Pylos (, ; el, Πύλος), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former
municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
in
Messenia
Messenia or Messinia ( ; el, Μεσσηνία ) is a regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') in the southwestern part of the Peloponnese region, in Greece. Until the implementation of the Kallikratis plan on 1 January 2011, Messenia was a ...
,
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
,
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the municipality
Pylos-Nestoras
Pylos-Nestoras ( el, Δήμος Πύλου - Νέστορος) is a municipality in the Messenia regional unit, Peloponnese, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Pylos. The municipality has an area of 554.265 km2.
Municipality
The mun ...
, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit.
It was the capital of the former
Pylia Province. It is the main harbour on the Bay of Navarino. Nearby villages include
Gialova
Gialova (Greek: Γιάλοβα) is a village on Navarino Bay in the municipality of Pylos-Nestor in the regional unit of Messenia in the south-west Peloponnese, Greece, about six kilometres north of Pylos. The name derives from Greek γιαλός ...
, Pyla, Elaiofyto, Schinolakka, and Palaionero. The town of Pylos has 2,345 inhabitants, the municipal unit of Pylos 5,287 (2011).
The municipal unit has an area of 143.911 km
2.
Pylos has been inhabited since
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
times. It was a significant kingdom in
Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in ...
, with remains of the so-called "
Palace of Nestor
The Palace of Nestor (Modern Greek: Ανάκτορο του Νέστορα) was an important centre in Mycenaean times, and described in Homer's ''Odyssey'' and ''Iliad'' as Nestor's kingdom of "sandy Pylos".
The palace featured in the story of ...
" excavated nearby, named after
Nestor, the king of Pylos in
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
's ''
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
''. In
Classical times
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, the site was uninhabited, but became the site of the
Battle of Pylos
The naval Battle of Pylos took place in 425 BC during the Peloponnesian War at the peninsula of Pylos, on the present-day Bay of Navarino in Messenia, and was an Athenian victory over Sparta. An Athenian fleet had been driven ashore at Pylos b ...
in 425 BC, during the
Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
. After that, Pylos is scarcely mentioned until the 13th century, when it became part of the
Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
Principality of Achaea
The Principality of Achaea () or Principality of Morea was one of the three vassal states of the Latin Empire, which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom o ...
. Increasingly known by its French name of ''Port-de-Jonc'' or its Italian name ''Navarino'', in the 1280s the Franks built the
Old Navarino castle
The Old Navarino castle ( el, Παλαιό Ναυαρίνο) is a 13th-century Frankish fortress near Pylos, Greece. It is one of two castles guarding the strategic bay on which it sits; the other is the Ottoman-built New Navarino fortress. In ju ...
on the site. Pylos came under the control of the
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
from 1417 until 1500, when it was conquered by the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. The Ottomans used Pylos and its bay as a naval base, and built the
New Navarino fortress
The fortress of New Navarino ( el, Νέο Ναυαρίνο; Ottoman Turkish: ''Anavarin-i cedid'') is an Ottoman fortification near Pylos, Greece. It is one of two castles guarding the strategic Bay of Pylos, on which it sits; New Navarino is lo ...
there. The area remained under Ottoman control, with the exception of a brief period of
renewed Venetian rule in 1685–1715 and a Russian occupation in 1770–71, until the outbreak of the
Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
in 1821.
Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt
Ibrahim Pasha ( tr, Kavalalı İbrahim Paşa; ar, إبراهيم باشا ''Ibrāhīm Bāshā''; 1789 – 10 November 1848) was an Ottoman Albanian general in the Egyptian army and the eldest son of Muhammad Ali, the Wāli and unrecognised ...
recovered it for the Ottomans in 1825, but the defeat of the Turco-Egyptian fleet in the 1827
Battle of Navarino
The Battle of Navarino was a naval battle fought on 20 October (O. S. 8 October) 1827, during the Greek War of Independence (1821–29), in Navarino Bay (modern Pylos), on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. Allied fo ...
and the French military intervention of the 1828
Morea expedition
The Morea expedition (french: link=no, Expédition de Morée) is the name given to the land intervention of the French Army in the PeloponneseMorea is the name of the Peloponnese region in Greece, which was mainly used from the medieval peri ...
forced Ibrahim to withdraw from the Peloponnese and confirmed Greek independence. The current city was built outside the fortress walls by the military engineers of the Morea expedition from 1829 and the name ''Pylos'' was
revived by royal decree in 1833.
Name

Pylos retained its ancient name into Byzantine times, but after the
Frankish conquest in the early 13th century, two new names appear:
* a French one, ("
Rush
Rush(es) may refer to:
Places
United States
* Rush, Colorado
* Rush, Kentucky
* Rush, New York
* Rush City, Minnesota
* Rush Creek (Kishwaukee River tributary), Illinois
* Rush Creek (Marin County, California), a stream
* Rush Creek (Mono Cou ...
Harbour") or , with some variants and derivatives: in Italian , or , in medieval Catalan , in Latin , ( or ) in Greek, etc. It takes that name from the marshes surrounding the place.
* a Greek one, (), later shortened to () or lengthened to () by
epenthesis
In phonology, epenthesis (; Greek ) means the addition of one or more sounds to a word, especially in the beginning syllable ('' prothesis'') or in the ending syllable (''paragoge'') or in-between two syllabic sounds in a word. The word ''epenth ...
, which became in Italian (probably by
rebracketing
Rebracketing (also known as resegmentation or metanalysis) is a process in historical linguistics where a word originally derived from one set of morphemes is broken down or bracketed into a different set. For example, ''hamburger'', originally ...
) and in French.
Its etymology is not certain. A traditional etymology, proposed by the early 15th-century traveller
Nompar de Caumont and repeated as late as the works of
Karl Hopf Karl Hopf may refer to:
* Karl Hopf (historian)
Karl Hopf (Hamm, Westphalia, February 19, 1832 – Wiesbaden, August 23, 1873) or Carl Hermann Friedrich Johann Hopf was a historian and an expert in Medieval Greece, both Byzantine and Frankish.
...
, ascribed the name to the
Navarrese Company
The Navarrese Company ( es, Compañía navarra; eu, Nafarroako konpainia) was a company of mercenaries, mostly from Navarre and Gascony, which fought in Greece during the late 14th century and early 15th century, in the twilight of Frankish power ...
, but that is clearly an error since the name was in use long before the Navarrese presence in Greece. In 1830,
Fallmereyer proposed that it could originate from a body of
Avars who settled there, a view adopted by a few later scholars like
William Miller. Modern scholarship, on the other hand, considers it more likely that it originates from a
Slavic name meaning "place of
maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http ...
s".
The name of /, although in use before the Frankish period, came into widespread use and eclipsed the French name of and its derivations only in the 15th century, after the collapse of the Frankish
Principality of Achaea
The Principality of Achaea () or Principality of Morea was one of the three vassal states of the Latin Empire, which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom o ...
.
In the late 14th or early 15th century, when it was held by the
Navarrese Company
The Navarrese Company ( es, Compañía navarra; eu, Nafarroako konpainia) was a company of mercenaries, mostly from Navarre and Gascony, which fought in Greece during the late 14th century and early 15th century, in the twilight of Frankish power ...
, it was also known as , and called (, "village of the Spaniards") by the local Greeks.
Under
Ottoman rule (1498–1685, 1715–1821), the Turkish name was (). After the construction of the new Ottoman fortress () in 1571/2, it became known as ( or , "new castle") among the local Greeks, while the old Frankish castle became known as ( or , "old castle").
History
Neolithic Pylos
The region of Pylos has a long history, which goes hand in hand with that of Peloponnese. It starts in the depths of prehistory, as the region has been inhabited since the
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
, when populations from
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
began to spread in the Balkans and Greece around 6500 BC, bringing with them the practice of agriculture and farming. Excavations have demonstrated a continuous human presence from the Late Neolithic period (5300 BC) on several sites of
Pylia
Pylia ( el, Πυλία) was one of the provinces of the Messenia Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipality Pylos-Nestor (except for the municipal unit Nestoras) and the municipal units Aipeia
Aipeia ( el, Α� ...
, in particular in those of
''Voidokilia'' and of ''Nestor's'' ''cave'', where numerous
ostraca
An ostracon (Greek language, Greek: ''ostrakon'', plural ''ostraka'') is a piece of pottery, usually broken off from a vase or other earthenware vessel. In an archaeology, archaeological or epigraphy, epigraphical context, ''ostraca'' refer ...
or fragments of painted, black and polished ceramics have been found, as well as later engraved and written pottery. The Neolithic period ended with the appearance of
bronze metallurgy around 3000 BC.
Mycenaean Pylos

During the
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
(3000–1000 BC), the
Mycenaean civilization
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
developed, particularly in Peloponnese. Pylos then became the capital of one of the most important human centers of this civilization and of a powerful kingdom, often referred to as
Nestor's kingdom of "sandy Pylos" (''ἠμαθόεις'') and described later by
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
in both his ''
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odysse ...
'' and his ''
Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek Epic poetry, epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by moder ...
'' (Book 17) when
Telemachus
Telemachus ( ; grc, Τηλέμαχος, Tēlemakhos, lit=far-fighter), in Greek mythology, is the son of Odysseus and Penelope, who is a central character in Homer's ''Odyssey''. When Telemachus reached manhood, he visited Pylos and Sparta in se ...
says:

The Mycenaean state of Pylos (1600–1200 BC) covered an area of and had a minimum population of 50,000 according to the
Linear B
Linear B was a syllabic script used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of Greek. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries. The oldest Mycenaean writing dates to about 1400 BC. It is descended from ...
tablets discovered there, or even perhaps as large as 80,000–120,000.
Jack L. Davis
Jack L. Davis (born August 13, 1950) is Carl W. Blegen Professor of Greek Archaeology at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio and is a former Director of the American School of Classical Studies at Athens.
Brief biography
Jack L. Davis has direc ...
, ''Sandy Pylos: An Archaeological History from Nestor to Navarino'', University of Texas Press 1998; Greek Translation 2004; second edition 2007). With S.E. Alcock, J. Bennet, Y. Lolos, C. Shelmerdine, and E. Zangger. It should not however be confused with the current city of Pylos. The urban center of ancient Pylos indeed remains only partially identified to date. The various archaeological remains of palaces and administrative or residential infrastructures that have been found in the region so far suggest to modern scholars that the ancient city would have developed over a much larger area, that of the
Pylia Province.
The typical point of reference for the Mycenaean city remains the
Palace of Nestor
The Palace of Nestor (Modern Greek: Ανάκτορο του Νέστορα) was an important centre in Mycenaean times, and described in Homer's ''Odyssey'' and ''Iliad'' as Nestor's kingdom of "sandy Pylos".
The palace featured in the story of ...
, but many other palaces (such as those of
Nichoria Nichoria ( el, Νιχώρια) is a site in Messenia, on a ridgetop near modern Rizomylos, at the northwestern corner of the Messenian Gulf. From the Middle to Late Bronze Age it cultivated olive and terebinth for export.Palaima (2000), p. 17. Duri ...
and
Iklaina
Iklaina ( el, Ίκλαινα) is a historic village in the municipal unit of Pylos, Messenia, Greece. The settlement, which is situated in low hills approximately northeast of Pylos, stands upon the remains of a Late Bronze Age (ca. 1600-1100 BC) ...
) or villages (such as Malthi) of the Mycenaean era have been recently discovered, which were quickly subordinated to Pylos.
Its
port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
and its
acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
were probably established on the ''Koryphasion'' promontory (or ''Cape Coryphasium'') commanding the northern entrance to the bay, 4 km north of the modern city and south of Nestor's palace, but no remains were found.

The Pylos site is located on the hill of Ano Englianos, about 9 km northeast of the bay , near the village of
Chora and about 17 kilometres from the modern city of Pylos. It hosts one of the most important Mycenaean palaces in Greece, known as the great "
Palace of Nestor
The Palace of Nestor (Modern Greek: Ανάκτορο του Νέστορα) was an important centre in Mycenaean times, and described in Homer's ''Odyssey'' and ''Iliad'' as Nestor's kingdom of "sandy Pylos".
The palace featured in the story of ...
" described in the Homeric poems. This palace remains today the best preserved palace in Greece and one of the most important of all Mycenaean civilization. It was discovered and first excavated in 1939 by American archaeologist
Carl Blegen
Carl William Blegen (January 27, 1887 – August 24, 1971) was an American archaeologist who worked at the site of Pylos in Greece and Troy in modern-day Turkey. He directed the University of Cincinnati excavations of the mound of Hisarlik, the ...
(1887–1971) of the
University of Cincinnati
The University of Cincinnati (UC or Cincinnati) is a public research university in Cincinnati, Ohio. Founded in 1819 as Cincinnati College, it is the oldest institution of higher education in Cincinnati and has an annual enrollment of over 44,00 ...
and the
American School of Classical Studies at Athens
, native_name_lang = Greek
, image = American School of Classical Studies at Athens.jpg
, image_size =
, image_alt =
, caption = The ASCSA main building as seen from Mount Lykavittos
, latin_name =
, other_name =
, former_name =
, mo ...
, and by
Konstantinos Kourouniotis
Konstantinos or Constantinos (Κωνσταντίνος, ''Konstantínos'') is a Greek language, Greek male given name.
* Konstantinos (occultist), Konstantinos (born 1972), occultist
* Kosta Barbarouses, Konstantinos "Kosta" Barbarouses (born 1 ...
(1872–1945) of the Greek archaeological service. Their excavations were interrupted by the Second World War, and then resumed in 1952 under the direction of Blegen until 1966. He found many architectural elements such as the throne room with its foyer, an anteroom, rooms and passageways all covered with
fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaste ...
es of Minoan inspiration, and also large warehouses, the external walls of the palace, unique baths, galleries, and 90 meters outside the palace, a
beehive "tholos" tomb, perfectly restored in 1957 (''Tholos tomb IV'').

In addition to the archaeological remains of the palace, Blegen also found there thousands of clay tablets with inscriptions written in
Linear B
Linear B was a syllabic script used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of Greek. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries. The oldest Mycenaean writing dates to about 1400 BC. It is descended from ...
, a
syllabic script used between 1425 and 1200 BC for writing
Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the most ancient attested form of the Greek language, on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC), before the hypothesised Dorian invasion, often cited as the ''terminus ad quem'' for the ...
. Pylos is the largest source in Greece of these tablets with 1,087 fragments found on the site of the Nestor's Palace. In 1952, when self-taught linguist
Michael Ventris
Michael George Francis Ventris, (; 12 July 1922 – 6 September 1956) was an English architect, classicist and philologist who deciphered Linear B, the ancient Mycenaean Greek script. A student of languages, Ventris had pursued deciphermen ...
and
John Chadwick
John Chadwick, (21 May 1920 – 24 November 1998) was an English linguist and classical scholar who was most notable for the decipherment, with Michael Ventris, of Linear B.
Early life, education and wartime service
John Chadwick was born at ...
deciphered the script, Mycenaean Greek turned out to be the earliest
attested form of
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, some elements of which have survived in the language of Homer thanks to a long oral tradition of epic poetry. Thus, these clay tablets, generally used for administrative purposes or for recording economic transactions, clearly demonstrate that the site itself was already called "Pylos" by its Mycenaean inhabitants (''Pulos'' in Mycenaean Greek; attested in Linear B as


''pu-ro,'' ).

In 2015, the team of American archaeologists
Sharon Stocker
Sharon (Shari) Stocker is an American archaeologist who is best known, along with her husband, archaeologist Jack L. Davis, for leading an international team of researchers who discovered a previously undisturbed tomb of a Bronze Age warrior in ...
and
Jack L. Davis
Jack L. Davis (born August 13, 1950) is Carl W. Blegen Professor of Greek Archaeology at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio and is a former Director of the American School of Classical Studies at Athens.
Brief biography
Jack L. Davis has direc ...
of the
University of Cincinnati
The University of Cincinnati (UC or Cincinnati) is a public research university in Cincinnati, Ohio. Founded in 1819 as Cincinnati College, it is the oldest institution of higher education in Cincinnati and has an annual enrollment of over 44,00 ...
and under the aegis of the
American School of Classical Studies at Athens
, native_name_lang = Greek
, image = American School of Classical Studies at Athens.jpg
, image_size =
, image_alt =
, caption = The ASCSA main building as seen from Mount Lykavittos
, latin_name =
, other_name =
, former_name =
, mo ...
, discovered near the ''Tholos tomb IV'', a
shaft tomb
A shaft tomb or shaft grave is a type of deep rectangular burial structure, similar in shape to the much shallower cist grave, containing a floor of pebbles, walls of rubble masonry, and a roof constructed of wooden planks.
Practice
The practi ...
(non-tholos) dated to the
Late Helladic IIA (LHIIA, 1600–1470 BC), of an individual of 30–35 years old and 1.70 m tall, the "Griffin warrior", named for the mythological creature, part eagle, part lion, engraved on an ivory plaque in his tomb. The tomb also contained armor, weapons, mirror and many pearl and gold jewels, including several gold signet rings of exceptional craftsmanship and thoroughness. Researchers believe it could be the grave of a
Wanax
(Greek: ; from earlier , ') is an ancient Greek word for "tribal chief, lord, (military) leader".. It is one of the two Greek titles traditionally translated as "king", the other being basileus, and is inherited from Mycenaean Greece. It is nota ...
, a tribal king, lord or military leader during the Mycenaean era. It was also in this tomb that was found the
Pylos Combat Agate
The Pylos Combat Agate is a Minoan sealstone of the Mycenaean era, likely manufactured in Late Minoan Crete. It depicts two warriors engaged in hand-to-hand combat, with a third warrior lying on the ground. It was discovered in the Griffin Warri ...
, a seal made of
agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Ancie ...
dated from around 1450 BCE, which represents a warrior engaged in a hand-to-hand combat.
In 2017, the same team discovered two other exceptional tholos tombs, ''Tholos tombs VI and VII''. Although their domes had collapsed, they discovered that they were littered with flakes of gold leaf that once papered the walls and found a multitude of cultural artifacts and delicate jewelry, including a gold pendant representing the head of the Egyptian goddess
Hathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky ...
, which showed for the first time that Pylos clearly had trade relations with Egypt and the Middle East around 1500 BCE.
[Rory Sullivan and Elinda Labropoulou]
Archaeologists uncover treasure-filled 'princely' tombs in Greece
cnn.com, 18 December 2019.[Archaeologists find Bronze Age tombs lined with gold](_blank)
heritagedaily.com, 18 December 2019.
Pylos was the only palace of that time to have no walls or fortifications. It was destroyed by fire around 1180 BC and many clay tablets in linear B clearly bear the stigmata of the fire. The Linear B archives found there, preserved by the heat of the fire that destroyed the palace, mention hasty defence preparations due to an imminent attack without giving any detail about the attacking force. The site of the Mycenaean Pylos then seems to have been abandoned during the
Dark Ages (1100–800 BC). The region of Pylos, together with that of the
ancient Messene, was later enslaved by
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
.
The ruins of a crude stone fortress on nearby
Sphacteria
Sphacteria ( el, Σφακτηρία - ''Sfaktiria'') also known as Sphagia (Σφαγία) is a small island at the entrance to the bay of Pylos in the Peloponnese, Greece. It was the site of three battles:
*the 425 BC Battle of Sphacteria in the ...
, apparently of Mycenaean origin, were used by the
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
ns during the
Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
. (Thucydides iv. 31)
Classical Pylos
It was one of the last places which held out against the Spartans in the
Second Messenian War
The Second Messenian War was a war which occurred ca. 660–650 BC between the Ancient Greek states of Messenia and Sparta, with localized resistance possibly lasting until the end of the century. It started around 40 years after the end of the Fi ...
, after which the inhabitants emigrated to
Cyllene, and from there, with the other
Messenians
Messenia or Messinia ( el, Μεσσηνία) was an ancient district of the southwestern Peloponnese, more or less overlapping the modern Messenia region of Greece. To the north it had a border with Elis along the Neda river. From there the borde ...
, to
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
. Its name is mentioned again in the seventh year of the Peloponnesian War. According to the Greek historian
Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of "scientifi ...
in his ''
History of the Peloponnesian War
The ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), which was fought between the Peloponnesian League (led by Sparta) and the Delian League (led by Athens). It was written by Thucydides, an ...
'', the area was "together with most of the country round, unpopulated". The ancient city was not located at the modern Pylos, but north of the isle of
Sphacteria
Sphacteria ( el, Σφακτηρία - ''Sfaktiria'') also known as Sphagia (Σφαγία) is a small island at the entrance to the bay of Pylos in the Peloponnese, Greece. It was the site of three battles:
*the 425 BC Battle of Sphacteria in the ...
. In 425 BC the
Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
politician
Cleon
Cleon (; grc-gre, Κλέων, ; died 422 BC) was an Athenian general during the Peloponnesian War. He was the first prominent representative of the commercial class in Athenian politics, although he was an aristocrat himself. He strongly advocate ...
sent an expedition to Pylos where the Athenians fortified the rocky promontory now known as Koryphasion (Κορυφάσιον) or
Old Pylos at the northern edge of the bay, near the
Gialova Lagoon
Gialova Lagoon ( el, Γιάλοβα, ) – also known as Divari, from the Latin word ''vivarium'', meaning "fishery" – is a brackish body of water in the municipality of Pylos-Nestor, Greece, about north of Pylos. The lagoon, together with Vo ...
, and after a conflict with Spartan ships in the
Battle of Pylos
The naval Battle of Pylos took place in 425 BC during the Peloponnesian War at the peninsula of Pylos, on the present-day Bay of Navarino in Messenia, and was an Athenian victory over Sparta. An Athenian fleet had been driven ashore at Pylos b ...
, seized and occupied the bay.
Demosthenes
Demosthenes (; el, Δημοσθένης, translit=Dēmosthénēs; ; 384 – 12 October 322 BC) was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual prow ...
, the Athenian commander, completed the fort in 424 BC.
The erection of this fort led to one of the most memorable events in the Peloponnesian War. Thucydides has given a minute account of the topography of the district, which, though clear and consistent with itself, does not coincide, in all points, with the existing locality, Thucydides describes the harbour, of which the promontory Coryphasium (''Koryphasion'') formed the northern termination, as fronted and protected by the island Sphacteria, which stretched along the coast, leaving only two narrow entrances to the harbour,--the one at the northern end, opposite to Coryphasium, being only wide enough to admit two triremes abreast, and the other at the southern end wide enough for eight or nine triremes. The island was about 15 stadia in width, covered with wood, uninhabited and untrodden.
Pausanias Pausanias ( el, Παυσανίας) may refer to:
*Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium''
*Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
*Pausanias of Sicily, physician of th ...
also says that the island Sphacteria lies before the harbour of Pylos like Rheneia before the anchorage of Delos. A little later the Athenians captured a number of Spartan troops besieged on the adjacent island of Sphacteria (see
Battle of Sphacteria
The Battle of Sphacteria was a land battle of the Peloponnesian War, fought in 425 BC between Athens and Sparta. Following the Battle of Pylos and subsequent peace negotiations, which failed, a number of Spartans were stranded on the island of S ...
). Spartan anxiety over the return of the prisoners, who were taken to Athens as hostages, contributed to their acceptance of the
Peace of Nicias
The Peace of Nicias was a peace treaty signed between the Greek city-states of Athens and Sparta in March 421 BC that ended the first half of the Peloponnesian War.
In 425 BC, the Spartans had lost the battles of Pylos and Sphacteria, a severe d ...
in 421 BC.
Middle Ages

Little is known of Pylos under
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
rule, except for a mention of raids by
Cretan Saracens
The Emirate of Crete ( ar, إقريطش, Iqrīṭish or , ''Iqrīṭiya''; gr, Κρήτη, Krētē) was an Islamic state that existed on the Mediterranean island of Crete from the late 820s to the reconquest of the island by the Byzantine Empir ...
in the area c. 872/3.
In the 12th century, the Muslim geographer
al-Idrisi mentioned it as the "commodious port" of ''Irūda'' in his ''Nuzhat al-Mushtaq''.
In 1204, following the
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
, the Peloponnese became the
Principality of Achaea
The Principality of Achaea () or Principality of Morea was one of the three vassal states of the Latin Empire, which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom o ...
, a
Crusader state
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political int ...
. Pylos fell quickly to the Crusaders according to a brief reference in the ''
Chronicle of the Morea
The ''Chronicle of the Morea'' ( el, Τὸ χρονικὸν τοῦ Μορέως) is a long 14th-century history text, of which four versions are extant: in French, Greek (in verse), Italian and Aragonese. More than 9,000 lines long, the ''Ch ...
'', but it is not until the 1280s that it is mentioned again. According to the French and Greek versions of the ''Chronicle'',
Nicholas II of Saint Omer
Nicholas II of Saint Omer was the lord of half of Thebes in Frankish Greece from 1258 to his death in 1294. From his two marriages he became one of the richest and most powerful barons of his time, building a splendid castle at Thebes as well as t ...
, the lord of
Thebes, who in c. 1281 received extensive lands in Messenia in exchange for his wife's possessions of
Kalamata
Kalamáta ( el, Καλαμάτα ) is the second most populous city of the Peloponnese peninsula, after Patras, in southern Greece and the largest city of the homonymous administrative region. As the capital and chief port of the Messenia reg ...
and
Chlemoutsi
Chlemoutsi ( el, Χλεμούτσι or Χλουμούτσι ''Chloumoútsi''), also known as Clermont, is a medieval castle in the northwest of the Elis regional unit in the Peloponnese peninsula of southern Greece, in the Kastro-Kyllini municip ...
, erected a
castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
at Navarino. According to the Greek version, he intended this as a future fief for his nephew,
Nicholas III, although the Aragonese version attributes the construction to Nicholas III himself, a few years later. According to A. Bon, a construction under Nicholas II in the 1280s is more likely, possibly in the period 1287–89 when he served as the viceroy (''
bailli
A bailiff (french: bailli, ) was the king's administrative representative during the ''ancien régime'' in northern France, where the bailiff was responsible for the application of justice and control of the administration and local finances in h ...
'') of Achaea.
Despite Nicholas II's intentions, however, it is unclear whether his nephew did indeed inherit Navarino. If he did, it remained his until his death in 1317, when it and all the Messenian lands of the family reverted to the princely domain, as Nicholas III had no children.
The fortress remained relatively unimportant thereafter, except for the
naval battle
Naval warfare is combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river. Mankind has fought battles on the sea for more than 3,000 years. Even in the interior of large lan ...
in 1354 between
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
and
Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the List of cities in Italy, sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian ce ...
,
and an episode in 1364, during the conflict between
Mary of Bourbon
Mary of Bourbon or Marie de Bourbon (29 October 1515 – 28 September 1538) was a daughter of Charles, Duke of Vendôme, and Françoise d'Alençon, daughter of René, Duke of Alençon. Mary was the subject of marriage negotiations of James V of ...
and the Prince
Philip of Taranto, due to Mary's attempt to claim the Principality following the death of her husband,
Robert of Taranto
Robert II of Taranto (1319 or early winter 1326 – 10 September 1364Peter Lock, ''The Franks in the Aegean: 1204-1500'', (Routledge, 1988), 129.), of the Capetian House of Anjou, Angevin family, Principality of Taranto, Prince of Taranto (1331 ...
. Mary had been given possession of Navarino (along with Kalamata and
Mani
Mani may refer to:
Geography
* Maní, Casanare, a town and municipality in Casanare Department, Colombia
* Mani, Chad, a town and sub-prefecture in Chad
* Mani, Evros, a village in northeastern Greece
* Mani, Karnataka, a village in Dakshi ...
) by Robert in 1358, and the local
castellan
A castellan is the title used in Medieval Europe for an appointed official, a governor of a castle and its surrounding territory referred to as the castellany. The title of ''governor'' is retained in the English prison system, as a remnant o ...
, loyal to Mary, briefly imprisoned the new Prince's ''bailli'', Simon del Poggio. Mary retained control of Navarino until her death in 1377. At about this time,
Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Se ...
settled in the area, while in 1381/2, Navarrese, Gascon and Italian mercenaries were active there.
From the early years of the 15th century, Venice set its eyes on the fortress of Navarino, fearing lest its rivals the Genoese seize it and use it as a base for attacks against the Venetian outposts of
Modon and
Coron. In the event, the Venetians seized the fortress themselves in 1417 and, after prolonged diplomatic manoeuvring, succeeded in legitimizing their new possession in 1423.
First Venetian and first Ottoman periods

In 1423, Navarino, like the rest of the Peloponnese, suffered its first Ottoman raid, led by
Turakhan Bey
Turahan Bey or Turakhan Beg ( tr, Turahan Bey/Beğ; sq, Turhan Bej; el, Τουραχάνης, Τουραχάν μπέης or Τουραχάμπεης;PLP 29165 died in 1456) was a prominent Ottoman military commander and governor of Thessaly ...
, which was repeated in 1452.
It was also at Navarino that Emperor
John VIII Palaiologos
John VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( gr, Ἰωάννης Παλαιολόγος, Iōánnēs Palaiológos; 18 December 1392 – 31 October 1448) was the penultimate Byzantine emperor, ruling from 1425 to 1448.
Biography
John VIII was ...
embarked in 1437, heading for the
Council of Ferrara
The Council of Florence is the seventeenth ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held between 1431 and 1449. It was convoked as the Council of Basel by Pope Martin V shortly before his death in February 1431 and took place in ...
, and where the last
Despot of the Morea
The Despotate of the Morea ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μορέως) or Despotate of Mystras ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μυστρᾶ) was a province of the Byzantine Empire which existed between the mid-14th and mid-15th centu ...
,
Thomas Palaiologos
Thomas Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, Θωμᾶς Παλαιολόγος; 1409 – 12 May 1465) was Despot of the Morea from 1428 until the fall of the despotate in 1460, although he continued to claim the title until his death five years late ...
, embarked with his family in 1460, following the Ottoman conquest of the Despotate of the Morea.
After 1460, the fortress, along with the other Venetian outposts and
Monemvasia
Monemvasia ( el, Μονεμβασιά, Μονεμβασία, or ) is a town and municipality in Laconia, Greece. The town is located on a small island off the east coast of the Peloponnese, surrounded by the Myrtoan Sea. The island is connected t ...
and the
Mani Peninsula
The Mani Peninsula ( el, Μάνη, Mánē), also long known by its medieval name Maina or Maïna (Μαΐνη), is a geographical and cultural region in Southern Greece that is home to the Maniots (Mανιάτες, ''Maniátes'' in Greek), who cla ...
, were the only Christian-held areas in the peninsula.
Venetian control over Navarino survived the
First Ottoman–Venetian War
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
(1463–79), but not the
Second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
(1499–1503): following the Venetian defeat in the
Battle of Modon in August 1500, the 3,000-strong garrison surrendered, although it was well provisioned for a siege. The Venetians recaptured it shortly after, on 3/4 December, but on 20 May 1501, a joint Ottoman land and sea attack under
Kemal Reis
Kemal Reis (c. 1451 – 1511) was an Ottoman and Turkish privateer and admiral. He was also the paternal uncle of the famous Ottoman admiral and cartographer Piri Reis, who accompanied him in most of his important naval expeditions.
Backgroun ...
and
Hadım Ali Pasha
Hadım Ali Pasha (Turkish: ''Hadım Ali Paşa''; died July 1511), also known as Atik Ali Pasha (Turkish: ''Atik Ali Paşa''), was an Ottoman statesman and eunuch (''hadım'' means "eunuch" in Turkish) of Bosnian origin. He served as governor of ...
retook it.

The Ottomans used Navarino (which they called ''Anavarin'' or ''Avarna'') as a naval base, either for piratical raids or for major fleet operations in the Ionian and Adriatic seas.
In 1572/3, the Ottoman chief admiral (''
Kapudan Pasha
The Kapudan Pasha ( ota, قپودان پاشا, modern Turkish: ), was the Grand Admiral of the navy of the Ottoman Empire. He was also known as the ( ota, قپودان دریا, links=no, modern: , "Captain of the Sea"). Typically, he was based ...
'')
Uluç Ali Reis
Occhiali (Giovanni Dionigi Galeni or ''Giovan Dionigi Galeni'', also ''Uluj Ali'', tr, Uluç Ali ''Reis'', later ''Uluç Ali Paşa'' and finally Kılıç Ali Paşa; 1519 – 21 June 1587) was an Italian farmer, then Ottoman privateer and ...
built a
new fortress
The New Fortress of Corfu ( gr, Νέο Φρούριο; ) is a Venetian fortress built on the hill of St. Mark in Corfu in stages. The original architect of the fort was the military engineer Ferrante Vitelli. The current buildings which exist w ...
at Navarino (''Anavarin-i Cedid'', "New Navarino", or ''Neokastro'' in Greek), to replace the outdated Frankish castle.
The Venetians briefly captured Navarino in the 1650s during the
Cretan War.
In 1668,
Evliya Çelebi
Derviş Mehmed Zillî (25 March 1611 – 1682), known as Evliya Çelebi ( ota, اوليا چلبى), was an Ottoman explorer who travelled through the territory of the Ottoman Empire and neighboring lands over a period of forty years, recording ...
described the city in his ''
Seyahatname'':
Anavarin-i Atik is an unequalled castle... the harbor is a safe anchorage...
in most streets of Anavarin-i Cedid there are many fountains of running water... The city is embellished with trees and vines so that the sun does not beat into the fine marketplace at all, and
all the city notables sit here, playing backgammon, chess, various kinds of draughts, and other board games....
Second Venetian period and Ottoman reconquest
In 1685, during the early stages of the
Morean War
The Morean War ( it, Guerra di Morea), also known as the Sixth Ottoman–Venetian War, was fought between 1684–1699 as part of the wider conflict known as the "Great Turkish War", between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire. Military ...
, the Venetians under
Francesco Morosini
Francesco Morosini (26 February 1619 – 16 January 1694) was the Doge of Venice from 1688 to 1694, at the height of the Great Turkish War. He was one of the many Doges and generals produced by the noble Venetian family of Morosini.Encyclopæd ...
and
Otto Wilhelm Königsmarck
Count Otto Wilhelm Königsmarck (5 January 1639 – 5 September 1688) was a Swedish military officer from Minden. He attained the rank of field marshal in 1676, commanded the Battle of Stralsund (1678), and became Governor General for Swedish ...
invaded the Peloponnese and captured most of it, successfully storming the two fortresses of Navarino in the process. With the peninsula safely in Venetian hands, Navarino became an administrative centre in the new "
Kingdom of the Morea
The Kingdom of the Morea or Realm of the Morea ( it, Regno di Morea) was the official name the Republic of Venice gave to the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece (which was more widely known as the Morea until the 19th century) when it was c ...
", as the Venetian province was called, until 1715, when the Ottomans
recovered the Peloponnese.
The Venetian census of 1689 gave the population as 1,413, while twenty years later it had risen to 1,797 inhabitants.
After the Ottoman reconquest, Navarino became the centre of a ''
kaza
A kaza (, , , plural: , , ; ota, قضا, script=Arab, (; meaning 'borough')
* bg, околия (; meaning 'district'); also Кааза
* el, υποδιοίκησις () or (, which means 'borough' or 'municipality'); also ()
* lad, kaza
, ...
'' in the
Sanjak of the Morea
The Eyalet of the Morea ( ota, ایالت موره; Eyālet-i Mōrâ) was a first-level province (''eyalet'') of the Ottoman Empire, centred on the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece.
History
From the Ottoman conquest to the 17th century ...
.
On 10 April 1770, after a six-day siege, the fortress of New Navarino surrendered to the Russians during the
Orlov Revolt. The Ottoman garrison was allowed to depart for Crete, while the Russians repaired the fortress to make it their base. On 1 June, however, the Russians left, and the Ottomans re-entered the fort and burned and partially demolished it.
Meanwhile, the population gathered there had escaped to nearby Sphacteria, where Albanian mercenaries of the Ottomans slaughtered most of them.
The Greek War of Independence of 1821

After the outbreak of the
Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
against the Ottoman occupation in mid-March 1821, the Greeks quickly won many victories and proclaimed their independence on 1 January 1822. Navarino was besieged by the local Greeks on 29 March. The garrison, augmented by the local Muslim population of
Kyparissia
Kyparissia ( el, Κυπαρισσία) is a town and a former municipality in northwestern Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Trifylia, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. ...
, held out until the first week of August, when they were forced to capitulate. Despite their promise for safe conduct, the Greeks
massacred
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
them all.
The Greek victories was short lived. The Sultan called for aid from his Egyptian vassal
Muhammad Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and activist. Nicknamed "The Greatest", he is regarded as one of the most significant sports figures of the 20th century, a ...
, who dispatched his son
Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt
Ibrahim Pasha ( tr, Kavalalı İbrahim Paşa; ar, إبراهيم باشا ''Ibrāhīm Bāshā''; 1789 – 10 November 1848) was an Ottoman Albanian general in the Egyptian army and the eldest son of Muhammad Ali, the Wāli and unrecognised ...
to Greece with a fleet and 8,000 men, and later added 25,000 troops.
[''An Index of events in the military history of the Greek nation.'', Hellenic Army General Staff, Army History Directorate, Athens, 1998, pp. 51 and 54. ] Ibrahim's intervention proved decisive: the region of Pylos fell on 18 May 1825 after the battles of
Sphacteria
Sphacteria ( el, Σφακτηρία - ''Sfaktiria'') also known as Sphagia (Σφαγία) is a small island at the entrance to the bay of Pylos in the Peloponnese, Greece. It was the site of three battles:
*the 425 BC Battle of Sphacteria in the ...
(8 May) and
Neokastro (11 May), much of the
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
was reconquered in 1825; the gateway town of
Messolonghi
Missolonghi or Messolonghi ( el, Μεσολόγγι, ) is a municipality of 34,416 people (according to the 2011 census) in western Greece. The town is the capital of Aetolia-Acarnania regional unit, and the seat of the municipality of Iera Polis ...
fell in 1826; and Athens was taken in 1827. The only territory still held by Greek nationalists was in
Nafplion
Nafplio ( ell, Ναύπλιο) is a coastal city located in the Peloponnese in Greece and it is the capital of the regional unit of Argolis and an important touristic destination. Founded in antiquity, the city became an important seaport in the ...
,
Mani
Mani may refer to:
Geography
* Maní, Casanare, a town and municipality in Casanare Department, Colombia
* Mani, Chad, a town and sub-prefecture in Chad
* Mani, Evros, a village in northeastern Greece
* Mani, Karnataka, a village in Dakshi ...
,
Hydra
Hydra generally refers to:
* Lernaean Hydra, a many-headed serpent in Greek mythology
* ''Hydra'' (genus), a genus of simple freshwater animals belonging to the phylum Cnidaria
Hydra or The Hydra may also refer to:
Astronomy
* Hydra (constel ...
,
Spetses
Spetses ( el, Σπέτσες, grc, Πιτυούσσα "Pityussa", Arvanitika: Πετσε̱) is an upscale affluent island in Attica, Greece. It is included as one of the Saronic Islands. Until 1948, it was part of the old prefecture of Argolis ...
and
Aegina
Aegina (; el, Αίγινα, ''Aígina'' ; grc, Αἴγῑνα) is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece in the Saronic Gulf, from Athens. Tradition derives the name from Aegina (mythology), Aegina, the mother of the hero Aeacus, who was born ...
.
[C. M. Woodhouse, ''The Philhellenes'', London, Hodder et Stoughton, 1969, 192 p.]
The Naval Battle of Navarino (20 October 1827)

A strong current of
philhellenism
Philhellenism ("the love of Greek culture") was an intellectual movement prominent mostly at the turn of the 19th century. It contributed to the sentiments that led Europeans such as Lord Byron and Charles Nicolas Fabvier to advocate for Greek i ...
had developed in Western Europe, especially after the fall in 1826 of Missolonghi, where the poet
Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and Peerage of the United Kingdom, peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and h ...
had died in 1824. Many artists and intellectuals like
Chateaubriand,
Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
,
Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
,
Gioachino Rossini
Gioachino Antonio Rossini (29 February 1792 – 13 November 1868) was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces, and some sacred music. He set new standards f ...
,
Hector Berlioz
In Greek mythology, Hector (; grc, Ἕκτωρ, Hektōr, label=none, ) is a character in Homer's Iliad. He was a Trojan prince and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. Hector led the Trojans and their allies in the defense o ...
or
Eugène Delacroix
Ferdinand Victor Eugène Delacroix ( , ; 26 April 1798 – 13 August 1863) was a French Romantic artist regarded from the outset of his career as the leader of the French Romantic school.Noon, Patrick, et al., ''Crossing the Channel: Britis ...
(in his paintings ''Scenes massacres of Scio'' in 1824, and ''Greece on the ruins of Missolonghi'' in 1826), amplified the current of sympathy for the Greek cause in the public opinion. By the
Treaty of London of July 1827, France, Russia and the United Kingdom recognised the autonomy of Greece, which remained a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire. The three powers agreed to a limited intervention in order to convince the
Porte
Porte may refer to:
*Sublime Porte, the central government of the Ottoman empire
*Porte, Piedmont, a municipality in the Piedmont region of Italy
*John Cyril Porte, British/Irish aviator
*Richie Porte, Australian professional cyclist who competes ...
to accept the terms of the convention. A plan to send a naval expedition as a demonstration of force was proposed and adopted; subsequently a fleet of 27 warships of the allied navies of
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
was sent to exert diplomatic pressure against Constantinople.
It included twelve British ships (for 456 guns), seven French ships (352 guns) and eight Russian ships (490 guns), for a total firepower of nearly 1,300 guns. The
Battle of Navarino
The Battle of Navarino was a naval battle fought on 20 October (O. S. 8 October) 1827, during the Greek War of Independence (1821–29), in Navarino Bay (modern Pylos), on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. Allied fo ...
(20 October 1827) resulted in the total destruction of the combined Ottoman–Egyptian fleet (around 60 warships destroyed).
An obelisk-shaped memorial dedicated to the victory of the Allied fleets and their three admirals, the British
Edward Codrington
Sir Edward Codrington, (27 April 1770 – 28 April 1851) was a British admiral, who took part in the Battle of Trafalgar and the Battle of Navarino.
Early life and career
The youngest of three brothers born to Edward Codrington the elder (1732 ...
, the French
Henri de Rigny
Marie Henri Daniel Gauthier, comte de Rigny (; 2 February 1782 – 6 November 1835) was the commander of the French squadron at the Battle of Navarino in the Greek War of Independence.
Biography
Family
He was a nephew of Baron Joseph Domini ...
and the Russian
Lodewijk van Heiden
Lodewijk Sigismund Vincent Gustaaf Reichsgraf van Heiden (german: Ludwig Sigismund Vinzent Gustav Reichsgraf van Heyden, russian: Ло́ггин Петро́вич Ге́йден, transliterated Russian name: ''Loggin Petrovich Geyden''; 6 Septemb ...
was later erected on the central square of Pylos. The monument was the work of the sculptor Thomas Thomopoulos (1873–1937) and its unveiling took place in 1930, although it was completed in 1933.
The liberation of Pylos (6 October 1828) and the construction of the modern city
On 6 October 1828, Pylos was definitively liberated from the Ottoman–Egyptian troops of Ibrahim Pasha by the French troops of the
Morea expedition
The Morea expedition (french: link=no, Expédition de Morée) is the name given to the land intervention of the French Army in the PeloponneseMorea is the name of the Peloponnese region in Greece, which was mainly used from the medieval peri ...
commanded by
Marshal Nicolas-Joseph Maison.
[ Marshal Nicolas-Joseph Maison, ''Dépêches adressées au ministre de la Guerre Louis-Victor de Caux, vicomte de Blacquetot'', octobre 1828, in Jacques Mangeart, Supplemental Chapter of the ]
Souvenirs de la Morée: recueillis pendant le séjour des Français dans le Péloponèse
', Igonette, Paris, 1830. The mission of this expeditionary corps of 15,000 men, sent by king
Charles X of France
Charles X (born Charles Philippe, Count of Artois; 9 October 1757 – 6 November 1836) was King of France from 16 September 1824 until 2 August 1830. An uncle of the uncrowned Louis XVII and younger brother to reigning kings Louis XVI and Lou ...
to the Peloponnese between 1828 and 1833, was to implement the Treaty London of 1827, an agreement under which the Greeks would have the right to an independent state. The French troops liberated the cities of Navarino (Pylos), Modon (
Methoni), Coron (
Koroni
Koroni or Corone ( el, Κορώνη) is a town and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pylos ...
) and
Patras
)
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 =
, demographics1_info2 =
, timezone1 = EET
, utc_offset1 = +2
, ...
in October 1828.
The current city of Pylos was built starting in the spring of 1829, outside the walls of Neokastro, on the model of the
bastide
Bastides are fortified new towns built in medieval Languedoc, Gascony, Aquitaine, England and Wales during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, although some authorities count Mont-de-Marsan and Montauban, which was founded in 1144, as the f ...
s of Southwest France and the cities of the
Ionian Islands (which share common features, such as a central geometrical square bordered by covered galleries built with a succession of contiguous
arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.
Arches may be synonymous with vaul ...
es, each supported by a
colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curv ...
, as the
arcades of Pylos or
Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The isl ...
).
[ Kalogerakou Pigi P. (''Καλογεράκου Πηγή Π.''), ''The contribution of the French expeditionary force to the restoration of the fortresses and the cities of Messinia'' (]
Η συμβολή του Γαλλικού εκστρατευτικού σώματος στην αποκατάσταση των φρουρίων και των πόλεων της Μεσσηνίας
'', in Οι πολιτικοστρατιωτικές σχέσεις Ελλάδας - Γαλλίας (19ος - 20ός αι.), Directorate of the Army History (''Διεύθυνση Ιστορίας Στρατού''), 13-41, Athens, 2011. Pylos's urban framework was designed by
Joseph-Victor Audoy, lieutenant-colonel of the
military engineering
Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining lines of military transport and military communications. Military engineers are also responsible for logistics be ...
of the Morea expedition, who originated from
Tarn, a department of Southwest France. This plan was approved by the governor of independent Greece
Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (10 or 11 February 1776 – 9 October 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias ( el, Κόμης Ιωάννης Αντώνιος Καποδίστριας, Komis Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias; russian: � ...
on 15 January 1831, making it the second urban plan (after that of Methoni) in the history of the modern Greek state. The fortifications of ''Neokastro'' were raised, a barracks was built (the "Maison's building" which houses nowadays the Archaeological Museum of Pylos), many improvements were made to the city (installation of school, hospital, church, postal service, shops, bridges, squares, fountains, gardens, etc.), the old Ottoman aqueduct, which had fallen into ruins until 1828, was restored (it then served until 1907), and the road between Navarin and Modon, the first road of independent Greece (which is still used today), was also built by the French engineers.
Part of the Morea expedition were also 19 scientists from the "Morea Scientific Mission",
Jean-Baptiste Bory de Saint-Vincent
Jean-Baptiste Geneviève Marcellin Bory de Saint-Vincent was a French naturalist, officer and politician. He was born on 6 July 1778 in Agen ( Lot-et-Garonne) and died on 22 December 1846 in Paris. Biologist and geographer, he was particularly i ...
,
Relation de l'Expédition scientifique de Morée: Section des sciences physiques
', F.-G. Levrault, Paris, 1836. whose work proved essential to the ongoing development of the
new Greek State and, more broadly, marked a major milestone in the modern history of archaeology, cartography and natural sciences, as well as in the study of Greece. According to one of their population censuses in the province of Navarino in 1829, it had a total of 1,596 inhabitants.
Some French merchants and officers of the Morea expedition, who remained in the city with their families after the troops returned to France in 1833, settled in a district located in the north of the city, near a Catholic church that has since been demolished. This district is still called today "Francomahalas" (in
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: Φραγκομαχαλάς, from
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
: محلة (''
mahallah
is an Arabic word variously translated as district, quarter, ward, or "neighborhood" in many parts of the Arab world, the Balkans, Western Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and nearby nations.
History
Historically, mahallas were autonomous social ins ...
''), district) or "Francoklisa" (in
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: Φραγκοκλησά, church of the French).
The French always had a particular interest in the city, and at that time, the greatest French writers wrote texts specifically dedicated to Pylos, such as
François-René de Chateaubriand
François-René, vicomte de Chateaubriand (4 September 1768 – 4 July 1848) was a French writer, politician, diplomat and historian who had a notable influence on French literature of the nineteenth century. Descended from an old aristocrati ...
in 1806,
Eugène Sue
Marie-Joseph "Eugène" Sue (; 26 January 18043 August 1857) was a French novelist. He was one of several authors who popularized the genre of the serial novel in France with his very popular and widely imitated ''The Mysteries of Paris'', which ...
and
Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
in 1827,
Edgar Quinet
Edgar Quinet (; 17 February 180327 March 1875) was a French historian and intellectual.
Biography
Early years
Quinet was born at Bourg-en-Bresse, in the ''département'' of Ain. His father, Jérôme Quinet, had been a commissary in the army, b ...
in 1830
[Edgar Quinet (member of the scientific commission of the Morea expedition), ]
De la Grèce moderne, et de ses rapports avec l'antiquité.
', F.-G. Levrault, Paris, 1830. and
Alphonse de Lamartine
Alphonse Marie Louis de Prat de Lamartine (; 21 October 179028 February 1869), was a French author, poet, and statesman who was instrumental in the foundation of the Second Republic and the continuation of the Tricolore as the flag of France. ...
in 1832.
In 1833, after the departure of the French, the name "Pylos" (in reference to the ancient city of King Nestor) was given to the new city of Navarino by royal decree of the newly installed king
Otto I of Greece
Otto (, ; 1 June 181526 July 1867) was a Bavarian prince who ruled as King of Greece from the establishment of the monarchy on 27 May 1832, under the Convention of London, until he was deposed on 23 October 1862.
The second son of King Ludw ...
.
20th century
The fortress of Pylos was transformed into a place of deportation of political opponents during the
totalitarian regime of Metaxas between 1936 and 1941. Administratively, Pylos was the seat of the Municipality of Pylos between 1912 and 1946, then became the seat of the Deme of Pylos between 1946 and 2010. Since the 2011 reform, Pylos has been the seat of the new Municipality of
Pylos-Nestor
Pylos-Nestoras ( el, Δήμος Πύλου - Νέστορος) is a municipality in the Messenia regional unit, Peloponnese, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Pylos. The municipality has an area of 554.265 km2.
Municipality
The m ...
.
Geography
Site
The city of Pylos is located at the foot of a promontory which extends Mount Aghios Nikolaos (482 m) and carries the fortress. It is located at the south-western end of
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
, on the
Ionian coast. It is an important shipping center and, in recent years, it has experienced significant tourist development, exploiting its magnificent coastline. The narrow
island of Sphacteria serves as a natural breakwater for Navarino Bay, making the port of Pylos one of the safest anchors of the Ionian coast.
Communication
Pylos has excellent roads and all the communication amenities of a modern city.
Greek National Road 82
National Road 82 ( el, Εθνική Οδός 82, abbreviated as EO82) is a single carriageway road in southern Greece. It connects Pylos with Sparti via Kalamata. It passes through the regional units Messenia and Laconia, on the Peloponnese penin ...
departs from the center of Pylos and connects directly to
Kalamata
Kalamáta ( el, Καλαμάτα ) is the second most populous city of the Peloponnese peninsula, after Patras, in southern Greece and the largest city of the homonymous administrative region. As the capital and chief port of the Messenia reg ...
in less than an hour, and from there to
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
in two hours.
Kalamata International Airport
Kalamata International Airport ( el, Κρατικός Αερολιμένας Καλαμάτας) "Captain Vassilis Constantakopoulos" is an airport in the city of Kalamata, Greece. It mainly receives flights during the summer. In March 2013, A ...
(KLX, Captain Vassilis C. Constantakopoulos Airport), which is expanding rapidly, offers many scheduled flights to the major cities of Greece, and many charter flights during the touristic season from many international destinations.
Population
According to the census of 2011, the municipality (deme) of Pylos-Nestor has 21,077 inhabitants. The municipal unit of Pylos has 5,287 inhabitants, while Pylos intramural has 2,345 inhabitants, making it the seventh most populous city in
Messenia
Messenia or Messinia ( ; el, Μεσσηνία ) is a regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') in the southwestern part of the Peloponnese region, in Greece. Until the implementation of the Kallikratis plan on 1 January 2011, Messenia was a ...
, after the capital
Kalamata
Kalamáta ( el, Καλαμάτα ) is the second most populous city of the Peloponnese peninsula, after Patras, in southern Greece and the largest city of the homonymous administrative region. As the capital and chief port of the Messenia reg ...
(54,100),
Messini
Messini ( el, Μεσσήνη, before 1867: Νησί ''Nisi'') is a municipal unit (''dimotiki enotita'') and the seat town (''edra'') of the municipality (''dimos'') of Messini within the regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') of Messenia in th ...
(6,065),
Filiatra
Filiatra ( el, Φιλιατρά), is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Trifylia, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area ...
(5,969),
Kyparissia
Kyparissia ( el, Κυπαρισσία) is a town and a former municipality in northwestern Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Trifylia, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. ...
(5,131),
Gargalianoi
Gargalianoi ( el, Γαργαλιάνοι) is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Trifylia, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has ...
(5,007) and
Chora (3,454).
Urban landscape
Navarino castles

The city of Pylos has two castles (''Kastra''): the Frankish ''Paleokastro'' (old castle) and the Ottoman ''Neokastro'' (new castle). The first is located northwest of Navarino Bay and north of the
island of Sphacteria, while the second is southwest of the bay, on the heights of the city of Pylos. The ''Paleokastro'', located on the top of the promontory of Coryphasium ''(Koryphasion)'' (which is in geological continuity with the island of Sphacteria from which it is only separated by the narrow pass of ''Sykia''), is built on the site of the ancient acropolis of Pylos. It offers a panoramic view, stretching from the
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including C ...
to the Plain of
Pylia
Pylia ( el, Πυλία) was one of the provinces of the Messenia Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipality Pylos-Nestor (except for the municipal unit Nestoras) and the municipal units Aipeia
Aipeia ( el, Α� ...
. Below is Nestor's cave, where, according to mythology, the king of Pylos raised his oxen, and the
bay of Voidokilia, whose beach is regularly ranked among the most beautiful in the world.
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
,
'My favourite beach in the world'
' – readers' tips, Thursday 11 February 2016.The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally.
It was fo ...
,
20 last-minute holidays to empty European beaches
', by Chris Leadbeater, 9 April 2019. It borders the
Gialova lagoon
Gialova Lagoon ( el, Γιάλοβα, ) – also known as Divari, from the Latin word ''vivarium'', meaning "fishery" – is a brackish body of water in the municipality of Pylos-Nestor, Greece, about north of Pylos. The lagoon, together with Vo ...
(''Osman-aga lake''), located to the east and Navarino bay to the south. However, access to the ''Paleokastro'' may present some risks for the safety of visitors, due to its great deterioration. On the other side of the Navarino bay, the ''Neokastro'', which is in a better state of conservation, looks out onto the island of Sphacteria, the bay of Navarino, and the city. It is one of the best preserved castles in Greece. It contains within its walls the well-preserved ''Church of the Transfiguration of the Savior'', built by the Franks, later transformed into a mosque, then again into a Christian church. In the pine forest of the ''Neokastro'' is also the old barracks built by the French troops of the Morea expedition, which now houses th
new archaeological museum of Pylos
Navarino aqueduct
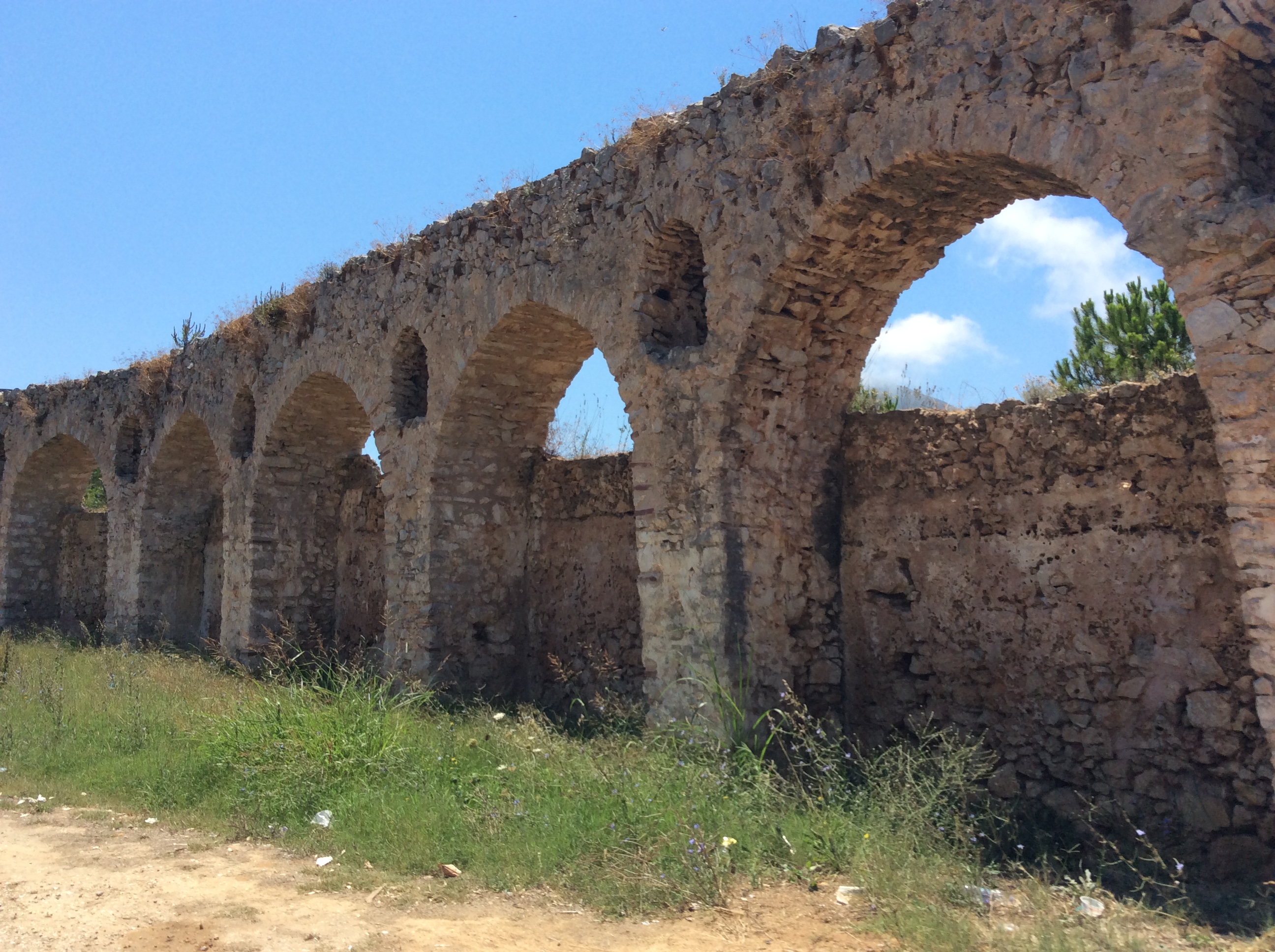

South of the city of Pylos, on the road to Methoni, is the old Navarino
aqueduct, built in the 16th century by the Ottomans to meet the water supply needs of the ''Neokastro''. Composed by two hydraulic systems, it led the waters from the water intakes of the ''plateau of Koumbeh'' (located near the town of Chandrinou about 15 kilometers northeast of Pylos on the road to Kalamata) and ''Paleo Nero'' (located near the village of Palaionero). The two systems combined into a single system that can still be seen today around Pylos in the district of ''Kamares''. Then, thanks to an underground conduit of the aqueduct, the water penetrated inside the fortress to feed there the fountains of the ''Neokastro''.' Fallen into ruins until 1828, it was restored in 1832 by the French engineers of the Morea expedition, and was used to supply Pylos with water until 1907.
Pylos city center

Leaning against two hills, one of which is overlooked by the fortress of the ''Neokastro,'' the town of Pylos faces the bay of Navarino. Pylos preserves many houses from the 19th century. These are built of stone, with typical
Messenia
Messenia or Messinia ( ; el, Μεσσηνία ) is a regional unit (''perifereiaki enotita'') in the southwestern part of the Peloponnese region, in Greece. Until the implementation of the Kallikratis plan on 1 January 2011, Messenia was a ...
n architecture and surrounded by spacious courtyards and gardens. They are built mainly between narrow streets, generally symmetrical, and according to the original urban plan established by French military engineers of the
Morea expedition
The Morea expedition (french: link=no, Expédition de Morée) is the name given to the land intervention of the French Army in the PeloponneseMorea is the name of the Peloponnese region in Greece, which was mainly used from the medieval peri ...
at the beginning of the 19th century.
Many of the streets have retained their original stone paving, and several of those which climb the hills, are pedestrianized and have steps.
Near the seafront is the
central city square, the Square of the Three Admirals, surrounded by buildings whose ground floor houses, most often under
arcade
Arcade most often refers to:
* Arcade game, a coin-operated game machine
** Arcade cabinet, housing which holds an arcade game's hardware
** Arcade system board, a standardized printed circuit board
* Amusement arcade, a place with arcade games
* ...
galleries, markets, bakeries, shops and traditional cafes. The seaside, to the north-west of the city, follows a recently
pedestrianized street which leads from the central square to the
modern port, passing through the ''Francomahalas'' district. In this street, aligned along the old port, are several traditional
fish taverns. The port is dominated by the
City Hall of Pylos. Next to it is recently renovated two-story house of the
Olympic champion Kostis Tsiklitiras, in which a museum has been installed, which exposes a collection of paintings, engravings and ancient documents collected by the French philhellene, historian and writer
René Puaux (1878–1936). A little further, still following the seaside, is the historic building of the College of Pylos which was founded in September 1921 by royal decree and built in 1924.
The Historical College of Pylos (1921–1987)
(Ιστορικό Γυμνάσιο Πύλου)'', Archaiologia.gr, 4 June 2020. In Greek. After the cessation of its activities in 1987, the building housed until very recently the Institute of Physical Astrophysics "Nestor" of the National Observatory of Greece. The institute is in charge of the international research project NESTOR and its
underwater neutrino detector, which is installed more than 4,000 meters deep, in the deepest
marine trench of the Mediterranean Sea, 31 km off Pylos. In September 1992, the historic building of the College of Pylos was classified by the Ministry of Culture as a ''Preserved Historic Monument
'' and will house soon in the near future the public library and gallery of the municipality of Pylos.
The city also has bank branches, a post office, various clinics, a health center, a fire station, a sailing school, nurseries, primary schools, a college, a high school and a music conservatory recognized by the State. The city is also home to several cultural and development associations.
The central square of the Three Admirals

Also built by French troops of the
Morea expedition
The Morea expedition (french: link=no, Expédition de Morée) is the name given to the land intervention of the French Army in the PeloponneseMorea is the name of the Peloponnese region in Greece, which was mainly used from the medieval peri ...
in 1829, the central square of Pylos is characterized by its triangular geometric pattern, one of the sides of which opens onto the sea and the port of Pylos, and whose two other sides are bordered by covered galleries with
arcades, built with a succession of contiguous
arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.
Arches may be synonymous with vaul ...
es, each supported by a
colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curv ...
, recalling the architecture of the central squares of the
bastide
Bastides are fortified new towns built in medieval Languedoc, Gascony, Aquitaine, England and Wales during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, although some authorities count Mont-de-Marsan and Montauban, which was founded in 1144, as the f ...
s of Southwest France and those of the cities of the
Ionian Islands (such as
Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The isl ...
).
These galleries are home to many small markets and businesses, as well as traditional and more modern cafes and restaurants. Most of their terraces extend over the square itself, which is shaded by several hundred-year-old
plane trees
''Platanus'' is a genus consisting of a small number of tree species native to the Northern Hemisphere. They are the sole living members of the family Platanaceae.
All mature members of ''Platanus'' are tall, reaching in height. All except f ...
. In the center, surrounded by two majestic
phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
, is a monument commemorating the
battle of Navarino
The Battle of Navarino was a naval battle fought on 20 October (O. S. 8 October) 1827, during the Greek War of Independence (1821–29), in Navarino Bay (modern Pylos), on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. Allied fo ...
, an
obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by Anc ...
dedicated to the victory of the Allied fleets and their three
admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, ...
s, the British
Edward Codrington
Sir Edward Codrington, (27 April 1770 – 28 April 1851) was a British admiral, who took part in the Battle of Trafalgar and the Battle of Navarino.
Early life and career
The youngest of three brothers born to Edward Codrington the elder (1732 ...
, the French
Henri de Rigny
Marie Henri Daniel Gauthier, comte de Rigny (; 2 February 1782 – 6 November 1835) was the commander of the French squadron at the Battle of Navarino in the Greek War of Independence.
Biography
Family
He was a nephew of Baron Joseph Domini ...
and the Russian
Lodewijk van Heiden
Lodewijk Sigismund Vincent Gustaaf Reichsgraf van Heiden (german: Ludwig Sigismund Vinzent Gustav Reichsgraf van Heyden, russian: Ло́ггин Петро́вич Ге́йден, transliterated Russian name: ''Loggin Petrovich Geyden''; 6 Septemb ...
.
Churches
On the eastern slope of Pylos hill is the Church of the Dormition of the Virgin Mary (''Ieros Naos tis Kimiseos tis Theotokou''), while to the west, inside the ''Neokastro'', is the former Church of the Transfiguration of the Savior (''Ieros Naos tis Metamorphosis tou Sotiros''), both of which belong to the Metropolis of Messenia. The Church of the Transfiguration occasionally organizes religious activities (it has been converted into a museum and exhibition center), while that of the Dormition of the Virgin Mary still gathers many faithful during its regular services, and particularly during the celebration of Easter and the Myrtidiotissa Virgin (the Virgin with
myrtles, to whom the church is dedicated) which attract many pilgrims from Athens and abroad who come to take part in processions that take place in the center of the city.
File:Pylos, Holy Assumption Church 1.jpg, The Church of the Dormition of the Virgin Mary
File:Ναός της Μεταμορφώσεως του Σωτήρος (Νιόκαστρο, Πύλος) Θέα απο το κάστρο.STG 7387-2.jpg, The Church of the Transfiguration of the Savior
The port and the marina

The port of Pylos is one of the safest boarding destinations for ships traveling in the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. Navarino Bay continues to regularly serve as a shelter for ships during storms in the Mediterranean Sea. In addition, its strategic location between the
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including C ...
and the
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek language, Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish language, Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It ...
makes it an ideal destination for an intermediate station on the route to the
Cyclades
The Cyclades (; el, Κυκλάδες, ) are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The nam ...
, the
Dodecanese Islands
The Dodecanese (, ; el, Δωδεκάνησα, ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger plus 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Turkey's Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. ...
or to
Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
. With its modern pier, it frequently welcomes many
cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports-of-call, where passengers may go on tours known as "s ...
s during the summer season. To the east of the port, there is also the
marina
A marina (from Spanish , Portuguese and Italian : ''marina'', "coast" or "shore") is a dock or basin with moorings and supplies for yachts and small boats.
A marina differs from a port in that a marina does not handle large passenger ships o ...
of Pylos, for which a project of modernization is currently running to meet the requirements for the rapid tourism development of the region.
Around Pylos
The Palace of Nestor

North of Pylos () and south of the town of
Chora (4 kilometres), is the hill of ''Ano Englianos'' which houses the Mycenaean
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
palace known as the "Palace of Nestor" (1600–1200 BC). This palace remains today in Greece the best preserved palace and one of the most important of all
Mycenaean civilization
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
. The remains of the palace consist of the throne room with its foyer, an anteroom, passageways, large warehouses, the external walls of the palace, unique baths, galleries, and 90 meters away from the palace, a
beehive tholos tomb (funerary chamber with dome) perfectly restored in 1957 (''Tholos tomb IV)''. Very recently, in 2015, the team of American archaeologists
Sharon Stocker
Sharon (Shari) Stocker is an American archaeologist who is best known, along with her husband, archaeologist Jack L. Davis, for leading an international team of researchers who discovered a previously undisturbed tomb of a Bronze Age warrior in ...
and
Jack L. Davis
Jack L. Davis (born August 13, 1950) is Carl W. Blegen Professor of Greek Archaeology at the University of Cincinnati in Ohio and is a former Director of the American School of Classical Studies at Athens.
Brief biography
Jack L. Davis has direc ...
of the
University of Cincinnati
The University of Cincinnati (UC or Cincinnati) is a public research university in Cincinnati, Ohio. Founded in 1819 as Cincinnati College, it is the oldest institution of higher education in Cincinnati and has an annual enrollment of over 44,00 ...
discovered and excavated, near the palace, the
tomb of the "Griffin Warrior", and even more recently in 2017, two other tholos tombs (''Tholos tombs VI and VII''), all three containing a multitude of cultural artifacts and jewels of exceptional delicacy (such as the
Pylos Combat Agate
The Pylos Combat Agate is a Minoan sealstone of the Mycenaean era, likely manufactured in Late Minoan Crete. It depicts two warriors engaged in hand-to-hand combat, with a third warrior lying on the ground. It was discovered in the Griffin Warri ...
or a golden pendant depicting the head of the Egyptian goddess
Hathor
Hathor ( egy, ḥwt-ḥr, lit=House of Horus, grc, Ἁθώρ , cop, ϩⲁⲑⲱⲣ, Meroitic: ) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion who played a wide variety of roles. As a sky deity, she was the mother or consort of the sky ...
, which show that Pylos had trading connections, previously unknown, with Egypt and the Near East around 1500 B.C.E).
In June 2016, the site reopened to the public after 3 years of work to replace the old roof of the 1960s with a modern structure with elevated walkways for visitors. The archaeological site of the Palace of Nestor can be visited every day, except on holidays and on Tuesdays.
[Admission days and hours on the site of the Ministry of Culture and Sports: ]
Palace of Nestor
'
File:Two Mycenaean chariot warriors on a fresco from Pylos about 1350 BC.jpg, Warriors on a chariot. Fresco in Nestor's palace (LHIIIA/B period, around 1350 BC)
File:Lyre Player and Bird Fresco from Pylos Throne Room.jpg, Lyre Player and Bird. Fresco in Nestor's palace (LHIIIB period, around 1300 BC)
File:Battle Scene Fresco from Pylos.jpg, Battle Scene. Fresco in Nestor's palace (LHIIIB period, around 1300 BC)
The Archaeological Museum of Chora

The archaeological museum is located in the center of the village of
Chora, located 4 kilometres north of the Palace of Nestor. The museum was built in 1969 to house the artifacts discovered in Nestor's Palace and in the rest of the region. However, some of them are currently exposed in the
National Archaeological Museum of Athens
The National Archaeological Museum ( el, Εθνικό Αρχαιολογικό Μουσείο) in Athens houses some of the most important artifacts from a variety of archaeological locations around Greece from prehistory to late antiquity. It is ...
, in the first room devoted to Mycenaean civilization. The Museum of Chora has three rooms. The first room contains finds almost exclusively from the tombs of the region: pots, weapons and jewelry. The second room contains finds from the region of Englianos and from the Palace of Nestor. In addition to the large storage jars and other ceramics from the palace warehouses, there are some wall
fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaste ...
es, such as that depicting a lyre player with a bird, as well as war and hunting scenes. In the last room are exposed other finds from the hill of Englianos and the Palace of Nestor and in particular part of the contents of the tombs of this region, such as giant vases, cups and jewelry. The Archaeological Museum of Chora can be visited every day, except on public holidays and on Tuesdays.
[Admission days and hours on the site of the Ministry of Culture and Sports: ]
Archaeological Museum of Chora
'
The lagoon of Gialova and the beaches of Voïdokilia and Divari
North of Navarino Bay, near the village of
Gialova
Gialova (Greek: Γιάλοβα) is a village on Navarino Bay in the municipality of Pylos-Nestor in the regional unit of Messenia in the south-west Peloponnese, Greece, about six kilometres north of Pylos. The name derives from Greek γιαλός ...
, the
Gialova wetland (''Osman-aga lake'') is one of 10 major lagoons in Greece.
Part of the
Natura 2000 network
Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectively ...
, it is considered a place of remarkable natural beauty and as one of the important bird areas in Europe. It has also been listed as a 1500-acre archaeological site, lying between Gialova and the bay of Voidokilia. Its alternative name of ''Vivari'' is Latin, meaning 'fishponds'. With a depth, at its deepest point, of no more than four meters, its pond constitutes an
ornithological reserve of exceptional importance in Europe, as it is the southernmost stopover of
birds migrating between the Balkans and Africa. It gives shelter to no fewer than 270 bird species, among them
greater flamingo
The greater flamingo (''Phoenicopterus roseus'') is the most widespread and largest species of the flamingo family. It is found in Africa, the Indian subcontinent, the Middle East, and in southern Europe.
Taxonomy
The greater flamingo was desc ...
s,
glossy ibis
The glossy ibis (''Plegadis falcinellus'') is a water bird in the order Pelecaniformes and the ibis and spoonbill family Threskiornithidae. The scientific name derives from Ancient Greek ''plegados'' and Latin, ''falcis'', both meaning "sickle" a ...
,
grey heron
The grey heron (''Ardea cinerea'') is a long-legged wading bird of the heron family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe and Asia and also parts of Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more northern ...
s,
great egret
The great egret (''Ardea alba''), also known as the common egret, large egret, or (in the Old World) great white egret or great white heron is a large, widely distributed egret. The four subspecies are found in Asia, Africa, the Americas, and ...
s,
little egrets,
Eurasian curlew
The Eurasian curlew or common curlew (''Numenius arquata'') is a very large wader in the family Scolopacidae. It is one of the most widespread of the curlews, breeding across temperate Europe and Asia. In Europe, this species is often referred t ...
s,
golden plovers,
black-winged stilt
The black-winged stilt (''Himantopus himantopus'') is a widely distributed very long-legged wader in the avocet and stilt family (Recurvirostridae). The scientific name ''H. himantopus'' is sometimes applied to a single, almost cosmopolitan speci ...
s,
great cormorant
The great cormorant (''Phalacrocorax carbo''), known as the black shag in New Zealand and formerly also known as the great black cormorant across the Northern Hemisphere, the black cormorant in Australia, and the large cormorant in India, is a w ...
s,
common kingfisher
The common kingfisher (''Alcedo atthis''), also known as the Eurasian kingfisher and river kingfisher, is a small kingfisher with seven subspecies recognized within its wide distribution across Eurasia and North Africa. It is resident in much of ...
s,
ruff
Ruff may refer to:
Places
*Ruff, Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community
*Ruff, Washington, United States, an unincorporated community
Other uses
*Ruff (bird) (''Calidris pugnax'' or ''Philomachus pugnax''), a bird in the wader fami ...
s,
garganey
The garganey (''Spatula querquedula'') is a small dabbling duck. It breeds in much of Europe and across the Palearctic, but is strictly migratory, with the entire population moving to southern Africa, India (in particular Santragachi), Banglades ...
s, but also
Audouin's gull
Audouin's gull (''Ichthyaetus audouinii'') is a large gull restricted to the Mediterranean and the western coast of Saharan Africa and the Iberian Peninsula. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''ikhthus'', "fish", and ''aetos'', "eagle", and
t ...
s and birds of prey (
lesser kestrel
The lesser kestrel (''Falco naumanni'') is a small falcon. This species breeds from the Mediterranean across Afghanistan and Central Asia, to China and Mongolia. It is a summer bird migration, migrant, wintering in Africa and Pakistan and sometim ...
s,
osprey
The osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), , also called sea hawk, river hawk, and fish hawk, is a diurnal, fish-eating bird of prey with a cosmopolitan range. It is a large raptor reaching more than in length and across the wings. It is brown o ...
s,
peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (Bird of prey, raptor) in the family (biology), family Falco ...
s and
imperial eagles). It is Gialova, too, which plays host to a very rare species, nearing extinction throughout Europe, the
African chameleon
The African chameleon or Sahel chameleon (''Chamaeleo africanus'') is a species of chameleon native to the Sahel and Nile Valley, with an introduced population present in Greece. An average size may be around long, including its tail.
Range ...
. The observation post of the Greek Ornithological Society allows visitors to find out more and to watch the shallow brackish waters of the lake; they can walk the paths that circumscribe Gialova's different ecosystems.At the western end of the lagoon is the small
bay of Voidokilia, whose cove-shaped beach is regularly ranked among the most beautiful in the world.
It is bordered on one side (to the east) by the
Divari lagoon from which it is separated by a dune bank, on the other side (to the west) by the
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including C ...
onto which it opens, and finally on a third side (to the south) by the Navarino bay. The beach is also part of the
Natura 2000 network
Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectively ...
. It is free to access and can be reached by two routes: either by a road from the village of
Gialova
Gialova (Greek: Γιάλοβα) is a village on Navarino Bay in the municipality of Pylos-Nestor in the regional unit of Messenia in the south-west Peloponnese, Greece, about six kilometres north of Pylos. The name derives from Greek γιαλός ...
which crosses the Divari lagoon, or by a path which crosses the village of
Petrochori. On the northern promontory at the entrance to the
Voidokilia lagoon is a Mycenaean
beehive tholos tomb known as "''
Thrasymedes
Thrasymedes of Paros ( el, Θρασυμήδης ο Παριανός) was an ancient Greek sculptor. Formerly he was regarded as a pupil of Phidias because he set up in the temple of Asclepius at Epidaurus a seated statue of that deity made of iv ...
''
', the son of king Nestor. On the heights of the beach, going up towards the ''Paleokastro'', is the cave known as "''Cave'' ''of Nestor''", in which, according to mythology, the king of Pylos was raising his
oxen.
On the way from Voïdokilia to the village of
Gialova
Gialova (Greek: Γιάλοβα) is a village on Navarino Bay in the municipality of Pylos-Nestor in the regional unit of Messenia in the south-west Peloponnese, Greece, about six kilometres north of Pylos. The name derives from Greek γιαλός ...
to the east, an asphalt road follows the narrow strip of land passing between the
Divari lagoon and Navarino bay. Along this road is a long white sandy beach which runs along the bay of Navarino: the Beach of the Golden Coast (''Paralia tis Chrysis Aktis'') or Divari beach. It joins to the east another beach, within the village of Gialova, the beach of Gialova.

Events
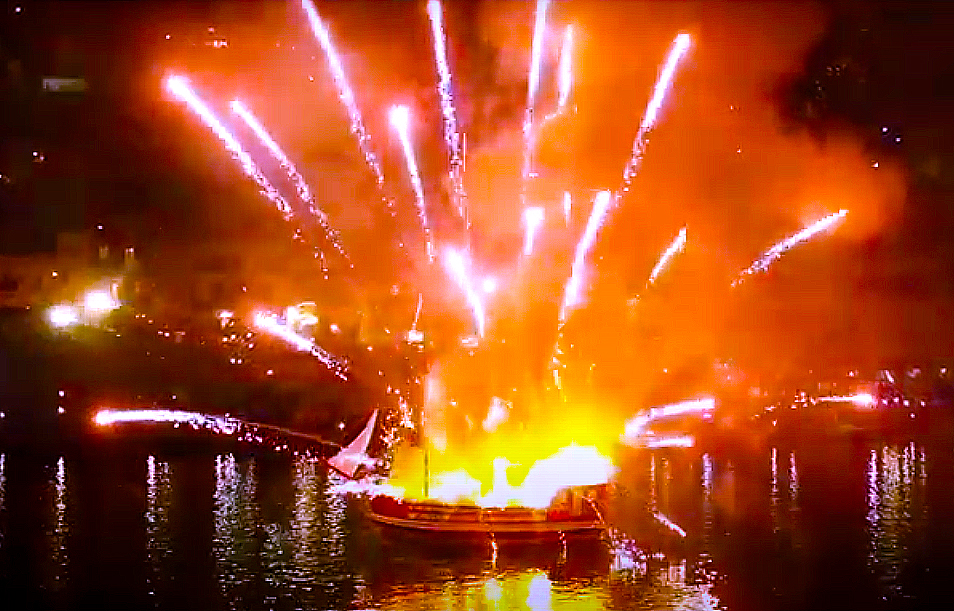
Since 2017, every year around October 20, the “Navarinia” are organized in memory of the
battle of Navarino (20 October 1827) by the municipality of Pylos-Nestor and the volunteers of the local association who is in charge to organize the event.
[Official page of the event : https://navarinia.gr/] Spread over a period of several days, the celebrations culminate on the anniversary of the battle in the port of Pylos, with the participation of the
Hellenic Navy
The Hellenic Navy (HN; el, Πολεμικό Ναυτικό, Polemikó Naftikó, War Navy, abbreviated ΠΝ) is the naval force of Greece, part of the Hellenic Armed Forces. The modern Greek navy historically hails from the naval forces of vari ...
and diplomatic and military representatives of the three Allied countries.
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and ...
s of the Hellenic, British, French and Russian navies, as well as many
old sailing ships take part in the reenactment of the famous battle organized with an impressive
sound and light show. The evening most often ends with the firing of a reconstructed ship that supposedly took part in the battle and with an impressive
fireworks display
Fireworks are a class of low explosive pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a large number of devices in ...
fired from the port.
The celebrations are also accompanied on previous days by various cultural events that take place in parallel in other parts of the city (ceremonies and tributes to the dead on the various memorials of Pylos and of the region, national and international conferences, parades in the streets of Pylos, traditional musical and dance performances, etc.).
Although organized at the end of the touristic season, these celebrations generally attract a large crowd of spectators. In 2019, the demonstrations, which took place in the presence of the
President of the Hellenic Republic
The president of Greece, officially the President of the Hellenic Republic ( el, Πρόεδρος της Ελληνικής Δημοκρατίας, Próedros tis Ellinikís Dimokratías), commonly referred to in Greek as the President of the Rep ...
, gathered more than 10,000 visitors. In 2020, the Navarinia have been awarded the ''Gold Tourism Award 2020'' in the category Cultural Tourism.
Gold Tourism Award 2020
' (category "specialty travel - cultural tourism") attributed to « Navarinia – Municipality of Pylos–Nestoros, Navarinia Committee and Active Media Group ». In winners.tourismawards.gr
Notable people
*
Nestor : hero of
Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
, son of
Neleus
Neleus (; Ancient Greek: Νηλεύς) was a mythological king of Pylos. In some accounts, he was also counted as an Argonaut instead of his son, Nestor.
Family
Neleus was the son of Poseidon and Tyro. According to Pausanias, Neleus was the so ...
and
Chloris
In Greek mythology, the name Chloris (; Greek Χλωρίς ''Chlōrís'', from χλωρός ''chlōrós'', meaning "greenish-yellow", "pale green", "pale", "pallid", or "fresh") appears in a variety of contexts. Some clearly refer to different char ...
and legendary king of Pylos. According to
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
, he is the oldest and wisest of the heroes of the
Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has ...
.
*
Periclymenus In Greek mythology, the name Periclymenus (; Ancient Greek: Περικλύμενος ''Periklymenos'') may refer to:
*Periclymenus, a Pylian prince as the son of King Neleus (the son of Poseidon) and Chloris. He was one of the Argonauts. His grand ...
: hero of Greek mythology, son of
Neleus
Neleus (; Ancient Greek: Νηλεύς) was a mythological king of Pylos. In some accounts, he was also counted as an Argonaut instead of his son, Nestor.
Family
Neleus was the son of Poseidon and Tyro. According to Pausanias, Neleus was the so ...
and
Chloris
In Greek mythology, the name Chloris (; Greek Χλωρίς ''Chlōrís'', from χλωρός ''chlōrós'', meaning "greenish-yellow", "pale green", "pale", "pallid", or "fresh") appears in a variety of contexts. Some clearly refer to different char ...
and an
Argonaut
The Argonauts (; Ancient Greek: ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, ''Argo'', ...
.
*
Edward Codrington
Sir Edward Codrington, (27 April 1770 – 28 April 1851) was a British admiral, who took part in the Battle of Trafalgar and the Battle of Navarino.
Early life and career
The youngest of three brothers born to Edward Codrington the elder (1732 ...
(1770–1851) : British admiral, commander of the British fleet during the Battle of Navarino.
*
Lodewijk van Heiden
Lodewijk Sigismund Vincent Gustaaf Reichsgraf van Heiden (german: Ludwig Sigismund Vinzent Gustav Reichsgraf van Heyden, russian: Ло́ггин Петро́вич Ге́йден, transliterated Russian name: ''Loggin Petrovich Geyden''; 6 Septemb ...
(1773–1850) : Russian admiral, commander of the Russian fleet during the Battle of Navarino.
*
Henri de Rigny
Marie Henri Daniel Gauthier, comte de Rigny (; 2 February 1782 – 6 November 1835) was the commander of the French squadron at the Battle of Navarino in the Greek War of Independence.
Biography
Family
He was a nephew of Baron Joseph Domini ...
(1782–1835) : French admiral, commander of the French fleet during the Battle of Navarino and
Minister of Marine
One of France's Secretaries of State under the Ancien Régime was entrusted with control of the French Navy (Secretary of State of the Navy (France).) In 1791, this title was changed to Minister of the Navy. Before January 1893, this position also ...
(1831), and then of
Foreign Affairs
''Foreign Affairs'' is an American magazine of international relations and U.S. foreign policy published by the Council on Foreign Relations, a nonprofit, nonpartisan, membership organization and think tank specializing in U.S. foreign policy and ...
(between 1834 and 1835).
*
Nicolas-Joseph Maison (1770–1851) : Chief commander of the Morea expedition (between 1828 and 1829),
Marshal of France
Marshal of France (french: Maréchal de France, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished (1 ...
(1829),
Minister of Foreign Affairs
A foreign affairs minister or minister of foreign affairs (less commonly minister for foreign affairs) is generally a cabinet minister in charge of a state's foreign policy and relations. The formal title of the top official varies between cou ...
(1830), and then of
Minister of War
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
(between 1835 and 1836).
*
Joseph-Victor Audoy (1782–1871) : Lieutenant-colonel and commander of the military engineering of the Morea expedition, he was commissioned by the governor of Greece
Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (10 or 11 February 1776 – 9 October 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias ( el, Κόμης Ιωάννης Αντώνιος Καποδίστριας, Komis Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias; russian: � ...
to draw up the first urban plan for Pylos and then to build the current city from 1829.
*
Carl Blegen
Carl William Blegen (January 27, 1887 – August 24, 1971) was an American archaeologist who worked at the site of Pylos in Greece and Troy in modern-day Turkey. He directed the University of Cincinnati excavations of the mound of Hisarlik, the ...
(1887–1971) : American archaeologist, he directed the first archaeological excavations of the Palace of Nestor between 1939 and 1952.
*
Konstantinos Tsiklitiras
Konstantinos "Kostas" Tsiklitiras ( el, Κωνσταντίνος "Κώστας" Τσικλητήρας; 30 October 1888 – 10 February 1913) was a Greek athlete and Olympic champion.
Born in Pylos, he moved to Athens in 1905 to study commerce ...
(1888–1913) : Athlete and Olympic champion, who won medals at the
1908 London Summer Olympics ( ''Silver medal'' in Standing long jump, ''Silver medal'' in Standing high jump) and at the
1912 Stockholm Summer Olympics ( ''Gold medal'' in Standing long jump, ''Bronze medal'' in Standing high jump).
*
Antonis Samaras
Antonis Samaras ( el, Αντώνης Σαμαράς, ; born 23 May 1951) is a Greek politician who served as 14th Prime Minister of Greece from 2012 to 2015. A member of the New Democracy party, he was its president from 2009 until 2015. Samara ...
(1951–) : former
Prime Minister of Greece
The prime minister of the Hellenic Republic ( el, Πρωθυπουργός της Ελληνικής Δημοκρατίας, Prothypourgós tis Ellinikís Dimokratías), colloquially referred to as the prime minister of Greece ( el, Πρωθυ� ...
between 2012 and 2015, several times Minister and MP for the region of Pylos since 1977.
See also
*
Enkhelyawon, a person whom modern scholars regard as a possible king of Mycenaean Pylos
*
List of settlements in Messenia
This is a list of settlements in Messenia, Greece.
* Achladochori
* Adriani
* Aetos
* Agaliani
* Agios Floros
* Agios Nikolaos
* Agios Nikon
* Agios Sostis
* Agrilia
* Agrilia
* Agrilos
* Agrilovouno
* Aithaia
* Akritochori
* Alagonia ...
References
Sources
*
John Bennet, Jack L. Davis, Fariba Zarinebaf-Shahr, "Pylos Regional Archaeological Project, Part III: Sir William Gell's Itinerary in the Pylia and Regional Landscapes in the Morea in the Second Ottoman Period", ''Hesperia'' 69:3:343-380 (July–September 2000
at JSTOR* Fariba Zarinebaf, John Bennet, and Jack L. Davis, ''A Historical and Economic Geography of Ottoman Greece: The Southwestern Morea in the 18th century'', ''Hesperia Supplement'' 34, Princeton, 2005. . A study combining archaeological and survey results with information from the Ottoman archives.
* Diana Gilliland Wright, ''book review'' of Zarinebaf ''et al.'', ''Electronic Journal of Oriental Studies'' 8:10:1-16 (2005). A very complete summary of Zarinebaf
PDF
* Jack L. Davis (ed.), ''Sandy Pylos. An Archaeological History from Nestor to Navarino''. Second edition. Princeton, NJ: ASCSA Publications, 2008. Pp. lix, 342; figs. 135.
*
External links
*
Pylos Regional Archaeological Project (PRAP)–
University of Cincinnati
The University of Cincinnati (UC or Cincinnati) is a public research university in Cincinnati, Ohio. Founded in 1819 as Cincinnati College, it is the oldest institution of higher education in Cincinnati and has an annual enrollment of over 44,00 ...
PRAP: Tour of Hall 64 and its Environs– QuickTime reconstruction and tour of Hall 64 and surroundings
Perseus on Pylos
– University of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota, formally the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities, (UMN Twin Cities, the U of M, or Minnesota) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Tw ...
Pylos (Epano Englianos)
– Metis QTVR collection of QT panoramas relating to the site
Παλαιό Ναυαρίνο (Old Navarino)
Greek Ministry of Culture
Νιόκαστρο (New Navarino)
Greek Ministry of Culture
{{Authority control
Cities in ancient Peloponnese
Archaeological sites in the Peloponnese (region)
Aegean palaces of the Bronze Age
Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece
Mycenaean sites in the Peloponnese (region)
Articles containing video clips
Helladic civilization
Populated places in ancient Messenia
Late Bronze Age collapse
Populated places in Messenia
 Pylos retained its ancient name into Byzantine times, but after the Frankish conquest in the early 13th century, two new names appear:
* a French one, ("
Pylos retained its ancient name into Byzantine times, but after the Frankish conquest in the early 13th century, two new names appear:
* a French one, (" During the
During the  The Mycenaean state of Pylos (1600–1200 BC) covered an area of and had a minimum population of 50,000 according to the
The Mycenaean state of Pylos (1600–1200 BC) covered an area of and had a minimum population of 50,000 according to the  The Pylos site is located on the hill of Ano Englianos, about 9 km northeast of the bay , near the village of Chora and about 17 kilometres from the modern city of Pylos. It hosts one of the most important Mycenaean palaces in Greece, known as the great "
The Pylos site is located on the hill of Ano Englianos, about 9 km northeast of the bay , near the village of Chora and about 17 kilometres from the modern city of Pylos. It hosts one of the most important Mycenaean palaces in Greece, known as the great " In addition to the archaeological remains of the palace, Blegen also found there thousands of clay tablets with inscriptions written in
In addition to the archaeological remains of the palace, Blegen also found there thousands of clay tablets with inscriptions written in  In 2015, the team of American archaeologists
In 2015, the team of American archaeologists  Little is known of Pylos under
Little is known of Pylos under  In 1423, Navarino, like the rest of the Peloponnese, suffered its first Ottoman raid, led by
In 1423, Navarino, like the rest of the Peloponnese, suffered its first Ottoman raid, led by  The Ottomans used Navarino (which they called ''Anavarin'' or ''Avarna'') as a naval base, either for piratical raids or for major fleet operations in the Ionian and Adriatic seas. In 1572/3, the Ottoman chief admiral (''
The Ottomans used Navarino (which they called ''Anavarin'' or ''Avarna'') as a naval base, either for piratical raids or for major fleet operations in the Ionian and Adriatic seas. In 1572/3, the Ottoman chief admiral ('' After the outbreak of the
After the outbreak of the  A strong current of
A strong current of  The city of Pylos has two castles (''Kastra''): the Frankish ''Paleokastro'' (old castle) and the Ottoman ''Neokastro'' (new castle). The first is located northwest of Navarino Bay and north of the island of Sphacteria, while the second is southwest of the bay, on the heights of the city of Pylos. The ''Paleokastro'', located on the top of the promontory of Coryphasium ''(Koryphasion)'' (which is in geological continuity with the island of Sphacteria from which it is only separated by the narrow pass of ''Sykia''), is built on the site of the ancient acropolis of Pylos. It offers a panoramic view, stretching from the
The city of Pylos has two castles (''Kastra''): the Frankish ''Paleokastro'' (old castle) and the Ottoman ''Neokastro'' (new castle). The first is located northwest of Navarino Bay and north of the island of Sphacteria, while the second is southwest of the bay, on the heights of the city of Pylos. The ''Paleokastro'', located on the top of the promontory of Coryphasium ''(Koryphasion)'' (which is in geological continuity with the island of Sphacteria from which it is only separated by the narrow pass of ''Sykia''), is built on the site of the ancient acropolis of Pylos. It offers a panoramic view, stretching from the  South of the city of Pylos, on the road to Methoni, is the old Navarino aqueduct, built in the 16th century by the Ottomans to meet the water supply needs of the ''Neokastro''. Composed by two hydraulic systems, it led the waters from the water intakes of the ''plateau of Koumbeh'' (located near the town of Chandrinou about 15 kilometers northeast of Pylos on the road to Kalamata) and ''Paleo Nero'' (located near the village of Palaionero). The two systems combined into a single system that can still be seen today around Pylos in the district of ''Kamares''. Then, thanks to an underground conduit of the aqueduct, the water penetrated inside the fortress to feed there the fountains of the ''Neokastro''.' Fallen into ruins until 1828, it was restored in 1832 by the French engineers of the Morea expedition, and was used to supply Pylos with water until 1907.
South of the city of Pylos, on the road to Methoni, is the old Navarino aqueduct, built in the 16th century by the Ottomans to meet the water supply needs of the ''Neokastro''. Composed by two hydraulic systems, it led the waters from the water intakes of the ''plateau of Koumbeh'' (located near the town of Chandrinou about 15 kilometers northeast of Pylos on the road to Kalamata) and ''Paleo Nero'' (located near the village of Palaionero). The two systems combined into a single system that can still be seen today around Pylos in the district of ''Kamares''. Then, thanks to an underground conduit of the aqueduct, the water penetrated inside the fortress to feed there the fountains of the ''Neokastro''.' Fallen into ruins until 1828, it was restored in 1832 by the French engineers of the Morea expedition, and was used to supply Pylos with water until 1907.
 Leaning against two hills, one of which is overlooked by the fortress of the ''Neokastro,'' the town of Pylos faces the bay of Navarino. Pylos preserves many houses from the 19th century. These are built of stone, with typical
Leaning against two hills, one of which is overlooked by the fortress of the ''Neokastro,'' the town of Pylos faces the bay of Navarino. Pylos preserves many houses from the 19th century. These are built of stone, with typical  Also built by French troops of the
Also built by French troops of the  North of Pylos () and south of the town of Chora (4 kilometres), is the hill of ''Ano Englianos'' which houses the Mycenaean
North of Pylos () and south of the town of Chora (4 kilometres), is the hill of ''Ano Englianos'' which houses the Mycenaean  The archaeological museum is located in the center of the village of Chora, located 4 kilometres north of the Palace of Nestor. The museum was built in 1969 to house the artifacts discovered in Nestor's Palace and in the rest of the region. However, some of them are currently exposed in the
The archaeological museum is located in the center of the village of Chora, located 4 kilometres north of the Palace of Nestor. The museum was built in 1969 to house the artifacts discovered in Nestor's Palace and in the rest of the region. However, some of them are currently exposed in the 
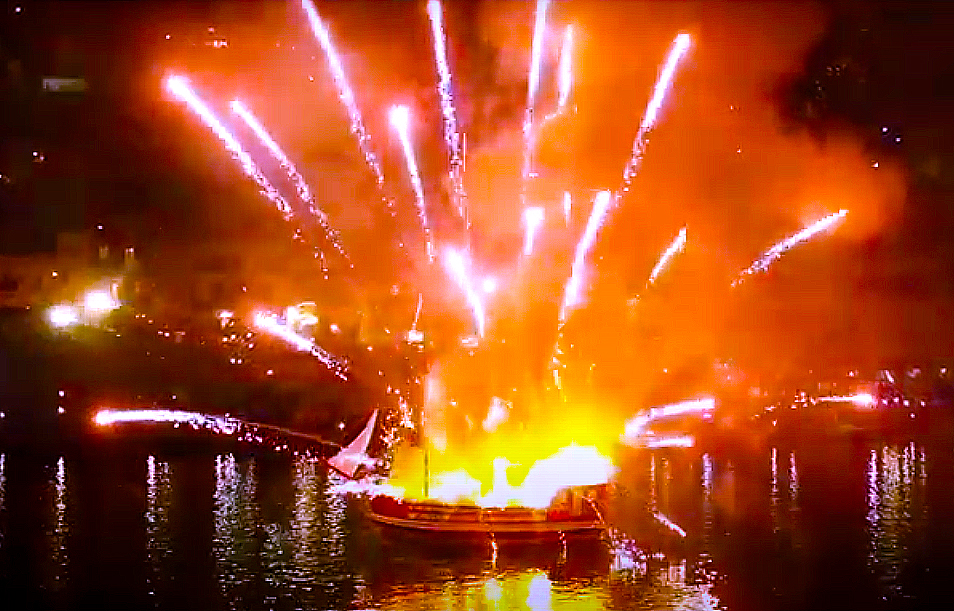 Since 2017, every year around October 20, the “Navarinia” are organized in memory of the battle of Navarino (20 October 1827) by the municipality of Pylos-Nestor and the volunteers of the local association who is in charge to organize the event.Official page of the event : https://navarinia.gr/ Spread over a period of several days, the celebrations culminate on the anniversary of the battle in the port of Pylos, with the participation of the
Since 2017, every year around October 20, the “Navarinia” are organized in memory of the battle of Navarino (20 October 1827) by the municipality of Pylos-Nestor and the volunteers of the local association who is in charge to organize the event.Official page of the event : https://navarinia.gr/ Spread over a period of several days, the celebrations culminate on the anniversary of the battle in the port of Pylos, with the participation of the