MAOI on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a 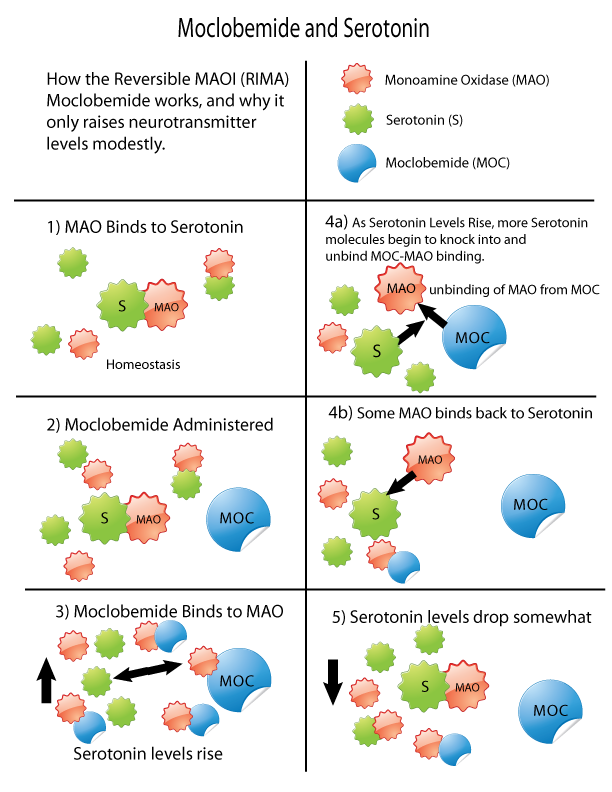
 MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of
MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of
 MAOIs act by inhibiting the activity of monoamine oxidase, thus preventing the breakdown of
MAOIs act by inhibiting the activity of monoamine oxidase, thus preventing the breakdown of
class of drugs
A drug class is a set of medications and other compounds that have a similar chemical structures, the same mechanism of action (i.e. binding to the same biological target), a related mode of action, and/or are used to treat the same disease.
In ...
that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s: monoamine oxidase A
Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOA'' gene. This gene is one of two neighboring gene family members that encode mitochondrial enzymes which catalyze the oxidative deamination of amines, ...
(MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B
Monoamine oxidase B, also known as MAOB, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOB'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the flavin monoamine oxidase family. It is an enzyme located in the outer mitochondrial membrane. ...
(MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ...
s, especially for treatment-resistant depression
Treatment-resistant depression is a term used in psychiatry to describe people with major depressive disorder (MDD) who do not respond adequately to a course of appropriate antidepressant medication within a certain time. Definitions of treatment- ...
and atypical depression
Atypical depression is defined in the ''DSM IV'' as depression that shares many of the typical symptoms of major depressive disorder or dysthymia but is characterized by improved mood in response to positive events. In contrast to those with at ...
. They are also used to treat panic disorder
Panic disorder is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, short ...
, social anxiety disorder
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impaired ability to function in at least some aspects ...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
, and several other disorders.
Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit
Inhibitor or inhibition may refer to:
In biology
* Enzyme inhibitor, a substance that binds to an enzyme and decreases the enzyme's activity
* Reuptake inhibitor, a substance that increases neurotransmission by blocking the reuptake of a neurotr ...
the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia
Dysthymia ( ), also known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD), is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically a disorder primarily of mood, consisting of similar cognitive and physical problems as major depressive disorder, but with lo ...
. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. 
Medical uses
panic disorder
Panic disorder is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, short ...
with agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by symptoms of anxiety in situations where the person perceives their environment to be unsafe with no easy way to escape. These situations can in ...
, social phobia
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impaired ability to function in at least some aspects ...
, atypical depression or mixed anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a cluster of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal function are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause physi ...
and depression, bulimia
Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging or fasting, and excessive concern with body shape and weight. The aim of this activity is to expel the body of calories eate ...
, and post-traumatic stress disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that can develop because of exposure to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats on ...
, as well as borderline personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD), also known as emotionally unstable personality disorder (EUPD), is a personality disorder characterized by a long-term pattern of unstable interpersonal relationships, distorted sense of self, and strong ...
, and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Obsession may refer to:
Psychology
* Celebrity worship syndrome, obsessive addictive disorder to a celebrity's personal and professional life
* Fixation (psychology), a persistent attachment to an object or idea
* Idée fixe (psychology), a preo ...
(OCD). MAOIs appear to be particularly effective in the management of bipolar depression
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with ...
according to a retrospective-analysis from 2009. There are reports of MAOI efficacy in obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), trichotillomania
Trichotillomania (TTM), also known as hair-pulling disorder or compulsive hair pulling, is a mental disorder characterized by a long-term urge that results in the pulling out of one's own hair. A brief positive feeling may occur as hair is remov ...
, body dysmorphic disorder
Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD), occasionally still called dysmorphophobia, is a mental disorder characterized by the obsessive idea that some aspect of one's own body part or appearance is severely flawed and therefore warrants exceptional meas ...
, and avoidant personality disorder
Avoidant personality disorder (AvPD) is a Cluster C personality disorder characterized by excessive social anxiety and inhibition, fear of intimacy (despite an intense desire for it), severe feelings of inadequacy and inferiority, and an overre ...
, but these reports are from uncontrolled case reports.
MAOIs can also be used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease by targeting MAO-B in particular (therefore affecting dopaminergic neuron
Dopaminergic cell groups, DA cell groups, or dopaminergic nuclei are collections of neurons in the central nervous system that synthesize the neurotransmitter dopamine. In the 1960s, dopaminergic neurons or ''dopamine neurons'' were first ident ...
s), as well as providing an alternative for migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hou ...
prophylaxis
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, consists of measures taken for the purposes of disease prevention.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental hea ...
. Inhibition of both MAO-A and MAO-B is used in the treatment of clinical depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introdu ...
and anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
.
MAOIs appear to be particularly indicated for outpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care ...
s with dysthymia
Dysthymia ( ), also known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD), is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically a disorder primarily of mood, consisting of similar cognitive and physical problems as major depressive disorder, but with lo ...
complicated by panic disorder or hysteroid dysphoria Hysteroid dysphoria is a name given to repeated episodes of depressed mood in response to feeling rejected.
Hysteroid dysphoria has been described in outpatient populations and is thought to be a subtype of atypical depression involving rejection s ...
Newer MAOIs such as selegiline (typically used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease) and the reversible MAOI moclobemide
Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in ...
provide a safer alternative and are now sometimes used as first-line therapy.
Side effects
Hypertensive crisis
People taking MAOIs generally need to change their diets to limit or avoid foods and beverages containingtyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-b ...
, which is found in products such as cheese, soy sauce, and salami. If large amounts of tyramine are consumed, they may develop a hypertensive crisis
Severely elevated blood pressure (equal to or greater than a systolic 180 or diastolic of 120—sometimes termed malignant or accelerated hypertension) is referred to as a hypertensive crisis, as blood pressure at this level confers a high risk ...
, which can be fatal. Examples of foods and beverages with potentially high levels of tyramine include animal liver and fermented substances, such as alcoholic beverages and aged cheeses.Mosher, Clayton James, and Scott Akins. Drugs and Drug Policy : The Control of Consciousness Alteration. Thousand Oaks, Calif.: Sage, 2007. Excessive concentrations of tyramine in blood plasma can lead to hypertensive crisis by increasing the release of norepinephrine (NE), which causes blood vessels to constrict by activating alpha-1 adrenergic receptor
alpha-1 (α1) adrenergic receptors are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) associated with the Gq heterotrimeric G protein. α1-adrenergic receptors are subdivided into three highly homologous subtypes, i.e., α1A-, α1B-, and α1D-adrenergic ...
s. Ordinarily, MAO-A would destroy the excess NE; when MAO-A is inhibited, however, NE levels get too high, leading to dangerous increases in blood pressure.
RIMAs are displaced from MAO-A in the presence of tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-b ...
, rather than inhibiting its breakdown in the liver as general MAOIs do. Additionally, MAO-B
Monoamine oxidase B, also known as MAOB, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOB'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the flavin monoamine oxidase family. It is an enzyme located in the outer mitochondrial membrane. ...
remains free and continues to metabolize tyramine in the stomach, although this is less significant than the liver action. Thus, RIMAs are unlikely to elicit tyramine-mediated hypertensive crisis; moreover, dietary modifications are not usually necessary when taking a reversible inhibitor of MAO-A (i.e., moclobemide
Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in ...
) or low doses of selective MAO-B inhibitors (e.g., selegiline 6 mg/24 hours transdermal patch).
Drug interactions
The most significant risk associated with the use of MAOIs is the potential fordrug interaction
Drug interactions occur when a drug's mechanism of action is disturbed by the concomitant administration of substances such as foods, beverages, or other drugs. The cause is often the inhibition of the specific receptors available to the drug, ...
s with over-the-counter, prescription, or illegally obtained medications, and some dietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
s (e.g., St. John's wort
''Hypericum perforatum'', known as St. John's wort, is a flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae and the type species of the genus ''Hypericum''.
Possibly a hybrid between ''Hypericum maculatum, H. maculatum'' and ''Hypericum attenuatum, H. ...
, tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic ...
). It is vital that a doctor supervise such combinations to avoid adverse reactions. For this reason, many users carry an MAOI-card, which lets emergency medical personnel know what drugs to avoid (e.g. adrenaline pinephrinedosage should be reduced by 75%, and duration is extended.)
Tryptophan supplements can be consumed with MAOIs, but can result in transient serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a group of symptoms that may occur with the use of certain serotonergic medications or drugs. The degree of symptoms can range from mild to severe, including a potentiality of death. Symptoms in mild cases include high ...
.
MAOIs should not be combined with other psychoactive substances (antidepressants, painkillers, stimulants, including prescribed, OTC and illegally acquired drugs, etc.) except under expert care. Certain combinations can cause lethal reactions; common examples including SSRI
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellul ...
s, tricyclics
Tricyclics are chemical compounds that contain three interconnected rings of atoms.
Many compounds have a tricyclic structure, but in pharmacology, the term has traditionally been reserved to describe heterocyclic drugs. Among these are ant ...
, MDMA
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly seen in Tablet (pharmacy), tablet form (ecstasy) and crystal form (molly or mandy), is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant properties primarily used for Recreational dru ...
, meperidine
Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisl ...
, tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Ultram among others, is an opioid pain medication used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an ...
, dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a medication most often used as a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It is sold in syrup, tablet, spray, and lozenge forms. In 2022, the FDA approved a formulation of it combined with bu ...
, LSD
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known colloquially as acid, is a potent psychedelic drug. Effects typically include intensified thoughts, emotions, and sensory perception. At sufficiently high dosages LSD manifests primarily mental, vi ...
, Psilocybin
Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P.&nbs ...
, and DMT. Drugs that affect the release or reuptake of epinephrine, norepinephrine, or dopamine typically need to be administered at lower doses due to the resulting potentiated and prolonged effect. MAOIs also interact with tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
-containing products (e.g. cigarettes) and may potentiate the effects of certain compounds in tobacco. This may be reflected in the difficulty of smoking cessation, as tobacco contains naturally occurring MAOI compounds in addition to the nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
.
While safer than general MAOIs, still possess significant and potentially serious drug interactions with many common drugs; in particular, they can cause serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a group of symptoms that may occur with the use of certain serotonergic medications or drugs. The degree of symptoms can range from mild to severe, including a potentiality of death. Symptoms in mild cases include high ...
or hypertensive crisis when combined with almost any antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ...
or stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
, common migraine medications, certain herbs, or most cold medicines (including decongestant
A decongestant, or nasal decongestant, is a type of pharmaceutical drug that is used to relieve nasal congestion in the upper respiratory tract. The active ingredient in most decongestants is either pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine (the latter ...
s, antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provid ...
s, and cough syrup
Cold medicines are a group of medications taken individually or in combination as a treatment for the symptoms of the common cold and similar conditions of the upper respiratory tract. The term encompasses a broad array of drugs, including ...
).
Ocular alpha-2 agonists such as brimonidine and apraclonidine
Apraclonidine ( INN), also known under the brand name Iopidine, is a sympathomimetic used in glaucoma therapy. It is an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist and a weak α1 adrenergic receptor agonist.
Topical apraclonidine is administered at a conc ...
are glaucoma medications which reduce intraocular pressure by decreasing aqueous production. These alpha-2 agonists should not be given with oral MAOIs due to the risk of hypertensive crisis.
Withdrawal
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, heada ...
including MAOIs have some dependence-producing effects, the most notable one being a discontinuation syndrome, which may be severe especially if MAOIs are discontinued abruptly or too rapidly. The dependence-producing potential of MAOIs or antidepressants in general is not as significant as benzodiazepines, however. Discontinuation symptoms can be managed by a gradual reduction in dosage over a period of days, weeks or sometimes months to minimize or prevent withdrawal symptoms.
MAOIs, as with most antidepressant medication, may not alter the course of the disorder in a significant, permanent way, so it is possible that discontinuation can return the patient to the pre-treatment state. This consideration complicates prescribing between an MAOI and an SSRI, because it is necessary to clear the system completely of one drug before starting another. One physician organization recommends the dose to be tapered down over a minimum of four weeks, followed by a two-week washout period. The result is that a depressed patient will have to bear the depression without chemical help during the drug-free interval. This may be preferable to risking the effects of an interaction between the two drugs.
Mechanism of action
 MAOIs act by inhibiting the activity of monoamine oxidase, thus preventing the breakdown of
MAOIs act by inhibiting the activity of monoamine oxidase, thus preventing the breakdown of monoamine neurotransmitter
Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromaticity, aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
All mo ...
s and thereby increasing their availability. There are two isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isof ...
s of monoamine oxidase, MAO-A and MAO-B. MAO-A preferentially deaminates serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vas ...
, melatonin, epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
, and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad'', ...
. MAO-B preferentially deaminates phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amin ...
and certain other trace amine
Trace amines are an endogenous group of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonists – and hence, monoaminergic neuromodulators – that are structurally and metabolically related to classical monoamine neurotransmitters. Compared to the ...
s; in contrast, MAO-A preferentially deaminates other trace amines, like tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-b ...
, whereas dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
is equally deaminated by both types.
Reversibility
The early MAOIs covalently bound to the monoamine oxidase enzymes, thus inhibiting them irreversibly; the bound enzyme could not function and thus enzyme activity was blocked until the cell made new enzymes. The enzymes turn over approximately every two weeks. A few newer MAOIs, a notable one beingmoclobemide
Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in ...
, are reversible, meaning that they are able to detach from the enzyme to facilitate usual catabolism
Catabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that breaks down molecules into smaller units that are either oxidized to release energy or used in other anabolic reactions. Catabolism breaks down large molecules (such as polysaccharides, lipids, ...
of the substrate. The level of inhibition in this way is governed by the concentrations of the substrate and the MAOI.
Harmaline
Harmaline is a fluorescent indole alkaloid from the group of harmala alkaloids and beta-carbolines. It is the partly hydrogenated form of harmine.
Occurrence in nature
Various plants contain harmaline including ''Peganum harmala'' (Syrian rue) ...
found in ''Peganum harmala
''Peganum harmala'', commonly called wild rue, Syrian rue, African rue, esfand or espand,Mahmoud OmidsalaEsfand: a common weed found in Persia, Central Asia, and the adjacent areasEncyclopedia Iranica Vol. VIII, Fasc. 6, pp. 583–584. Originall ...
'', ''Banisteriopsis caapi
''Banisteriopsis caapi'', also known as ayahuasca, caapi, soul vine, or yagé (yage), is a South American liana of the family Malpighiaceae. It is one half of ayahuasca, a decoction with a long history of its entheogenic (connecting to spirit) us ...
'', and '' Passiflora incarnata'' is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA).
Selectivity
In addition to reversibility, MAOIs differ by their selectivity of the MAO enzyme subtype. Some MAOIs inhibit both MAO-A and MAO-B equally, other MAOIs have been developed to target one over the other. MAO-A inhibition reduces the breakdown of primarily serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; selective inhibition of MAO-A allows fortyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-b ...
to be metabolised via MAO-B. Agents that act on serotonin if taken with another serotonin-enhancing agent may result in a potentially fatal interaction called serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a group of symptoms that may occur with the use of certain serotonergic medications or drugs. The degree of symptoms can range from mild to severe, including a potentiality of death. Symptoms in mild cases include high ...
or with irreversible and unselective inhibitors (such as older MAOIs), of MAO a hypertensive crisis
Severely elevated blood pressure (equal to or greater than a systolic 180 or diastolic of 120—sometimes termed malignant or accelerated hypertension) is referred to as a hypertensive crisis, as blood pressure at this level confers a high risk ...
as a result of tyramine food interactions is particularly problematic with older MAOIs. Tyramine is broken down by MAO-A and MAO-B, therefore inhibiting this action may result in its excessive build-up, so diet must be monitored for tyramine intake.
MAO-B inhibition reduces the breakdown mainly of dopamine and phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amin ...
so there are no dietary restrictions associated with this. MAO-B would also metabolize tyramine, as the only differences between dopamine, phenethylamine, and tyramine are two phenylhydroxyl groups on carbons 3 and 4. The 4-OH would not be a steric hindrance to MAO-B on tyramine. Selegiline is selective for MAO-B at low doses, but non-selective at higher doses.
History
The knowledge of MAOIs began with the serendipitous discovery thatiproniazid
Iproniazid (Marsilid, Rivivol, Euphozid, Iprazid, Ipronid, Ipronin) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It is a xenobiotic that was originally designed to treat tuberculosis, but was lat ...
was a potent MAO inhibitor (MAOI). Originally intended for the treatment of tuberculosis, in 1952, iproniazid's antidepressant properties were discovered when researchers noted that the depressed patients given iproniazid experienced a relief of their depression. Subsequent in vitro work led to the discovery that it inhibited MAO and eventually to the monoamine theory of depression. MAOIs became widely used as antidepressants in the early 1950s. The discovery of the 2 isoenzymes of MAO has led to the development of selective MAOIs that may have a more favorable side-effect profile.
The older MAOIs' heyday was mostly between the years 1957 and 1970. The initial popularity of the 'classic' non-selective irreversible MAO inhibitors began to wane due to their serious interactions with sympathomimetic
Sympathomimetic drugs (also known as adrenergic drugs and adrenergic amines) are stimulant compounds which mimic the effects of endogenous agonists of the sympathetic nervous system. Examples of sympathomimetic effects include increases in hea ...
drugs and tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-b ...
-containing foods that could lead to dangerous hypertensive emergencies. As a result, the use by medical practitioners of these older MAOIs declined. When scientists discovered that there are two different MAO enzymes (MAO-A and MAO-B), they developed selective compounds for MAO-B, (for example, selegiline, which is used for Parkinson's disease), to reduce the side-effects and serious interactions. Further improvement occurred with the development of compounds (moclobemide
Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in ...
and toloxatone
Toloxatone (Humoryl) is an antidepressant launched in 1984 in France by Sanofi Aventis for the treatment of depression. It was discontinued in 2002. It acts as a selective reversible inhibitor of MAO-A
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) ...
) that not only are selective but cause reversible MAO-A inhibition and a reduction in dietary and drug interactions. Moclobemide
Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in ...
, was the first reversible inhibitor of MAO-A to enter widespread clinical practice.
A transdermal patch form of the MAOI selegiline, called Emsam
Selegiline, also known as L-deprenyl and sold under the brand names Eldepryl and Emsam among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and major depressive disorder. It is provided in the form of a capsule o ...
, was approved for use in depression by the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
on 28 February 2006.
List of MAO inhibiting drugs
Marketed MAOIs
* Nonselective MAO-A/MAO-B inhibitors **Hydrazine (antidepressant)
The hydrazine antidepressants are a group of non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) which were discovered and initially marketed in the 1950s and 1960s. Most have been withdrawn due to toxicity, namely hepatotoxicity, ...
*** Iproniazid
Iproniazid (Marsilid, Rivivol, Euphozid, Iprazid, Ipronid, Ipronin) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It is a xenobiotic that was originally designed to treat tuberculosis, but was lat ...
(Marsilid, Iprozid, Ipronid, Rivivol, Propilniazida) (available in France)
***Isocarboxazid
Isocarboxazid (Marplan, Marplon, Enerzer) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs s ...
(Marplan)
*** Hydracarbazine
***Phenelzine
Phenelzine, sold under the brand name Nardil, among others, is a non-selective and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class which is primarily used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic. Along with tranylcypromine an ...
(Nardil, Nardelzine)
** Non-hydrazines
*** Tranylcypromine
Tranylcypromine, sold under the brand name Parnate among others,Drugs.co Page accessed April 17, 2016 is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). More specifically, tranylcypromine acts as nonselective and irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme mono ...
(Parnate, Jatrosom)
* Selective MAO-A inhibitors
** Bifemelane
Bifemelane (INN) (Alnert, Celeport), or bifemelane hydrochloride (JAN), also known as 4-(''O''-benzylphenoxy)-''N''-methylbutylamine, is an antidepressant and cerebral activator that is widely used in the treatment of cerebral infarction patient ...
(Alnert, Celeport) (available in Japan)
** Methylthioninium chloride
Methylthioninium chloride, commonly called methylene blue, is a salt used as a dye and as a medication. Methylene blue is a thiazine dye. As a medication, it is mainly used to treat methemoglobinemia by converting the ferric iron in hemoglob ...
(Urelene blue, Provayblue, Proveblue)
** Moclobemide
Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in ...
(Aurorix, Manerix, Moclamine)
** Pirlindole
Pirlindole (Lifril, Pyrazidol) is mainly a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) and secondly a SNRI which was developed and is used in Russia as an antidepressant. It is structurally and pharmacologically related to metralindole. ...
(Pirazidol) (available in Russia)
* Selective MAO-B inhibitors
** Rasagiline
Rasagiline (Azilect, Azipron) is an irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase-B used as a monotherapy to treat symptoms in early Parkinson's disease or as an adjunct therapy in more advanced cases.
The racemic form of the drug was invented b ...
(Azilect)
** Selegiline (Deprenyl, Eldepryl, Emsam, Zelapar)
** Safinamide
Safinamide (INN; brand name Xadago) is a drug used as an add-on treatment for Parkinson's disease with "off" episodes; it has multiple modes of action, including the inhibition of monoamine oxidase B. SeFDA index page for NDA 207145for updates ...
(Xadago)
Linezolid
Linezolid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci, van ...
is an antibiotic drug with weak, reversible MAO-inhibiting activity.
Methylthioninium chloride (methylene blue
Methylthioninium chloride, commonly called methylene blue, is a salt used as a dye and as a medication. Methylene blue is a thiazine dye. As a medication, it is mainly used to treat methemoglobinemia by converting the ferric iron in hemoglobin ...
), the antidote indicated for drug-induced methemoglobinemia on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health ...
, among a plethora of other off-label uses, is a highly potent, reversible MAO inhibitor.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved these MAOIs to treat depression:
* Isocarboxazid (Marplan)
* Phenelzine (Nardil)
* Selegiline (Emsam)
* Tranylcypromine (Parnate)
MAOIs that have been withdrawn from the market
* Nonselective MAO-A/MAO-B inhibitors **Hydrazines
Hydrazines (R2N−NR2) are a class of chemical compounds with two nitrogen atoms linked via a covalent bond and which carry from one up to four alkyl or aryl substituents. Hydrazines can be considered as derivatives of the inorganic hydrazine ( ...
***Benmoxin
Benmoxin (trade names Neuralex, Nerusil), also known as mebamoxine, is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It was synthesized in 1967 and was subsequently used as an antidepressant in E ...
(Nerusil, Neuralex)
*** Iproclozide (Sursum)
*** Mebanazine
Mebanazine (trade name Actomol) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was previously used as an antidepressant in the 1960s, but has since been withdrawn drug, withdrawn due to hepatotoxicity.
Mebanazine in ...
(Actomol)
*** Nialamide
Nialamide (Niamid, Niamide, Nuredal, Surgex) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class that was used as an antidepressant. It was withdrawn by Pfizer several decades ago due to the risk of hepa ...
(Niamid)
*** Octamoxin (Ximaol, Nimaol)
***Pheniprazine
Pheniprazine (INN; also known as amphethydrazine and amphetamine hydrazide; brand names Catron and Cavodil; codename JB-516) is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was used ...
(Catron)
***Phenoxypropazine
Phenoxypropazine (trade name Drazine) is an irreversible and non- selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine family. It was introduced as an antidepressant in 1961, but was subsequently withdrawn in 1966 due to hepatotoxici ...
(Drazine)
*** Pivalylbenzhydrazine (Tersavid)
***Safrazine
Safrazine (Safra) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class that was introduced as an antidepressant in the 1960s, but has since been discontinued.
See also
* Hydrazine (antidepressant)
T ...
(Safra) (discontinued worldwide except for Japan)
** Non-hydrazines
*** Caroxazone (Surodil, Timostenil)
*Selective MAO-A inhibitors
**Minaprine
Minaprine ( INN, USAN, BAN) (brand names Brantur, Cantor) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressant drug that was used in France for the treatment of depression until it was withdrawn from the market in 1996 because it caused convulsion ...
(Cantor)
** Toloxatone
Toloxatone (Humoryl) is an antidepressant launched in 1984 in France by Sanofi Aventis for the treatment of depression. It was discontinued in 2002. It acts as a selective reversible inhibitor of MAO-A
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) ...
(Humoryl)
List of RIMAs
Marketed pharmaceuticals *Moclobemide
Moclobemide, sold under the brand names Amira, Aurorix, Clobemix, Depnil and Manerix among others, is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) drug primarily used to treat depression and social anxiety. It is not approved for use in ...
(Aurorix, Manerix, Moclamine)
Other pharmaceuticals
* Brofaromine (Consonar)
* Caroxazone (Surodil, Timostenil)
* Eprobemide (Befol)
* Methylene blue
Methylthioninium chloride, commonly called methylene blue, is a salt used as a dye and as a medication. Methylene blue is a thiazine dye. As a medication, it is mainly used to treat methemoglobinemia by converting the ferric iron in hemoglobin ...
* Metralindole
Metralindole (Inkazan) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) which was investigated in Russia as a potential antidepressant. It is structurally
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a mat ...
(Inkazan)
* Minaprine
Minaprine ( INN, USAN, BAN) (brand names Brantur, Cantor) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressant drug that was used in France for the treatment of depression until it was withdrawn from the market in 1996 because it caused convulsion ...
(Cantor)
* Pirlindole
Pirlindole (Lifril, Pyrazidol) is mainly a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) and secondly a SNRI which was developed and is used in Russia as an antidepressant. It is structurally and pharmacologically related to metralindole. ...
(Pirazidol)
Naturally occurring RIMAs in plants
* Curcumin
Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the ''Curcuma longa'' species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric (''Curcuma longa''), a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmetic ...
(selectivity for MAO-A and reliability of research on curcumin are disputed)
* Harmaline
Harmaline is a fluorescent indole alkaloid from the group of harmala alkaloids and beta-carbolines. It is the partly hydrogenated form of harmine.
Occurrence in nature
Various plants contain harmaline including ''Peganum harmala'' (Syrian rue) ...
* Harmine
Harmine is a beta-carboline and a harmala alkaloid. It occurs in a number of different plants, most notably the Syrian rue and ''Banisteriopsis caapi''. Harmine reversibly inhibits monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), an enzyme which breaks down monoamin ...
* Rosiridin
Rosiridin is a chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule cons ...
(''in vitro'')
Research compounds
* Amiflamine
Amiflamine (FLA-336) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), thereby being a RIMA, and, to a lesser extent, semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO), as well as a serotonin releasing agent (SRA). It is a derivative of the p ...
(FLA-336)
* Befloxatone
Befloxatone (MD-370,503) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A.
References
Reversible inhibitors of MAO-A
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Trifluoromethyl compounds
Secondary alcohols
3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-oxazolidinones
{ ...
(MD-370,503)
* Cimoxatone
Cimoxatone (MD 780515) is a reversible inhibitor of MAO-A (RIMA). It has a significant food interaction–related adverse effect in combination with tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a na ...
(MD-780,515)
* Esuprone
Esuprone is an experimental drug candidate being investigated as an antidepressant. It acts as a monoamine oxidase A
Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOA'' gene. This gene is one of tw ...
* Sercloremine (CGP-4718-A)
* Tetrindole
Tetrindole was a drug candidate that functions by reversibly inhibiting monoamine oxidase A
Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOA'' gene. This gene is one of two neighboring gene family ...
* CX157 (TriRima)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Antidepressants