Magdalenian era on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; French: ''Magdalénien'') are later
 The culture spans from approximately 17,000 to 12,000 BP, toward the end of the most recent
The culture spans from approximately 17,000 to 12,000 BP, toward the end of the most recent
 Bones, reindeer antlers and animal teeth display crude pictures carved or etched on them of seals, fish, reindeer, mammoths and other creatures.
The best of Magdalenian artworks are a mammoth engraved on a fragment of its own ivory; a dagger of reindeer antler, with a handle in form of a reindeer; a cave-bear cut on a flat piece of
Bones, reindeer antlers and animal teeth display crude pictures carved or etched on them of seals, fish, reindeer, mammoths and other creatures.
The best of Magdalenian artworks are a mammoth engraved on a fragment of its own ivory; a dagger of reindeer antler, with a handle in form of a reindeer; a cave-bear cut on a flat piece of
File:Propulseur Mas d'Azil.png
File:Magdalenian horse.jpg
File:Paleolithic horse3.JPG
File:Speerschleuder LaMadeleine.jpg
File:Lascaux painting.jpg,
Picture Gallery of the Paleolithic (reconstructional palaeoethnology)
Libor Balák at the Czech Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Archaeology in Brno, The Center for Paleolithic and Paleoethnological Research {{Authority control Industries (archaeology) Upper Paleolithic cultures of Europe Archaeological cultures in Belgium Archaeological cultures in the Czech Republic Archaeological cultures in France Archaeological cultures in Germany Archaeological cultures in Portugal Archaeological cultures in Spain
culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
s of the Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coin ...
and Mesolithic in western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years ago. It is named after the type site
In archaeology, a type site is the site used to define a particular archaeological culture or other typological unit, which is often named after it. For example, discoveries at La Tène and Hallstatt led scholars to divide the European Iron A ...
of La Madeleine, a rock shelter located in the Vézère valley, commune of Tursac
Tursac () is a commune in the Dordogne department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France. ''Abri de la Madeleine'' is the site of Magdalenian prehistoric finds.
Population
See also
*Communes of the Dordogne department
The following ...
, in France's Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; oc, Dordonha ) is a large rural department in Southwestern France, with its prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and the Pyrenees, it is name ...
department.
Édouard Lartet
Édouard Lartet (15 April 180128 January 1871) was a French geologist and paleontologist, and a pioneer of Paleolithic archaeology.
Biography
Lartet was born near Castelnau-Barbarens, ' of Gers, France, where his family had lived for more than ...
and Henry Christy
Henry Christy (26 July 1810 – 4 May 1865) was an English banker and collector, who left his substantial collections to the British Museum.
Early life
Christy was born at Kingston upon Thames, the second son of William Miller Christy of Woodbi ...
originally termed the period ''L'âge du renne'' (the Age of the Reindeer). They conducted the first systematic excavations of the type site, publishing in 1875. The Magdalenian epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
is associated with reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 sub ...
hunters, although Magdalenian sites contain extensive evidence for the hunting of red deer, horses, and other large mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
present in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
toward the end of the last glacial period. The culture was geographically widespread, and later Magdalenian sites stretched from Portugal in the west to Poland in the east, and as far north as France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, the Channel Islands
The Channel Islands ( nrf, Îles d'la Manche; french: îles Anglo-Normandes or ''îles de la Manche'') are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
. It is the third epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
of Gabriel de Mortillet's cave chronology system, corresponding roughly to the Late Pleistocene.
Besides La Madeleine, the chief stations of the epoch are Les Eyzies
Les Eyzies (; oc, Las Aisiás) is a commune in the Dordogne department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France. It was established on 1 January 2019 by merger of the former communes of Les Eyzies-de-Tayac-Sireuil (the seat), Manaurie and ...
, Laugerie-Basse
Laugerie-Basse is an important Upper Paleolithic archaeological site within the territory of the French commune Les Eyzies-de-Tayac-Sireuil in Dordogne. It is known for several works of art from the Magdalenian. In 1979, Laugerie-Basse, along ...
, and Gorges d'Enfer in the Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; oc, Dordonha ) is a large rural department in Southwestern France, with its prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and the Pyrenees, it is name ...
; Grotte du Placard in Charente and others in south-west France.
Period biology
The Magdalenian epoch is represented by numerous sites, whose contents show progress in arts and culture. It was characterized by a cold and dry climate, humans in association with the reindeer, and the extinction of themammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks an ...
. The use of bone and ivory as implements, begun in the preceding Solutrean
The Solutrean industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Paleolithic of the Final Gravettian, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP. Solutrean sites have been found in modern-day France, Spain and Portugal.
Details
...
epoch, increased, making the period essentially a bone period. Bone instruments are quite varied: spear-points, harpoon
A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument and tool used in fishing, whaling, sealing, and other marine hunting to catch and injure large fish or marine mammals such as seals and whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the target animal ...
-heads, borers, hooks and needles.
The fauna of the Magdalenian epoch seems to have included tigers and other tropical species along with reindeer, arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. It is well adapted to living in ...
es, arctic hare
The Arctic hare (''Lepus arcticus'') is a species of hare highly adapted to living in the Arctic tundra and other icy biomes. The Arctic hare survives with shortened ears and limbs, a small nose, fat that makes up close to 20% of its body, and a ...
s, and other polar creatures. Magdalenian humans appear to have been of short stature, dolichocephalic
Dolichocephaly (derived from the Ancient Greek δολιχός 'long' and κεφαλή 'head') is a condition where the head is longer than would be expected, relative to its width. In humans, scaphocephaly is a form of dolichocephaly.
Dolichoce ...
, with a low retreating forehead and prominent brow ridge
The brow ridge, or supraorbital ridge known as superciliary arch in medicine, is a bony ridge located above the eye sockets of all primates. In humans, the eyebrows are located on their lower margin.
Structure
The brow ridge is a nodule or crest ...
s.
Chronology
 The culture spans from approximately 17,000 to 12,000 BP, toward the end of the most recent
The culture spans from approximately 17,000 to 12,000 BP, toward the end of the most recent ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
. Magdalenian tool culture is characterised by regular blade
A blade is the portion of a tool, weapon, or machine with an edge that is designed to puncture, chop, slice or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are to be used on. Histor ...
industries struck from carinate
Carinate is a shape in pottery, glassware and artistic design usually applied to amphorae or vases. The shape is defined by the joining of a rounded base to the sides of an inward sloping vessel. This design is seen in ancient cultures such as ...
d cores.
The Magdalenian epoch is divided into six phases generally agreed to have chronological significance (Magdalenian I through VI, I being the earliest and VI being the latest). The earliest phases are recognised by the varying proportion of blades and specific varieties of scrapers, the middle phases marked by the emergence of a microlithic component (particularly the distinctive denticulated microliths
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. Th ...
), and the later phases by the presence of uniserial (phase5) and biserial 'harpoons' (phase6) made of bone, antler and ivory.
Debate continues about the nature of the earliest Magdalenian assemblages, and it remains questionable whether the Badegoulian culture is the earliest phase of Magdalenian culture. Similarly, finds from the forest of Beauregard near Paris have been suggested as belonging to the earliest Magdalenian. The earliest Magdalenian sites are in France. The Epigravettian
The Epigravettian (Greek: ''epi'' "above, on top of", and Gravettian) was one of the last archaeological industries and cultures of the European Upper Paleolithic. It emerged after the Last Glacial Maximum around ~21,000 cal. BP or 19,050 BC, ...
is a similar culture appearing at the same time. Its known range extends from southeast France to the western shores of the Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchme ...
, Russia, with many sites in Italy.
The later phases of Magdalenian culture are contemporaneous with the human re-settlement of north-western Europe after the Last Glacial Maximum during the Late Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eu ...
. As hunter gatherers, Magdalenians did not re-settle permanently in northwest Europe, instead following herds and seasons.
By the end of the Magdalenian epoch, lithic technology shows a pronounced trend toward increased microlithisation. The bone harpoons and points have the most distinctive chronological markers within the typological sequence. As well as flint tools, Magdalenians are known for their elaborate worked bone, antler and ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals i ...
that served both functional and aesthetic purposes, including perforated batons.
The sea shells and fossils found in Magdalenian sites may be sourced to relatively precise areas and have been used to support hypotheses of Magdalenian hunter-gatherer seasonal ranges, and perhaps trade routes.
In northern Spain and south-west France this tool culture was superseded by the Azilian
The Azilian is a Mesolithic industry of the Franco-Cantabrian region of northern Spain and Southern France. It dates approximately 10,000–12,500 years ago. Diagnostic artifacts from the culture include projectile points (microliths with ro ...
culture. In northern Europe it was followed by variants of the Tjongerian techno-complex. It has been suggested that key Late-glacial sites in south-western Britain may be attributed to Magdalenian culture, including Kent's Cavern
Kents Cavern is a cave system in Torquay, Devon, England. It is notable for its archaeological and geological features. The cave system is open to the public and has been a geological Site of Special Scientific Interest since 1952 and a Schedu ...
.
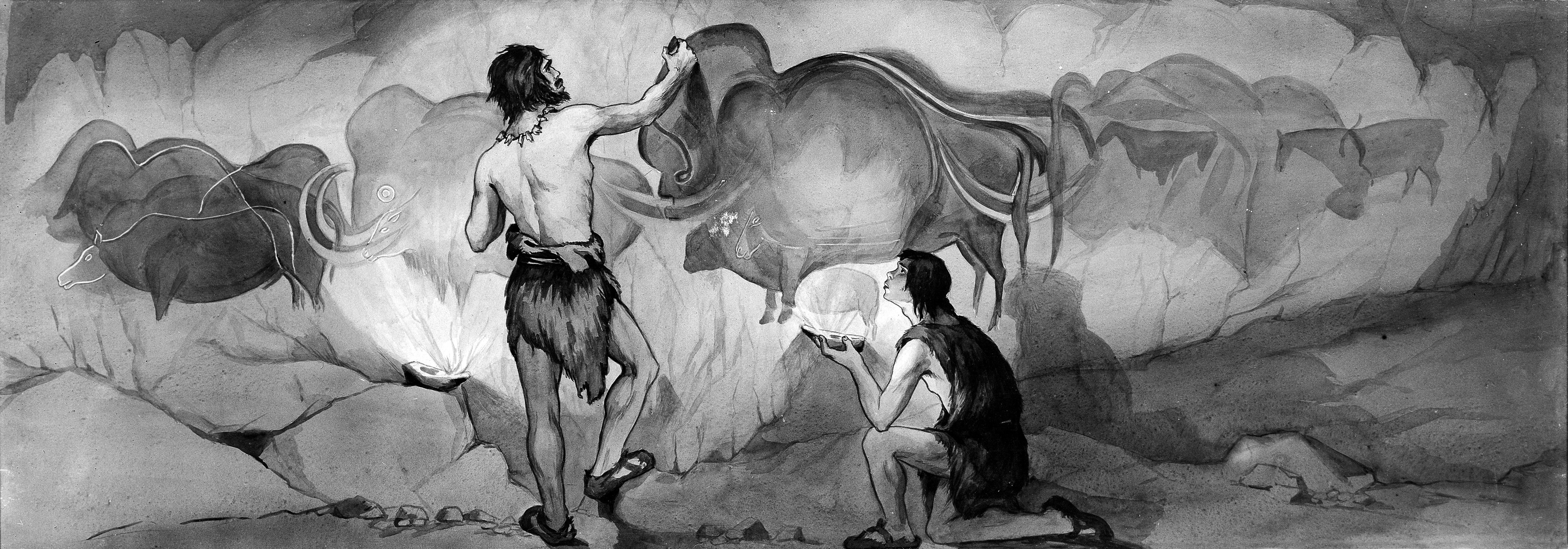
Art
schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes ...
; a seal on a bear's tooth; a fish drawn on a reindeer antler; and a complete picture, also on reindeer antler, showing horses, an aurochs, trees, and a snake biting a man's leg. The man is naked, which, together with the snake, suggests a warm climate in spite of the presence of the reindeer.
In the Tuc d'Audoubert cave, an 18-inch clay statue of two bison sculpted in relief was discovered in the deepest room, now known as the Room of the Bisons.
Examples of Magdalenian portable art include batons, figurine
A figurine (a diminutive form of the word ''figure'') or statuette is a small, three-dimensional sculpture that represents a human, deity or animal, or, in practice, a pair or small group of them. Figurines have been made in many media, with clay ...
s, and intricately engraved projectile points, as well as items of personal adornment including sea shells, perforated carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other s ...
teeth (presumably necklaces), and fossils.
Cave sites such as Lascaux
Lascaux ( , ; french: Grotte de Lascaux , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, in the department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 parietal wall paintings cover the interior walls and ceilings of ...
contain the best known examples of Magdalenian cave art. The site of Altamira
Altamira may refer to:
People
*Altamira (surname)
Places
* Cave of Altamira, a cave in Cantabria, Spain famous for its paintings and carving
*Altamira, Pará, a city in the Brazilian state of Pará
* Altamira, Huila, a town and municipality in ...
in Spain, with its extensive and varied forms of Magdalenian mobiliary art
Portable art (sometimes called mobiliary art) refers to the small examples of Prehistoric art that could be carried from place to place, which is especially characteristic of the Art of the Upper Palaeolithic and Mesolithic eras. Often made of iv ...
has been suggested to be an agglomeration site where groups of Magdalenian hunter-gatherers congregated.
Gallery
Lascaux
Lascaux ( , ; french: Grotte de Lascaux , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, in the department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 parietal wall paintings cover the interior walls and ceilings of ...
cave painting
File:Lascaux II.jpg, Lascaux cave painting
File:Lascaux 017.jpg
File:Lascaux 015.jpg
File:Lascaux-IV 01.jpg
File:Lascaux, Megaloceros.jpg
File:Lascaux2.jpg
File:Reproduction cave of Altamira 02.jpg, Altamira
Altamira may refer to:
People
*Altamira (surname)
Places
* Cave of Altamira, a cave in Cantabria, Spain famous for its paintings and carving
*Altamira, Pará, a city in the Brazilian state of Pará
* Altamira, Huila, a town and municipality in ...
cave painting
File:9 Bisonte Magdaleniense polícromo.jpg
File:Examples of supposed Magdalenian writing on bony substances Wellcome M0015751.jpg
File:Atlatls, 17-12 kya, upper from La Madeleine rockshelter, lower from Le Mas d'Azil, France - Houston Museum of Natural Science - DSC02033.JPG
File:Propulseur - Faon aux oiseaux.jpg
File:Aiguille os 246.1 Perspective.jpg
File:Magdalenian deer, bird and fish.JPG
File:Magdalenian hinds.JPG
File:Grotte d'Enlène gravures engravings Gravuren.jpg
File:Spear thrower carved as a mammothDSCF6961.jpg
File:MNP - Petroglphe 6 Pferde.jpg
File:Parc de la préhistoire - Cheval bondissant.jpg
File:Asta de ciervo tallada (51390102966).jpg
File:Magdalenian tools 17000 9000 BCE Abri de la Madeleine Tursac Dordogne France.jpg
File:Espátula en forma de pez de la cueva de El Pendo.jpg
File:Cheval de Lourdes.jpg
File:Museum für Vor- und Frühgeschichte Berlin 059.jpg
File:Biche et poissons gravés sur os - grotte de La Vache (Ariège).jpg
File:Bisons Tuc d'Audoubert Musée d'Archéologie Nationale 01042018.jpg
File:Sleeping Reindeer 3 2918856445 7d66cc4796 o.jpg
File:Laténium-dame-Monruz.jpg
Treatment of the dead
Human bones from the Magdalenian often show cut marks and breakage, consistent with cannibalism with both flesh and bone marrow being consumed. Some skulls were cleaned of soft tissues, then had the facial regions removed, with the remainingbrain case
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skul ...
retouched, possibly to make the broken edges more regular. This manipulation suggests the shaping of skulls to produce skull cup
A skull cup is a drinking vessel or eating bowl made from an inverted human calvaria that has been cut away from the rest of the skull. The use of a human skull as a drinking cup in ritual use or as a trophy is reported in numerous sources throug ...
s.

Genetics
The genes of seven Magdalenians, the El Miron Cluster in Iberia, have shown close relationship to a population who had lived in Northern Europe some 20,000 years previously. The analyses suggested that 70-80% of the ancestry of these individuals was from the population represented by Goyet Q116-1, associated with the Aurignacian culture of about 35,000 BP, from theGoyet Caves
The Goyet Caves (french: Grottes de Goyet) are a series of connected caves located in Wallonia in a limestone cliff about 15 m (50 ft) above the river Samson near the village of Mozet in the Gesves municipality of the Namur province, Belgium. The ...
in modern Belgium.
The three samples of Y-DNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abse ...
included two samples of haplogroup I and one sample of HIJK. All samples of mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
belonged to U, including five samples of U8b and one sample of U5b.
See also
* Magdalenian Girl * Swimming Reindeer *Art of the Upper Paleolithic
The art of the Upper Paleolithic represents the oldest form of prehistoric art. Figurative art is present in Europe and Southeast Asia, beginning between about 40,000 to 35,000 years ago.
Non-figurative cave paintings, consisting of hand ...
*List of Stone Age art
This is a descriptive list of Stone Age art, the period of prehistory characterised by the widespread use of stone tools. This article contains, by sheer volume of the artwork discovered, a very incomplete list of the works of the painters, sculpt ...
*Haplogroup I (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup I (M170) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is a subgroup of haplogroup IJ, which itself is a derivative of the haplogroup IJK. Subclades I1 and I2 can be found in most present-day European populations, with peaks in some Nort ...
*Pre-Celtic
The pre-Celtic period in the prehistory of Central Europe and Western Europe occurred before the expansion of the Celts or their culture in Iron Age Europe and Anatolia (9th to 6th centuries BC), but after the emergence of the Proto-Celtic lang ...
References
Notes
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * *External links
*Picture Gallery of the Paleolithic (reconstructional palaeoethnology)
Libor Balák at the Czech Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Archaeology in Brno, The Center for Paleolithic and Paleoethnological Research {{Authority control Industries (archaeology) Upper Paleolithic cultures of Europe Archaeological cultures in Belgium Archaeological cultures in the Czech Republic Archaeological cultures in France Archaeological cultures in Germany Archaeological cultures in Portugal Archaeological cultures in Spain