a regional governing body solely charged with the management of surface water in the environment. Water boards are independent of administr ...
"'' ("water boards") or ''" hoogheemraadschappen"'' ("high home councils") started to appear, whose job it was to maintain the water level and to protect a region from floods; these agencies continue to exist. As the ground level dropped, the dikes by necessity grew and merged into an integrated system. By the 13th century windmill
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called windmill sail, sails or blades, specifically to mill (grinding), mill grain (gristmills), but the term is also extended to windpumps, wind turbines, and ...
s had come into use to pump water out of areas below sea level. The windmills were later used to drain lakes, creating the famous polder
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are:
# Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed
# Flood plains s ...
s.
In 1932 the ''Afsluitdijk'' ("Closure Dike") was completed, blocking the former ''Zuiderzee
The Zuiderzee or Zuider Zee (; old spelling ''Zuyderzee'' or ''Zuyder Zee'') was a shallow bay of the North Sea in the northwest of the Netherlands, extending about 100 km (60 miles) inland and at most 50 km (30 miles) wide, with an o ...
'' (Southern Sea) from the North Sea and thus creating the IJsselmeer (IJssel
The IJssel (; nds-nl, Iessel(t) ) is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer (before the 1932 completion of the Afsluitdijk known as the Zuiderzee), a North Sea natural harbour ...
Lake). It became part of the larger Zuiderzee Works in which four polders totalling were reclaimed from the sea.
The Netherlands is one of the countries that may suffer most from climate change. Not only is the rising sea a problem, but erratic weather patterns may cause the rivers to overflow.
Delta Works
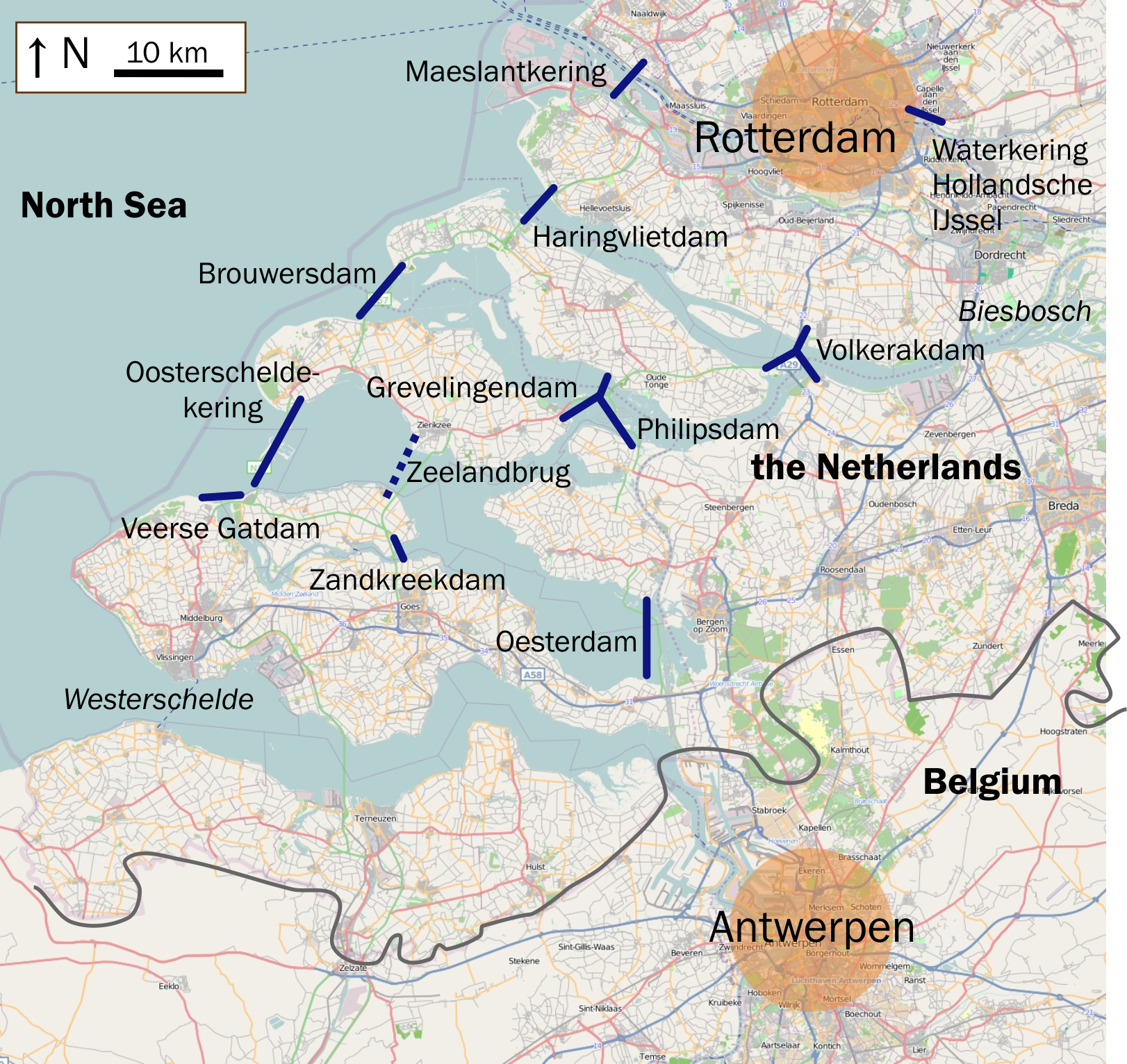 After the North Sea Flood of 1953, 1953 disaster, the Delta Works was constructed, which is a comprehensive set of civil works throughout the Dutch coast. The project started in 1958 and was largely completed in 1997 with the completion of the Maeslantkering. Since then, new projects have been periodically started to renovate and renew the Delta Works. The main goal of the Delta project was to reduce the risk of flooding in South Holland and Zeeland to once per 10,000 years (compared to once per 4000 years for the rest of the country). This was achieved by raising of outer sea-dikes and of the inner, canal, and river dikes, and by closing off the sea
After the North Sea Flood of 1953, 1953 disaster, the Delta Works was constructed, which is a comprehensive set of civil works throughout the Dutch coast. The project started in 1958 and was largely completed in 1997 with the completion of the Maeslantkering. Since then, new projects have been periodically started to renovate and renew the Delta Works. The main goal of the Delta project was to reduce the risk of flooding in South Holland and Zeeland to once per 10,000 years (compared to once per 4000 years for the rest of the country). This was achieved by raising of outer sea-dikes and of the inner, canal, and river dikes, and by closing off the sea estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
of the Zeeland province. New risk assessments occasionally show problems requiring additional Delta project dike reinforcements. The Delta project is considered by the American Society of Civil Engineers as one of the Wonders of the World#American Society of Civil Engineers, seven wonders of the modern world.
It is anticipated that global warming in the 21st century will result in a rise in sea level. The Netherlands is actively preparing for a sea-level rise. A politically neutral Delta Commission has formulated an action plan to cope with a sea-level rise of and a simultaneous land height decline of . The plan encompasses the reinforcement of the existing coastal defences like Levee, dikes and dunes with of additional flood protection. Climate change will not only threaten the Netherlands from the seaside but could also alter rainfall patterns and river run-off. To protect the country from river flooding, another programme is already being executed. The Room for the River (Netherlands), Room for the River plan grants more flow space to rivers, protects the major populated areas and allows for periodic flooding of indefensible lands. The few residents who lived in these so-called "overflow areas" have been moved to higher ground, with some of that ground having been raised above anticipated flood levels.
Climate change
Nature
The Netherlands has 20 national parks and hundreds of other nature reserves, that include lakes, heathland, Woodland, woods, dunes, and other habitats. Most of these are owned by Staatsbosbeheer, the national department for forestry and Habitat conservation, nature conservation and Vereniging Natuurmonumenten, Natuurmonumenten (literally 'Natures monuments'), a private organisation that buys, protects and manages nature reserves. The Dutch part of the Wadden Sea in the north, with its tidal flats and wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
s, is rich in biodiversity, biological diversity, and was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site, World Heritage Nature Site in 2009.
 The Oosterschelde, formerly the northeast
The Oosterschelde, formerly the northeast estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
of the river Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of Netherlands, the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corr ...
was designated a national park in 2002, thereby making it the largest national park in the Netherlands at an area of . It consists primarily of the salt waters of the Oosterschelde but also includes mudflats, meadows, and shoals. Because of the large variety of sea life, including unique regional species, the park is popular with Scuba diving, Scuba divers. Other activities include sailing, fishing, cycling, and bird watching.
Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, the European Netherlands is shared between the Atlantic European and Central European provinces of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, the European territory of the Netherlands belongs to the ecoregion of Atlantic mixed forests.
Caribbean islands
In the Lesser Antilles islands of the Caribbean, the territories of Curaçao, Aruba and Sint Maarten have a constituent country status within the wider Kingdom of the Netherlands. Another three territories which make up the Caribbean Netherlands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographics ...
are designated as special municipalities of the Netherlands. The Caribbean Netherlands have maritime borders with Anguilla, Curaçao, France (Saint Barthélemy), Saint Kitts and Nevis, Sint Maarten, the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands and Venezuela. Within this island group:
*
Within this island group:
* Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC i ...
is part of the ABC islands (Lesser Antilles), ABC islands within the Leeward Antilles island chain off the Venezuelan coast. The Leeward Antilles have a mixed volcanic and coral origin.
* Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), L ...
and Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius (, ), also known locally as Statia (), is an island in the Caribbean. It is a special municipality (officially " public body") of the Netherlands.
The island lies in the northern Leeward Islands portion of the West Indies, so ...
are part of the SSS islands. They are located east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands. Although in the English language they are considered part of the Leeward Islands, French, Spanish, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
and the English spoken locally consider them part of the Windward Islands. The Windward Islands are all of volcanic origin and hilly, leaving little ground suitable for agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
. The highest point is Mount Scenery
Mount Scenery is an active volcano in the Caribbean Netherlands. Its lava dome forms the summit of the Saba island stratovolcano. At an elevation of , it is the highest point in both the Kingdom of the Netherlands, and, since the dissolution of th ...
, , on Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), L ...
. This is the highest point in the country and is also the highest point of the entire Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
.
The islands of the Caribbean Netherlands enjoy a tropical climate with warm weather all year round. The Leeward Antilles are warmer and drier than the Windward islands. In summer, the Windward Islands can be subject to hurricanes.
Government and politics
 The Netherlands has been a
The Netherlands has been a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
since 1815, and due to the efforts of Johan Rudolph ThorbeckeMark Rutte
Mark Rutte (; born 14 February 1967) is a Dutch politician who has served as Prime Minister of the Netherlands since 2010 and Leader of the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) since 2006.
After a business career working for Unilever ...
has been Prime Minister since October 2010; the Prime Minister had been the leader of the largest party of the governing coalition continuously since 1973.
The cabinet is Ministerial responsibility, responsible to the Bicameralism, bicameral parliament, the States General The word States-General, or Estates-General, may refer to:
Currently in use
* Estates-General on the Situation and Future of the French Language in Quebec, the name of a commission set up by the government of Quebec on June 29, 2000
* States Genera ...
, which also has Legislative, legislative powers. The 150 members of the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
, the lower house, are elected in direct elections on the basis of party-list proportional representation. These are held every four years, or sooner in case the cabinet falls (for example: when one of the chambers carries a motion of no confidence, the cabinet offers its resignation to the monarch). The provincial assemblies, the States-Provincial
The provincial council (, PS), also known as the States Provincial, is the provincial parliament and legislative assembly in each of the provinces of the Netherlands. It is elected for each province simultaneously once every four years and has ...
, are directly elected every four years as well. The members of the provincial assemblies elect the 75 members of the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, the upper house, which has the power to reject laws, but not propose or amend them. Both houses send members to the Benelux Parliament, a consultative council.
Political culture
Both trade unions and employers organisations are consulted beforehand in policymaking in the financial, economic and social areas. They meet regularly with the government in the Social-Economic Council. This body advises government and its advice cannot be put aside easily.
The Netherlands has a tradition of social tolerance
Toleration is the allowing, permitting, or acceptance of an action, idea, object, or person which one dislikes or disagrees with. Political scientist Andrew R. Murphy explains that "We can improve our understanding by defining "toleration" as ...
. In the 18th century, while the Dutch Reformed Church was the state religion, Roman Catholicism in the Netherlands, Catholicism, other forms of Protestantism, such as Baptists and Lutherans, as well as History of the Jews in the Netherlands, Judaism were tolerated but discriminated against.
In the late 19th century this Dutch tradition of religious tolerance transformed into a system of pillarisation
Pillarisation (from the nl, verzuiling) is the politico-denominational segregation of a society into groups by religion and associated political beliefs. These societies were (and in some areas, still are) vertically divided into two or more gr ...
, in which religious groups coexisted separately and only interacted at the level of government. This tradition of tolerance influences Dutch criminal justice system of the Netherlands, criminal justice policies on Drug policy of the Netherlands, recreational drugs, prostitution
Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in Sex work, sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, n ...
, LGBT rights in the Netherlands, LGBT rights, euthanasia, and abortion in the Netherlands, abortion, which are among the most liberal in the world.
Political parties
No single party has held a majority in parliament since the 19th century, and as a result, coalition government, coalition cabinets had to be formed. Since suffrage became universal Pacification of 1917, in 1917, the Dutch political system has been dominated by three families of political parties: Christian democracy, Christian Democrats (currently the Christian Democratic Appeal, CDA), Social democracy, Social Democrats (currently the Labour Party (Netherlands), PvdA), and Liberalism in the Netherlands, Liberals (currently the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy, VVD).
These parties co-operated in coalition cabinets in which the Christian Democrats had always been a partner: so either a centre-left coalition of the Christian Democrats and Social Democrats was ruling or a centre-right coalition of Christian Democrats and Liberals. In the 1970s, the party system became more volatile: the Christian Democratic parties lost seats, while new parties became successful, such as the Radicalism (historical), radical democrat and Progressivism, progressive liberal Democrats 66 (D66) or the Ecology, ecologist party GroenLinks (GL).
In the Dutch general election, 1994, 1994 election, the CDA lost its dominant position. A "Purple (government), purple" cabinet was formed by the VVD, D66, and PvdA. In the Dutch general election, 2002, 2002 elections, this cabinet lost its majority, because of an increased support for the CDA and the rise of the right-wing Lijst Pim Fortuyn, LPF, a new political party, around Pim Fortuyn, who was assassinated a week before the elections. A short-lived First Balkenende cabinet, cabinet was formed by CDA, VVD, and LPF, which was led by the CDA Leader Jan Peter Balkenende. After the Dutch general election, 2003, 2003 elections, in which the LPF lost most of its seats, a Balkenende II, cabinet was formed by the CDA, VVD, and D66. The cabinet initiated an ambitious programme of reforming the welfare state, the Healthcare in the Netherlands, healthcare system, and Border control#Immigration law and policy, immigration policy.
In June 2006, the cabinet fell after D66 voted in favour of a motion of no confidence against the Ministry of Justice and Security (Netherlands), Minister of Immigration and Integration, Rita Verdonk, who had instigated an investigation of the asylum procedure of Ayaan Hirsi Ali, a VVD Member of parliament, MP. A Third Balkenende cabinet, caretaker cabinet was formed by the CDA and VVD, and Dutch general election, 2006, general elections were held on 22 November 2006. In these elections, the CDA remained the largest party and the Socialist Party (Netherlands), Socialist Party made the largest gains. The 2006–07 Dutch cabinet formation, formation of a new cabinet took three months, resulting in a Netherlands cabinet Balkenende-4, coalition of CDA, PvdA, and Christian Union (Netherlands), Christian Union.
On 20 February 2010, the cabinet fell when the PvdA refused to prolong the involvement of the Dutch Army in Uruzgan, Afghanistan. Snap elections were held on Dutch general election, 2010, 9 June 2010, with devastating results for the previously largest party, the CDA, which lost about half of its seats, resulting in 21 seats. The VVD became the largest party with 31 seats, closely followed by the PvdA with 30 seats. The big winner of the 2010 elections was Geert Wilders, whose right wing Party for Freedom, PVV, the ideological successor to the Pim Fortuyn List, LPF, more than doubled its number of seats. 2010 Dutch cabinet formation, Negotiation talks for a new government resulted in a minority government, led by VVD (a first) in coalition with CDA, which was sworn in on 14 October 2010. This unprecedented minority government was supported by PVV, but proved ultimately to be unstable, when on 21 April 2012, Wilders, leader of PVV, unexpectedly 'torpedoed seven weeks of austerity talks' on new austerity measures, paving the way for early elections.
VVD and PvdA won a majority in the House of Representatives during the Dutch general election, 2012, 2012 general election. On 5 November 2012 they formed the second Rutte cabinet. After the Dutch general election, 2017, 2017 general election, VVD, Christian Democratic Appeal, Democrats 66 and ChristenUnie formed the third Rutte cabinet. This cabinet resigned in January 2021, two months before the general election, after a Netherlands child welfare fraud scandal, child welfare fraud scandal. In March 2021, centre-right VVD of Prime Minister Mark Rutte
Mark Rutte (; born 14 February 1967) is a Dutch politician who has served as Prime Minister of the Netherlands since 2010 and Leader of the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) since 2006.
After a business career working for Unilever ...
was the winner of the 2021 Netherlands general election, elections, securing 34 out of 150 seats. The second biggest party was the centre-left D66 with 24 seats. Geert Wilders' far-right party lost support. Prime Minister Mark Rutte, in power since 2010, formed his fourth coalition government, the Fourth Rutte cabinet, consisting of the same parties as the previous one.
Government
Administrative divisions
 The Netherlands is divided into twelve provinces, each under a King's Commissioner (''Commissaris van de Koning''). Informally in Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg province this position is named Governor (''Gouverneur''). All provinces are divided into Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipalities (''gemeenten''), of which there are 344 (2022).
The Netherlands is divided into twelve provinces, each under a King's Commissioner (''Commissaris van de Koning''). Informally in Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg province this position is named Governor (''Gouverneur''). All provinces are divided into Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipalities (''gemeenten''), of which there are 344 (2022).Caribbean Netherlands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographics ...
, is outside the twelve provinces. These islands have the status of ''openbare lichamen (Public body (Netherlands), public bodies)''.
Foreign relations
 The history of foreign relations of the Netherlands, Dutch foreign policy has been characterised by its neutral state, neutrality. Since World War II, the Netherlands has become a member of a large number of international organisations, most prominently the UN,
The history of foreign relations of the Netherlands, Dutch foreign policy has been characterised by its neutral state, neutrality. Since World War II, the Netherlands has become a member of a large number of international organisations, most prominently the UN, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
and the EU. The Dutch economy is very open and relies strongly on international trade.
The foreign policy of the Netherlands is based on four basic commitments: to atlanticism, Atlantic co-operation, to European integration, to international development and to international law. One of the more controversial international issues surrounding the Netherlands is its Drug policy of the Netherlands, liberal policy towards soft drugs.
During and after the Dutch Golden Age
The Dutch Golden Age ( nl, Gouden Eeuw ) was a period in the history of the Netherlands, roughly spanning the era from 1588 (the birth of the Dutch Republic) to 1672 (the Rampjaar, "Disaster Year"), in which Dutch trade, science, and Dutch art, ...
, the Dutch people built up a commercial and colonial empire. The most important colonies were present-day Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. Indonesia became independent after the Indonesian National Revolution in the 1940s following a war of independence, international pressure and several United Nations Security Council resolutions. Suriname became independent in 1975. The historical ties inherited from its colonial past still influence the foreign relations of the Netherlands. In addition, many people from these countries are living permanently in the Netherlands.
Military
 The Netherlands has one of the oldest standing armies in Europe; it was first established as such by Maurice of Nassau in the late 1500s. The Dutch army was used throughout the Dutch Empire. After the defeat of Napoleon, the Dutch army was transformed into a conscription army. The army was unsuccessfully deployed during the Belgian Revolution in 1830. After 1830, it was deployed mainly in the Dutch colonies, as the Netherlands remained neutral in European wars (including the First World War), until the Battle of the Netherlands, Netherlands was invaded in World War II and defeated by the Wehrmacht in May 1940.
The Netherlands has one of the oldest standing armies in Europe; it was first established as such by Maurice of Nassau in the late 1500s. The Dutch army was used throughout the Dutch Empire. After the defeat of Napoleon, the Dutch army was transformed into a conscription army. The army was unsuccessfully deployed during the Belgian Revolution in 1830. After 1830, it was deployed mainly in the Dutch colonies, as the Netherlands remained neutral in European wars (including the First World War), until the Battle of the Netherlands, Netherlands was invaded in World War II and defeated by the Wehrmacht in May 1940.
 The Netherlands abandoned its neutrality in 1948 when it signed the Treaty of Brussels, and became a founding member of
The Netherlands abandoned its neutrality in 1948 when it signed the Treaty of Brussels, and became a founding member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
in 1949. The Dutch military was therefore part of the NATO strength in Cold War Europe, deploying its army to several bases in Germany. More than 3,000 Dutch soldiers were assigned to the 2nd Infantry Division (United States), 2nd Infantry Division of the United States Army during the Korean War. In 1996 conscription was suspended, and the Dutch army was once again transformed into a professional army. Since the 1990s the Dutch army has been involved in the Bosnian War and the Kosovo War, it held a province in Iraq after the defeat of Saddam Hussein, and it was engaged in War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan.
The military is composed of four branches, all of which carry the prefix ''Koninklijke'' (Royal):
* ''Koninklijke Marine'' (KM), the Royal Netherlands Navy, including the Naval Air Service and Marine Corps;
* ''Koninklijke Landmacht'' (KL), the Royal Netherlands Army;
* ''Koninklijke Luchtmacht'' (KLu), the Royal Netherlands Air Force;
* ''Koninklijke Marechaussee'' (KMar), the Royal Marechaussee (Military Police), tasks include military police and border control.
The submarine service opened to women on 1 January 2017. The Korps Commandotroepen, the Special Operations Force of the Netherlands Army, is open to women, but because of the extremely high physical demands for initial training, it is almost impossible for a woman to become a commando. The Dutch Ministry of Defence employs more than 70,000 personnel, including over 20,000 civilians and over 50,000 military personnel. In April 2011 the government announced a major reduction in its military because of a cut in government expenditure, including a decrease in the number of tanks, fighter aircraft, naval ships and senior officials.
The Netherlands has ratified many international conventions concerning International humanitarian law, war law. The Netherlands decided not to sign the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Economy

 The Netherlands has a developed economy and has been playing a special role in the European economy for many centuries. Since the 16th century, shipping, fishing, agriculture, trade, and banking have been leading sectors of the Dutch economy. The Netherlands has List of countries by economic freedom, a high level of economic freedom. The Netherlands is one of the top countries in the Global Enabling Trade Report (2nd in 2016), and was ranked the fifth most competitive economy in the world by the Swiss International Institute for Management Development in 2017. In addition, the country was ranked the 5th most innovative nation in the world in the 2022 Global Innovation Index down from 2nd in 2018.
, the key trading partners of the Netherlands were Germany, Belgium, the United Kingdom, the United States, France, Italy, China and Russia. The Netherlands is one of the world's 10 leading exporting countries. Foodstuffs form the largest industrial sector. Other major industries include chemicals, metallurgy, machinery, electrical goods, trade, services and tourism. Examples of international Dutch companies operating in Netherlands include Randstad Holding, Randstad, Unilever, Heineken International, Heineken, KLM, financial services (ING Group, ING, ABN AMRO, Rabobank), chemicals (DSM (company), DSM, AkzoNobel, AKZO), petroleum refining (Royal Dutch Shell), electronic machinery (Philips, ASML Holding, ASML), and satellite navigation (TomTom).
The Netherlands has the List of countries by GDP (nominal), 17th-largest economy in the world, and List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, ranks 11th in GDP (nominal) per capita. Between 1997 and 2000 annual economic growth (GDP) averaged nearly 4%, well above the European average. Growth slowed considerably from 2001 to 2005 with the global economic slowdown, but accelerated to 4.1% in the third quarter of 2007. In May 2013, inflation was at 2.8% per year. In April 2013, unemployment was at 8.2% (or 6.7% following the International Labour Organization, ILO definition) of the labour force. In February 2019, this was reduced to 3.4%.
In Q3 and Q4 2011, the Dutch economy contracted by 0.4% and 0.7%, respectively, because of European Debt Crisis, while in Q4 the Eurozone economy shrunk by 0.3%. The Netherlands also has a relatively low Gini coefficient, GINI coefficient of 0.326. Despite ranking 11th in GDP per capita, UNICEF ranked the Netherlands 1st in child well-being in rich countries, both in 2007 and in 2013. On the Index of Economic Freedom Netherlands is the 14th most free market capitalist economy out of 180 surveyed countries.
The Netherlands has a developed economy and has been playing a special role in the European economy for many centuries. Since the 16th century, shipping, fishing, agriculture, trade, and banking have been leading sectors of the Dutch economy. The Netherlands has List of countries by economic freedom, a high level of economic freedom. The Netherlands is one of the top countries in the Global Enabling Trade Report (2nd in 2016), and was ranked the fifth most competitive economy in the world by the Swiss International Institute for Management Development in 2017. In addition, the country was ranked the 5th most innovative nation in the world in the 2022 Global Innovation Index down from 2nd in 2018.
, the key trading partners of the Netherlands were Germany, Belgium, the United Kingdom, the United States, France, Italy, China and Russia. The Netherlands is one of the world's 10 leading exporting countries. Foodstuffs form the largest industrial sector. Other major industries include chemicals, metallurgy, machinery, electrical goods, trade, services and tourism. Examples of international Dutch companies operating in Netherlands include Randstad Holding, Randstad, Unilever, Heineken International, Heineken, KLM, financial services (ING Group, ING, ABN AMRO, Rabobank), chemicals (DSM (company), DSM, AkzoNobel, AKZO), petroleum refining (Royal Dutch Shell), electronic machinery (Philips, ASML Holding, ASML), and satellite navigation (TomTom).
The Netherlands has the List of countries by GDP (nominal), 17th-largest economy in the world, and List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, ranks 11th in GDP (nominal) per capita. Between 1997 and 2000 annual economic growth (GDP) averaged nearly 4%, well above the European average. Growth slowed considerably from 2001 to 2005 with the global economic slowdown, but accelerated to 4.1% in the third quarter of 2007. In May 2013, inflation was at 2.8% per year. In April 2013, unemployment was at 8.2% (or 6.7% following the International Labour Organization, ILO definition) of the labour force. In February 2019, this was reduced to 3.4%.
In Q3 and Q4 2011, the Dutch economy contracted by 0.4% and 0.7%, respectively, because of European Debt Crisis, while in Q4 the Eurozone economy shrunk by 0.3%. The Netherlands also has a relatively low Gini coefficient, GINI coefficient of 0.326. Despite ranking 11th in GDP per capita, UNICEF ranked the Netherlands 1st in child well-being in rich countries, both in 2007 and in 2013. On the Index of Economic Freedom Netherlands is the 14th most free market capitalist economy out of 180 surveyed countries.
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
is the financial and business capital of the Netherlands.euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . ...
, the Netherlands replaced (for accounting purposes) its former currency, the "gulden" (Dutch guilder, guilder), on 1 January 1999, along with 15 other adopters of the euro. Actual euro coins and Euro banknotes, banknotes followed on 1 January 2002. One euro was equivalent to 2.20371 Dutch guilders. In the Caribbean Netherlands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographics ...
, the United States dollar is used instead of the euro.
 The Dutch location gives it prime access to markets in the UK and Germany, with the
The Dutch location gives it prime access to markets in the UK and Germany, with the Port of Rotterdam
The Port of Rotterdam is the largest seaport in Europe, and the world's largest seaport outside of East Asia, located in and near the city of Rotterdam, in the province of South Holland in the Netherlands. From 1962 until 2004, it was the List o ...
being the largest port in Europe. Other important parts of the economy are international trade (Dutch colonialism started with co-operative private enterprises such as the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
), banking and transport. The Netherlands successfully addressed the issue of public finances and stagnating job growth long before its European partners. Amsterdam is the 5th-busiest tourist destination in Europe with more than 4.2 million international visitors.[. ez.amsterdam.nl] Since the enlargement of the EU large numbers of migrant workers have arrived in the Netherlands from Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe.
The Netherlands continues to be one of the leading European nations for attracting foreign direct investment and is one of the five largest investors in the United States. The economy experienced a slowdown in 2005, but in 2006 recovered to the fastest pace in six years on the back of increased exports and strong investment. The pace of job growth reached 10-year highs in 2007. The Netherlands is the fourth-most competitive economy in the world, according to the World Economic Forum's Global Competitiveness Report.
Natural gas
 Beginning in the 1950s, the Netherlands discovered huge natural gas resources. The sale of natural gas generated enormous revenues for the Netherlands for decades, adding, over sixty years, hundreds of billions of euros to the government's budget.
Beginning in the 1950s, the Netherlands discovered huge natural gas resources. The sale of natural gas generated enormous revenues for the Netherlands for decades, adding, over sixty years, hundreds of billions of euros to the government's budget.[The Dutch curse: how billions from natural gas went up in smoke](_blank)
LEES MEER, 17 June 2009 However, the unforeseen consequences of the country's huge energy wealth impacted the competitiveness of other sectors of the economy, leading to the theory of Dutch disease. Apart from coal and gas, the country has no mining resources. The last coal mine was closed in 1974. The Groningen gas field, one of the largest natural-gas fields in the world, is situated near Slochteren. The exploitation of this field has resulted in €159 billion in accumulated revenue since the mid-1970s.
Apart from coal and gas, the country has no mining resources. The last coal mine was closed in 1974. The Groningen gas field, one of the largest natural-gas fields in the world, is situated near Slochteren. The exploitation of this field has resulted in €159 billion in accumulated revenue since the mid-1970s.[ and represented 35% of the energy mix in 2014.][ Furthermore, the energy market in the Netherlands remains to be dominated by few major corporations Nuon, RWE, E.ON, Eneco, and Delta that have significant influence over the energy policy.][
]
Agriculture and natural resources
From a biological resource perspective, the Netherlands has a low endowment: the Netherlands’ biocapacity totals only 0.8 global hectares per person in 2016, 0.2 of which are dedicated to agriculture.[
The Dutch agricultural sector is highly mechanised, and has a strong focus on international exports. It employs about 4% of the Dutch labour force but produces large surpluses in the food-processing industry and accounts for 21% of the Dutch total export value. The Dutch rank first in the European Union and second worldwide in value of agricultural exports, behind only the United States, with agricultural exports earning €80.7 billion in 2014,]
Demographics
 The Netherlands had an estimated population of 17,493,969 as of 30 April 2021.
The Netherlands had an estimated population of 17,493,969 as of 30 April 2021. The fertility rate in the Netherlands is 1.78 children per woman (2018 estimate),
The fertility rate in the Netherlands is 1.78 children per woman (2018 estimate),Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
n, 2.4% Germans, German, 2.2% Turkish-Dutch, Turkish, 2.0% Surinamese people, Surinamese, 1.9% Morocco, Moroccan, 0.8% Netherlands Antilles, Antillean and Aruban, and 7.4% others. Some 150,000 to 200,000 people living in the Netherlands are expatriates, mostly concentrated in and around Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
and The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
, now constituting almost 10% of the population of these cities.
The Dutch are the tallest people in the world, by nationality, According to Eurostat, in 2010 there were 1.8 million Foreign born, foreign-born residents in the Netherlands, corresponding to 11.1% of the total population. Of these, 1.4 million (8.5%) were born outside the EU and 0.43 million (2.6%) were born in another EU Member State. On 21 November 2016, there were 3.8 million residents in the Netherlands with at least one foreign-born parent ("migration background"). On 1 January 2016, 26,2% of persons aged 0–50 had at least one parent born in a foreign country. 11,4% of persons aged 0–50 'of Dutch background' belonged to the 'third generation'. Of these 739,000 had western grandparents, 120,000 non-western. The third generation constitutes from persons born from two second generation immigrants or one second generation immigrant and one person with a Dutch background. First and second generation immigrants and the third generation were 34,5% of the population aged 0–50. Over half the young people in Amsterdam and Rotterdam have a non-western background. Dutch people, or Dutch diaspora, descendants of Dutch people, are also found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Canada, Australia, South Africa and the United States. According to the United States Census Bureau (2006), more than 5 million Americans claim total or partial Dutch American, Dutch ancestry. There are close to 3 million Dutch-descended Afrikaners living in South Africa. In 1940, there were 290,000 Europeans and Eurasians in Indonesia, but most have since left the country.
The Randstad is the country's largest conurbation located in the west of the country and contains the four largest cities:
According to Eurostat, in 2010 there were 1.8 million Foreign born, foreign-born residents in the Netherlands, corresponding to 11.1% of the total population. Of these, 1.4 million (8.5%) were born outside the EU and 0.43 million (2.6%) were born in another EU Member State. On 21 November 2016, there were 3.8 million residents in the Netherlands with at least one foreign-born parent ("migration background"). On 1 January 2016, 26,2% of persons aged 0–50 had at least one parent born in a foreign country. 11,4% of persons aged 0–50 'of Dutch background' belonged to the 'third generation'. Of these 739,000 had western grandparents, 120,000 non-western. The third generation constitutes from persons born from two second generation immigrants or one second generation immigrant and one person with a Dutch background. First and second generation immigrants and the third generation were 34,5% of the population aged 0–50. Over half the young people in Amsterdam and Rotterdam have a non-western background. Dutch people, or Dutch diaspora, descendants of Dutch people, are also found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Canada, Australia, South Africa and the United States. According to the United States Census Bureau (2006), more than 5 million Americans claim total or partial Dutch American, Dutch ancestry. There are close to 3 million Dutch-descended Afrikaners living in South Africa. In 1940, there were 290,000 Europeans and Eurasians in Indonesia, but most have since left the country.
The Randstad is the country's largest conurbation located in the west of the country and contains the four largest cities: Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
in the province North Holland, Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"N ...
and The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of ...
in the province South Holland
South Holland ( nl, Zuid-Holland ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.7 million as of October 2021 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely ...
, and Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
in the province Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
. The Randstad has a population of about 8.2 million inhabitants and is the List of metropolitan areas in Europe by population, 5th largest metropolitan area in Europe. According to Dutch Central Statistics Bureau, in 2015, 28 per cent of the Dutch population had a spendable income above 45,000 euros (which does not include spending on health care or education).
Functional urban areas
 "Functional urban areas" are a type of urban areas with large populations where commuters from nearby areas work in the core area. There are several functional urban areas officially identified in the Netherlands. The largest ones (with populations over 300,000) are listed below, which count the populations of the core city and their "commuting zones".
"Functional urban areas" are a type of urban areas with large populations where commuters from nearby areas work in the core area. There are several functional urban areas officially identified in the Netherlands. The largest ones (with populations over 300,000) are listed below, which count the populations of the core city and their "commuting zones".
Language
 The official language is
The official language is Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, which is spoken by the vast majority of the inhabitants. The dialects most spoken in the Netherlands are the Brabantian-Hollandic dialects.
Besides Dutch, West Frisian is recognised as a second official language in the northern province of Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
(''Fryslân'' in West Frisian). West Frisian has a formal status for government correspondence in that province. In the European part of the kingdom two other regional languages are recognised under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages.
The first of these recognised regional languages is Dutch Low Saxon, Low Saxon (''Nedersaksisch'' in Dutch). Low Saxon consists of several dialects of the Low German language spoken in the north and east of the Netherlands, like Tweants in the region of Twente, and Drents in the province of Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nov ...
.
Secondly, Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg (Netherlands), L ...
is also recognised as a regional language. It consists of Dutch varieties of Meuse-Rhenish Franconian languages and is spoken in the south-eastern province of Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg.Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), L ...
and Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius (, ), also known locally as Statia (), is an island in the Caribbean. It is a special municipality (officially " public body") of the Netherlands.
The island lies in the northern Leeward Islands portion of the West Indies, so ...
. It is widely spoken on these islands. Papiamento
Papiamento () or Papiamentu (; nl, Papiaments) is a Portuguese-based creole language spoken in the Dutch Caribbean. It is the most widely spoken language on the Caribbean ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao), with official status in Arub ...
has a formal status in the special municipality of Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC i ...
. Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ver ...
and the Romani language were recognised in 1996 as non-territorial languages.
The Netherlands has a long tradition of learning foreign languages, formalised in Dutch education laws. Some 90% of the total population indicate English in the Netherlands, they are able to converse in English, 70% in German, and 29% in French. English is a mandatory course in all secondary schools.[Schedule of the Central Exams of 2009](_blank)
Examenblad In higher level secondary schools (Hoger algemeen voortgezet onderwijs, HAVO and Voorbereidend Wetenschappelijk Onderwijs, VWO), the acquisition of two additional modern foreign language skills is mandatory during the first three years. Only during the last three years in VWO one foreign language is mandatory. Besides English, the standard modern languages are French language, French and German language, German, although schools can replace one of these modern languages with Chinese language, Chinese, Spanish language, Spanish, Russian language, Russian, Italian language, Italian, Turkish language, Turkish or Arabic.[Examenblad talen, vwo in 2019](_blank)
Examenblad Additionally, schools in Friesland teach and have exams in West Frisian, and schools across the country teach and have exams in Ancient Greek and Latin for secondary school (called Gymnasium (school), Gymnasium or VWO+).
Religion
The population of the Netherlands was predominantly Christianity, Christian until the late 20th century, divided into a number of denominations. Although significant religious diversity remains, there has been a decline of religious adherence. The Netherlands is now one of the most secular societies in the world.
In 2019, Statistics Netherlands found that 54.1% of the total population declared itself to be non-religious. Groups that represent the non-religious in the Netherlands include Humanistisch Verbond. Catholics comprised 20.1% of the total population, Protestants (14.8%). Muslims comprised 5.0% of the total population and followers of other Christian denominations and other religions (like Judaism, Buddhism and Hinduism) comprised the remaining 5.9%.Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. During the 1990s, Muslim refugees arrived from countries like Bosnia and Herzegovina, Iran, Iraq, Somalia, and Afghanistan.
Another religion practised is Hinduism, with around 215,000 adherents (slightly over 1% of the population). Most of these are Indo-Surinamese. There are also sizeable populations of Hindu immigrants from India and Sri Lanka, and some Western adherents of Hinduism in the West, Hinduism-orientated new religious movements such as International Society for Krishna Consciousness, Hare Krishnas. The Netherlands has an estimated 250,000 Buddhism in the Netherlands, Buddhists or people strongly attracted to this religion, mainly ethnic Dutch people. In addition, there are about 45,000 History of the Jews in the Netherlands, Jews in the Netherlands.
The Constitution of the Netherlands guarantees freedom of education, which means that all schools that adhere to general quality criteria receive the same government funding. This includes schools based on religious principles by religious groups (especially Catholic and various Protestant). Three political parties in the Dutch parliament, (Christian Democratic Appeal, CDA, and two small parties, ChristianUnion and Reformed Political Party, SGP) are based upon the Christian belief. Several Christian religious holidays are national holidays (Christmas, Easter, Pentecost and the Ascension of Jesus).
Upon the country's independence, Protestants were predominant in most of the country, while Roman Catholics were dominant in the south, especially North Brabant and Limburg. In the late 19th century, secularism, atheism and pillarisation
Pillarisation (from the nl, verzuiling) is the politico-denominational segregation of a society into groups by religion and associated political beliefs. These societies were (and in some areas, still are) vertically divided into two or more gr ...
gained adherents. By 1960, Catholics equalled Protestants in number; thereafter, both Christian branches began to decline. Conversely, Islam grew considerably as the result of Demography of the Netherlands#Migration and ethnicity, immigration. Since 2000 there has been raised awareness of religion, mainly due to Muslim extremism.
The Monarchy of the Netherlands, Dutch royal family has been traditionally associated with Calvinism, specifically the Dutch Reformed Church, which has merged into the Protestant Church in the Netherlands. The Dutch Reformed Church was the only major Protestant church in the Netherlands from the Protestant Reformation, Reformation until the 19th century. Denominational splits 1834 Dutch Reformed Church split, in 1834 and 1886 Dutch Reformed Church split, in 1886 diversified Dutch Calvinism. In 2013, a Catholic became Queen consort.
A survey in December 2014 concluded that for the first time there were more atheists (25%) than theists (17%) in the Netherlands, while the remainder of the population was agnostic (31%) or ietsism, ietsistic (27%).
Education
 Education in the Netherlands is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16. If a child does not have a "starting qualification" (HAVO, VWO or MBO 2+ degree) they are still forced to attend classes until they achieve such a qualification or reach the age of 18.
All children in the Netherlands usually attend elementary school from (on average) ages 4 to 12. It comprises eight grades, the first of which is facultative. Based on an aptitude test, the eighth grade teacher's recommendation and the opinion of the pupil's parents or caretakers, a choice is made for one of the three main streams of secondary education. After completing a particular stream, a pupil may still continue in the penultimate year of the next stream.
Education in the Netherlands is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16. If a child does not have a "starting qualification" (HAVO, VWO or MBO 2+ degree) they are still forced to attend classes until they achieve such a qualification or reach the age of 18.
All children in the Netherlands usually attend elementary school from (on average) ages 4 to 12. It comprises eight grades, the first of which is facultative. Based on an aptitude test, the eighth grade teacher's recommendation and the opinion of the pupil's parents or caretakers, a choice is made for one of the three main streams of secondary education. After completing a particular stream, a pupil may still continue in the penultimate year of the next stream.
 The Voorbereidend middelbaar beroepsonderwijs, VMBO has four grades and is subdivided over several levels. Successfully completing the VMBO results in a low-level vocational degree that grants access to the MBO. The MBO (middle-level applied education) is a form of education that primarily focuses on teaching a practical trade or a vocational degree. With the MBO certification, a student can apply for the HBO. The Hoger algemeen voortgezet onderwijs, HAVO has 5 grades and allows for admission to the HBO. The HBO (higher professional education) are Vocational university, universities of professional education (applied sciences) that award professional bachelor's degrees; similar to polytechnic degrees. An HBO degree gives access to the university system. The Voorbereidend wetenschappelijk onderwijs, VWO (comprising Atheneum (school), atheneum and Gymnasium (school), gymnasium) has 6 grades and prepares for studying at a research university. Universities offer a three-year bachelor's degree, followed by a one or two-year master's degree, which in turn can be followed by a four or five-year doctoral degree programme. Netherlands was ranked 5th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, down from 4th in 2019.
Doctoral candidates in the Netherlands are generally non-tenured employees of a university. All Dutch schools and universities are publicly funded and managed with the exception of religious schools that are publicly funded but not managed by the state even though requirements are necessary for the funding to be authorised. Dutch universities have a tuition fee of about 2,000 euros a year for students from the Netherlands and the European Union. The amount is about 10,000 euros for non-EU students.
The Voorbereidend middelbaar beroepsonderwijs, VMBO has four grades and is subdivided over several levels. Successfully completing the VMBO results in a low-level vocational degree that grants access to the MBO. The MBO (middle-level applied education) is a form of education that primarily focuses on teaching a practical trade or a vocational degree. With the MBO certification, a student can apply for the HBO. The Hoger algemeen voortgezet onderwijs, HAVO has 5 grades and allows for admission to the HBO. The HBO (higher professional education) are Vocational university, universities of professional education (applied sciences) that award professional bachelor's degrees; similar to polytechnic degrees. An HBO degree gives access to the university system. The Voorbereidend wetenschappelijk onderwijs, VWO (comprising Atheneum (school), atheneum and Gymnasium (school), gymnasium) has 6 grades and prepares for studying at a research university. Universities offer a three-year bachelor's degree, followed by a one or two-year master's degree, which in turn can be followed by a four or five-year doctoral degree programme. Netherlands was ranked 5th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, down from 4th in 2019.
Doctoral candidates in the Netherlands are generally non-tenured employees of a university. All Dutch schools and universities are publicly funded and managed with the exception of religious schools that are publicly funded but not managed by the state even though requirements are necessary for the funding to be authorised. Dutch universities have a tuition fee of about 2,000 euros a year for students from the Netherlands and the European Union. The amount is about 10,000 euros for non-EU students.
Healthcare
In 2016, the Netherlands maintained its number one position at the top of the annual Euro health consumer index (EHCI), which compares healthcare systems in Europe, scoring 916 of a maximum 1,000 points. The Netherlands has been among the top three countries in each report published since 2005. On 48 indicators such as patient rights and information, accessibility, prevention and outcomes, the Netherlands secured its top position among 37 European countries for six years in a row.
The Netherlands was ranked first in a study in 2009 comparing the health care systems of the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany and New Zealand.
Ever since a major reform of the health care system in 2006, the Dutch system received more points in the Index each year. According to the HCP (Health Consumer Powerhouse), the Netherlands has 'a chaos system', meaning patients have a great degree of freedom from where to buy their health insurance, to where they get their healthcare service. The difference between the Netherlands and other countries is that the chaos is managed. Healthcare decisions are being made in a dialogue between the patients and healthcare professionals.
Health insurance in the Netherlands is mandatory. Healthcare in the Netherlands is covered by two statutory forms of insurance:
* Zorgverzekeringswet (ZVW), often called "basic insurance", covers common medical care.
* Algemene Wet Bijzondere Ziektekosten (AWBZ) covers long-term nursing and care.
While Dutch residents are automatically insured by the government for AWBZ, everyone has to take out their own basic healthcare insurance (basisverzekering), except those under 18 who are automatically covered under their parents' premium. If a person decides not to carry out an insurance coverage, the person may be fined. Insurers have to offer a universal package for everyone over the age of 18 years, regardless of age or state of health – it's illegal to refuse an application or impose special conditions. In contrast to many other European systems, the Dutch government is responsible for the accessibility and quality of the healthcare system in the Netherlands, but not in charge of its management.
Healthcare in the Netherlands can be divided in several ways: three echelons, in somatic and mental health care and in 'cure' (short term) and 'care' (long term). Home doctors (''huisartsen'', comparable to general practitioners) form the largest part of the first echelon. Being referenced by a member of the first echelon is mandatory for access to the second and third echelon.[J.M. Boot, 'De Nederlandse Gezondheidszorg', Bohn Stafleu van Loghum 2011] The health care system is in comparison to other Western countries quite effective but not the most cost-effective.[Boston Consulting Group, 'Zorg voor Waarde', 2011.]
Healthcare in the Netherlands is financed by a dual system that came into effect in January 2006. Long-term treatments, especially those that involve semi-permanent hospitalisation, and also disability costs such as wheelchairs, are covered by a state-controlled mandatory insurance. This is laid down in the ''AWBZ, Algemene Wet Bijzondere Ziektekosten'' ("General Law on Exceptional Healthcare Costs") which first came into effect in 1968. In 2009 this insurance covered 27% of all health care expenses.
Transport
Mobility on Dutch roads has grown continuously since the 1950s and now exceeds 200 billion km travelled per year, three quarters of which are done by car.
Road transport
 With a total Roads in the Netherlands, road network of 139,295 km, which includes 2,758 km of expressways, the Netherlands has one of the densest road networks in the world—much denser than Germany and France, but still not as dense as Belgium.
As part of its commitment to environmental sustainability, the Government of the Netherlands initiated a plan to establish over 200 recharging stations for electric vehicles across the country. The rollout will be undertaken by Switzerland-based power and automation company ABB (company), ABB and Dutch startup Fastned, and will aim to provide at least one station within a radius of every home in the Netherlands. Currently, the Netherlands alone hosts approximately 30% of all recharging stations in the European Union. Moreover, newly sold cars in the Netherlands have on average the lowest emissions in the EU.
With a total Roads in the Netherlands, road network of 139,295 km, which includes 2,758 km of expressways, the Netherlands has one of the densest road networks in the world—much denser than Germany and France, but still not as dense as Belgium.
As part of its commitment to environmental sustainability, the Government of the Netherlands initiated a plan to establish over 200 recharging stations for electric vehicles across the country. The rollout will be undertaken by Switzerland-based power and automation company ABB (company), ABB and Dutch startup Fastned, and will aim to provide at least one station within a radius of every home in the Netherlands. Currently, the Netherlands alone hosts approximately 30% of all recharging stations in the European Union. Moreover, newly sold cars in the Netherlands have on average the lowest emissions in the EU.
Public transport
About 13% of all distance is travelled by public transport, the majority of which by train.
Cycling
 Cycling in the Netherlands, Cycling is a ubiquitous mode of transport in the Netherlands. Almost as many kilometres are covered by bicycle as by train.
Cycling in the Netherlands, Cycling is a ubiquitous mode of transport in the Netherlands. Almost as many kilometres are covered by bicycle as by train.
Water transport
Until the introduction of trains, ships were the primary mode of transport in the Netherlands. And shipping has remained crucial afterwards. The Port of Rotterdam
The Port of Rotterdam is the largest seaport in Europe, and the world's largest seaport outside of East Asia, located in and near the city of Rotterdam, in the province of South Holland in the Netherlands. From 1962 until 2004, it was the List o ...
is the largest port in Europe and the largest port in the world outside East-Asia, with the rivers Meuse and Rhine providing excellent access to the hinterland upstream reaching to Basel, Switzerland, and into Germany and France. , Rotterdam was the world's eighth largest container port handling 440.5 million metric tonnes of cargo annually. The port's main activities are petrochemical industries and general cargo handling and transshipment. The harbour functions as an important transit point for bulk material handling, bulk materials and between the European continent and overseas. From Rotterdam goods are transported by ship, river barge, train or road. The Volkeraksluizen between Rotterdam and Antwerp are the biggest sluices for inland navigation in the world in terms of tonnage passing through them. In 2007, the Betuweroute, a new fast freight railway from Rotterdam to Germany, was completed. The Netherlands also hosts Europe's 4th largest port in Port of Amsterdam, Amsterdam. The Inland navigation, inland shipping fleet of the Netherlands is the largest in Europe. The Netherlands also has the largest fleet of active historical ships in the world. Boats are used for passenger travel as well, such as the Watertaxies in Rotterdam. The ferry network in Amsterdam and the Waterbus network in Rotterdam are part of the public transport system.
Air transport
Amsterdam Airport Schiphol, Schiphol Airport, just southwest of Amsterdam, is the main international airport in the Netherlands, and the List of the busiest airports in Europe, third busiest airport in Europe by number of passengers. Schiphol is the main hub for KLM, the nation's flag carrier and the world's oldest airline. In 2016, the Schiphol Group, Royal Schiphol Group airports handled 70 million passengers.
Culture

Art, architecture and philosophy
The Netherlands has had many well-known painters. In the Middle Ages Hieronymus Bosch and Pieter Bruegel the Elder were leading Dutch pioneers. During the Dutch Golden Age
The Dutch Golden Age ( nl, Gouden Eeuw ) was a period in the history of the Netherlands, roughly spanning the era from 1588 (the birth of the Dutch Republic) to 1672 (the Rampjaar, "Disaster Year"), in which Dutch trade, science, and Dutch art, ...
, the Dutch Republic was prosperous and witnessed a flourishing artistic movement. The "Dutch Masters", spanning this 17th century era, included Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, Rembrandt van Rijn, Johannes Vermeer, Jan Steen, and Jacob van Ruisdael. Famous Dutch painters of the 19th and 20th century included Vincent van Gogh and Piet Mondrian. M. C. Escher is a well-known graphic artist.
Literature flourished as well during the Dutch Golden Age, with Joost van den Vondel and Pieter Corneliszoon Hooft, P. C. Hooft as the most famous writers. In the 19th century, Multatuli wrote about the poor treatment of the natives in the Dutch colony. The Diary of a Young Girl, ''Diary of a Young Girl'' by Anne Frank is the most translated book from Dutch. Other important 20th century authors include Harry Mulisch, Jan Wolkers, Hella S. Haasse, Willem Frederik Hermans, Cees Nooteboom and Gerard Reve. Janwillem van de Wetering wrote successful detectives, Dick Bruna (doubling as illustrator) and Annie M. G. Schmidt children's books.
Various architectural styles can be distinguished in the Netherlands. The Romanesque architecture was built between the years 950 and 1250. This architectural style is most concentrated in the provinces of Gelderland and Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg. The Gothic architecture was used in the Netherlands from about 1230. Gothic buildings had large windows, pointed arches and were richly decorated. Brabantine Gothic originated with the rise of the Duchy of Brabant and spread throughout the Burgundian provinces. Dutch Baroque architecture (1525 – 1630) and classicism (1630 – 1700) is especially evident in the west of the Netherlands. Other common architectural styles are Style Louis XIV, Art Nouveau, Rationalism (architecture), Rationalism, Neoclassicism, Expressionist architecture, Expressionism, De Stijl, Traditionalist School (architecture), Traditionalism and Brutalism.
Erasmus and Baruch Spinoza, Spinoza were famous Dutch philosophers. The Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens (1629–1695) discovered Saturn's moon Titan (moon), Titan, argued that light travelled as waves, invented the pendulum clock, and was the first physicist to use mathematical formulae. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe and describe Microorganism, single-celled organisms with a microscope.
Windmills, tulips, Clog (shoe), wooden shoes, cheese, Delftware pottery, and cannabis (drug), cannabis have grown to symbolize the Netherlands, especially among tourists.
Dutch value system
Dutch society is Egalitarianism, egalitarian and Modernism, modern. The Dutch have an aversion to the non-essential. Dutch manners are open and direct with a no-nonsense attitude—informality combined with adherence to basic behaviour. According to a humorous source on Dutch culture, "Their directness gives many the impression that they are rude and crude—attributes they prefer to call openness."
Dutch manners are open and direct with a no-nonsense attitude—informality combined with adherence to basic behaviour. According to a humorous source on Dutch culture, "Their directness gives many the impression that they are rude and crude—attributes they prefer to call openness."[Colin White & Laurie Boucke (1995). The UnDutchables: An observation of the Netherlands, its culture and its inhabitants (3rd Ed.). White-Boucke Publishing.] A well known more serious source on Dutch etiquette is "Dealing with the Dutch" by Jacob Vossestein: "Dutch egalitarianism is the idea that people are equal, especially from a moral point of view, and accordingly, causes the somewhat ambiguous stance the Dutch have towards hierarchy and status." As always, manners differ between groups. Asking about basic rules will not be considered impolite. "What may strike you as being blatantly blunt topics and comments are no more embarrassing or unusual to the Dutch than discussing the weather."
Ecology
As of 2018, the Netherlands had one of the highest rates of carbon dioxide emissions per capita in the European Union. In addition, the Dutch waste more food than any other EU citizen, at over three times the EU average On the upside, in 2015, Amsterdam and Rotterdam were ranked fourth and fifth, respectively, on the Arcadis NV, Arcadis Sustainable Cities Index.
The goal of the Dutch Government is to have a Sustainability, sustainable, reliable and affordable energy system, by 2050, in which Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, emissions have been halved and 40 per cent of electricity is derived from Sustainability, sustainable sources.
Music
 The Netherlands has multiple music traditions. Traditional Dutch music is a genre known as "Levenslied", meaning ''Song of life'', to an extent comparable to a French Chanson or a German Schlager music, Schlager. These songs typically have a simple melody and rhythm, and a straightforward structure of verses and choruses. Themes can be light, but are often sentimental and include love, death and loneliness. Traditional musical instruments such as the accordion and the barrel organ are a staple of levenslied music, though in recent years many artists also use synthesisers and guitars. Artists in this genre include Jan Smit (singer), Jan Smit, Frans Bauer and André Hazes.
Contemporary Dutch Rock music, rock and pop music (Nederpop) originated in the 1960s, heavily influenced by popular music from the United States and United Kingdom, Britain. In the 1960s and 1970s the lyrics were mostly in English, and some tracks were instrumental. Bands such as Shocking Blue, Golden Earring, Tee Set, George Baker Selection and Focus (band), Focus enjoyed international success. From the 1980s, more and more pop musicians started working in the Dutch language, partly inspired by the huge success of the band Doe Maar. Today Dutch rock and pop music thrives in both languages, with some artists recording in both.
Current symphonic metal bands Epica (band), Epica, Delain, ReVamp, The Gathering (band), The Gathering, Asrai, Autumn, Ayreon and Within Temptation as well as jazz and pop singer Caro Emerald are having international success. Also, metal bands like Hail of Bullets, God Dethroned, Izegrim, Asphyx, Textures (band), Textures, Present Danger, Heidevolk and Slechtvalk are popular guests at the biggest metal festivals in Europe. Contemporary local stars include pop singer Anouk (singer), Anouk, country pop singer Ilse DeLange, South Guelderish and
The Netherlands has multiple music traditions. Traditional Dutch music is a genre known as "Levenslied", meaning ''Song of life'', to an extent comparable to a French Chanson or a German Schlager music, Schlager. These songs typically have a simple melody and rhythm, and a straightforward structure of verses and choruses. Themes can be light, but are often sentimental and include love, death and loneliness. Traditional musical instruments such as the accordion and the barrel organ are a staple of levenslied music, though in recent years many artists also use synthesisers and guitars. Artists in this genre include Jan Smit (singer), Jan Smit, Frans Bauer and André Hazes.
Contemporary Dutch Rock music, rock and pop music (Nederpop) originated in the 1960s, heavily influenced by popular music from the United States and United Kingdom, Britain. In the 1960s and 1970s the lyrics were mostly in English, and some tracks were instrumental. Bands such as Shocking Blue, Golden Earring, Tee Set, George Baker Selection and Focus (band), Focus enjoyed international success. From the 1980s, more and more pop musicians started working in the Dutch language, partly inspired by the huge success of the band Doe Maar. Today Dutch rock and pop music thrives in both languages, with some artists recording in both.
Current symphonic metal bands Epica (band), Epica, Delain, ReVamp, The Gathering (band), The Gathering, Asrai, Autumn, Ayreon and Within Temptation as well as jazz and pop singer Caro Emerald are having international success. Also, metal bands like Hail of Bullets, God Dethroned, Izegrim, Asphyx, Textures (band), Textures, Present Danger, Heidevolk and Slechtvalk are popular guests at the biggest metal festivals in Europe. Contemporary local stars include pop singer Anouk (singer), Anouk, country pop singer Ilse DeLange, South Guelderish and Limburgish
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg (Netherlands), L ...
dialect singing folk band Rowwen Hèze, rock band BLØF and duo Nick & Simon. Trijntje Oosterhuis, one of the country's most well known and versatile singers, has made multiple albums with famous American composers Vince Mendoza and Burt Bacharach.
Early 1990s Dutch and Belgium, Belgian house music came together in Eurodance project 2 Unlimited. Selling 18 million records, the two singers in the band are the most successful Dutch music artists to this day. Tracks like "Get Ready for This" are still popular themes of U.S. sports events, like the NHL. In the mid-1990s Dutch language Hip hop music, rap and hip hop (''Dutch hip hop, Nederhop'') also came to fruition and has become popular in the Netherlands and Belgium. Artists with North African, Caribbean or Middle Eastern origins have strongly influenced this genre.
Since the 1990s, Dutch electronic dance music (EDM) gained widespread popularity in the world in many forms, from trance music, trance, techno and gabber to hardstyle. Some of the world's best known dance music DJs hail from the Netherlands, including Armin van Buuren, Tiësto, Hardwell, Martin Garrix, Dash Berlin, Julian Jordan, Nicky Romero, W&W, Don Diablo, Ummet Ozcan, Headhunterz, Sander van Doorn and Afrojack; the first four of which have been ranked as best in the world by DJ Mag Top 100 DJs. The Amsterdam Dance Event (ADE) is the world's leading electronic music conference and the biggest club festival for the many electronic subgenres on the planet. These DJs also contribute to the world's mainstream pop music, as they frequently collaborate and produce for high-profile international artists.
The Netherlands has Netherlands in the Eurovision Song Contest, participated in the Eurovision Song Contest since its first edition in 1956, and has won five times.
In classical music, Jan Sweelinck ranks as the most famous Dutch composer, with Louis Andriessen amongst the best known contemporary Dutch classical composers. Ton Koopman is a Dutch conductor, organist and harpsichordist. Notable violinists are Janine Jansen and André Rieu. The latter, together with his Johann Strauss Orchestra, has taken classical and waltz (music), waltz music on worldwide concert tours, the size and revenue of which are otherwise only seen from the world's biggest rock and pop music acts.
Film and television
Some Dutch films – mainly by director Paul Verhoeven – have received international distribution and recognition, such as ''Turkish Delight (1973 film), Turkish Delight'' ("''Turks Fruit''", 1973), ''Soldier of Orange'' ("''Soldaat van Oranje''", 1977), ''Spetters'' (1980) and ''The Fourth Man (1983 film), The Fourth Man'' ("''De Vierde Man''", 1983). Verhoeven then went on to direct big Cinema of the United States, Hollywood movies like ''RoboCop'' (1987), ''Total Recall (1990 film), Total Recall'' (1990) and ''Basic Instinct'' (1992), and returned with Dutch film ''Black Book (film), Black Book'' ("''Zwartboek''", 2006).
Other well-known Dutch film directors are Jan de Bont (''Speed (1994 film), Speed''), Anton Corbijn (''A Most Wanted Man (film), A Most wanted Man''), Dick Maas (''De Lift''), Fons Rademakers (''The Assault (1986 film), The Assault''), and documentary makers Bert Haanstra and Joris Ivens. Film director Theo van Gogh (film director), Theo van Gogh achieved international notoriety in 2004 when he was murdered by Mohammed Bouyeri in the streets of Amsterdam after directing the short film ''Submission (2004 film), Submission''.
Internationally, successful directors of photography from the Netherlands are Hoyte van Hoytema (''Interstellar (film), Interstellar'', ''Spectre (2015 film), Spectre'', ''Dunkirk (2017 film), Dunkirk'') and Theo van de Sande (''Wayne's World'' and ''Blade (1998 film), Blade''). Van Hoytema went to the National Film School in Łódź (Poland) and Van de Sande went to the Netherlands Film Academy. Internationally successful Dutch actors include Famke Janssen (X-Men (film series), ''X-Men''), Carice van Houten (''Game of Thrones''), Michiel Huisman (''Game of Thrones''), Rutger Hauer (''Blade Runner''), Jeroen Krabbé (''The Living Daylights'') and Derek de Lint (''Three Men and a Baby'').
The Netherlands has a well developed television market, with both multiple commercial and public broadcasters. Imported TV programmes, as well as interviews with responses in a foreign language, are virtually always shown with the original sound and subtitled. Only foreign shows for children are dubbed.
Webcasting Worldwide: Business Models of an Emerging Global Medium
'. Routledge; 2013. . p. 101–103.Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
, Endemol has around 90 companies in over 30 countries. Endemol and its subsidiaries create and run reality, talent, and game show franchises worldwide, including ''Big Brother (franchise), Big Brother'' and ''Deal or No Deal''. John de Mol later started his own company Tien (TV channel), Talpa which created show franchises like The Voice (TV series), ''The Voice'' and ''Utopia (U.S. reality TV series), Utopia''.
Sports
 Approximately 4.5 million of the 16.8 million people in the Netherlands are registered in one of the 35,000 sports clubs in the country. About two-thirds of the population between 15 and 75 participate in sports weekly. Association football, Football is the most popular team sport in the Netherlands, followed by field hockey and volleyball. Tennis, gymnastics and golf are the three most widely engaged in individual sports.
Approximately 4.5 million of the 16.8 million people in the Netherlands are registered in one of the 35,000 sports clubs in the country. About two-thirds of the population between 15 and 75 participate in sports weekly. Association football, Football is the most popular team sport in the Netherlands, followed by field hockey and volleyball. Tennis, gymnastics and golf are the three most widely engaged in individual sports.
Cuisine
 Originally, the country's cuisine was shaped by the practices of fishing and farming, including the cultivation of the soil for growing crops and raising domesticated animals. Dutch cuisine is simple and straightforward, and contains many dairy products. Breakfast and lunch are typically bread with toppings, with cereal for breakfast as an alternative. Traditionally, dinner consists of potatoes, a portion of meat, and (seasonal) vegetables. The Dutch diet was relatively high in carbohydrates and fat, reflecting the dietary needs of the labourers whose culture moulded the country. Without many refinements, it is best described as rustic, though many holidays are still celebrated with special foods. In the course of the twentieth century this diet changed and became much more Multiculturalism, cosmopolitan, with most global cuisines being represented in the major cities.
Modern culinary writers distinguish between three general regional forms of Dutch cuisine. The regions in the northeast of the Netherlands, roughly the provinces of
Originally, the country's cuisine was shaped by the practices of fishing and farming, including the cultivation of the soil for growing crops and raising domesticated animals. Dutch cuisine is simple and straightforward, and contains many dairy products. Breakfast and lunch are typically bread with toppings, with cereal for breakfast as an alternative. Traditionally, dinner consists of potatoes, a portion of meat, and (seasonal) vegetables. The Dutch diet was relatively high in carbohydrates and fat, reflecting the dietary needs of the labourers whose culture moulded the country. Without many refinements, it is best described as rustic, though many holidays are still celebrated with special foods. In the course of the twentieth century this diet changed and became much more Multiculturalism, cosmopolitan, with most global cuisines being represented in the major cities.
Modern culinary writers distinguish between three general regional forms of Dutch cuisine. The regions in the northeast of the Netherlands, roughly the provinces of Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
, Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of ...
, Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nov ...
, Overijssel and Gelderland north of the Grote rivieren, great rivers are the least populated areas of the Netherlands. The late (18th century) introduction of large scale agriculture means that the cuisine is generally known for its many kinds of meats. The relative lack of farms allowed for an abundance of game (meat), game and Animal husbandry, husbandry, though dishes near the coastal regions of Friesland, Groningen and the parts of Overijssel bordering the IJsselmeer also include a large amount of fish. The various dried sausages, belonging to the metworst-family of Dutch sausages are found throughout this region and are highly prized for their often very strong taste. Also smoked sausages are common, of which (''Gelderse'') ''rookworst'' is the most renowned. The sausage contains a lot of fat and is very juicy. Larger sausages are often eaten alongside ''stamppot'', ''hutspot'' or ''zuurkool'' (sauerkraut); whereas smaller ones are often eaten as a street food. The provinces are also home to hard textured rye bread, pastries and cookies, the latter heavily spiced with ginger or succade or containing small bits of meat. Various kinds of ''Kruidkoek'' (such as :nl:Groninger koek, Groninger koek), '':nl:Fryske dúmkes, Fryske dúmkes'' and '':nl:spekdik, spekdikken'' (small savoury pancakes cooked in a waffle iron) are considered typical. A notable characteristic of ''Fries roggebrood'' (Frisian rye bread) is its long baking time (up to 20 hours), resulting in a sweet taste and a deep dark colour. In terms of alcoholic beverages, the region is renowned for its many bitters (such as ''Beerenburg'') and other high-proof liquors rather than beer, which is, apart from ''Jenever'', typical for the rest of the country. As a coastal region, Friesland is home to low-lying grasslands, and thus has a cheese production in common with the Western cuisine. ''Friese Nagelkaas'' (Friesian Clove) is a notable example. The ''oliebol'' (in its modern form) and ''Zeeuwse bolus'' are good examples. Cookies are also produced in great number and tend to contain a lot of butter and sugar, like ''stroopwafel'', as well as a filling of some kind, mostly almond, like '':nl:Gevulde koek, gevulde koek''. The traditional alcoholic beverages of this region are beer (strong pale lager) and ''Jenever'', a high proof juniper-flavoured spirit, that came to be known in England as gin. A noted exception within the traditional Dutch alcoholic landscape, ''Advocaat'', a rich and creamy liqueur made from eggs, sugar and brandy, is also native to this region.
The provinces of North Holland, South Holland
South Holland ( nl, Zuid-Holland ) is a province of the Netherlands with a population of over 3.7 million as of October 2021 and a population density of about , making it the country's most populous province and one of the world's most densely ...
, Zeeland, and Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, pro ...
and the Gelderlandic area of Betuwe make up the region in which western Dutch cuisine is found. Because of the abundance of water and flat grasslands that are found here, the area is known for its many dairy products, which include prominent cheeses such as Gouda (cheese), Gouda, Leyden cheese, Leyden (spiced cheese with cumin), and Edam (cheese), Edam (traditionally in small spheres) as well as Leerdammer and Beemster Cheese, Beemster, while the adjacent Zaanstreek in North Holland has since the 16th century been known for its mayonnaise, typical whole-grain mustard (condiment), mustards, and chocolate industry. Zeeland and South Holland produce a lot of butter, which contains a larger amount of milkfat than most other European butter varieties. A by-product of the butter-making process, ''karnemelk'' (buttermilk), is also considered typical for this region. Seafood such as soused herring, Blue mussel, mussels (called ''Zeeuwse Mossels'', since all Dutch mussels for consumption are cleaned in Zeeland's Oosterschelde), European eel, eels, oysters and shrimps are widely available and typical for the region. '':nl:Kibbeling, Kibbeling'', once a local delicacy consisting of small chunks of battered Whitefish (fisheries term), white fish, has become a national fast food, just as :nl:Lekkerbekje, lekkerbek. Pastries in this area tend to be quite doughy, and often contain large amounts of sugar; either caramelised, powdered or crystallised.
The Southern Dutch cuisine consists of the cuisines of the Dutch provinces of North Brabant and Limburg (Netherlands), Limburg and the Flemish Region in Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
. It is renowned for its many rich pastries, soups, stews and vegetable dishes and is often called Burgundian which is a Dutch idiom invoking the rich Burgundian court which ruled the Low Countries in the Middle Ages, renowned for its splendour and great feasts. It is the only Dutch culinary region that developed an haute cuisine. Pastries are abundant, often with rich fillings of cream, custard or fruits. Cakes, such as the ''Vlaai'' from Limburg and the ''Moorkop'' and ''Bossche Bol'' from Brabant, are typical pastries. Savoury pastries also occur, with the (a roll with a sausage of ground beef, literally translates into sausage bread) being the most popular. The traditional alcoholic beverage of the region is beer. There are many local brands, ranging from ''Trappist beer, Trappist'' to ''Kriek lambic, Kriek''. 5 of the 10 ''International Trappist Association'' recognised breweries in the world, are located in the Southern Dutch cultural area. Beer, like wine in French cuisine, is also used in cooking; often in stews.
In early 2014, Oxfam ranked the Netherlands as the country with the most nutritious, plentiful and healthy food, in a comparison of 125 countries.
See also
* Outline of the Netherlands
Notes
References
Further reading
; Geography and environment
* Burke, Gerald L. ''The making of Dutch towns: A study in urban development from the 10th–17th centuries''. (1960) Hassell Street Press 2021. ISBN 978-1013598852
* Lambert, Audrey M. ''The Making of the Dutch Landscape: An Historical Geography of the Netherlands'' (1985) ISBN 978-0128670507; focus on the history of land reclamation
* Meijer, Henk. ''Compact geography of the Netherlands'' (1985)
* Riley, R. C., and G. J. Ashworth. ''Benelux: An Economic Geography of Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg'' (1975
online
; History
* Paul Arblaster. ''A History of the Low Countries''. Palgrave Essential Histories Series New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2006. 298 pp. .
* J. C. H. Blom and E. Lamberts, eds. ''History of the Low Countries'' (1998)
* Jonathan Israel. ''The Dutch Republic: Its Rise, Greatness, and Fall 1477–1806''. Oxford: Clarendon Press (1995). ISBN 978-0198207344
* J. A. Kossmann-Putto and E. H. Kossmann. ''The Low Countries: History of the Northern and Southern Netherlands'' (1987)
* Amry Vandenbosch, ''Dutch Foreign Policy since 1815'' (1959).
; Economic indicators
Holland Compared 2nd edition 2017
– 95 page booklet by Holland's commercial website, with facts and figures about the Netherlands, comparing the country's economic indicators with those of other countries.
External links
; Articles
*
*
; General information
Netherlands
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Netherlands
from UCB Libraries GovPubs
*
*
I am Expat – General information about the Netherlands
* [https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-17740800 Netherlands profile] from the BBC News
*
*
Key Development Forecasts for the Netherlands
from International Futures
; Government
Overheid.nl
– official Dutch government portal
Government.nl
– official Dutch government web site
(CBS) – Key figures from the Dutch bureau of statistics
*
; Travel
Holland.com
– English website of the Netherlands tourist office
– Organisation responsible for promoting the Netherlands nationally and internationally
; Photographs
{{Authority control
Netherlands,
Member states of the Council of Europe
Dutch-speaking countries and territories
Germanic countries and territories
Kingdom of the Netherlands
Northwestern European countries
Countries in Europe
Member states of NATO
States and territories established in 1815
Transcontinental countries
OECD members
 The prehistory of the area that is now the Netherlands was largely shaped by the sea and the rivers that constantly shifted the low-lying geography. The oldest human (
The prehistory of the area that is now the Netherlands was largely shaped by the sea and the rivers that constantly shifted the low-lying geography. The oldest human ( To the north of the Franks, climatic conditions improved, and during the
To the north of the Franks, climatic conditions improved, and during the  The Frankish
The Frankish  The
The 
 Following the
Following the  After declaring their independence, the provinces of
After declaring their independence, the provinces of 
 In the
In the  The Netherlands was able to remain neutral during
The Netherlands was able to remain neutral during  In 1954, the
In 1954, the  According to the Central Bureau of Statistics, the European Netherlands has a total area of , including water bodies; and a land area of . The
According to the Central Bureau of Statistics, the European Netherlands has a total area of , including water bodies; and a land area of . The  Over the centuries, the Dutch coastline has changed considerably as a result of natural disasters and human intervention.
On 14 December 1287,
Over the centuries, the Dutch coastline has changed considerably as a result of natural disasters and human intervention.
On 14 December 1287,  The impact of disasters was, to an extent, increased through human activity. Relatively high-lying
The impact of disasters was, to an extent, increased through human activity. Relatively high-lying  After the North Sea Flood of 1953, 1953 disaster, the Delta Works was constructed, which is a comprehensive set of civil works throughout the Dutch coast. The project started in 1958 and was largely completed in 1997 with the completion of the Maeslantkering. Since then, new projects have been periodically started to renovate and renew the Delta Works. The main goal of the Delta project was to reduce the risk of flooding in South Holland and Zeeland to once per 10,000 years (compared to once per 4000 years for the rest of the country). This was achieved by raising of outer sea-dikes and of the inner, canal, and river dikes, and by closing off the sea
After the North Sea Flood of 1953, 1953 disaster, the Delta Works was constructed, which is a comprehensive set of civil works throughout the Dutch coast. The project started in 1958 and was largely completed in 1997 with the completion of the Maeslantkering. Since then, new projects have been periodically started to renovate and renew the Delta Works. The main goal of the Delta project was to reduce the risk of flooding in South Holland and Zeeland to once per 10,000 years (compared to once per 4000 years for the rest of the country). This was achieved by raising of outer sea-dikes and of the inner, canal, and river dikes, and by closing off the sea  The Oosterschelde, formerly the northeast
The Oosterschelde, formerly the northeast  Within this island group:
*
Within this island group:
*  The Netherlands has been a
The Netherlands has been a  The history of foreign relations of the Netherlands, Dutch foreign policy has been characterised by its neutral state, neutrality. Since World War II, the Netherlands has become a member of a large number of international organisations, most prominently the UN,
The history of foreign relations of the Netherlands, Dutch foreign policy has been characterised by its neutral state, neutrality. Since World War II, the Netherlands has become a member of a large number of international organisations, most prominently the UN,  The Netherlands has one of the oldest standing armies in Europe; it was first established as such by Maurice of Nassau in the late 1500s. The Dutch army was used throughout the Dutch Empire. After the defeat of Napoleon, the Dutch army was transformed into a conscription army. The army was unsuccessfully deployed during the Belgian Revolution in 1830. After 1830, it was deployed mainly in the Dutch colonies, as the Netherlands remained neutral in European wars (including the First World War), until the Battle of the Netherlands, Netherlands was invaded in World War II and defeated by the Wehrmacht in May 1940.
The Netherlands has one of the oldest standing armies in Europe; it was first established as such by Maurice of Nassau in the late 1500s. The Dutch army was used throughout the Dutch Empire. After the defeat of Napoleon, the Dutch army was transformed into a conscription army. The army was unsuccessfully deployed during the Belgian Revolution in 1830. After 1830, it was deployed mainly in the Dutch colonies, as the Netherlands remained neutral in European wars (including the First World War), until the Battle of the Netherlands, Netherlands was invaded in World War II and defeated by the Wehrmacht in May 1940.
 The Netherlands abandoned its neutrality in 1948 when it signed the Treaty of Brussels, and became a founding member of
The Netherlands abandoned its neutrality in 1948 when it signed the Treaty of Brussels, and became a founding member of 
 Beginning in the 1950s, the Netherlands discovered huge natural gas resources. The sale of natural gas generated enormous revenues for the Netherlands for decades, adding, over sixty years, hundreds of billions of euros to the government's budget.The Dutch curse: how billions from natural gas went up in smoke
Beginning in the 1950s, the Netherlands discovered huge natural gas resources. The sale of natural gas generated enormous revenues for the Netherlands for decades, adding, over sixty years, hundreds of billions of euros to the government's budget.The Dutch curse: how billions from natural gas went up in smoke Apart from coal and gas, the country has no mining resources. The last coal mine was closed in 1974. The Groningen gas field, one of the largest natural-gas fields in the world, is situated near Slochteren. The exploitation of this field has resulted in €159 billion in accumulated revenue since the mid-1970s. The field is operated by government-owned Gasunie and output is jointly exploited by the government, Royal Dutch Shell, and Exxon Mobil through NAM (Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij). "Gas extraction has resulted in increasingly strong earth tremors, some measuring as much as 3.6 on the Richter magnitude scale. The cost of damage repairs, structural improvements to buildings, and compensation for home value decreases has been estimated at €6.5 billion. Around 35,000 homes are said to be affected." The Netherlands has an estimated 25% of natural gas reserves in the EU. The total energy sector accounted for almost 11% of the GDP in 2014. Netherlands' economy, mainly due to the large shares of natural gas reserves, is considered to have "very high" energy intensity rating.
The Netherlands is faced with future challenges as the energy supply is forecasted to fall short of the demand by 2025 in the gas sector. This is attributed to the depletion of the Netherlands' major gas field, Groningen, and the earthquakes that have hit the Groningen region. In addition, there is ambiguity surrounding the feasibility of producing unconventional gas. The Netherlands relies heavily on natural gas to provide energy. Gas is the main source of heating for households in the Netherlands and represented 35% of the energy mix in 2014. Furthermore, The European Union climate and energy package, European Union 2020 package (20% reduction in GHG emissions, 20% renewables in the energy mix and 20% improvement in energy efficiency) enacted in 2009 has influenced the domestic energy politics of Netherlands and pressured non-state actors to give consent to more aggressive energy reforms that would reduce reliance on natural resources as a source of income to the economy. Therefore, a Renewable energy in the Netherlands, transition towards renewable energy has been a key objective by Netherlands in order to safeguard the energy security of the country from natural resources depletion, mainly gas. Netherlands has set a 14% renewable energy target of the total energy mix by 2020. However, the continuation of providing tax breaks to electricity generated by coal and gas, and to the exploration and extraction of gas from fields that are "insufficiently" profitable, renders a successful transition towards renewable energy more difficult to achieve due to inconsistencies in the policy mix. In 2011, it was estimated that the renewable energy sector received 31% (EUR 743MM), while the conventional energy sector received 69% (EUR 1.6B), of the total energy subsidies by the government. Furthermore, the energy market in the Netherlands remains to be dominated by few major corporations Nuon, RWE, E.ON, Eneco, and Delta that have significant influence over the energy policy. Renewable energy share in the energy mix is estimated to reach 12.4% by 2020, falling 1.6% short of the 14% target.
Apart from coal and gas, the country has no mining resources. The last coal mine was closed in 1974. The Groningen gas field, one of the largest natural-gas fields in the world, is situated near Slochteren. The exploitation of this field has resulted in €159 billion in accumulated revenue since the mid-1970s. The field is operated by government-owned Gasunie and output is jointly exploited by the government, Royal Dutch Shell, and Exxon Mobil through NAM (Nederlandse Aardolie Maatschappij). "Gas extraction has resulted in increasingly strong earth tremors, some measuring as much as 3.6 on the Richter magnitude scale. The cost of damage repairs, structural improvements to buildings, and compensation for home value decreases has been estimated at €6.5 billion. Around 35,000 homes are said to be affected." The Netherlands has an estimated 25% of natural gas reserves in the EU. The total energy sector accounted for almost 11% of the GDP in 2014. Netherlands' economy, mainly due to the large shares of natural gas reserves, is considered to have "very high" energy intensity rating.
The Netherlands is faced with future challenges as the energy supply is forecasted to fall short of the demand by 2025 in the gas sector. This is attributed to the depletion of the Netherlands' major gas field, Groningen, and the earthquakes that have hit the Groningen region. In addition, there is ambiguity surrounding the feasibility of producing unconventional gas. The Netherlands relies heavily on natural gas to provide energy. Gas is the main source of heating for households in the Netherlands and represented 35% of the energy mix in 2014. Furthermore, The European Union climate and energy package, European Union 2020 package (20% reduction in GHG emissions, 20% renewables in the energy mix and 20% improvement in energy efficiency) enacted in 2009 has influenced the domestic energy politics of Netherlands and pressured non-state actors to give consent to more aggressive energy reforms that would reduce reliance on natural resources as a source of income to the economy. Therefore, a Renewable energy in the Netherlands, transition towards renewable energy has been a key objective by Netherlands in order to safeguard the energy security of the country from natural resources depletion, mainly gas. Netherlands has set a 14% renewable energy target of the total energy mix by 2020. However, the continuation of providing tax breaks to electricity generated by coal and gas, and to the exploration and extraction of gas from fields that are "insufficiently" profitable, renders a successful transition towards renewable energy more difficult to achieve due to inconsistencies in the policy mix. In 2011, it was estimated that the renewable energy sector received 31% (EUR 743MM), while the conventional energy sector received 69% (EUR 1.6B), of the total energy subsidies by the government. Furthermore, the energy market in the Netherlands remains to be dominated by few major corporations Nuon, RWE, E.ON, Eneco, and Delta that have significant influence over the energy policy. Renewable energy share in the energy mix is estimated to reach 12.4% by 2020, falling 1.6% short of the 14% target.
 The Netherlands had an estimated population of 17,493,969 as of 30 April 2021. It is the Area and population of European countries, 5th most densely populated country in Europe, and except for Malta and very small city-states like Monaco, Vatican City and San Marino, it is the most densely populated country in Europe. And it is the List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density, 16th most densely populated country in the world with a density of . It is the List of countries by population, 67th most populous country in the world. Between 1900 and 1950, the country's population almost doubled from 5.1 to 10 million. From 1950 to 2000, the population further increased, to 15.9 million, though this represented a lower rate of population growth. The estimated growth rate is 0.44%.
The Netherlands had an estimated population of 17,493,969 as of 30 April 2021. It is the Area and population of European countries, 5th most densely populated country in Europe, and except for Malta and very small city-states like Monaco, Vatican City and San Marino, it is the most densely populated country in Europe. And it is the List of sovereign states and dependent territories by population density, 16th most densely populated country in the world with a density of . It is the List of countries by population, 67th most populous country in the world. Between 1900 and 1950, the country's population almost doubled from 5.1 to 10 million. From 1950 to 2000, the population further increased, to 15.9 million, though this represented a lower rate of population growth. The estimated growth rate is 0.44%.
 According to Eurostat, in 2010 there were 1.8 million Foreign born, foreign-born residents in the Netherlands, corresponding to 11.1% of the total population. Of these, 1.4 million (8.5%) were born outside the EU and 0.43 million (2.6%) were born in another EU Member State. On 21 November 2016, there were 3.8 million residents in the Netherlands with at least one foreign-born parent ("migration background"). On 1 January 2016, 26,2% of persons aged 0–50 had at least one parent born in a foreign country. 11,4% of persons aged 0–50 'of Dutch background' belonged to the 'third generation'. Of these 739,000 had western grandparents, 120,000 non-western. The third generation constitutes from persons born from two second generation immigrants or one second generation immigrant and one person with a Dutch background. First and second generation immigrants and the third generation were 34,5% of the population aged 0–50. Over half the young people in Amsterdam and Rotterdam have a non-western background. Dutch people, or Dutch diaspora, descendants of Dutch people, are also found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Canada, Australia, South Africa and the United States. According to the United States Census Bureau (2006), more than 5 million Americans claim total or partial Dutch American, Dutch ancestry. There are close to 3 million Dutch-descended Afrikaners living in South Africa. In 1940, there were 290,000 Europeans and Eurasians in Indonesia, but most have since left the country.
The Randstad is the country's largest conurbation located in the west of the country and contains the four largest cities:
According to Eurostat, in 2010 there were 1.8 million Foreign born, foreign-born residents in the Netherlands, corresponding to 11.1% of the total population. Of these, 1.4 million (8.5%) were born outside the EU and 0.43 million (2.6%) were born in another EU Member State. On 21 November 2016, there were 3.8 million residents in the Netherlands with at least one foreign-born parent ("migration background"). On 1 January 2016, 26,2% of persons aged 0–50 had at least one parent born in a foreign country. 11,4% of persons aged 0–50 'of Dutch background' belonged to the 'third generation'. Of these 739,000 had western grandparents, 120,000 non-western. The third generation constitutes from persons born from two second generation immigrants or one second generation immigrant and one person with a Dutch background. First and second generation immigrants and the third generation were 34,5% of the population aged 0–50. Over half the young people in Amsterdam and Rotterdam have a non-western background. Dutch people, or Dutch diaspora, descendants of Dutch people, are also found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Canada, Australia, South Africa and the United States. According to the United States Census Bureau (2006), more than 5 million Americans claim total or partial Dutch American, Dutch ancestry. There are close to 3 million Dutch-descended Afrikaners living in South Africa. In 1940, there were 290,000 Europeans and Eurasians in Indonesia, but most have since left the country.
The Randstad is the country's largest conurbation located in the west of the country and contains the four largest cities:  "Functional urban areas" are a type of urban areas with large populations where commuters from nearby areas work in the core area. There are several functional urban areas officially identified in the Netherlands. The largest ones (with populations over 300,000) are listed below, which count the populations of the core city and their "commuting zones".
"Functional urban areas" are a type of urban areas with large populations where commuters from nearby areas work in the core area. There are several functional urban areas officially identified in the Netherlands. The largest ones (with populations over 300,000) are listed below, which count the populations of the core city and their "commuting zones".
 The official language is
The official language is  Education in the Netherlands is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16. If a child does not have a "starting qualification" (HAVO, VWO or MBO 2+ degree) they are still forced to attend classes until they achieve such a qualification or reach the age of 18.
All children in the Netherlands usually attend elementary school from (on average) ages 4 to 12. It comprises eight grades, the first of which is facultative. Based on an aptitude test, the eighth grade teacher's recommendation and the opinion of the pupil's parents or caretakers, a choice is made for one of the three main streams of secondary education. After completing a particular stream, a pupil may still continue in the penultimate year of the next stream.
Education in the Netherlands is compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16. If a child does not have a "starting qualification" (HAVO, VWO or MBO 2+ degree) they are still forced to attend classes until they achieve such a qualification or reach the age of 18.
All children in the Netherlands usually attend elementary school from (on average) ages 4 to 12. It comprises eight grades, the first of which is facultative. Based on an aptitude test, the eighth grade teacher's recommendation and the opinion of the pupil's parents or caretakers, a choice is made for one of the three main streams of secondary education. After completing a particular stream, a pupil may still continue in the penultimate year of the next stream.
 The Voorbereidend middelbaar beroepsonderwijs, VMBO has four grades and is subdivided over several levels. Successfully completing the VMBO results in a low-level vocational degree that grants access to the MBO. The MBO (middle-level applied education) is a form of education that primarily focuses on teaching a practical trade or a vocational degree. With the MBO certification, a student can apply for the HBO. The Hoger algemeen voortgezet onderwijs, HAVO has 5 grades and allows for admission to the HBO. The HBO (higher professional education) are Vocational university, universities of professional education (applied sciences) that award professional bachelor's degrees; similar to polytechnic degrees. An HBO degree gives access to the university system. The Voorbereidend wetenschappelijk onderwijs, VWO (comprising Atheneum (school), atheneum and Gymnasium (school), gymnasium) has 6 grades and prepares for studying at a research university. Universities offer a three-year bachelor's degree, followed by a one or two-year master's degree, which in turn can be followed by a four or five-year doctoral degree programme. Netherlands was ranked 5th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, down from 4th in 2019.
Doctoral candidates in the Netherlands are generally non-tenured employees of a university. All Dutch schools and universities are publicly funded and managed with the exception of religious schools that are publicly funded but not managed by the state even though requirements are necessary for the funding to be authorised. Dutch universities have a tuition fee of about 2,000 euros a year for students from the Netherlands and the European Union. The amount is about 10,000 euros for non-EU students.
The Voorbereidend middelbaar beroepsonderwijs, VMBO has four grades and is subdivided over several levels. Successfully completing the VMBO results in a low-level vocational degree that grants access to the MBO. The MBO (middle-level applied education) is a form of education that primarily focuses on teaching a practical trade or a vocational degree. With the MBO certification, a student can apply for the HBO. The Hoger algemeen voortgezet onderwijs, HAVO has 5 grades and allows for admission to the HBO. The HBO (higher professional education) are Vocational university, universities of professional education (applied sciences) that award professional bachelor's degrees; similar to polytechnic degrees. An HBO degree gives access to the university system. The Voorbereidend wetenschappelijk onderwijs, VWO (comprising Atheneum (school), atheneum and Gymnasium (school), gymnasium) has 6 grades and prepares for studying at a research university. Universities offer a three-year bachelor's degree, followed by a one or two-year master's degree, which in turn can be followed by a four or five-year doctoral degree programme. Netherlands was ranked 5th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020, down from 4th in 2019.
Doctoral candidates in the Netherlands are generally non-tenured employees of a university. All Dutch schools and universities are publicly funded and managed with the exception of religious schools that are publicly funded but not managed by the state even though requirements are necessary for the funding to be authorised. Dutch universities have a tuition fee of about 2,000 euros a year for students from the Netherlands and the European Union. The amount is about 10,000 euros for non-EU students.
 With a total Roads in the Netherlands, road network of 139,295 km, which includes 2,758 km of expressways, the Netherlands has one of the densest road networks in the world—much denser than Germany and France, but still not as dense as Belgium.
As part of its commitment to environmental sustainability, the Government of the Netherlands initiated a plan to establish over 200 recharging stations for electric vehicles across the country. The rollout will be undertaken by Switzerland-based power and automation company ABB (company), ABB and Dutch startup Fastned, and will aim to provide at least one station within a radius of every home in the Netherlands. Currently, the Netherlands alone hosts approximately 30% of all recharging stations in the European Union. Moreover, newly sold cars in the Netherlands have on average the lowest emissions in the EU.
With a total Roads in the Netherlands, road network of 139,295 km, which includes 2,758 km of expressways, the Netherlands has one of the densest road networks in the world—much denser than Germany and France, but still not as dense as Belgium.
As part of its commitment to environmental sustainability, the Government of the Netherlands initiated a plan to establish over 200 recharging stations for electric vehicles across the country. The rollout will be undertaken by Switzerland-based power and automation company ABB (company), ABB and Dutch startup Fastned, and will aim to provide at least one station within a radius of every home in the Netherlands. Currently, the Netherlands alone hosts approximately 30% of all recharging stations in the European Union. Moreover, newly sold cars in the Netherlands have on average the lowest emissions in the EU.
 Cycling in the Netherlands, Cycling is a ubiquitous mode of transport in the Netherlands. Almost as many kilometres are covered by bicycle as by train. The Dutch are estimated to have at least 18 million bicycles, which makes more than one per capita, and twice as many as the circa 9 million motor vehicles on the road. In 2013, the European Cyclists' Federation ranked both the Netherlands and Denmark as the most bike-friendly countries in Europe, but more of the Dutch (36%) than of the Danes (23%) list the bike as their most frequent mode of transport on a typical day. Cycling infrastructure is comprehensive. Busy roads have received some 35,000 km of Segregated cycle facilities, dedicated cycle tracks, physically segregated from motorised traffic. Busy junctions are often equipped with bicycle-specific traffic lights. There are large bicycle parking facilities, particularly in city centres and at train stations.
Cycling in the Netherlands, Cycling is a ubiquitous mode of transport in the Netherlands. Almost as many kilometres are covered by bicycle as by train. The Dutch are estimated to have at least 18 million bicycles, which makes more than one per capita, and twice as many as the circa 9 million motor vehicles on the road. In 2013, the European Cyclists' Federation ranked both the Netherlands and Denmark as the most bike-friendly countries in Europe, but more of the Dutch (36%) than of the Danes (23%) list the bike as their most frequent mode of transport on a typical day. Cycling infrastructure is comprehensive. Busy roads have received some 35,000 km of Segregated cycle facilities, dedicated cycle tracks, physically segregated from motorised traffic. Busy junctions are often equipped with bicycle-specific traffic lights. There are large bicycle parking facilities, particularly in city centres and at train stations.

 Dutch manners are open and direct with a no-nonsense attitude—informality combined with adherence to basic behaviour. According to a humorous source on Dutch culture, "Their directness gives many the impression that they are rude and crude—attributes they prefer to call openness."Colin White & Laurie Boucke (1995). The UnDutchables: An observation of the Netherlands, its culture and its inhabitants (3rd Ed.). White-Boucke Publishing. A well known more serious source on Dutch etiquette is "Dealing with the Dutch" by Jacob Vossestein: "Dutch egalitarianism is the idea that people are equal, especially from a moral point of view, and accordingly, causes the somewhat ambiguous stance the Dutch have towards hierarchy and status." As always, manners differ between groups. Asking about basic rules will not be considered impolite. "What may strike you as being blatantly blunt topics and comments are no more embarrassing or unusual to the Dutch than discussing the weather."
The Netherlands is one of the most secular countries of Europe, and religion in the Netherlands is generally considered as a personal matter which is not supposed to be propagated in public, although it often remains a discussion subject. For only 17% of the population religion is important and 14% goes to church weekly.
The Netherlands has a long history of social tolerance and today is regarded as a liberal country, considering Drug policy of the Netherlands, its drug policy and its legalisation of Euthanasia in the Netherlands, euthanasia. On 1 April 2001, the Netherlands became the first nation to legalise same-sex marriage in the Netherlands, same-sex marriage.
Dutch manners are open and direct with a no-nonsense attitude—informality combined with adherence to basic behaviour. According to a humorous source on Dutch culture, "Their directness gives many the impression that they are rude and crude—attributes they prefer to call openness."Colin White & Laurie Boucke (1995). The UnDutchables: An observation of the Netherlands, its culture and its inhabitants (3rd Ed.). White-Boucke Publishing. A well known more serious source on Dutch etiquette is "Dealing with the Dutch" by Jacob Vossestein: "Dutch egalitarianism is the idea that people are equal, especially from a moral point of view, and accordingly, causes the somewhat ambiguous stance the Dutch have towards hierarchy and status." As always, manners differ between groups. Asking about basic rules will not be considered impolite. "What may strike you as being blatantly blunt topics and comments are no more embarrassing or unusual to the Dutch than discussing the weather."
The Netherlands is one of the most secular countries of Europe, and religion in the Netherlands is generally considered as a personal matter which is not supposed to be propagated in public, although it often remains a discussion subject. For only 17% of the population religion is important and 14% goes to church weekly.
The Netherlands has a long history of social tolerance and today is regarded as a liberal country, considering Drug policy of the Netherlands, its drug policy and its legalisation of Euthanasia in the Netherlands, euthanasia. On 1 April 2001, the Netherlands became the first nation to legalise same-sex marriage in the Netherlands, same-sex marriage.
 The Netherlands has multiple music traditions. Traditional Dutch music is a genre known as "Levenslied", meaning ''Song of life'', to an extent comparable to a French Chanson or a German Schlager music, Schlager. These songs typically have a simple melody and rhythm, and a straightforward structure of verses and choruses. Themes can be light, but are often sentimental and include love, death and loneliness. Traditional musical instruments such as the accordion and the barrel organ are a staple of levenslied music, though in recent years many artists also use synthesisers and guitars. Artists in this genre include Jan Smit (singer), Jan Smit, Frans Bauer and André Hazes.
Contemporary Dutch Rock music, rock and pop music (Nederpop) originated in the 1960s, heavily influenced by popular music from the United States and United Kingdom, Britain. In the 1960s and 1970s the lyrics were mostly in English, and some tracks were instrumental. Bands such as Shocking Blue, Golden Earring, Tee Set, George Baker Selection and Focus (band), Focus enjoyed international success. From the 1980s, more and more pop musicians started working in the Dutch language, partly inspired by the huge success of the band Doe Maar. Today Dutch rock and pop music thrives in both languages, with some artists recording in both.
Current symphonic metal bands Epica (band), Epica, Delain, ReVamp, The Gathering (band), The Gathering, Asrai, Autumn, Ayreon and Within Temptation as well as jazz and pop singer Caro Emerald are having international success. Also, metal bands like Hail of Bullets, God Dethroned, Izegrim, Asphyx, Textures (band), Textures, Present Danger, Heidevolk and Slechtvalk are popular guests at the biggest metal festivals in Europe. Contemporary local stars include pop singer Anouk (singer), Anouk, country pop singer Ilse DeLange, South Guelderish and
The Netherlands has multiple music traditions. Traditional Dutch music is a genre known as "Levenslied", meaning ''Song of life'', to an extent comparable to a French Chanson or a German Schlager music, Schlager. These songs typically have a simple melody and rhythm, and a straightforward structure of verses and choruses. Themes can be light, but are often sentimental and include love, death and loneliness. Traditional musical instruments such as the accordion and the barrel organ are a staple of levenslied music, though in recent years many artists also use synthesisers and guitars. Artists in this genre include Jan Smit (singer), Jan Smit, Frans Bauer and André Hazes.
Contemporary Dutch Rock music, rock and pop music (Nederpop) originated in the 1960s, heavily influenced by popular music from the United States and United Kingdom, Britain. In the 1960s and 1970s the lyrics were mostly in English, and some tracks were instrumental. Bands such as Shocking Blue, Golden Earring, Tee Set, George Baker Selection and Focus (band), Focus enjoyed international success. From the 1980s, more and more pop musicians started working in the Dutch language, partly inspired by the huge success of the band Doe Maar. Today Dutch rock and pop music thrives in both languages, with some artists recording in both.
Current symphonic metal bands Epica (band), Epica, Delain, ReVamp, The Gathering (band), The Gathering, Asrai, Autumn, Ayreon and Within Temptation as well as jazz and pop singer Caro Emerald are having international success. Also, metal bands like Hail of Bullets, God Dethroned, Izegrim, Asphyx, Textures (band), Textures, Present Danger, Heidevolk and Slechtvalk are popular guests at the biggest metal festivals in Europe. Contemporary local stars include pop singer Anouk (singer), Anouk, country pop singer Ilse DeLange, South Guelderish and  Approximately 4.5 million of the 16.8 million people in the Netherlands are registered in one of the 35,000 sports clubs in the country. About two-thirds of the population between 15 and 75 participate in sports weekly. Association football, Football is the most popular team sport in the Netherlands, followed by field hockey and volleyball. Tennis, gymnastics and golf are the three most widely engaged in individual sports. Organisation of sports began at the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century. Federations for sports were established, rules were unified and sports clubs came into existence. A NOC*NSF, Dutch National Olympic Committee was established in 1912.
The Netherlands national football team, national football team was runner-up in the FIFA World Cup, World Cup of 1974, 1978, and 2010, and won the UEFA European Championship, European Championship of 1988. Of Sports Illustrated, SI's 50 greatest footballers of all time, Johan Cruyff (#5), Marco van Basten (#19), Ruud Gullit (#25), and Johan Neeskens (#36) are Dutch. The Netherlands women's national football team, women's national team was runner-up in 2019 FIFA Women's World Cup, 2019 World Cup and won the European Championship of 2017. The Netherlands women's national field hockey team, Netherlands women's field hockey team won 9 out of 15 Women's Hockey World Cup, World Cups. The Netherlands national baseball team, Netherlands baseball team have won the European Baseball Championship, European championship 24 times out of 33 events. The Netherlands women's national volleyball team, volleyball national women's team won the 1995 Women's European Volleyball Championship, European Championship in 1995 and the 2007 FIVB Volleyball World Grand Prix, World Grand Prix in 2007.
The Netherlands has won 266 medals at the Summer Olympic Games and another 110 medals at the Winter Olympic Games. Joop Zoetemelk won the 1979 Vuelta a Espana, the 1980 Tour de France, and the 1985 UCI World Championship. Jan Janssen won the 1968 Tour de France, Tom Dumoulin the 2017 Giro d'Italia. Max Verstappen, the youngest Formula 1 driver to make his debut and to win a race, was the 2016 Spanish Grand Prix, first Dutchman to win a Grand Prix and a 2021 Abu Dhabi Grand Prix, Formula One World Drivers Championship. Dutch K-1 Kickboxing, kickboxers have won the K-1 World Grand Prix 15 times out of 19 tournaments.
Approximately 4.5 million of the 16.8 million people in the Netherlands are registered in one of the 35,000 sports clubs in the country. About two-thirds of the population between 15 and 75 participate in sports weekly. Association football, Football is the most popular team sport in the Netherlands, followed by field hockey and volleyball. Tennis, gymnastics and golf are the three most widely engaged in individual sports. Organisation of sports began at the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century. Federations for sports were established, rules were unified and sports clubs came into existence. A NOC*NSF, Dutch National Olympic Committee was established in 1912.
The Netherlands national football team, national football team was runner-up in the FIFA World Cup, World Cup of 1974, 1978, and 2010, and won the UEFA European Championship, European Championship of 1988. Of Sports Illustrated, SI's 50 greatest footballers of all time, Johan Cruyff (#5), Marco van Basten (#19), Ruud Gullit (#25), and Johan Neeskens (#36) are Dutch. The Netherlands women's national football team, women's national team was runner-up in 2019 FIFA Women's World Cup, 2019 World Cup and won the European Championship of 2017. The Netherlands women's national field hockey team, Netherlands women's field hockey team won 9 out of 15 Women's Hockey World Cup, World Cups. The Netherlands national baseball team, Netherlands baseball team have won the European Baseball Championship, European championship 24 times out of 33 events. The Netherlands women's national volleyball team, volleyball national women's team won the 1995 Women's European Volleyball Championship, European Championship in 1995 and the 2007 FIVB Volleyball World Grand Prix, World Grand Prix in 2007.
The Netherlands has won 266 medals at the Summer Olympic Games and another 110 medals at the Winter Olympic Games. Joop Zoetemelk won the 1979 Vuelta a Espana, the 1980 Tour de France, and the 1985 UCI World Championship. Jan Janssen won the 1968 Tour de France, Tom Dumoulin the 2017 Giro d'Italia. Max Verstappen, the youngest Formula 1 driver to make his debut and to win a race, was the 2016 Spanish Grand Prix, first Dutchman to win a Grand Prix and a 2021 Abu Dhabi Grand Prix, Formula One World Drivers Championship. Dutch K-1 Kickboxing, kickboxers have won the K-1 World Grand Prix 15 times out of 19 tournaments.