Metal Mining In Wales on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mining in Wales provided a significant source of income to the
 There had been small-scale mining in Wales in the pre-Roman British Iron Age, but it would be undertaken on an industrial scale under the
There had been small-scale mining in Wales in the pre-Roman British Iron Age, but it would be undertaken on an industrial scale under the
 During the first half of the nineteenth century mining was often at the centre of working-class discontent in Wales, and a number of uprisings such as the
During the first half of the nineteenth century mining was often at the centre of working-class discontent in Wales, and a number of uprisings such as the
The raff will never torri when I go up and down
It's bara when I'm hungry
And cwrw when I'm dry
It's gwely when I'm tired
And nefoedd when I die
The complete English translation is the following. I am a little collier and working underground
The rope will never break when I go up and down
It's bread when I'm hungry
And beer when I'm dry
It's bed when I'm tired
And heaven when I die

(closed) *
Welsh Coal Mines
- all the Welsh pits and their brief histories
BBC Wales Coal House website
42 pages of mining photos compiled by John Cornwell and held on Gathering the Jewels
*
AditNow
– Photographic database of mines
Welsh Mines Society
– Society with a focus on the research, recording and exploration of the metal mines of Wales {{DEFAULTSORT:Mining In Wales Economy of Wales
economy of Wales
The economy of Wales ( Welsh: ''Economi Cymru'') refers to the production and consumption of goods and services and the supply of money in Wales.
The percentage of all individuals, living in relative income poverty in Wales in 2016–17 was 23 ...
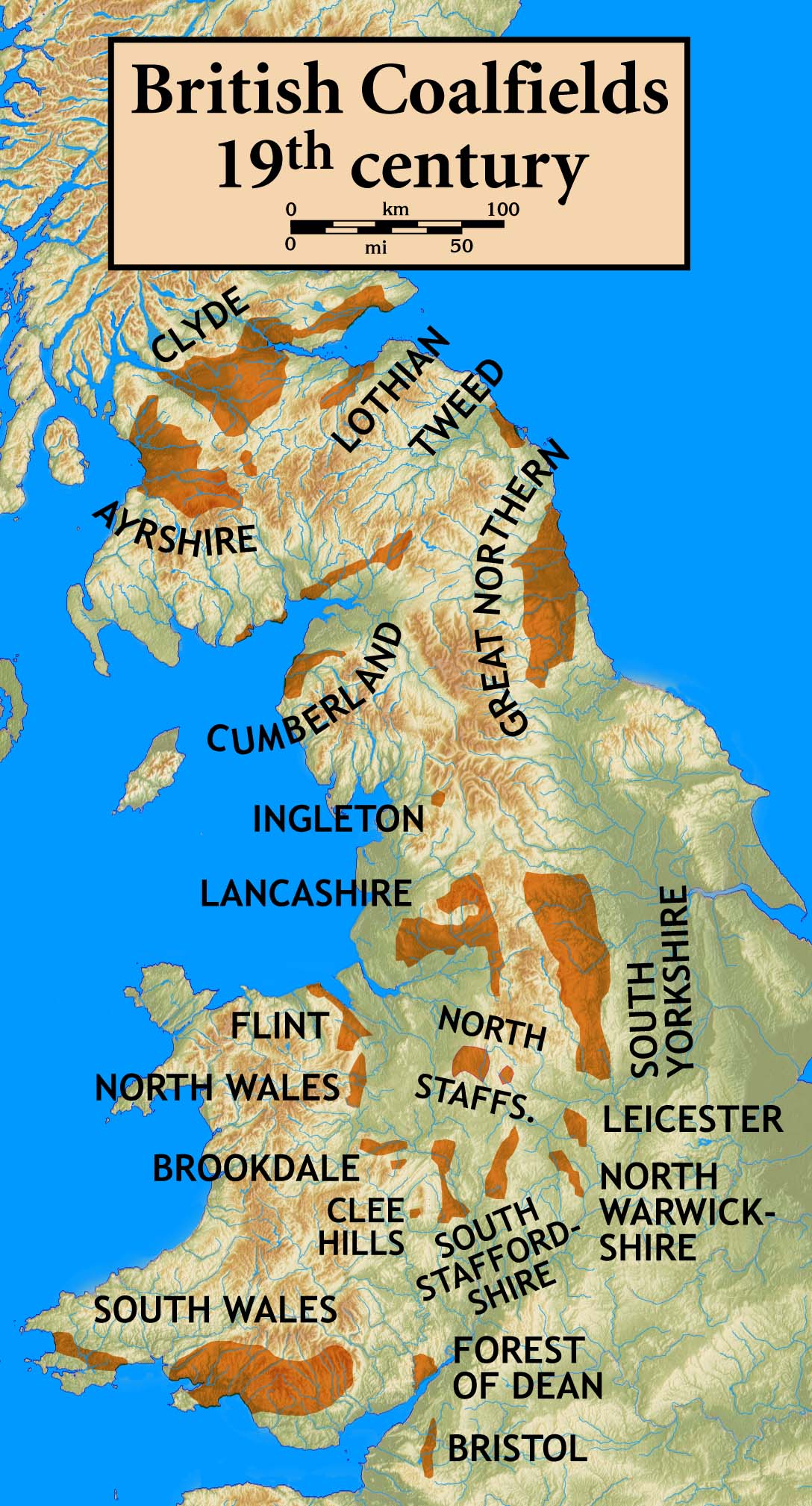
throughout the nineteenth century and early twentieth century. It was key to the Industrial Revolution.
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
was famous for its coal mining, in the Rhondda Valley
Rhondda , or the Rhondda Valley ( cy, Cwm Rhondda ), is a former coalmining area in South Wales, historically in the county of Glamorgan. It takes its name from the River Rhondda, and embraces two valleys – the larger Rhondda Fawr valley ...
, the South Wales Valleys and throughout the South Wales coalfield
The South Wales Coalfield ( cy, Maes glo De Cymru) extends across Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Blaenau Gwent and Torfaen. It is rich in coal deposits, espe ...
and by 1913 Barry Barry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Barry (name), including lists of people with the given name, nickname or surname, as well as fictional characters with the given name
* Dancing Barry, stage name of Barry Richards (born c. 19 ...
had become the largest coal exporting port in the world, with Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingd ...
as second, as coal was transported down by rail. Northeast Wales also had its own coalfield and Tower Colliery
Tower Colliery ( Welsh: Glofa'r Tŵr) was the oldest continuously working deep-coal mine in the United Kingdom, and possibly the world, until its closure in 2008. It was the last mine of its kind to remain in the South Wales Valleys. It was loca ...
(closed January 2008) near Hirwaun is regarded by many as the oldest open coal mine and one of the largest in the world. Wales has also had a significant history of mining for slate, gold and various metal ores.
History
 There had been small-scale mining in Wales in the pre-Roman British Iron Age, but it would be undertaken on an industrial scale under the
There had been small-scale mining in Wales in the pre-Roman British Iron Age, but it would be undertaken on an industrial scale under the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
, who completed their conquest of Wales in AD 78. Substantial quantities of gold, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, and lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
were extracted, along with lesser amounts of zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
. Mining would continue until the process was no longer practical or profitable, at which time the mine would be abandoned. The extensive excavations of the Roman operations at Dolaucothi
The Dolaucothi Gold Mines (; cy, Mwynfeydd Aur Dolaucothi) (), also known as the Ogofau Gold Mine, are ancient Roman surface and underground mines located in the valley of the River Cothi, near Pumsaint, Carmarthenshire, Wales. The gold mi ...
provide a picture of the high level of Roman technology
Roman technology is the collection of antiques, skills, methods, processes, and engineering practices which supported Roman civilization and made possible the expansion of the economy and military of ancient Rome (753 BC – 476 AD).
The Roma ...
and the expertise of Roman engineering in the ancient era.
Coal mining
 During the first half of the nineteenth century mining was often at the centre of working-class discontent in Wales, and a number of uprisings such as the
During the first half of the nineteenth century mining was often at the centre of working-class discontent in Wales, and a number of uprisings such as the Merthyr Rising
The Merthyr Rising, also referred to as the Merthyr Riots, of 1831 was the violent climax to many years of simmering unrest among the large working class population of Merthyr Tydfil in Wales and the surrounding area. The Rising marked the fi ...
in 1831 against employers were a characteristic of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in Wales, Dic Penderyn
Richard Lewis (1807/8 – 13 August 1831), known as Dic Penderyn, was a Welsh labourer and coal miner who lived in Merthyr Tydfil and was involved with the Merthyr Rising of 3 June 1831. In the course of the riot he was arrested alongside Lewis ...
became a martyr to industrial workers. The Chartist movement
Chartism was a working-class movement for political reform in the United Kingdom that erupted from 1838 to 1857 and was strongest in 1839, 1842 and 1848. It took its name from the People's Charter of 1838 and was a national protest movement, w ...
and the 1839 Newport Rising
The Newport Rising was the last large-scale armed rising in Wales, by Chartists whose demands included democracy and the right to vote with a secret ballot. On Monday 4 November 1839, approximately 4,000 Chartism, Chartist sympathisers, under ...
showed the growing concerns and awareness of the work force of their value to the nation.
There is a well-known mining song part in Welsh and part in English.
I am a little collier and gweithio underground The raff will never torri when I go up and down
It's bara when I'm hungry
And cwrw when I'm dry
It's gwely when I'm tired
And nefoedd when I die
The complete English translation is the following. I am a little collier and working underground
The rope will never break when I go up and down
It's bread when I'm hungry
And beer when I'm dry
It's bed when I'm tired
And heaven when I die

Big Pit National Coal Museum & other mining museums in Wales
Other museums preserving the memories and heritage of the coal mining industry in Wales are at : *South Wales Miners' Museum
The South Wales Miners' Museum is a museum of the coal mining industry and its workforce in the South Wales Coalfield. It is located at Cynonville within the Afan Forest Park Visitor Centre in the Afan Forest Park, near the small village of Cym ...
near Cymmer
*Cefn Coed Colliery Museum
Cefn Coed Colliery Museum is a former coal mine, now operating as a museum. It is located at Crynant near Neath in the South Wales Valleys.
Background
Coal mining in the Neath area began with the development of the port of Neath in the 16th ...
near Crynant
Crynant ( cy, Y Creunant) is a village and community in the Dulais Valley in Wales. It lies 7¾ miles north-east from the town of Neath in Neath Port Talbot, situated between the mountains of Mynydd Marchywel to the west, Hirfynydd to the east ...
*Rhondda Heritage Park
Rhondda Heritage Park, Trehafod, Rhondda, South Wales is a tourist attraction which offers an insight into the life of the coal mining community that existed in the area until the 1980s.
Visitors can experience the life of the coal miners on a g ...
near Trehafod
Trehafod is a village and community in the Rhondda Valley between Porth and Pontypridd in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales, with a population of 698 in the 2011 census.(The earlier name ''Hafod'' was altered in 1905 to avoid confu ...
Slate quarrying
There has been slate quarrying in Wales since the Roman period, when slate was used toroof
A roof ( : roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of te ...
the fort at Segontium
Segontium ( owl, Cair Segeint) is a Roman fort on the outskirts of Caernarfon in Gwynedd, North Wales. The fort, which survived until the end of the Roman occupation of Britain, was garrisoned by Roman auxiliaries from present-day Belgium and Ge ...
, now Caernarfon
Caernarfon (; ) is a royal town, community and port in Gwynedd, Wales, with a population of 9,852 (with Caeathro). It lies along the A487 road, on the eastern shore of the Menai Strait, opposite the Isle of Anglesey. The city of Bangor is ...
. The slate industry grew slowly until the early 18th century, then expanded rapidly until the late 19th century, at which time the most important slate producing areas were in northwest Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, including the Penrhyn Quarry
The Penrhyn quarry is a slate quarry located near Bethesda, North Wales. At the end of the nineteenth century it was the world's largest slate quarry; the main pit is nearly long and deep, and it was worked by nearly 3,000 quarrymen. It has ...
near Bethesda, the Dinorwic Quarry near Llanberis
(; ) is a village, community and electoral ward in Gwynedd, northwest Wales, on the southern bank of the lake and at the foot of Snowdon, the highest mountain in Wales. It is a centre for outdoor activities in Snowdonia, including walking ...
, the Nantlle Valley quarries, and Blaenau Ffestiniog, where the slate was mined rather than quarried. Penrhyn and Dinorwig were the two largest slate quarries in the world, and the Oakeley mine at Blaenau Ffestiniog was the largest slate mine in the world. Slate is mainly used for roofing, but is also produced as thicker slab for a variety of uses including flooring, worktops and headstones.
The slate industry in North Wales is on the tentative World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
list whilst Welsh slate has been designated by the International Union of Geological Sciences as a Global Heritage Stone Resource
The Global Heritage Stone Resource (GHSR) designation seeks international recognition of natural stone resources that have achieved widespread utilisation in human culture. Details of the “Global Heritage Stone Resource” proposal were first pr ...
.
Metal mining
Metal mining inWales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
affected large areas of what are now very rural parts of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
and left behind a legacy of contaminated waste heaps and a very few ruined buildings.
There are a number of areas that have been mined for a variety of metals
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typical ...
.
Gold mining
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
was mined as early as the Roman period at Dolaucothi
The Dolaucothi Gold Mines (; cy, Mwynfeydd Aur Dolaucothi) (), also known as the Ogofau Gold Mine, are ancient Roman surface and underground mines located in the valley of the River Cothi, near Pumsaint, Carmarthenshire, Wales. The gold mi ...
in Carmarthenshire
Carmarthenshire ( cy, Sir Gaerfyrddin; or informally ') is a county in the south-west of Wales. The three largest towns are Llanelli, Carmarthen and Ammanford. Carmarthen is the county town and administrative centre. The county is known as ...
and possibly elsewhere. In the 19th century gold was being extracted from a number of small mines at the southern end of Snowdonia with most activity centred in the valley of the River Mawddach
The Afon Mawddach ( en, River Mawddach, italic=yes) is a river in Gwynedd, Wales, which has its source in a wide area north of Dduallt in Snowdonia. It is 28 miles (45 km) in length, and is much branched; many of the significant tri ...
and its tributaries.
Lead and silver
The principal areas were centred on the upland areas of theRiver Ystwyth
The River Ystwyth (; cy, Afon Ystwyth "winding river") is a river in Ceredigion, Wales. The length of the main river is . Its catchment area covers . Its source is a number of streams that include the Afon Diliw, located on the west slopes of ...
and River Rheidol
The Afon Rheidol is a river in Ceredigion, Wales, in length. The source is Plynlimon. Receiving an average annual rainfall of , Plynlimon is also the source of both the Wye and the Severn.
Geography and geology
The Rheidol rises in the head ...
with some outliers to the east in the catchment of the River Severn
, name_etymology =
, image = SevernFromCastleCB.JPG
, image_size = 288
, image_caption = The river seen from Shrewsbury Castle
, map = RiverSevernMap.jpg
, map_size = 288
, map_c ...
and some to the south in the headwaters of the River Teifi
, name_etymology =
, image = File:Llyn Teifi - geograph.org.uk - 41773.jpg
, image_size =
, image_caption = Llyn Teifi, the source of the Teifi
, map =
, map_size =
, map_caption ...
. The largest of these mines were the Cwmystwyth and Rheidol United mines in Cwm Rheidol. The ore extracted was galena which in many cases had a high silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
content, especially at Cwm Ystwyth. It also occurred alongside large quantities of sphalerite, the principal ore of zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
. However, the zinc was only occasionally processed and much remains on the very extensive discard heaps around the mines.
Amongst the very many mines that have existed the following list identifies those known to have existed between the 17th and 19th centuries in north Cardiganshire and west Montgomeryshire
, HQ= Montgomery
, Government= Montgomeryshire County Council (1889–1974)Montgomeryshire District Council (1974–1996)
, Origin=
, Status=
, Start=
, End= ...
:
Aberffrwd, Alma, Blaenceunant, Blaencwmsymlog, Bron floyd, Bryn Glas, Bwa Drain, Bwlch, Cwm Mawr, Cwmystwyth, Cwm Ystwyth South, Cwm Ystwyth West, Cwmbryno, Cwmdarren, Cwmsymlog
Cwmsymlog is a short valley, sheltering a hamlet of the same name, in Ceredigion, in the west of Wales. Once an important mining area, but the mining slowly declined and finally came to an end in 1901. Now it is peaceful, open countryside with a ...
, De Broke, Dyffryn Castell, Elgar, Esgair Lle, Esgairmwyn, Fron Goch, Fron Goch East, Gelli, Glog fach, Glog Fawr, Goginan, Goginan west, Graig Goch, Grogwynion, Gwaith coch, Lisburne South, Llwynmalus, Llywernog, Logau Las, Melindwr, Mynyddgorddu, Nanteos, Pen Rhiw, Powell, Rheidol United, Temple, Ystumtuen
Metal mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic ...
in the Gwydir Forest dates back to the 17th century, but its heyday came in the latter half of the 19th century. These mines predominantly produced lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, and the last mine to close – Park Mine – closed in the 1960s.
Smaller areas of lead exploitation included Halkyn
Halkyn ( cy, Helygain ; Flintshire Welsh: ''Lygian '') is a village and community in Flintshire, north-east Wales and situated between Pentre Halkyn, Northop and Rhosesmor. At the 2001 Census the population of the community was 2,876, increas ...
Mountain in Flintshire
, settlement_type = County
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_shield = Arms of Flint ...
and in the Clyne valley in west Swansea.
Copper
Copper mining
Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper consists of a series of physical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, loca ...
is probably the oldest known mining activity in Wales with documented evidence of Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
mining on the Great Orme
The Great Orme ( cy, Y Gogarth) is a limestone headland on the north coast of Wales, north-west of the town of Llandudno. Referred to as ''Cyngreawdr Fynydd'' by the 12th-century poet Gwalchmai ap Meilyr, its English name derives from the Old N ...
near Llandudno and at Copa Hill
Cwmystwyth mines are located in Cwmystwyth, Ceredigion, Wales and exploited a part of the Central Wales Orefield.
Mining heritage
Cwm Ystwyth is considered the most important non-ferrous metal mining site in Wales providing a premier example ...
in the valley of the River Ystwyth
The River Ystwyth (; cy, Afon Ystwyth "winding river") is a river in Ceredigion, Wales. The length of the main river is . Its catchment area covers . Its source is a number of streams that include the Afon Diliw, located on the west slopes of ...
in Ceredigion
Ceredigion ( , , ) is a county in the west of Wales, corresponding to the historic county of Cardiganshire. During the second half of the first millennium Ceredigion was a minor kingdom. It has been administered as a county since 1282. Cer ...
. Further copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
discoveries were exploited in Snowdonia
Snowdonia or Eryri (), is a mountainous region in northwestern Wales and a national park of in area. It was the first to be designated of the three national parks in Wales, in 1951.
Name and extent
It was a commonly held belief that the na ...
just to the east of Beddgelert
Beddgelert () is a village and community in the Snowdonia area of Gwynedd, Wales. The population of the community taken at the 2011 census was 455, and includes Nantmor and Nant Gwynant. It is reputed to be named after the legendary hound ...
where the Sygun Copper Mine, within the Snowdonia National Park
Snowdonia or Eryri (), is a mountainous region in northwestern Wales and a national park of in area. It was the first to be designated of the three national parks in Wales, in 1951.
Name and extent
It was a commonly held belief that the nam ...
, gives an idea of the conditions faced by copper miners and is a popular tourist attraction. In the 18th century the massive deposits of copper together with a range of other metals was discovered and exploited at Parys Mountain
Parys Mountain ( cy, Mynydd Parys) is located south of the town of Amlwch in north east Anglesey, Wales. It is the site of a large copper mine that was extensively exploited in the late 18th century. Parys Mountain is a mountain in name only, bei ...
on Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ...
.
Iron
Commercial iron ore exploitation has been relatively uncommon in Wales during the last hundred years, despite the dominance of theiron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
and steel industry in South Wales. However ironstone
Ironstone is a sedimentary rock, either deposited directly as a ferruginous sediment or created by chemical replacement, that contains a substantial proportion of an iron ore compound from which iron (Fe) can be smelted commercially. Not to be con ...
is a component of the Lower Coal Measures rock sequence and where it outcrops along the northern edge of the South Wales Coalfield
The South Wales Coalfield ( cy, Maes glo De Cymru) extends across Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Blaenau Gwent and Torfaen. It is rich in coal deposits, espe ...
, it was extensively worked for the production of iron and was important in the initiation of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in South Wales. Commercial exploitation also took place in the Vale of Glamorgan
The Vale of Glamorgan ( cy, Bro Morgannwg ), often referred to as The Vale, is a county borough in the south-east of Wales. It borders Bridgend County Borough to the west, Cardiff to the east, Rhondda Cynon Taf to the north, and the Bristol ...
. The Forest of Dean
The Forest of Dean is a geographical, historical and cultural region in the western part of the county of Gloucestershire, England. It forms a roughly triangular plateau bounded by the River Wye to the west and northwest, Herefordshire to ...
was an important source of iron for many centuries, and dates from at least the Roman period.
Lead
Lead ore
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, l ...
was first mined in North Wales
North Wales ( cy, Gogledd Cymru) is a region of Wales, encompassing its northernmost areas. It borders Mid Wales to the south, England to the east, and the Irish Sea to the north and west. The area is highly mountainous and rural, with Snowdonia N ...
during Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
times at Pentre Halkyn
Pentre Halkyn ( cy, Pentre Helygain) is a small village in Flintshire, Wales. It is situated approximately two miles from Holywell, Flintshire, Holywell, and is off Junction 32 of the A55 road, A55 North Wales Expressway. It has a quarry, a smal ...
to be smelted at Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
. The lead that was produced there was stamped with the inscription Deceangli
The Deceangli or Deceangi (Welsh: Tegeingl) were one of the Celtic tribes living in Britain, prior to the Roman invasion of the island. The tribe lived in the region near the modern city of Chester but it is uncertain whether their territory co ...
, which was the name of the Celtic tribe occupying the area. In the 17th century an intensive period of Welsh lead mining commenced, bringing a large number of miners from Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the nor ...
into Wales. There are substantial reserves of the metal in Ceredigion
Ceredigion ( , , ) is a county in the west of Wales, corresponding to the historic county of Cardiganshire. During the second half of the first millennium Ceredigion was a minor kingdom. It has been administered as a county since 1282. Cer ...
, probably first exploited in the Roman period, and extensively during the revival of metal mining in the reign of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
El ...
.
Arsenic
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, ...
has been mined in association with metals and in Wales commercial extraction has probably only occurred in the Clyne valley near Swansea.
Working mines
Following the miners' strike, only two deep mines remained working in Wales.Tower Colliery
Tower Colliery ( Welsh: Glofa'r Tŵr) was the oldest continuously working deep-coal mine in the United Kingdom, and possibly the world, until its closure in 2008. It was the last mine of its kind to remain in the South Wales Valleys. It was loca ...
, Hirwaun, had been run by a miner's co-operative since 1994. Due to dwindling coal seams, the colliery was last worked on 18 January 2008, followed by official closure on 25 January. Drift mining
Drift mining is either the mining of an ore deposit by underground methods, or the working of coal seams accessed by adits driven into the surface outcrop of the coal bed. A drift mine is an underground mine in which the entry or access is abov ...
continued at Aberpergwm Colliery, a smaller mine closed by the National Coal Board
The National Coal Board (NCB) was the statutory corporation created to run the nationalised coal mining industry in the United Kingdom. Set up under the Coal Industry Nationalisation Act 1946, it took over the United Kingdom's collieries on "ve ...
in 1985 but reopened in 1996. Aberpergwm colliery is currently owned and operated by Energybuild and supplies the carbon market. Several other small mines still exist, including the Blaentillery drift mine near to the Big Pit National Coal Museum.
List of mines in Wales
Coal
*Abercynon Colliery
Abercynon Colliery was a coal mine located in Abercynon, South Wales. Opened in 1889, it closed in 1988.
Development
The colliery Mining in Wales, was developed at a cost of £270,000 from 1889, by the Dowlais Iron Dowlais Ironworks, Company, t ...
*Abernant Colliery
Abernant Colliery was a coal mine in the River Amman valley at Pwllfawatkin, north of Pontardawe and north of Swansea, West Wales.
Development
Abernant was developed by the National Coal Board as one of the West Wales "super pits" alongside Cyn ...
*Aberpergwm
Aberpergwm is the site of a colliery in the Vale of Neath near Glynneath in south Wales.
Mine history
The site at Aberpergwm had been worked since 1811 as a series of drift mines, but full commercial working began from the 1860s when W. William ...
(anthracite coal, drift mine, active in 2014 with 64 employee(closed) *
Albion Colliery
Albion Colliery was a coal mine in South Wales Valleys, located in the village of Cilfynydd, one mile north of Pontypridd.
Location
The Colliery was located along the well known A470 road , a long-distance road from Cardiff to Llandudno. The ...
in Cilfynydd
Cilfynydd is a village in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales, a mile from the South Wales Valleys town of Pontypridd, and 13 miles north of the capital city, Cardiff. Cilfynydd is also an electoral ward for the county council and ...
, Pontypridd
() ( colloquially: Ponty) is a town and a community in Rhondda Cynon Taf, Wales.
Geography
comprises the electoral wards of , Hawthorn, Pontypridd Town, 'Rhondda', Rhydyfelin Central/Ilan ( Rhydfelen), Trallwng ( Trallwn) and Treforest (). ...
- work began 1884 and the mine closed in 1966
* Bargoed Colliery sunk in 1887, closed 1977.
* Bedwas Navigation Colliery (closed 1985)
* Bersham Colliery (closed 1986)
* Big Pit National Coal Museum
* Blaenant Colliery (closed 1990)
*Bute Merthyr Colliery
The Bute Merthyr Colliery, in Treherbert in the Rhondda Valley, was the first colliery to produce steam coal in the Rhondda valley. A trial pit was dug in 1851, and the colliery was closed in 1926.
Opening
In 1849, Marquess of Bute bought the Cwms ...
*Bwllfa Colliery
Bwllfa Colliery was a coal mine located in the Dare valley near Cwmdare in Rhondda Cynon Taf, South Wales. It operated from 1856 to 1957, remaining open as a ventilation shaft for Mardy Colliery until 1989.
Development
Bwllfa No.1
In 1853, Sam a ...
*Cambrian Colliery
The Cambrian Colliery was a large coal mine that operated between 1872 and 1967 near Clydach Vale in the Rhondda Valley, south Wales. It is notable for its huge production and for two infamous explosion disasters, in 1905 and 1965, in which a tota ...
*Cefn Coed Colliery Museum
Cefn Coed Colliery Museum is a former coal mine, now operating as a museum. It is located at Crynant near Neath in the South Wales Valleys.
Background
Coal mining in the Neath area began with the development of the port of Neath in the 16th ...
*Celynen North Colliery in Newbridge
* Celynen South Colliery in Abercarn (closed 1985)
*Coedely Colliery, Tonyrefail (closed 1985); linked underground to Cwm Colliery Beddau (closed 1986)
*Cynheidre Colliery
Cynheidre Colliery was a coal mine located in the Gwendraeth valley, in Carmarthenshire, South Wales. Opened in 1954, it closed in 1989.
Cynheidre was developed by the National Coal Board as one of the West Wales "super pits" alongside Abernant C ...
(closed 1989)
* Darran Colliery, Deri sunk 1868, closed 1919.
*Deep Navigation Colliery
Deep Navigation Colliery was a coal mine in South Wales, that operated from 1872 until 1991.
Located next to the co-developed village of Treharris in the borough of Merthyr Tydfil, on development it was the deepest coalmine in South Wales Coalf ...
, Treharris (closed 1991)
*Ferndale Colliery
Ferndale Colliery was a series of nine coal mines, located close to the village of Ferndale, Rhondda Cynon Taf in the Rhondda Valley, South Wales.
History
The first development was by David Davis of Blaengwawr from 1857, in accessing the high qua ...
*Ffos-y-fran Land Reclamation Scheme
The Ffos-y-fran Land Reclamation Scheme is a major opencast coaling operation to the north-east of Merthyr Tydfil in South Wales. The contracted excavator/reclaiming company is Merthyr (South Wales) Ltdprev Miller Argent, which is owned by Gwent ...
(still under consideration as of 2013)
* Garw/Ffaldau Colliery
* Gresford Colliery (closed 1973)
* Great Western Mine
* Groesfaen Colliery, Bargoed. Sunk 1902, closed 1968.
* Hafodyrynys Colliery
* Lady Windsor Colliery in Ynysybwl (closed 1988); linked underground to Abercynon Colliery
Abercynon Colliery was a coal mine located in Abercynon, South Wales. Opened in 1889, it closed in 1988.
Development
The colliery Mining in Wales, was developed at a cost of £270,000 from 1889, by the Dowlais Iron Dowlais Ironworks, Company, t ...
(Closed 1988)
* Llancaiach Colliery
*Llay Hall Colliery, Cefn y Bedd, North Wales 1877-1947
*Mardy Colliery
Maerdy Colliery was a coal mine located in the South Wales village of Maerdy ( cy, Y Maerdy), in the Rhondda Valley, located in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, and within the historic county boundaries of Glamorgan, Wales. Opened in 18 ...
in Maerdy
Maerdy (, cy, Y Maerdy) is a village and community (and electoral ward) in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, and within the historic county boundaries of Glamorgan, Wales, lying at the head of the Rhondda Fach Valley.
History
"Maerdy" i ...
(closed 1990, site cleared and now occupied by Avon Rubber
Avon Protection plc is a British company that specialises in the engineering and manufacturing of respiratory protection equipment for military, law enforcement and fire personnel. Its corporate headquarters are south of Melksham in Wiltshir ...
); linked underground to Tower Colliery
Tower Colliery ( Welsh: Glofa'r Tŵr) was the oldest continuously working deep-coal mine in the United Kingdom, and possibly the world, until its closure in 2008. It was the last mine of its kind to remain in the South Wales Valleys. It was loca ...
* Marine Colliery in Cwm, Blaenau Gwent
Cwm (from cy, Y Cwm, ) is a former coal mining village, community and electoral ward south of Ebbw Vale in the county borough of Blaenau Gwent, Wales, within the historic boundaries of Monmouthshire, United Kingdom. In the far north of the com ...
, merged with Six Bells Colliery in the 1970s, closed in 1989
*Mostyn Colliery
Mostyn Colliery was a coal mine in Flintshire, North Wales, that was owned in the later part of its operating life by the influential Mostyn family. The colliery was located at Mostyn on the banks of the River Dee.
Early history
The Welsh write ...
(closed 1887 after flooding)
*Nantgarw Colliery
Nantgarw Colliery was a coal mine and later developed Coking coal works, located in the village on Nantgarw, Mid Glamorgan, Wales located just north of Cardiff.
Opened in 1910, it closed in 1986. The site is now redeveloped as the industrial estat ...
(amalgamated with Windsor Colliery in 1974, closed 1986); deepest pit in the South Wales Coalfield
The South Wales Coalfield ( cy, Maes glo De Cymru) extends across Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Blaenau Gwent and Torfaen. It is rich in coal deposits, espe ...
when sunk in 1915
*Navigation Colliery in Crumlin
* Nine Mile Point Colliery at Cwmfelinfach (closed 1964)
*Oakdale Colliery
Oakdale Colliery was a coal mine located in the Sirhowy Valley, one of the valleys of South Wales.
In the early years of the twentieth century the need for coal was growing both in America and Europe, and local business men in Wales were looking f ...
at Ty Mellyn in the Sirhowy Valley
The Sirhowy Valley ( ) is an industrialised valley in the eastern part of the Valleys region of Wales. It is named from the Sirhowy River () which runs through it. Its upper reaches are occupied by the town of Tredegar within the unitary area of ...
(closed 1989; linked to Markham and Celynen North)
*Ogilvie Colliery, Deri, South Wales. Closed 1975.
* Parc Slip Colliery
*Penallta Colliery
Penallta Colliery was a coal mine, located close to Hengoed in the Rhymney Valley in the South Wales Valleys. A coal mine which in 1935 held the European record for coal wound in a 24-hour period, it is now the site of an original redevelopment ...
* Pentremawr Colliery
*Prince of Wales Colliery
The Prince of Wales Colliery was a coal mine that operated for over 130 years in Pontefract, West Yorkshire, England. It was permanently closed in 2002 after geological problems were found to make accessing remaining coal reserves unprofitable, ...
in Abercarn closed 1959. Greatest mining disaster in Monmouthshire, 1878.
*Point of Ayr
:''There are two other similarly named points in the British Isles: Point of Ayre, Isle of Man and Point of Ayre, Orkney, Scotland.''
Point of Ayr ( cy, Y Parlwr Du) is the northernmost point of mainland Wales. It is situated immediately t ...
(closed 1996)
* Primrose Colliery
* Seven Sisters anthracite; closed 1963
*Six Bells Colliery
Six Bells Colliery was a colliery located in Six Bells, Abertillery, Gwent, Wales. On 28 June 1960 it was the site of an underground explosion which killed 45 of the 48 miners working in that part of the mine. It is now the site of the artisti ...
in Abertillery
Abertillery (; cy, Abertyleri) is a town and a community of the Ebbw Fach valley in the historic county of Monmouthshire, Wales. Following local government reorganisation it became part of the Blaenau Gwent County Borough administrative area ...
, site of the Six Bells Colliery Disaster in 1960, merged with Marine Colliery in the 1970s, closed in 1988
*Taff Merthyr
Taff Merthyr was a deep navigation colliery
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries ...
* Tarenni Colliery
*Tower Colliery
Tower Colliery ( Welsh: Glofa'r Tŵr) was the oldest continuously working deep-coal mine in the United Kingdom, and possibly the world, until its closure in 2008. It was the last mine of its kind to remain in the South Wales Valleys. It was loca ...
(closed 1994 and re-opened after an employees' buy-out by Goitre Tower Anthracite in 1995; closed 2008 after exhaustion of the seam, but with plans to establish an opencast mine in its place)
* Universal Colliery at Senghenydd, site of the Senghenydd Colliery Disaster
The Senghenydd colliery disaster, also known as the Senghenydd explosion ( cy, Tanchwa Senghennydd), occurred at the Universal Colliery in Senghenydd, near Caerphilly, Glamorgan, Wales, on 14 October 1913. The explosion, which killed 439 mine ...
; converted to a ventilation facility for Windsor Colliery and then closed in 1988
* Windsor Colliery in Abertridwr, Caerphilly; closed 1986
*Wyllie Colliery Wyllie Colliery was located in the Sirhowy Valley, South Wales.
The coal mine was sunk by the Tredegar Iron and Coal Company and opened in 1926. The colliery was named after a director of the company, Alexander Wyllie. Wyllie
Wyllie is a surname ...
in the Sirhowy Valley
The Sirhowy Valley ( ) is an industrialised valley in the eastern part of the Valleys region of Wales. It is named from the Sirhowy River () which runs through it. Its upper reaches are occupied by the town of Tredegar within the unitary area of ...
; closed 1968
Metal ores
* Bryntail lead mine (No longer in use) *Cilcain
Cilcain is a village and community, near Mold in Flintshire, north-east Wales. The village has an industrial history and includes the Millennium Woods, a post office, a public house, a parish church, a primary school (Ysgol y Foel) and a village ...
lead mine (No longer in use)
* Clogau Gold Mine
* Cwmystwyth Mines
*Dolaucothi Gold Mines
The Dolaucothi Gold Mines (; cy, Mwynfeydd Aur Dolaucothi) (), also known as the Ogofau Gold Mine, are ancient Roman surface and underground mines located in the valley of the River Cothi, near Pumsaint, Carmarthenshire, Wales. The gold mi ...
*Great Orme
The Great Orme ( cy, Y Gogarth) is a limestone headland on the north coast of Wales, north-west of the town of Llandudno. Referred to as ''Cyngreawdr Fynydd'' by the 12th-century poet Gwalchmai ap Meilyr, its English name derives from the Old N ...
copper
* Gwydir Forest various metal mines
* Gwynfynydd gold mine (No longer in use)
* Klondyke mine lead mine (No longer in use)
* Llywernog Mine silver-lead mine
* Minera Leadmines (No longer in use)
*Parys Mountain
Parys Mountain ( cy, Mynydd Parys) is located south of the town of Amlwch in north east Anglesey, Wales. It is the site of a large copper mine that was extensively exploited in the late 18th century. Parys Mountain is a mountain in name only, bei ...
copper mine
* Sygun Copper Mine (No longer in use as a mine)
* Van Leadmine Llanidloes
* Penrhyn Du mines (no longer in use)
Popular culture
The theme of Public Service Broadcasting's third album, Every Valley, follows the rise and fall of Welsh coal mining. It was recorded in the former steelworks town of Ebbw Vale, Wales, and released on 7 July 2017.See also
* Coal mining *Mining accident
A mining accident is an accident that occurs during the process of mining minerals or metals. Thousands of miners die from mining accidents each year, especially from underground coal mining, although accidents also occur in hard rock mining. ...
*Miners' institute
Miners' institutes, sometimes known as ''workingmen's institutes'', ''mine workers' institutes'', or ''miners' welfare halls'' are large institutional buildings that were typically built during the height of the industrial period as a meeting and ...
References
Further reading
* Benson, John. ''British Coal-Miners in the Nineteenth Century: A Social History'' (Holmes & Meier, 1980) * Berger, Stefan Llafur. "Working-Class Culture and the Labour Movement in the South Wales and the Ruhr Coalfields, 1850-2000: A Comparison," ''Journal of Welsh Labour History/Cylchgrawn Hanes Llafur Cymru'' (2001) 8#2 pp 5-40. * Curtis, Ben. ''The South Wales Miners, 1964-1985'' (University of Wales Press, distributed by University of Chicago Press; 2013) 301 pages * Curtis, Ben. "A Tradition of Radicalism: The Politics of the South Wales Miners, 1964-1985," ''Labour History Review'' (2011) 76#1 pp 34-50External links
Welsh Coal Mines
- all the Welsh pits and their brief histories
BBC Wales Coal House website
42 pages of mining photos compiled by John Cornwell and held on Gathering the Jewels
*
AditNow
– Photographic database of mines
Welsh Mines Society
– Society with a focus on the research, recording and exploration of the metal mines of Wales {{DEFAULTSORT:Mining In Wales Economy of Wales