Military Camouflage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
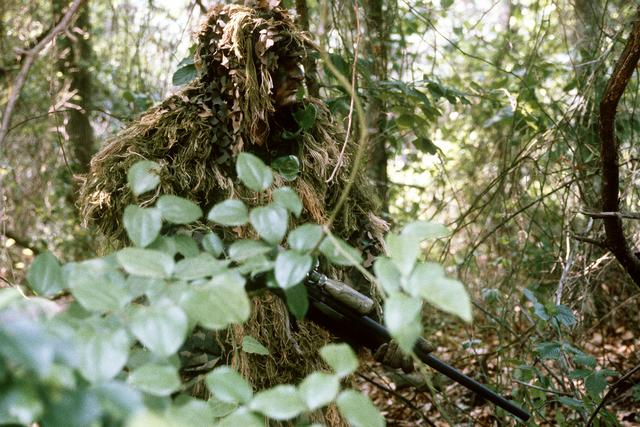 Military camouflage is the use of
Military camouflage is the use of
 Military camouflage is part of the art of military deception. The main objective of military camouflage is to deceive the enemy as to the presence, position and intentions of military formations. Camouflage techniques include concealment, disguise, and dummies, applied to troops, vehicles, and positions.
Vision is the main sense of orientation in humans, and the primary function of camouflage is to deceive the human eye. Camouflage works through concealment (whether by countershading, preventing casting shadows, or disruption of outlines), mimicry, or possibly by
Military camouflage is part of the art of military deception. The main objective of military camouflage is to deceive the enemy as to the presence, position and intentions of military formations. Camouflage techniques include concealment, disguise, and dummies, applied to troops, vehicles, and positions.
Vision is the main sense of orientation in humans, and the primary function of camouflage is to deceive the human eye. Camouflage works through concealment (whether by countershading, preventing casting shadows, or disruption of outlines), mimicry, or possibly by
 While camouflage tricks are in principle limitless, both cost and practical considerations limit the choice of methods and the time and effort devoted to camouflage. Paint and uniforms must also protect vehicles and soldiers from the elements. Units need to move, fire their weapons and perform other tasks to keep functional, some of which run counter to camouflage. Camouflage may be dropped altogether. Late in the Second World War, the
While camouflage tricks are in principle limitless, both cost and practical considerations limit the choice of methods and the time and effort devoted to camouflage. Paint and uniforms must also protect vehicles and soldiers from the elements. Units need to move, fire their weapons and perform other tasks to keep functional, some of which run counter to camouflage. Camouflage may be dropped altogether. Late in the Second World War, the
 Camouflage patterns serve cultural functions alongside concealment. Apart from concealment, uniforms are also the primary means for soldiers to tell friends and enemies apart. The camouflage experts and evolutionary zoologists L. Talas, R. J. Baddeley and
Camouflage patterns serve cultural functions alongside concealment. Apart from concealment, uniforms are also the primary means for soldiers to tell friends and enemies apart. The camouflage experts and evolutionary zoologists L. Talas, R. J. Baddeley and
 Seasons may play a role in some regions. A dramatic change in colour and texture is created by seasonal snowy conditions in northern latitudes, necessitating repainting of vehicles and separate snow oversuits. The Eastern and northern European countries have a tradition for separate winter uniforms rather than oversuits. During the Second World War, the
Seasons may play a role in some regions. A dramatic change in colour and texture is created by seasonal snowy conditions in northern latitudes, necessitating repainting of vehicles and separate snow oversuits. The Eastern and northern European countries have a tradition for separate winter uniforms rather than oversuits. During the Second World War, the
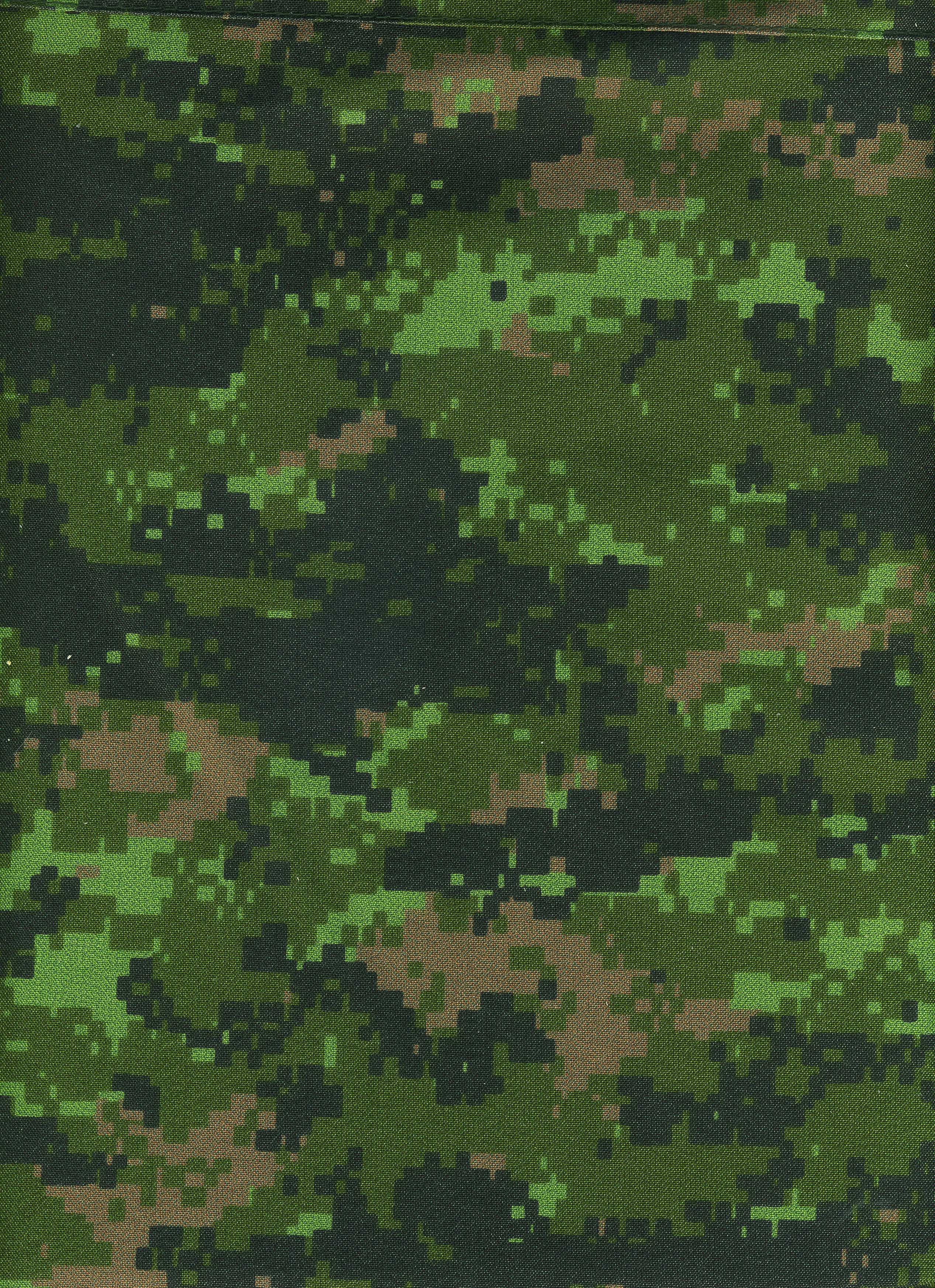 Digital camouflage provides a disruptive effect through the use of pixellated patterns at a range of scales, meaning that the camouflage helps to defeat observation at a range of distances. Such patterns were first developed during the Second World War, when Johann Georg Otto Schick designed a number of patterns for the
Digital camouflage provides a disruptive effect through the use of pixellated patterns at a range of scales, meaning that the camouflage helps to defeat observation at a range of distances. Such patterns were first developed during the Second World War, when Johann Georg Otto Schick designed a number of patterns for the
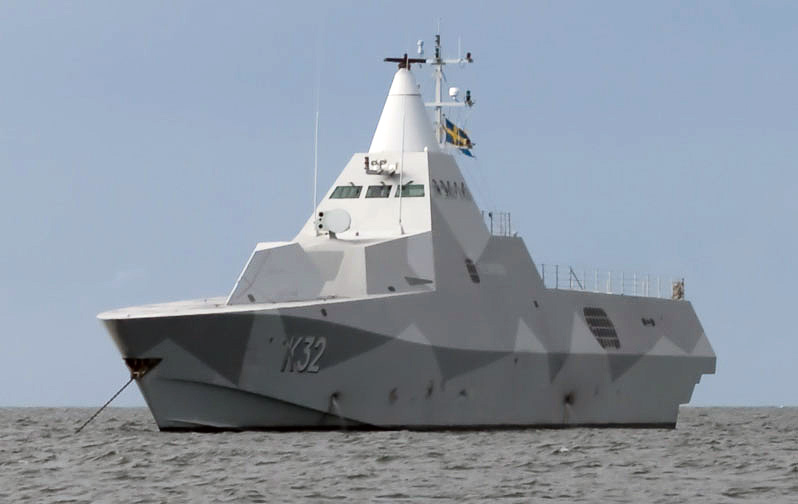 With the birth of
With the birth of
 The tradition was continued by British
The tradition was continued by British
camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
by an armed force to protect personnel and equipment from observation by enemy forces. In practice, this means applying colour and materials to military equipment of all kinds, including vehicles, ships, aircraft, gun positions and battledress
A combat uniform, also called field uniform, battledress or military fatigues, is a casual type of uniform used by military, police, fire and other public uniformed services for everyday fieldwork and combat duty purposes, as opposed to dress ...
, either to conceal it from observation ( crypsis), or to make it appear as something else ( mimicry). The French slang word ''camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
'' came into common English usage during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
when the concept of visual deception developed into an essential part of modern military tactics. In that war, long-range artillery and observation from the air combined to expand the field of fire, and camouflage was widely used to decrease the danger of being targeted or to enable surprise. As such, military camouflage is a form of military deception.
Camouflage was first practiced in simple form in the mid 18th century by rifle units. Their tasks required them to be inconspicuous, and they were issued green and later other drab colour uniforms. With the advent of longer range and more accurate weapons, especially the repeating rifle, camouflage was adopted for the uniforms of all armies, spreading to most forms of military equipment including ships and aircraft. Many modern camouflage textiles address visibility not only to visible light but also near infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from arou ...
, for concealment from night vision devices. Camouflage is not only visual; heat, sound, magnetism and even smell can be used to target weapons, and may be intentionally concealed. Some forms of camouflage have elements of scale invariance
In physics, mathematics and statistics, scale invariance is a feature of objects or laws that do not change if scales of length, energy, or other variables, are multiplied by a common factor, and thus represent a universality.
The technical term ...
, designed to disrupt outlines at different distances, typically digital camouflage
Multi-scale camouflage is a type of military camouflage combining patterns at two or more scales, often (though not necessarily) with a digital camouflage pattern created with computer assistance. The function is to provide camouflage over a ra ...
patterns made of pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
s. Camouflage patterns also have cultural functions such as political identification.
Camouflage for equipment and positions was extensively developed for military use by the French in 1915, soon followed by other World War I armies. In both world wars, artists were recruited as camouflage officers. Ship camouflage developed via conspicuous dazzle camouflage schemes during WWI, but since the development of radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
, ship camouflage has received less attention. Aircraft, especially in World War II, were often countershaded: painted with different schemes above and below, to camouflage them against the ground and sky respectively.
Military camouflage patterns have been popular in fashion and art from as early as 1915. Camouflage patterns have appeared in the work of artists such as Andy Warhol
Andy Warhol (; born Andrew Warhola Jr.; August 6, 1928 – February 22, 1987) was an American visual artist, film director, and producer who was a leading figure in the Art movement, visual art movement known as pop art. His works explore th ...
and Ian Hamilton Finlay
Ian Hamilton Finlay, CBE (28 October 1925 – 27 March 2006) was a Scottish poet, writer, artist and gardener.
Life
Finlay was born in Nassau, Bahamas, to James Hamilton Finlay and his wife, Annie Pettigrew, both of Scots descent.
He was e ...
, sometimes with an anti-war message. In fashion, many major designers have exploited camouflage's style and symbolism, and military clothing or imitations of it have been used both as street wear and as a symbol of political protest.
Principles
dazzle
Dazzle may refer to:
* Glare (vision), difficulty seeing in the presence of bright light
* Dazzle (fabric), a type of polyester fabric
* ''Dazzle'' (manga), a Japanese manga series by Minari Endoh
* "Dazzle" (song), a song by Siouxsie & the Bans ...
. In modern warfare, some forms of camouflage, for example face paints, also offer concealment from infrared sensors, while CADPAT
Canadian Disruptive Pattern (CADPAT; french: links=no, dessin de camouflage canadien, DcamC) is the computer-generated digital camouflage pattern developed for use by the Canadian Armed Forces. Four operational variations of CADPAT have been use ...
textiles in addition help to provide concealment from radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
.
Compromises
 While camouflage tricks are in principle limitless, both cost and practical considerations limit the choice of methods and the time and effort devoted to camouflage. Paint and uniforms must also protect vehicles and soldiers from the elements. Units need to move, fire their weapons and perform other tasks to keep functional, some of which run counter to camouflage. Camouflage may be dropped altogether. Late in the Second World War, the
While camouflage tricks are in principle limitless, both cost and practical considerations limit the choice of methods and the time and effort devoted to camouflage. Paint and uniforms must also protect vehicles and soldiers from the elements. Units need to move, fire their weapons and perform other tasks to keep functional, some of which run counter to camouflage. Camouflage may be dropped altogether. Late in the Second World War, the USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
abandoned camouflage paint for some aircraft to lure enemy fighters to attack, while in the Cold War, some aircraft similarly flew with polished metal skins, to reduce drag and weight, or to reduce vulnerability to radiation from nuclear weapons.
No single camouflage pattern is effective in all terrains. The effectiveness of a pattern depends on contrast as well as colour tones. Strong contrasts which disrupt outlines are better suited for environments such as forests where the play of light and shade is prominent, while low contrasts are better suited to open terrain with little shading structure. Terrain-specific camouflage patterns, made to match the local terrain, may be more effective in that terrain than more general patterns. However, unlike an animal or a civilian hunter, military units may need to cross several terrain types like woodland, farmland and built up areas in a single day. While civilian hunting clothing may have almost photo-realistic depictions of tree bark or leaves (indeed, some such patterns are based on photographs), military camouflage is designed to work in a range of environments. With the cost of uniforms in particular being substantial, most armies operating globally have two separate full uniforms, one for woodland/jungle and one for desert and other dry terrain. An American attempt at a global camouflage pattern for all environments (the 2004 UCP) was however withdrawn after a few years of service. On the other end of the scale are terrain specific patterns like the "Berlin camo", applied to British vehicles operating in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
during the Cold War, where square fields of various gray shades was designed to hide vehicles against the mostly concrete architecture of post-war Berlin.
Other functions
 Camouflage patterns serve cultural functions alongside concealment. Apart from concealment, uniforms are also the primary means for soldiers to tell friends and enemies apart. The camouflage experts and evolutionary zoologists L. Talas, R. J. Baddeley and
Camouflage patterns serve cultural functions alongside concealment. Apart from concealment, uniforms are also the primary means for soldiers to tell friends and enemies apart. The camouflage experts and evolutionary zoologists L. Talas, R. J. Baddeley and Innes Cuthill Innes C. Cuthill (born 1960) is a professor of behavioural ecology at the University of Bristol. His main research interest is in camouflage, in particular how it evolves in response to the colour vision of other animals such as predators.
Life
In ...
analyzed calibrated photographs of a series of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
and Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist repub ...
uniform patterns and demonstrated that their evolution did not serve any known principles of military camouflage intended to provide concealment. Instead, when the Warsaw Pact was dissolved, the uniforms of the countries that began to favour the West politically started to converge on the colours and textures of NATO patterns. After the death of Marshal Tito and the breakup of what had been Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, the camouflage patterns of the new nations changed, coming to resemble the camouflage patterns used by the armies of their neighbours. The authors note that military camouflage resembles animal coloration in having multiple simultaneous functions.
Snow camouflage
 Seasons may play a role in some regions. A dramatic change in colour and texture is created by seasonal snowy conditions in northern latitudes, necessitating repainting of vehicles and separate snow oversuits. The Eastern and northern European countries have a tradition for separate winter uniforms rather than oversuits. During the Second World War, the
Seasons may play a role in some regions. A dramatic change in colour and texture is created by seasonal snowy conditions in northern latitudes, necessitating repainting of vehicles and separate snow oversuits. The Eastern and northern European countries have a tradition for separate winter uniforms rather than oversuits. During the Second World War, the Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
went a step further, developing reversible uniforms with separate schemes for summer and autumn, as well as white winter oversuits.
Movement
While patterns can provide more effective crypsis than solid colour when the camouflaged object is stationary, any pattern, particularly one with high contrast, stands out when the object is moving. Jungle camouflage uniforms were issued during theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, but both the British and American forces found that a simple green uniform provided better camouflage when soldiers were moving. After the war, most nations returned to a unicoloured uniform for their troops. Some nations, notably Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, continue to use solid colour combat uniforms today. Similarly, while larger military aircraft traditionally had a disruptive pattern with a darker top over a lighter lower surface (a form of countershading), modern fast fighter aircraft often wear gray overall.
Digital camouflage
 Digital camouflage provides a disruptive effect through the use of pixellated patterns at a range of scales, meaning that the camouflage helps to defeat observation at a range of distances. Such patterns were first developed during the Second World War, when Johann Georg Otto Schick designed a number of patterns for the
Digital camouflage provides a disruptive effect through the use of pixellated patterns at a range of scales, meaning that the camouflage helps to defeat observation at a range of distances. Such patterns were first developed during the Second World War, when Johann Georg Otto Schick designed a number of patterns for the Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
, combining micro- and macro-patterns in one scheme. The German Army developed the idea further in the 1970s into Flecktarn
''Flecktarn'' (; "mottled camouflage"; also known as ''Flecktarnmuster'' or ''Fleckentarn'') is a family of 3-, 4-, 5- or 6-color disruptive camouflage patterns, the most common being the five-color pattern, consisting of dark green, light green, ...
, which combines smaller shapes with dithering; this softens the edges of the large scale pattern, making the underlying objects harder to discern. Pixellated
In computer graphics, pixelation (or pixellation in British English) is caused by displaying a bitmap or a section of a bitmap at such a large size that individual pixels, small single-colored square display elements that comprise the bitmap, a ...
shapes pre-date computer aided design by many years, already being used in Soviet Union experiments with camouflage patterns, such as " TTsMKK" developed in 1944 or 1945.
In the 1970s, US Army officer Timothy R. O'Neill suggested that patterns consisting of square blocks of colour would provide effective camouflage. By 2000, O'Neill's idea was combined with patterns like the German ''Flecktarn'' to create pixellated patterns such as CADPAT
Canadian Disruptive Pattern (CADPAT; french: links=no, dessin de camouflage canadien, DcamC) is the computer-generated digital camouflage pattern developed for use by the Canadian Armed Forces. Four operational variations of CADPAT have been use ...
and MARPAT
MARPAT (short for Marine pattern) is a multi-scale camouflage pattern in use with the United States Marine Corps, designed in 2001 and introduced from late 2002 to early 2005 with the Marine Corps Combat Utility Uniform (MCCUU), which replace ...
. Battledress in digital camouflage patterns was first designed by the Canadian Forces
}
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; french: Forces armées canadiennes, ''FAC'') are the unified military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air elements referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Forc ...
. The "digital" refers to the coordinates of the pattern, which are digitally defined. The term is also used of computer generated patterns like the non-pixellated Multicam and the Italian fractal ''Vegetato'' pattern. Pixellation does not in itself contribute to the camouflaging effect. The pixellated style, however, simplifies design and eases printing on fabric.
Non-visual
 With the birth of
With the birth of radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
and sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on o ...
and other means of detecting military hardware not depending on the human eye, came means of camouflaging against them. Collectively these are known as stealth technology. Aircraft and ships can be shaped to reflect radar impulses away from the sender, and covered with radar-absorbing materials, to reduce their radar signature. The use of heat-seeking missiles has also led to efforts to hide the heat signature of aircraft engines. Methods include exhaust ports shaped to mix hot exhaust gases with cold surrounding air, and placing the exhaust ports on the upper side of the airframe. Multi-spectral camouflage attempts to hide objects from detection methods such as infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
, radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
, and millimetre-wave imaging simultaneously.
Auditory camouflage, at least in the form of noise reduction, is practised in various ways. The rubberized hull of military submarines absorbs sonar waves and can be seen as a form of auditory camouflage. Some modern helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
s are designed to be quiet. Combat uniforms are usually equipped with buttons rather than snap fastener
A snap fastener, also called snap button, press stud, press fastener, dome fastener, popper, snap and tich (or tich button), is a pair of interlocking discs, made out of a metal or plastic, commonly used in place of traditional buttons to fasten ...
s or velcro
Velcro, officially known as Velcro IP Holdings LLC and trading as Velcro Companies, is a British privately held company, founded by Swiss electrical engineer George de Mestral in the 1950s. It is the original manufacturer of hook-and-loop fast ...
to reduce noise.
Olfactory camouflage is said to be rare; examples include ghillie suits, special garments for military snipers made from strips of hessian cloth, which are sometimes treated with mud and even manure to give them an "earthy" smell to cover the smell of the sniper.
Magnetic camouflage in the form of "degaussing
Degaussing is the process of decreasing or eliminating a remnant magnetic field. It is named after the gauss, a unit of magnetism, which in turn was named after Carl Friedrich Gauss. Due to magnetic hysteresis, it is generally not possible to red ...
" coils has been used since the Second World War to protect ships from magnetic mines and other weapons with magnetic sensors. Horizontal coils around the whole or parts of the ship generate magnetic fields to "cancel out" distortions to the earth's magnetic field created by the ship.
History
Reconnaissance and riflemen
Ship camouflage
Ship camouflage is a form of military deception in which a ship is painted in one or more colors in order to obscure or confuse an enemy's visual observation. Several types of marine camouflage have been used or prototyped: blending or crypsis, ...
was occasionally used in ancient times. Vegetius
Publius (or Flavius) Vegetius Renatus, known as Vegetius (), was a writer of the Later Roman Empire (late 4th century). Nothing is known of his life or station beyond what is contained in his two surviving works: ''Epitoma rei militaris'' (also r ...
wrote in the 4th century that "Venetian blue" (bluish-green, like the sea) was used for camouflage in the years 56–54 BC during the Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homel ...
, when Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
sent his scout ships to gather intelligence along the coast of Britain. The bluish-green scout ships carried sailors and marines dressed in the same colour.
The emphasis on hand-to-hand combat, and the short range of weapons such as the musket, meant that recognition and cohesion were more important than camouflage in combat clothing well into the baroque period. The introduction of infantry weapons with longer range, especially the Baker rifle
The Baker rifle (officially known as the Pattern 1800 Infantry Rifle) was a flintlock rifle used by the rifle regiments of the British Army during the Napoleonic Wars. It was the first standard-issue, British-made rifle accepted by the British ...
, opened up new roles which needed camouflaged clothing. In the colonial Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
(1756–1763), the rifle-armed Rogers' Rangers wore gray or green uniforms. John Graves Simcoe
John Graves Simcoe (25 February 1752 – 26 October 1806) was a British Army general and the first lieutenant governor of Upper Canada from 1791 until 1796 in southern Ontario and the watersheds of Georgian Bay and Lake Superior. He founded Yor ...
, one of the unit's later commanders, noted in 1784:
Rifle Regiments
A rifle regiment is a military unit consisting of a regiment of infantry troops armed with rifles and known as riflemen. While all infantry units in modern armies are typically armed with rifled weapons the term is still used to denote regiments t ...
who adopted rifle green
Shades of chartreuse are listed below. Historically, many of these colors have gone under the name of either yellow or green, as the specifics of their color composition was not known until later.
Wrapping the spectrum into a color wheel
In a ...
for the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
.
During the Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
fielded light infantry units known as '' Caçadores'', who wore brown-jackets which helped conceal them. The brown color was considered to be more adequate for a concealment in the landscape of most of Portuguese regions, in general more arid than the greener landscapes of Central and Northern Europe. Other nations soon followed suit, dressing their rifle regiments and sometimes also light troops in suitable drab tones, usually variations of green or gray.
The first introduction of drab general uniform was by the British Corps of Guides in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
in 1848. Initially the drab uniform was specially imported from England, with one of the reasons being to "make them invisible in a land of dust". However, when a larger quantity was required the army improvised, using a local dye to produce uniform locally. This type of drab uniform soon became known as khaki
The color khaki (, ) is a light shade of tan with a slight yellowish tinge.
Khaki has been used by many armies around the world for uniforms and equipment, particularly in arid or desert regions, where it provides camouflage relative to sandy ...
(Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
'' mazari palm. The example was followed by other British units during the
 While long range rifles became the standard weapon in the 1830s, armies were slow to adapt their tactics and uniforms, perhaps as a result of mainly fighting colonial wars against less well armed opponents. Not until the
While long range rifles became the standard weapon in the 1830s, armies were slow to adapt their tactics and uniforms, perhaps as a result of mainly fighting colonial wars against less well armed opponents. Not until the

 The
The
 In 1909 an American artist and amateur
In 1909 an American artist and amateur
 Printed camouflage for shelter halves was introduced for the Italian and German armies in the interwar period, the "splotchy" M1929 Telo mimetico in Italy and the angular Splittermuster 31 in Germany. During the War, both patterns were used for paratrooper uniforms for their respective countries. The British soon followed suit with a brush-stroke type pattern for their paratroopers' Denison smock, and the Soviets introduced an "amoeba" pattern overgarment for their snipers.
Printed camouflage for shelter halves was introduced for the Italian and German armies in the interwar period, the "splotchy" M1929 Telo mimetico in Italy and the angular Splittermuster 31 in Germany. During the War, both patterns were used for paratrooper uniforms for their respective countries. The British soon followed suit with a brush-stroke type pattern for their paratroopers' Denison smock, and the Soviets introduced an "amoeba" pattern overgarment for their snipers.
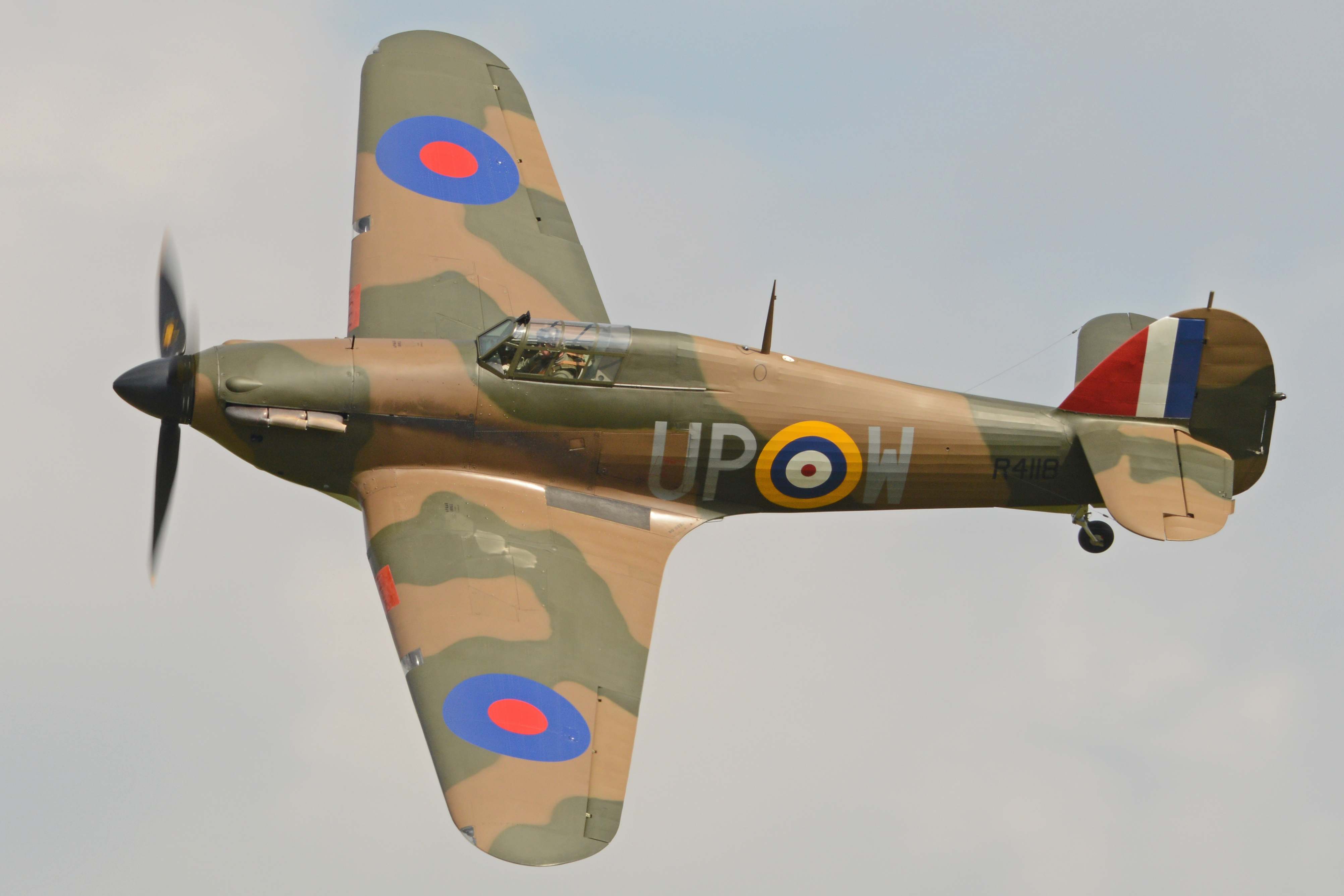 The British
The British
 The role of uniform is not only to hide each soldier, but also to identify friend from foe. Issue of the " Frogskin" uniforms to US troops in Europe during the Second World War was halted as it was too often mistaken for the disruptively patterned German uniform worn by the Waffen-SS. Camouflage uniforms need to be made and distributed to a large number of soldiers. The design of camouflage uniforms therefore involves a tradeoff between camouflaging effect, recognizability, cost, and manufacturability.
Armies facing service in different theatres may need several different camouflage uniforms. Separate issues of temperate/jungle and desert camouflage uniforms are common. Patterns can to some extent be adapted to different terrains by adding means of fastening pieces of vegetation to the uniform. Helmets often have netting covers; some jackets have small loops for the same purpose. Being able to find appropriate camouflage vegetation or in other ways modify the issued battle uniform to suit the local terrain is an important skill for infantry soldiers.
Countries in boreal climates often need snow camouflage, either by having reversible uniforms or simple overgarments.
The role of uniform is not only to hide each soldier, but also to identify friend from foe. Issue of the " Frogskin" uniforms to US troops in Europe during the Second World War was halted as it was too often mistaken for the disruptively patterned German uniform worn by the Waffen-SS. Camouflage uniforms need to be made and distributed to a large number of soldiers. The design of camouflage uniforms therefore involves a tradeoff between camouflaging effect, recognizability, cost, and manufacturability.
Armies facing service in different theatres may need several different camouflage uniforms. Separate issues of temperate/jungle and desert camouflage uniforms are common. Patterns can to some extent be adapted to different terrains by adding means of fastening pieces of vegetation to the uniform. Helmets often have netting covers; some jackets have small loops for the same purpose. Being able to find appropriate camouflage vegetation or in other ways modify the issued battle uniform to suit the local terrain is an important skill for infantry soldiers.
Countries in boreal climates often need snow camouflage, either by having reversible uniforms or simple overgarments.
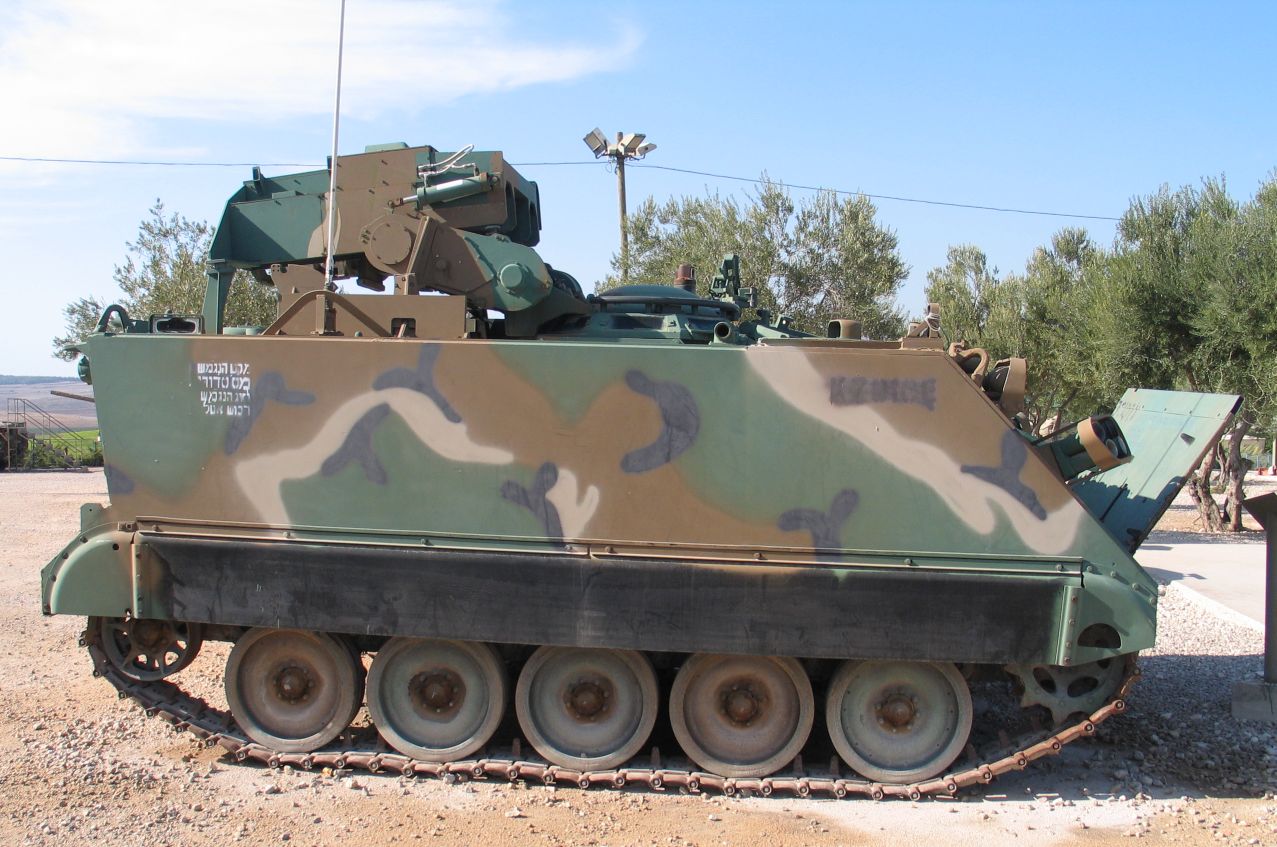 The purpose of vehicle and equipment camouflage differs from personal camouflage in that the primary threat is
The purpose of vehicle and equipment camouflage differs from personal camouflage in that the primary threat is  The British Army's Special Air Service used pink as the primary colour on its desert-camouflaged Land Rover Series IIA patrol vehicles, nicknamed ''Pink Panthers''; the colour had been observed to be indistinguishable from sand at a distance.
Nets can be effective at defeating visual observation. Traditional camouflage nets use a textile 'garnish' to generate an apparent texture with a depth of shadow created beneath it, and the effect can be reinforced with pieces of vegetation. Modern nets tend to be made of a continuous woven material, which is easier to deploy over a vehicle and lack the "windows" between patches of garnish of traditional nets. Some nets can remain in place while vehicles move. Simple nets are less effective in defeating radar and thermal sensors. Heavier, more durable "mobile camouflage systems", essentially conformal
The British Army's Special Air Service used pink as the primary colour on its desert-camouflaged Land Rover Series IIA patrol vehicles, nicknamed ''Pink Panthers''; the colour had been observed to be indistinguishable from sand at a distance.
Nets can be effective at defeating visual observation. Traditional camouflage nets use a textile 'garnish' to generate an apparent texture with a depth of shadow created beneath it, and the effect can be reinforced with pieces of vegetation. Modern nets tend to be made of a continuous woven material, which is easier to deploy over a vehicle and lack the "windows" between patches of garnish of traditional nets. Some nets can remain in place while vehicles move. Simple nets are less effective in defeating radar and thermal sensors. Heavier, more durable "mobile camouflage systems", essentially conformal
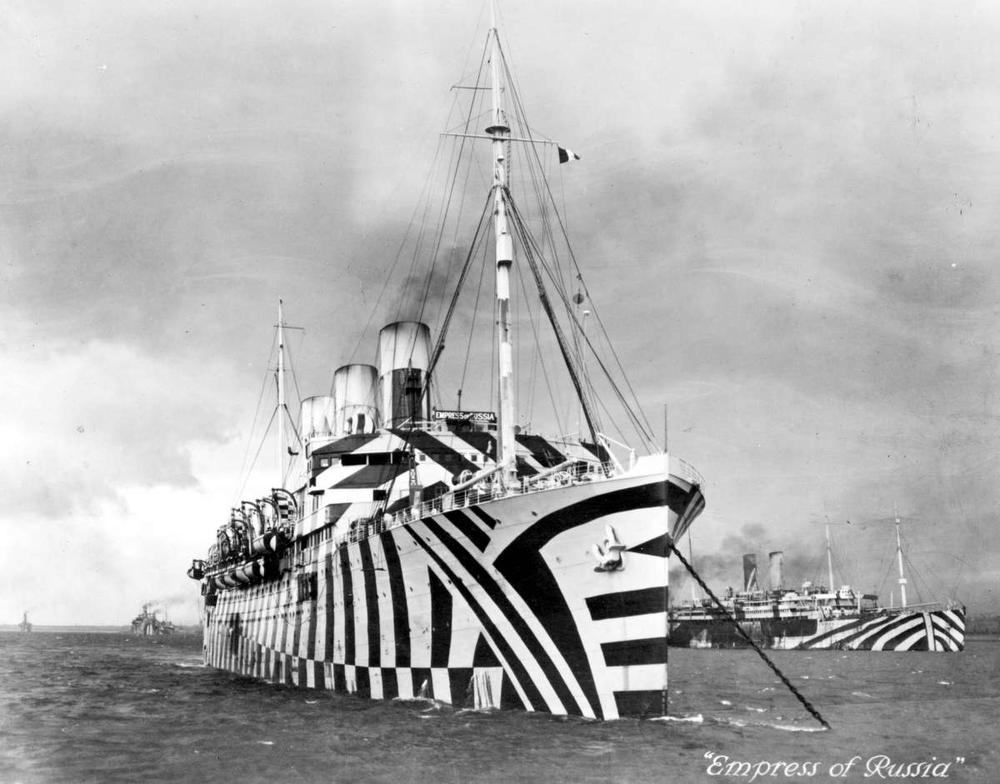 Until the 20th century, naval weapons had a short range, so camouflage was unimportant for ships, and for the men on board them. Paint schemes were selected on the basis of ease of maintenance or aesthetics, typically buff upperworks (with polished brass fittings) and white or black hulls. Around the start of the 20th century, the increasing range of naval engagements, as demonstrated by the Battle of Tsushima, prompted the introduction of the first camouflage, in the form of some solid shade of gray overall, in the hope that ships would fade into the mist.
Until the 20th century, naval weapons had a short range, so camouflage was unimportant for ships, and for the men on board them. Paint schemes were selected on the basis of ease of maintenance or aesthetics, typically buff upperworks (with polished brass fittings) and white or black hulls. Around the start of the 20th century, the increasing range of naval engagements, as demonstrated by the Battle of Tsushima, prompted the introduction of the first camouflage, in the form of some solid shade of gray overall, in the hope that ships would fade into the mist.
 First and Second World War dazzle camouflage, pioneered by English artist Norman Wilkinson, was used not to make ships disappear, but to make them seem smaller or faster, to encourage misidentification by an enemy, and to make the ships harder to hit. In the Second World War, the
First and Second World War dazzle camouflage, pioneered by English artist Norman Wilkinson, was used not to make ships disappear, but to make them seem smaller or faster, to encourage misidentification by an enemy, and to make the ships harder to hit. In the Second World War, the
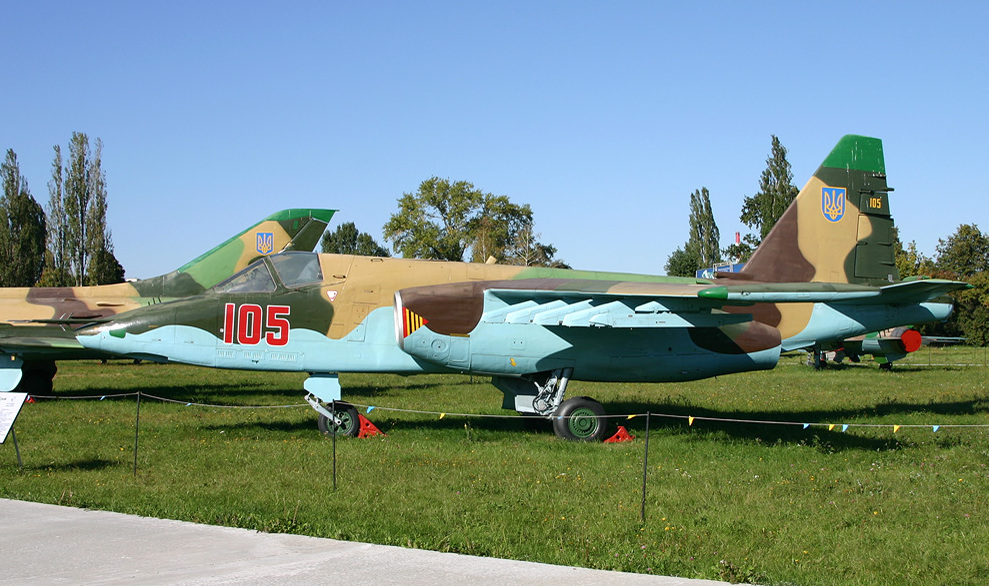 Aircraft camouflage faces the challenge that an aircraft's background varies widely, according to whether the observer is above or below the aircraft, and with the background, e.g. farmland or desert. Aircraft camouflage schemes have often consisted of a light colour underneath and darker colours above.
Other camouflage schemes acknowledge that aircraft may be seen at any angle and against any background while in combat, so aircraft are painted all over with a disruptive pattern or a neutral colour such as gray.
Aircraft camouflage faces the challenge that an aircraft's background varies widely, according to whether the observer is above or below the aircraft, and with the background, e.g. farmland or desert. Aircraft camouflage schemes have often consisted of a light colour underneath and darker colours above.
Other camouflage schemes acknowledge that aircraft may be seen at any angle and against any background while in combat, so aircraft are painted all over with a disruptive pattern or a neutral colour such as gray.
 Second World War maritime patrol aircraft such as the
Second World War maritime patrol aircraft such as the
 While many artists helped to develop camouflage during and since
While many artists helped to develop camouflage during and since
 In the US in the 1960s, military clothing became increasingly common (mostly olive drab rather than patterned camouflage); it was often found worn by anti-war protestors, initially within groups such as
In the US in the 1960s, military clothing became increasingly common (mostly olive drab rather than patterned camouflage); it was often found worn by anti-war protestors, initially within groups such as
"Abbott Thayer's Camouflage Demonstrations: Countershading, Disruption and Background Picturing"
Shipcamouflage.com
* ttp://college.hmco.com/history/readerscomp/mil/html/ml_008100_camouflage.htm Guy Hartcup – Camouflage: A History of Concealment and Deception in War (1980)
WWII War Department Field Manual FM 5-20B: Camouflage of Vehicles (1944)
Patterns compared
Camouflage paint colours
* Cécile Coutin
Camouflage
in
{{DEFAULTSORT:Military Camouflage Camouflage patterns
'' mazari palm. The example was followed by other British units during the
mutiny of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the for ...
, dying their white drill uniforms to inconspicuous tones with mud, tea, coffee or coloured inks. The resulting hue varied from dark or slate grey
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed o ...
through light brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
to off-white, or sometimes even lavender
''Lavandula'' (common name lavender) is a genus of 47 known species of flowering plants in the mint family, Lamiaceae. It is native to the Old World and is found in Cape Verde and the Canary Islands, and from Europe across to northern and easte ...
. This improvised measure gradually became widespread among the troops stationed in India and North-West Frontier, and sometimes among the troops campaigning on the African continent.
Rifle fire
 While long range rifles became the standard weapon in the 1830s, armies were slow to adapt their tactics and uniforms, perhaps as a result of mainly fighting colonial wars against less well armed opponents. Not until the
While long range rifles became the standard weapon in the 1830s, armies were slow to adapt their tactics and uniforms, perhaps as a result of mainly fighting colonial wars against less well armed opponents. Not until the First Boer War
The First Boer War ( af, Eerste Vryheidsoorlog, literally "First Freedom War"), 1880–1881, also known as the First Anglo–Boer War, the Transvaal War or the Transvaal Rebellion, was fought from 16 December 1880 until 23 March 1881 betwee ...
of 1880/81 did a major European power meet an opponent well equipped with and well versed in the use of modern long range repeating firearms, forcing an immediate change in tactics and uniforms. Khaki-coloured uniform became standard service dress for both British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and British Indian Army troops stationed in British India in 1885, and in 1896 khaki drill uniform was adopted by British Army for the service outside of Europe in general, but not until the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
, in 1902, did the entire British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
standardise on khaki (officially known as "drab") for Service Dress
Service dress uniform is the informal type of uniform used by military, police, fire and other public uniformed services for everyday office, barracks and non-field duty purposes and sometimes for ceremonial occasions. It frequently consists of ...
.
The US military
The United States Armed Forces are the Military, military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six Military branch, service branches: the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States N ...
, who had blue-jacketed rifle units in the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
, were quick to follow the British, going khaki in the same year. Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
followed, partially, in 1908. The Italian Army
"The safeguard of the republic shall be the supreme law"
, colors =
, colors_labels =
, march = ''Parata d'Eroi'' ("Heroes's parade") by Francesco Pellegrino, ''4 Maggio'' (May 4) ...
used ''grigio-verde'' ("grey-green") in the Alps from 1906 and across the army from 1909. The Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
adopted ''feldgrau
''Feldgrau'' (English: field-grey) is a grayish green color. It was the official basic color of military uniforms of the German armed forces from the early 20th century until 1945 (West Germany) or 1989 (East Germany). Armed forces of other co ...
'' ("field grey") in 1910. By the outbreak of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in 1914, France was the only major power to still field soldiers dressed in traditional conspicuous uniforms.
The First World War

 The
The First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
was the first full scale industrial conflict fought with modern firearms. The first attempt at disruptive camouflaged garment for the French army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Force ...
was proposed in 1914 by the painter Louis Guingot, but was refused by the army, which nevertheless kept a sample of the clothing. In collaboration with a Russian chemist friend, Guingot had developed a process of painting on weather-resistant fabric before the war and had registered a patent for it. But the casualty rate on the Western Front forced the French to finally relinquish their blue coats and red trousers, adopting a grayish "horizon blue" uniform.
The use of rapid firing machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) ar ...
s and long range breech loading artillery quickly led to camouflaging of vehicles and positions. Artillery pieces were soon painted in contrasting bold colours to obscure their outlines. Another early trend was building observation trees, made of steel with bark camouflage. Such trees became popular with the British and French armies in 1916. The observation tree was invented by French painter Lucien-Victor Guirand de Scévola, who led the French army's camouflage unit, the first of its kind in any army. He also invented painted canvas netting to hide machine gun positions, and this was quickly taken up for hiding equipment and gun positions from 1917, 7 million square yards being used by the end of the war.
The First World War also saw the birth of aerial warfare, and with it the need not only to conceal positions and vehicles from being spotted from the air, but also the need to camouflage the aircraft themselves. In 1917, Germany started using a lozenge camouflage covering Central Powers aircraft, possibly the earliest printed camouflage. A similarly disruptive splinter pattern in earth tones, ''Buntfarbenanstrich 1918'', was introduced for tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engi ...
s in 1918, and was also used on the Stahlhelm (steel helmet), becoming the first use of a standardized camouflage pattern for soldiers.
''Camoufleurs''
 In 1909 an American artist and amateur
In 1909 an American artist and amateur zoologist
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and d ...
, Abbott Thayer
Abbott Handerson Thayer (August 12, 1849May 29, 1921) was an American artist, naturalist and teacher. As a painter of portraits, figures, animals and landscapes, he enjoyed a certain prominence during his lifetime, and his paintings are represen ...
published a book, '' Concealing-Coloration in the Animal Kingdom'', which was widely read by military leaders, although his advocacy of countershading was unsuccessful, despite his patent for countershading submarines and surface ships.
The earliest camouflage artists were members of the Post- Impressionist and Fauve schools of France. Contemporary artistic movements such as cubism, vorticism
Vorticism was a London-based modernist art movement formed in 1914 by the writer and artist Wyndham Lewis. The movement was partially inspired by Cubism and was introduced to the public by means of the publication of the Vorticist manifesto in ...
and impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passage ...
also influenced the development of camouflage as they dealt with disrupting outlines, abstraction and colour theory.The French established a ''Section de Camouflage'' (Camouflage Department) at Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme department in the region of Hauts-de-France. In 2021, the population of ...
in 1915, headed by Lucien-Victor Guirand de Scévola. His ''camoufleurs'' included the artists Jacques Villon
Jacques Villon (July 31, 1875 – June 9, 1963), also known as Gaston Duchamp, was a French Cubist and Abstract art, abstract painter and printmaker.
Early life
Born Émile Méry Frédéric Gaston Duchamp in Damville, Eure, Damville, Eure, ...
, André Dunoyer de Segonzac
André Dunoyer de Segonzac (6 July 1884 – 17 September 1974) was a French painter and graphic artist.
Biography
Segonzac was born in Boussy-Saint-Antoine and spent his childhood there and in Paris. His parents wanted him to attend the military ...
, Charles Camoin and André Mare
Charles André Mare (1885–1932), or André-Charles Mare, was a French painter and textile designer, and co-founder of the Company of French Art (''la Compagnie des Arts Français'') in 1919. He was a designer of colorful textiles, and was one o ...
.
Camouflage schemes of the First World War and Interwar periods that employed dazzle patterns were often described as "cubist" by commentators, and Picasso claimed with typical hyperbole "Yes, it is we who made it, that is cubism". Most of the artists employed as ''camoufleurs'' were traditional representative painters, not cubists, but de Scévola claimed "In order to deform totally the aspect of the object, I had to employ the means that cubists use to represent it."
Other countries soon saw the advantage of camouflage, and established their own units of artists, designers and architects. The British established a Camouflage Section in late 1916 at Wimereux, and the U.S. followed suit with the New York Camouflage Society in April 1917, the official Company A of 40th Engineers in January 1918 and the Women's Reserve Camouflage Corps. The Italians set up the ''Laboratorio di mascheramento'' in 1917. By 1918 de Scévola was in command of camouflage workshops with over 9,000 workers, not counting the ''camoufleurs'' working at the front itself. Norman Wilkinson who first proposed dazzle camouflage to the British military employed 5 male designers and 11 women artists, who by the end of the war had painted more than 2,300 vessels. French women were employed behind the lines of both the British and American armies, sewing netting to disguise equipment and designing apparel for soldiers to wear.
From the Second World War
 Printed camouflage for shelter halves was introduced for the Italian and German armies in the interwar period, the "splotchy" M1929 Telo mimetico in Italy and the angular Splittermuster 31 in Germany. During the War, both patterns were used for paratrooper uniforms for their respective countries. The British soon followed suit with a brush-stroke type pattern for their paratroopers' Denison smock, and the Soviets introduced an "amoeba" pattern overgarment for their snipers.
Printed camouflage for shelter halves was introduced for the Italian and German armies in the interwar period, the "splotchy" M1929 Telo mimetico in Italy and the angular Splittermuster 31 in Germany. During the War, both patterns were used for paratrooper uniforms for their respective countries. The British soon followed suit with a brush-stroke type pattern for their paratroopers' Denison smock, and the Soviets introduced an "amoeba" pattern overgarment for their snipers.
Hugh Cott
Hugh Bamford Cott (6 July 1900 – 18 April 1987) was a British zoologist, an authority on both natural and military camouflage, and a scientific illustrator and photographer. Many of his field studies took place in Africa, where he was espec ...
's 1940 book '' Adaptive Coloration in Animals'' systematically covered the different forms of camouflage and mimicry by which animals protect themselves, and explicitly drew comparisons throughout with military camouflage:
Both British and Soviet aircraft were given wave-type camouflage paintwork for their upper surfaces throughout the war, while American ones remained simple two-colour schemes (different upper and under sides) or even dispensed with camouflage altogether. Italian and some Japanese aircraft wore sprayed-on spotted patterns. German aircraft mostly used an angular splint-pattern camouflage, but Germany experimented with different schemes, particularly in the later stages of the war. They also experimented with various spray-on camouflage patterns for tanks and other vehicles, while Allied vehicles remained largely uni-coloured. As they had volunteered in the first World War, women sewed camouflage netting, organizing formalized groups for the work in Australia, Britain, New Zealand and the United States who took part as camoufleurs during the second war.
 The British
The British Middle East Command Camouflage Directorate
The British Middle East Command Camouflage Directorate (also known as the Camouflage Unit or Camouflage Branch) organised major deception operations for Middle East Command in the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. It provided camo ...
, consisting mainly of artists recruited into the Royal Engineers, developed the use of camouflage for large-scale military deception. Operations combined the disguise of actual installations, vehicles and stores with the simultaneous display of dummies, whether to draw fire or to give a false idea of the strength of forces or likely attack directions. In Operation Bertram
Operation Bertram was a Second World War deception operation practised by the Allied forces in Egypt led by Bernard Montgomery, in the months before the Second Battle of El Alamein in 1942. Bertram was devised by Dudley Clarke to deceive Erwin ...
for the decisive battle at El Alamein, a whole dummy armoured division was constructed, while real tanks were disguised as soft-skinned transport using "Sunshield" covers. The capabilities so developed were put to use not only in the western desert, but also in Europe as in the Operation Bodyguard deception for the Invasion of Normandy, and in the Pacific campaign, as in the Battle of Goodenough Island
The Battle of Goodenough Island (22–27 October 1942), also known as Operation Drake, was a battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II. The Allies landed on Goodenough Island, Papua, and clashed with a Japanese ''Kaigun Rikusentai' ...
.
The introduction of strategic bombing
Strategic bombing is a military strategy used in total war with the goal of defeating the enemy by destroying its morale, its economic ability to produce and transport materiel to the theatres of military operations, or both. It is a systematica ...
led to efforts to camouflage airfields and strategic production centres. This form of positional camouflage could be quite elaborate, and even include false houses and cars. With the threat from nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s in the post-war era such elaborate camouflage was no longer seen as useful, as a direct hit would not be necessary with strategic nuclear weapon
A strategic nuclear weapon (SNW) refers to a nuclear weapon that is designed to be used on targets often in settled territory far from the battlefield as part of a strategic plan, such as military bases, military command centers, arms industries, ...
s to destroy infrastructure. The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
's doctrine
Doctrine (from la, doctrina, meaning "teaching, instruction") is a codification of beliefs or a body of teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the essence of teachings in a given branch of knowledge or in a belief syste ...
of military deception defines the need for surprise through means including camouflage, based on experiences such as the Battle of Kursk
The Battle of Kursk was a major World War II Eastern Front engagement between the forces of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union near Kursk in the southwestern USSR during late summer 1943; it ultimately became the largest tank battle in history ...
where camouflage helped the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
to overwhelm a powerful enemy.
Application
Uniforms
 The role of uniform is not only to hide each soldier, but also to identify friend from foe. Issue of the " Frogskin" uniforms to US troops in Europe during the Second World War was halted as it was too often mistaken for the disruptively patterned German uniform worn by the Waffen-SS. Camouflage uniforms need to be made and distributed to a large number of soldiers. The design of camouflage uniforms therefore involves a tradeoff between camouflaging effect, recognizability, cost, and manufacturability.
Armies facing service in different theatres may need several different camouflage uniforms. Separate issues of temperate/jungle and desert camouflage uniforms are common. Patterns can to some extent be adapted to different terrains by adding means of fastening pieces of vegetation to the uniform. Helmets often have netting covers; some jackets have small loops for the same purpose. Being able to find appropriate camouflage vegetation or in other ways modify the issued battle uniform to suit the local terrain is an important skill for infantry soldiers.
Countries in boreal climates often need snow camouflage, either by having reversible uniforms or simple overgarments.
The role of uniform is not only to hide each soldier, but also to identify friend from foe. Issue of the " Frogskin" uniforms to US troops in Europe during the Second World War was halted as it was too often mistaken for the disruptively patterned German uniform worn by the Waffen-SS. Camouflage uniforms need to be made and distributed to a large number of soldiers. The design of camouflage uniforms therefore involves a tradeoff between camouflaging effect, recognizability, cost, and manufacturability.
Armies facing service in different theatres may need several different camouflage uniforms. Separate issues of temperate/jungle and desert camouflage uniforms are common. Patterns can to some extent be adapted to different terrains by adding means of fastening pieces of vegetation to the uniform. Helmets often have netting covers; some jackets have small loops for the same purpose. Being able to find appropriate camouflage vegetation or in other ways modify the issued battle uniform to suit the local terrain is an important skill for infantry soldiers.
Countries in boreal climates often need snow camouflage, either by having reversible uniforms or simple overgarments.
Land vehicles
 The purpose of vehicle and equipment camouflage differs from personal camouflage in that the primary threat is
The purpose of vehicle and equipment camouflage differs from personal camouflage in that the primary threat is aerial reconnaissance
Aerial reconnaissance is reconnaissance for a military or strategic purpose that is conducted using reconnaissance aircraft. The role of reconnaissance can fulfil a variety of requirements including artillery spotting, the collection of i ...
. The goal is to disrupt the characteristic shape of the vehicle, to reduce shine, and to make the vehicle difficult to identify even if it is spotted.
Paint is the least effective measure, but forms a basis for other techniques. Military vehicles often become so dirty that pattern-painted camouflage is not visible, and although matt colours reduce shine, a wet vehicle can still be shiny, especially when viewed from above. Patterns are designed to make it more difficult to interpret shadows and shapes. The British Army adopted a disruptive scheme for vehicles operating in the stony desert of the North African Campaign and Greece, retrospectively known as the Caunter scheme. It used up to six colours applied with straight lines.
 The British Army's Special Air Service used pink as the primary colour on its desert-camouflaged Land Rover Series IIA patrol vehicles, nicknamed ''Pink Panthers''; the colour had been observed to be indistinguishable from sand at a distance.
Nets can be effective at defeating visual observation. Traditional camouflage nets use a textile 'garnish' to generate an apparent texture with a depth of shadow created beneath it, and the effect can be reinforced with pieces of vegetation. Modern nets tend to be made of a continuous woven material, which is easier to deploy over a vehicle and lack the "windows" between patches of garnish of traditional nets. Some nets can remain in place while vehicles move. Simple nets are less effective in defeating radar and thermal sensors. Heavier, more durable "mobile camouflage systems", essentially conformal
The British Army's Special Air Service used pink as the primary colour on its desert-camouflaged Land Rover Series IIA patrol vehicles, nicknamed ''Pink Panthers''; the colour had been observed to be indistinguishable from sand at a distance.
Nets can be effective at defeating visual observation. Traditional camouflage nets use a textile 'garnish' to generate an apparent texture with a depth of shadow created beneath it, and the effect can be reinforced with pieces of vegetation. Modern nets tend to be made of a continuous woven material, which is easier to deploy over a vehicle and lack the "windows" between patches of garnish of traditional nets. Some nets can remain in place while vehicles move. Simple nets are less effective in defeating radar and thermal sensors. Heavier, more durable "mobile camouflage systems", essentially conformal duvet
A duvet (, ; ), usually called a comforter or (''down-filled'') quilt in US English, and a doona in Australian English, is a type of bedding consisting of a soft flat bag filled with either down, feathers, wool, cotton, silk, or a synthetic a ...
s with thermal and radar properties, provide a degree of concealment without the delay caused by having to spread nets around a vehicle.
Active camouflage
Active camouflage or adaptive camouflage is camouflage that adapts, often rapidly, to the surroundings of an object such as an animal or military vehicle. In theory, active camouflage could provide perfect concealment from visual detection.
Activ ...
for vehicles, using heated or cooled Peltier plates to match the infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
background, has been prototyped in industry but has not yet been put into production.
Ships
 Until the 20th century, naval weapons had a short range, so camouflage was unimportant for ships, and for the men on board them. Paint schemes were selected on the basis of ease of maintenance or aesthetics, typically buff upperworks (with polished brass fittings) and white or black hulls. Around the start of the 20th century, the increasing range of naval engagements, as demonstrated by the Battle of Tsushima, prompted the introduction of the first camouflage, in the form of some solid shade of gray overall, in the hope that ships would fade into the mist.
Until the 20th century, naval weapons had a short range, so camouflage was unimportant for ships, and for the men on board them. Paint schemes were selected on the basis of ease of maintenance or aesthetics, typically buff upperworks (with polished brass fittings) and white or black hulls. Around the start of the 20th century, the increasing range of naval engagements, as demonstrated by the Battle of Tsushima, prompted the introduction of the first camouflage, in the form of some solid shade of gray overall, in the hope that ships would fade into the mist.
 First and Second World War dazzle camouflage, pioneered by English artist Norman Wilkinson, was used not to make ships disappear, but to make them seem smaller or faster, to encourage misidentification by an enemy, and to make the ships harder to hit. In the Second World War, the
First and Second World War dazzle camouflage, pioneered by English artist Norman Wilkinson, was used not to make ships disappear, but to make them seem smaller or faster, to encourage misidentification by an enemy, and to make the ships harder to hit. In the Second World War, the Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack submar ...
trialled a form of active camouflage
Active camouflage or adaptive camouflage is camouflage that adapts, often rapidly, to the surroundings of an object such as an animal or military vehicle. In theory, active camouflage could provide perfect concealment from visual detection.
Activ ...
, counter-illumination, using diffused lighting to prevent ships from appearing as dark shapes against a brighter sky during the night. It reduced visibility by up to 70%, but was unreliable and never went into production.
After the Second World War, the use of radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
made camouflage generally less effective. However, camouflage may have helped to protect US warships from Vietnamese shore batteries using optical rangefinders.
Coastal patrol boats such as those of the Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
, Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
and Indonesian navies continue to use terrestrial style disruptively patterned camouflage.
Aircraft
 Aircraft camouflage faces the challenge that an aircraft's background varies widely, according to whether the observer is above or below the aircraft, and with the background, e.g. farmland or desert. Aircraft camouflage schemes have often consisted of a light colour underneath and darker colours above.
Other camouflage schemes acknowledge that aircraft may be seen at any angle and against any background while in combat, so aircraft are painted all over with a disruptive pattern or a neutral colour such as gray.
Aircraft camouflage faces the challenge that an aircraft's background varies widely, according to whether the observer is above or below the aircraft, and with the background, e.g. farmland or desert. Aircraft camouflage schemes have often consisted of a light colour underneath and darker colours above.
Other camouflage schemes acknowledge that aircraft may be seen at any angle and against any background while in combat, so aircraft are painted all over with a disruptive pattern or a neutral colour such as gray.
 Second World War maritime patrol aircraft such as the
Second World War maritime patrol aircraft such as the Consolidated PBY Catalina
The Consolidated PBY Catalina is a flying boat and amphibious aircraft that was produced in the 1930s and 1940s. In Canadian service it was known as the Canso. It was one of the most widely used seaplanes of World War II. Catalinas served wi ...
flying boat were painted white, as aircraft generally appear dark against the sky (including at night), and hence are least visible when painted in as light a colour as possible. The problem of appearing dark against the sky was explored in the U.S. Navy's Yehudi lights
Yehudi lights are lamps of automatically controlled brightness placed on the front and leading edges of an aircraft to raise the aircraft's luminance to the average brightness of the sky, a form of active camouflage using counter-illumination. T ...
project in 1943, using counter-illumination to raise the average brightness of a plane, when seen head-on, from a dark shape to the same as the sky. The experiments worked, enabling an aircraft to approach to within before being seen, whereas aircraft without the lights were noticed away.
The higher speeds of modern aircraft, and the reliance on radar and missiles in air combat have reduced the value of visual camouflage, while increasing the value of electronic " stealth" measures. Modern paint is designed to absorb electromagnetic radiation used by radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
, reducing the signature of the aircraft, and to limit the emission of infrared light used by heat seeking missiles to detect their target. Further advances in aircraft camouflage are being investigated in the field of active camouflage
Active camouflage or adaptive camouflage is camouflage that adapts, often rapidly, to the surroundings of an object such as an animal or military vehicle. In theory, active camouflage could provide perfect concealment from visual detection.
Activ ...
.
In fashion and art
Fashion and the "Dazzle Ball"
The transfer of camouflage patterns from battle to exclusively civilian uses is not recent. Dazzle camouflage inspired a trend of dazzlesque patterns used on clothing in England, starting in 1919 with the "Dazzle Ball" held by Chelsea Arts Club. Those attending wore dazzle-patterned black and white clothing, influencing twentieth-century fashion and art via postcards (see illustration) and magazine articles. TheIllustrated London News
''The Illustrated London News'' appeared first on Saturday 14 May 1842, as the world's first illustrated weekly news magazine. Founded by Herbert Ingram, it appeared weekly until 1971, then less frequently thereafter, and ceased publication i ...
announced
Camouflage in art
 While many artists helped to develop camouflage during and since
While many artists helped to develop camouflage during and since World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the disparate sympathies of the two cultures restrained the use of "militaristic" forms other than in the work of war artists. Since the 1960s, several artists have exploited the symbolism of camouflage. For example, Andy Warhol
Andy Warhol (; born Andrew Warhola Jr.; August 6, 1928 – February 22, 1987) was an American visual artist, film director, and producer who was a leading figure in the Art movement, visual art movement known as pop art. His works explore th ...
's 1986 camouflage series was his last major work, including Camouflage Self-Portrait. Alain Jacquet created many camouflage works from 1961 to the 1970s. Ian Hamilton Finlay
Ian Hamilton Finlay, CBE (28 October 1925 – 27 March 2006) was a Scottish poet, writer, artist and gardener.
Life
Finlay was born in Nassau, Bahamas, to James Hamilton Finlay and his wife, Annie Pettigrew, both of Scots descent.
He was e ...
's 1973 ''Arcadia'' was a screenprint of a leafily-camouflaged tank, "an ironic parallel between this idea of a natural paradise and the camouflage patterns on a tank", as the Tate Collection describes it. Veruschka
Vera Lehndorff (German: Vera Anna Gottliebe Gräfin von Lehndorff; born 14 May 1939), known professionally as Veruschka, is a German aristocrat, model, actress and artist. She is considered the "first German supermodel.“
Early life
von Lehn ...
, the pseudonym of Vera von Lehndorff and Holger Trülzsch, created "Nature, Signs & Animals" and "Mimicry-Dress-Art" in 1970–1973. Thomas Hirschhorn
Thomas Hirschhorn (born 16 May 1957) is a Swiss artist. He lives and works in Paris.Randy Kennedy (June 27, 2013)Bringing Art and Change to Bronx''New York Times''.
Life and works
In the 1980s, Thomas Hirschhorn came to Paris with the will to ...
made ''Utopia : One World, One War, One Army, One Dress'' in 2005.
War protesters and fashionistas
 In the US in the 1960s, military clothing became increasingly common (mostly olive drab rather than patterned camouflage); it was often found worn by anti-war protestors, initially within groups such as
In the US in the 1960s, military clothing became increasingly common (mostly olive drab rather than patterned camouflage); it was often found worn by anti-war protestors, initially within groups such as Vietnam Veterans Against the War
Vietnam Veterans Against the War (VVAW) is an American tax-exempt non-profit organization and corporation founded in 1967 to oppose the United States policy and participation in the Vietnam War. VVAW says it is a national veterans' organization ...
but then increasingly widely as a symbol of political protest.
Fashion
Fashion is a form of self-expression and autonomy at a particular period and place and in a specific context, of clothing, footwear, lifestyle, accessories, makeup, hairstyle, and body posture. The term implies a look defined by the fashion i ...
often uses camouflage as inspiration – attracted by the striking designs, the "patterned disorder" of camouflage, its symbolism (to be celebrated or subverted), and its versatility. Early designers include Marimekko (1960s), Jean-Charles de Castelbajac (1975–), Stephen Sprouse
Stephen Sprouse (September 12, 1953 – March 4, 2004) was an American fashion designer and artist credited with pioneering the 1980s mix of "uptown sophistication in clothing with a downtown punk and pop sensibility".
Career
Stephen Sprouse's in ...
(using Warhol prints, 1987–1988), and Franco Moschino
Franco Moschino (27 February 1950 – 18 September 1994) was an Italian fashion designer best known as the founder of the Italian fashion house Moschino.
Early years
He was born in Abbiategrasso, Lombardy, located c. 22 km from Milan. ...
(1986), but it was not until the 1990s that camouflage became a significant and widespread facet of dress from streetwear to high-fashion labels – especially the use of "faux-camouflage". Producers using camouflage in the 1990s and beyond include: John Galliano
John Charles Galliano (born 28 November 1960) is a British fashion designer from Gibraltar. He was the creative director of his eponymous label John Galliano and French fashion houses Givenchy and Dior. Since 2014, Galliano has been the crea ...
for Christian Dior, Marc Jacobs for Louis Vuitton
Louis Vuitton Malletier, commonly known as Louis Vuitton (, ), is a French high-end luxury fashion house and company founded in 1854 by Louis Vuitton. The label's LV monogram appears on most of its products, ranging from luxury bags and leather ...
, Comme des Garçons
Comme des Garçons (also known as CDG) is a Japanese fashion label based in Paris that was created and led by Rei Kawakubo. Its French flagship store is located in Paris. This label owns a world-wide store chain featuring various lines of pro ...
, Chanel, Tommy Hilfiger
Thomas Jacob Hilfiger ( /hɪlˈfɪgər/; born March 24, 1951) is an American fashion designer and the founder of Tommy Hilfiger Corporation.
After starting his career by co-founding a chain of jeans/fashion stores called People's Place in upst ...
, Dolce & Gabbana
Dolce & Gabbana (), also known by initials D&G, is an Italian luxury fashion house founded in 1985 in Legnano by Italian designers Domenico Dolce and Stefano Gabbana. The house specializes in ready-to-wear, handbags, accessories, and cosmet ...
, Issey Miyake
was a Japanese fashion designer. He was known for his technology-driven clothing designs, exhibitions and fragrances, such as '' L'eau d'Issey'', which became his best-known product.
Life and career
Miyake was born on 22 April 1938 in Hiroshi ...
, Armani, Yves Saint-Laurent.
Companies closely associated with camouflage patterns include 6876, A Bathing Ape, Stone Island
Stone Island is an Italian luxury men's apparel and accessories brand. It was established in 1982 in Ravarino by Massimo Osti. In December 2020, Stone Island was acquired by the Italian fashion house Moncler.
History
Designer Massimo Osti fo ...
, Stüssy
Stüssy ( ) is an American privately held fashion house founded in the early 1980s by Shawn Stussy. It benefited from the surfwear trend originating in Orange County, California, but was later adopted by the skateboard and hip hop scenes.
Hist ...
, Maharishi, mhi, Zoo York, Addict, and Girbaud, using and overprinting genuine military surplus fabric; others use camouflage patterns in bright colours such as pink or purple. Some, such as Emma Lundgren and Stüssy, have created their own designs or integrated camouflage patterns with other symbols.
Restrictions
Some countries such asBarbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
, Aruba, and other Caribbean nations have laws prohibiting camouflage clothing from being worn by non-military personnel, including tourists and children. Civilian possession of camouflage is still banned in Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
.
See also
* ''Camouflage'' (1944 film), World War II camouflage training film produced by the US Army Air Forces *List of military clothing camouflage patterns
This is a list of military clothing camouflage patterns used for battledress. Military camouflage is the use of camouflage by a military force to protect personnel and equipment from observation by enemy forces. Textile patterns for uniforms hav ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
"Abbott Thayer's Camouflage Demonstrations: Countershading, Disruption and Background Picturing"
Shipcamouflage.com
* ttp://college.hmco.com/history/readerscomp/mil/html/ml_008100_camouflage.htm Guy Hartcup – Camouflage: A History of Concealment and Deception in War (1980)
WWII War Department Field Manual FM 5-20B: Camouflage of Vehicles (1944)
Patterns compared
Camouflage paint colours
* Cécile Coutin
Camouflage
in
{{DEFAULTSORT:Military Camouflage Camouflage patterns