Moa (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Moa (
 Moa skeletons were traditionally reconstructed in an upright position to create impressive height, but analysis of their vertebral articulations indicates that they probably carried their heads forward,Worthy & Holdaway (2002) in the manner of a
Moa skeletons were traditionally reconstructed in an upright position to create impressive height, but analysis of their vertebral articulations indicates that they probably carried their heads forward,Worthy & Holdaway (2002) in the manner of a
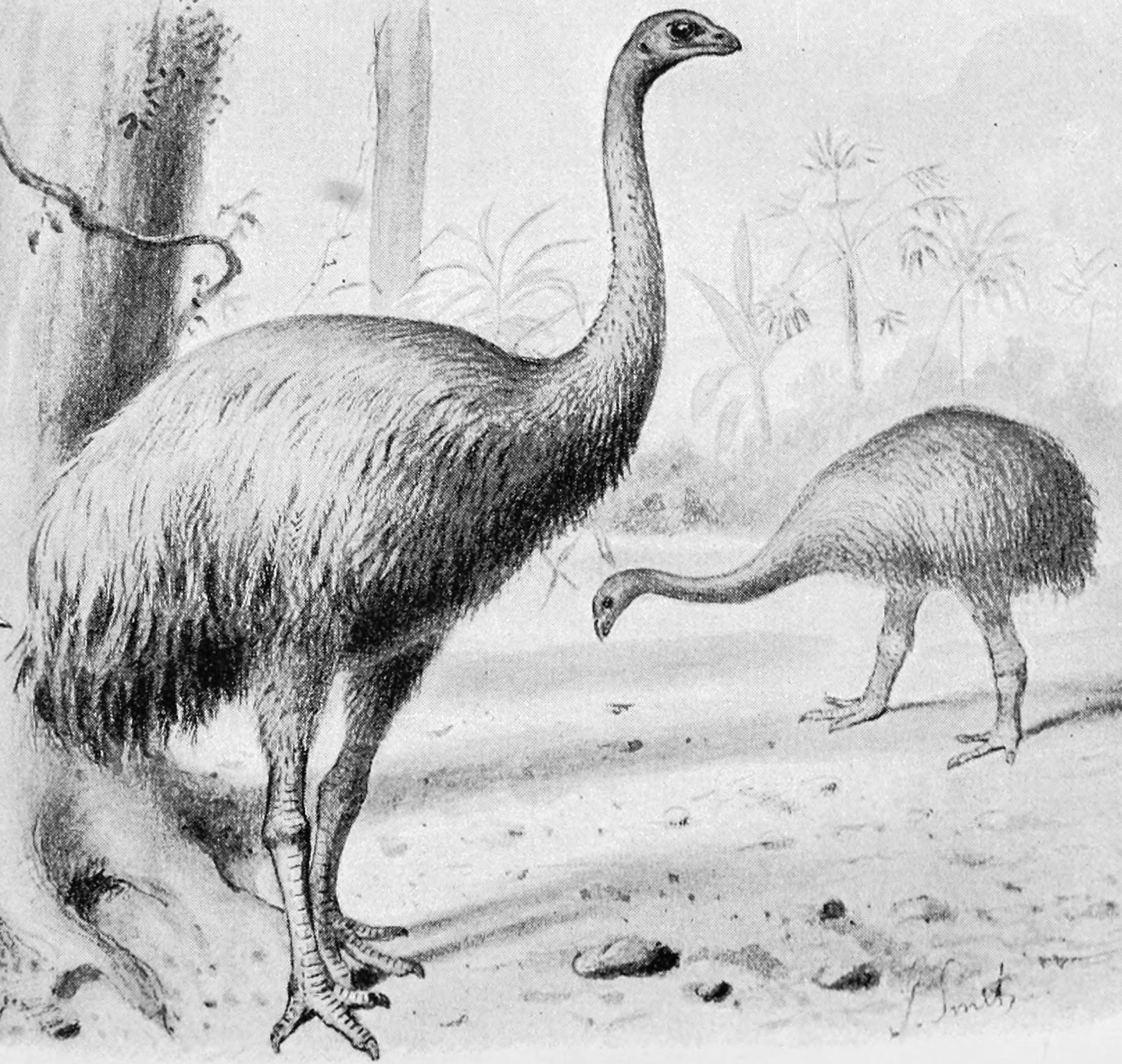 The two main faunas identified in the South Island include:
: The fauna of the high-rainfall west coast beech ('' Nothofagus'') forests that included ''Anomalopteryx didiformis'' (bush moa) and ''Dinornis robustus'' (South Island giant moa), and
: The fauna of the dry rainshadow forest and shrublands east of the Southern Alps that included ''Pachyornis elephantopus'' (heavy-footed moa), ''Euryapteryx gravis'', ''Emeus crassus'', and ''Dinornis robustus''.
A ' subalpine fauna' might include the widespread ''D. robustus'', and the two other moa species that existed in the South Island:
:: ''Pachyornis australis'', the rarest moa species, the only moa species not yet found in Māori
The two main faunas identified in the South Island include:
: The fauna of the high-rainfall west coast beech ('' Nothofagus'') forests that included ''Anomalopteryx didiformis'' (bush moa) and ''Dinornis robustus'' (South Island giant moa), and
: The fauna of the dry rainshadow forest and shrublands east of the Southern Alps that included ''Pachyornis elephantopus'' (heavy-footed moa), ''Euryapteryx gravis'', ''Emeus crassus'', and ''Dinornis robustus''.
A ' subalpine fauna' might include the widespread ''D. robustus'', and the two other moa species that existed in the South Island:
:: ''Pachyornis australis'', the rarest moa species, the only moa species not yet found in Māori
File:The skeleton of female upland moa.JPG, The skeleton of female upland moa with egg in unlaid position within the pelvic cavity in Otago Museum
File:Emeus egg and embryo.jpg, An egg and embryo fragments of ''Emeus crassus''
File:Megalapteryx.png, Restoration of an upland moa
 Since the discovery of the first moa bones in the late 1830s, thousands more have been found. They occur in a range of late
Since the discovery of the first moa bones in the late 1830s, thousands more have been found. They occur in a range of late

TerraNature list of New Zealand's extinct birds
Tree of Life classification and references
Moa article
in Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand
3D model of a moa skull
{{Authority control * Extinct flightless birds Higher-level bird taxa restricted to New Zealand Late Quaternary prehistoric birds Extinct birds of New Zealand Ratites Bird extinctions since 1500 Holocene extinctions Species made extinct by human activities Animals with only two limbs Miocene first appearances Taxa named by Charles Lucien Bonaparte Notopalaeognathae
order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
Dinornithiformes) are an extinct group of flightless birds formerly endemic to New Zealand.OSNZ (2009) During the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of ...
-Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
, there were nine species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
(in six genera). The two largest species, ''Dinornis robustus
The South Island giant moa (''Dinornis robustus'') is an extinct moa from the genus ''Dinornis.''
Context
The moa were ratites, flightless birds with a sternum without a keel. They also had a distinctive palate. The origin of these birds is b ...
'' and '' Dinornis novaezelandiae'', reached about in height with neck outstretched, and weighed about Davies, S.J.J.F. (2003) while the smallest, the bush moa (''Anomalopteryx didiformis''), was around the size of a turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. Estimates of the moa population when Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
settled New Zealand circa 1300 vary between 58,000 and approximately 2.5 million.
Moa are traditionally placed in the ratite
A ratite () is any of a diverse group of flightless, large, long-necked, and long-legged birds of the infraclass Palaeognathae. Kiwi, the exception, are much smaller and shorter-legged and are the only nocturnal extant ratites.
The systematics ...
group. However, genetic studies have found that their closest relatives are the flighted South American tinamou
Tinamous () form an order of birds called Tinamiformes (), comprising a single family called Tinamidae (), divided into two distinct subfamilies, containing 46 species found in Mexico, Central America, and South America. The word "tinamou" come ...
s, once considered a sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and t ...
to ratites. The nine species of moa were the only wingless birds, lacking even the vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
wings that all other ratites have. They were the largest terrestrial animals and dominant herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
s in New Zealand's forest, shrubland, and subalpine ecosystems until the arrival of the Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
, and were hunted only by the Haast's eagle. Moa extinction occurred within 100 years of human settlement of New Zealand, primarily due to overhunting.
Etymology
The word ''moa'' is a Polynesian term for domestic fowl. The name was not in common use among the Māori by the time of European contact, likely because the bird it described had been extinct for some time, and traditional stories about it were rare. The earliest record of the name was by missionaries William Williams andWilliam Colenso
William Colenso (17 November 1811 – 10 February 1899) FRS was a Cornish Christian missionary to New Zealand, and also a printer, botanist, explorer and politician. He attended the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi and later wrote an accou ...
in January 1838; Colenso speculated that the birds may have resembled gigantic fowl. In 1912, Māori chief Urupeni Pūhara claimed that the moa's traditional name was "te kura" (the red bird).
Description
 Moa skeletons were traditionally reconstructed in an upright position to create impressive height, but analysis of their vertebral articulations indicates that they probably carried their heads forward,Worthy & Holdaway (2002) in the manner of a
Moa skeletons were traditionally reconstructed in an upright position to create impressive height, but analysis of their vertebral articulations indicates that they probably carried their heads forward,Worthy & Holdaway (2002) in the manner of a kiwi
Kiwi most commonly refers to:
* Kiwi (bird), a flightless bird native to New Zealand
* Kiwi (nickname), a nickname for New Zealanders
* Kiwifruit, an edible berry
* Kiwi dollar or New Zealand dollar, a unit of currency
Kiwi or KIWI may also refe ...
. The spine was attached to the rear of the head rather than the base, indicating the horizontal alignment. This would have let them graze on low vegetation, while being able to lift their heads and browse trees when necessary. This has resulted in a reconsideration of the height of larger moa. However, Māori rock art
In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also ...
depicts moa or moa-like birds (likely geese or adzebills) with necks upright, indicating that moa were more than capable of assuming both neck postures.
No records survive of what sounds moa made, though some idea of their calls
Call or Calls may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Games
* Call, a type of betting in poker
* Call, in the game of contract bridge, a bid, pass, double, or redouble in the bidding stage
Music and dance
* Call (band), from Lahore, Paki ...
can be gained from fossil evidence. The trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
of moa were supported by many small rings of bone known as tracheal rings. Excavation of these rings from articulated skeletons has shown that at least two moa genera (''Euryapteryx'' and ''Emeus'') exhibited tracheal elongation, that is, their trachea were up to 1 m (3 ft) long and formed a large loop within the body cavity. They are the only ratites known to exhibit this feature, which is also present in several other bird groups, including swan
Swans are birds of the family (biology), family Anatidae within the genus ''Cygnus''. The swans' closest relatives include the goose, geese and ducks. Swans are grouped with the closely related geese in the subfamily Anserinae where they form t ...
s, cranes
Crane or cranes may refer to:
Common meanings
* Crane (bird), a large, long-necked bird
* Crane (machine), industrial machinery for lifting
** Crane (rail), a crane suited for use on railroads
People and fictional characters
* Crane (surname), ...
, and guinea fowl. The feature is associated with deep resonant vocalisations that can travel long distances.
Evolutionary relationships
The moa's closest relatives are small terrestrial South American birds called the tinamous, which can fly.Phillips, et al. (2010) Previously, thekiwi
Kiwi most commonly refers to:
* Kiwi (bird), a flightless bird native to New Zealand
* Kiwi (nickname), a nickname for New Zealanders
* Kiwifruit, an edible berry
* Kiwi dollar or New Zealand dollar, a unit of currency
Kiwi or KIWI may also refe ...
, the Australian emu
The emu () (''Dromaius novaehollandiae'') is the second-tallest living bird after its ratite relative the ostrich. It is endemic to Australia where it is the largest native bird and the only extant member of the genus ''Dromaius''. The emu' ...
, and cassowary
Cassowaries ( tpi, muruk, id, kasuari) are flightless birds of the genus ''Casuarius'' in the order Casuariiformes. They are classified as ratites (flightless birds without a keel on their sternum bones) and are native to the tropical forest ...
Turvey et al. (2005) were thought to be most closely related to moa.
Although dozens of species were described in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many were based on partial skeletons and turned out to be synonyms
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all ...
. Currently, 11 species are formally recognised, although recent studies using ancient DNA recovered from bones in museum collections suggest that distinct lineages exist within some of these. One factor that has caused much confusion in moa taxonomy is the intraspecific variation of bone sizes, between glacial and interglacial periods (see Bergmann’s rule
Bergmann's rule is an ecogeographical rule that states that within a broadly distributed taxonomic clade, populations and species of larger size are found in colder environments, while populations and species of smaller size are found in warmer r ...
and Allen’s rule) as well as sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
being evident in several species. '' Dinornis'' seems to have had the most pronounced sexual dimorphism, with females being up to 150% as tall and 280% as heavy as males—so much bigger that they were classified as separate species until 2003.Huynen, L.J., et al. (2003)Bunce, M., et al. (2003) A 2009 study showed that ''Euryapteryx curtus'' and ''E. gravis'' were synonyms. A 2010 study explained size differences among them as sexual dimorphism. A 2012 morphological study interpreted them as subspecies, instead.
Analyses of ancient DNA have determined that a number of cryptic evolutionary lineages occurred in several moa genera. These may eventually be classified as species or subspecies; ''Megalapteryx benhami'' (Archey) is synonymised with ''M. didinus'' (Owen) because the bones of both share all essential characters. Size differences can be explained by a north–south cline combined with temporal variation such that specimens were larger during the Otiran glacial period (the last ice age in New Zealand). Similar temporal size variation is known for the North Island's '' Pachyornis mappini''. Some of the other size variation for moa species can probably be explained by similar geographic and temporal factors.
The earliest moa remains come from the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
Saint Bathans Fauna
The St Bathans fauna is found in the lower Bannockburn Formation of the Manuherikia Group of Central Otago, in the South Island of New Zealand. It comprises a suite of fossilised prehistoric animals from the late Early Miocene (Altonian) period, ...
. Known from multiple eggshells and hind limb elements, these represent at least two already fairly large-sized species.
Classification
Taxonomy
The currently recognised genera and species are: *Order †Dinornithiformes (Gadow 1893) Ridgway 1901 inornithes Gadow 1893; Immanes Newton 1884(moa) **Family Dinornithidae Owen 1843 alapteryginae Bonaparte 1854; Palapterygidae Haast 1874; Dinornithnideae Stejneger 1884(giant moa) ***Genus '' Dinornis'' ****North Island giant moa
The North Island giant moa (''Dinornis novaezealandiae'') is an extinct moa in the genus ''Dinornis''. Even though it might have walked with a lowered posture, standing upright, it would have been the tallest bird ever to exist, with a height ...
, ''Dinornis novaezealandiae'' (North Island, New Zealand)
****South Island giant moa
The South Island giant moa (''Dinornis robustus'') is an extinct moa from the genus ''Dinornis.''
Context
The moa were Ratite, ratites, flightless birds with a sternum without a Keel (bird anatomy), keel. They also had a distinctive palate. T ...
, ''Dinornis robustus'' (South Island, New Zealand)
**Family Emeidae
The lesser moa (family Emeidae) were a family in the moa order Dinornithiformes. About two-thirds of all moa species are in the lesser moa family. The moa were ratites from New Zealand. Ratites are flightless birds with a sternum without a keel. ...
(Bonaparte 1854) meinae Bonaparte 1854; Anomalopterygidae Oliver 1930; Anomalapteryginae Archey 1941(lesser moa)
***Genus '' Anomalopteryx''
**** Bush moa, ''Anomalopteryx didiformis'' (North and South Island, New Zealand)
***Genus '' Emeus''
****Eastern moa
The eastern moa (''Emeus crassus'') is an extinct species of moa. When the first specimens were originally described by Richard Owen, they were placed within the genus ''Dinornis'' as three different species, but, was later split off into their ...
, ''Emeus crassus'' (South Island, New Zealand)
***Genus ''Euryapteryx
The broad-billed, stout-legged moa or coastal moa (''Euryapteryx curtus'') is an extinct species of moa. These moa lived in both the North Island, North and the South Island, South Islands of New Zealand, and on Stewart Island. Its habitat was ...
''
****Broad-billed moa
The broad-billed, stout-legged moa or coastal moa (''Euryapteryx curtus'') is an extinct species of moa. These moa lived in both the North and the South Islands of New Zealand, and on Stewart Island. Its habitat was in the lowlands (duneland, f ...
, ''Euryapteryx curtus'' (North and South Island, New Zealand)
***Genus ''Pachyornis
''Pachyornis'' is an extinct genus of ratites from New Zealand which belonged to the moa family. Like all ratites it was a member of the Order (biology), order Struthioniformes. The Struthioniformes are flightless birds with a sternum without a k ...
''
****Heavy-footed moa
The heavy-footed moa (''Pachyornis elephantopus'') is a species of moa from the lesser moa family. The heavy-footed moa was widespread only in the South Island of New Zealand, and its habitat was the lowlands (shrublands, dunelands, grasslands, ...
, ''Pachyornis elephantopus'' (South Island, New Zealand)
****Mantell's moa
Mantell's moa (''Pachyornis geranoides'') also known as Mappin's moa is an extinct species of moa from the North Island of New Zealand. Its habitat was the lowlands (shrublands, grasslands, dunelands, and forests). The moa were ratites, flight ...
, ''Pachyornis geranoides'' (North Island, New Zealand)
****Crested moa
The crested moa (''Pachyornis australis'') is an extinct species of moa. It is one of the 9 known species of moa to have existed.
Moa are grouped together with emus, ostriches, kiwi, cassowaries, rheas, and tinamous in the clade Palaeognathae. ...
, '' Pachyornis australis'' (South Island, New Zealand)Stephenson, Brent (2009)
**Family Megalapterygidae
The upland moa (''Megalapteryx didinus'') was a species of moa endemic to New Zealand. It was a ratite, a grouping of flightless birds with no keel on the sternum. It was the last moa species to become extinct, vanishing in 1445 CE, and was pr ...
***Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
'' Megalapteryx''
**** Upland moa, ''Megalapteryx didinus'' (South Island, New Zealand)
Two unnamed species from the Saint Bathans Fauna.
Phylogeny
Because moa are a group of flightless birds with no vestiges of wing bones, questions have been raised about how they arrived in New Zealand, and from where. Many theories exist about the moa's arrival and radiation in New Zealand, but the most recent theory suggests that they arrived in New Zealand about 60 million years ago (Mya) and split from the "basal" (see below) moa species, ''Megalapteryx'', about 5.8 Mya instead of the 18.5 Mya split suggested by Baker et al. (2005). This does not necessarily mean there was no speciation between the arrival 60 Mya and the basal split 5.8 Mya, but the fossil record is lacking and most likely the early moa lineages existed, but became extinct before the basal split 5.8 Mya. The presence ofMiocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
-aged species certainly suggests that moa diversification began before the split between ''Megalapteryx'' and the other taxa.
The Oligocene Drowning Maximum event, which occurred about 22 Mya, when only 18% of present-day New Zealand was above sea level, is very important in the moa radiation. Because the basal moa split occurred so recently (5.8 Mya), it was argued that ancestors of the Quaternary moa lineages could not have been present on both the South and North Island remnants during the Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the ...
drowning. This does not imply that moa were previously absent from the North Island, but that only those from the South Island survived, because only the South Island was above sea level. Bunce et al. (2009) argued that moa ancestors survived on the South Island and then recolonised the North Island about 2 Myr later, when the two islands rejoined after 30 Myr of separation. The presence of Miocene moa in the Saint Bathans fauna seems to suggest that these birds increased in size soon after the Oligocene drowning event, if they were affected by it at all.
Bunce et al. also concluded that the highly complex structure of the moa lineage was caused by the formation of the Southern Alps about 6 Mya, and the habitat fragmentation on both islands resulting from Pleistocene glacial cycles, volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called ...
, and landscape changes. The cladogram below is a phylogeny of Palaeognathae generated by Mitchell (2014) with some clade names after Yuri ''et al.'' (2013). It provides the position of the moa (Dinornithiformes) within the larger context of the "ancient jawed" (Palaeognathae) birds:
The cladogram below gives a more detailed, species-level phylogeny, of the moa branch (Dinornithiformes) of the "ancient jawed" birds (Palaeognathae) shown above:
Distribution and habitat
Analyses of fossil moa bone assemblages have provided detailed data on the habitat preferences of individual moa species, and revealed distinctive regional moa faunas:South Island
 The two main faunas identified in the South Island include:
: The fauna of the high-rainfall west coast beech ('' Nothofagus'') forests that included ''Anomalopteryx didiformis'' (bush moa) and ''Dinornis robustus'' (South Island giant moa), and
: The fauna of the dry rainshadow forest and shrublands east of the Southern Alps that included ''Pachyornis elephantopus'' (heavy-footed moa), ''Euryapteryx gravis'', ''Emeus crassus'', and ''Dinornis robustus''.
A ' subalpine fauna' might include the widespread ''D. robustus'', and the two other moa species that existed in the South Island:
:: ''Pachyornis australis'', the rarest moa species, the only moa species not yet found in Māori
The two main faunas identified in the South Island include:
: The fauna of the high-rainfall west coast beech ('' Nothofagus'') forests that included ''Anomalopteryx didiformis'' (bush moa) and ''Dinornis robustus'' (South Island giant moa), and
: The fauna of the dry rainshadow forest and shrublands east of the Southern Alps that included ''Pachyornis elephantopus'' (heavy-footed moa), ''Euryapteryx gravis'', ''Emeus crassus'', and ''Dinornis robustus''.
A ' subalpine fauna' might include the widespread ''D. robustus'', and the two other moa species that existed in the South Island:
:: ''Pachyornis australis'', the rarest moa species, the only moa species not yet found in Māori midden
A midden (also kitchen midden or shell heap) is an old dump for domestic waste which may consist of animal bone, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofact ...
s. Its bones have been found in caves in the northwest Nelson and Karamea
Karamea is a town on the West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is the northernmost settlement of any real size on the West Coast, and is located northeast by road from Westport. Apart from a narrow coastal strip, the town of Karam ...
districts (such as Honeycomb Hill Cave), and some sites around the Wānaka district.
:: ''Megalapteryx didinus'', more widespread, named "upland moa" because its bones are commonly found in the subalpine zone. However, it also occurred down to sea level, where suitable steep and rocky terrain (such as Punakaiki
Punakaiki is a small village on the West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is located between Westport and Greymouth on , the only through-road on the West Coast. Punakaiki is immediately adjacent to Paparoa National Park, and is a ...
on the west coast and Central Otago
Central Otago is located in the inland part of the Otago region in the South Island of New Zealand. The motto for the area is "A World of Difference".
The area is dominated by mountain ranges and the upper reaches of the Clutha River and tributa ...
) existed. Their distributions in coastal areas have been rather unclear, but were present at least in several locations such as on Kaikōura, Otago Peninsula, and Karitane.
North Island
Significantly less is known about North Island paleofaunas, due to a paucity of fossil sites compared to the South Island, but the basic pattern of moa-habitat relationships was the same. The South Island and the North Island shared some moa species (''Euryapteryx gravis'', ''Anomalopteryx didiformis''), but most were exclusive to one island, reflecting divergence over several thousand years since lower sea level in theIce Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
had made a land bridge across the Cook Strait.
In the North Island, ''Dinornis novaezealandiae'' and ''Anomalopteryx didiformis'' dominated in high-rainfall forest habitat, a similar pattern to the South Island. The other moa species present in the North Island (''Euryapteryx gravis'', ''E. curtus'', and ''Pachyornis geranoides'') tended to inhabit drier forest and shrubland habitats. ''P. geranoides'' occurred throughout the North Island. The distributions of ''E. gravis'' and ''E. curtus'' were almost mutually exclusive, the former having only been found in coastal sites around the southern half of the North Island.
Behaviour and ecology
About eight moa trackways, with fossilised moa footprint impressions in fluvial silts, have been found in the North Island, includingWaikanae
Waikanae (, ) is a town on the Kapiti Coast, 60 kilometres north of the Wellington CBD. The name is a Māori word meaning "waters" (''wai'') "of the grey mullet".
The town lies between Paraparaumu, eight kilometres to the southwest, and Ōtak ...
Creek (1872), Napier Napier may refer to:
People
* Napier (surname), including a list of people with that name
* Napier baronets, five baronetcies and lists of the title holders
Given name
* Napier Shaw (1854–1945), British meteorologist
* Napier Waller (1893–19 ...
(1887), Manawatū River (1895), Marton (1896), Palmerston North
Palmerston North (; mi, Te Papa-i-Oea, known colloquially as Palmy) is a city in the North Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Manawatū-Whanganui region. Located in the eastern Manawatu Plains, the city is near the north bank of the ...
(1911) (see photograph to left), Rangitīkei River
The Rangitīkei River is one of New Zealand's longest rivers, long.
Its headwaters are to the southeast of Lake Taupō in the Kaimanawa Ranges. It flows from the Central Plateau south past Taihape, Mangaweka, Hunterville, Marton, and Bu ...
(1939), and under water in Lake Taupō
Lake Taupō (also spelled Taupo; mi, Taupō-nui-a-Tia or ) is a large crater lake in New Zealand's North Island, located in the caldera of the Taupō Volcano. The lake is the namesake of the town of Taupō, which sits on a bay in the lake's nor ...
(1973). Analysis of the spacing of these tracks indicates walking speeds between 3 and 5 km/h (1.75–3 mph).
Diet
Their diet has been deduced fromfossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
ised contents of their gizzardsWood (2007) and coprolite
A coprolite (also known as a coprolith) is fossilized feces. Coprolites are classified as trace fossils as opposed to body fossils, as they give evidence for the animal's behaviour (in this case, diet) rather than morphology. The name is de ...
s, as well as indirectly through morphological analysis of skull and beak, and stable isotope analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, abundance of certain stable isotopes of chemical elements within organic and inorganic compounds. Isotopic analysis can be used to understand the flow of energy through a food web ...
of their bones. Moa fed on a range of plant species and plant parts, including fibrous twigs and leaves taken from low trees and shrubs. The beak of ''Pachyornis
''Pachyornis'' is an extinct genus of ratites from New Zealand which belonged to the moa family. Like all ratites it was a member of the Order (biology), order Struthioniformes. The Struthioniformes are flightless birds with a sternum without a k ...
elephantopus'' was analogous to a pair of secateur
Pruning shears, also called hand pruners (in American English), or secateurs (in British English), are a type of scissors for use on plants. They are strong enough to prune hard branches of trees and shrubs, sometimes up to two centimetres t ...
s, and could clip the fibrous leaves of New Zealand flax ('' Phormium tenax'') and twigs up to at least 8 mm in diameter.
Moa filled the ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for ...
occupied in other countries by large browsing mammals such as antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mammals ...
and llamas. Some biologists contend that a number of plant species evolved to avoid moa browsing. Divaracating plants such as ''Pennantia corymbosa
''Pennantia corymbosa'', commonly known as kaikomako (from the Māori ), is a small dioecious forest tree of New Zealand.
Small creamy, white flowers are produced between November and February, followed by a shiny black fruit in autumn. They ar ...
'' (the kaikōmako), which have small leaves and a dense mesh of branches, and '' Pseudopanax crassifolius'' (the horoeka or lancewood), which has tough juvenile leaves, are possible examples of plants that evolved in such a way.
Like many other birds, moa swallowed gizzard stones ( gastroliths), which were retained in their muscular gizzards, providing a grinding action that allowed them to eat coarse plant material. These stones were commonly smooth rounded quartz pebbles, but stones over long have been found among preserved moa gizzard contents. ''Dinornis'' gizzards could often contain several kilograms of stones. Moa likely exercised a certain selectivity in the choice of gizzard stones and chose the hardest pebbles.
Reproduction
The pairs of species of moa described as ''Euryapteryx curtus'' / ''E. exilis'', ''Emeus huttonii'' / ''E. crassus'', and ''Pachyornis septentrionalis'' / ''P. mappini'' have long been suggested to constitute males and females, respectively. This has been confirmed by analysis for sex-specific genetic markers of DNA extracted from bone material. For example, before 2003, three species of ''Dinornis'' were recognised: South Island giant moa (''D. robustus''), North Island giant moa (''D. novaezealandiae''), and slender moa (''D. struthioides''). However, DNA showed that all ''D. struthioides'' were males, and all ''D. robustus'' were females. Therefore, the three species of ''Dinornis'' were reclassified as two species, one each formerly occurring on New Zealand's North Island (''D. novaezealandiae'') and South Island (''D. robustus''); ''D. robustus'' however, comprises three distinct genetic lineages and may eventually be classified as many species, as discussed above. Examination of growth rings in moa cortical bone has revealed that these birds wereK-selected
In ecology, ''r''/''K'' selection theory relates to the selection of combinations of traits in an organism that trade off between quantity and quality of offspring. The focus on either an increased quantity of offspring at the expense of individ ...
, as are many other large endemic New Zealand birds. They are characterised by having a low fecundity and a long maturation period, taking about 10 years to reach adult size. The large ''Dinornis'' species took as long to reach adult size as small moa species, and as a result, had fast skeletal growth during their juvenile years.
No evidence has been found to suggest that moa were colonial nesters. Moa nesting is often inferred from accumulations of eggshell fragments in caves and rock shelters, little evidence exists of the nests themselves. Excavations of rock shelters in the eastern North Island during the 1940s found moa nests, which were described as "small depressions obviously scratched out in the soft dry pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular vol ...
". Moa nesting material has also been recovered from rock shelters in the Central Otago
Central Otago is located in the inland part of the Otago region in the South Island of New Zealand. The motto for the area is "A World of Difference".
The area is dominated by mountain ranges and the upper reaches of the Clutha River and tributa ...
region of the South Island, where the dry climate has preserved plant material used to build the nesting platform (including twigs clipped by moa bills).Wood, J.R. (2008) Seeds
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm pl ...
and pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophyt ...
within moa coprolites found among the nesting material provide evidence that the nesting season was late spring to summer.
Fragments of moa eggshell are often found in archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
sites and sand dunes
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, fl ...
around the New Zealand coast. Thirty-six whole moa eggs exist in museum collections and vary greatly in size (from in length and wide). The outer surface of moa eggshell is characterised by small, slit-shaped pores. The eggs of most moa species were white, although those of the upland moa (''Megalapteryx didinus'') were blue-green.Huynen, Leon; Gill, Brian J.; Millar, Craig D.; and Lambert, David M. (2010)
A 2010 study by Huynen et al. found that the eggs of certain species were fragile, only around a millimetre in shell thickness: "Unexpectedly, several thin-shelled eggs were also shown to belong to the heaviest moa of the genera ''Dinornis'', ''Euryapteryx'', and ''Emeus'', making these, to our knowledge, the most fragile of all avian eggs measured to date. Moreover, sex-specific DNA recovered from the outer surfaces of eggshells belonging to species of ''Dinornis'' and ''Euryapteryx'' suggest that these very thin eggs were likely to have been incubated by the lighter males. The thin nature of the eggshells of these larger species of moa, even if incubated by the male, suggests that egg breakage in these species would have been common if the typical contact method of avian egg incubation was used." Despite the bird's extinction, the high yield of DNA available from recovered fossilised eggs has allowed the moa's genome to be sequenced.
Pre-human forests
Studies of accumulated dried vegetation in the pre-human mid-lateHolocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
period suggests a low ''Sophora microphylla
''Sophora microphylla'', common name kōwhai, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to New Zealand. Growing to tall and broad, it is an evergreen shrub or small tree. Each leaf is long with up to 40 pairs of shiny oval ...
'' or Kōwai forest ecosystem in Central Otago
Central Otago is located in the inland part of the Otago region in the South Island of New Zealand. The motto for the area is "A World of Difference".
The area is dominated by mountain ranges and the upper reaches of the Clutha River and tributa ...
that was used and perhaps maintained by moa, for both nesting material and food. Neither the forests nor moa existed when European settlers came to the area in the 1850s.
Relationship with humans
Extinction
Before the arrival of humans, the moa's only predator was the massive Haast's eagle. New Zealand had been isolated for 80 million years and had few predators before human arrival, meaning that not only were its ecosystems extremely vulnerable to perturbation by outside species, but also the native species were ill-equipped to cope with human predators. Polynesians arrived sometime before 1300, and all moa genera were soon driven to extinction by hunting and, to a lesser extent, by habitat reduction due to forest clearance. By 1445, all moa had become extinct, along with Haast's eagle, which had relied on them for food. Recent research usingcarbon-14 dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
of midden
A midden (also kitchen midden or shell heap) is an old dump for domestic waste which may consist of animal bone, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofact ...
s strongly suggests that the events leading to extinction took less than a hundred years, rather than a period of exploitation lasting several hundred years as previously hypothesised.
An expedition in the 1850s under Lieutenant A. Impey reported two emu-like birds on a hillside in the South Island; an 1861 story from the ''Nelson Examiner'' told of three-toed footprints measuring between Tākaka
Tākaka is a small town situated at the southeastern end of Golden Bay, at the northern end of New Zealand's South Island, located on the lower reaches of the Tākaka River. State Highway 60 runs through Takaka and follows the river valley b ...
and Riwaka
Riwaka ( mi, Riuwaka) is a small settlement in the Tasman District of New Zealand's South Island. It lies beside Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere, five kilometres north of Motueka, and close to the mouth of the Riuwaka River. The land where the tow ...
that were found by a surveying party; and finally in 1878, the ''Otago Witness
The ''Otago Witness'' was a prominent illustrated weekly newspaper in the early years of the European settlement of New Zealand, produced in Dunedin, the provincial capital of Otago. Published weekly it existed from 1851 to 1932. The introduction ...
'' published an additional account from a farmer and his shepherd. An 80-year-old woman, Alice McKenzie
The Whitechapel murders were committed in or near the largely impoverished Whitechapel district in the East End of London between 3 April 1888 and 13 February 1891. At various points some or all of these eleven unsolved murders of women have be ...
, claimed in 1959 that she had seen a moa in Fiordland bush in 1887, and again on a Fiordland beach when she was 17 years old. She claimed that her brother had also seen a moa on another occasion. In childhood, Mackenzie saw a large bird that she believed to be a takahē
The South Island takahē (''Porphyrio hochstetteri'') is a flightless swamphen indigenous to New Zealand and the largest living member of the rail family. It is often known by the abbreviated name takahē, which it shares with the recently ...
, but after its rediscovery in the 1940s, she saw a picture of it and concluded that she had seen something else.
Some authors have speculated that a few ''Megalapteryx didinus'' may have persisted in remote corners of New Zealand until the 18th and even 19th centuries, but this view is not widely accepted.Anderson (1989) Some Māori hunters claimed to be in pursuit of the moa as late as the 1770s; however, these accounts possibly did not refer to the hunting of actual birds as much as a now-lost ritual among South Islanders. Whalers and sealers Sealer may refer either to a person or ship engaged in seal hunting, or to a sealant; associated terms include:
Seal hunting
* Sealer Hill, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica
* Sealers' Oven, bread oven of mud and stone built by sealers around 180 ...
recalled seeing monstrous birds along the coast of the South Island, and in the 1820s, a man named George Pauley made an unverified claim of seeing a moa in the Otago region of New Zealand. Occasional speculation since at least the late 19th century, and as recently as 2008, has suggested that some moa may still exist, particularly in the wilderness of South Westland and Fiordland. A 1993 report initially interested the Department of Conservation, but the animal in a blurry photograph was identified as a red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
. Cryptozoologists continue to search for them, but their claims and supporting evidence (such as of purported footprints)Laing, Doug (2008) have earned little attention from experts and are pseudoscientific
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
.
The rediscovery of the takahē in 1948 after none had been seen since 1898 showed that rare birds can exist undiscovered for a long time. However, the takahē is a much smaller bird than the moa, and was rediscovered after its tracks were identified—yet no reliable evidence of moa tracks has ever been found, and experts still contend that moa survival is extremely unlikely, since they would have to be living unnoticed for over 500 years in a region visited often by hunters and hikers.
Surviving remains
Joel Polack, a trader who lived on the East Coast of the North Island from 1834 to 1837, recorded in 1838 that he had been shown "several large fossil ossifications" found near Mt Hikurangi. He was certain that these were the bones of a species of emu or ostrich, noting that "the Natives add that in times long past they received the traditions that very large birds had existed, but the scarcity of animal food, as well as the easy method of entrapping them, has caused their extermination". Polack further noted that he had received reports from Māori that a "species ofStruthio
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There are ...
" still existed in remote parts of the South Island.
Dieffenbach also refers to a fossil from the area near Mt Hikurangi, and surmises that it belongs to "a bird, now extinct, called Moa (or Movie) by the natives". 'Movie' is the first transcribed name for the bird. In 1839, John W. Harris, a Poverty Bay
Poverty Bay (Māori: ''Tūranganui-a-Kiwa'') is the largest of several small bays on the east coast of New Zealand's North Island to the north of Hawke Bay. It stretches for from Young Nick's Head in the southwest to Tuaheni Point in the north ...
flax trader who was a natural-history enthusiast, was given a piece of unusual bone by a Māori who had found it in a river bank. He showed the fragment of bone to his uncle, John Rule, a Sydney surgeon, who sent it to Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.
Owe ...
, who at that time was working at the Hunterian Museum at the Royal College of Surgeons
The Royal College of Surgeons is an ancient college (a form of corporation) established in England to regulate the activity of surgeons. Derivative organisations survive in many present and former members of the Commonwealth. These organisations a ...
in London.
Owen puzzled over the fragment for almost four years. He established it was part of the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with ...
of a big animal, but it was uncharacteristically light and honeycombed. Owen announced to a skeptical scientific community and the world that it was from a giant extinct bird like an ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There are ...
, and named it ''Dinornis''. His deduction was ridiculed in some quarters, but was proved correct with the subsequent discoveries of considerable quantities of moa bones throughout the country, sufficient to reconstruct skeletons of the birds.Fuller, Errol (1987)
In July 2004, the Natural History Museum in London placed on display the moa bone fragment Owen had first examined, to celebrate 200 years since his birth, and in memory of Owen as founder of the museum.
 Since the discovery of the first moa bones in the late 1830s, thousands more have been found. They occur in a range of late
Since the discovery of the first moa bones in the late 1830s, thousands more have been found. They occur in a range of late Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
and Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic matter, organic particles at Earth#Surface, Earth's surface, followed by cementation (geology), cementation. Sedimentati ...
deposits, but are most common in three main types of site: cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
s, dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, f ...
s, and swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
s.
Bones are commonly found in caves or ''tomo'' (the Māori word for doline or sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
, often used to refer to pitfalls or vertical cave shafts). The two main ways that the moa bones were deposited in such sites were birds that entered the cave to nest or escape bad weather, and subsequently died in the cave and birds that fell into a vertical shaft and were unable to escape. Moa bones (and the bones of other extinct birds) have been found in caves throughout New Zealand, especially in the limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
/marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. Marble is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the ...
areas of northwest Nelson, Karamea
Karamea is a town on the West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is the northernmost settlement of any real size on the West Coast, and is located northeast by road from Westport. Apart from a narrow coastal strip, the town of Karam ...
, Waitomo
Waitomo is a rural community in the King Country region of New Zealand's North Island. There are several solutional cave systems in the area around the village, which are popular tourist attractions. Restaurants and accommodation are centred in ...
, and Te Anau.
Moa bones and eggshell fragments sometimes occur in active coastal sand dunes, where they may erode from paleosols and concentrate in ' blowouts' between dune ridges. Many such moa bones antedate human settlement, although some originate from Māori midden sites, which frequently occur in dunes near harbours and river mouths (for example the large moa hunter sites at Shag River, Otago, and Wairau Bar, Marlborough
Marlborough may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Marlborough, Wiltshire, England
** Marlborough College, public school
* Marlborough School, Woodstock in Oxfordshire, England
* The Marlborough Science Academy in Hertfordshire, England
Austral ...
).
Densely intermingled moa bones have been encountered in swamps throughout New Zealand. The most well-known example is at Pyramid Valley
Pyramid Valley is a locality in the Hurunui District of New Zealand. It is well known for its prominent limestone rock formations. It is located near Waikari in the North Canterbury region, 80 km north-west of Christchurch.
On the foot of the ...
in north Canterbury, where bones from at least 183 individual moa have been excavated, mostly by Roger Duff
Roger Shepherd Duff (11 July 1912 – 30 October 1978) was a New Zealand ethnologist and museum director.
Biography
Duff was born in Invercargill, New Zealand in 1912. He is the son of Oliver Duff founding editor of the New Zealand Listener, and ...
of Canterbury Museum. Many explanations have been proposed to account for how these deposits formed, ranging from poisonous spring waters to floods and wildfires. However, the currently accepted explanation is that the bones accumulated slowly over thousands of years, from birds that entered the swamps to feed and became trapped in the soft sediment.
Many New Zealand and international museums hold moa bone collections. Auckland War Memorial Museum – Tāmaki Paenga Hira has a significant collection, and in 2018 several moa skeletons were imaged and 3D scanned to make the collections more accessible. There is also a major collection in Otago Museum
Tūhura Otago Museum is located in the city centre of Dunedin, New Zealand. It is adjacent to the University of Otago campus in Dunedin North, 1,500 metres northeast of the city centre. It is one of the city's leading attractions and has one of t ...
in Dunedin
Dunedin ( ; mi, Ōtepoti) is the second-largest city in the South Island of New Zealand (after Christchurch), and the principal city of the Otago region. Its name comes from , the Scottish Gaelic name for Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. Th ...
.
Feathers and soft tissues
Several remarkable examples of moa remains have been found which exhibit soft tissues (muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
, skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
, feathers), that were preserved through desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container.
...
when the bird died in a naturally dry site (for example, a cave with a constant dry breeze blowing through it). Most of these specimens have been found in the semiarid Central Otago
Central Otago is located in the inland part of the Otago region in the South Island of New Zealand. The motto for the area is "A World of Difference".
The area is dominated by mountain ranges and the upper reaches of the Clutha River and tributa ...
region, the driest part of New Zealand. These include:
* Dried muscle on bones of a female ''Dinornis robustus'' found at Tiger Hill in the Manuherikia River Valley by gold miners in 1864Owen, R. (1879) (currently held by Yorkshire Museum
The Yorkshire Museum is a museum in York, England. It was opened in 1830, and has five permanent collections, covering biology, geology, archaeology, numismatics and astronomy.
History
The museum was founded by the Yorkshire Philosophical Soci ...
)
* Several bones of ''Emeus crassus'' with muscle attached, and a row of neck vertebrae with muscle, skin, and feathers collected from Earnscleugh Cave near the town of Alexandra in 1870 (currently held by Otago Museum
Tūhura Otago Museum is located in the city centre of Dunedin, New Zealand. It is adjacent to the University of Otago campus in Dunedin North, 1,500 metres northeast of the city centre. It is one of the city's leading attractions and has one of t ...
)
*An articulated foot of a male ''D. giganteus'' with skin and foot pads preserved, found in a crevice on the Knobby Range in 1874Buller, W.L. (1888) (currently held by Otago Museum
Tūhura Otago Museum is located in the city centre of Dunedin, New Zealand. It is adjacent to the University of Otago campus in Dunedin North, 1,500 metres northeast of the city centre. It is one of the city's leading attractions and has one of t ...
)
* The type specimen of ''Megalapteryx didinus'' found near Queenstown in 1878 (currently held by Natural History Museum, London; see photograph of foot on this page)
* The lower leg of ''Pachyornis elephantopus'', with skin and muscle, from the Hector Range in 1884; (currently held by the Zoology Department, Cambridge University
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts.
Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge.
, established =
, other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Schola ...
)
* The complete feathered leg of a ''M. didinus'' from Old Man Range
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
*Old, Baranya, Hungary
*Old, Northamptonshire, England
*Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Mai ...
in 1894 (currently held by Otago Museum
Tūhura Otago Museum is located in the city centre of Dunedin, New Zealand. It is adjacent to the University of Otago campus in Dunedin North, 1,500 metres northeast of the city centre. It is one of the city's leading attractions and has one of t ...
)
* The head of a ''M. didinus'' found near Cromwell sometime before 1949 (currently held by the Museum of New Zealand).
Two specimens are known from outside the Central Otago region:
* A complete foot of ''M. didinus'' found in a cave on Mount Owen near Nelson in the 1980s (currently held by the Museum of New Zealand)
* A skeleton of ''Anomalopteryx didiformis'' with muscle, skin, and feather bases collected from a cave near Te Anau in 1980.
In addition to these specimens, loose moa feathers have been collected from caves and rock shelters in the southern South Island, and based on these remains, some idea of the moa plumage has been achieved. The preserved leg of ''M. didinus'' from the Old Man Range reveals that this species was feathered right down to the foot. This is likely to have been an adaptation to living in high-altitude, snowy environments, and is also seen in the Darwin’s rhea, which lives in a similar seasonally snowy habitat.
Moa feathers are up to long, and a range of colours has been reported, including reddish-brown, white, yellowish, and purplish. Dark feathers with white or creamy tips have also been found, and indicate that some moa species may have had plumage with a speckled appearance.
Potential revival
The creature has frequently been mentioned as a potential candidate for revival by cloning. Its iconic status, coupled with the facts that it only became extinct a few hundred years ago and that substantial quantities of moa remains exist, mean that it is often listed alongside such creatures as thedodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The ...
as leading candidates for de-extinction. Preliminary work involving the extraction of DNA has been undertaken by Japanese geneticist Ankoh Yasuyuki Shirota.
Interest in the moa's potential for revival was further stirred in mid-2014 when New Zealand Member of Parliament Trevor Mallard suggested that bringing back some smaller species of moa within 50 years was a viable idea. The idea was ridiculed by many, but gained support from some natural history experts.
In literature and culture

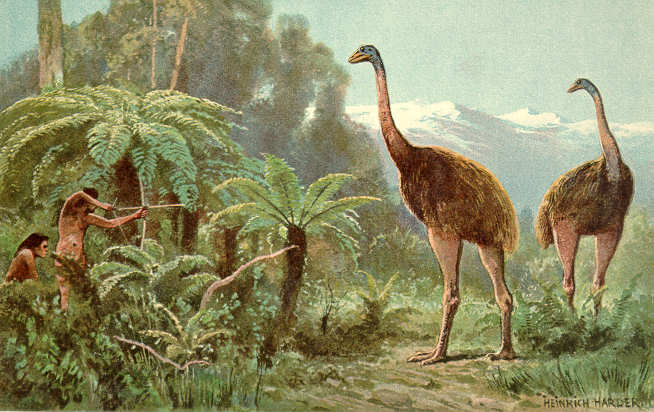
Heinrich Harder
Heinrich Harder (2 June 1858 – 5 February 1935) was a German artist and an art professor at the Prussian Academy of Arts in Berlin best known for his depictions of extinct animals.
Life
Heinrich Harder was born in Putzar, Pomerania, the son ...
portrayed moa being hunted by Māori in the classic German collecting cards about extinct and prehistoric animals, "Tiere der Urwelt", in the early 1900s.
Allen Curnow
Thomas Allen Monro Curnow (17 June 1911 – 23 September 2001) was a New Zealand poet and journalist.
Life
Curnow was born in Timaru, New Zealand, the son of a fourth generation New Zealander, an Anglican clergyman, and he grew up in a relig ...
's poem, "The Skeleton of the Great Moa in the Canterbury Museum, Christchurch" was published in 1943.Curnow, Allen (1944). ''Sailing or Drowning''. Wellington: Progressive Publishing Society.
See also
* List of New Zealand species extinct in the Holocene *Moa-nalo
The moa-nalo are a group of extinct aberrant, goose-like ducks that lived on the larger Hawaiian Islands, except Hawaii itself, in the Pacific. They were the major herbivores on most of these islands until they became extinct after human settle ...
, several flightless ducks from the Hawaiian Islands that grew to be as large as geese.
* Elephant birds, flightless ratite
A ratite () is any of a diverse group of flightless, large, long-necked, and long-legged birds of the infraclass Palaeognathae. Kiwi, the exception, are much smaller and shorter-legged and are the only nocturnal extant ratites.
The systematics ...
s up to over 3 metres tall that once lived on the island of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
.
General:
* Late Quaternary prehistoric birds
* Island gigantism
* Megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
Footnotes
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
TerraNature list of New Zealand's extinct birds
Tree of Life classification and references
Moa article
in Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand
3D model of a moa skull
{{Authority control * Extinct flightless birds Higher-level bird taxa restricted to New Zealand Late Quaternary prehistoric birds Extinct birds of New Zealand Ratites Bird extinctions since 1500 Holocene extinctions Species made extinct by human activities Animals with only two limbs Miocene first appearances Taxa named by Charles Lucien Bonaparte Notopalaeognathae