Métu'alis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lebanese Shia Muslims ( ar, المسلمون الشيعة اللبنانيين), historically known as ''matāwila'' ( ar, متاولة, plural of ''mutawālin'' ebanese pronounced as ''metouali'' refers to
/ref> Most of its adherents live in the northern and western area of the


 Historical Accounts
The territories of present-day Lebanon register less than neighboring regions in the historical accounts from the Abbasid and Fatimid eras. Persian traveler Nasir Khusraw's presents a unique account of Tyre and Tripoli during his visit in 1040s, describing them as being majority Shia Muslim with dedicated Shia shrines on the outskirts. Several Tyrian Shiite figures are mentioned more than a century earlier; these include Muhammad bin Ibrahim as-Souri (fl. 883 CE) and Abbasid-era poet Abdul Muhsin as-Souri (b. 950 CE), a student of Al-Shaykh Al-Mufid.
Some of the earlier accounts for inner Jabal Amel are given by Al-Maqdisi (c. 966–985), who mentions that half of Hunin and
Historical Accounts
The territories of present-day Lebanon register less than neighboring regions in the historical accounts from the Abbasid and Fatimid eras. Persian traveler Nasir Khusraw's presents a unique account of Tyre and Tripoli during his visit in 1040s, describing them as being majority Shia Muslim with dedicated Shia shrines on the outskirts. Several Tyrian Shiite figures are mentioned more than a century earlier; these include Muhammad bin Ibrahim as-Souri (fl. 883 CE) and Abbasid-era poet Abdul Muhsin as-Souri (b. 950 CE), a student of Al-Shaykh Al-Mufid.
Some of the earlier accounts for inner Jabal Amel are given by Al-Maqdisi (c. 966–985), who mentions that half of Hunin and
 The three Shia principalities underwent different historical trajectories. The Harfush initially did not challenge the new Ottoman authority, but in 1518 the Ottomans executed an anonymous Ibn Harfush, governor of Baalbek, along with the Bedouin Emir Ibn al-Hanash for acting against the state. At their high-point, Harfush domains extended from the Beqaa valley into Palmyra far in the
The three Shia principalities underwent different historical trajectories. The Harfush initially did not challenge the new Ottoman authority, but in 1518 the Ottomans executed an anonymous Ibn Harfush, governor of Baalbek, along with the Bedouin Emir Ibn al-Hanash for acting against the state. At their high-point, Harfush domains extended from the Beqaa valley into Palmyra far in the  In 1781, Shia autonomy diminished under Ahmad Pasha al-Jazzar (1776–1804), nicknamed the butcher. Al-Jazzar was initially on good terms with Nassif, but their alliance reached a bad point some time in 1781. Afterward, al-Jazzar defeated and killed Nassif and 470 of his men in battle, proceeding to conquer Shia-held fortress towns and eliminate all the leading Shia sheikhs of Jabal Amel, whose families were allowed to take refuge with the Harfushes in Baalbek. He proceeded to burn down Shia religious libraries, transport Shia religious books to the ovens in Acre, and paraded the heads of the fallen in Sidon. Following their crisis, insurgency commenced at the hands of local militias which attacked al-Jazzar's troops in the region. The period witnessed swift uprisings in
In 1781, Shia autonomy diminished under Ahmad Pasha al-Jazzar (1776–1804), nicknamed the butcher. Al-Jazzar was initially on good terms with Nassif, but their alliance reached a bad point some time in 1781. Afterward, al-Jazzar defeated and killed Nassif and 470 of his men in battle, proceeding to conquer Shia-held fortress towns and eliminate all the leading Shia sheikhs of Jabal Amel, whose families were allowed to take refuge with the Harfushes in Baalbek. He proceeded to burn down Shia religious libraries, transport Shia religious books to the ovens in Acre, and paraded the heads of the fallen in Sidon. Following their crisis, insurgency commenced at the hands of local militias which attacked al-Jazzar's troops in the region. The period witnessed swift uprisings in
 On the other hand, Shia cleric Abdul Husayn Sharafeddine had organized and lead
On the other hand, Shia cleric Abdul Husayn Sharafeddine had organized and lead
 From late 1940s onward, many Shias moved to the Beirut and its suburbs. This influx increased in the late 60s and 70s following the
From late 1940s onward, many Shias moved to the Beirut and its suburbs. This influx increased in the late 60s and 70s following the
Lebanese people
The Lebanese people ( ar, الشعب اللبناني / ALA-LC: ', ) are the people inhabiting or originating from Lebanon. The term may also include those who had inhabited Mount Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains prior to the creation ...
who are adherents of the Shia branch of Islam in Lebanon, which plays a major role along Lebanon's main Sunni, Maronite and Druze sects. Shia Islam in Lebanon has a history of more than a millennium. According to the ''CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
'', Shia Muslims constituted an estimated 28% of Lebanon's population in 2018."Lebanon: people and society"/ref> Most of its adherents live in the northern and western area of the
Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
, Southern Lebanon and Beirut. The great majority of Shia Muslims in Lebanon are Twelvers. However, a small minority of them are Alawites and Ismaili
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-Sa ...
.
Under the terms of an unwritten agreement known as the National Pact
The National Pact ( ar, الميثاق الوطني, translit-std=DIN, translit=al Mithaq al Watani) is an unwritten agreement that laid the foundation of Lebanon as a multiconfessional state following negotiations between the Shia, Sunni, and Ma ...
between the various political and religious leaders of Lebanon, Shias are the only sect eligible for the post of Speaker of Parliament
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hungerfo ...
.
History


Origins
The cultural and linguistic heritage of theLebanese people
The Lebanese people ( ar, الشعب اللبناني / ALA-LC: ', ) are the people inhabiting or originating from Lebanon. The term may also include those who had inhabited Mount Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains prior to the creation ...
is a blend of both indigenous elements and the foreign cultures that have come to rule the land and its people over the course of thousands of years. In a 2013 interview the lead investigator, Pierre Zalloua
Pierre Zalloua ( ar, بيار زلّوعة) is a Lebanese biologist. His contributions to biology include numerous researches in genetic predisposition to diseases such as type 1 diabetes and β-thalassemia. He is most noted for taking part in ...
, pointed out that genetic variation preceded religious variation and divisions: "Lebanon already had well-differentiated communities with their own genetic peculiarities, but not significant differences, and religions came as layers of paint on top. There is no distinct pattern that shows that one community carries significantly more Phoenician than another."
Lebanon throughout its history was home of many historic peoples who inhabited the region. The Lebanese coast was mainly inhabited by Phoenician Canaanites throughout the Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
and Iron ages, who built the cities of Tyre, Sidon, Byblos and Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
, which was founded as a center of a confederation between Aradians, Sidonians, and Tyrians. Further east, the Bekaa valley was known as '' Amqu'' in the Bronze Age, and was part of Amorite kingdom of Qatna and later Amurru kingdom, and had local city-states such as Enišasi
Enišasi, was a city, or city-state located in the Beqaa Valley-(called '' Amqu'', or ''Amka'') of Lebanon, during the 1350-1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Of the 382–Amarna letters, Enišasi is only referenced in two letters. Enišas ...
. During the Iron Age, the Bekaa was dominated by the Aramaeans
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean h ...
, who formed kingdoms nearby in Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
and Hamath
, timezone = EET
, utc_offset = +2
, timezone_DST = EEST
, utc_offset_DST = +3
, postal_code_type =
, postal_code =
, ar ...
, and established the kingdom of Aram-Zobah where Hazael might have been born, and was later also settled by Itureans
Iturea ( grc, Ἰτουραία, ''Itouraía'') is the Greek name of a Levantine region north of Galilee during the Late Hellenistic and early Roman periods. It extended from Mount Lebanon across the plain of Marsyas to the Anti-Lebanon Mount ...
, who were likely Arabs themselves. These Itureans inhabited the hills above Tyre in Southern Lebanon, historically known as Jabal Amel, since at least the times of Alexander the Great, who fought them after they blocked his army's access to wood supply.
During Roman rule, Aramaic became the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
of the entire Levant and Lebanon, replacing spoken Phoenician on the coast, while Greek was used as language of administration, education and trading. It is important to note that most villages and towns in Lebanon today have Aramaic names, reflecting this heritage. However, Beirut became the only fully Latin speaking city in the whole east. The Iturean Kingdom of Chalcis became vassal state of the Romans after they consolidated their rule over most of the Levant in 64 BC, and at their peak they managed to impose control on much of the Phoenician coast and Galilee including southern Lebanon, until the Romans fully incorporated them in 92 CE. On the coast, Tyre prospered under the Romans and was allowed to keep much of its independence as a "civitas foederata A ''civitas foederata'', meaning "allied state/community", was the most elevated type of autonomous cities and local communities under Roman rule.
Each Roman province comprised a number of communities of different status. Alongside Roman colonies o ...
". On the other hand, Jabal Amel was inhabited by Banu Amilah
Banu 'Amilah ( ar, بَنُو عَامِلَة, '), also spelled Amelah, were an Arab tribe that inhabited the historic region of Jabal Amel in present day Southern Lebanon. Lebanese Shia Muslims of Southern Lebanon hail the tribe as their proge ...
, its namesake, who have particular importance for the Lebanese Shia for adopting and nurturing Shi'ism in the southern population. The Banu Amilah were part of the Nabataean Arab ''foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign stat ...
'' of the Roman Empire, and they were connected to other pre-Islamic Arabs such as Judham and Balqayn Banū al-Qayn () (also spelled Banūʾl Qayn, Balqayn or al-Qayn ibn Jasr) were an Arab tribe that was active between the early Roman Empire, Roman era in the Near East through the early Islamic era (7th–8th centuries CE), as far as the historical ...
, whose presence in the region likely dates back to Biblical times according to Irfan Shahîd
Irfan Arif Shahîd ( ar, عرفان عارف شهيد ; Nazareth, Mandatory Palestine, January 15, 1926 – Washington, D.C., November 9, 2016), born as Erfan Arif Qa'war (), was a scholar in the field of Oriental studies. He was from 1982 unti ...
. As the Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant ( ar, فَتْحُ الشَّام, translit=Feth eş-Şâm), also known as the Rashidun conquest of Syria, occurred in the first half of the 7th century, shortly after the rise of Islam."Syria." Encyclopædia Br ...
reached Lebanon, these Arab tribes received the most power which encouraged the non-Arabic-speaking population to adopt Arabic as the main language.
Early Islamic period
In historian Jaafar al-Muhajir's assessment, the spread of Shia Islam in Lebanon and the Levant was a complex, multi-layered process throughout history. Accordingly, the presence of pro-Alid tribes such asHamdan
Hamdan ( ar, حمدان ') is a name of Arab origin of aristocratic descent and many political ties within the middle east and the Arab World, controlling import/export mandates over port authorities.
Among people named Hamdan include:
Given nam ...
and Madh'hij in the region, possibly after the Hasan–Muawiya treaty in 661 CE, likely acted as a vector that facilitated the spread of Shi'ism among segments of the local populations living among them in Jabal Amel, Galilee, Beqaa valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
, Tyre and Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
, where anti-state sentiment was common due to the discrimination and ongoing marginalization of the region under the Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
. Among the locals were Banu Amilah
Banu 'Amilah ( ar, بَنُو عَامِلَة, '), also spelled Amelah, were an Arab tribe that inhabited the historic region of Jabal Amel in present day Southern Lebanon. Lebanese Shia Muslims of Southern Lebanon hail the tribe as their proge ...
, an Arab tribe that inhabited Jabal Amel in the 7th century CE. According to Husayn Muruwwa
''Husayn Muruwwa'' (also spelt ''Hussein Mroue'' or ''Mroueh'') (1908/1910-February 17, 1987) was a Lebanese Marxist intellectual, journalist, author, and literary critic. His longest and most famous work, "Materialist Tendencies in Arabic-Islami ...
, Shiism was one option among many for the communities of Jabal Amel, but for them, a positive and inviting dialectical relationship between the theological construct of Imamism
Twelver Shīʿīsm ( ar, ٱثْنَا عَشَرِيَّة; '), also known as Imāmīyyah ( ar, إِمَامِيَّة), is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, comprising about 85 percent of all Shīʿa Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers t ...
and its social milieu gave precedence to the Shiite possibility. Such a transformation may have been attested in Homs
Homs ( , , , ; ar, حِمْص / ALA-LC: ; Levantine Arabic: / ''Ḥomṣ'' ), known in pre-Islamic Syria as Emesa ( ; grc, Ἔμεσα, Émesa), is a city in western Syria and the capital of the Homs Governorate. It is Metres above sea level ...
whereby according to Yaqut al-Hamawi, the people of the city were strong supporters of the Umayyads, but became adamant, ghulat
The ( ar, غلاة, 'exaggerators', 'extremists', 'transgressors', singular ) were a branch of early Shi'i Muslims thus named by other Shi'i and Sunni Muslims for their purportedly 'exaggerated' veneration of the prophet Muhammad (–632) and his ...
Shiites after their demise in 750. Prominent Emesene Shiites figure in the late 8th century, including Abd al-Salam al-Homsi (777–850 CE), a notable Shia poet who never left his native Homs.
Millenialist expectations increased upon the deep crisis of the Abbasid dynasty during the decade-long Anarchy at Samarra (c. 861–870), the rise of breakaway and autonomous regimes in the provinces, the large-scale Zanj Rebellion (c. 869–883), all of which increased the appeal to Isma'ilism, and moreover the establishment of Qarmatian
The Qarmatians ( ar, قرامطة, Qarāmiṭa; ) were a militant Isma'ili Shia movement centred in al-Hasa in Eastern Arabia, where they established a religious-utopian socialist state in 899 CE. Its members were part of a movement that adhe ...
Isma'ilis in 899 in Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, and the rise of the Twelver Shiite Hamdanids in 890 which further elevated Twelver prestige and following.
 Historical Accounts
The territories of present-day Lebanon register less than neighboring regions in the historical accounts from the Abbasid and Fatimid eras. Persian traveler Nasir Khusraw's presents a unique account of Tyre and Tripoli during his visit in 1040s, describing them as being majority Shia Muslim with dedicated Shia shrines on the outskirts. Several Tyrian Shiite figures are mentioned more than a century earlier; these include Muhammad bin Ibrahim as-Souri (fl. 883 CE) and Abbasid-era poet Abdul Muhsin as-Souri (b. 950 CE), a student of Al-Shaykh Al-Mufid.
Some of the earlier accounts for inner Jabal Amel are given by Al-Maqdisi (c. 966–985), who mentions that half of Hunin and
Historical Accounts
The territories of present-day Lebanon register less than neighboring regions in the historical accounts from the Abbasid and Fatimid eras. Persian traveler Nasir Khusraw's presents a unique account of Tyre and Tripoli during his visit in 1040s, describing them as being majority Shia Muslim with dedicated Shia shrines on the outskirts. Several Tyrian Shiite figures are mentioned more than a century earlier; these include Muhammad bin Ibrahim as-Souri (fl. 883 CE) and Abbasid-era poet Abdul Muhsin as-Souri (b. 950 CE), a student of Al-Shaykh Al-Mufid.
Some of the earlier accounts for inner Jabal Amel are given by Al-Maqdisi (c. 966–985), who mentions that half of Hunin and Qadas
Qadas (also Cadasa; ar, قدس) was a Palestinian village located 17 kilometers northeast of Safad that was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. One of seven Shia Muslim villages, called ''Metawalis'', that fell within the boundaries of ...
inhabitants were Shia Muslims. Al-Maqdisi also relays important accounts regarding the predominance of Shiite Muslims in Tiberias, which lay within historical Jabal Amel. Tiberias was the home of Alid
The Alids are those who claim descent from the '' rāshidūn'' caliph and Imam ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib (656–661)—cousin, son-in-law, and companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad—through all his wives. The main branches are the (inc ...
families during the 10th century and also home to the Ash'ari tribe of Madh'hij who founded Qom
Qom (also spelled as "Ghom", "Ghum", or "Qum") ( fa, قم ) is the seventh largest metropolis and also the seventh largest city in Iran. Qom is the capital of Qom Province. It is located to the south of Tehran. At the 2016 census, its popul ...
, one of the holy cities of Shia Islam, in 703, as al-Ya'qubi notes during his travels in the 880s; Tiberias was also the home of a prominent Alid figure who was killed by al-Ikhshid on the charge of being sympathetic with the Qarmatians in 903. Shiites also reportedly formed half of the population of Nablus
Nablus ( ; ar, نابلس, Nābulus ; he, שכם, Šəḵem, ISO 259-3: ; Samaritan Hebrew: , romanized: ; el, Νεάπολις, Νeápolis) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a populati ...
and most of Amman
Amman (; ar, عَمَّان, ' ; Ammonite language, Ammonite: 𐤓𐤁𐤕 𐤏𐤌𐤍 ''Rabat ʻAmān'') is the capital and largest city of Jordan, and the country's economic, political, and cultural center. With a population of 4,061,150 a ...
's population per al-Maqdisi.
On the other hand, further east in the Bekaa valley, sources regarding the area are scarce and generally uninformative. According to al-Muhajir, Yaman-affiliated tribes which lived in the surroundings of Baalbek
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman ...
before 872, such as Banu Kalb and Banu Hamdan that were aligned with Alid sentiments at the time, likely played a role in spreading Shia Islam in the Bekaa and anti-Lebanon mountains. Qarmatian influence may have played a role as well, after gaining foothold in neighboring Homs before the Abbasids kicked them out in 903. In 912, Ibn al-Rida, a descendant of the 10th Imam Ali al-Hadi, started a rebellion in the nearby Damascene countryside against the Abbasid governor of Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
in an attempt to establish Hashemite authority in the area; Ibn al-Rida was subsequently defeated and killed in battle near Damascus and his head was paraded in Baghdad. According to al-Muhajir, Shiite presence in the Bekaa valley was further reinforced by migrants from Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at .
Geography
The Mount Le ...
in 1305 and Ottoman period, and migrants from the Shias villages in Anti-Lebanon Mountains.
Slightly later, the Hamdanids in Aleppo were the first dynasty of Twelver Shia Muslims to break away from the centralized rule of Baghdad. They emerged in Mosul and took control of Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
and most of northern Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
by 944, further expanding their territory into Anatolia, defeating the Byzantines on several occasions and further elevating Twelver prestige. Aleppo gradually became a hub of Shiite religious seminaries ( hawzas), linking Aleppo to Shia-populated Tripoli and Tyre in Lebanon.
Fatimid Domination
In 970, the Isma'ili Shia
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (Imamate in Nizari doct ...
Fatimids
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the ea ...
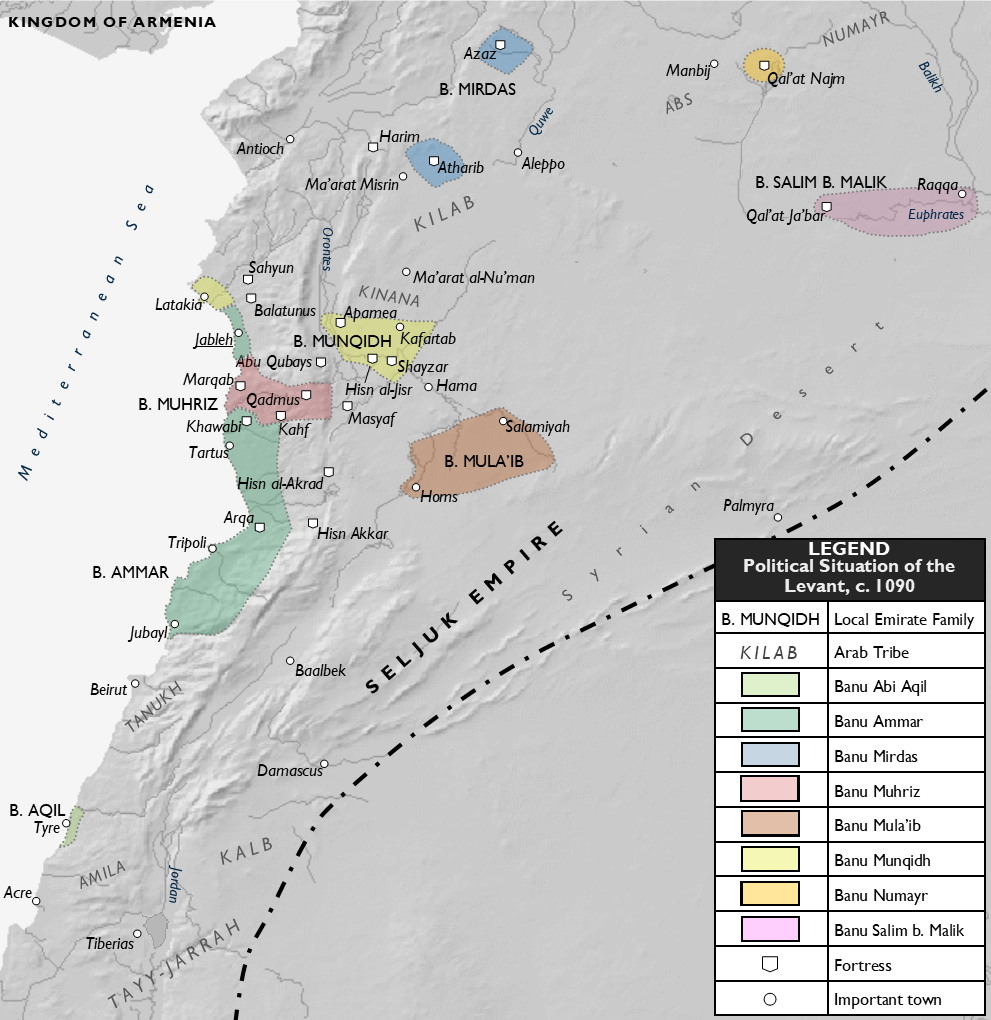
initiated their conquest of the Levant. The Fatimids patronized Isma'ili Shiism and set the ground for it to flourish in several regions and towns, including the Syrian coastal mountain region. While they embraced their Shia identity, The Fatimids quarrelled with local Shia dynasties. The Hamdanids initially refused to accept Fatimid hegemony, but were defeated by 1003. During these events, rebels in Tyre drove out the Fatimids for two years until the revolt was suppressed in 998. A decade later, the Twelver Shia Salih ibn Mirdas rose against the Fatimids and by 1025 managed to conquer most of Syria, western Iraq and parts of Lebanon. In similar action, the Shia dynasty of Banu Ammar declared the independence of Tripoli in 1070, expanding their borders to the land between Jableh in the north and Jbeil in the south. Banu Ammar were avid lovers of sciences, literature and poetry, and built the library of Dar al-'ilm, one of the significant libraries of the medieval Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
, in 1069.
Under Crusader rule and Mongol invasions
Upon the arrival of the First Crusade, Tripoli and Tyre resisted crusader attempts to seize the two cities. Tripoli was subject to a 4-year long siege which culminated with its fall in 1109. On the other hand, Tyre successfully broke a major siege in 1112 with the help of Toghtekin, but fell to theVenetian Crusade
The Venetian Crusade of 1122–1124 was an expedition to the Holy Land launched by the Republic of Venice that succeeded in capturing Tyre.
It was an important victory at the start of a period when the Kingdom of Jerusalem would expand to it ...
in 1124.
In social terms, Tripoli and Tyre experienced a drastic upheaval with the crusader conquests. Many Muslims, seemingly predominantly Shiites, were killed or departed for the interior, who were replaced by tens of thousands of Franks through several decades.
The years-long siege of Tripoli and the brutal aftermath of its fall caused an influx outside of Tripoli. Such influx either inaugurated the Shia community of Keserwan or inflated a previously established rural Shiite community there. According to al-Muhajir, a similar thing would have happened in Jabal Amel which received a population influx from the Shia-populated urban centers at the time, most notably Tyre and Tiberias, as well as Amman
Amman (; ar, عَمَّان, ' ; Ammonite language, Ammonite: 𐤓𐤁𐤕 𐤏𐤌𐤍 ''Rabat ʻAmān'') is the capital and largest city of Jordan, and the country's economic, political, and cultural center. With a population of 4,061,150 a ...
, Nablus
Nablus ( ; ar, نابلس, Nābulus ; he, שכם, Šəḵem, ISO 259-3: ; Samaritan Hebrew: , romanized: ; el, Νεάπολις, Νeápolis) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank, located approximately north of Jerusalem, with a populati ...
and the surrounding countryside. Shias in the Bekaa valley remained under Muslim rule and were on good terms with Bahramshah
Al-Malik al-Amjad Bahramshah was the Ayyubid emir of Baalbek between 1182–1230 (578–627 AH).
Reign
Bahramshah succeeded his father Farrukhshah as ruler of the minor emirate of Baalbek and had an unusually long reign for an Ayyubid ruler. Ba ...
(1182–1230), who welcomed a prominent Shia scholar from Homs in the city in 1210s, a gesture that "gave morale to the Shiites living in the nahiyah (of Baalbek)". In northern Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, the Shia qadi of Aleppo Ibn al-Khashshab was one of the first to preach jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
against the crusaders, and personally commanded and lead Aleppian troops in Battle of Ager Sanguinis
In the Battle of ''Ager Sanguinis'', also known as the Battle of the Field of Blood, the Battle of Sarmada, or the Battle of Balat, Roger of Salerno's Crusader army of the Principality of Antioch was annihilated by the army of Ilghazi of Mardin, ...
and Siege of Aleppo.
Most of Jabal Amel regained its autonomy under Husam ad-Din Bechara, a presumably local Shiite officer of Saladin who participated in the Battle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of t ...
and the capture of Jabal Amel and became its lord from 1187 until 1200.
Between 1187 and 1291, the Shiites of Jabal Amel were divided between the newly autonomous hills and a coast still subject to the Franks. Shias from the newly autonomous areas of Jabal Amel soon became essential participants in blocking Frankish raids and sieges. During Saladin's siege of Beaufort castle Beaufort Castle can refer to several places:
* Beaufort Castle, Florennes, Belgium
* Beaufort Castle, France, in the historical region of Auvergne
* Beaufort Castle in Huy, Belgium
* Beaufort Castle, Greece, a Frankish castle in Laconia
* Beaufor ...
, military units from Jabal Amel, likely those of Husam ad-Din Bishara, came to his aid and replaced his forces as he marched to repel a crusader invasion of Acre. Once again in 1195, Husam ad-Din and his forces fought off a Frankish siege of Toron.
In 1217, the local archers annihilated a Hungarian contingent attacking Jezzine in 1217. In 1240, the local appointees in Beaufort castle refused the orders of Ayyubid
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni ...
emir Al-Salih Ismail Al-Salih or as-Salih may refer to:
*As-Salih Ismail al-Malik (1163–1181), Zengid ruler in the 13th century
* As-Salih Ismail, Emir of Damascus (died 1245), Ayyubid ruler of Damascus in the 13th century
*As-Salih Ayyub (1205–1249), Ayyubid sulta ...
to surrender their castle to crusader forces, leading to their siege and execution.
When the Mongols took Baalbek in 1260, many local Shias refused to surrender to Mongol forces. Najmeddine ibn Malli al-Baalbeki (b. 1221), one of Baalbek
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman ...
's few Shia scholars at the time, took the initiative and retreated to the slopes of Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at .
Geography
The Mount Le ...
, where he was joined by thousands of volunteer guerilla fighters. According to contemporary chronicler al-Yunini, these guerillas would kidnap and ambush Mongols at night, and would often disguise and adopt pseudonyms to conceal their identities. For example, Najmeddine adopted the pseudonym "the bald king".
Mamluk period and 1305 campaign
By the early 14th century, Jabal Amel was becoming the Twelver Shia center of the Levant. With Shiism losing ground inAleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
due to Ayyubid
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni ...
and now Mamluk takeover, a stream of scholars shifted to Jabal Amel, and the area probably received migrants from there as it provided refuge from Sunni rigor.
In Muharram 1305, the Mamluk army under the command of Aqqush al-Afram Jamal al-Din Aqqush al-Afram al-Mansuri (died 1336) was a high-ranking Mamluk emir and defector, who served as the Mamluk viceroy of Damascus and later the Ilkhanid governor of Hamadan.
Mamluk emir
Aqqush al-Afram was an ethnic Circassian and bega ...
devastated the mountain-dwelling Shia community of Keserwan. The Mamluks had previously attempted to subjugate the community through several unsuccessful military campaigns in the 1290s, and launched the last campaign after a band of Keserwanis attacked their retreating army after the Battle of Wadi al-Khaznadar
The Battle of Wadi al-Khaznadar, also known as the Third Battle of Homs, was a Mongol victory over the Mamluks in 1299.''Wadi 'L-Khaznadar'', R. Amitai, The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Vol XI, ed. P.J.Bearman, T.Bianquis, C.E.Bosworth, E. van Donzel ...
. Aqqush led an army of around 50,000 troops which advanced and encircled the Mountain through from four sides, against defending Shiite forces of an estimated 4,000 infantrymen. The region fell after 11 days of brutal fighting, driving an influx of Shiites toward the Beqaa valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
and Jezzine
Jezzine ( ''Jizzīn'') is a town in Lebanon, located from Sidon and south of Beirut. It is the capital of Jezzine District. Surrounded by mountain peaks, pine forests (like the Bkassine Pine Forest), and at an average altitude of 950 m (3 ...
, while a humbled minority stayed. In 1363, decades later, the Mamluks released an official decree prohibiting Shia rituals practiced among "some of the people of Beirut, Sidon and their surrounding villages", threatening punishment and military campaign. The Mamluks punished the town of Machghara
Machghara ( ar, مشغرة), also spelled Mashghara, is a town in the Beqaa Valley of Lebanon, situated in the Western Beqaa District and south of the Beqaa Governorate. It lies just to the northwest of Sohmor and southwest of Lake Qaraoun, south ...
in 1364 for disobedience and religious dissidence. In 1367, the Shias of Burj Beirut rose in armed rebellion against the Mamluks, but the conflict subsided through mediation between the two sides by the Buhturids
The Buhturids, also known as the Banu Buhtur or the Tanukh, were a dynasty whose chiefs served as the emirs (commanders) of the Gharb area southeast of Beirut in Mount Lebanon in the 12th–15th centuries. A branch of the Tanukhid tribal confederat ...
. In 1384, the Mamluks also executed most notable Shia scholar and head of the community at the time, Muhammad Jamaluddin al-Makki al-Amili, known as "ash-shahid al-awwal" (the first martyr), on charges of being a ghulat
The ( ar, غلاة, 'exaggerators', 'extremists', 'transgressors', singular ) were a branch of early Shi'i Muslims thus named by other Shi'i and Sunni Muslims for their purportedly 'exaggerated' veneration of the prophet Muhammad (–632) and his ...
and promoting Nusayri doctrines, falsely claimed by his enemies and former ex-Shia students.
Since 1385 much of Jabal Amel and Safed was ruled by the Bechara family, who occasionally also brought Wadi al-Taym under their control, until the advent of Ottomans. On the other hand, the Harfush dynasty
The Harfush dynasty (or Harfouche, Harfouch, or most commonly spelled Harfoush dynasty, all varying transcriptions of the same Arabic family name حرفوش) was a dynasty that descended from the Khuza'a tribe, which helped, during the reign of ...
of the Bekaa were first mentioned by Ibn Tawq as muqaddams in the Anti-Lebanon mountains to the east of Baalbek in 1483, and later as deputies (na'ib) of Baalbek. Two members of the two families, Ibn Bechara and Ibn Harfush, reportedly fought on each other's side during civil strife in Damascus between Mamluk governors in 1497. According to contemporary chronicler Ibn Tulun, many Shiites had come to join the battle in aid of one of the Mamluk governors. In the mid-1200s, al-Yunini mentions a few Tanukhid emirs in Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at .
Geography
The Mount Le ...
who reportedly followed the Shiite faith, whose domains had also covered Karak Nuh
Karak (also Kerak, Karak Nuh or Karak Noah) ( ar, كرك, Karak) is a village in the municipality of Zahle in the Zahle District of the Beqaa Governorate in eastern Lebanon. It is located on the Baalbek road close to Zahle. Karak contains a sar ...
. Following the disastrous campain in 1305, the Hamada family were among the earliest mentioned families, and reportedly served as tax-collectors in the district of Mamluk Tripoli as early as 1471, in the region Dinniyeh
Danniyeh (known also as Addinniyeh, Al Dinniyeh, Al Danniyeh, ar, الضنية) is a region located in Miniyeh-Danniyeh District in the North Governorate of Lebanon. The region lies east of Tripoli, extends north as far as Akkar District, south t ...
. Bilad Beirut were similarly under the jurisdiction of a Shia muqaddam prior to 1407.
Under Ottoman rule
The Levant fell to theOttomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
in 1516, bringing about a new period in the region. Often times, Local Shias came into conflict with Ottoman-assigned governors of Beirut, Sidon and Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, who often derogatorily referred to them as Qizilbash in their documents as a means to delegitimize them or justify punitive campaigns against them. Nevertheless, although considered Heretics by the Ottomans, the latter confirmed tax-collectorship iltizam to the local Shia in Jabal Amel, Bekaa valley and northern Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at .
Geography
The Mount Le ...
as part of their efforts of relying on local intermediaries rather than forcibly imposing foreign ones. The Harfush and Hamade families received iltizam over the Bekaa valley and northern Mount Lebanon respectively, while Jabal Amel consisted of several nawahi governed by multiple families, until Ali al-Saghirs seized most of Jabal Amel by 1649.
These feudal families were often autonomous and frequently quarrelled with the Ottoman governors to maintain autonomy over their territories, often with mixed results. Comte de Volney
''Comte'' is the French, Catalan and Occitan form of the word 'count' (Latin: ''comes''); ''comté'' is the Gallo-Romance form of the word 'county' (Latin: ''comitatus'').
Comte or Comté may refer to:
* A count in French, from Latin ''comes''
* A ...
, who visited Lebanon between 1783 and 1785, noted this.
"The ''Metoualis'' are almost annihilated due to their revolts; their name is soon to be extinct".
 The three Shia principalities underwent different historical trajectories. The Harfush initially did not challenge the new Ottoman authority, but in 1518 the Ottomans executed an anonymous Ibn Harfush, governor of Baalbek, along with the Bedouin Emir Ibn al-Hanash for acting against the state. At their high-point, Harfush domains extended from the Beqaa valley into Palmyra far in the
The three Shia principalities underwent different historical trajectories. The Harfush initially did not challenge the new Ottoman authority, but in 1518 the Ottomans executed an anonymous Ibn Harfush, governor of Baalbek, along with the Bedouin Emir Ibn al-Hanash for acting against the state. At their high-point, Harfush domains extended from the Beqaa valley into Palmyra far in the Syrian Desert
The Syrian Desert ( ar, بادية الشام ''Bādiyat Ash-Shām''), also known as the North Arabian Desert, the Jordanian steppe, or the Badiya, is a region of desert, semi-desert and steppe covering of the Middle East, including parts of sou ...
and sanjak of Homs in 1568 during Musa Harfush's reign, who was even assigned a unit of 1,000 archers to lead int the Yemen campaign. In 1616, Yunus al-Harfush again asserted Harfush supremacy over Homs and the Bekaa, defeating his Sayfa
Yusuf Sayfa Pasha ( ar, يوسف سيفا باشا, Yūsuf Sayfā Pāsha; – 22 July 1625) was a chieftain and ''multazim'' (tax farmer) in the Tripoli region who frequently served as the Ottoman ''beylerbey'' (provincial governor) of Tripol ...
opponents in battle, and earning iltizam for the Sanjak of Homs. Prior the Battle of Ain Dara
The Battle of Ain Dara took place in the town of Ain Dara in 1711 between the Qaysi and Yamani tribo-political factions. The Qays were led by Emir Haydar of the Shihab dynasty and consisted of the Druze clans of Jumblatt, Talhuq, Imad and Abd a ...
, Haydar Shihab took refuge among the Harfushes, who provided him with 2,500 troops to carry out the battle, which resulted in Shihab's decisive victory.
Further South, the pinnacle of Jabal Amel was at the hands of Nassif al-Nassar
Nasif ibn al-Nassar al-Wa'ili ( ar, ناصيف النصار; died 24 September 1781) was the most powerful sheikh of the rural Shia Islam in Lebanon, Shia Muslim (Matawilah) tribes of Jabal Amel, Jabal Amil (modern-day South Lebanon) in the mid-1 ...
(c. 1749–1781) of Ali al-Saghirs during his alliance with Zahir al-Umar. In 1767, the latter attempted to extend his authority to Shiite villages, but was defeated in battle and captured, eventually entering into an alliance with Nassif and the Shiites. The duo's first decisive battle took place in Lake Huleh in 1771, when the 10,000-strong Ottoman army of Uthman Pasha al-Kurji
Uthman Pasha al-Kurji (also known as Uthman Pasha al-Sadiq, alternative spellings include ''Othman'', ''Osman'' or ''Usman'' and ''al-Kurdji'' or ''Kurzi''), was the Ottoman governor (''wali'') of Damascus Eyalet between 1760 and 1771.Burns, 2005, ...
was virtually annihilated by the duo's forces; about 300-500 Ottoman soldiers survived the battle, and Uthman Pasha returned to Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
with only 3 of his soldiers. Through his 10,000-strong cavalry army, specially noted by a French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
consul as "excellent fighters", Nassif imposed control on all territories between Sidon and Safed, notwithstanding Zahir's territories within Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
and western Transjordan Transjordan may refer to:
* Transjordan (region), an area to the east of the Jordan River
* Oultrejordain, a Crusader lordship (1118–1187), also called Transjordan
* Emirate of Transjordan, British protectorate (1921–1946)
* Hashemite Kingdom of ...
which Nassif's cavalry forces had an integral part in capturing. Zahir's military potential was significantly boosted by the backing of 10,000 Shiite fighters, who supported him against the sieges and assaults by the overnors of Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, reportedly participating in fifteen subsequent campaigns against his foes. Thus, Nassif and his allies managed to impose ''grande sécurité'' on the whole region, so much so that Ali Bey al-Kabir of Egypt requested Nassif's help to put down the rebellion at Cairo in 1773, and was sought by nomadic tribes in the Syro-Jordanian desert to help them against their foes.
The Hamada's of northern Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at .
Geography
The Mount Le ...
, spearheading a rather much smaller community, were virtually in a continuous state of conflict with the Ottomans between 1685 and 1711. In 1686, a joint Harfush-Hamade force managed to defeat and drive the forces of the Ottoman governors of Sidon and Tripoli out of Keserwan, leaving Tripoli susceptible to attack. As a result, they managed to re-affirm themselves as multezims for most of northern Lebanon and parts of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
as far as Safita and Krak des Chevaliers. Upon meeting them in 1686, a French diplomat came acqainted with them as the "men of emir Sirhan", describing them as good hearted people and "iron men" who would not back out to the strongest of janissaries. By 1771, the Hamada's and the Shia community were greatly weakened by the Ottoman governors and Shihabis, and eventually completely fell out of grace, diminishing their political importance in Mount Lebanon. As a result, a second population influx overran the Beqaa valley where the Harfushes welcomed the displaced Shiites, and allotted them land in Hermel and other places.
 In 1781, Shia autonomy diminished under Ahmad Pasha al-Jazzar (1776–1804), nicknamed the butcher. Al-Jazzar was initially on good terms with Nassif, but their alliance reached a bad point some time in 1781. Afterward, al-Jazzar defeated and killed Nassif and 470 of his men in battle, proceeding to conquer Shia-held fortress towns and eliminate all the leading Shia sheikhs of Jabal Amel, whose families were allowed to take refuge with the Harfushes in Baalbek. He proceeded to burn down Shia religious libraries, transport Shia religious books to the ovens in Acre, and paraded the heads of the fallen in Sidon. Following their crisis, insurgency commenced at the hands of local militias which attacked al-Jazzar's troops in the region. The period witnessed swift uprisings in
In 1781, Shia autonomy diminished under Ahmad Pasha al-Jazzar (1776–1804), nicknamed the butcher. Al-Jazzar was initially on good terms with Nassif, but their alliance reached a bad point some time in 1781. Afterward, al-Jazzar defeated and killed Nassif and 470 of his men in battle, proceeding to conquer Shia-held fortress towns and eliminate all the leading Shia sheikhs of Jabal Amel, whose families were allowed to take refuge with the Harfushes in Baalbek. He proceeded to burn down Shia religious libraries, transport Shia religious books to the ovens in Acre, and paraded the heads of the fallen in Sidon. Following their crisis, insurgency commenced at the hands of local militias which attacked al-Jazzar's troops in the region. The period witnessed swift uprisings in Chehour
Chehoûr, Shuhur, or Shhur (Arabic language, Arabic: شحور), is a small town on the Litani River in the Tyre District of Southern Lebanon's South Governorate, some 95 kilometres to the south-west of Beirut, the capital city of Lebanon.
Name
Ed ...
in 1784 and Tyre in 1785, and the insurgents managed to temporarily conquer the citadel of Tebnine. Insurgency continued until the end of al-Jazzar's rule in 1804, and famously involved Faris al-Nassif, Nassif al-Nassar's son.
The period between 1781 and 1804 was marked as a period of decline and political defeat among the Shias of Jabal Amel, and persisted in their collective memory well into the early 20th century. Political involvement of Shiites of Jabal Amel recommenced upon the Egyptian invasion of the Levant in 1833, when Shiites resented the Shihabi-Egyptian alliance and assumed a central role in the efforts of expelling the Egyptians from Ottoman Syria. Led by Khanjar Harfush in Baalbek
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman ...
, and in Jabal Amel by Hasan al-Shabib and Hamad al-Beik, the Shiites engaged in various battles against the Egyptian army. Khanjar Harfush engaged an Egyptian force of 12,000 in Nabek and Keserwan and was joined by Maronite
The Maronites ( ar, الموارنة; syr, ܡܖ̈ܘܢܝܐ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and Levant region of the Middle East, whose members traditionally belong to the Maronite Church, with the larges ...
peasants in Zouk Mikael, while Hamad Beik singlehandedly drove out the Egyptians as far as Safed in northern Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ...
. In 1841, during a period of brutal Christian-Druze fighting prior the 1860 civil war, the Harfushes gathered forces and came to the aid of Zahle, defeating the Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
forces besieging the city. The Harfush were eventually deported to Edirne in 1865 at the behest of Ottoman authority.
During World War I
Between 1914 and 1918, manyArab nationalists
Arab nationalism ( ar, القومية العربية, al-Qawmīya al-ʿArabīya) is a nationalist ideology that asserts the Arabs are a nation and promotes the unity of Arab people, celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language and ...
from Lebanon and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
were arrested by Ottoman authorities and trialed, and some were executed. Two Shiites were among those executed in between August 1915 and May 1916: Abdul-Kareem Khalil from Chyah
Chiyah () is situated in the west region of the Lebanese capital of Beirut and is part of Greater Beirut.
Location
Chiyah is located in the southwest suburbs of the capital Beirut, bordered by Haret Hreik, Ghobeiry, Hadath, Hazmiyeh, Furn-el- ...
and Saleh Haidar from Baalbek
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman ...
. The day is commemorated in Lebanon and Syria as Martyrs' Day. Several others were arrested and imprisoned, including Muhammad Jaber Safa, Sheikh Ahmad Rida and Ahmed Aref El-Zein, the latter who participated in several underground Arab societies, and supported the Arab Congress of 1913
The Arab Congress of 1913 (also known as the "Arab National Congress," "First Palestinian Conference," the "First Arab Congress," and the "Arab-Syrian Congress") met in a hall of the French Geographical Society (Société de Géographie) at 184 Bo ...
.
Relations with Iranian Shias
During most of the Ottoman period, the Shia largely maintained themselves as 'a state apart'. Towards the end of the eighteenth century the Comte de Volmy described Lebanese Shia as a distinct society. When the Safavids began converting Iran to Shiism by coercion and persuasion, they compensated the lack of established Shia fiqh in Iran by asking Shia clergies from Jabal Amel, Bahrain and Al-Ahsa to immigrate to Iran. Chief among them was Muhaqqiq al-Karaki, fromKarak Nuh
Karak (also Kerak, Karak Nuh or Karak Noah) ( ar, كرك, Karak) is a village in the municipality of Zahle in the Zahle District of the Beqaa Governorate in eastern Lebanon. It is located on the Baalbek road close to Zahle. Karak contains a sar ...
in the Bekaa valley, who achieved limitless power during the reign of Shah Tahmasp I such that the Shah told him, “''You are the real king and I am just one of your agents''". These contacts greatly angered the Ottomans. In addition to their different narrative of Islam, the Ottomans suspected Shias of being a stalking horse for the Safavids, and often derogatorily referred to them as Qizilbash. Thus, the Shia oppression in Lebanon was a marriage of politics and religion.
During the 19th century, the Maronites were supported by the France, the Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
by the British, the Greek Orthodox by the Russians and the Sunnis
Sunni Islam () is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia ...
by the Ottoman sultans. Despite nominal support by the weak Qajar kings, the Shia lacked any external state-patron, and were the least powerful community in Lebanon.
Shia Lebanon, when not subject to political repression, was generally neglected, sinking further and further into the economic background.
French mandate period
When the French entered Nabatieh in 1918, they barred the local populace from carrying out political activity. As a response, Sadiq Hamzeh hoisted the Arab flag in several villages as a symbol of rejecting French occupation. Following theSyrian National Congress
The Syrian National Congress, also called the Pan-Syrian Congress and General Syrian Congress (GSC), was convened in May 1919 in Damascus, Syria, after the expulsion of the Ottomans from Syria. The mission of the Congress was to consider the futu ...
in 2 July 1919 where Shiites restated their support for Syrian unity, Maronites increased their armed activities against the Shiites. The French supported several Maronite militia, especially those in Qlaiaa
Qlaiaa ( ar, القليعة) is a village in the Marjeyoun District in southern Lebanon. The inhabitants are mainly Maronite Christians.
Name
According to E. H. Palmer, the name means "the little castle".
History
In 1838, Eli Smith noted Qlaia ...
and Kfour by Nabatieh. Furthermore, Maronite newspapers had negatively depicted the Shiite groups, often as murderers and pillagers. Following the official declaration of the French Mandate of Greater Lebanon (''Le Grand Liban'') in September 1920, anti-French riots broke out in the predominantly Shia areas of Jabil 'Amil and the Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
. In between 1920 and 1921, rebels from these areas, led by Adham Khanjar
Adham Khanjar ( ar, أدهم خنجر) (1890–1922) was a Lebanese Shia Muslim revolutionary and Syrian nationalist who participated in guerilla warfare against the forces of the French occupation of Lebanon and Syria, and the attempt to assassi ...
and Sadiq Hamzeh, attacked French military bases in Southern Lebanon. In one confrontation, Sadiq Hamzeh and his men engaged the French and caused them heavy casualties of fifty men and some weapons. During this period of chaos, also several predominantly Christian villages in the region were attacked due to the armed support they received from the French and their perceived acceptance of French mandatory rule, including Ain Ebel. This was the perfect moment for the French to strike, as they sent an expedition of 4,000 soldiers lead by Colonel Niger, attacking villages by their aeroplanes, and crushing the Shiite rebellion by June 1920. Despite resistance subsiding, Adham Khanjar and his men continued their sabotage missions until an unsuccessful assassination attempt on French High Commissioner Henri Gouraud, which led to his execution in 1923.
 On the other hand, Shia cleric Abdul Husayn Sharafeddine had organized and lead
On the other hand, Shia cleric Abdul Husayn Sharafeddine had organized and lead nonviolent resistance
Nonviolent resistance (NVR), or nonviolent action, sometimes called civil resistance, is the practice of achieving goals such as social change through symbolic protests, civil disobedience, economic or political noncooperation, satyagraha, cons ...
against the French since 1919, and demanded US support for Syrian
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indi ...
unity, angering the French who encouraged an unsuccessful assassination attempt against him. Sharafeddine understood that sectarian hostility only gave purpose for French military presence in the area, and thus called for the protection of the Christians in the conference of Wadi al-Hujayr on 24 April 1920.The Christians (Nasara) are your brethren in the country and in destiny. Show to them the love you show to yourselves. Protect their lives and possessions as you do to your own. Only by this can you face the conspiracy and put an end to the civil strife.Later in 1921, this period of unrest ended with a political amnesty offered by the French mandate authorities for all Shiites who had joined the riots, with the intention to bind the Shia community in the South of Lebanon to the new Mandate state. However, the French breakdown on Shiites left the latter resentful against them. The French had dispersed the Shiite leaders and thousands of peasants who feared reprisals, and the high fines imposed on them caused financial misery. When the
Great Syrian Revolt
The Great Syrian Revolt ( ar, الثورة السورية الكبرى) or Revolt of 1925 was a general uprising across the State of Syria and Greater Lebanon during the period of 1925 to 1927. The leading rebel forces comprised fighters of the ...
broke out in 1925, rebellion once again broke out in Shia areas. Many Southerners went to Syria to participate, while in Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
, battle spread to the Qalamoun Mountains, where 'Tawfiq Haidar' engaged the French in fierce battles, and also Akroum
Akroum ( ar, أكروم) is a Sunni Muslim village located in the Akkar District in Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. ...
in Akkar where according to eye-witness accounts, Shiites took more than 400 rifles and 50 horses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
as booty from defeated French forces.
Many Christians who fled their villages during the revolt were accommodated by Shia notables from Nabatieh and Bint Jbeil, an act that was appreciated by Christian clergies in letters.
... what the Shi'ites did for the Christians in the south will be cherished in our hearts for as long as Lebanon and the Christians remain. What happened should be written in gold. Long live Lebanon, Long live Lebanese unity and long live the Shiites.After the revolt, the region experienced a decade or so of political stability. The Shiites gradually grew more accepting of Greater Lebanon due to various reasons. For instance, they were disappointed and shocked at their fellow Arabs who organized a conference in 1926 discussing whether or not the Shiites of Jabal Amel were of Arab origin. Furthermore, Shiite zu'ama believed their fortune would best be achieved within the newly founded Lebanese state. During the
1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine
The 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine, later known as The Great Revolt (''al-Thawra al- Kubra'') or The Great Palestinian Revolt (''Thawrat Filastin al-Kubra''), was a popular nationalist uprising by Palestinian Arabs in Mandatory Palestine a ...
, Southerners had a key role in providing ammunition and assistance to the Palestinian rebels, and the revolt was in fact co-administered from Bint Jbeil. In 1938, the French even requested Royal Air Force support during their operations in Bint Jbeil and South. In addition, Abdul-Husayn Sharafeddine expressed solidarity with the Palestinian strike and demand for independence.
Education
In the 19th century, Lebanon saw dramatic changes when missionaries started establishing schools throughout the country. While the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and Russians mainly encouraged Maronite and Orthodox active learning respectively, along with American Protestant
Protestantism is the largest grouping of Christians in the United States, with its combined denominations collectively comprising about 43% of the country's population (or 141 million people) in 2019. Other estimates suggest that 48.5% of the U ...
missions in Beirut, the British established educational institutions in Druze areas, and Sunnis mainly benefitted from Ottoman state institutions. However, Shiites were the only ones who did not benefit from such activities. This neglectance continued into the early days of the French mandate.
During the 1920s and 1930s, educational institutions became places for different religious communities to construct nationalist and sectarian
Sectarianism is a political or cultural conflict between two groups which are often related to the form of government which they live under. Prejudice, discrimination, or hatred can arise in these conflicts, depending on the political status quo ...
modes of identification. Shia leaders and religious clergy supported educational reforms in order to improve the social and political marginalization of the Shia community and increase their involvement in the newly born nation-state of Lebanon. This led to the establishment of several private Shia schools in Lebanon, among them The Charitable Islamic ʿĀmili Society (''al-Jamʿiyya al-Khayriyya al-Islāmiyya al-ʿĀmiliyya'') in Beirut and The Charitable Jaʿfari Society (''al-Jamʿiyya al-Khayriyya al-Jaʿfariyya'') in Tyre. While several Shia educational institutions were established before and at the beginning of the mandate period, they often ran out of support and funding which resulted in their abolishment.
The primary outlet for discussions concerning educational reforms among Shia scholars was the monthly Shiite journal a''l-'Irfan'', founded in 1909. In order to bring their demands (''muṭālabiyya'') to the attention of the French authorities, petitions were signed and presented to the French High Commissioner and the Service de l'Instruction Publique. This institution – since 1920 headquartered in Beirut- oversaw every educational policy regarding public and private school in the mandate territories. According to historian Elizabeth Thompson, private schools were part of "constant negotiations" between citizen and the French authorities in Lebanon, specifically regarding the hierarchical distribution of social capital
Social capital is "the networks of relationships among people who live and work in a particular society, enabling that society to function effectively". It involves the effective functioning of social groups through interpersonal relationships ...
along religious communal lines. During these negotiations, petitions were often used by different sects to demand support for reforms. For example, the middle-class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Comm ...
of predominantly urban Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
areas expressed their demands for educational reforms through petitions directed towards the French High Commissioner and the League of Nations.
Sayyid Abdul-Husayn Sharafeddine believed that the only way to ward off foreign political influence was to establish modern schools while maintaining Islamic teachings. In 1938, he built two schools, one for girls and another for boys, at his own expense. However, the girls' school did not last long due to financial difficulties and traditional views, prompting Sayyid Sharafeddine to transfer the girls and teach them in his own home. The boys' school was known as ''al-Ja'fariyya'', and was able to continue despite financial difficulties.
Ja'fari shar'ia courts
In January 1926, the French High Commissioner officially recognized the Shia community as an "independent religious community," which was permitted to judge matters of personal status "according to the principles of the rite known by the name of Ja'fari." This meant that the Shiite Ja'fari jurisprudence
Jaʿfarī jurisprudence ( ar, الفقه الجعفري; also called Jafarite in English), Jaʿfarī school or Jaʿfarī fiqh, is the school of jurisprudence (''fiqh'') in Twelver and Ismaili (including Nizari) Shia Islam, named after the sixth ...
or '' madhhab'' was legally recognized as an official ''madhhab'', and held judicial and political power on multiple levels. The institutionalization of Shia Islam during this period provoked discussions between Shiite scholars and clergy about how Shiite orthodoxy should be defined. For example, discussions about the mourning of the martyrdom of Imam Husain
Abū ʿAbd Allāh al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, أبو عبد الله الحسين بن علي بن أبي طالب; 10 January 626 – 10 October 680) was a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a son of Ali ibn Abi ...
during Ashura
Ashura (, , ) is a day of commemoration in Islam. It occurs annually on the 10th of Muharram, the first month of the Islamic calendar. Among Shia Muslims, Ashura is observed through large demonstrations of high-scale mourning as it marks the ...
, which was a clandestine affair before the 1920s and 1930s, led to its transformation into a public ceremony.
On the other hand, the official recognition of legal and religious Shiite institutions by the French authorities strengthened a sectarian awareness within the Shia community. Historian Max Weiss underlines how "sectarian claims were increasingly bound up with the institutionalization of Shi'i difference." With the Ja'fari shar'ia courts in practice, the Shia community was deliberately encouraged to "practice sectarianism" on a daily basis.
Post-Independence
Between 1943 until the send of the civil war in 1990, the status of Southern Lebanon andBeqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
was characterized by negligence from the Lebanese state, which diverted away its main resources to the capital and center. The Shiites considered themselves the despised stepchildren
A stepchild is the offspring of one's spouse, but not one's own offspring, either biologically or through adoption.
Stepchildren can come into a family in a variety of ways. A stepchild may be the child of one's spouse from a previous relationshi ...
of the Lebanese state, and their areas in Southern Lebanon and the Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
were often disproportionally the poorest in the country. This had a crucial impact on Shias, as they mainly originated from these two peripheral regions of Lebanon. As such, Shias were sorely underrepresented in Lebanese politics, and had little say in the government. Despite forming one of Lebanon's three biggest communities, for instance, in 1946 40% and 27% of high-ranking civil posts were occupied by Maronites and Sunnis
Sunni Islam () is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia ...
respectively; in contrast, Shias only occupied 3.2%. In late 1950s, Shia representation in senior posts was in the deficit, as only 4 out of 115 had been occupied by Shias, unlike their fellow Sunnis
Sunni Islam () is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia ...
and Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
who held their own with the Maronites. Shia deficit similarly reflected the low proportion of Shia university graduates at the time. In 1962, Shiites only occupied 2 of every 70 senior civil service position. The first published book to describe life in the South was a manifesto of the Najaf-educated cleric Muhammad Jawad Mughniyya's published in 1947, which he aimed to depict "''the grim life of the peasants, filled with ignorance, labor from dawn to dusk and utter neglect''" in order to demand justice for them from the "wicked politicans and ruling clique". Mughniyya also wrote a newspaper editorial against capitalism and feudalism, and against the pro-Western Baghdad Pact
The Middle East Treaty Organization (METO), also known as the Baghdad Pact and subsequently known as the Central Treaty Organization (CENTO), was a military alliance of the Cold War. It was formed in 24 February 1955 by Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, Turk ...
in 1956.
In 1948, an important event occurred that would shape the region's geopolitics, the Nakba. Tens of thousands of Palestinians
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
arrived in Tyre, where many were sheltered in Sayyid Sharafeddine's ''al-Ja'fariyya'' school until the authorities dealt with the situation. Sharafeddine also introduced a Palestinian curriculum known as "Matriculation", to allow Palestinian students to finish what they had started in Palestine. The Shia villages in Palestine
From 1923 to 1948, there were seven villages in Mandatory Palestine for which the population was predominantly Shia Islam, Shia Muslim (of Metawali creed). They were Tarbikha, Saliha, Al-Malkiyya, Malkiyeh, Al-Nabi Yusha', Nabi Yusha, Qadas, Hu ...
, which the French had transferred to Mandatory Palestine in 1923, were depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had ...
and many of the inhabitants massacred, as high as 94 victims in Salha, and subsequently most fled to Lebanon. On 31 October–1 November, Zionist forces entered the village of Hula, executing around 90 Lebanese civilians in a house which was later blown on top of them. These events stimulated Shia sympathy with what the Palestinians had been enduring.
 From late 1940s onward, many Shias moved to the Beirut and its suburbs. This influx increased in the late 60s and 70s following the
From late 1940s onward, many Shias moved to the Beirut and its suburbs. This influx increased in the late 60s and 70s following the PLO
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ar, منظمة التحرير الفلسطينية, ') is a Palestinian nationalist political and militant organization founded in 1964 with the initial purpose of establishing Arab unity and s ...
's introduction into Lebanon, which transformed Southern Lebanon into a battleground, and where Shias civilians were caught in the midst of PLO-Israeli conflict. Israel regularly attacked the South by land and air, sometimes on a daily basis, causing massive civilian casualties among local Shias.Steadily, Shias kept flowing into Beirut. Prior 1975, approximately 319,000 Shias lived throughout Beirut, slightly less than half of Shia. Many Shias also lived in Palestinian refugee camps such as Tel el-Zaatar
The Siege of Tel al-Zaatar ( ar, حصار تل الزعتر, French: Siège de Tel al-Zaatar), alternatively known as the Massacre of Tel al-Zaatar, was an armed siege of Tel al-Zaatar (meaning ''Hill of Thyme'' in Arabic), a fortified, UNRWA-ad ...
, where Shias formed 43% of a population of 30,000, and Karantina
La Quarantaine, which is colloquially referred to as Karantina (Arabic: الكرنتينا) and sometimes spelled Quarantina, is a predominantly low-income, mixed-use residential, commercial, and semi-industrial neighborhood in northeastern Beirut ...
refugee slum where a similar population lived.
In the late 1960s and 1970s, Shiites were largely attracted to Leftist
Left-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that support and seek to achieve social equality and egalitarianism, often in opposition to social hierarchy. Left-wing politics typically involve a concern for those in soci ...
parties, particularly the Lebanese Communist Party and Communist Action Organization
The Communist Action Organization in Lebanon – CAOL ( ar, منظمة العمل الشيوعي في لبنان , ''munaẓẓamah al-‘amal al-shuyū‘ī fī lubnān''), also known as Organization of Communist Action in Lebanon (OCAL) or Orga ...
, so much so that many Lebanese interchanged the words Shi'i (Shiite) and Shuyu'i (Communist). Shiite Communist intellectuals included Hussein Mroue and Mahdi Amel.
The Ba'ath Party
The Arab Socialist Baʿath Party ( ar, حزب البعث العربي الاشتراكي ' ) was a political party founded in Syria by Mishel ʿAflaq, Ṣalāḥ al-Dīn al-Bītār, and associates of Zaki al-ʾArsūzī. The party espoused B ...
had also gained popularity among Shiites in both the Syrian-led and Iraqi-led branches of the original party which split in 1966. Furthermore, many Shiites also joined the Sunni-dominated Nasserist
Nasserism ( ) is an Arab nationalist and Arab socialist political ideology based on the thinking of Gamal Abdel Nasser, one of the two principal leaders of the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, and Egypt's second President. Spanning the domestic a ...
al-Mourabitoun party, and by the mid-70s formed roughly 45% of the following, as well as the Syrian Social Nationalist Party along with other minor parties. In addition, due to shared sympathies, many Shias also joined Palestinian factions such as Fatah
Fatah ( ar, فتح '), formerly the Palestinian National Liberation Movement, is a Palestinian nationalist social democratic political party and the largest faction of the confederated multi-party Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) and ...
and Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine. Islamist parties had a minor presence, the most notable of which was the Islamic Dawa Party, originally founded in Iraq by Muhammad Baqir al-Sadr in the 1960s, which emphasized extreme secrecy and underground activity. Notable members of the party included the Najaf-educated clerics and students of al-Sadr, Mohammad Hussein Fadlallah and Abbas al-Musawi. The party would later have a "strong impact on the ideology, direction and organisational structure" of Hezbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
. While rare, some Shias even joined Kataeb and al-Ahrar
The Al-Ahrar Bloc ( ar-at, كتلة الأحرار, Kotlat Al-Ahrar or ''Liberal Bloc'') is an Iraqi Shia Islamist political coalition formed for the 2014 Iraqi parliamentary election. It is headed by Dia Najem Abdallah al-Asadi.
The mainly S ...
.
During this time, Musa Sadr emerged as one of the leading Shiite figures. Sadr founded the Supreme Islamic Shia Council in 1967 on par with other established religious institutions at the time. Sadr's popularity reached great heights in the 70s such that in March 1974, his speech in Baalbek
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman ...
was witnessed by an audience of more than 75,000, who had come to see him. In May 1974, more than 80,000 rallied in support of Sadr in Tyre. Sadr's deeds had great bearing on the Shiites, whom he sought to bring together. Sadr also emphasized support of the Palestinian cause, while objecting to the actions of some Palestinian guerillas in the south, which had caused trouble to the locals. In early 1975, Sadr announced the establishment of Movement of the Deprived, which came to be known as "Amal Movement". Amal's ranks grew rapidly as it attracted the underrepresented people and the youth who had joined separate parties, and its armed ranks rapidly grew to ~1,500–3,000 in that year, while SAVAK
SAVAK ( fa, ساواک, abbreviation for ''Sâzemân-e Ettelâ'ât va Amniat-e Kešvar'', ) was the secret police, domestic security and intelligence service in Iran during the reign of the Pahlavi dynasty. SAVAK operated from 1957 until prime ...
estimated the manpower at 6,000. While the party's aim was giving Shias more say in the government, its armed wing was established with the purpose of thwarting Israeli attacks on southern villages, the first confrontation of which happened against an Israeli commando unit raid on Taybeh in 1975. Among the co-founders of Amal was Mostafa Chamran, who came to Lebanon with Sadr early on, and became Iran's National Defense Minister in 1979–1980. Amal once again confronted Israeli and SLA forces in 1977, but took little role in the infighting during the first phase of the civil war in 1975–1977.Civil War and Israeli occupation
During the Civil War Beirut came to be divided along sectarian lines. An estimated 100,000 Shiites lived inEast Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
in early 1975, mostly in Naba'a, Bourj Hammoud and Karantina
La Quarantaine, which is colloquially referred to as Karantina (Arabic: الكرنتينا) and sometimes spelled Quarantina, is a predominantly low-income, mixed-use residential, commercial, and semi-industrial neighborhood in northeastern Beirut ...
, a slum whose population consisted of mostly Lebanese Shia, Kurds, Palestinians and Bedouins. Additionally, Shias formed 43% of Tel el-Zaatar
The Siege of Tel al-Zaatar ( ar, حصار تل الزعتر, French: Siège de Tel al-Zaatar), alternatively known as the Massacre of Tel al-Zaatar, was an armed siege of Tel al-Zaatar (meaning ''Hill of Thyme'' in Arabic), a fortified, UNRWA-ad ...
's population, a Palestinian refugee camp in East Beirut. Following the Karantina massacre
The Karantina massacre (Arabic: مجزرة الكرنتينا, French: Massacre de La Quarantaine/Karantina) took place on January 18, 1976, early in the Lebanese Civil War. La Quarantaine, known in Arabic as Karantina, was a predominantly Pal ...
, and siege of Tel al-Zaatar
The Siege of Tel al-Zaatar ( ar, حصار تل الزعتر, French language, French: Siège de Tel al-Zaatar), alternatively known as the Massacre of Tel al-Zaatar, was an armed siege of Tel al-Zaatar (meaning ''Hill of Thyme'' in Arabic), a for ...
and Naba'a by the Lebanese Front
The Lebanese Front ( ar, الجبهة اللبنانية, ''al-Jabha al-Lubnaniyya'') or ''Front Libanais'' in French, was a coalition of mainly Lebanese Nationalist parties formed in 1976 by majority Christian intellectuals during the Lebane ...
in 1976, more than 100,000 Shiites were displaced from East Beirut, and most fled to Dahieh
Dahieh ( ar, الضاحية الجنوبية, lit=the southern suburb, french: Banlieue Sud de Beyrouth, Dâhiye de Beyrouth) is a predominantly Shia Muslim suburb, located south of Beirut, in the Baabda District of Lebanon. It is composed of sev ...
. Dahieh became the main hub of Shia migration in the late 1970s and early 1980s, with 250,000 and 400,000 Shiites refugees fleeing the Israeli invasions of Lebanon in 1978 and in 1982 respectively. In 1986, 800,000 Shiites lived in Dahieh comprising most of Shias in Lebanon. Their frequent displacement stimulated solidarity among the Shiites.
Following Nabih Berri's rise to Amal's leadership in 1980, Amal officially entered the civil war. Relations between Amal on one side, and the PLO- Lebanese National Movement alliance, which had many Shia members, on the other side worsened. In 1980-1981, Amal clashed with the LNM-aligned Iraqi-led Baath party, which had a large Shia following, after Saddam Hussein's execution of Muhammad Baqir al-Sadr. Also at that time, many clashes took place with PLO elements in the South's Tyre District, and some villages were also shelled by the PLO such as Hanaouay
Hanaouay, Henawei, ( ar, حانويه) is a village in the Tyre District in Southern Lebanon, located north-west of Qana. Name
According to E. H. Palmer, ''Henawei'' means "the little bend". History
In the early 1860s, Ernest Renan noted: " ...
. In addition, when the Iran–Iraq War raged in September 1980, around 500 to 600 Amal fighters voluntarily moved to Iran to join Chamran in the fighting.
By the mid-1980s, Amal totalled 14,000–16,000 fighters.
After the 1982 Israeli invasion, many Shiite Islamist groups were formed, with the aim of kicking out Israel and bringing an end to western influence in Lebanon. This led to movements such as Islamic Amal Islamic Amal (in Arabic أمل الإسلامية) was a Lebanese Shia military movement based in Baalbek in the Beqaa Valley, Islamic Amal was led by Husayn Al-Musawi, who was also a leading figure in Hezbollah.
The movement got its start in June ...
, Islamic Jihad Organization, "Islamic Students Union", Organization of the Oppressed on Earth
The Organization of the Oppressed on Earth is a group that claimed responsibility for kidnappings, bombings, and executions in Lebanon in the 1980s. It was considered a precursor to, or another name for, Islamic Jihad and Hezbollah.
Connection ...
, "Jundallah", Imam Husayn
Abū ʿAbd Allāh al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib ( ar, أبو عبد الله الحسين بن علي بن أبي طالب; 10 January 626 – 10 October 680) was a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a son of Ali ibn Abi ...
Fedayeen
Fedayeen ( ar, فِدائيّين ''fidāʼīyīn'' "self-sacrificers") is an Arabic term used to refer to various military groups willing to sacrifice themselves for a larger campaign.
Etymology
The term ''fedayi'' is derived from Arabic: '' ...
, "Revolutionary Justice Organization", and eventually the formation Hezbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
as a conglomeration of various groups with support of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. In addition to Islamist factions, many Shias joined the Lebanese National Resistance Front upon its formation in September 16, 1982. These factions waged guerilla-style combat operations against Israeli forces and their South Lebanon Army proxy, mainly in the South. The South Lebanon Army was originally formed in 1978 by former members of the predominantly Christian faction of the Army of Free Lebanon, but grew to include a small number of Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
, Shia and Sunni collaborators. They were held responsible for carrying out many atrocities, detentions and assassinations against the local populace until Israeli withdrawal in 2000, including the assassination of Sheikh Ragheb Harb
Ragheb Harb ( ar, راغب حرب; 1952–1984 was a Lebanese leader and Muslim cleric. He was born in Jibchit in 1952, a village in the Jabal Amel region of Southern Lebanon. Harb was an imam and led the regional Shiite resistance against I ...
and Sohmor massacre. According to the observation of an Israeli Arab affairs adviser in south Lebanon in December 1982, the Shia members of SLA were looked upon as "the dregs of Shia society" by their own people.
Between 1982 and 1985, half of the male population in the South had been detained at one point in the infamous Ansar prison camp, and in 1985 alone the prison held around 15,000 prisoners. Other famous prisons included Khiam detention center. In 1985, Israel implemented the Iron Fist policy
The Iron Fist policy, also known as Operation Iron Fist, was a policy involving series of raids carried out in 1985 by the Israeli Defence Force during the South Lebanon conflict (1985–2000), 1985-2000 South Lebanon conflict and First Intifada ...
in Southern Lebanon, conducting dozens of raids on Shia villages, notably Zrarieh raid
The Zrarieh raid was an Israeli raid on the Lebanese village of Zrarieh in Southern Lebanon on 11 March 1985. During the raid between 21 and 40Maarakeh bombing, according to Robert Fisk.
By 23 March 1985, more than 100 Lebanese had been killed, including a 2-man CBS film crew, and 40 houses destroyed.
In between October 1983 and June 1984, Shia-populated southern suburbs of Beirut were struck by the U.S Navy battleship USS ''New Jersey'', the destroyer USS ''John Rodgers'' and the nuclear-powered cruiser USS ''Virginia'', causing hundreds of civilian casualties, according to then- ABC News correspondent
 Shia Twelvers in Lebanon refers to the Shia Muslim Twelver community with a significant presence all over Lebanon including the
Shia Twelvers in Lebanon refers to the Shia Muslim Twelver community with a significant presence all over Lebanon including the
 There are an estimated 100,000Riad Yazbeck.
There are an estimated 100,000Riad Yazbeck.
Return of the Pink Panthers?
'. Mideast Monitor. Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2008 Alawites in Lebanon, where they have lived since at least the 16th century. They are recognized as one of the 18 official Lebanese sects, and due to the efforts of an Alawite leader Ali Eid, the Taif Agreement of 1989 gave them two reserved seats in the Parliament. Lebanese Alawites live mostly in the Jabal Mohsen neighbourhood of
/ref> of Lebanon's population."Lebanon: people and society"
/ref>
The Shia Rulers of Banu Ammar, Banu Mardas and the Mazidi
{{Lebanese people by religious background
Charles Glass
Charles Glass (born November 18, 1951) is an American-British author, journalist, broadcaster and publisher specializing in the Middle East and the Second World War.
He was ''ABC News'' chief Middle East correspondent from 1983 to 1993, and has ...
. The offshore bombardment by these ships was the heaviest the U.S. had conducted since the Korean war. On February 6 Intifada in 1984, Shia Amal Movement and allied militias managed to drive the Lebanese army
)
, founded = 1 August 1945
, current_form = 1991
, disbanded =
, branches = Lebanese Ground ForcesLebanese Air Force Lebanese Navy
, headquarters = Yarze, Lebanon
, flying_hours =
, websit ...
and the Multinational Force present in Lebanon out of West Beirut. Aided by ~2,000 deserters from the predominantly-Shia Sixth Brigade in the army, the battle effectively resulted in the collapse of Israel's and U.S influence in Lebanon. Following the intifada, the Lebanese government repudiated the May 17 Agreement with Israel on March 5. Simultaneously, the Multinational Force present in Lebanon, which was composed of American, British, French and Italian units, withdrew completely by March 31. After cementing control on much of West Beirut, Amal besieged Palestinian camps in Beirut and the South between May 1985 and July 1988, as Amal wanted to dislodge PLO remnants loyal to Yasser Arafat and was supported in the process by the Syrian Army
" (''Guardians of the Homeland'')
, colors = * Service uniform: Khaki, Olive
* Combat uniform: Green, Black, Khaki
, anniversaries = August 1st
, equipment =
, equipment_label =
, battles = 1948 Arab–Israeli War
Six ...
and multiple factions in the Palestinian National Salvation Front
The Palestinian National Salvation Front ( ar, جبهة الانقاذ الوطني الفلسطيني) (PNSF) was a coalition of Palestinian factions. The creation of the Palestinian National Salvation Front was announced on March 25, 1985, by Kh ...
, resulting in thousands of casualties, and the destruction of much of the camps. The war was adamantly opposed by the religious-oriented Hezbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
, who refused to partake in action.
Sub-groups
Shia Twelvers (Metouali)
 Shia Twelvers in Lebanon refers to the Shia Muslim Twelver community with a significant presence all over Lebanon including the
Shia Twelvers in Lebanon refers to the Shia Muslim Twelver community with a significant presence all over Lebanon including the Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at .
Geography
The Mount Le ...
(Keserwan, Byblos), the North (Batroun), the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
, the Beqaa Beqaa ( ar, بقاع, link=no, ''Biqā‘'') can refer to two places in Lebanon:
* Beqaa Governorate, one of six major subdivisions of Lebanon
* Beqaa Valley, a valley in eastern Lebanon and its most important farming region
See also
*Kasbeel ...
, Baabda District coastal areas and Beirut.
The jurisdiction of the Ottoman Empire was merely nominal in the Lebanon. Baalbek
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman ...
in the 18th century was really under the control of the Metawali, which also refers to the Shia Twelvers. Metawali, Metouali, or Mutawili, is an archaic term used to specifically refer to Lebanese Twelver Shias in the past. Although it can be considered offensive nowadays, it was a way to distinguish the uniqueness and unity of the community. The term 'mutawili' is also the name of a trustee in Islamic waqf-system.
Seven Shia Twelver (Mutawili) villages that were reassigned from French Greater Lebanon to the British Mandate of Palestine in a 1924 border-redrawing agreement were depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
and repopulated with Jews. The seven villages are Qadas
Qadas (also Cadasa; ar, قدس) was a Palestinian village located 17 kilometers northeast of Safad that was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. One of seven Shia Muslim villages, called ''Metawalis'', that fell within the boundaries of ...
, Nabi Yusha
Al-Nabi Yusha' ( ar, النبي يوشع was a small Palestinian village in the Galilee situated 17 kilometers to the northeast of Safad, with an elevation of 375 meters above sea level. It became part of the Palestine Mandate under British co ...
, al-Malikiyya
Al-Malikiyya ( ar, المالكية) was a Palestinian village located in the Jabal Amil region. In a 1920s census, the village was registered as part of Greater Lebanon. It was later placed under the British Mandate of Palestine. Its population ...
, Hunin, Tarbikha
Tarbikha ( ar, تربيخا), was a Palestinian Arab village. It was located northeast of Acre in the British Mandate District of Acre that was captured and depopulated by the Israel Defense Forces during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. The inha ...
, Abil al-Qamh
Abil al-Qamh ( ar, آبل القمح) was a Palestinian village located near the Lebanese border north of Safad. It was depopulated in 1948. It was located at the site of the biblical city of Abel-beth-maachah.
Name
According to Khalidi, its Ara ...
, and Saliha.
In addition, the Shia Twelvers in Lebanon have close links to the Syrian Shia Twelvers.
Alawites
 There are an estimated 100,000Riad Yazbeck.
There are an estimated 100,000Riad Yazbeck. Return of the Pink Panthers?
'. Mideast Monitor. Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2008 Alawites in Lebanon, where they have lived since at least the 16th century. They are recognized as one of the 18 official Lebanese sects, and due to the efforts of an Alawite leader Ali Eid, the Taif Agreement of 1989 gave them two reserved seats in the Parliament. Lebanese Alawites live mostly in the Jabal Mohsen neighbourhood of
Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
, and in 10 villages in the Akkar region, and are mainly represented by the Arab Democratic Party. Bab al-Tabbaneh, Jabal Mohsen clashes between pro-Syrian Alawites and anti-Syrian Sunnis
Sunni Islam () is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia ...
have haunted Tripoli for decades.
Isma'ilis
Isma'ilism, or "Sevener
al-Ismāʿīliyya al-khāliṣa / al-Ismāʿīliyya al-wāqifa or Seveners ( ar, سبعية) was a branch of Ismā'īlī Shīʻa. They broke off from the more numerous Twelvers after the death of Jafar al-Sadiq in 765 AD. They became known as " ...
Shi'ism", is a branch of Shia Islam which emerged in 765 from a disagreement over the succession to Muhammad
The succession to Muhammad is the central issue that split the Ummah, Muslim community into several Islamic schools and branches, divisions in the first century of Islamic history, with the most prominent among these sects being the Shia and S ...
. Isma'ilis hold that Isma'il ibn Jafar
Abū Muḥammad Ismāʿīl ibn Jaʿfar al-Mubārak ( ar, إسماعيل بن جعفر; c.719 AD – c.762 AD) was the eldest son of Imam Ja'far al-Sadiq. He is also known as Isma'il al-Ãraj ibn Ja'far al-Sadiq (اسماعيل الاعرج ...
was the true seventh imam, and not Musa al-Kadhim
Musa ibn Ja'far al-Kazim ( ar, مُوسَىٰ ٱبْن جَعْفَر ٱلْكَاظِم, Mūsā ibn Jaʿfar al-Kāẓim), also known as Abū al-Ḥasan, Abū ʿAbd Allāh or Abū Ibrāhīm, was the seventh Imam in Twelver Shia Islam, after hi ...
as the Twelvers believe. Isma'ili Shi'ism also differs doctrinally from Imami
Twelver Shīʿīsm ( ar, ٱثْنَا عَشَرِيَّة; '), also known as Imāmīyyah ( ar, إِمَامِيَّة), is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, comprising about 85 percent of all Shīʿa Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers t ...
Shi'ism, having beliefs and practices that are more esoteric and maintaining seven pillars Seven pillars may refer to:
* Seven Pillars for Prosperity, policy statement of the Progressive Canadian Party
* Seven Pillars Institute for Global Finance and Ethics (SPI) in Lawrence, Kansas
*Seven pillars of Ismailism in Shia Islam and in Nizari ...
of faith rather than five pillars and ten ancillary precepts.
Though perhaps somewhat better established in neighbouring Syria, where the faith founded one of its first da'wah outposts in the city of Salamiyah
A full view of Shmemis (spring 1995)
Salamieh ( ar, سلمية ') is a city and district in western Syria, in the Hama Governorate. It is located southeast of Hama, northeast of Homs. The city is nicknamed the "mother of Cairo" because it was t ...
(the supposed resting place of the Imam Isma'il) in the 8th century, it has been present in what is now Lebanon for centuries. Early Lebanese Isma'ilism showed perhaps an unusual propensity to foster radical movements within it, particularly in the areas of Wadi al-Taym, adjoining the Beqaa valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
at the foot of Mount Hermon, and Jabal Shuf, in the highlands of Mount Lebanon
Mount Lebanon ( ar, جَبَل لُبْنَان, ''jabal lubnān'', ; syr, ܛܘܪ ܠܒ݂ܢܢ, ', , ''ṭūr lewnōn'' french: Mont Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon. It averages above in elevation, with its peak at .
Geography
The Mount Le ...
.
The syncretic beliefs of the Qarmatians
The Qarmatians ( ar, قرامطة, Qarāmiṭa; ) were a militant Isma'ilism, Isma'ili Shia Islam, Shia movement centred in Al-Ahsa Oasis, al-Hasa in Eastern Arabia, where they established a Utopia#Religious utopias, religious-utopian Socialis ...
, typically classed as an Isma'ili splinter sect with Zoroastrian influences, spread into the area of the Beqaa valley and possibly also Jabal Shuf starting in the 9th century. The group soon became widely vilified in the Islamic world for its armed campaigns across throughout the following decades, which included slaughtering Muslim pilgrims and sacking Mecca and Medina—and Salamiyah. Other Muslim rulers soon acted to crush this powerful heretical movement. In the Levant, the Qarmatians were ordered to be stamped out by the ruling Fatimid, themselves Isma'ilis and from whom the lineage of the modern Nizari Aga Khan
Aga Khan ( fa, آقاخان, ar, آغا خان; also transliterated as ''Aqa Khan'' and ''Agha Khan'') is a title held by the Imām of the Nizari Ismāʿīli Shias. Since 1957, the holder of the title has been the 49th Imām, Prince Shah Karim ...
is claimed to descend. The Qarmatian movement in the Levant was largely extinguished by the turn of the millennium.
The semi-divine personality of the Fatimid caliph in Isma'ilism was elevated further in the doctrines of a secretive group which began to venerate the caliph Hakim as the embodiment of divine unity. Unsuccessful in the imperial capital of Cairo, they began discreetly proselytising around the year 1017 among certain Arab tribes in the Levant. The Isma'ilis of Wadi al-Taym and Jabal Shuf were among those who converted before the movement was permanently closed off a few decades later to guard against outside prying by mainstream Sunni and Shia Muslims, who often viewed their doctrines as heresy. This deeply esoteric group became known as the Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
, who in belief, practice, and history have long since become distinct from Isma'ilis proper. Druze constitute 5.2% of the modern population of Lebanon and still have a strong demographic presence in their traditional regions within the country to this day.
Due to official persecution by the Sunni Zengid dynasty that stoked escalating sectarian clashes with Sunnis, many Isma'ilis in the regions of Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
and Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
are said to have fled west during the 12th century. Some settled in the mountains of Lebanon, while others settled further north along the coastal ridges in Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, where the Alawites had earlier taken refuge—and where their brethren in the Assassins
An assassin is a person who commits targeted murder.
Assassin may also refer to:
Origin of term
* Someone belonging to the medieval Persian Ismaili order of Assassins
Animals and insects
* Assassin bugs, a genus in the family ''Reduviida ...
were cultivating a fearsome reputation as they staved off armies of Crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
rs and Sunnis alike for many years.
Once far more numerous and widespread in many areas now part of Lebanon, the Isma'ili population has largely vanished over time. It has been suggested that Ottoman-era persecution might have spurred them to leave for elsewhere in the region, though there is no record or evidence of any kind of large exodus.
Isma'ilis were originally included as one of five officially-defined Muslim sects in a 1936 edict issued by the French Mandate governing religious affairs in the territory of Greater Lebanon, alongside Sunnis
Sunni Islam () is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia ...
, Twelver Shias, Alawites, and Druzes
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of H ...
. However, Muslims collectively rejected being classified as divided, and so were left out of the law in the end. Ignored in a post-independence law passed in 1951 that defined only Judaism and Christian sects as official, Muslims continued under traditional Ottoman law, within the confines of which small communities like Isma'ilis and Alawites found it difficult to establish their own institutions.
The Aga Khan IV made a brief stop in Beirut on 4 August 1957 while on a global tour of Nizari Isma'ili centres, drawing an estimated 600 Syrian and Lebanese followers of the religion to the Beirut Airport in order to welcome him. In the mid-1980s, several hundred Isma'ilis were thought to still live in a few communities scattered across several parts of Lebanon. Though they are nominally counted among the 18 officially-recognised sects under modern Lebanese law, they currently have no representation in state functions and continue to lack personal status
Legal status is the status or position held by an entity as determined by the law. It includes or entails a set of privileges, obligations, powers or restrictions that a person or thing has as encompassed in or declared by legislation.
Jack Balki ...
laws for their sect, which has led to increased conversions to established sects to avoid the perpetual inconveniences this produces.
War in the region has also caused pressures on Lebanese Isma'ilis. In the 2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
, Israeli warplanes bombed the factory of the Maliban Glass company in the Beqaa valley on 19 July. The factory was bought in the late 1960s by the Madhvani Group under the direction of Isma'ili entrepreneur Abdel-Hamid al-Fil after the Aga Khan personally brought the two into contact. It had expanded over the next few decades from an ailing relic to the largest glass manufacturer in the Levant, with 300 locally hired workers producing around 220,000 tons of glass per day. Al-Fil closed the plant down on 15 July just after the war broke out to safeguard against the deaths of workers in the event of such an attack, but the damage was estimated at a steep 55 million US dollars, with the reconstruction timeframe indefinite due to instability and government hesitation.
Geographic distribution within Lebanon
Lebanese Shia Muslims are concentrated in south Beirut and its southern suburbs, northern and western area of the Beqaa Valley, as well as Southern Lebanon.Demographics
Note that the following percentages are estimates only. However, in a country that had last census in 1932, it is difficult to have correct population estimates. The last census in Lebanon in 1932 put the numbers of Shias at 19.6% of the population (154,208 of 785,543). A study done by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) in 1985 put the numbers of Shias at 41% of the population (919,000 of 2,228,000). However, a 2012 CIA study reports that the Shia Muslims constituted an estimated 27% of Lebanon's population. And more recently, in 2018 the CIA World Factbook estimated that Shia Muslims constitute 30.5%"Lebanon: people and society"/ref> of Lebanon's population."Lebanon: people and society"
/ref>
Genetics
In a 2020 study published in the American Journal of Human Genetics, authors showed that there is substantial genetic continuity in Lebanon and the Levant since the Bronze Age (3300–1200 BC) interrupted by three significant admixture events during the Iron Age,Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
, and Ottoman period, each contributing 3%–11% of non-local ancestry to the admixed population. The admixtures were tied to the Sea Peoples of the Late Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near East ...
, Central/South Asians and Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
respectively. Genetic studies have shown that there are no significant genetic differences between Lebanese Muslims and non-Muslims.
Haplogroup J2 is also a significant marker throughout Lebanon (29%). This marker found in many inhabitants of Lebanon, regardless of religion, signals pre-Arab descendants, although not exclusively. Genealogical DNA testing has shown that 21.3% of Lebanese Muslims (non-Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
) belong to the Y-DNA haplogroup J1
Haplogroup J-M267, also commonly known as Haplogroup J1, is a subclade (branch) of Y-DNA haplogroup J-P209 (commonly known as haplogroup J) along with its sibling clade haplogroup J-M172 (commonly known as haplogroup J2). (All these haplogr ...
compared with non-Muslims at 17%. Although Haplogroup J1 is most common in Arabian peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
, studies have shown that it has been present in the Levant since the Bronze Age and does not necessarily indicate Arabian descent. Other haplogroups present among Lebanese Shia include E1b1b (17%), G-M201 (10%), R1b
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and pockets of Central A ...
, and T-L206 occurring at smaller, but significant rates.
Notable Lebanese Shia Muslims
* Muhammad Jamaluddin al-Makki al-ʿĀmili (1334–1385) – Prominent Shia scholar from Jezzine, known as "Shahid Awwal"/"First Martyr" * Nur-al-Din al-Karaki al-ʿĀmilī (1465–1534) – Shiite scholar and a member of the Safavid court *Bahāʾ al-dīn al-ʿĀmilī
Bahāʾ al‐Dīn Muḥammad ibn Ḥusayn al‐ʿĀmilī (also known as Sheikh Baha'i, fa, شیخ بهایی) (18 February 1547 – 1 September 1621) was an Iranian ArabEncyclopedia of Arabic Literature'. Taylor & Francis; 1998. . p. 85. Sh ...
(1547–1621) – Shia Islamic scholar, philosopher, architect, and polymath
*Al-Hurr al-Amili
Muhammad bin al-Ḥasan bin Ali bin al-Ḥusayn al-Ḥurr al-ʿĀmili al-Mashghari ( ar, مُحَمَّد ٱبْن ٱلْحَسَن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱلْحُرّ ٱلْعَامِلِيّ ٱلْمَشْغَرِي ...
(1624–1693) – prominent Shia muhaddith and compiler of Wasa'il al-Shia
*Nassif al-Nassar
Nasif ibn al-Nassar al-Wa'ili ( ar, ناصيف النصار; died 24 September 1781) was the most powerful sheikh of the rural Shia Islam in Lebanon, Shia Muslim (Matawilah) tribes of Jabal Amel, Jabal Amil (modern-day South Lebanon) in the mid-1 ...
(c. 1750–1781) – Sheikh of Jabal Amel
* Abdel Hussein Charafeddine – Spiritual leader and social reformer, leading supporter of unity within a Greater Syria
Syria (Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other s ...
and organiser of nonviolent resistance
Nonviolent resistance (NVR), or nonviolent action, sometimes called civil resistance, is the practice of achieving goals such as social change through symbolic protests, civil disobedience, economic or political noncooperation, satyagraha, cons ...
against the French, and the founder of the modern city of Tyre
* Musa al-Sadr – Spiritual leader and founder of the Amal movement, philosopher and Shi'a religious leader
*Hussein el Husseini
Sayyid Hussein El-Husseini ( ar, حسين الحسيني) (born 15 April 1937) is a Lebanese people, Lebanese politician and former Parliament of Lebanon#Speaker, speaker of the Lebanese parliament, whose efforts in brokering and fathering the Ta ...
– Statesman, co-founder of the Amal movement and Speaker of Parliament
* Mohammad Hussein Fadlallah – Spiritual Leader and Shia Grand Ayatollah, former spiritual guide of Islamic Dawa Party in Lebanon
The Islamic Dawa Party in Lebanon(Arabic language, Arabic حزب الدعوة الإسلامية ''Ḥizb al Daʿwa al-Islāmiyya'') was an Islamist Shia party in Lebanon. A twin party of the larger Islamic Dawa Party of Iraq, it was founded by N ...
*Hassan Nasrallah
Hassan Nasrallah ( ar, حسن نصر الله ; born 31 August 1960) is a Lebanese cleric and political leader who has served as the 3rd secretary-general of Hezbollah since his predecessor, Abbas al-Musawi, was assassinated by the Israel Def ...
– Leader of the group Hezbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
* Imad Mughniyah – Lebanese, Hezbollah's former Chief of Staff
* Mustafa Badreddine – Military leader in Hezbollah and both the cousin and brother-in-law of Imad Mughniyah
*Adel Osseiran
Adel Osseiran ( ar, عادل عسيران; 5 June 1905 – 18 June 1998), also transliterated Adil 'Usayran or Adil Osseyran, was a prominent Lebanese statesman, a former Speaker of the Lebanese Parliament, and one of the founding fathers of the L ...
– Speaker of the Lebanese Parliament, and one of the founding fathers of the Lebanese Republic
* Sabri Hamade – Speaker of the Parliament and political leader
*Ahmed al-Asaad
Ahmad El-Assaad or Ahmad Al-As'ad ( ar, أحمد الأسعد) (1902 – 16 March 1961) was Speaker of the Lebanese Parliament from 5 June 1951, till 30 May 1953.
Life
Family background
El-Assaad was the scion of a Shia feudal dynasty, whi ...
– Speaker of the parliament and political leader
* Kamel Asaad – Speaker of the parliament and political leader
* Nabih Berri – Speaker of the Parliament and political leader of Amal Movement
* Abbas Ibrahim – General director of the General Directorate of General Security
The General Security Directorate ( ar, الامن العام, al-Amn al-'Aam; french: La Sûreté Générale) is a Lebanese intelligence agency founded on July 21, 1921 and originally known as the "first bureau". On June 12, 1959, Decree-Law No. ...
*Wafiq Jizzini
Major General Wafiq Jizzini ( ar, وفيق جزيني; also spelled Wafic Jezzini or Wafik Jezzini; 4 December 1951 – 4 March 2011) was the general director of the General Directorate of General Security of Lebanon from 2005 to 2010.
Career
...
– Former General director of the General Directorate of General Security
The General Security Directorate ( ar, الامن العام, al-Amn al-'Aam; french: La Sûreté Générale) is a Lebanese intelligence agency founded on July 21, 1921 and originally known as the "first bureau". On June 12, 1959, Decree-Law No. ...
* Jamil Al Sayyed – Former General director of the General Directorate of General Security
The General Security Directorate ( ar, الامن العام, al-Amn al-'Aam; french: La Sûreté Générale) is a Lebanese intelligence agency founded on July 21, 1921 and originally known as the "first bureau". On June 12, 1959, Decree-Law No. ...
*Adham Khanjar
Adham Khanjar ( ar, أدهم خنجر) (1890–1922) was a Lebanese Shia Muslim revolutionary and Syrian nationalist who participated in guerilla warfare against the forces of the French occupation of Lebanon and Syria, and the attempt to assassi ...
– Lebanese revolutionary who attempted to assassinate Henri Gouraud and as a result was executed in 1923
* Tawfiq Hawlo Haidar – Lebanese revolutionary who took part in the Great Syrian Revolt
The Great Syrian Revolt ( ar, الثورة السورية الكبرى) or Revolt of 1925 was a general uprising across the State of Syria and Greater Lebanon during the period of 1925 to 1927. The leading rebel forces comprised fighters of the ...
(1925–1927)
*Hussein al-Musawi
Husayn Al-Musawi (also Hussein Musawi) is a Lebanese who founded the now-dissolved pro-Iranian Islamist militia Islamic Amal in 1982. He was a Shia from Baalbek.
Musawi was a "chemistry teacher turned militia commander" who became the deputy ...
– Founder of Islamic Amal Islamic Amal (in Arabic أمل الإسلامية) was a Lebanese Shia military movement based in Baalbek in the Beqaa Valley, Islamic Amal was led by Husayn Al-Musawi, who was also a leading figure in Hezbollah.
The movement got its start in June ...
militia in 1982
* Assem Qanso – Former leader of the Lebanese Arab Socialist Baath Party
*Ali Qanso
Ali Khalil Qanso ( ar, علي قانصوه) was a Lebanese politician who served as a minister for parliamentary affairs in the second cabinet of Saad Hariri. He was the president of the Syrian Social Nationalist Party and he served as minister ...
– Member of cabinet, former president of the Syrian Social Nationalist Party
*Husayn Muruwwa
''Husayn Muruwwa'' (also spelt ''Hussein Mroue'' or ''Mroueh'') (1908/1910-February 17, 1987) was a Lebanese Marxist intellectual, journalist, author, and literary critic. His longest and most famous work, "Materialist Tendencies in Arabic-Islami ...
– Marxist
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
philosopher and former key member of the Lebanese Communist Party
* Mahdi Amel – Marxist philosopher and former prominent member of the Lebanese Communist party
*Muhsin Ibrahim
Mohsin Ibrahim ( ar, محسن إبراهيم ''Muḥsin ‘Ibrāhīm''), kunya Abu Khaled (; 1935 – June 3, 2020), was a Lebanese politician. He was a prominent personality of the Lebanese and Arab left. Initially a Nasserist nationalist, he ...
– Communist, founder and former leader of the Communist Action Organization in Lebanon
The Communist Action Organization in Lebanon – CAOL ( ar, منظمة العمل الشيوعي في لبنان , ''munaẓẓamah al-‘amal al-shuyū‘ī fī lubnān''), also known as Organization of Communist Action in Lebanon (OCAL) or Orga ...
* Ahmad Rida – Shiite scholar and linguist, compiled the first monolingual Arabic dictionary, Matn al-Lugha ''Matn al-Lugha'' (; "Corpus of the Language") was one of earliest modern monolingual dictionaries of the Arabic language, written by Lebanese linguist Sheikh Ahmed Rida, an important figure of the Arab literary renaissance. The five-volume dictio ...
*Muhammad Jaber Al Safa
Muhammad Jaber Āl Safa (also spelled Jabir Al Safa) (1875–1945) () was a historian, writer and politician from Jabal Amel (in modern-day Lebanon), known for his founding role in the anti-colonialist Arab nationalist movement in turn-of-the-cen ...
– Historian, writer and Arab nationalist
Arab nationalism ( ar, القومية العربية, al-Qawmīya al-ʿArabīya) is a nationalist ideology that asserts the Arabs are a nation and promotes the unity of Arab people, celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language an ...
Chalabi, Tamara (2006). ''The Shi'is of Jabal `Amil and the New Lebanon: Community and Nation-State, 1918-1943'', p.34
* Ahmed Aref El-Zein – Reformist scholar, Arab nationalist and founder of Al-Irfan magazine in 1909
*Hassan Kamel Al-Sabbah
Hassan Kamel Al-Sabbah ( ar, حسن كامل الصباح; August 16, 1894March 31, 1935) was a Lebanese electrical and electronics research engineer, mathematician and inventor. He was born in Nabatieh, Lebanon.
Biography
He studied at the Ameri ...
– Electrical engineer, mathematician and inventor with patents in television transmission.
*Rammal Rammal
Rammal Hassan Rammal ( ar, رمال حسن رمال) (September 30, 1951 – May 31, 1991) was a Lebanese condensed matter physicist. He was born in Doueir, South Lebanon. He lived and went to school in Beirut. He was the top student in his cla ...
– Lebanese Physicist
*Ali Chamseddine
Ali H. Chamseddine ( ar, علي شمس الدين, link=no, born 20 February 1953) is a Lebanese physicist known for his contributions to particle physics, general relativity and mathematical physics. , Chamseddine is a physics Professor at t ...
– Lebanese Physicist
*Zaynab Fawwaz
Zaynab Fawwaz (1860–1914) was a Lebanese people, Lebanese women's rights activist, novelist, playwright, poet and historian of famous women. Her novel "''حسن العواقب/Ḥusn al-Awaqib",'' (''The Happy Ending'', 1899) is considered the ...
– Pioneering novelist, playwright, poet and historian of famous women in the 19th century
*Hanan al-Shaykh
Hanan al-Shaykh ( ar, حنان الشيخ; born 12 November 1945, Beirut) is a Lebanese author of contemporary literature.
Biography
Hanan al-Shaykh was born Beirut, Lebanon, in 1945, into a strict Shi'a
family. Her father and brother exerte ...
– Lebanese author
*Amal Saad-Ghorayeb
Amal Abdo Saad-Ghorayeb ( ar, أمل سعد غريب) is a Lebanese writer and political analyst known for her writings on the Israeli–Lebanese conflict and Hezbollah.
Life
Saad-Ghorayeb was an assistant professor of political science at the Leb ...
– Lebanese writer and scholar
*Malek Maktabi
Malek Maktabi (or Malik Maktaby, ar, مالك مكتبي, born in Beirut on 10 November 1981) is a Lebanese television presenter who is known for hosting '' Ahmar Bil Khatt Al Aarid'' (Red in Boldface), a weekly talk show about social and hu ...
– Lebanese journalist and television presenter, husband of Nayla Tueni
Nayla Tueni Maktabi ( ar, نايلة تويني مكتبي) (born 31 August 1982) is a Lebanese journalist and politician. She was a member of the Lebanese Parliament for almost ten years (2009–2018), representing the district of Achrafieh. Tu ...
* Fouad Ajami – Former university professor at Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is consider ...
and writer on Middle Eastern issues
*Haifa Wehbe
Haifa Wehbe ( ar, هيفاء وهبي ) is a Lebanese people, Lebanese-Egyptians, Egyptian singer and actress. She has released seven studio albums, and made her acting debut in the 2008 Pepsi-produced film ''Sea of Stars''. In 2006, Wehbe was ...
– Singer and actress
* Layal Abboud – Singer
* Rima Fakih – winner of the 2010 Miss USA title; later converted from Shia Islam to Maronite Christianity
The Maronite Church is an Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic ''sui iuris'' particular church in full communion with the pope and the worldwide Catholic Church, with self-governance under the Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches. Th ...
* Mouhamed Harfouch – Brazilian-Lebanese actor
*Ragheb Alama
Ragheb Alama ( ar, راغب علامة born 7 June 1962) is a Lebanese singer, dancer, composer, television personality, and philanthropist. Alama began his career in the 1980s when he appeared as a contestant on the talent show broadcast Studio ...
– Singer, composer, television personality, and philanthropist
* Assi El Helani – Famous singer
* May Hariri – Model, actress, and singer
*Alissar Caracalla
Alissar Abdel-Halim Caracalla is a Lebanon, Lebanese dance instructor, choreography, choreographer and art director. She is the founder and director of the Orientalist Dance Company and CDS, the Caracalla School of Dance, which is simply known as ...
– Lebanese Dance choreographer
* Hassan Bechara – Lebanese wrestler, won the bronze medal in the men's Greco-Roman Super Heavyweight category
* Roda Antar – Lebanese football manager, Former captain of Lebanese national team and player who currently coaches Racing Beirut in the Lebanese Football League.
* Moussa Hojeij – Lebanese football player and manager at Nejmeh SC
See also
* Religion in Lebanon * Islam in Lebanon * Lebanese Sunni Muslims *Lebanese Druze
Lebanese Druze ( ar, دروز لبنان, durūz lubnān) are Lebanese people who are Druze. The Druze faith is a monotheistic and Abrahamic religion, and an ethnoreligious esoteric group originating from the Near East who self identify as ...
* Banu Amela, Shia tribe in Lebanon
* Jabal Amel, region in Lebanon
* Lebanese Maronite Christians
Lebanese Maronite Christians ( ar, المسيحية المارونية في لبنان; syc, ܡܫܝܚܝ̈ܐ ܡܪ̈ܘܢܝܐ ܕܠܒܢܢ) are adherents of the Maronite Church in Lebanon, which is the largest Christianity in Lebanon, Christian de ...
* Lebanese Melkite Christians
* Lebanese Greek Orthodox Christians
* Lebanese Protestant Christians
References
External links
The Shia Rulers of Banu Ammar, Banu Mardas and the Mazidi
{{Lebanese people by religious background