Minishogi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Minishogi (5五将棋 ''gogo shōgi'' "5V chess" or "5×5 chess") is a modern
Minishogi (5五将棋 ''gogo shōgi'' "5V chess" or "5×5 chess") is a modern
Minishogi
at ''
Website of the Japanese Minishogi Association
(in Japanese, but contains game records which can be understood without knowing Japanese)
6x5 Mini Shogi iPhone software
UEC Minishogi website
(mostly Japanese)
for playing Minishogi {{Shogi variants Shogi variants
 Minishogi (5五将棋 ''gogo shōgi'' "5V chess" or "5×5 chess") is a modern
Minishogi (5五将棋 ''gogo shōgi'' "5V chess" or "5×5 chess") is a modern variant
Variant may refer to:
In arts and entertainment
* ''Variant'' (magazine), a former British cultural magazine
* Variant cover, an issue of comic books with varying cover art
* ''Variant'' (novel), a novel by Robison Wells
* " The Variant", 2021 e ...
of shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' ...
(Japanese chess). The game was invented (or rediscovered) around 1970 by Shigenobu Kusumoto of Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2. ...
, Japan. The rules are nearly identical to those of standard shogi, with the exception that it is played on a 5x5 board with a reduced number of pieces, and each player's promotion zone consists only of the rank farthest from the player.
Rules of the game
Objective
Like in standard shogi, each player aims to checkmate the opponent'sking
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
.
Game equipment
Two players play on a board ruled into a grid of five ranks (rows) by five files (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. Each player begins with a set of 6 wedge-shaped pieces; these are: *1king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
*1 rook
Rook (''Corvus frugilegus'') is a bird of the corvid family. Rook or rooks may also refer to:
Games
*Rook (chess), a piece in chess
*Rook (card game), a trick-taking card game
Military
* Sukhoi Su-25 or Rook, a close air support aircraft
* USS ...
*1 bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
*1 gold general
*1 silver general
*1 pawn
Pawn most often refers to:
* Pawn (chess), the weakest and most numerous piece in the game
* Pawnbroker or pawnshop, a business that provides loans by taking personal property as collateral
Pawn may also refer to:
Places
* Pawn, Oregon, an his ...
Their movements are identical to those of their namesakes in standard shogi.
Setup
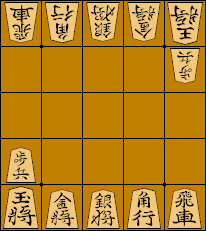
Each player places their pieces in the positions shown below, pointing towards the opponent. In the rank nearest to the player: *The king is placed in the leftmost file; *The gold general is placed in the adjacent file to the king; *The silver general is placed adjacent to the gold general; *The bishop is placed adjacent to the silver general; *The rook is placed in the rightmost file, adjacent to the bishop. That is, the setup of the first rank is as follows: , K, G, S, B, R, . In the second rank, each player places the pawn in the same file as the king (i.e. directly in front of the king).Promotion
Like in standard shogi, a piece may (but is not obliged to) be promoted when it is moves into, within, or out of the promotion zone. The zone only lies within the rank farthest from the player (unlike in the standard game, where it lies within the last ''three'' ranks). All pieces promote the same way as their namesakes in standard shogi (and likewise, the kings and gold generals do not promote at all). The pawns ''must'' be promoted once they reach the farthest rank (since otherwise they would not have any legal moves).Drops
The rules for dropping pieces are identical to those in standard shogi: all dropped pieces must start unpromoted (even if they have been captured as promoted pieces and/or are dropped into the farthest rank); a pawn may not be dropped onto the farthest rank, or onto a square that results in an immediate checkmate; the two pawns may not lie in the same file when they belong to the same player.Repetition
If the same position (with the same side to move and same pieces in hand) occurs for the fourth time, the game ends and the final result is a loss for the player that made the very first move in the game (this is different from regular shogi, where such a scenario would result in a draw). The only exception to this rule is when one player perpetually checks the opponent; in that case the checking side loses the game.Strategy
Due to the small size of the board, the rook and bishop lose a significant amount of their relative strength, relative to the gold and silver generals. Because of the reduced ability for each player to achieve king safety, threats of checkmate are always present, and having pieces on hand presents many checkmate threats which reduce the opponent's mobility. This must be balanced against the defense of one's own king by friendly pieces on the board. As in many variants of chess, a common strategy is to develop the less powerful pieces (i.e. gold and silver generals) before the more powerful pieces (i.e. rooks and bishops).Handicap play
The traditional rook, bishop, and 2-piece handicaps inshogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' ...
may be applied to this game. Additionally, there exist 3-piece, 4-piece, and even naked-king handicaps. In naked-king-handicap game, black can theoretically force a mate in 8 plies.
Computer Minishogi
Minishogi is popular with artificial-intelligence researchers and there are many strong programs that play it. Due to minishogi being smaller, it can play a much stronger game than on the standard board size. Several tournaments in which such programs can enter to compete against each other are organized yearly, often associated with scientific conferences. The most prestigious of these tournaments is the UEC Cup, organized by the University of Electro-Communication in Tokyo. Other such events are TAAI (in Taiwan) and the ICGA Computer Olympiad. Minishogi can use the same standard protocols as regular shogi for communicating between graphical interfaces (which display a shogi board) and the artificial intelligence modules ('engines'), such as USI (Universal Shogi Interface) or XBoard protocol. There are several free strong minishogi engines that can be used with the WinBoard interface, which support bothXBoard
XBoard is a graphical user interface chessboard for chess engines under the X Window System. It is developed and maintained as free software by the GNU project. WinBoard is a port of XBoard to run natively on Microsoft Windows.
Overview
Origin ...
protocol and USI.
See also
*Shogi variant
A shogi variant is a game related to or derived from shogi (Japanese chess). Many shogi variants have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest. A few of these variant ...
*Tori shogi
Tori shōgi (禽将棋 or 鳥将棋, 'bird chess') is a variant of shogi (Japanese chess), which was invented by Toyota Genryu in 1799 despite being traditionally attributed to his master Ōhashi Sōei. It was first published in 1828 and again in ...
*Microshogi
Microshogi (五分摩訶将棋 ''gofun maka shōgi'' "5-minute (scarlet) poppy chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess), with very different rules for promotion, and demotion. Kerry Handscomb of NOSTNOST (kNights of the Square Table) ...
*Judkins shogi
Judkins shogi (ジャドケンス将棋 ''Jadokensu shōgi'' "Judkins chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess), however it is not Japanese. Credit for its invention has been given to Paul Judkins of Norwich, UK, prior to April 1998.
...
*Kyoto shogi
is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess). It was invented by Tamiya Katsuya c. 1976.
Kyoto shogi is played like standard shogi, but with a reduced number of pieces on a 5×5 board. However, the pieces alternately promote and demote with e ...
*Cannon shogi
A shogi variant is a game related to or derived from shogi (Japanese chess). Many shogi variants have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest. A few of these variant ...
*Yari shogi
Yari shogi (槍将棋 ''yari shōgi'', spear chess, where 'spear' is another name for the lance piece) is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess); however, it is not Japanese. It was invented in 1981 by Christian Freeling of the Netherlands. Th ...
External links
Minishogi
at ''
The Chess Variant Pages
''The Chess Variant Pages'' is a non-commercial website devoted to chess variants. It was created by Hans Bodlaender in 1995. The site is "run by hobbyists for hobbyists" and is "the most wide-ranging and authoritative web site on chess variants". ...
''
Website of the Japanese Minishogi Association
(in Japanese, but contains game records which can be understood without knowing Japanese)
6x5 Mini Shogi iPhone software
UEC Minishogi website
(mostly Japanese)
for playing Minishogi {{Shogi variants Shogi variants