Najd Fault System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of
here
The Invasion of Nejd happened in Rabi‘ Ath-Thani or Jumada Al-Ula, 4 AH (i.e. in October, 625 AD). Muhammad led his fighters to Nejd to scare off some tribes he believed had suspicious intentions. Some scholars say the
'. The Ansar, the leaders of the tribes of Medina, met in a hall or house called
pp. 191 ff.
/ref> Ottoman control over these lands varied over the next four centuries with the fluctuating strength or weakness of the Empire's central authority. The emergence of what was to become the Saudi royal family, known as the Al Saud, began in
 The Arabic word ''najd'' literally means "upland" and was once applied to a variety of regions within the Arabian Peninsula. However, the most famous of these in recent times was the central region of the Peninsula roughly bounded on the west by the mountains of the
The Arabic word ''najd'' literally means "upland" and was once applied to a variety of regions within the Arabian Peninsula. However, the most famous of these in recent times was the central region of the Peninsula roughly bounded on the west by the mountains of the
File:Lake at Wadi Hanifah (5218227168).jpg, Lake at the 120 km long Wadi Hanifa valley that cuts through Riyadh
File:من عقدة اللي ما يزحزح قناها - panoramio.jpg, The area of 'Uqdah on the outskirts of Ha'il
File:Saudi-desert.gif, The An Nafud desert in the outskirts of Riyadh with the Jabal
 In the early 20th century, Najd produced coarse
In the early 20th century, Najd produced coarse
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the House of Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1727–1818), and ...
to bring Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
under a single polity and under the Salafi
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a reform branch movement within Sunni Islam that originated during the nineteenth century. The name refers to advocacy of a return to the traditions of the "pious predecessors" (), the first three generat ...
jurisprudence
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning a ...
.
Historic Najd was divided into three modern administrative regions
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
still in use today. The Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the R ...
region, featuring Wadi Hanifa and the Tuwaiq
Jabal Tuwaiq ( ar, جَبَل طُوَيْق, Tuwaiq Mountain) is a narrow escarpment that cuts through the plateau of Najd in central Arabia, running approximately from the southern border of Al-Qasim in the north, to the northern edge of the ...
escarpment, which houses easterly Yamama with the Saudi capital, Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the R ...
since 1824
May 7: The almost completely deaf Beethoven premieres his Symphony No. 9 (Beethoven) , Ninth Symphony
Events
January–March
* January 8 – After much controversy, Michael Faraday is finally elected as a member of the Royal Society, ...
, and the Sudairi
The Sudairi Seven ( ar, السديريون السبعة, ''As Sudayriyyūn as Sabʿah''), also spelled ''Sudairy'' or ''Sudayri'', is the commonly used name for a powerful alliance of seven full brothers within the Saudi royal family. They are al ...
region, which has its capital in Majmaah
Al Majma'ah ( ar, المجمعة) is a city and a governorate in Ar Riyad Province, Saudi Arabia. It is located at around , and it is the capital of the Sudair region. The city has an area of 30,000 square kilometres. The population of the town i ...
. The second administrative unit, Al-Qassim, houses the fertile oases and date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Eas ...
orchards spread out in the region's highlands along Wadi Rummah in central Najd with its capital in Buraidah, the second largest Najdi city, with the region historically contested by the House of Rashid
The Rasheed dynasty, also called Al Rasheed or the House of Rasheed ( ar, آل رشيد ; ), was a historic Arabian House or dynasty that existed in the Arabian Peninsula between 1836 and 1921. Its members were rulers of the Emirate of Ha'il a ...
to its north and the House of Saud to its east and south. The third administrative unit is northerly Ḥaʼil
Hail ( ar, حَائِل ') is a city in north-western Saudi Arabia. It is the capital and largest city of Ha'il Region, with a population of about 605,930 (2018)
Hail is largely agricultural, with significant grain, date, and fruit production ...
, which features the mountains of Jabal Shammar housing the Tayy capital of Ḥaʼil
Hail ( ar, حَائِل ') is a city in north-western Saudi Arabia. It is the capital and largest city of Ha'il Region, with a population of about 605,930 (2018)
Hail is largely agricultural, with significant grain, date, and fruit production ...
.
History
Pre-6th century
The Najd region is home toAl-Magar
Al-Magar was an advanced prehistoric civilization of the Neolithic whose epicenter lied in modern-day southwestern Najd in Saudi Arabia. Al-Magar is possibly the first civilizations in the world where widespread domestication of animals occurred, ...
, which was an advanced prehistoric culture of the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
whose epicenter lay in modern-day southwestern Najd. Al-Magar is possibly one of the first cultures in the world where widespread agriculture and the domestication of animals occurred, particularly that of the horse, during the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period, before climate changes in the region resulted in desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
. Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
of several objects discovered at Al-Magar indicate an age of about 9,000 years.
In November 2017 hunting scenes showing images of what appears to be domesticated dogs resembling the Canaan dog and wearing leashes were discovered in Shuwaymis, an area about 370 km southwest of the city of Ha'il. Dated at 8000 years before the present, these are thought of as the earliest known depictions of dogs in the world.
In ancient times, the Najd was settled by numerous tribes such as the Kindites, Tayy, and many others. Led by Usma bin Luai ( ar, عصمة بن لؤي), the Tayy sacked the mountains of Aja
Aja or AJA may refer to:
Acronyms
*AJ Auxerre, a French football club
*Ajaccio Napoleon Bonaparte Airport's IATA airport code
*Al Jazeera America, an American news channel
*American Jewish Archives
*''American Journal of Archaeology''
*, a Germa ...
and Samra from Banu Tamim
Banū Tamīm ( ar, بَنُو تَمِيم) is an Arab tribe that originated in Najd in the Arabian Peninsula. It is mainly present in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, Jordan, Algeria, and has a strong presence in Morocco, Palestine, Tunisia ...
in northern Arabia in their exodus from Yemen circa CE 115. These mountains are now known as the Shammar Mountains. The Tayy Shammaris became pastoral nomadic camel herders and horse breeders in northern Najd for centuries with a sedentary faction ruling the tribal league from within their capital city of Ha’il.
In the 5th century AD, the tribes of North Arabia became a major threat to the trade line between Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. The Ḥimyarites of Sheba decided to establish a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
that controlled Central and North Arabia. The Kindites, mentioned in Greek sources as the Chinedakolpitai (), gained strength and numbers to play that role and in AD 425 the Ḥimyarite king Ḥasan ibn 'Amr ibn Tubba’ made Ḥujr 'Akīl al-Murār ibn 'Amr the first King ( Ḥujr) of Kindah. They established the Kingdom of Kinda in Najd in central Arabia unlike the organized states of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
; its kings exercised an influence over a number of associated tribes more by personal prestige than by coercive settled authority. Their first capital was Qaryat Dhāt Kāhil, today known as Qaryat al-Fāw
Qaryat Al Faw ( ar, قرية الفاو) was the capital of the first Kindah kingdom. It is located about 100 km south of Wadi ad-Dawasir, and about 700 km southwest of Riyadh, the capital city of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, off ...
.
The Ghassānids, Lakhmids and Kindites were all Kahlānī and Qaḥṭānī kingdoms which thrived in Najd. In the 5th and 6th centuries AD, the Kindites made the first real concerted effort to unite all the tribes of Central Arabia through alliances, and focused on wars with the Lakhmids. Al-Ḥārith ibn 'Amr, the most famous of their kings, finally succeeded in capturing the Lakhmid capital of al-Ḥirah in southern modern-day Iraq. Later however in about 529, al-Mundhir recaptured the city and put King Ḥārith and about fifty members of his family to death.
In 525, the Aksumites
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in wha ...
invaded Ḥimyar, and this had a knock-on effect with the Kindites, who lost the support of the Ḥimyarites. Within three years the Kindite kingdom had split into four groups: Asad, Taghlib, Qays and Kinānah, each led by a prince of Kindah. These small principalities were then overthrown in the 530s and 540s in a series of uprisings of the ‘Adnānī tribes of Najd and Ḥijāz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as ...
. In 540, the Lakhmids destroyed all the Kindite settlements in Nejd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the H ...
, forcing the majority of them to move to Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
. The Kindites and most of the Arab tribes switched their alliances to the Lakhmids.
The Era of Muhammad
During theIslamic prophet
Prophets in Islam ( ar, الأنبياء في الإسلام, translit=al-ʾAnbiyāʾ fī al-ʾIslām) are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God in Islam, God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. So ...
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, di ...
's era, Muhammad carried out military expeditions in the area. The first was the Nejd Caravan Raid against the Quraysh
The Quraysh ( ar, قُرَيْشٌ) were a grouping of Arab clans that historically inhabited and controlled the city of Mecca and its Kaaba. The Islamic prophet Muhammad was born into the Hashim clan of the tribe. Despite this, many of the Qur ...
, which took place in 624. The Meccans led by Safwan ibn Umayyah, who lived on trade, left in summer for Syria for their seasonal trade business. After Muhammad received intelligence about the Caravan's route, Muhammad ordered Zayd ibn Haritha to go after the Caravan, and they successfully raided it and captured 100,000 dirhams worth of booty.Mubarakpuri, The sealed nectar: biography of the Noble Prophet, p. 290. Note: Book contains a list of battles of Muhammad in Arabic, English translation availablhere
The Invasion of Nejd happened in Rabi‘ Ath-Thani or Jumada Al-Ula, 4 AH (i.e. in October, 625 AD). Muhammad led his fighters to Nejd to scare off some tribes he believed had suspicious intentions. Some scholars say the
Expedition of Dhat al-Riqa
The expedition of Dhat al-Riqa took place in July AD 625 (or April 626, Muharram AH 5 of the Islamic calendar according to al-Waqidi),. or after the Battle of Khaybar in AD 628, i.e. AH 7 of the Islamic calendar. Two Quran verses, 5:11 and 4:101 ...
took place in Nejd as part of this invasion.
The most authentic opinion according to "Saifur Rahman al Mubararakpuri", however, is that the Dhat Ar-Riqa' campaign took place after the fall of Khaibar (and not as part of the Invasion of Nejd). This is supported by the fact that Abu Hurairah
Abu Hurayra ( ar, أبو هريرة, translit=Abū Hurayra; –681) was one of the companions of Islamic prophet Muhammad and, according to Sunni Islam, the most prolific narrator of hadith.
He was known by the ''kunyah'' Abu Hurayrah "Fathe ...
and Abu Musa Al-Ash'ari witnessed the battle. Abu Hurairah embraced Islam only some days before Khaibar, and Abu Musa Al-Ash'ari came back from Abyssinia (Ethiopia) and joined Muhammad at Khaibar. The rules relating to the prayer of fear, which Muhammad observed at the Dhat Ar-Riqa' campaign, were revealed at the Asfan Invasion and these scholars say, took place after Al-Khandaq (the Battle of the Trench
The Battle of the Trench ( ar, غزوة الخندق, Ghazwat al-Khandaq), also known as the Battle of Khandaq ( ar, معركة الخندق, Ma’rakah al-Khandaq) and the Battle of the Confederates ( ar, غزوة الاحزاب, Ghazwat al- ...
).
The Expedition of Qatan
The Expedition of Qatan, was the first Raid on the Banu Asad bin Khuzaymah tribe, which occurred directly after the Battle of Hamra al-Asad in the year 4 A.H of the Islamic calendar.Note: Book contains a list of battles of Muhammad in Arabic, Eng ...
also took place in Nejd. The Banu Asad ibn Khuzaymah tribe (not to be confused with the Banu Asad tribe) was a powerful tribe connected with the Quraysh. They resided near the hill of Katan, in the vicinity of Fayd
Fayd or Fa'idah is a village in Makkah Province, in western Saudi Arabia.National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. GeoNames database entry.search) Accessed 13 May 2011. The Expedition of Qatan was ordered by Muhammad and took place here.Mubarakpur ...
, in Nejd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the H ...
. Muhammad received intelligence reports that they were planning a raid on Medina, so he dispatched a force of 150 men under the leadership of Abu Salama 'Abd Allah ibn 'Abd al-Asad
Abū Salamah ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿAbd al-Asad ( ar, أَبُو سَلَمَة عَبْد ٱلله ٱبْن عَبْد ٱلْأَسَد ) was one of the Companians of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was also a cousin and a foster-brother of Muhamm ...
to make a sudden attack on this tribe.Mubarakpuri, The sealed nectar: biography of the Noble Prophet, p. 349.Ibn Sa’d, vol.ii, p. 150.
Post-Muhammad
Ridda wars
After Muhammad's death, previously dormant tensions between the Meccanimmigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
, the Muhajirun
The ''Muhajirun'' ( ar, المهاجرون, al-muhājirūn, singular , ) were the first converts to Islam and the Islamic prophet Muhammad's advisors and relatives, who emigrated with him from Mecca to Medina, the event known in Islam as the ''Hijr ...
, and the Medinan converts, the Ansar, threatened to split the Ummah
' (; ar, أمة ) is an Arabic word meaning "community". It is distinguished from ' ( ), which means a nation with common ancestry or geography. Thus, it can be said to be a supra-national community with a common history.
It is a synonym for ' ...
. Other Arabic tribes also wished to revert from Islam to local leadership and split from Medina's control; in some places, people such as Al-Aswad Al-Ansi and Musaylima claimed prophethood and started to establish leaderships in opposition to Medina. Fred M. Donner, "Muhammad and the Believers: At the Origins of Islam", Harvard University Press, 2010; '. The Ansar, the leaders of the tribes of Medina, met in a hall or house called
saqifah
The Saqifa ( ar, سَّقِيفَة, translit=Saqīfah) of the Banu Sa'ida clan refers to the location of an event in early Islam where some of the companions of the Islamic prophet Muhammad pledged their allegiance to Abu Bakr as the first cali ...
, to discuss whom they would support as their new leader. When Abu Bakr was informed of the meeting, he, Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate o ...
, Abu Ubaidah ibn al-Jarrah
ʿĀmir ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Jarrāḥ ( ar, عامر بن عبدالله بن الجراح; 583–639 CE), better known as Abū ʿUbayda ( ar, أبو عبيدة ) was a Muslim commander and one of the Companions of the Islamic prophet M ...
and a few others rushed to prevent the Ansar from making a premature decision. During the meeting Umar declared that Abu Bakr should be the new leader, and declared his allegiance to Abu Bakr, followed by Abu Ubaidah ibn al-Jarrah, and thus Abu Bakr became the first caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
.
Apostasy and rebellion in central Arabia were led by Musaylima in the fertile region of Yamamah. He was mainly supported by the powerful tribe of Banu Hanifa
Banu Hanifa ( ar, بنو حنيفة) is an ancient Arab tribe inhabiting the area of al-Yamama in the central region of modern-day Saudi Arabia. The tribe belongs to the great Rabi'ah branch of North Arabian tribes, which also included Abdu ...
. At Buzakha in north central Arabia, another claimed prophet, Tulayha, a tribal chief of Banu Asad, led the rebellion against Medina, aided by the allied tribes of Banu Ghatafan
The Ghaṭafān ( ar, غطفان) were an Arab tribal confederation originally based northeast of Medina. The main branches of the Ghatafan were the tribes of Banu Abs, Banu Dhubyan and Ashja'. They were one of the Arab tribes that interacted wit ...
, the Hawazin, and the Tayy. At Najd, Malik ibn Nuweira led the tribes of Banu Tamim
Banū Tamīm ( ar, بَنُو تَمِيم) is an Arab tribe that originated in Najd in the Arabian Peninsula. It is mainly present in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, Jordan, Algeria, and has a strong presence in Morocco, Palestine, Tunisia ...
against the authority of Medina.
On receiving intelligence of the Muslims' preparations, Tulayha too prepared for a battle, and was further reinforced by the contingents of the allied tribes. Before launching Khalid
Khalid (variants include Khaled and Kalid; Arabic: خالد) is a popular Arabic male given name meaning "eternal, everlasting, immortal", and it also appears as a surname.
against Tulayha, Abu Bakr sought ways and means of reducing the latter's strength, so that the battle could be fought with the maximum prospects of victory. Nothing could be done about the tribes of Banu Asad and Banu Ghatafan
The Ghaṭafān ( ar, غطفان) were an Arab tribal confederation originally based northeast of Medina. The main branches of the Ghatafan were the tribes of Banu Abs, Banu Dhubyan and Ashja'. They were one of the Arab tribes that interacted wit ...
, which stood solidly behind Tulayha, but the Tayy were not so staunch in their support of Tulayha, and their chief, Adi ibn Hatim
Adi ibn Hatim al-Tai () was a leader of the Arab tribe of Tayy, and one of the companions of Muhammad. He was the son of the poet Hatim al-Tai who was widely known for his chivalry, masculinity, and generosity among Arabs. Adi remained antagonisti ...
, was a devout Muslim. Adi was appointed by Abu Bakr to negotiate with the tribal elders to withdraw their contingent from Tulayha's army. The negotiations were a success, and Adi brought with him 500 horsemen of his tribe to reinforce Khalid's army.
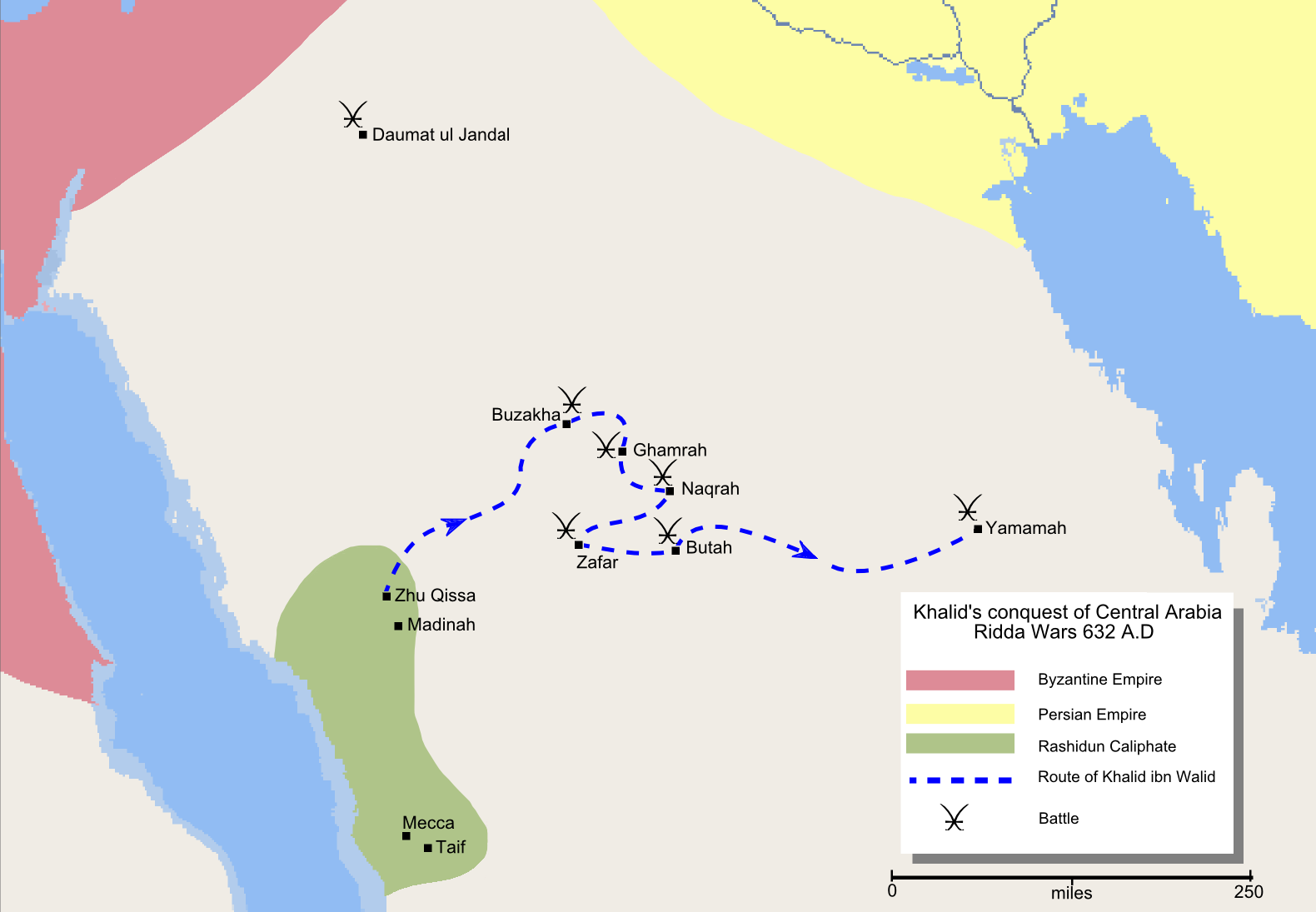
Khalid next marched against another apostate tribe, Jadila. Here again, Adi ibn Hatim offered his services to persuade the tribe to submit without bloodshed. Bani Jadila submitted, and their 1000 warriors joined Khalid's army. Khalid, now much stronger than when he had left Zhu Qissa, marched for Buzakha. There, in mid-September 632, he defeated Tulayha in the Battle of Buzakha. The remaining army of Tulayha retreated to Ghamra, 20 miles from Buzakha, and was defeated in the Battle of Ghamra in the third week of September.A.I. Akram, ''The Sword of Allah: Khalid bin al-Waleed, His Life and Campaigns'', Nat. Publishing. House, Rawalpindi (1970); .
Several tribes submitted to the Caliph after Khalid's decisive victories. Moving south from Buzakha, Khalid reached Naqra in October, with an army now 6000 strong, and defeated the rebel tribe of Banu Saleem
Banu Salim or Banu Saleem or Bani Salim was a tribe during the Islamic prophet Muhammad's era. They participated in the Al Kudr Invasion. On Khalid ibn Walid's return from Nakhla expedition to destroy al-Uzza, Khalid bin Al-Waleed at the head of ...
in the Battle of Naqra
The Battle of Naqra took place in October 633 between rebel armies and Khalid ibn al-Walid's army during the Ridda Wars.
After the defeat of Tulayha in the Battle of Buzakha
The Battle of Buzakha took place between Khalid ibn al-Walid a ...
. In the third week of October, Khalid defeated a tribal chieftess, Salma, in the battle of Zafar
The Battle of Zafar took place in 632 between Khalid ibn al-Walid - a companion of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad - and a tribal chieftess called Salma. Khalid defeated her and she died on the battlefield. The battle was part of the Ridda War ...
.
Afterwards, he moved to Najd against the rebel tribe of Banu Tamim
Banū Tamīm ( ar, بَنُو تَمِيم) is an Arab tribe that originated in Najd in the Arabian Peninsula. It is mainly present in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, Jordan, Algeria, and has a strong presence in Morocco, Palestine, Tunisia ...
and their Sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a ...
Malik ibn Nuwayrah
Malik ibn Nuwayra ( ar, مالك بن نويرة: died 632), was the chief of the Banu Yarbu, a clan of the Banu Hanzala, a large section of the powerful tribe of Bani Tamim which inhabited the north-eastern region of Arabia, between Bahrain and ...
. At Najd, getting the news of Khalid's decisive victories against apostates in Buzakha, many clans of Banu Tamim hastened to visit Khalid, but the Banu Yarbu', a branch of Banu Tamim, under their chief, Malik ibn Nuwayrah
Malik ibn Nuwayra ( ar, مالك بن نويرة: died 632), was the chief of the Banu Yarbu, a clan of the Banu Hanzala, a large section of the powerful tribe of Bani Tamim which inhabited the north-eastern region of Arabia, between Bahrain and ...
, hung back. Malik was a chief of some distinction: a warrior, noted for his generosity, and a famous poet. Bravery, generosity, and poetry were the three qualities most admired among the Arabs. At the time of Muhammad, he had been appointed as a tax collector for the tribe of Banu Tamim. As soon as Malik heard of the death of Muhammad, he gave back all the tax to his tribespeople, saying, "Now you are the owner of your wealth." Moreover, he was to be charged because he signed a pact with the prophet Sajjah
Sajah bint Al-Harith ibn Suayd ( ar, سجاح بنت الحارث بن سويد, fl. 630s CE) from the tribe of Banu Taghlib, was an Arab Christian protected first by her tribe; then causing a split within the Arab tribes and finally defended by ...
. This agreement stated that first, they would deal with local enemy tribes together, and then they would confront the state of Madinah.
His riders were stopped by Khalid's army at the town of Buttah. Khalid asked them about the signing of pact with Sajjah; they said it was just because they wanted revenge against their terrible enemies. When Khalid reached Najd he found no opposing army. He sent his cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
to nearby villages and ordered them to call the Azaan
Adhan ( ar, أَذَان ; also variously transliterated as athan, adhane (in French), azan/azaan (in South Asia), adzan (in Southeast Asia), and ezan (in Turkish), among other languages) is the Islamic call to public prayer (salah) in a mosq ...
(call to prayer) to each party they meet.
Zirrar bin Azwar, a squadron leader, arrested the family of Malik, claiming they did not answer the call to prayer. Malik avoided direct contact with Khalid's army and ordered his followers to scatter, and he and his family apparently moved away across the desert. He refused to give zakat
Zakat ( ar, زكاة; , "that which purifies", also Zakat al-mal , "zakat on wealth", or Zakah) is a form of almsgiving, often collected by the Muslim Ummah. It is considered in Islam as a religious obligation, and by Quranic ranking, is ne ...
, hence differentiating between prayer and zakat. Nevertheless, Malik was accused of rebellion against the state of Medina. He was also to be charged for his entering in an anti-Caliphate alliance with the prophetess Sajjah. Malik was arrested along with his clan men,
Malik was asked by Khalid about his crimes. Malik's response was "your master said this, your master said that," referring to Abu Bakr. Khalid declared Malik a rebel apostate and ordered his execution.reference=Tabari: Vol. 2, p. 5). Khalid bin Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid ibn al-Mughira al-Makhzumi (; died 642) was a 7th-century Arab military commander. He initially headed campaigns against Muhammad on behalf of the Quraysh. He later became a Muslim and spent the remainder of his career in ...
killed Malik ibn Nuwayra.
Ikrimah ibn Abi-Jahl
( ar, عكرمة بن أبي جهل عمرو بن هشام; born: 598 CE) was a leading opponent-turned Companions of the Prophet, companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a Muslim commander in the Ridda wars and the Muslim conquest of the ...
, one of the corps commanders, was instructed to make contact with Musaylima at Yamamah, but not to engage in fighting until Khalid joined him. Abu Bakr's intention in giving Ikrimah this mission was to tie Musaylima down at Yamamah. With Ikrimah on the horizon, Musaylima would remain in expectation of a Muslim attack, and thus not be able to leave his base. With Musaylima so committed, Khalid would be free to deal with the apostate tribes of north-central Arabia without interference from Yamamah. Meanwhile, Abu Bakr sent Shurhabil's corps to reinforce Ikrama at Yamamah.
However, Ikrimah attacked Musaylima's forces in early September 632 and was defeated. He wrote the details of his actions to Abu Bakr, who, both pained and angered by the rashness of Ikrimah and his disobedience, ordered him to proceed with his force to Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
to assist Hudaifa; once Hudaifa had completed his task, to march to Mahra to help Arfaja, and thereafter go to Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
to help Muhajir.John Glubb, The Great Arab Conquests, 1963, p. 112.
Meanwhile, Abu Bakr sent orders to Khalid to march against Musaylima. Shurhabil's corps, that was stationed at Yamamah, was to reinforce Khalid's corps. In addition to this Abu Bakr assembled a fresh army of Ansar and Muhajireen
The ''Muhajirun'' ( ar, المهاجرون, al-muhājirūn, singular , ) were the first converts to Islam and the Islamic prophet Muhammad's advisors and relatives, who emigrated with him from Mecca to Medina, the event known in Islam as the ''Hijr ...
in Medina that joined Khalid's corps at Butah. From Butah Khalid marched to Yamamah to join with Shurhabil's corps. Though Abu Bakr had instructed Shurhabil not to engage Musaylima's forces until the arrival of Khalid, shortly before the arrival of Khalid, Shurhabil engaged Musaylima's forces and was defeated too.
Khalid joined with the corps of Shurhabil early in December 632. The combined force of Muslims, now 13,000 strong, defeated Musaylima's army in the Battle of Yamama, which was fought in the third week of December. The fortified city of Yamamah surrendered peacefully later that week. Khalid established his headquarters at Yamamah, from where he despatched columns to all over the plain of Aqraba to subdue the region around Yamamah and to kill or capture all who resisted. Thereafter all of central Arabia submitted to Medina. What remained of the apostasy in the less vital areas of Arabia was rooted out by the Muslims in a series of well-planned campaigns within five months.
Post–Ridda wars, until the 10th century
Muhammad's followers rapidly expanded the territory under Muslim rule beyond Arabia, conquering huge swathes of territory from theIberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
in the west to modern day Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
in the east in a matter of decades. The bulk of the tribes that helped the Caliphate's expansion into Persia and the Levant were composed of Nejdi tribes such as Banu Tamim
Banū Tamīm ( ar, بَنُو تَمِيم) is an Arab tribe that originated in Najd in the Arabian Peninsula. It is mainly present in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, Jordan, Algeria, and has a strong presence in Morocco, Palestine, Tunisia ...
. The Caliphate's use of these once-rebellious tribes allowed Abu Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honor ...
and Umar
ʿUmar ibn al-Khaṭṭāb ( ar, عمر بن الخطاب, also spelled Omar, ) was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () as the second caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate o ...
to quickly deploy battle hardened men and experienced generals such as Al-Qa'qa' ibn Amr al-Tamimi into the front-lines against the Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
and Byzantines.
Najd soon became a politically peripheral region of the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
as the focus shifted to the more developed conquered lands. The conquering tribes of Nejd soon shifted into the Levant, Persia and North Africa, playing a role in future conflicts in the caliphate, becoming governors and even birthing emirates such as the Aghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a cen ...
.
16th century to the unification of Saudi Arabia
In the 16th century, theOttomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
added the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
and Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), me ...
coast (the Hejaz, Asir
The ʿAsir Region ( ar, عَسِيرٌ, ʿAsīr, lit=difficult) is a region of Saudi Arabia located in the southwest of the country that is named after the ʿAsīr tribe. It has an area of and an estimated population of 2,211,875 (2017). It is ...
and al-Ahsa) to the Empire and claimed suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
over the interior. One reason was to thwart Portuguese attempts to attack the Red Sea (hence the Hejaz) and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
.William J. Bernstein (2008) ''A Splendid Exchange: How Trade Shaped the World''. Grove Presspp. 191 ff.
/ref> Ottoman control over these lands varied over the next four centuries with the fluctuating strength or weakness of the Empire's central authority. The emergence of what was to become the Saudi royal family, known as the Al Saud, began in
Nejd
Najd ( ar, نَجْدٌ, ), or the Nejd, forms the geographic center of Saudi Arabia, accounting for about a third of the country's modern population and, since the Emirate of Diriyah, acting as the base for all unification campaigns by the H ...
in central Arabia in 1744, when Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the dynasty, joined forces with the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, founder of the Wahhabi movement, a strict puritanical form of Sunni Islam.
This alliance formed in the 18th century provided the ideological impetus to Saudi expansion and remains the basis of Saudi Arabian dynastic rule today. The first "Saudi state" established in 1744 in the area around Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the R ...
rapidly expanded and briefly controlled most of the present-day territory of Saudi Arabia, but was destroyed by 1818 by the Ottoman viceroy of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, Mohammed Ali Pasha
Muhammad Ali Pasha al-Mas'ud ibn Agha, also known as Muhammad Ali of Egypt and the Sudan ( sq, Mehmet Ali Pasha, ar, محمد علي باشا, ; ota, محمد علی پاشا المسعود بن آغا; ; 4 March 1769 – 2 August 1849), was ...
.
A much smaller second "Saudi state", located mainly in Nejd, was established in 1824 by Turki
Chagatai (چغتای, ''Čaġatāy''), also known as ''Turki'', Eastern Turkic, or Chagatai Turkic (''Čaġatāy türkīsi''), is an extinct Turkic literary language that was once widely spoken across Central Asia and remained the shared literar ...
. Throughout the rest of the 19th century, the Al Saud contested control of the interior of what was to become Saudi Arabia with another Arabian ruling family, the Al Rashid. By 1891, the Al Rashid were victorious and the Al Saud were driven into exile in Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the nort ...
.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
continued to control or have suzerainty over most of the peninsula. Subject to this suzerainty, Arabia was ruled by a patchwork of tribal rulers, with the Sharif of Mecca
The Sharif of Mecca ( ar, شريف مكة, Sharīf Makkah) or Hejaz ( ar, شريف الحجاز, Sharīf al-Ḥijāz, links=no) was the title of the leader of the Sharifate of Mecca, traditional steward of the holy cities of Mecca and Medina and ...
having pre-eminence and ruling the Hejaz.
In 1902, Abdul Rahman's son, Abdul Aziz—later to be known as Ibn Saud
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud ( ar, عبد العزيز بن عبد الرحمن آل سعود, ʿAbd al ʿAzīz bin ʿAbd ar Raḥman Āl Suʿūd; 15 January 1875Ibn Saud's birth year has been a source of debate. It is generally accepted ...
—recaptured control of Riyadh, bringing the Al Saud back to Nejd. Ibn Saud gained the support of the Ikhwan
The Ikhwan ( ar, الإخوان, al-ʾIkhwān, The Brethren), commonly known as Ikhwan min ta'a Allah ( ar, إخوان من أطاع الله), was a traditionalist religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a signif ...
, a tribal army inspired by Wahhabism, and which had grown quickly after its foundation in 1912. With the aid of the Ikhwan, Ibn Saud captured al-Ahsa from the Ottomans in 1913.
In 1916, with the encouragement and support of Britain (which was fighting the Ottomans in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
), the Sharif of Mecca, Hussein bin Ali
Abū ʿAbd Allāh al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, أبو عبد الله الحسين بن علي بن أبي طالب; 10 January 626 – 10 October 680) was a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a son of Ali ibn Abi ...
, led a pan-Arab revolt against the Ottoman Empire to create a united Arab state. Although the Arab Revolt of 1916 to 1918 failed in its objective, the Allied victory in World War I resulted in the end of Ottoman suzerainty and control in Arabia.
Ibn Saud avoided involvement in the Arab Revolt and instead continued his struggle with the Al Rashid. Following the latter's final defeat, he took the title Sultan of Nejd in 1921. With the help of the Ikhwan, the Hejaz was conquered in 1924–25 and on 10 January 1926, Ibn Saud declared himself King of the Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Provin ...
. A year later, he added the title of King of Nejd. For the next five years, he administered the two parts of his dual kingdom as separate units.
After the conquest of the Hejaz, the Ikhwan leadership turned to expansion of the Wahhabist realm into the British protectorates of Transjordan Transjordan may refer to:
* Transjordan (region), an area to the east of the Jordan River
* Oultrejordain, a Crusader lordship (1118–1187), also called Transjordan
* Emirate of Transjordan, British protectorate (1921–1946)
* Hashemite Kingdom of ...
, Iraq and Kuwait, and began raiding those territories. This met with Ibn Saud's opposition, as he recognized the danger of a direct conflict with the British. At the same time, the Ikhwan became disenchanted with Ibn Saud's domestic policies, which appeared to favor modernization and the increase in the number of non-Muslim foreigners in the country. As a result, they turned against Ibn Saud and, after a two-year struggle, were defeated in 1930 at the Battle of Sabilla
The Battle of Sabilla (29 March, 1929) was the main battle of the Ikhwan Revolt in northern Arabia between the rebellious Ikhwan forces and the army of Abdulaziz al-Saud. It is the last tribal uprising in Saudi Arabia. It was also the last maj ...
, where their leaders were massacred. In 1932 the two kingdoms of the Hejaz and Nejd were united as the ''Kingdom of Saudi Arabia''.
Geography
Boundaries
 The Arabic word ''najd'' literally means "upland" and was once applied to a variety of regions within the Arabian Peninsula. However, the most famous of these in recent times was the central region of the Peninsula roughly bounded on the west by the mountains of the
The Arabic word ''najd'' literally means "upland" and was once applied to a variety of regions within the Arabian Peninsula. However, the most famous of these in recent times was the central region of the Peninsula roughly bounded on the west by the mountains of the Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Provin ...
and Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and to the east by the historical region of Eastern Arabia and the north by Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
.
Medieval Muslim geographers spent a great amount of time debating the exact boundaries between Hejaz and Najd in particular, but generally set the western boundaries of Najd to be wherever the western mountain ranges and lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
beds began to slope eastwards, and set the eastern boundaries of Najd at the narrow strip of red sand dunes known as the Ad-Dahna Desert, some east of modern-day Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the R ...
. The southern border of Najd has always been set at the large sea of sand dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, f ...
s known today as Rub' al Khali
The Rub' al KhaliOther standardized transliterations include: / . The ' is the assimilated Arabic definite article, ', which can also be transliterated as '. (; ar, ٱلرُّبْع ٱلْخَالِي (), the "Empty Quarter") is the sand des ...
(the Empty Quarter), while the southwestern boundaries are marked by the valleys of Wadi Ranyah, Wadi Bisha, and Wadi Tathlith.
The northern boundaries of Najd have fluctuated greatly over time and received far less attention from the medieval geographers. In the early Islamic centuries, Najd was considered to extend as far north as the River Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
, or more specifically, the "Walls of Khosrau", constructed by the Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
as a barrier between Arabia and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
immediately prior to the advent of Islam. The modern usage of the term encompasses the region of Al-Yamama
Al-Yamama ( ar, اليَمامَة, al-Yamāma) is a historical region in the southeastern Najd in modern-day Saudi Arabia, or sometimes more specifically, the now-extinct ancient village of Jaww al-Yamamah, near al-Kharj, after which the rest ...
, which was not always considered part of Najd historically, and became incorporated into the larger definition of Nejd in the past centuries.
Topography
Najd is aplateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ha ...
ranging from in height and sloping downwards from west to east. The eastern sections (historically better known as Al-Yamama) are marked by oasis settlements with much farming and trading activities, while the rest has traditionally been sparsely occupied by nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
ic Bedouins. The main topographical features include the twin mountains of Aja and Salma
The South American land mammal ages (SALMA) establish a geologic timescale for prehistoric South American fauna beginning 64.5 Ma during the Paleocene and continuing through to the Late Pleistocene (0.011 Ma). These periods are referred to as a ...
in the north near Ha'il, the high land of Jabal Shammar and the Tuwaiq
Jabal Tuwaiq ( ar, جَبَل طُوَيْق, Tuwaiq Mountain) is a narrow escarpment that cuts through the plateau of Najd in central Arabia, running approximately from the southern border of Al-Qasim in the north, to the northern edge of the ...
mountain range running through its center from north to south. Also important are the various dry river-beds (''wadi
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water onl ...
s'') such as Wadi Hanifa near Riyadh, Wadi Na'am in the south, Wadi Al-Rumah in the Al-Qassim Province
The Qassim Province ( ar, منطقة القصيم ' , Najdi Arabic: ), also known as the Qassim Region, is one of the 13 provinces of Saudi Arabia. Located at the heart of the country near the geographic center of the Arabian Peninsula, it ha ...
in the north, and Wadi ad-Dawasir
Wadi Al Dawasir ( ar, وادي الدواسر) is a town in Najd, Saudi Arabia, in the Dawasir valley. The town is the homeland of the tribe of Al-Dawasir.
The municipality had a population of 106,152 at the 2010 Census. It is divided into three ...
at the southernmost tip of Najd on the border with Najran. Most Najdi villages and settlements are located along these wadis, due to ability of these wadis to preserve precious rainwater in the arid desert climate, while others are located near oases
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical imp ...
.
Historically, Najd itself has been divided into small provinces made up of constellations of small towns, villages and settlements, with each one usually centered on one "capital". These subdivisions are still recognized by Najdis today, as each province retains its own variation of the Najdi dialect and Najdi customs. The most prominent among these provinces are Al-'Aridh, which includes Riyadh and the historical Saudi capital of Diriyah; Al-Qassim, with its capital in Buraidah; Sudair, centered on Al Majma'ah; Al-Washm, centered on Shaqraa; and Jebel Shammar
The Emirate of Jabal Shammar ( ar, إِمَارَة جَبَل شَمَّر), also known as the Emirate of Haʾil () or the Rashidi Emirate (), was a state in the northern part of the Arabian Peninsula, including Najd, existing from the mid-n ...
, with its capital, Ha'il. Under modern-day Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
, however, Najd is divided into three administrative regions: Ha'il, Al-Qassim, and Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the R ...
, comprising a combined area of .
Tuwaiq
Jabal Tuwaiq ( ar, جَبَل طُوَيْق, Tuwaiq Mountain) is a narrow escarpment that cuts through the plateau of Najd in central Arabia, running approximately from the southern border of Al-Qasim in the north, to the northern edge of the ...
in the background
Major towns
Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the R ...
is the largest city in Najd, as well as the largest city in the country as a whole, with a population of more than 7,676,654 as of 2018. Other cities include Ḥaʼil
Hail ( ar, حَائِل ') is a city in north-western Saudi Arabia. It is the capital and largest city of Ha'il Region, with a population of about 605,930 (2018)
Hail is largely agricultural, with significant grain, date, and fruit production ...
(936,465 in 2021), Buraidah (745,353 in 2021), Unaizah (163,729 in 2010) and Ar Rass
Rass (also spelled Ar Rass, or Al-Ras; ar, الرس) is a Saudi Arabian City, located in Al Qassim Province. It lies southwest of Buraydah, the capital of the province and north of Riyadh, the national capital.
Arrass is the largest city in A ...
(133,000 in 2010). Smaller towns and villages include Sudair, Al-Kharj, Dawadmi
Dawadmi or Ad Dawadimi ( ar, الدوادمي) is a town in Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia. Google Maps spells the name as Al Duwadimi. As of the 2004 census it had a population of 53,071 people. The town is mostly inhabited by the tribe of Banu 'U ...
, 'Afif
Afif ( ar, عفيف ) is a city in central Saudi Arabia, in the Najd region. It is situated approximately halfway between Riyadh and Mecca. The modern town was established in the 1910s as a ''hijra'', or "settlement", for the nomadic tribes of t ...
, Al-Zilfi
Az Zulfi (also Zulfi, Zulfy City or Al Zulfi or Az Zilfi) is a city in Riyadh Province in central Saudi Arabia, about 260 kilometres northwest of Riyadh. It is connected by Roads 418 and 535 which both link with the main Highway 65 which connect ...
, Al Majma'ah, Shaqraa, Tharmada'a
Tharmada ( ar, ثرمداء) is a Saudi Arabian town, located about 170 kilometers north of the capital Riyadh.
Naming
The town is named after the plant Altharmad (''Halexylon Salicornicum'') which abounds in the region.
See also
* List of ...
, Dhurma
Dhurma or Darma ( ar, ضرما) is a small town located by road northwest of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. It is the center of the small Dhurma Governorate of Riyadh Province, and had a population of 10,267 people according to the 2004 census.
It lie ...
, Al-Gway'iyyah, Al-Hareeq, Hotat Bani Tamim Hotat Bani Tamim ( ar, حوطة بني تميم) is a Saudi Arabian town, adjacent to Riyadh. Its population is about 40,000. Most of the residents are from the Tamimi tribe. Hotat Bani Tamim is located 135 km south of Riyadh's southern ring ro ...
, Layla
"Layla" is a song written by Eric Clapton and Jim Gordon, originally recorded by Derek and the Dominos, as the thirteenth track from their only studio album, ''Layla and Other Assorted Love Songs'' (1970). Its contrasting movements were compose ...
, As Sulayyil
Al Sulayyil ( ar, السليل) or As Sulayyil is a village in Ar Riyad Province, Saudi Arabia. The city is located about 575 km South of Riyadh city proper and 80 km North-East of Wadi ad-Dawasir, another relatively larger city. It has ...
, and Wadi ad-Dawasir
Wadi Al Dawasir ( ar, وادي الدواسر) is a town in Najd, Saudi Arabia, in the Dawasir valley. The town is the homeland of the tribe of Al-Dawasir.
The municipality had a population of 106,152 at the 2010 Census. It is divided into three ...
, the southernmost settlement in Najd.
Population
Social and ethnic groups
Prior to the formation of the modern Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the native population was largely made up ofArabian tribes
The Tribes of Arabia () or Arab tribes () are the ethnic Arab tribes and clans that originated in the Arabian Peninsula. The tribes of Arabia descend from either one of the two Arab ancestors, Adnan or Qahtan. Arab tribes have historically inhabit ...
, who were either nomads (''bedouins''), who were a minority of inhabitants, or part of the majority class of sedentary farmers and merchants who lived in villages and towns dotted around central Arabia. The rest of the population consisted mainly of Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s who were, for various reasons, unaffiliated with any tribes, and who mostly lived in the towns and villages of Najd working in various trades such as carpentry or as ''Sonnaa (craftsmen
Craftsman may refer to:
A profession
*Artisan, a skilled manual worker who makes items that may be functional or strictly decorative
* Master craftsman, an artisan who has achieved such a standard that he may establish his own workshop and take ...
). There was also a small segment of the population made up of African as well as some East and South Eastern European slaves and freedmen.
Most of the Najdi tribes are of Adnanite origin and emigrated from Tihamah
Tihamah or Tihama ( ar, تِهَامَةُ ') refers to the Red Sea coastal plain of the Arabian Peninsula from the Gulf of Aqaba to the Bab el Mandeb.
Etymology
Tihāmat is the Proto-Semitic language's term for 'sea'. Tiamat (or Tehom, in mas ...
and Hijaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Provinc ...
to Najd in ancient times. The most famous Najdi tribes in the pre-Islamic era were Banu Hanifa
Banu Hanifa ( ar, بنو حنيفة) is an ancient Arab tribe inhabiting the area of al-Yamama in the central region of modern-day Saudi Arabia. The tribe belongs to the great Rabi'ah branch of North Arabian tribes, which also included Abdu ...
, who occupied the area around modern-day Riyadh, Banu Tamim
Banū Tamīm ( ar, بَنُو تَمِيم) is an Arab tribe that originated in Najd in the Arabian Peninsula. It is mainly present in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, Jordan, Algeria, and has a strong presence in Morocco, Palestine, Tunisia ...
, who occupied areas further north, the tribe of Banu Abs who were centered in Al-Qassim, the tribe of Tayy, centered on modern-day Ha'il, and the tribe of Banu 'Amir in southern Najd.
In the 15th through 18th centuries, there was considerable tribal influx from the west, increasing both the nomadic and settled population of the area and providing fertile soil for the Wahhabi movement. By the 20th century, many of the ancient tribes had morphed into new confederations or emigrated from other areas of the Middle East, and many tribes from other regions of the Peninsula had moved into Najd. However, the largest proportion of native Najdis today still belong to these ancient Najdi tribes or to their newer incarnations.
Many of the Najdi tribes even in ancient times were not nomadic or bedouin but rather very well settled farmers and merchants. The royal family of Saudi Arabia, Al Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1727–1818), and ...
, for example, trace their lineage to Banu Hanifa. On the eve of the formation of Saudi Arabia, the major nomadic tribes of Najd included Dawasir, Mutayr, 'Utaybah The Otaibah (, also spelled Otaiba, Utaybah) is one of the biggest Arab tribes originating in the Arabian Peninsula. Their distribution spans throughout Saudi Arabia, especially in Najd. and the Middle East. The Otaibah are descended from the Bedoui ...
, Shammar
The tribe of Shammar ( ar, شَمَّر, Šammar) is a tribal Arab Qahtan confederation, descended from the Yemeni tribe of Tayy as they originated in Yemen before migrating into present day Saudi Arabia, It is the biggest branch of Tayy tribe. I ...
(historically known as Tayy) Subay', Suhool The Suhool ( ar, السهول, sing. Sahli) are an Arab tribe of the region of Nejd in central Saudi Arabia. They are descendants of the larger tribe of Banu 'Amir, also known as 'Amir ibn Sa'sa'a, and are considered the cousins of Subay'.
bran ...
, Harb, and the Qahtanites in southern Najd. In addition to those tribes, many of the sedentary population belonged to Anizzah, Banu Tamim, Banu Hanifa
Banu Hanifa ( ar, بنو حنيفة) is an ancient Arab tribe inhabiting the area of al-Yamama in the central region of modern-day Saudi Arabia. The tribe belongs to the great Rabi'ah branch of North Arabian tribes, which also included Abdu ...
, Banu Khalid
Bani Khalid ( ar, بني خالد) is an Arab tribal confederation mainly inhabiting Eastern Arabia and Najd. The tribe ruled southern Iraq, Kuwait, and Eastern Arabia (al-Hasa and al-Qatif) from the 15th century to the 18th century, and ag ...
, and Banu Zayd Banu Zayd ( ar, بنو زيد) is a Najdi tribe that traces its roots to Zayd who settled Shaqraa in Najd.Banu Zayd, al-qabilah al-Quda 'iyah fi hadirat Najd by Shuqayr, Abd al-Rahman ibn Abd Allah. Riyad : al-Mu'allif, 2002.
Notable people
Among ...
.
Most of the minority nomadic tribes are now settled either in cities such as Riyadh, or in special settlements, known as hijras, that were established in the early part of the 20th century as part of a country-wide policy undertaken by King Abdul-Aziz to put an end to nomadic life. Nomads still exist in the Kingdom, however, in very small numbers – a far cry from the days when they made up the majority of the people of the Arabian Peninsula.
Since the formation of modern Saudi Arabia, Najd, and particularly Riyadh, has seen an influx of immigrants from all regions of the country and from virtually every social class. The native Najdi population has also largely moved away from its native towns and villages to the capital, Riyadh. However, most of these villages still retain a small number of their native inhabitants.
About a quarter of the population of Najd, including about a third of the population of Riyadh, are non-Saudi expatriates, including both skilled professionals and unskilled laborers. Slavery was abolished in Saudi Arabia by King Faisal in 1962. Some of those freed slaves chose to continue working for their former slave-owners, particularly those whose former owners were members of the royal family.
Unlike the Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Provin ...
and Tihamah
Tihamah or Tihama ( ar, تِهَامَةُ ') refers to the Red Sea coastal plain of the Arabian Peninsula from the Gulf of Aqaba to the Bab el Mandeb.
Etymology
Tihāmat is the Proto-Semitic language's term for 'sea'. Tiamat (or Tehom, in mas ...
, Najd is remote and stayed outside of the reign of important Islamic empires such as the Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. This fact largely shaped its current dissimilarity to Hejaz.
Religion
The region is traditionally known as aHanbali
The Hanbali school ( ar, ٱلْمَذْهَب ٱلْحَنۢبَلِي, al-maḏhab al-ḥanbalī) is one of the four major traditional Sunni schools (''madhahib'') of Islamic jurisprudence. It is named after the Arab scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal ...
stronghold, and after the 18th century became known for its strict interpretation of Islam and is generally considered a bastion of religious conservatism. The founder of the interpretation of Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagre ...
called Wahhabism
Wahhabism ( ar, ٱلْوَهَّابِيَةُ, translit=al-Wahhābiyyah) is a Sunni Islamic revivalist and fundamentalist movement associated with the reformist doctrines of the 18th-century Arabian Islamic scholar, theologian, preacher, an ...
, Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, was born in 'Uyayna
Al-'Uyayna or al-'Uyaynah ( ar, العيينة) is a village in central Saudi Arabia, located some northwest of the Saudi capital Riyadh. Al-Uyaynah was the birthplace of Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. Today, Uyaynah is a small village and forms t ...
, a village in the Najd.
The majority of people in the region consider themselves as Salafi Muslims. The name derives from advocating a return to the traditions of the "ancestors" (salaf), the first three generations of Muslims said to know the unadulterated, pure form of Islam. Those generations include the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his companions (the Sahabah), their successors (the Tabi‘un), and the successors of the successors (the Taba al-Tabi‘in). Practically, Salafis maintain that Muslims ought to rely on the Qur'an, the Sunnah and the 'Ijma (consensus) of the salaf, giving them precedence over later Islamic hermeneutic teachings. Bin Ali Mohamed (2015). ''The Roots of Religious Extremism: Understanding the Salafi Doctrine of Al-wala‘ Wal Bara‘''. Bara World Scientific. . p. 61.
Language
The people of Najd have spokenArabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
, in one form or another, for practically all of recorded history. As in other regions of the Peninsula, there is a divergence between the dialect of the nomadic Bedouins and the dialect of the sedentary townspeople. The variation, however, is far less pronounced in Najd than it is elsewhere in the country, and the Najdi sedentary dialect seems to be descended from the Bedouin dialect, just as many sedentary Najdis are descendants of nomadic Bedouins themselves. The Najdi dialect is seen by some to be the least foreign-influenced of all modern Arabic dialects, due to the isolated location and harsh climate of the Najdi plateau, as well as the apparent absence of any substratum from a previous language. Indeed, not even the ancient South Arabian language appears to have been widely spoken in Najd in ancient times, unlike southern Saudi Arabia, for example.
Within Najd itself, the different regions and towns have their own distinctive accents and sub-dialects. However, these have largely merged in recent times and have become heavily influenced by Arabic dialects from other regions and countries. This is particularly the case in Riyadh.
Economy
 In the early 20th century, Najd produced coarse
In the early 20th century, Najd produced coarse wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
cloth and a wide range of agricultural products.
In popular culture
Bahiyyih Nakhjavani
__NOTOC__
Bahiyyih Nakhjavani is an Iranian writer who grew up in Uganda in the 1960s. She was educated at Dr Williams School, Dolgellau, United Kingdom and the United States. She taught European and American literature in Belgium, and later mov ...
's first novel ''The Saddlebag – A Fable for Doubters and Seekers'' describes events set in the Najd plateau along the pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
route between Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
and Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
in 1844–1845.
A contest held in the Middle East brought light to a new character in famed SNK Playmore video game, ''The King of Fighters XIV
''(KOF XIV)'' is a 2016 Japanese fighting game. Part of SNK's franchise ''The King of Fighters'' (''KOF'') series, with this installment being published by Atlus USA in North America and Deep Silver in Europe. After the 13th installment that ...
''. This character goes under the name Najd.
See also
* *History of Saudi Arabia
The history of Saudi Arabia as a nation state began with the emergence of the Al Saud dynasty in central Arabia in 1727 and the subsequent establishment of the Emirate of Diriyah. Pre-Islamic Arabia, the territory that constitutes modern Saudi ...
* Kingdom of Nejd and Hejaz
The Kingdom of Hejaz and Nejd ( ar, مملكة الحجاز ونجد, '), initially the Kingdom of Hejaz and Sultanate of Nejd (, '), was a dual monarchy ruled by Abdulaziz of Saudi Arabia, Abdulaziz following the Saudi conquest of Hejaz, victory ...
* List of expeditions of Muhammad in Nejd
* Nejd Expedition
The Najd Expedition ( tr, Nejd Seferi) was a series of military conflicts waged by Egypt on behalf of the Ottoman Empire from 1817–1818. It was part of the Ottoman–Saudi War that lasted from 1811 to 1818. The campaign of 1817/8 was led by ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control Geography of Saudi Arabia Historical regions Historical regions in Saudi Arabia Regions of Asia