|
Parys Mountain
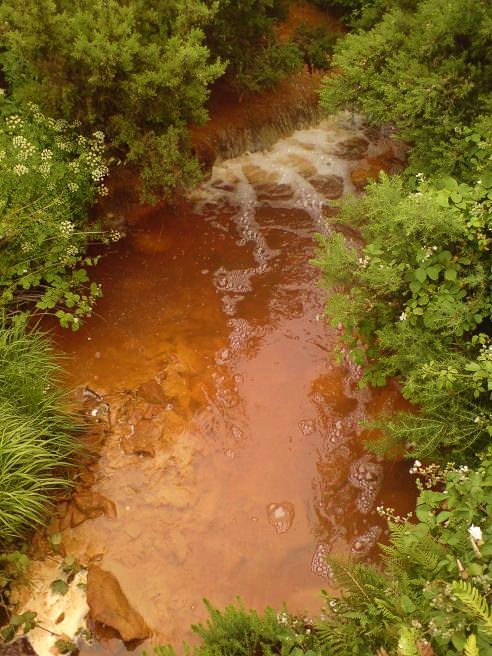
Parys Mountain ( cy, Mynydd Parys) is located south of the town of Amlwch in north east Anglesey, Wales. It is the site of a large copper mine that was extensively exploited in the late 18th century. Parys Mountain is a mountain in name only, being a hill with an elevation of barely 150m. History Parys Mountain was mined for copper ore in the early Bronze Age, as shown by sub-surface debris nearly 4,000 years old revealed during excavations in 2002. Since then access has been regained to the sealed underground workings of the Parys mine revealing further evidence for this ancient mining. Parys Mountain is thus one of the few sites in Britain where there is evidence for the prehistoric beginnings of the British metal mining industry. The 18th century miners recognised that they were following in the steps of much earlier workers, an observation that was then linked to the discovery locally of copper ingots bearing Roman inscriptions. In 1764 Charles Roe of Macclesfield was gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mynydd Parys
Parys Mountain ( cy, Mynydd Parys) is located south of the town of Amlwch in north east Anglesey, Wales. It is the site of a large copper mine that was extensively exploited in the late 18th century. Parys Mountain is a mountain in name only, being a hill with an elevation of barely 150m. History Parys Mountain was mined for copper ore in the early Bronze Age, as shown by sub-surface debris nearly 4,000 years old revealed during excavations in 2002. Since then access has been regained to the sealed underground workings of the Parys mine revealing further evidence for this ancient mining. Parys Mountain is thus one of the few sites in Britain where there is evidence for the prehistoric beginnings of the British metal mining industry. The 18th century miners recognised that they were following in the steps of much earlier workers, an observation that was then linked to the discovery locally of copper ingots bearing Roman inscriptions. In 1764 Charles Roe of Macclesfield was gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island, at , is the largest in Wales, the seventh largest in Britain, largest in the Irish Sea and second most populous there after the Isle of Man. Isle of Anglesey County Council administers , with a 2011 census population of 69,751, including 13,659 on Holy Island. The Menai Strait to the mainland is spanned by the Menai Suspension Bridge, designed by Thomas Telford in 1826, and the Britannia Bridge, built in 1850 and replaced in 1980. The largest town is Holyhead on Holy Island, whose ferry service with Ireland handles over two million passengers a year. The next largest is Llangefni, the county council seat. From 1974 to 1996 Anglesey was part of Gwynedd. Most full-time residents are habitual Welsh speakers. The Welsh name Ynys M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double sulfate salt of aluminium with the general formula , where is a monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the formula . Other alums are named after the monovalent ion, such as sodium alum and ammonium alum. The name "alum" is also used, more generally, for salts with the same formula and structure, except that aluminium is replaced by another trivalent metal ion like chromium, and/or sulfur is replaced by another chalcogen like selenium. The most common of these analogs is chrome alum . In most industries, the name "alum" (or "papermaker's alum") is used to refer to aluminium sulfate, , which is used for most industrial flocculation (the variable is an integer whose size depends on the amount of water absorbed into the alum). In medicine, "alum" may also refer to aluminium hydroxide gel used as a vaccine adjuvant. History Alum found at ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amlwch Port
Amlwch Port ( cy, Porth Amlwch) is a port village in Anglesey, Wales. It is effectively an eastern suburb of the larger town of Amlwch. Between the 1991 Census and the 2001 Census the records showed Amlwch Port's population had dropped by over 1,000, to 2,628. Anglesey County Council were unsure why the population had dropped (or even whether it had been miscounted). Prior to the 2013 county council elections, Amlwch Port was one of the 40 electoral ward A ward is a local authority area, typically used for electoral purposes. In some countries, wards are usually named after neighbourhoods, thoroughfares, parishes, landmarks, geographical features and in some cases historical figures connected to ...s to the Isle of Anglesey Council. It ceased to be a county ward as a result of ''The Isle of Anglesey (Electoral Arrangements) Order 2012''. According to the 2011 census the population of the ward was 2,507. References External links Former wards of Anglesey Villages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waymarking
Trail blazing or way marking is the practice of marking paths in outdoor recreational areas with signs or markings that follow each other at certain, though not necessarily exactly defined, distances and mark the direction of the trail. A blaze in the beginning meant "a mark made on a tree by slashing the bark" (''The Canadian Oxford Dictionary''). Originally a waymark was "any conspicuous object which serves as a guide to travellers; a landmark" (''Oxford English Dictionary''). There are several ways of marking trails, including paint, carvings, affixed markers, posts, flagging, cairns, and crosses, with paint being the most widely used. Types of signage Paint A painted marking of a consistent shape or shapes (often rectangular), dimension and colour or combination of colours is used along the trail route. The system by which blazes are used to signify turns and endpoints in trails (see below) strongly favors the use of paint blazes. European countries usually use systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Sulpice Beudant
François Sulpice Beudant (5 September 1787 – 10 December 1850), was a French mineralogist and geologist. The mineral beudantite was named after him. Life He was born in Paris. He was educated at the Ecole Polytechnique and Ecole Normale, and in 1811 was appointed professor of mathematics at the lycée of Avignon. Thence he was called, in 1813, to the lycée of Marseilles to fill the post of professor of physics, where he carried out the first measurements of the speed of sound in seawater. In the following year the royal mineralogical cabinet was committed to his charge to be conveyed into England, and from that time his attention was directed principally towards geology and cognate sciences. In 1817 he published a paper on the phenomena of crystallization, treating especially of the variety of forms assumed by the same mineral substance. In 1818 he undertook, at the expense of the French government, a geological journey through Hungary, and the results of his researches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Withering
William Withering FRS (17 March 1741 – 6 October 1799) was an English botanist, geologist, chemist, physician and first systematic investigator of the bioactivity of digitalis. Withering was born in Wellington, Shropshire, the son of a surgeon. He trained as a physician and studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh Medical School. He worked at Birmingham General Hospital from 1779. The story is that he noticed a person with dropsy (swelling from congestive heart failure) improve remarkably after taking a traditional herbal remedy; Withering became famous for recognising that the active ingredient in the mixture came from the foxglove plant. The active ingredient is now known as digoxin, after the plant's scientific name. In 1785, Withering published ''An Account of the Foxglove and some of its Medical Uses'', which contained reports on clinical trials and notes on digitalis's effects and toxicity. Biography Born in England, Withering attended Edinburgh Medical School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglesite
Anglesite is a lead sulfate mineral with the chemical formula PbSO4. It occurs as an oxidation product of primary lead sulfide ore, galena. Anglesite occurs as prismatic orthorhombic crystals and earthy masses, and is isomorphous with barite and celestine. It contains 74% of lead by mass and therefore has a high specific gravity of 6.3. Anglesite's color is white or gray with pale yellow streaks. It may be dark gray if impure. It was first recognized as a mineral species by William Withering in 1783, who discovered it in the Parys copper-mine in Anglesey; the name anglesite, from this locality, was given by F. S. Beudant in 1832. The crystals from Anglesey, which were formerly found abundantly on a matrix of dull limonite, are small in size and simple in form, being usually bounded by four faces of a prism and four faces of a dome; they are brownish-yellow in colour owing to a stain of limonite. Crystals from some other localities, notably from in Sardinia, are transparent an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
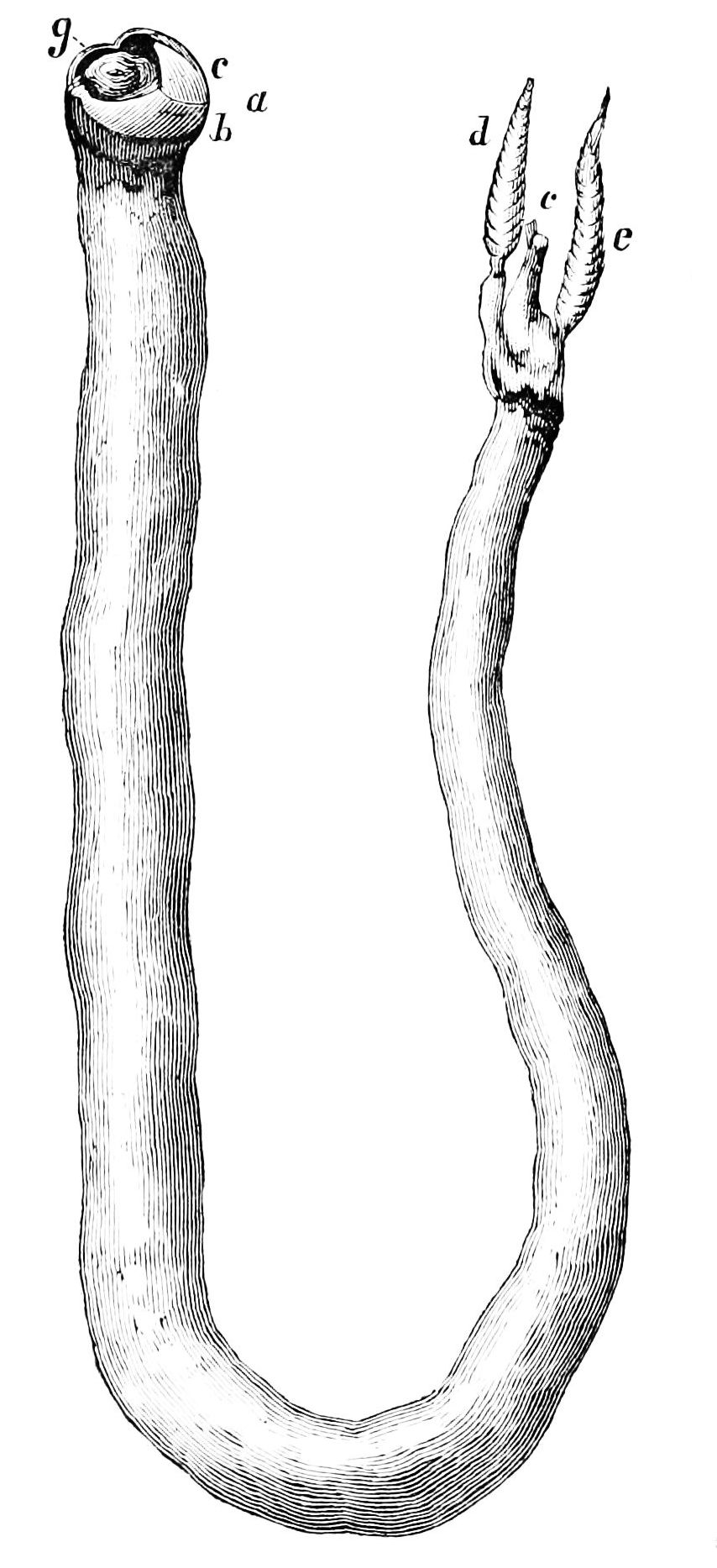
Shipworm
The shipworms are marine bivalve molluscs in the family Teredinidae: a group of saltwater clams with long, soft, naked bodies. They are notorious for boring into (and commonly eventually destroying) wood that is immersed in sea water, including such structures as wooden piers, docks and ships; they drill passages by means of a pair of very small shells (“ valves”) borne at one end, with which they rasp their way through. Sometimes called "termites of the sea", they also are known as " Teredo worms" or simply Teredo (from grc, τερηδών, , translit=terēdṓn, lit=wood-worm via ). Carl Linnaeus assigned the common name '' Teredo'' to the best-known genus of shipworms in the 10th edition of his taxonomic '' magnum opus'', '' Systema Naturæ'' (1758). Description Removed from its burrow, the fully grown teredo ranges from several centimetres to about a metre in length, depending on the species. The body is cylindrical, slender, naked and superficially vermiform, meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnacle
A barnacle is a type of arthropod constituting the subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacea, and is hence related to crabs and lobsters. Barnacles are exclusively marine, and tend to live in shallow and tidal waters, typically in erosive settings. They are sessile (nonmobile) and most are suspension feeders, but those in infraclass Rhizocephala are highly specialized parasites on crustaceans. They have four nektonic (active swimming) larval stages. Around 1,000 barnacle species are currently known. The name is Latin, meaning "curl-footed". The study of barnacles is called cirripedology. Description Barnacles are encrusters, attaching themselves temporarily to a hard substrate or a symbiont such as a whale (whale barnacles), a sea snake (''Platylepas ophiophila''), or another crustacean, like a crab or a lobster (Rhizocephala). The most common among them, "acorn barnacles" (Sessilia), are sessile where they grow their shells directly onto the substrate. Pedunculat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
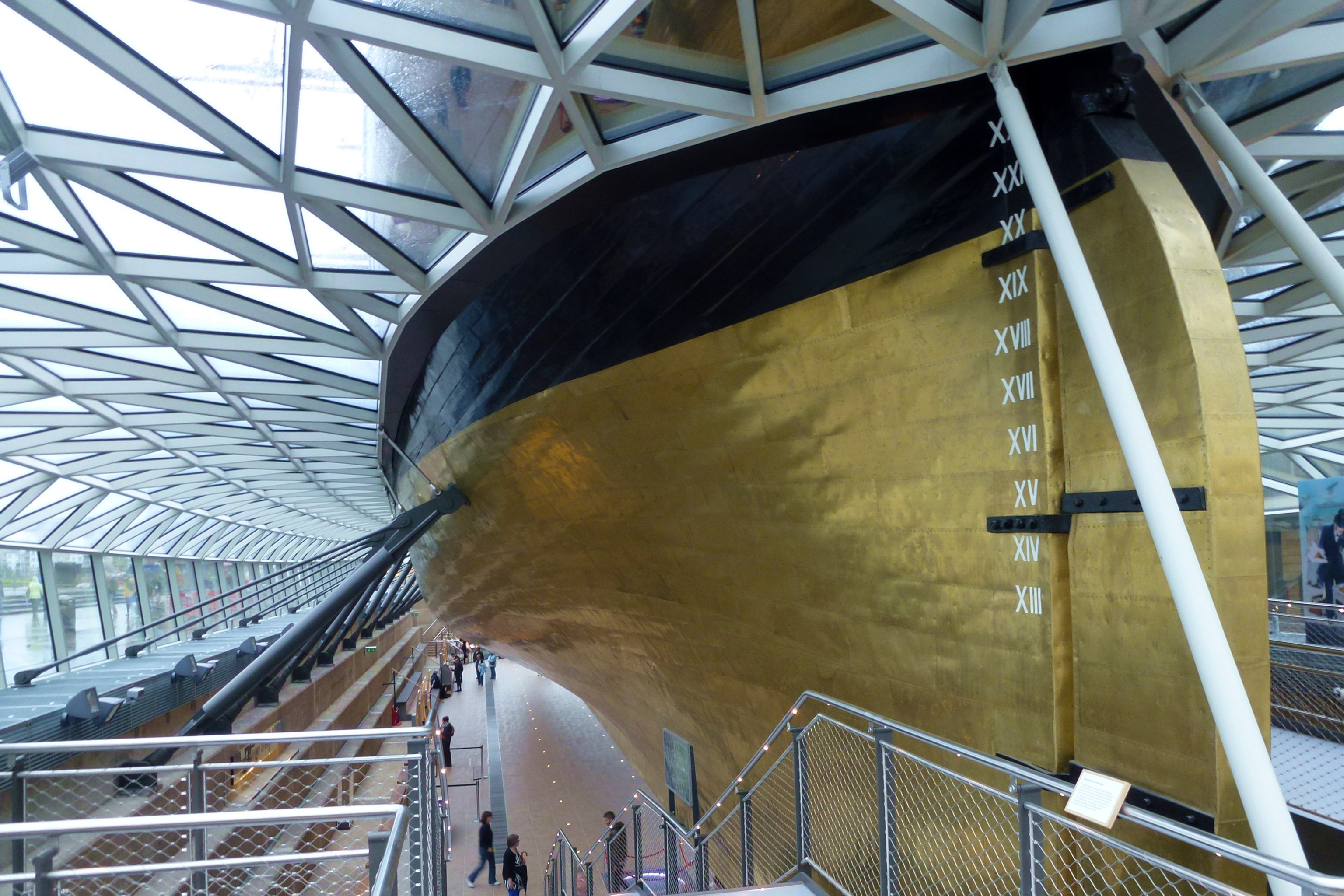
Copper Sheathing
Copper sheathing is the practice of protecting the under-water hull of a ship or boat from the corrosive effects of salt water and biofouling through the use of copper plates affixed to the outside of the hull. It was pioneered and developed by the Royal Navy during the 18th century. In antiquity, ancient Greeks used lead plates to protect the underwater hull. Development Deterioration of the hull of a wooden ship was a significant problem during the Age of Sail. Ships' hulls were under continuous attack by shipworm, barnacles and various marine weeds, all of which had some adverse effect on the ship, be it structurally, in the case of the worm, or affecting speed and handling in the case of the weeds. The most common methods of dealing with these problems were through the use of wood, and sometimes lead, sheathing. Expendable wood sheathing effectively provided a non-structural skin to the hull for the worm to attack, and could be easily replaced in dry dock at regular inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |