Name of Liechtenstein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a


 The oldest traces of human existence in the area of present-day Liechtenstein date back to the Middle Paleolithic era.History
The oldest traces of human existence in the area of present-day Liechtenstein date back to the Middle Paleolithic era.History
swissworld.org. Retrieved 27 June 2009
Nationsencyclopedia.com. Retrieved 27 November 2009
Nationsonline.org. Retrieved 27 November 2009. The area that later became Liechtenstein remained under Frankish hegemony (
 In 1929, 75-year-old Franz I, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Franz I succeeded to the throne. He had just married Elisabeth von Gutmann, a wealthy woman from Vienna whose father was a Jewish businessman from Moravia. Although Liechtenstein had no official Nazi party, a Nazi sympathy movement arose within its National Union party. Local Liechtenstein Nazis identified Elisabeth as their Jewish "problem".
In March 1938, just after the Anschluss, annexation of Austria by Nazi Germany, Franz named as regent his 31-year-old grandnephew and heir-presumptive, Franz Joseph II, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Franz Joseph. Franz died in July that year, and Franz Joseph succeeded to the throne. Franz Joseph II first moved to Liechtenstein in 1938, a few days after Austria's annexation.
During World War II, Liechtenstein remained officially neutral, looking to neighbouring Switzerland for assistance and guidance, while family treasures from dynastic lands and possessions in Bohemia,
In 1929, 75-year-old Franz I, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Franz I succeeded to the throne. He had just married Elisabeth von Gutmann, a wealthy woman from Vienna whose father was a Jewish businessman from Moravia. Although Liechtenstein had no official Nazi party, a Nazi sympathy movement arose within its National Union party. Local Liechtenstein Nazis identified Elisabeth as their Jewish "problem".
In March 1938, just after the Anschluss, annexation of Austria by Nazi Germany, Franz named as regent his 31-year-old grandnephew and heir-presumptive, Franz Joseph II, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Franz Joseph. Franz died in July that year, and Franz Joseph succeeded to the throne. Franz Joseph II first moved to Liechtenstein in 1938, a few days after Austria's annexation.
During World War II, Liechtenstein remained officially neutral, looking to neighbouring Switzerland for assistance and guidance, while family treasures from dynastic lands and possessions in Bohemia,
", 2019 ''CEO World''. 18 September 2019. The country's population enjoys one of the List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, world's highest standards of living.

 Liechtenstein has a monarch as head of state, and an elected parliament that enacts the law. It is also a direct democracy, where voters can propose and enact constitutional amendments and legislation independently of the legislature. The Constitution of Liechtenstein was Liechtenstein constitutional referendum, 2003, adopted in March 2003, replacing the 1921 constitution. The 1921 constitution had established Liechtenstein as a constitutional monarchy headed by the reigning prince of the Princely House of Liechtenstein; a parliamentary system had been established, although the reigning Prince retained substantial political authority.
The reigning Prince is the Head of State and represents Liechtenstein in its international relations (although Switzerland has taken responsibility for much of Liechtenstein's diplomatic relations). The Prince may veto laws adopted by parliament. The Prince may call referendums, propose new legislation, and dissolve parliament, although dissolution of parliament may be subject to a referendum.
Executive authority is vested in a collegiate government comprising the head of government (prime minister) and four government councillors (ministers). The head of government and the other ministers are appointed by the Prince upon the proposal of parliament and with its concurrence, and reflect the balance of parties in parliament. The constitution stipulates that at least two government members be chosen from each of the two regions. The members of the government are collectively and individually responsible to parliament; parliament may ask the Prince to remove an individual minister or the entire government.
Legislative authority is vested in the unicameral Landtag of Liechtenstein, Landtag, made up of 25 members elected for maximum four-year terms according to a proportional representation formula. Fifteen members are elected from the Oberland (electoral district), Oberland (Upper Country or region) and ten from the Unterland (electoral district), Unterland (Lower Country or region). Parties must receive at least 8% of the national vote to win seats in parliament, i.e., enough for two seats in the 25-seat legislature. Parliament proposes and approves a government, which the Prince formally appoints. Parliament may also pass votes of no confidence in the entire government or individual members.
Parliament elects from among its members a "Landesausschuss" (National Committee) made up of the president of the parliament and four additional members. The National Committee is charged with performing functions of parliamentary supervision. Parliament can call for referendums on proposed legislation. Parliament shares the authority to propose new legislation with the Prince and with the number of Citizenship, citizens required for to initiate a referendum.
The courts of Liechtenstein, Judicial authority is vested in the Regional Court at Vaduz, the Princely High Court of Appeal at Vaduz, the Princely Supreme Court, the Administrative Court, and the State Court. The State Court rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution and has five members elected by parliament.
On 1 July 1984, Liechtenstein became the last country in Europe to grant women the right to vote. The Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum, 1984, referendum on women's suffrage, in which only men were allowed to participate, passed with 51.3% in favour.
Liechtenstein has a monarch as head of state, and an elected parliament that enacts the law. It is also a direct democracy, where voters can propose and enact constitutional amendments and legislation independently of the legislature. The Constitution of Liechtenstein was Liechtenstein constitutional referendum, 2003, adopted in March 2003, replacing the 1921 constitution. The 1921 constitution had established Liechtenstein as a constitutional monarchy headed by the reigning prince of the Princely House of Liechtenstein; a parliamentary system had been established, although the reigning Prince retained substantial political authority.
The reigning Prince is the Head of State and represents Liechtenstein in its international relations (although Switzerland has taken responsibility for much of Liechtenstein's diplomatic relations). The Prince may veto laws adopted by parliament. The Prince may call referendums, propose new legislation, and dissolve parliament, although dissolution of parliament may be subject to a referendum.
Executive authority is vested in a collegiate government comprising the head of government (prime minister) and four government councillors (ministers). The head of government and the other ministers are appointed by the Prince upon the proposal of parliament and with its concurrence, and reflect the balance of parties in parliament. The constitution stipulates that at least two government members be chosen from each of the two regions. The members of the government are collectively and individually responsible to parliament; parliament may ask the Prince to remove an individual minister or the entire government.
Legislative authority is vested in the unicameral Landtag of Liechtenstein, Landtag, made up of 25 members elected for maximum four-year terms according to a proportional representation formula. Fifteen members are elected from the Oberland (electoral district), Oberland (Upper Country or region) and ten from the Unterland (electoral district), Unterland (Lower Country or region). Parties must receive at least 8% of the national vote to win seats in parliament, i.e., enough for two seats in the 25-seat legislature. Parliament proposes and approves a government, which the Prince formally appoints. Parliament may also pass votes of no confidence in the entire government or individual members.
Parliament elects from among its members a "Landesausschuss" (National Committee) made up of the president of the parliament and four additional members. The National Committee is charged with performing functions of parliamentary supervision. Parliament can call for referendums on proposed legislation. Parliament shares the authority to propose new legislation with the Prince and with the number of Citizenship, citizens required for to initiate a referendum.
The courts of Liechtenstein, Judicial authority is vested in the Regional Court at Vaduz, the Princely High Court of Appeal at Vaduz, the Princely Supreme Court, the Administrative Court, and the State Court. The State Court rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution and has five members elected by parliament.
On 1 July 1984, Liechtenstein became the last country in Europe to grant women the right to vote. The Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum, 1984, referendum on women's suffrage, in which only men were allowed to participate, passed with 51.3% in favour.

 Liechtenstein is situated in the Upper Rhine valley of the European
Liechtenstein is situated in the Upper Rhine valley of the European

 Despite its limited natural resources, Liechtenstein is one of the few countries in the world with more registered companies than citizens; it has developed a prosperous, highly industrialized free-enterprise economy and boasts a financial service sector as well as a living standard that compares favourably with those of the urban areas of Liechtenstein's much larger European neighbours.
Liechtenstein participates in a
Despite its limited natural resources, Liechtenstein is one of the few countries in the world with more registered companies than citizens; it has developed a prosperous, highly industrialized free-enterprise economy and boasts a financial service sector as well as a living standard that compares favourably with those of the urban areas of Liechtenstein's much larger European neighbours.
Liechtenstein participates in a
 The government of Liechtenstein taxes personal income, business income and principal (wealth). The basic rate of Income tax#Personal, personal income tax is 1.2%. When combined with the additional income tax imposed by the communes, the combined income tax rate is 17.82%. An additional income tax of 4.3% is levied on all employees under the country's social security programme. This rate is higher for the self-employed, up to a maximum of 11%, making the maximum income tax rate about 29% in total. The basic wealth tax, tax rate on wealth is 0.06% per annum, and the combined total rate is 0.89%. The tax rate on corporate profits is 12.5%.
Liechtenstein's gift tax, gift and Inheritance tax, estate taxes vary depending on the relationship the recipient has to the giver and the amount of the inheritance. The tax ranges between 0.5% and 0.75% for spouses and children and 18% to 27% for non-related recipients. The estate tax is progressive.
Liechtenstein has previously received significant revenues from ''Stiftungen'' ("foundations"), financial entities created to hide the true owner of nonresident foreigners' financial holdings. The foundation is registered in the name of a Liechtensteiner, often a lawyer. This set of laws used to make Liechtenstein a popular
The government of Liechtenstein taxes personal income, business income and principal (wealth). The basic rate of Income tax#Personal, personal income tax is 1.2%. When combined with the additional income tax imposed by the communes, the combined income tax rate is 17.82%. An additional income tax of 4.3% is levied on all employees under the country's social security programme. This rate is higher for the self-employed, up to a maximum of 11%, making the maximum income tax rate about 29% in total. The basic wealth tax, tax rate on wealth is 0.06% per annum, and the combined total rate is 0.89%. The tax rate on corporate profits is 12.5%.
Liechtenstein's gift tax, gift and Inheritance tax, estate taxes vary depending on the relationship the recipient has to the giver and the amount of the inheritance. The tax ranges between 0.5% and 0.75% for spouses and children and 18% to 27% for non-related recipients. The estate tax is progressive.
Liechtenstein has previously received significant revenues from ''Stiftungen'' ("foundations"), financial entities created to hide the true owner of nonresident foreigners' financial holdings. The foundation is registered in the name of a Liechtensteiner, often a lawyer. This set of laws used to make Liechtenstein a popular  The 2008 Liechtenstein tax affair is a series of tax investigations in numerous countries whose governments suspect that some of their citizens have evaded tax obligations by using banks and trusts in Liechtenstein; the affair broke open with the biggest complex of investigations ever initiated for tax evasion in Germany. It was also seen as an attempt to put pressure on Liechtenstein, then one of the remaining FATF blacklist, uncooperative tax havens—along with Andorra and Monaco—as identified by the Paris-based Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 2007. On 27 May 2009 the OECD removed Liechtenstein from the blacklist of uncooperative countries.
In August 2009, the British government department HM Revenue & Customs agreed with Liechtenstein to start exchanging information. It is believed that up to 5,000 British investors have roughly £3 billion deposited in accounts and trusts in the country.
In October 2015, the European Union and Liechtenstein signed a tax agreement to ensure the automatic exchange of financial information in case of tax disputes. The collection of data started in 2016. It is another step to bring the principality in line with other European countries regarding its taxation of private individuals and corporate assets.
The 2008 Liechtenstein tax affair is a series of tax investigations in numerous countries whose governments suspect that some of their citizens have evaded tax obligations by using banks and trusts in Liechtenstein; the affair broke open with the biggest complex of investigations ever initiated for tax evasion in Germany. It was also seen as an attempt to put pressure on Liechtenstein, then one of the remaining FATF blacklist, uncooperative tax havens—along with Andorra and Monaco—as identified by the Paris-based Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 2007. On 27 May 2009 the OECD removed Liechtenstein from the blacklist of uncooperative countries.
In August 2009, the British government department HM Revenue & Customs agreed with Liechtenstein to start exchanging information. It is believed that up to 5,000 British investors have roughly £3 billion deposited in accounts and trusts in the country.
In October 2015, the European Union and Liechtenstein signed a tax agreement to ensure the automatic exchange of financial information in case of tax disputes. The collection of data started in 2016. It is another step to bring the principality in line with other European countries regarding its taxation of private individuals and corporate assets.
 According to the Constitution of Liechtenstein, Catholicism is its official state religion:
Liechtenstein offers protection to adherents of all religions, and considers the "religious interests of the people" a priority of the government. In Liechtenstein's schools, although exceptions are allowed, religious education in Catholicism or Protestantism (either Lutheran or Calvinist, or both) is legally required. Tax exemption is granted by the government to religious organizations. According to the Pew Research Center, social conflict caused by religious hostilities is low in Liechtenstein, and so is government restriction on the practice of religion.
According to the 2010 census, 85.8% of the total population is Christian, of whom 75.9% adhere to the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, constituted in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Vaduz, Catholic Archdiocese of Vaduz, while 9.6% are either Protestant, mainly organized in the Evangelical Church in Liechtenstein (a United church, Lutheran & Reformed) and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Liechtenstein, or Orthodoxy, Orthodox, mainly organized in the Christian-Orthodox Church. The largest minority religion is Islam (5.4% of the total population).
According to the Constitution of Liechtenstein, Catholicism is its official state religion:
Liechtenstein offers protection to adherents of all religions, and considers the "religious interests of the people" a priority of the government. In Liechtenstein's schools, although exceptions are allowed, religious education in Catholicism or Protestantism (either Lutheran or Calvinist, or both) is legally required. Tax exemption is granted by the government to religious organizations. According to the Pew Research Center, social conflict caused by religious hostilities is low in Liechtenstein, and so is government restriction on the practice of religion.
According to the 2010 census, 85.8% of the total population is Christian, of whom 75.9% adhere to the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, constituted in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Vaduz, Catholic Archdiocese of Vaduz, while 9.6% are either Protestant, mainly organized in the Evangelical Church in Liechtenstein (a United church, Lutheran & Reformed) and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Liechtenstein, or Orthodoxy, Orthodox, mainly organized in the Christian-Orthodox Church. The largest minority religion is Islam (5.4% of the total population).
 The literacy rate of Liechtenstein is 100%. In 2006 Programme for International Student Assessment report, coordinated by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, ranked Liechtenstein's education as the 10th-best in the world. In 2012, Liechtenstein had the highest PISA scores of any European country.
Within Liechtenstein, there are four main centres for higher education:
*University of Liechtenstein
*Private University in the Principality of Liechtenstein
*Liechtenstein Institute
*International Academy of Philosophy, Liechtenstein
There are nine public high schools in the country. These include:
*Liechtensteinisches Gymnasium in Vaduz.
*Realschule Vaduz and Oberschule Vaduz, in the Schulzentrum Mühleholz II in VaduzWeiterführende Schulen Schaan
The literacy rate of Liechtenstein is 100%. In 2006 Programme for International Student Assessment report, coordinated by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, ranked Liechtenstein's education as the 10th-best in the world. In 2012, Liechtenstein had the highest PISA scores of any European country.
Within Liechtenstein, there are four main centres for higher education:
*University of Liechtenstein
*Private University in the Principality of Liechtenstein
*Liechtenstein Institute
*International Academy of Philosophy, Liechtenstein
There are nine public high schools in the country. These include:
*Liechtensteinisches Gymnasium in Vaduz.
*Realschule Vaduz and Oberschule Vaduz, in the Schulzentrum Mühleholz II in VaduzWeiterführende Schulen Schaan
." Commune of Schaan. Retrieved 12 May 2016. "Realschule Schaan Duxgass 55 9494 Schaan" and "Sportschule Liechtenstein Duxgass 55 9494 Schaan" and "Realschule Vaduz Schulzentrum Mühleholz II 9490 Vaduz" and "Oberschule Vaduz Schulzentrum Mühleholz II 9490 Vaduz" *Realschule Schaan and Sportschule Liechtenstein in
 There are about of paved roadway within Liechtenstein, with of marked bicycle paths.
A railway connects Austria and Switzerland through Liechtenstein. The Rail transport in Liechtenstein, country's railways are administered by the Austrian Federal Railways as part of the route between Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, Feldkirch,
There are about of paved roadway within Liechtenstein, with of marked bicycle paths.
A railway connects Austria and Switzerland through Liechtenstein. The Rail transport in Liechtenstein, country's railways are administered by the Austrian Federal Railways as part of the route between Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, Feldkirch,

 As a result of its small size, Liechtenstein has been strongly affected by external cultural influences, most notably those originating in the southern regions of German-speaking Europe, including Austria, Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Switzerland, and specifically German Tyrol, Tirol and Vorarlberg. The Historical Society of the Principality of Liechtenstein plays a role in preserving the culture and history of the country.
The largest museum is the Kunstmuseum Liechtenstein, an international museum of modern and contemporary art with an important international art collection. The building by the Swiss architects Morger, Degelo, and Kerez is a landmark in Vaduz. It was completed in November 2000 and forms a "black box" of tinted concrete and black basalt stone. The museum collection is also the national art collection of Liechtenstein.
The other important museum is the Liechtenstein National Museum (''Liechtensteinisches Landesmuseum'') showing permanent exhibitions on the cultural and natural history of Liechtenstein as well as special exhibitions. There is also a stamp museum, ski museum, and a 500-year-old Rural Lifestyle Museum.
The Liechtenstein State Library is the library that has legal deposit for all books published in the country.
The most famous historical sites are Vaduz Castle, Gutenberg Castle, the Red House, and the ruins of Schellenberg.
The Private Art Collection of the Prince of Liechtenstein, one of the world's leading private art collections, is shown at the Liechtenstein Museum in Vienna.
On the country's national holiday, all subjects are invited to the castle of the head of state. A significant portion of the population attends the national celebration at the castle where speeches are made and complimentary beer is served.
Music and theatre are important parts of the culture. There are numerous music organizations such as the Liechtenstein Musical Company, the annual Guitar Days, and the International Josef Gabriel Rheinberger Society, which play in two main theatres.
As a result of its small size, Liechtenstein has been strongly affected by external cultural influences, most notably those originating in the southern regions of German-speaking Europe, including Austria, Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria, Switzerland, and specifically German Tyrol, Tirol and Vorarlberg. The Historical Society of the Principality of Liechtenstein plays a role in preserving the culture and history of the country.
The largest museum is the Kunstmuseum Liechtenstein, an international museum of modern and contemporary art with an important international art collection. The building by the Swiss architects Morger, Degelo, and Kerez is a landmark in Vaduz. It was completed in November 2000 and forms a "black box" of tinted concrete and black basalt stone. The museum collection is also the national art collection of Liechtenstein.
The other important museum is the Liechtenstein National Museum (''Liechtensteinisches Landesmuseum'') showing permanent exhibitions on the cultural and natural history of Liechtenstein as well as special exhibitions. There is also a stamp museum, ski museum, and a 500-year-old Rural Lifestyle Museum.
The Liechtenstein State Library is the library that has legal deposit for all books published in the country.
The most famous historical sites are Vaduz Castle, Gutenberg Castle, the Red House, and the ruins of Schellenberg.
The Private Art Collection of the Prince of Liechtenstein, one of the world's leading private art collections, is shown at the Liechtenstein Museum in Vienna.
On the country's national holiday, all subjects are invited to the castle of the head of state. A significant portion of the population attends the national celebration at the castle where speeches are made and complimentary beer is served.
Music and theatre are important parts of the culture. There are numerous music organizations such as the Liechtenstein Musical Company, the annual Guitar Days, and the International Josef Gabriel Rheinberger Society, which play in two main theatres.
 Liechtenstein Association football, football teams play in the Swiss football leagues. The Liechtenstein Football Cup allows access for one Liechtenstein team each year to the UEFA Europa Conference League; FC Vaduz, a team playing in the Swiss Challenge League, the second division in Swiss football, is the most successful team in the Cup, and scored their greatest success in the 1996–97 UEFA Cup Winners' Cup, European Cup Winners' Cup in 1996 when they drew with and defeated the Latvian team FK Jelgava, FC Universitate Riga by 1–1 and 4–2, to go on to a lucrative fixture against Paris Saint-Germain F.C., which they lost 0–3 and 0–4.
The Liechtenstein national football team is regarded as an easy target for any team drawn against them; this was the basis for a book about Liechtenstein's unsuccessful qualifying campaign for the 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2002 World Cup by British author Charlie Connelly. In one surprising week during autumn 2004, however, the team managed a 2–2 draw with Portugal national football team, Portugal, who only a few months earlier had been the losing finalists in the UEFA Euro 2004, European Championships. Four days later, the Liechtenstein team traveled to Luxembourg, where they defeated Luxembourg national football team, the home team 4–0 in a 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup qualifying match. In the qualification stage of the European Championship 2008, Liechtenstein beat Latvia 1–0, which prompted the Latvian coach's resignation. They went on to beat Iceland 3–0 on 17 October 2007, which is considered one of the most dramatic losses of the Icelandic national football team. On 7 September 2010, they came within seconds of a 1–1 draw against Scotland national football team, Scotland in Glasgow, having led 1–0 earlier in the second half, but Liechtenstein lost 2–1 thanks to a goal by Stephen McManus in the 97th minute. On 3 June 2011, Liechtenstein defeated Lithuania national football team, Lithuania 2–0. On 15 November 2014, Liechtenstein defeated Moldova national football team, Moldova 0–1 with Franz Burgmeier's late free kick goal in Chișinău.
As an Alps, alpine country, the main sporting opportunity for Liechtensteiners to excel is in winter sports such as Downhill (ski competition), downhill skiing: the country's single ski area is Malbun. Hanni Wenzel won two gold medals and one silver medal in the 1980 Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics (she won bronze in 1976), her brother Andreas Wenzel, Andreas won one silver medal in 1980 and one bronze medal in 1984 in the Giant slalom skiing, giant slalom event, and her daughter Tina Weirather won a bronze medal in 2018 in the Super-G. With ten medals overall (all in alpine skiing), Liechtenstein has won more Olympic medals per capita than any other nation. It is the smallest nation to win a medal in any Olympics, Winter or Summer, and currently the only nation to win a medal in the Winter Games but not in the Summer Games. Other notable skiers from Liechtenstein are Marco Büchel, Willi Frommelt, Paul Frommelt and Ursula Konzett.
Another discipline unusually popular with Liechtensteiners is Auto racing, motorsport – American-born German-Colombian Rikky von Opel raced under the flag of Liechtenstein in Formula One in 1973 Formula One season, 1973 and 1974 Formula One season, 1974, and Manfred Schurti competed in 9 editions of the 24 Hours of Le Mans as a Porsche factory driver with a best finish of 4th overall in 1976 24 Hours of Le Mans, 1976. The nation is currently represented internationally by Fabienne Wohlwend in Ferrari Challenge and Formula 3, as well as Matthias Kaiser who competes in prototype Endurance racing (motorsport), endurance racing.
Other sports Liechtenstein athletes have had success in include tennis, with Stephanie Vogt and Kathinka von Deichmann both having varying degrees of success on the women's tour, as well as swimming (sport), swimming – both Julia Hassler and Christoph Meier represented the country at the 2016 Summer Olympics with the former the nations' flag bearer.
Liechtenstein Association football, football teams play in the Swiss football leagues. The Liechtenstein Football Cup allows access for one Liechtenstein team each year to the UEFA Europa Conference League; FC Vaduz, a team playing in the Swiss Challenge League, the second division in Swiss football, is the most successful team in the Cup, and scored their greatest success in the 1996–97 UEFA Cup Winners' Cup, European Cup Winners' Cup in 1996 when they drew with and defeated the Latvian team FK Jelgava, FC Universitate Riga by 1–1 and 4–2, to go on to a lucrative fixture against Paris Saint-Germain F.C., which they lost 0–3 and 0–4.
The Liechtenstein national football team is regarded as an easy target for any team drawn against them; this was the basis for a book about Liechtenstein's unsuccessful qualifying campaign for the 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2002 World Cup by British author Charlie Connelly. In one surprising week during autumn 2004, however, the team managed a 2–2 draw with Portugal national football team, Portugal, who only a few months earlier had been the losing finalists in the UEFA Euro 2004, European Championships. Four days later, the Liechtenstein team traveled to Luxembourg, where they defeated Luxembourg national football team, the home team 4–0 in a 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup qualifying match. In the qualification stage of the European Championship 2008, Liechtenstein beat Latvia 1–0, which prompted the Latvian coach's resignation. They went on to beat Iceland 3–0 on 17 October 2007, which is considered one of the most dramatic losses of the Icelandic national football team. On 7 September 2010, they came within seconds of a 1–1 draw against Scotland national football team, Scotland in Glasgow, having led 1–0 earlier in the second half, but Liechtenstein lost 2–1 thanks to a goal by Stephen McManus in the 97th minute. On 3 June 2011, Liechtenstein defeated Lithuania national football team, Lithuania 2–0. On 15 November 2014, Liechtenstein defeated Moldova national football team, Moldova 0–1 with Franz Burgmeier's late free kick goal in Chișinău.
As an Alps, alpine country, the main sporting opportunity for Liechtensteiners to excel is in winter sports such as Downhill (ski competition), downhill skiing: the country's single ski area is Malbun. Hanni Wenzel won two gold medals and one silver medal in the 1980 Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics (she won bronze in 1976), her brother Andreas Wenzel, Andreas won one silver medal in 1980 and one bronze medal in 1984 in the Giant slalom skiing, giant slalom event, and her daughter Tina Weirather won a bronze medal in 2018 in the Super-G. With ten medals overall (all in alpine skiing), Liechtenstein has won more Olympic medals per capita than any other nation. It is the smallest nation to win a medal in any Olympics, Winter or Summer, and currently the only nation to win a medal in the Winter Games but not in the Summer Games. Other notable skiers from Liechtenstein are Marco Büchel, Willi Frommelt, Paul Frommelt and Ursula Konzett.
Another discipline unusually popular with Liechtensteiners is Auto racing, motorsport – American-born German-Colombian Rikky von Opel raced under the flag of Liechtenstein in Formula One in 1973 Formula One season, 1973 and 1974 Formula One season, 1974, and Manfred Schurti competed in 9 editions of the 24 Hours of Le Mans as a Porsche factory driver with a best finish of 4th overall in 1976 24 Hours of Le Mans, 1976. The nation is currently represented internationally by Fabienne Wohlwend in Ferrari Challenge and Formula 3, as well as Matthias Kaiser who competes in prototype Endurance racing (motorsport), endurance racing.
Other sports Liechtenstein athletes have had success in include tennis, with Stephanie Vogt and Kathinka von Deichmann both having varying degrees of success on the women's tour, as well as swimming (sport), swimming – both Julia Hassler and Christoph Meier represented the country at the 2016 Summer Olympics with the former the nations' flag bearer.
 The Law enforcement in Liechtenstein, Liechtenstein National Police is responsible for keeping order within the country. It consists of 87 field officers and 38 civilian staff, totaling 125 employees. All officers are equipped with small arms. The country has one of the world's lowest Crime statistics, crime rates. Liechtenstein's prison holds few, if any, inmates, and those with sentences over two years are transferred to Judiciary of Austria, Austrian jurisdiction. The Liechtenstein National Police maintains a trilateral treaty with Austria and Switzerland that enables close cross-border cooperation among the police forces of the three countries.
Liechtenstein follows a policy of Neutrality (international relations), neutrality and is one of the few List of countries without armed forces, countries in the world that maintain no military although its police force maintains a paramilitary force, the Princely Liechtenstein Security Corps within the organisation that would act as its de facto army if an invasion of Liechtenstein ever occurred. The Princely Liechtenstein Security Corps provides heavy backup for the National Police as well as Honor Guards at the Royal Palace and official functions. However, Liechtenstein can reinstate its military if deemed necessary, although this is very unlikely.christopher-eger.suite101.com
The army was abolished for financial reasons soon after the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, in which Liechtenstein fielded an army of 80 men, although they were not involved in any fighting. No casualties were incurred; in fact, the unit numbered 81 upon return due to an Austrian military liaison who accompanied the army back home. The demise of the German Confederation in that war freed Liechtenstein from its international obligation to maintain an army, and parliament seized this opportunity and refused to provide funding for one. The Prince objected, as such a move would leave the country defenceless, but relented on 12 February 1868 and disbanded the force. The last soldier to serve under the colours of Liechtenstein died in 1939 at age 95.
* In 1985 the Swiss Army fired off shells during an exercise and mistakenly burned a patch of forest inside Liechtenstein. The incident was said to have been resolved "over a case of white wine".
* In March 2007, a 170-man Swiss infantry unit got lost during a training exercise and inadvertently crossed into Liechtenstein. The accidental invasion ended when the unit realized their mistake and turned back. The Swiss Army later informed Liechtenstein of the incursion and offered official apologies, to which an internal ministry spokesperson responded, "No problem, these things happen."
* On 20 September 2017, Liechtenstein signed the United Nations Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
The Law enforcement in Liechtenstein, Liechtenstein National Police is responsible for keeping order within the country. It consists of 87 field officers and 38 civilian staff, totaling 125 employees. All officers are equipped with small arms. The country has one of the world's lowest Crime statistics, crime rates. Liechtenstein's prison holds few, if any, inmates, and those with sentences over two years are transferred to Judiciary of Austria, Austrian jurisdiction. The Liechtenstein National Police maintains a trilateral treaty with Austria and Switzerland that enables close cross-border cooperation among the police forces of the three countries.
Liechtenstein follows a policy of Neutrality (international relations), neutrality and is one of the few List of countries without armed forces, countries in the world that maintain no military although its police force maintains a paramilitary force, the Princely Liechtenstein Security Corps within the organisation that would act as its de facto army if an invasion of Liechtenstein ever occurred. The Princely Liechtenstein Security Corps provides heavy backup for the National Police as well as Honor Guards at the Royal Palace and official functions. However, Liechtenstein can reinstate its military if deemed necessary, although this is very unlikely.christopher-eger.suite101.com
The army was abolished for financial reasons soon after the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, in which Liechtenstein fielded an army of 80 men, although they were not involved in any fighting. No casualties were incurred; in fact, the unit numbered 81 upon return due to an Austrian military liaison who accompanied the army back home. The demise of the German Confederation in that war freed Liechtenstein from its international obligation to maintain an army, and parliament seized this opportunity and refused to provide funding for one. The Prince objected, as such a move would leave the country defenceless, but relented on 12 February 1868 and disbanded the force. The last soldier to serve under the colours of Liechtenstein died in 1939 at age 95.
* In 1985 the Swiss Army fired off shells during an exercise and mistakenly burned a patch of forest inside Liechtenstein. The incident was said to have been resolved "over a case of white wine".
* In March 2007, a 170-man Swiss infantry unit got lost during a training exercise and inadvertently crossed into Liechtenstein. The accidental invasion ended when the unit realized their mistake and turned back. The Swiss Army later informed Liechtenstein of the incursion and offered official apologies, to which an internal ministry spokesperson responded, "No problem, these things happen."
* On 20 September 2017, Liechtenstein signed the United Nations Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Princely House of Liechtenstein
Parliament of Liechtenstein
Government of Liechtenstein
Official tourism of Liechtenstein
Statistics Office of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Liechtenstein
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Liechtenstein profile
from BBC News * * * {{Authority control Liechtenstein, 1719 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire Central European countries Christian states Countries in Europe German-speaking countries and territories Landlocked countries Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the European Free Trade Association Member states of the United Nations NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union NUTS 3 statistical regions of the European Union Principalities of the Holy Roman Empire Principalities States and territories established in 1866 States of the Confederation of the Rhine States of the German Confederation Tax avoidance Western European countries
German-speaking
German ( ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a ...
microstate located in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
between Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
headed by the prince of Liechtenstein
The prince regnant of Liechtenstein (german: Fürst von und zu Liechtenstein) is the monarch and head of state of Liechtenstein.Principality of Liechtenstein Family - Die fürstliche Familie (in German) The Liechtenstein family, after which t ...
.
Liechtenstein is bordered by Switzerland to the west and south and Austria to the east and north. It is Europe's fourth-smallest country, with an area of just over and a population of 38,749 (). Divided into 11 municipalities, its capital is Vaduz
Vaduz ( or , High Alemannic pronunciation: [])Hans Stricker, Toni Banzer, Herbert Hilbe: ''Liechtensteiner Namenbuch. Die Orts- und Flurnamen des Fürstentums Liechtenstein.'' Band 2: ''Die Namen der Gemeinden Triesenberg, Vaduz, Schaan.'' Hrsg. ...
, and its largest municipality is Schaan
Schaan () is the largest municipality of Liechtenstein by population. It is located to the north of Vaduz, the capital, in the central part of the country. it has a population of 6,039 making it the most populous administrative district in Lie ...
. It is also the smallest country to border two countries. Liechtenstein is a doubly landlocked country between Switzerland and Austria.
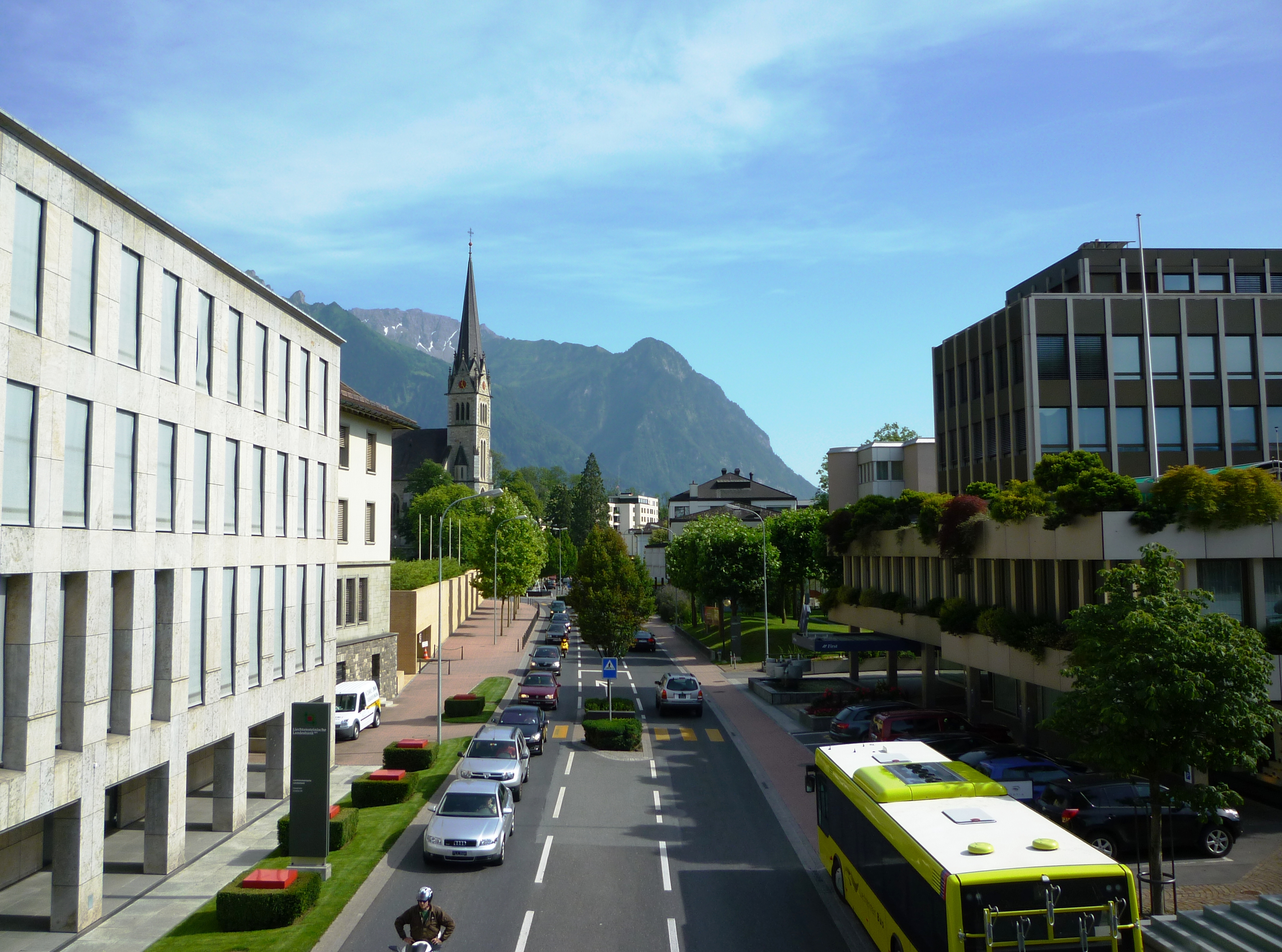
Economically, Liechtenstein has one of the highest gross domestic products per person in the world when adjusted for purchasing power parity. The country has a strong financial sector
Financial services are the economic services provided by the finance industry, which encompasses a broad range of businesses that manage money, including credit unions, banks, credit-card companies, insurance companies, accountancy companies, ...
centred in Vaduz. It was once known as a billionaire tax haven
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or n ...
, but is no longer on any official blacklists of uncooperative tax haven countries. An Alpine country, Liechtenstein is mountainous, making it a winter sport
Winter sports or winter activities are competitive sports or non-competitive recreational activities which are played on snow or ice. Most are variations of skiing, ice skating and sledding. Traditionally, such games were only played in cold are ...
destination.
Liechtenstein is a member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, the European Free Trade Association, and the Council of Europe. Although not a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
because it was not designed with microstates in mind, it participates in both the Schengen Area and the European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade As ...
. It has a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set up ...
and a monetary union
A currency union (also known as monetary union) is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more states sharing the same currency. These states may not necessarily have any further integration (such as an economic and monetary union, ...
with Switzerland.
History
Early history


 The oldest traces of human existence in the area of present-day Liechtenstein date back to the Middle Paleolithic era.History
The oldest traces of human existence in the area of present-day Liechtenstein date back to the Middle Paleolithic era.Historyswissworld.org. Retrieved 27 June 2009
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
farming settlements appeared in the valleys around 5300 BC.
The Hallstatt
Hallstatt ( , , ) is a small town in the district of Gmunden, in the Austrian state of Upper Austria. Situated between the southwestern shore of Hallstätter See and the steep slopes of the Dachstein massif, the town lies in the Salzkammergut ...
and La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defi ...
s flourished during the late Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
, from around 450 BC—possibly under some influence of both the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*The Etruscan language, an extinct language in ancient Italy
*Something derived from or related to the Etruscan civilization
**Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
** Etrusca ...
civilisations. One of the most important tribal groups in the Alpine region were the Helvetii. In 58 BC, at the Battle of Bibracte
The Battle of Bibracte was fought between the Helvetii and six Roman legions, under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar. It was the second major battle of the Gallic Wars.
Prelude
The Helvetii, a confederation of Gallic tribes, had begun a total ...
, Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
defeated the Alpine tribes, thereby bringing the region under close control of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
. By 15 BC, Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
—later the second Roman emperor—with his brother, Drusus
Drusus may refer to:
* Claudius (Tiberius Claudius Drusus) (10 BC–AD 54), Roman emperor from 41 to 54
* Drusus Caesar (AD 8–33), adoptive grandson of Roman emperor Tiberius
* Drusus Julius Caesar (14 BC–AD 23), son of Roman emperor Tiberiu ...
, conquered the entire Alpine area. Liechtenstein then became integrated into the Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west ...
. The area was garrisoned by the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
, which maintained large legionary camps at Brigantium (Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
), near Lake Constance, and at Magia (Swiss). The Romans built and maintained a road
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
which ran through the territory. Around AD 260 Brigantium was destroyed by the Alemanni, a Germanic people
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
who later settled in the area around AD 450.
In the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, the Alemanni settled the eastern Swiss plateau
The Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau (german: Schweizer Mittelland; french: plateau suisse; it, altopiano svizzero) is one of the three major landscapes in Switzerland, lying between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss Alps. It covers about 30% of ...
by the 5th century and the valleys of the Alps
The main valleys of the Alps, orographically by drainage basin.
Rhine basin (North Sea)
High Rhine
*Aare
**Limmat
***Linth (Glarus)
**** Lake Walen
***** Seeztal
**** Klöntal
**** Sernftal
**Reuss
***Lake Lucerne
**** Sarner Aa ( Brünig Pas ...
by the end of the 8th century, with Liechtenstein located at the eastern edge of Alemannia. In the 6th century the entire region became part of the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
following Clovis I's victory over the Alemanni at Tolbiac in AD 504.Switzerland historyNationsencyclopedia.com. Retrieved 27 November 2009
Nationsonline.org. Retrieved 27 November 2009. The area that later became Liechtenstein remained under Frankish hegemony (
Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
and Carolingian dynasties) until the Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
divided the Carolingian empire in AD 843, following the death of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
in 814. The territory of present-day Liechtenstein formed part of East Francia. It would later be reunified with Middle Francia
Middle Francia ( la, Francia media) was a short-lived Frankish kingdom which was created in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun after an intermittent civil war between the grandsons of Charlemagne resulted in division of the united empire. Middle Franc ...
under the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, around AD 1000. Until about 1100, the predominant language of the area was Romansch, but thereafter German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
began to gain ground in the territory. In 1300 another Alemannic population—the Walser
The Walser people are the speakers of the Walser German dialects, a variety of Highest Alemannic.
They inhabit the region of the Alps of Switzerland and Liechtenstein, as well as the fringes of Italy and Austria.
The Walser people are named a ...
s, who originated in Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
—entered the region and settled; the mountain village of Triesenberg
Triesenberg is a municipality in Liechtenstein with a population of 2,636. Its area of makes it the largest municipality in Liechtenstein. The center of the municipality rests at an elevation of .
History
Triesenberg is noted for its distinct di ...
today preserves features of the Walser dialect.
Foundation of a dynasty
By 1200, dominions across the Alpine plateau were controlled by the Houses of Savoy, Zähringer, Habsburg, and Kyburg. Other regions were accorded theImperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
that granted the empire direct control over the mountain passes. When the Kyburg dynasty fell in 1264, the Habsburgs under King Rudolph I (Holy Roman Emperor in 1273) extended their territory to the eastern Alpine plateau that included the territory of Liechtenstein. This region was enfeoffed
In the Middle Ages, especially under the European feudal system, feoffment or enfeoffment was the deed by which a person was given land in exchange for a pledge of service. This mechanism was later used to avoid restrictions on the passage of ti ...
to the Counts of Hohenems until the sale to the Liechtenstein dynasty
The House of Liechtenstein, from which the principality takes its name, is the family which reigns by hereditary right over the principality of Liechtenstein. Only dynastic members of the family are eligible to inherit the throne. The dynasty's me ...
in 1699.
In 1396 Vaduz
Vaduz ( or , High Alemannic pronunciation: [])Hans Stricker, Toni Banzer, Herbert Hilbe: ''Liechtensteiner Namenbuch. Die Orts- und Flurnamen des Fürstentums Liechtenstein.'' Band 2: ''Die Namen der Gemeinden Triesenberg, Vaduz, Schaan.'' Hrsg. ...
(the southern region of Liechtenstein) gained imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
, i.e. it became subject to the Holy Roman Emperor alone.
The family from which the principality takes its name originally came from Liechtenstein Castle
Liechtenstein Castle (german: Burg Liechtenstein) is a privately owned castle near Maria Enzersdorf in Lower Austria, bordering Vienna. It is on the edge of the '' Wienerwald'' (Vienna Woods). The castle, originally built during the 12th cen ...
in Lower Austria, which they had possessed from at least 1140 until the 13th century (and again from 1807 onwards). The Liechtensteins acquired land, predominantly in Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The m ...
, Lower Austria
Lower Austria (german: Niederösterreich; Austro-Bavarian: ''Niedaöstareich'', ''Niedaestareich'') is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Since 1986, the capital of Lower Austria has been Sankt P ...
, Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
, and Styria. As these territories were all held in feudal tenure from more senior feudal lords, particularly various branches of the Habsburgs, the Liechtenstein dynasty was unable to meet a primary requirement to qualify for a seat in the Imperial diet (parliament), the . Even though several Liechtenstein princes served several Habsburg rulers as close advisers, without any territory held directly from the Imperial throne, they held little power in the Holy Roman Empire.
For this reason, the family sought to acquire lands that would be classed as (not sellable) or held without any intermediate feudal tenure, directly from the Holy Roman Emperor. During the early 17th century Karl I of Liechtenstein
Karl I (30 July 1569 – 12 February 1627), was the first member of the Liechtenstein family to become a Prince of Liechtenstein, thus he was the founder of the Princely Family of Liechtenstein.
Karl was the elder son of Hartmann II, Baron of ...
was made a (prince) by the Holy Roman Emperor Matthias after siding with him in a political battle. Hans-Adam I was allowed to purchase the minuscule ('Lordship') of Schellenberg and the county of Vaduz (in 1699 and 1712 respectively) from the Hohenems. Tiny Schellenberg and Vaduz had exactly the political status required: no feudal lord other than their comital
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
sovereign and the suzerain Emperor.
Principality
On 23 January 1719, after the lands had been purchased, Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, decreed that Vaduz and Schellenberg were united and elevated the newly formed territory to the dignity of (' principality') with the name "Liechtenstein" in honour of " istrue servant,Anton Florian of Liechtenstein
Anton Florian (28 May 1656 – 11 October 1721) was the Prince of Liechtenstein between 1718 and 1721.
Anton Florian was born in Wilfersdorf, in what is now Lower Austria. During the War of the Spanish Succession, he went to Spain, where he was ...
". On this date, Liechtenstein became a sovereign member state of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
. It is a testimony to the mere political expediency of the purchase that the Princes of Liechtenstein did not visit their new principality for almost 100 years.
By the early 19th century, as a result of the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
in Europe, the Holy Roman Empire came under the effective control of France, following the crushing defeat at Austerlitz Austerlitz may refer to:
History
* Battle of Austerlitz, an 1805 victory by the French Grand Army of Napoleon Bonaparte
Places
* Austerlitz, German name for Slavkov u Brna in the Czech Republic, which gave its name to the Battle of Austerlitz a ...
by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
in 1805. In 1806 Emperor Francis II abdicated and dissolved the Holy Roman Empire, ending more than 960 years of feudal government. Napoleon reorganized much of the Empire into the Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria an ...
. This political restructuring had broad consequences for Liechtenstein: the historical imperial, legal, and political institutions had been dissolved. The state ceased to owe an obligation to any feudal lord beyond its borders.
Modern publications generally attribute Liechtenstein's sovereignty to these events. Its prince ceased to owe an obligation to any suzerain. From 25 July 1806, when the Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria an ...
was founded, the Prince of Liechtenstein was a member, in fact, a vassal, of its hegemon, styled ''protector'', the French Emperor Napoleon I, until the dissolution of the confederation on 19 October 1813.
Soon afterward, Liechtenstein joined the German Confederation (20 June 181523 August 1866), which was presided over by the Emperor of Austria.
In 1818, Johann I Joseph, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Johann I granted the territory a limited constitution. In that same year Aloys II, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Aloys became the first member of the House of Liechtenstein to set foot in the principality that bore their name. The next visit would not occur until 1842.
Developments during the 19th century included:
* 1836: the first factory for making ceramics was opened.
* 1861: the Savings and Loans Bank was founded along with the first cotton-weaving mill.
* 1866: the German Confederation was dissolved.
* 1868: the Liechtenstein Army was disbanded for financial reasons.
* 1872: a railway line between Switzerland and the Austro-Hungarian Empire was constructed through Liechtenstein.
* 1886: two bridges over the Rhine to Switzerland were built.
20th century
Until the end of World War I, Liechtenstein was closely tied first to the Austrian Empire and later to Austria-Hungary; the ruling princes continued to derive much of their wealth from estates in the Habsburg territories, and spent much of their time at their two palaces in Vienna. Johann II, Prince of Liechtenstein, Johann II appointed Carl von In der Maur, an Austrian aristocrat, to serve as the Prime Minister of Liechtenstein, Governor of Liechtenstein. The economic devastation caused by the First World War forced the country to conclude a Liechtenstein–Switzerland relations#Cooperation, customs and monetary union with its other neighbour, Switzerland. In 1929, 75-year-old Franz I, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Franz I succeeded to the throne. He had just married Elisabeth von Gutmann, a wealthy woman from Vienna whose father was a Jewish businessman from Moravia. Although Liechtenstein had no official Nazi party, a Nazi sympathy movement arose within its National Union party. Local Liechtenstein Nazis identified Elisabeth as their Jewish "problem".
In March 1938, just after the Anschluss, annexation of Austria by Nazi Germany, Franz named as regent his 31-year-old grandnephew and heir-presumptive, Franz Joseph II, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Franz Joseph. Franz died in July that year, and Franz Joseph succeeded to the throne. Franz Joseph II first moved to Liechtenstein in 1938, a few days after Austria's annexation.
During World War II, Liechtenstein remained officially neutral, looking to neighbouring Switzerland for assistance and guidance, while family treasures from dynastic lands and possessions in Bohemia,
In 1929, 75-year-old Franz I, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Franz I succeeded to the throne. He had just married Elisabeth von Gutmann, a wealthy woman from Vienna whose father was a Jewish businessman from Moravia. Although Liechtenstein had no official Nazi party, a Nazi sympathy movement arose within its National Union party. Local Liechtenstein Nazis identified Elisabeth as their Jewish "problem".
In March 1938, just after the Anschluss, annexation of Austria by Nazi Germany, Franz named as regent his 31-year-old grandnephew and heir-presumptive, Franz Joseph II, Prince of Liechtenstein, Prince Franz Joseph. Franz died in July that year, and Franz Joseph succeeded to the throne. Franz Joseph II first moved to Liechtenstein in 1938, a few days after Austria's annexation.
During World War II, Liechtenstein remained officially neutral, looking to neighbouring Switzerland for assistance and guidance, while family treasures from dynastic lands and possessions in Bohemia, Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The m ...
, and Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
were taken to Liechtenstein for safekeeping. At the close of the conflict, Czechoslovakia and Poland, acting to seize what they considered German possessions, expropriated all of the Liechtenstein dynasty's properties in those three regions. The expropriations (subject to Foreign relations of Liechtenstein#International dispute with Czechoslovakia, Czech Republic and Slovakia, modern legal dispute at the International Court of Justice) included over of agricultural and forest land (most notably the UNESCO listed Lednice–Valtice Cultural Landscape), and several family castles and palaces.
In 2005 it was revealed that Jewish slave labourers from the Strasshof an der Nordbahn, Strasshof concentration camp, provided by the ''Schutzstaffel, SS'', had worked on estates in Austria owned by Liechtenstein's Princely House.
Citizens of Liechtenstein were forbidden to enter Czechoslovakia during the Cold War. More recently the diplomatic conflict revolving around the controversial postwar Beneš decrees resulted in Liechtenstein not having international relations with the Czech Republic or Slovakia. Diplomatic relations were established between Liechtenstein and the Czech Republic on 13 July 2009, and with Slovakia on 9 December 2009.
Financial centre
Liechtenstein was in dire financial straits following the end of World War II. The Liechtenstein dynasty often resorted to selling family artistic treasures, including the portrait ''Ginevra de' Benci'' by Leonardo da Vinci, which was purchased by the National Gallery of Art of the United States in 1967 for 5 million ($ million in dollars), then a record price for a painting. By the late 1970s, Liechtenstein used its low corporate tax rates to draw many companies and became one of the wealthiest countries in the world. Liechtenstein is one of the few countries in Europe (along with Monaco and San Marino) Tax haven, not to have a tax treaty with the United States, and efforts toward one seem to have stalled. the Prince of Liechtenstein is the world's sixth List of the richest royals, wealthiest monarch, with an estimated wealth of 3.5 billion.These Are The World’s Richest Royals", 2019 ''CEO World''. 18 September 2019. The country's population enjoys one of the List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, world's highest standards of living.
Government


 Liechtenstein has a monarch as head of state, and an elected parliament that enacts the law. It is also a direct democracy, where voters can propose and enact constitutional amendments and legislation independently of the legislature. The Constitution of Liechtenstein was Liechtenstein constitutional referendum, 2003, adopted in March 2003, replacing the 1921 constitution. The 1921 constitution had established Liechtenstein as a constitutional monarchy headed by the reigning prince of the Princely House of Liechtenstein; a parliamentary system had been established, although the reigning Prince retained substantial political authority.
The reigning Prince is the Head of State and represents Liechtenstein in its international relations (although Switzerland has taken responsibility for much of Liechtenstein's diplomatic relations). The Prince may veto laws adopted by parliament. The Prince may call referendums, propose new legislation, and dissolve parliament, although dissolution of parliament may be subject to a referendum.
Executive authority is vested in a collegiate government comprising the head of government (prime minister) and four government councillors (ministers). The head of government and the other ministers are appointed by the Prince upon the proposal of parliament and with its concurrence, and reflect the balance of parties in parliament. The constitution stipulates that at least two government members be chosen from each of the two regions. The members of the government are collectively and individually responsible to parliament; parliament may ask the Prince to remove an individual minister or the entire government.
Legislative authority is vested in the unicameral Landtag of Liechtenstein, Landtag, made up of 25 members elected for maximum four-year terms according to a proportional representation formula. Fifteen members are elected from the Oberland (electoral district), Oberland (Upper Country or region) and ten from the Unterland (electoral district), Unterland (Lower Country or region). Parties must receive at least 8% of the national vote to win seats in parliament, i.e., enough for two seats in the 25-seat legislature. Parliament proposes and approves a government, which the Prince formally appoints. Parliament may also pass votes of no confidence in the entire government or individual members.
Parliament elects from among its members a "Landesausschuss" (National Committee) made up of the president of the parliament and four additional members. The National Committee is charged with performing functions of parliamentary supervision. Parliament can call for referendums on proposed legislation. Parliament shares the authority to propose new legislation with the Prince and with the number of Citizenship, citizens required for to initiate a referendum.
The courts of Liechtenstein, Judicial authority is vested in the Regional Court at Vaduz, the Princely High Court of Appeal at Vaduz, the Princely Supreme Court, the Administrative Court, and the State Court. The State Court rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution and has five members elected by parliament.
On 1 July 1984, Liechtenstein became the last country in Europe to grant women the right to vote. The Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum, 1984, referendum on women's suffrage, in which only men were allowed to participate, passed with 51.3% in favour.
Liechtenstein has a monarch as head of state, and an elected parliament that enacts the law. It is also a direct democracy, where voters can propose and enact constitutional amendments and legislation independently of the legislature. The Constitution of Liechtenstein was Liechtenstein constitutional referendum, 2003, adopted in March 2003, replacing the 1921 constitution. The 1921 constitution had established Liechtenstein as a constitutional monarchy headed by the reigning prince of the Princely House of Liechtenstein; a parliamentary system had been established, although the reigning Prince retained substantial political authority.
The reigning Prince is the Head of State and represents Liechtenstein in its international relations (although Switzerland has taken responsibility for much of Liechtenstein's diplomatic relations). The Prince may veto laws adopted by parliament. The Prince may call referendums, propose new legislation, and dissolve parliament, although dissolution of parliament may be subject to a referendum.
Executive authority is vested in a collegiate government comprising the head of government (prime minister) and four government councillors (ministers). The head of government and the other ministers are appointed by the Prince upon the proposal of parliament and with its concurrence, and reflect the balance of parties in parliament. The constitution stipulates that at least two government members be chosen from each of the two regions. The members of the government are collectively and individually responsible to parliament; parliament may ask the Prince to remove an individual minister or the entire government.
Legislative authority is vested in the unicameral Landtag of Liechtenstein, Landtag, made up of 25 members elected for maximum four-year terms according to a proportional representation formula. Fifteen members are elected from the Oberland (electoral district), Oberland (Upper Country or region) and ten from the Unterland (electoral district), Unterland (Lower Country or region). Parties must receive at least 8% of the national vote to win seats in parliament, i.e., enough for two seats in the 25-seat legislature. Parliament proposes and approves a government, which the Prince formally appoints. Parliament may also pass votes of no confidence in the entire government or individual members.
Parliament elects from among its members a "Landesausschuss" (National Committee) made up of the president of the parliament and four additional members. The National Committee is charged with performing functions of parliamentary supervision. Parliament can call for referendums on proposed legislation. Parliament shares the authority to propose new legislation with the Prince and with the number of Citizenship, citizens required for to initiate a referendum.
The courts of Liechtenstein, Judicial authority is vested in the Regional Court at Vaduz, the Princely High Court of Appeal at Vaduz, the Princely Supreme Court, the Administrative Court, and the State Court. The State Court rules on the conformity of laws with the constitution and has five members elected by parliament.
On 1 July 1984, Liechtenstein became the last country in Europe to grant women the right to vote. The Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum, 1984, referendum on women's suffrage, in which only men were allowed to participate, passed with 51.3% in favour.
Current constitution
In a Liechtenstein constitutional referendum, 2003, national referendum in March 2003, nearly two-thirds of the electorate voted in support of Hans-Adam II's proposed new constitution. The proposed constitution was criticised by many, including the Council of Europe, as expanding the powers of the monarchy (continuing the power to veto any law, and allowing the Prince to dismiss the government or any minister). The Prince threatened that if the constitution failed, he would, among other things, convert some royal property for commercial use and move to Austria. The princely family and the Prince enjoy tremendous public support inside the nation, and the resolution passed with about 64% in favour. A proposal to revoke the Prince's veto powers was rejected by 76% of voters in a Liechtenstein constitutional referendum, 2012, 2012 referendum.Municipalities
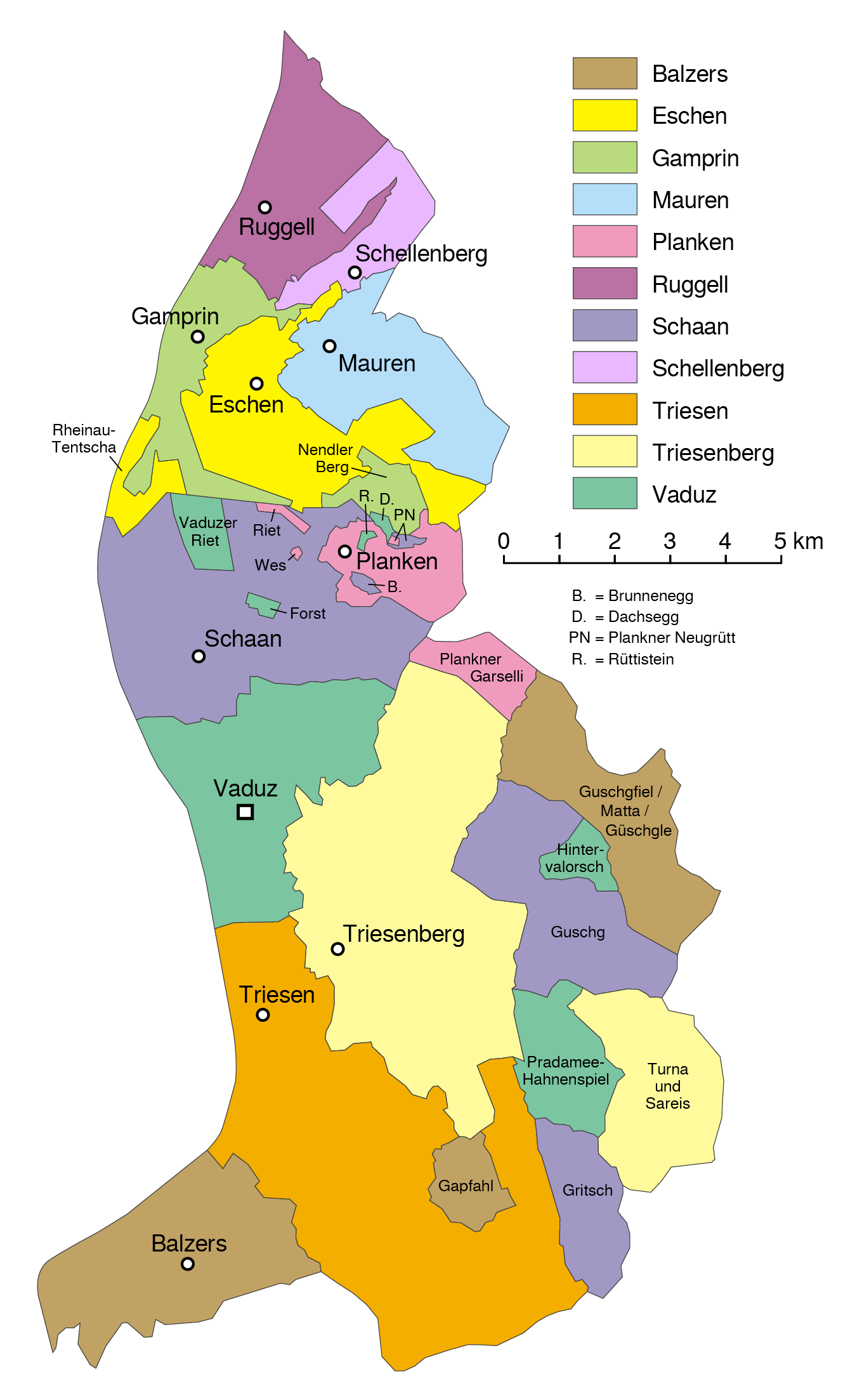
Municipalities of Liechtenstein are entitled to secede from the union by majority vote. The municipalities of Liechtenstein are divided between the two electoral districts of Unterland and Oberland. The country's political division is historical; the Unterland depends on Schellenberg, the Oberland on the county of Vaduz. The northern communities of Eschen, Gamprin, Mauren, Ruggell and Schellenberg belong to Unterland; the municipalities of Balzers, Planken, Schaan, Triesen, Triesenberg and Vaduz belong to the much larger Oberland. The autonomy of the Liechtenstein communities is in the upper range compared to the other Central European states along with Switzerland. Despite their small size, the municipalities have complex forms in terms of their territorial extent: in addition to a main part, seven municipalities also include one or more exclaves. Citizens' cooperatives, which exist in about half of Liechtenstein's municipalities, own forests and pastures for Collective farming, collective use, as well as parceled areas that are left for private use.International awards
In 2013, Liechtenstein won for the first time a SolarSuperState Prize in the Solar category recognizing the achieved level of the usage of photovoltaics per population within the state territory. The SolarSuperState Association justified this prize with the cumulative installed photovoltaic power of some 290 Watt per capita at the end of 2012. This placed Liechtenstein second in the world after Germany. Also in 2014, the SolarSuperState Association awarded the second place SolarSuperState Prize in the Solar category to Liechtenstein. In the years 2015 and 2016, Liechtenstein was honoured with the first place SolarSuperState Prize in the Solar category because it had the world's biggest cumulative installed photovoltaic power output per capita.
Foreign relations
In the absence of political or military power, Liechtenstein has sought to preserve its sovereignty over the past 200 years through membership in legal communities. Multilateralism, International cooperation and European integration are therefore constants of Liechtenstein's foreign policy, aimed at continuing to safeguard the country's sovereignty as recognized under international law. Decisive for the domestic legitimacy and sustainability of this foreign policy were and are strong direct-democratic and citizen-oriented decision-making mechanisms, which are anchored in Liechtenstein in the Constitution of 1921. Important historical stages in Liechtenstein's integration and cooperation policy were its accession to theConfederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria an ...
in 1806, to the German Confederation in 1815, the conclusion of bilateral customs and currency agreements with the Habsburg monarchy, Danube Monarchy in 1852, and finally the Customs Treaty with Switzerland in 1923, which was followed by a whole series of other important bilateral treaties.
Post-war economic reconstruction was followed by accession to the Statute of the International Court of Justice in 1950, Liechtenstein signed the CSCE Helsinki Final Act (today's OSCE) together with 34 other states in 1975, Liechtenstein joined the Council of Europe in 1978, and Liechtenstein was admitted to the United Nations (UN) on September 18, 1990. In 1991, Liechtenstein joined the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) as a full member, and since 1995 Liechtenstein has been a member of the European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade As ...
(EEA) and the World Trade Organization (WTO). In 2008, Liechtenstein joined the Schengen/Dublin Agreement together with Switzerland. From an economic and integration policy perspective, relations within the framework of the EEA and the EU occupy a special position in Liechtenstein's foreign policy. The Hereditary Prince of Liechtenstein also participates in the annual meetings of the heads of state of the List of countries and territories where German is an official language, German-speaking countries (consisting of EU and non-EU members).
Relations with Switzerland are particularly extensive because of the close cooperation in many areas; Switzerland performs tasks in some places that would be difficult for the Principality to handle on its own because of its small size. Since 2000, Switzerland has appointed an ambassador to Liechtenstein, but he resides in Bern. Liechtenstein's consular representation has been mostly handled by Switzerland since the Customs Treaty with Switzerland of 1923.
Liechtenstein maintains direct diplomatic missions in Vienna, Bern, Berlin, Brussels, Strasbourg, and Washington, D.C., as well as Permanent Missions in New York and Geneva to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
. Currently, diplomatic missions from 78 countries are accredited to Liechtenstein, but mostly reside in Bern. The Diplomatic mission, Embassy in Brussels coordinates contacts with the European Union, Belgium, and also the Holy See.
For a long time, diplomatic relations with Germany were maintained through a non-resident ambassador; that is, a contact person who was not permanently resident in Germany. Since 2002, however, Liechtenstein has had a permanent ambassador in Berlin, while the German embassy in Switzerland is also responsible for the Principality. Liechtenstein's Ministry of Foreign Affairs considers the contacts to be extremely fruitful and important for the country's development, especially on the economic level.
Conflicts over the handling of banking and tax data have repeatedly strained relations with Germany. On September 2, 2009, Liechtenstein and Germany signed an agreement on cooperation and the exchange of information in tax matters. The text of the agreement followed the OECD model agreement and provides for an exchange of information on tax matters upon request as of the 2010 tax year. In addition, Liechtenstein regards the Germany as an important partner in safeguarding its interests in European integration. At the cultural level, project sponsorship plays a particularly important role. For example, the Hilti Foundation financed the exhibition "Egypt's Sunken Treasures" in Berlin, and the state donated 20,000 euros following the fire at the Duchess Anna Amalia Library in Weimar.
Geography
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
and is bordered to the east by the Austrian state of Vorarlberg, to the south by the canton of Grisons (Switzerland) and to the west by the canton of St. Gallen (Switzerland). The Rhine forms the entire western border of Liechtenstein. Measured south to north the country is about long. Its highest point, the Grauspitz, is . Despite its Alpine location, prevailing southerly winds make the climate comparatively mild. In winter, the mountain slopes are well suited to winter sports.
New surveying, surveys using more accurate measurements of the country's borders in 2006 have set its area at , with borders of . Liechtenstein's borders are longer than previously thought.
Liechtenstein is one of the world's two doubly landlocked country, doubly landlocked countries – countries wholly surrounded by other landlocked countries (the other is Uzbekistan). Liechtenstein is the List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-smallest independent nation in the world by area.
The principality of Liechtenstein is Municipalities of Liechtenstein, divided into 11 communes called ''Gemeinden'' (singular ''Gemeinde''). The ''Gemeinden'' mostly consist of only a single town or village. Five of them (Eschen, Gamprin, Mauren, Ruggell, and Schellenberg) fall within the electoral district ''Unterland'' (the lower county), and the remainder (Balzers, Planken, Schaan
Schaan () is the largest municipality of Liechtenstein by population. It is located to the north of Vaduz, the capital, in the central part of the country. it has a population of 6,039 making it the most populous administrative district in Lie ...
, Triesen, Triesenberg
Triesenberg is a municipality in Liechtenstein with a population of 2,636. Its area of makes it the largest municipality in Liechtenstein. The center of the municipality rests at an elevation of .
History
Triesenberg is noted for its distinct di ...
, and Vaduz
Vaduz ( or , High Alemannic pronunciation: [])Hans Stricker, Toni Banzer, Herbert Hilbe: ''Liechtensteiner Namenbuch. Die Orts- und Flurnamen des Fürstentums Liechtenstein.'' Band 2: ''Die Namen der Gemeinden Triesenberg, Vaduz, Schaan.'' Hrsg. ...
) within ''Oberland'' (the upper county).
Climate
Despite its Alpine climate, alpine location, the prevailing southerly winds temper Liechtenstein's climate. Its climate is continental, with cloudy and cold winters, with frequent rain and snowfall. Summers are cool to slightly warm, cloudy, and humid. The country's climate is relatively mild despite its mountainous location. It is strongly influenced by the action of foehn (warm and dry fall wind), so the vegetation period is prolonged in spring and autumn and temperatures around 15 °C due to the strong foehn are not uncommon even in winter. The mountain ranges of Switzerland and the Vorarlberg upstream protect from the cold polar and Atlantic air, creating a typical alpine inland protective layer. The principality has orchards with leafy meadows and a long tradition of viticulture. Liechtenstein's small land area hardly plays a role in climatic differences, but the vertical division into different altitudes is of great importance, so that significant climatic differences arise. In winter the temperature rarely drops below minus 15 degrees Celsius, while in summer the average temperatures range between 20 and 28 degrees Celsius. Annual precipitation measurements amount to an average of about 900 to 1200 millimeters, in the direct alpine region, however, precipitation is often up to 1900 millimeters. The average duration of sunshine is about 1600 hours per year.Rivers and lakes
The Rhine is the longest and largest body of water in Liechtenstein. With a length of approximately 27 kilometers, it represents the natural border with Switzerland and is of great importance for Liechtenstein's water supply. Furthermore, the Rhine is an important recreational area for the population. At 10 kilometers, the Samina is the second longest river in the Principality. The troubled river begins at Triesenberg and flows into the Ill in Austria (near Feldkirch). The only naturally formed lake in Liechtenstein is the Gampriner Seelein, which was not formed until 1927 by a flooding of the Rhine with enormous erosion. In addition, there are other artificially created lakes, which are mainly used to generate electricity. One of them is the Steg Reservoir, the largest lake in Liechtenstein.Mountains
About half of Liechtenstein's territory is mountainous. Liechtenstein lies entirely in the Rätikon, Rhaetikon and is thus – depending on the classification of the Alps – assigned either to the Eastern Alps (two-part division of the Alps) or to the Central Alps (three-part division of the Alps). The highest point of Liechtenstein is the Vordere Grauspitz (Vordergrauspitz) with an altitude of 2599 m above sea level, while the lowest point is the Ruggeller Riet with an altitude of 430 m above sea level. In total, there are 32 mountains in Liechtenstein with an altitude of at least 2000 meters. The Falknishorn, at 2452 meters above sea level, is the fifth highest mountain in Liechtenstein and represents the southernmost point of the country. The Liechtenstein-Graubünden-Vorarlberg border triangle is the Naafkopf (2570 m above sea level). In addition to the peaks of the Alpine chain, which belong to the Limestone Alps, two inselbergs, Fläscherberg (1135 meters above sea level) in the south and Eschnerberg (698 m) in the north, rise from the Rhine Valley and belong to the Helvetic cover or flysch zone of the Alps. Eschnerberg represents an important settlement area in the Liechtenstein Unterland.Economy

 Despite its limited natural resources, Liechtenstein is one of the few countries in the world with more registered companies than citizens; it has developed a prosperous, highly industrialized free-enterprise economy and boasts a financial service sector as well as a living standard that compares favourably with those of the urban areas of Liechtenstein's much larger European neighbours.
Liechtenstein participates in a
Despite its limited natural resources, Liechtenstein is one of the few countries in the world with more registered companies than citizens; it has developed a prosperous, highly industrialized free-enterprise economy and boasts a financial service sector as well as a living standard that compares favourably with those of the urban areas of Liechtenstein's much larger European neighbours.
Liechtenstein participates in a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set up ...
with Switzerland and employs the Swiss franc as the national currency. The country imports about 85% of its energy. Liechtenstein has been a member of the European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade As ...
(an organization serving as a bridge between the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
) since May 1995.
The government is working to harmonize its economic policies with those of an integrated Europe. In 2008, the unemployment rate stood at 1.5%. Liechtenstein has only one hospital, the Liechtensteinisches Landesspital in Vaduz. As of 2014 the CIA World Factbook estimated the gross domestic product (GDP) on a purchasing power parity basis to be $4.978 billion. As of 2009 the estimate per capita was $139,100, the highest listed for the world.
Industries include electronics, textiles, precision instruments, metal manufacturing, power tools, anchor bolts, calculators, pharmaceuticals and food products. Its most recognizable international company and largest employer is Hilti, a manufacturer of Nail gun, direct fastening systems and other high-end power tools. Many cultivated fields and small farms are found both in the Oberland and Unterland. Liechtenstein produces wheat, barley, corn, potatoes, dairy products, livestock and Liechtenstein wine, wine.
Taxation
 The government of Liechtenstein taxes personal income, business income and principal (wealth). The basic rate of Income tax#Personal, personal income tax is 1.2%. When combined with the additional income tax imposed by the communes, the combined income tax rate is 17.82%. An additional income tax of 4.3% is levied on all employees under the country's social security programme. This rate is higher for the self-employed, up to a maximum of 11%, making the maximum income tax rate about 29% in total. The basic wealth tax, tax rate on wealth is 0.06% per annum, and the combined total rate is 0.89%. The tax rate on corporate profits is 12.5%.
Liechtenstein's gift tax, gift and Inheritance tax, estate taxes vary depending on the relationship the recipient has to the giver and the amount of the inheritance. The tax ranges between 0.5% and 0.75% for spouses and children and 18% to 27% for non-related recipients. The estate tax is progressive.
Liechtenstein has previously received significant revenues from ''Stiftungen'' ("foundations"), financial entities created to hide the true owner of nonresident foreigners' financial holdings. The foundation is registered in the name of a Liechtensteiner, often a lawyer. This set of laws used to make Liechtenstein a popular
The government of Liechtenstein taxes personal income, business income and principal (wealth). The basic rate of Income tax#Personal, personal income tax is 1.2%. When combined with the additional income tax imposed by the communes, the combined income tax rate is 17.82%. An additional income tax of 4.3% is levied on all employees under the country's social security programme. This rate is higher for the self-employed, up to a maximum of 11%, making the maximum income tax rate about 29% in total. The basic wealth tax, tax rate on wealth is 0.06% per annum, and the combined total rate is 0.89%. The tax rate on corporate profits is 12.5%.
Liechtenstein's gift tax, gift and Inheritance tax, estate taxes vary depending on the relationship the recipient has to the giver and the amount of the inheritance. The tax ranges between 0.5% and 0.75% for spouses and children and 18% to 27% for non-related recipients. The estate tax is progressive.
Liechtenstein has previously received significant revenues from ''Stiftungen'' ("foundations"), financial entities created to hide the true owner of nonresident foreigners' financial holdings. The foundation is registered in the name of a Liechtensteiner, often a lawyer. This set of laws used to make Liechtenstein a popular tax haven
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or n ...
for extremely wealthy individuals and businesses attempting to avoid or evade taxes in their home countries. In recent years, Liechtenstein has displayed stronger determination to prosecute international money launderers and worked to promote an image as a legitimate finance centre. In February 2008, the country's LGT Group, LGT Bank was implicated in a 2008 Liechtenstein tax affair, tax-fraud scandal in Germany, which strained the ruling family's relationship with the German government. Crown Prince Alois has accused the German government of trafficking in stolen goods, referring to its $7.3 million purchase of private banking information offered by a former employee of LGT Group. The United States Senate's subcommittee on tax haven banks said that the LGT bank, owned by the princely family, and on whose board they serve, "is a willing partner, and an aider and abettor to clients trying to evade taxes, dodge creditors or defy court orders".
 The 2008 Liechtenstein tax affair is a series of tax investigations in numerous countries whose governments suspect that some of their citizens have evaded tax obligations by using banks and trusts in Liechtenstein; the affair broke open with the biggest complex of investigations ever initiated for tax evasion in Germany. It was also seen as an attempt to put pressure on Liechtenstein, then one of the remaining FATF blacklist, uncooperative tax havens—along with Andorra and Monaco—as identified by the Paris-based Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 2007. On 27 May 2009 the OECD removed Liechtenstein from the blacklist of uncooperative countries.
In August 2009, the British government department HM Revenue & Customs agreed with Liechtenstein to start exchanging information. It is believed that up to 5,000 British investors have roughly £3 billion deposited in accounts and trusts in the country.
In October 2015, the European Union and Liechtenstein signed a tax agreement to ensure the automatic exchange of financial information in case of tax disputes. The collection of data started in 2016. It is another step to bring the principality in line with other European countries regarding its taxation of private individuals and corporate assets.
The 2008 Liechtenstein tax affair is a series of tax investigations in numerous countries whose governments suspect that some of their citizens have evaded tax obligations by using banks and trusts in Liechtenstein; the affair broke open with the biggest complex of investigations ever initiated for tax evasion in Germany. It was also seen as an attempt to put pressure on Liechtenstein, then one of the remaining FATF blacklist, uncooperative tax havens—along with Andorra and Monaco—as identified by the Paris-based Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 2007. On 27 May 2009 the OECD removed Liechtenstein from the blacklist of uncooperative countries.
In August 2009, the British government department HM Revenue & Customs agreed with Liechtenstein to start exchanging information. It is believed that up to 5,000 British investors have roughly £3 billion deposited in accounts and trusts in the country.
In October 2015, the European Union and Liechtenstein signed a tax agreement to ensure the automatic exchange of financial information in case of tax disputes. The collection of data started in 2016. It is another step to bring the principality in line with other European countries regarding its taxation of private individuals and corporate assets.
Tourism
Tourism accounts for a large portion of Liechtenstein's economy. Airbnb once offered to rent space for 450-900 guests in Liechtenstein for about US$70,000 per night.Demographics
With a population of 39,315 as of 31 December 2021, Liechtenstein is List of European countries by population, Europe's fourth-smallest country; Vatican City, San Marino, and Monaco have fewer residents. Its population is primarily Alemannic German, Alemannic-speaking, although one third is foreign-born, primarily German speakers from Germany,Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and Switzerland, along with other Swiss, Italians, and Turkish people, Turks. Foreign-born people make up two-thirds of the country's workforce.
Liechtensteiners have an average life expectancy at birth of 82.0 years, subdividing as male: 79.8 years, female: 84.8 years (2018 est.). The infant mortality rate is 4.2 deaths per 1,000 live births, according to 2018 estimates.
Languages
The official language is German, spoken by 92% of the population as their main language in 2020. 73% of Liechtenstein's population speak an Alemannic German, Alemannic dialect of German at home that is highly divergent from Standard German but closely related to dialects spoken in neighbouring regions such as Switzerland and Vorarlberg, Austria. InTriesenberg
Triesenberg is a municipality in Liechtenstein with a population of 2,636. Its area of makes it the largest municipality in Liechtenstein. The center of the municipality rests at an elevation of .
History
Triesenberg is noted for its distinct di ...
, a Walser German dialect promoted by the municipality is spoken. Swiss Standard German is also understood and spoken by most Liechtensteiners.
Religion
 According to the Constitution of Liechtenstein, Catholicism is its official state religion:
Liechtenstein offers protection to adherents of all religions, and considers the "religious interests of the people" a priority of the government. In Liechtenstein's schools, although exceptions are allowed, religious education in Catholicism or Protestantism (either Lutheran or Calvinist, or both) is legally required. Tax exemption is granted by the government to religious organizations. According to the Pew Research Center, social conflict caused by religious hostilities is low in Liechtenstein, and so is government restriction on the practice of religion.
According to the 2010 census, 85.8% of the total population is Christian, of whom 75.9% adhere to the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, constituted in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Vaduz, Catholic Archdiocese of Vaduz, while 9.6% are either Protestant, mainly organized in the Evangelical Church in Liechtenstein (a United church, Lutheran & Reformed) and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Liechtenstein, or Orthodoxy, Orthodox, mainly organized in the Christian-Orthodox Church. The largest minority religion is Islam (5.4% of the total population).
According to the Constitution of Liechtenstein, Catholicism is its official state religion:
Liechtenstein offers protection to adherents of all religions, and considers the "religious interests of the people" a priority of the government. In Liechtenstein's schools, although exceptions are allowed, religious education in Catholicism or Protestantism (either Lutheran or Calvinist, or both) is legally required. Tax exemption is granted by the government to religious organizations. According to the Pew Research Center, social conflict caused by religious hostilities is low in Liechtenstein, and so is government restriction on the practice of religion.
According to the 2010 census, 85.8% of the total population is Christian, of whom 75.9% adhere to the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, constituted in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Vaduz, Catholic Archdiocese of Vaduz, while 9.6% are either Protestant, mainly organized in the Evangelical Church in Liechtenstein (a United church, Lutheran & Reformed) and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Liechtenstein, or Orthodoxy, Orthodox, mainly organized in the Christian-Orthodox Church. The largest minority religion is Islam (5.4% of the total population).
Education
." Commune of Schaan. Retrieved 12 May 2016. "Realschule Schaan Duxgass 55 9494 Schaan" and "Sportschule Liechtenstein Duxgass 55 9494 Schaan" and "Realschule Vaduz Schulzentrum Mühleholz II 9490 Vaduz" and "Oberschule Vaduz Schulzentrum Mühleholz II 9490 Vaduz" *Realschule Schaan and Sportschule Liechtenstein in
Schaan
Schaan () is the largest municipality of Liechtenstein by population. It is located to the north of Vaduz, the capital, in the central part of the country. it has a population of 6,039 making it the most populous administrative district in Lie ...
Transport
 There are about of paved roadway within Liechtenstein, with of marked bicycle paths.
A railway connects Austria and Switzerland through Liechtenstein. The Rail transport in Liechtenstein, country's railways are administered by the Austrian Federal Railways as part of the route between Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, Feldkirch,
There are about of paved roadway within Liechtenstein, with of marked bicycle paths.
A railway connects Austria and Switzerland through Liechtenstein. The Rail transport in Liechtenstein, country's railways are administered by the Austrian Federal Railways as part of the route between Feldkirch, Vorarlberg, Feldkirch, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and Buchs, St. Gallen, Buchs, Switzerland. Liechtenstein is nominally within the Austrian Verkehrsverbund Vorarlberg tariff region.
There are four railway stations in Liechtenstein, namely Schaan-Vaduz railway station, Schaan-Vaduz, Forst Hilti railway station, Forst Hilti, Nendeln railway station, Nendeln and Schaanwald railway station, Schaanwald, served by an irregularly stopping train service between Feldkirch and Buchs provided by Austrian Federal Railways. While EuroCity and other long-distance international trains also travel along the route, they do not normally stop at the stations within the borders of Liechtenstein.
Liechtenstein Bus is a subsidiary of the PostBus Switzerland, Swiss Postbus system, but separately run, and connects to the Swiss bus network at Buchs, St. Gallen, Buchs and at Sargans. Buses also run to the Austrian town of Feldkirch.
Liechtenstein is one of only a few List of countries without an airport, countries without an airport. The nearest large airport is Zurich Airport near Zürich, Switzerland ( by road). The nearest small airport is St. Gallen-Altenrhein Airport, St. Gallen Airport (). Friedrichshafen Airport also provides access to Liechtenstein, as it is away. Balzers Heliport is available for chartered helicopter flights.
Culture

Media
The primary internet service provider and mobile network operator of Liechtenstein is Telecom Liechtenstein, located in Schaan. There are two conventional television channels in the country. The private channel 1FLTV was created in 2008 with a goal of joining the European Broadcasting Union, which it has not accomplished yet. The ''Landeskanal'' () is operated by the government's Unit for Information and Communication and carries government proceedings, Public affairs (broadcasting), public affairs programming, and cultural events. Both are seen on local cable providers, along with channels from the other German-speaking countries. The only free television is ORF (broadcaster), ORF from Austria, available via terrestrial overspill of its signal from Vorarlberg. Radio Liechtenstein (), which was established in 2004 along with the public-service broadcaster '':de:Liechtensteinischer Rundfunk, Liechtensteinischer Rundfunk'' (LRF) that operates it, is the country's only domestic radio station based in Triesen. Radio Liechtenstein and several programs of the Swiss Schweizer Radio und Fernsehen, SRF are broadcast from the Sender Erbi () overlooking Vaduz. Liechtenstein also has two major newspapers: ''Liechtensteiner Volksblatt'' and ''Liechtensteiner Vaterland''. Amateur radio is a hobby of some nationals and visitors. However, unlike virtually every other sovereign nation, Liechtenstein does not have its own ITU prefix. Conventionally, amateurs are issued call signs with the Swiss prefix "HB", followed by "0" or "L".Sports
 Liechtenstein Association football, football teams play in the Swiss football leagues. The Liechtenstein Football Cup allows access for one Liechtenstein team each year to the UEFA Europa Conference League; FC Vaduz, a team playing in the Swiss Challenge League, the second division in Swiss football, is the most successful team in the Cup, and scored their greatest success in the 1996–97 UEFA Cup Winners' Cup, European Cup Winners' Cup in 1996 when they drew with and defeated the Latvian team FK Jelgava, FC Universitate Riga by 1–1 and 4–2, to go on to a lucrative fixture against Paris Saint-Germain F.C., which they lost 0–3 and 0–4.
The Liechtenstein national football team is regarded as an easy target for any team drawn against them; this was the basis for a book about Liechtenstein's unsuccessful qualifying campaign for the 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2002 World Cup by British author Charlie Connelly. In one surprising week during autumn 2004, however, the team managed a 2–2 draw with Portugal national football team, Portugal, who only a few months earlier had been the losing finalists in the UEFA Euro 2004, European Championships. Four days later, the Liechtenstein team traveled to Luxembourg, where they defeated Luxembourg national football team, the home team 4–0 in a 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup qualifying match. In the qualification stage of the European Championship 2008, Liechtenstein beat Latvia 1–0, which prompted the Latvian coach's resignation. They went on to beat Iceland 3–0 on 17 October 2007, which is considered one of the most dramatic losses of the Icelandic national football team. On 7 September 2010, they came within seconds of a 1–1 draw against Scotland national football team, Scotland in Glasgow, having led 1–0 earlier in the second half, but Liechtenstein lost 2–1 thanks to a goal by Stephen McManus in the 97th minute. On 3 June 2011, Liechtenstein defeated Lithuania national football team, Lithuania 2–0. On 15 November 2014, Liechtenstein defeated Moldova national football team, Moldova 0–1 with Franz Burgmeier's late free kick goal in Chișinău.
As an Alps, alpine country, the main sporting opportunity for Liechtensteiners to excel is in winter sports such as Downhill (ski competition), downhill skiing: the country's single ski area is Malbun. Hanni Wenzel won two gold medals and one silver medal in the 1980 Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics (she won bronze in 1976), her brother Andreas Wenzel, Andreas won one silver medal in 1980 and one bronze medal in 1984 in the Giant slalom skiing, giant slalom event, and her daughter Tina Weirather won a bronze medal in 2018 in the Super-G. With ten medals overall (all in alpine skiing), Liechtenstein has won more Olympic medals per capita than any other nation. It is the smallest nation to win a medal in any Olympics, Winter or Summer, and currently the only nation to win a medal in the Winter Games but not in the Summer Games. Other notable skiers from Liechtenstein are Marco Büchel, Willi Frommelt, Paul Frommelt and Ursula Konzett.
Another discipline unusually popular with Liechtensteiners is Auto racing, motorsport – American-born German-Colombian Rikky von Opel raced under the flag of Liechtenstein in Formula One in 1973 Formula One season, 1973 and 1974 Formula One season, 1974, and Manfred Schurti competed in 9 editions of the 24 Hours of Le Mans as a Porsche factory driver with a best finish of 4th overall in 1976 24 Hours of Le Mans, 1976. The nation is currently represented internationally by Fabienne Wohlwend in Ferrari Challenge and Formula 3, as well as Matthias Kaiser who competes in prototype Endurance racing (motorsport), endurance racing.
Other sports Liechtenstein athletes have had success in include tennis, with Stephanie Vogt and Kathinka von Deichmann both having varying degrees of success on the women's tour, as well as swimming (sport), swimming – both Julia Hassler and Christoph Meier represented the country at the 2016 Summer Olympics with the former the nations' flag bearer.
Liechtenstein Association football, football teams play in the Swiss football leagues. The Liechtenstein Football Cup allows access for one Liechtenstein team each year to the UEFA Europa Conference League; FC Vaduz, a team playing in the Swiss Challenge League, the second division in Swiss football, is the most successful team in the Cup, and scored their greatest success in the 1996–97 UEFA Cup Winners' Cup, European Cup Winners' Cup in 1996 when they drew with and defeated the Latvian team FK Jelgava, FC Universitate Riga by 1–1 and 4–2, to go on to a lucrative fixture against Paris Saint-Germain F.C., which they lost 0–3 and 0–4.
The Liechtenstein national football team is regarded as an easy target for any team drawn against them; this was the basis for a book about Liechtenstein's unsuccessful qualifying campaign for the 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2002 World Cup by British author Charlie Connelly. In one surprising week during autumn 2004, however, the team managed a 2–2 draw with Portugal national football team, Portugal, who only a few months earlier had been the losing finalists in the UEFA Euro 2004, European Championships. Four days later, the Liechtenstein team traveled to Luxembourg, where they defeated Luxembourg national football team, the home team 4–0 in a 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup qualifying match. In the qualification stage of the European Championship 2008, Liechtenstein beat Latvia 1–0, which prompted the Latvian coach's resignation. They went on to beat Iceland 3–0 on 17 October 2007, which is considered one of the most dramatic losses of the Icelandic national football team. On 7 September 2010, they came within seconds of a 1–1 draw against Scotland national football team, Scotland in Glasgow, having led 1–0 earlier in the second half, but Liechtenstein lost 2–1 thanks to a goal by Stephen McManus in the 97th minute. On 3 June 2011, Liechtenstein defeated Lithuania national football team, Lithuania 2–0. On 15 November 2014, Liechtenstein defeated Moldova national football team, Moldova 0–1 with Franz Burgmeier's late free kick goal in Chișinău.
As an Alps, alpine country, the main sporting opportunity for Liechtensteiners to excel is in winter sports such as Downhill (ski competition), downhill skiing: the country's single ski area is Malbun. Hanni Wenzel won two gold medals and one silver medal in the 1980 Winter Olympic Games, Winter Olympics (she won bronze in 1976), her brother Andreas Wenzel, Andreas won one silver medal in 1980 and one bronze medal in 1984 in the Giant slalom skiing, giant slalom event, and her daughter Tina Weirather won a bronze medal in 2018 in the Super-G. With ten medals overall (all in alpine skiing), Liechtenstein has won more Olympic medals per capita than any other nation. It is the smallest nation to win a medal in any Olympics, Winter or Summer, and currently the only nation to win a medal in the Winter Games but not in the Summer Games. Other notable skiers from Liechtenstein are Marco Büchel, Willi Frommelt, Paul Frommelt and Ursula Konzett.
Another discipline unusually popular with Liechtensteiners is Auto racing, motorsport – American-born German-Colombian Rikky von Opel raced under the flag of Liechtenstein in Formula One in 1973 Formula One season, 1973 and 1974 Formula One season, 1974, and Manfred Schurti competed in 9 editions of the 24 Hours of Le Mans as a Porsche factory driver with a best finish of 4th overall in 1976 24 Hours of Le Mans, 1976. The nation is currently represented internationally by Fabienne Wohlwend in Ferrari Challenge and Formula 3, as well as Matthias Kaiser who competes in prototype Endurance racing (motorsport), endurance racing.
Other sports Liechtenstein athletes have had success in include tennis, with Stephanie Vogt and Kathinka von Deichmann both having varying degrees of success on the women's tour, as well as swimming (sport), swimming – both Julia Hassler and Christoph Meier represented the country at the 2016 Summer Olympics with the former the nations' flag bearer.
Youth
Liechtenstein national football team, Liechtenstein competes in the Switzerland U16 Cup Tournament, which offers young players an opportunity to play against top football clubs.Security and defence
 The Law enforcement in Liechtenstein, Liechtenstein National Police is responsible for keeping order within the country. It consists of 87 field officers and 38 civilian staff, totaling 125 employees. All officers are equipped with small arms. The country has one of the world's lowest Crime statistics, crime rates. Liechtenstein's prison holds few, if any, inmates, and those with sentences over two years are transferred to Judiciary of Austria, Austrian jurisdiction. The Liechtenstein National Police maintains a trilateral treaty with Austria and Switzerland that enables close cross-border cooperation among the police forces of the three countries.
Liechtenstein follows a policy of Neutrality (international relations), neutrality and is one of the few List of countries without armed forces, countries in the world that maintain no military although its police force maintains a paramilitary force, the Princely Liechtenstein Security Corps within the organisation that would act as its de facto army if an invasion of Liechtenstein ever occurred. The Princely Liechtenstein Security Corps provides heavy backup for the National Police as well as Honor Guards at the Royal Palace and official functions. However, Liechtenstein can reinstate its military if deemed necessary, although this is very unlikely.christopher-eger.suite101.com
The army was abolished for financial reasons soon after the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, in which Liechtenstein fielded an army of 80 men, although they were not involved in any fighting. No casualties were incurred; in fact, the unit numbered 81 upon return due to an Austrian military liaison who accompanied the army back home. The demise of the German Confederation in that war freed Liechtenstein from its international obligation to maintain an army, and parliament seized this opportunity and refused to provide funding for one. The Prince objected, as such a move would leave the country defenceless, but relented on 12 February 1868 and disbanded the force. The last soldier to serve under the colours of Liechtenstein died in 1939 at age 95.
* In 1985 the Swiss Army fired off shells during an exercise and mistakenly burned a patch of forest inside Liechtenstein. The incident was said to have been resolved "over a case of white wine".
* In March 2007, a 170-man Swiss infantry unit got lost during a training exercise and inadvertently crossed into Liechtenstein. The accidental invasion ended when the unit realized their mistake and turned back. The Swiss Army later informed Liechtenstein of the incursion and offered official apologies, to which an internal ministry spokesperson responded, "No problem, these things happen."
* On 20 September 2017, Liechtenstein signed the United Nations Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
The Law enforcement in Liechtenstein, Liechtenstein National Police is responsible for keeping order within the country. It consists of 87 field officers and 38 civilian staff, totaling 125 employees. All officers are equipped with small arms. The country has one of the world's lowest Crime statistics, crime rates. Liechtenstein's prison holds few, if any, inmates, and those with sentences over two years are transferred to Judiciary of Austria, Austrian jurisdiction. The Liechtenstein National Police maintains a trilateral treaty with Austria and Switzerland that enables close cross-border cooperation among the police forces of the three countries.
Liechtenstein follows a policy of Neutrality (international relations), neutrality and is one of the few List of countries without armed forces, countries in the world that maintain no military although its police force maintains a paramilitary force, the Princely Liechtenstein Security Corps within the organisation that would act as its de facto army if an invasion of Liechtenstein ever occurred. The Princely Liechtenstein Security Corps provides heavy backup for the National Police as well as Honor Guards at the Royal Palace and official functions. However, Liechtenstein can reinstate its military if deemed necessary, although this is very unlikely.christopher-eger.suite101.com
The army was abolished for financial reasons soon after the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, in which Liechtenstein fielded an army of 80 men, although they were not involved in any fighting. No casualties were incurred; in fact, the unit numbered 81 upon return due to an Austrian military liaison who accompanied the army back home. The demise of the German Confederation in that war freed Liechtenstein from its international obligation to maintain an army, and parliament seized this opportunity and refused to provide funding for one. The Prince objected, as such a move would leave the country defenceless, but relented on 12 February 1868 and disbanded the force. The last soldier to serve under the colours of Liechtenstein died in 1939 at age 95.
* In 1985 the Swiss Army fired off shells during an exercise and mistakenly burned a patch of forest inside Liechtenstein. The incident was said to have been resolved "over a case of white wine".
* In March 2007, a 170-man Swiss infantry unit got lost during a training exercise and inadvertently crossed into Liechtenstein. The accidental invasion ended when the unit realized their mistake and turned back. The Swiss Army later informed Liechtenstein of the incursion and offered official apologies, to which an internal ministry spokesperson responded, "No problem, these things happen."
* On 20 September 2017, Liechtenstein signed the United Nations Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
See also
*Outline of LiechtensteinReferences
External links
* (in German and English)Princely House of Liechtenstein
Parliament of Liechtenstein
Government of Liechtenstein
Official tourism of Liechtenstein
Statistics Office of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Liechtenstein
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Liechtenstein profile
from BBC News * * * {{Authority control Liechtenstein, 1719 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire Central European countries Christian states Countries in Europe German-speaking countries and territories Landlocked countries Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the European Free Trade Association Member states of the United Nations NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union NUTS 3 statistical regions of the European Union Principalities of the Holy Roman Empire Principalities States and territories established in 1866 States of the Confederation of the Rhine States of the German Confederation Tax avoidance Western European countries