Mike Strank on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Michael Strank (November 10, 1919 – March 1, 1945) was a United States Marine Corps sergeant who was killed in action during the
Retrieved March 14, 2020 Before Iwo Jima, Strank served with the
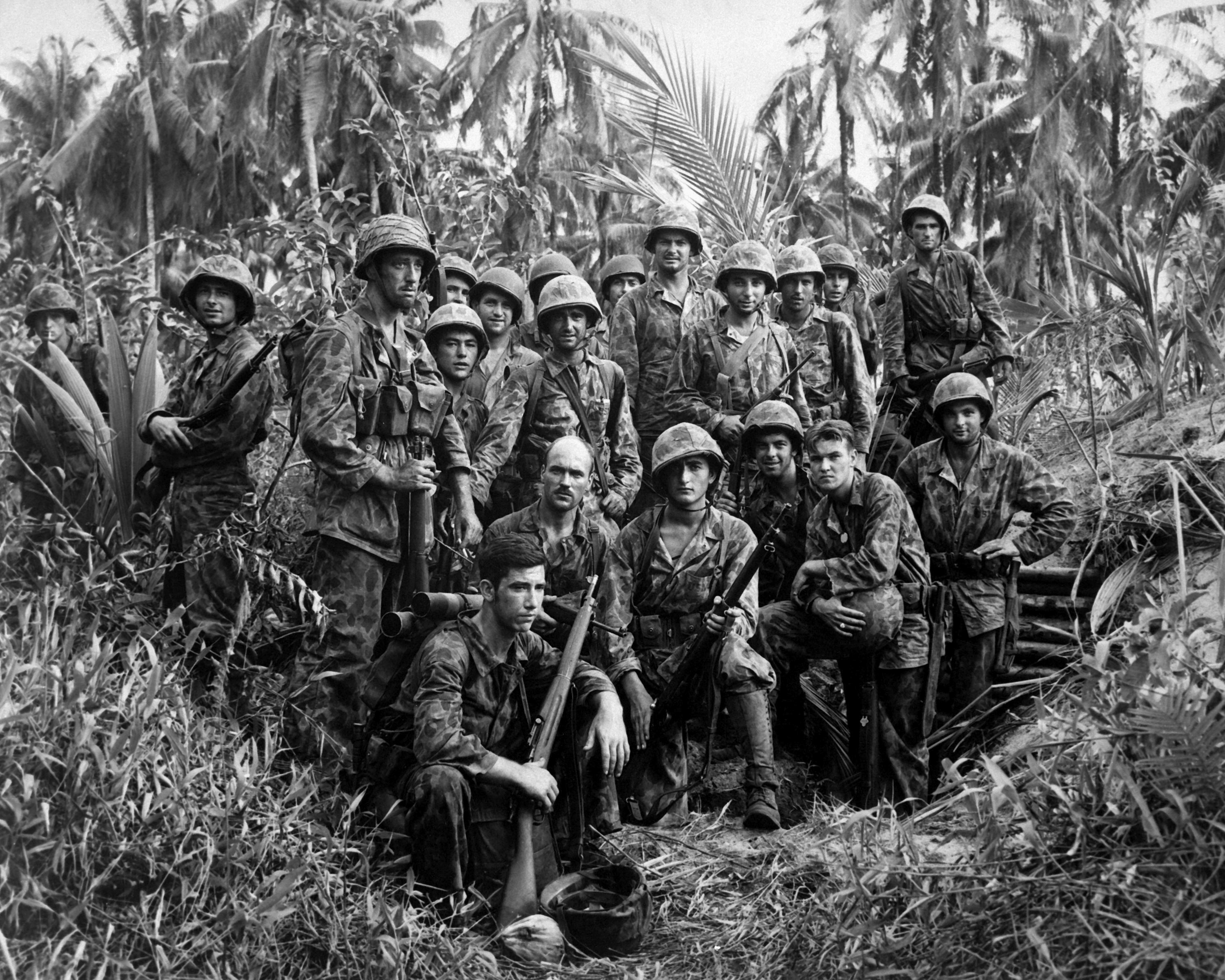 On January 26, 1942, Cpl. Strank was promoted to
On January 26, 1942, Cpl. Strank was promoted to
 Sgt. Strank took part in the Second Battalion,
Sgt. Strank took part in the Second Battalion,

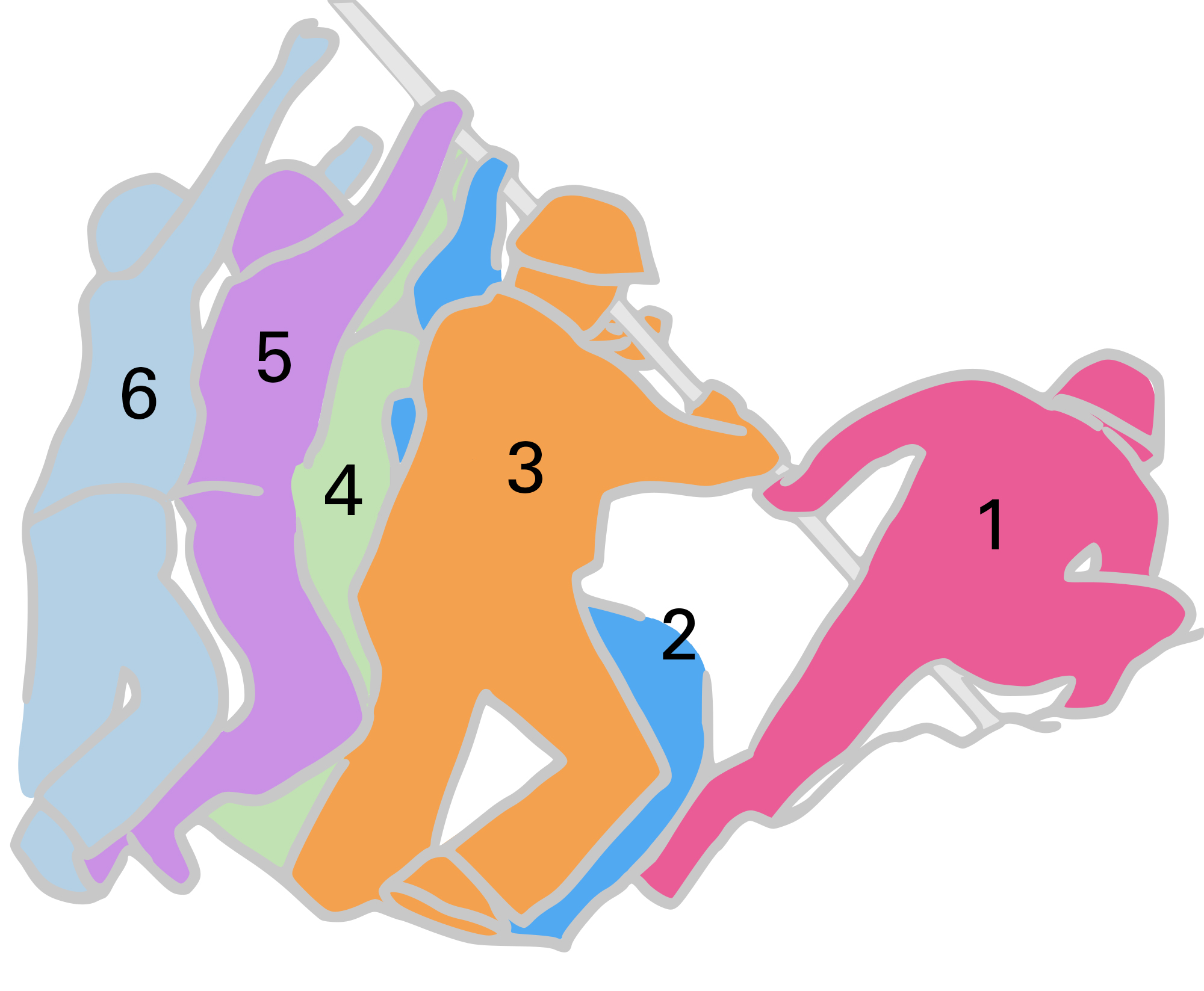
 In order for the American flag to be seen more by the thousands of Marines fighting on the other side of Mount Suribachi where most of the Japanese soldiers were located, it was decided that a larger flag should replace the battalion's flag on Mount Suribachi. Captain Severance ordered Sgt. Strank to ascend Mount Suribachi with three Marines from his rifle squad in Second Platoon and raise the replacement flag. Sgt. Strank then ordered Corporal Harlon Block, Private First Class Ira Hayes, and Private First Class Franklin Sousley to go with him up Mount Suribachi with communication wire (or supplies). Private First Class Rene Gagnon, the Second Battalion's runner (messenger) for E Company, was ordered to take the replacement flag up the mountain and return with the first flag.
Once Sgt. Strank's team was on top, Pfc. Hayes and Pfc. Sousley found a Japanese steel pipe to attach the flag to. After the two Marines took the pipe to Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block near the first flag, the flag was attached to the pipe. As the four Marines got into position to raise the flagstaff, Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block called out to two nearby Marines to help them raise the heavy flagstaff. Then, under Lt. Schrier's orders, the second flag was raised at approximately 1 p.m. by Sgt. Strank, Cpl. Block, Pfc. Hayes, Pfc. Sousley, Pfc. Harold Schultz, and Pfc. Harold Keller,USMC Statement on Marine Corps Flag Raisers
In order for the American flag to be seen more by the thousands of Marines fighting on the other side of Mount Suribachi where most of the Japanese soldiers were located, it was decided that a larger flag should replace the battalion's flag on Mount Suribachi. Captain Severance ordered Sgt. Strank to ascend Mount Suribachi with three Marines from his rifle squad in Second Platoon and raise the replacement flag. Sgt. Strank then ordered Corporal Harlon Block, Private First Class Ira Hayes, and Private First Class Franklin Sousley to go with him up Mount Suribachi with communication wire (or supplies). Private First Class Rene Gagnon, the Second Battalion's runner (messenger) for E Company, was ordered to take the replacement flag up the mountain and return with the first flag.
Once Sgt. Strank's team was on top, Pfc. Hayes and Pfc. Sousley found a Japanese steel pipe to attach the flag to. After the two Marines took the pipe to Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block near the first flag, the flag was attached to the pipe. As the four Marines got into position to raise the flagstaff, Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block called out to two nearby Marines to help them raise the heavy flagstaff. Then, under Lt. Schrier's orders, the second flag was raised at approximately 1 p.m. by Sgt. Strank, Cpl. Block, Pfc. Hayes, Pfc. Sousley, Pfc. Harold Schultz, and Pfc. Harold Keller,USMC Statement on Marine Corps Flag Raisers
Office of U.S. Marine Corps Communication, 23 June 2016 as the original flag came down. Pfc. Schultz and Pfc. Keller were members of Lt. Schrier's patrol. In order to keep the second flagstaff in a vertical position in the high winds on the summit, rocks were immediately added to the base of the flagstaff by Pfc. Schultz and Pfc. Keller, and another Marine. Three guy-ropes were then tied to the flagstaff to stabilize it. The six Marine flag-raisers were photographed in action by Associated Press photographer
 The
The
 Strank was born on November 10, the Marine Corps birthday. The members of Strank's rifle squad idolized him (Cpl. Harlon Block for one followed his every instruction without question), and many men since who served with and alongside him have stated he had a way of setting them at ease, making them feel that ''he'' could help them survive the war. Of the men photographed raising the second flag on Mount Suribachi, Strank at age 25, was the oldest, and Harold Keller and him the most experienced in combat.
In interviews of former Marines conducted years later, many documented in the book ''
Strank was born on November 10, the Marine Corps birthday. The members of Strank's rifle squad idolized him (Cpl. Harlon Block for one followed his every instruction without question), and many men since who served with and alongside him have stated he had a way of setting them at ease, making them feel that ''he'' could help them survive the war. Of the men photographed raising the second flag on Mount Suribachi, Strank at age 25, was the oldest, and Harold Keller and him the most experienced in combat.
In interviews of former Marines conducted years later, many documented in the book ''
The Flag-raisers on Iwojima.com
eFilmCritic.com interview with Barry Pepper on playing Michael Strank in "Flags of Our Fathers"
The story continues: Transcarpathian Michael Strank goes to Washington
Arlington National Cemetery
{{DEFAULTSORT:Strank, Michael 1919 births 1945 deaths American Eastern Catholics People from Stará Ľubovňa District People from Cambria County, Pennsylvania Military personnel from Pennsylvania Czechoslovak emigrants to the United States American people of Rusyn descent American people of Lemko descent American people of Ukrainian descent Ruthenian Greek Catholics United States Marine Corps personnel killed in World War II Burials at Arlington National Cemetery Civilian Conservation Corps people United States Marine Corps non-commissioned officers Battle of Iwo Jima People notable for being the subject of a specific photograph Bethlehem Steel people Articles containing video clips Marine Raiders Military personnel killed by friendly fire Friendly fire incidents of World War II
Battle of Iwo Jima
The Battle of Iwo Jima (19 February – 26 March 1945) was a major battle in which the United States Marine Corps (USMC) and United States Navy (USN) landed on and eventually captured the island of Iwo Jima from the Imperial Japanese Army (IJ ...
in World War II. He was one of the Marines who raised the second U.S. flag
The national flag of the United States of America, often referred to as the ''American flag'' or the ''U.S. flag'', consists of thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white, with a blue rectangle in the c ...
on Mount Suribachi
is a -high mountain on the southwest end of Iwo Jima in the northwest Pacific Ocean under the administration of Ogasawara Subprefecture, Tokyo Metropolis, Japan.
The mountain's name derives from its shape, resembling a ''suribachi'' or grindin ...
on February 23, 1945, as shown in the iconic photograph '' Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima'' by photographer Joe Rosenthal
Joseph John Rosenthal (October 9, 1911 – August 20, 2006) was an American photographer who received the Pulitzer Prize for his iconic World War II photograph '' Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima'', taken during the 1945 Battle of Iwo Jima.
H ...
. Of the six Marines depicted in the photo, Strank was the only one to be correctly identified from the beginning; the other five were either assigned the wrong locations ( Ira Hayes and Franklin Sousley), or, were given the names of Marines who were not in the photo.
The first flag raised over Mount Suribachi at the south end of Iwo Jima was deemed too small. Later that day, Strank, a rifle company squad leader in the 5th Marine Division
The 5th Marine Division was a United States Marine Corps ground combat division which was activated on 11 November 1943 (officially activated on 21 January 1944) at Camp Pendleton, California during World War II. The 5th Division saw its first ...
, was ordered up the mountain with three Marines to raise a larger flag. A photograph of the second flag-raising became famous and was widely reproduced. The second flag raising was also filmed in color.You Tube, Smithsonian Channel, 2008 Documentary (Genaust films) "Shooting Iwo Jima"Retrieved March 14, 2020 Before Iwo Jima, Strank served with the
Marine Raiders
The Marine Raiders are special operations forces originally established by the United States Marine Corps during World War II to conduct amphibious light infantry warfare. " Edson's" Raiders of 1st Marine Raider Battalion and " Carlson's" Ra ...
in the Battle of Bougainville.
The Marine Corps War Memorial
The United States Marine Corps War Memorial (Iwo Jima Memorial) is a national memorial located in Arlington County, Virginia. The memorial was dedicated in 1954 to all Marines who have given their lives in defense of the United States since 177 ...
in Arlington, Virginia, was modeled after Rosenthal's photograph of six Marines raising the second flag on Iwo Jima.
Early life
Michael Strank was born in a Rusyn family in the Prešov village of Orjabyna in the Czechoslovak Republic (today it is a district Stará Ľubovňa,Jarabina
Jarabina, also known as Orjabyna ( rue, Орябина; hu, Berkenyéd) is a village and municipality in Stará Ľubovňa District in the Prešov Region of northern Slovakia.
U.S. Marine Michael Strank, Flag Raiser at Iwo Jima, was born here.
H ...
), Prešov Region
The Prešov Region, also Priashiv Region ( sk, Prešovský kraj, ; hu, Eperjesi kerület; uk, Пряшівський край) is one of the eight Slovak administrative regions and consists of 13 districts (okresy) and 666 municipalities, 23 o ...
of northeastern Czechoslovakia (now in Slovakia). His two brothers, Petro and John, and his sister Mary were born in the United States to Vasil Strank (later, in the U.S., known as Charles Strank) and Marta Grófiková, Rusyn
Rusyn may refer to:
* Rusyns, Rusyn people, an East Slavic people
** Pannonian Rusyns, Pannonian Rusyn people, a branch of Rusyn people
** Lemkos, a branch of Rusyn (or Ukrainian) people
** Boykos, a branch of Rusyn (or Ukrainian) people
* Rusyn l ...
immigrants. In his application for American citizenship, Vasil Strenk's father indicated the nationality of his family as Ruthenian. Vasil Strank moved to Franklin Borough (near Johnstown, Pennsylvania, United States), found work in the coal mines for the Bethlehem Steel Corporation, and brought his family to Pennsylvania three years later, when he could pay for their voyage. Strank attended the public schools of Franklin Borough and graduated from Franklin Borough High School in 1937. He joined the Civilian Conservation Corps, served for 18 months, and afterwards became a Pennsylvania state highway laborer.
U.S. Marine Corps
Strank enlisted in the Marine Corps at Pittsburgh for four years service on October 6, 1939. He was assigned to the Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island in South Carolina. He completed recruit training in December and was transferred to Headquarters Company, Post Troop and then to Provisional Company W at Parris Island, on January 17, 1941. Private First Class Strank sailed forGuantánamo Bay
Guantánamo Bay ( es, Bahía de Guantánamo) is a bay in Guantánamo Province at the southeastern end of Cuba. It is the largest harbor on the south side of the island and it is surrounded by steep hills which create an enclave that is cut off ...
, Cuba, arriving on January 23, 1941. He was reassigned to Headquarters Company, 3rd Battalion, 7th Marine Regiment, 1st Marine Brigade (on February 1, the 1st Marine Brigade was redesignated the 1st Marine Division
The 1st Marine Division (1st MARDIV) is a Marine division of the United States Marine Corps headquartered at Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton, California. It is the ground combat element of the I Marine Expeditionary Force (I MEF).
It is the ...
). On April 8, now assigned to Company K, 3rd Battalion, 7th Marines, he returned to the United States and was sent back to Marine Corps Recruit Depot Parris Island. He was promoted to corporal on April 23, 1941. In September, Cpl. Strank moved with the 1st Marine Division to New River (North Carolina) ( Camp Lejeune), which is where he was stationed when the attack on Pearl Harbor occurred.
World War II
 On January 26, 1942, Cpl. Strank was promoted to
On January 26, 1942, Cpl. Strank was promoted to sergeant
Sergeant (abbreviated to Sgt. and capitalized when used as a named person's title) is a rank in many uniformed organizations, principally military and policing forces. The alternative spelling, ''serjeant'', is used in The Rifles and other uni ...
. On March 21, the 3rd Battalion, 7th Marines was detached from the 1st Marine Division and attached to the newly created 3rd Marine Brigade
The 3rd Marine Expeditionary Brigade is a United States Marine Corps unit that is the "middleweight" crises response force of choice in the Pacific Area of Operation. It is the Marine Corps’ only permanently forward-deployed Brigade sized Marin ...
. In early April, he was sent with the battalion to San Diego, California and deployed on April 12 (sailed April 13) to Samoa arriving in American Samoa on April 28;https://www.marines.mil/Portals/1/Publications/A%20Brief%20History%20of%20the%207th%20Marines%20%20PCN%2019000308200_1.pdf the 7th Marines were ordered to Samoa. On May 31, his battalion was transferred to Wallis (Urea) Island. In August, the 3rd Battalion, 7th Marines was detached from the 3rd Marine Brigade and reassigned to the 1st Marine Division; also during August, the 22nd Marine Regiment
The 22nd Marine Regiment (22nd Marines) is an inactive United States Marine Corps infantry regiment. The regiment was commissioned in 1942 and was placed under the command of the 1st Provisional Marine Brigade, and the 6th Marine Division. It t ...
relieved the 7th Marines which were ordered to reinforce Marine units fighting on Guadalcanal; a battalion of the 22nd Marines relieved the 3rd Battalion, 7th Marines on Urea. In September, after a short time with the 22nd Marines, Sgt. Strank was transferred to the newly organized 3rd Marine Raider Battalion
The Marine Raiders are special operations forces originally established by the United States Marine Corps during World War II to conduct amphibious light infantry warfare. " Edson's" Raiders of 1st Marine Raider Battalion and " Carlson's" Ra ...
under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Harry B. Liversedge
Brigadier General Harry Bluett Liversedge (September 21, 1894 – November 25, 1951), whose regiment figured in the historic raising the flag on Iwo Jima, was a United States Marine who died in 1951 after almost 25 years of service. His last assi ...
; D Company, 3rd Raider Battalion was organized on Urea and joined the rest of the 3rd Raider Battalion at Pago Pago, American Samoa on December 21. In January and February 1943, the 3rd Raiders were sent to Espiritu Santo ( Camp Rennie), New Hebrides, Islands and Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal (; indigenous name: ''Isatabu'') is the principal island in Guadalcanal Province of Solomon Islands, located in the south-western Pacific, northeast of Australia. It is the largest island in the Solomon Islands by area, and the seco ...
, British Solomon Islands
The British Solomon Islands Protectorate was first declared over the southern Solomons in 1893, when Captain Gibson, R.N., of , declared the southern islands a British protectorate. Other islands were subsequently declared to form part o ...
.
As a member of the 3rd Raiders using 10-man rubber boats in their first offensive action, Sgt. Strank (D Company) participated in the unopposed landing operations and occupation of Pavuvu (Operation Cleanslate
During World War II, Operation Cleanslate was the occupation of Russell Islands about sixty miles northwest of Guadalcanal by the United States on 21 February, 1943. The Japanese had captured the island in January, 1943, but abandoned them after o ...
) in the Russell Islands from February 21 to March 18, 1943. On March 19, the battalion left the island and returned to Guadalcanal and Espiritu Santo (Camp Rennie) on March 20. On May 1, D Company was designated as M Company, 3rd Raider Battalion, 1st Marine Raider Regiment, 1st Marine Amphibious Corps
The I Marine Amphibious Corps, or I MAC, was a formation of the United States Marine Corps.
It was created on 1 October 1942, with most of the staff transferred from Amphibious Corps, Pacific Fleet (ACPF). It was then deployed to the South Pacific ...
.
On November 1, 1943, the 2nd and 3rd Raider Battalions spearheaded the initial invasion of Bougainville by the 3rd Marine Division
The 3rd Marine Division is a division of the United States Marine Corps based at Camp Courtney, Marine Corps Base Camp Smedley D. Butler in Okinawa, Japan. It is one of three active duty infantry divisions in the Marine Corps and together with th ...
. Sgt. Strank, M Company, 3rd Raiders, landed on Green Beach #2 at Cape Torokina and participated in the seizure and occupation of Empress Augusta Bay ( Operation Cherryblossom). On January 12, the 3rd Raiders were removed from the combat zone and returned to Guadalcanal, arriving on January 14. On February 1, the 1st Marine Raider Regiment was redesignated the 4th Marine Regiment
The 4th Marine Regiment is an infantry regiment of the United States Marine Corps. Based at Camp Schwab in Okinawa, Japan, it is part of the 3rd Marine Division of the III Marine Expeditionary Force.
Mission
Close with and destroy the enemy by fi ...
. The 3rd Raider Battalion was disbanded and designated the 3rd Battalion, 4th Marine Regiment. On February 14, Sgt. Strank was sent to San Diego and allowed a leave to visit his family.
Battle of Iwo Jima
Sgt. Strank returned to duty in San Diego and was assigned to Second Platoon, Company E,2nd Battalion, 28th Marine Regiment
The 2nd Battalion, 28th Marine Regiment (2nd Battalion, 28th Marines) is an infantry battalion of the United States Marine Corps. The battalion (inactive since the Vietnam War) which is part of the 28th Marine Regiment, 5th Marine Division, fough ...
, 5th Marine Division
The 5th Marine Division was a United States Marine Corps ground combat division which was activated on 11 November 1943 (officially activated on 21 January 1944) at Camp Pendleton, California during World War II. The 5th Division saw its first ...
at Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton, as a squad leader. He was sent to Hawaii with his unit after extensive training, and began more training and preparation for the invasion of Iwo Jima
Iwo Jima (, also ), known in Japan as , is one of the Japanese Volcano Islands and lies south of the Bonin Islands. Together with other islands, they form the Ogasawara Archipelago. The highest point of Iwo Jima is Mount Suribachi at high.
...
.
First flag-raising
28th Marines
The 28th Marine Regiment (28th Marines) is an infantry regiment of the United States Marine Corps. The regiment (inactive since the Vietnam War) which is part of the 5th Marine Division, fought in the Battle of Iwo Jima during World War II. Six ...
, amphibious assault landing on Green Beach at the southern part of Iwo Jima near Mount Suribachi on February 19, 1945. The mission of the 28th Marines that day was to isolate Mount Suribachi, which it accomplished. The next day, the regiment secured the southern end of the island. Their mission afterwards, was to capture Mount Suribachi. After heavy opposition, the 28th Marines surrounded the mountain by the evening of February 22. On the morning of February 23, Lieutenant Colonel Chandler W. Johnson
Chandler Wilce Johnson (October 8, 1905 – March 2, 1945) was a highly decorated United States Marine Corps lieutenant colonel. He served as the commanding officer of 2nd Battalion, 28th Marines during the battle of Iwo Jima, leading his batt ...
, commander of the Second Battalion, 28th Marines, ordered E Company's executive officer, First Lieutenant Harold Schrier
Harold George Schrier (October 17, 1916 – June 3, 1971) was a United States Marine Corps lieutenant colonel who served in World War II and the Korean War. In World War II, he was awarded the Navy Cross for leading the patrol that captured the t ...
, to take a platoon-sized patrol up 556-foot high Mount Suribachi to seize and occupy the crest, and if possible, raise the battalion's American flag to signal the summit was secure. E Company's commander, Captain Dave Severance, assembled a 40-man patrol for the mission from the remainder of his Third Platoon and other members from the battalion.
The patrol left the base of Mount Suribachi at about 8:30 a.m. Once Lt. Schrier was on top with his men after some occasional sniper fire and a brief firefight at the rim of the crater, he and his men secured the top. After a Japanese steel pipe was found, Lt. Schrier and two other Marines attached the flag to it. The flagstaff was then taken to the highest position on top and raised by Lt. Schrier, Platoon Sgt. Ernest Thomas, Sergeant Henry Hansen, and Corporal Charles Lindberg at about 10:30 a.m. Seeing the raising of the national colors
National colours are frequently part of a country's set of national symbols. Many states and nations have formally adopted a set of colours as their official "national colours" while others have ''de facto'' national colours that have become well ...
immediately caused loud cheers from the Marines, sailors, and Coast Guardsmen on the beaches at the southern end of Iwo Jima and from the men on the ships near the beaches. The men at, around, and holding the flagstaff were photographed several times by Marine Staff Sergeant Louis R. Lowery, a photographer with ''Leatherneck'' magazine who accompanied the patrol up the mountain. Platoon Sgt. Thomas was killed in action on Iwo Jima on March 3 and Sgt. Hansen was killed on March 1.
Second flag-raising

 In order for the American flag to be seen more by the thousands of Marines fighting on the other side of Mount Suribachi where most of the Japanese soldiers were located, it was decided that a larger flag should replace the battalion's flag on Mount Suribachi. Captain Severance ordered Sgt. Strank to ascend Mount Suribachi with three Marines from his rifle squad in Second Platoon and raise the replacement flag. Sgt. Strank then ordered Corporal Harlon Block, Private First Class Ira Hayes, and Private First Class Franklin Sousley to go with him up Mount Suribachi with communication wire (or supplies). Private First Class Rene Gagnon, the Second Battalion's runner (messenger) for E Company, was ordered to take the replacement flag up the mountain and return with the first flag.
Once Sgt. Strank's team was on top, Pfc. Hayes and Pfc. Sousley found a Japanese steel pipe to attach the flag to. After the two Marines took the pipe to Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block near the first flag, the flag was attached to the pipe. As the four Marines got into position to raise the flagstaff, Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block called out to two nearby Marines to help them raise the heavy flagstaff. Then, under Lt. Schrier's orders, the second flag was raised at approximately 1 p.m. by Sgt. Strank, Cpl. Block, Pfc. Hayes, Pfc. Sousley, Pfc. Harold Schultz, and Pfc. Harold Keller,USMC Statement on Marine Corps Flag Raisers
In order for the American flag to be seen more by the thousands of Marines fighting on the other side of Mount Suribachi where most of the Japanese soldiers were located, it was decided that a larger flag should replace the battalion's flag on Mount Suribachi. Captain Severance ordered Sgt. Strank to ascend Mount Suribachi with three Marines from his rifle squad in Second Platoon and raise the replacement flag. Sgt. Strank then ordered Corporal Harlon Block, Private First Class Ira Hayes, and Private First Class Franklin Sousley to go with him up Mount Suribachi with communication wire (or supplies). Private First Class Rene Gagnon, the Second Battalion's runner (messenger) for E Company, was ordered to take the replacement flag up the mountain and return with the first flag.
Once Sgt. Strank's team was on top, Pfc. Hayes and Pfc. Sousley found a Japanese steel pipe to attach the flag to. After the two Marines took the pipe to Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block near the first flag, the flag was attached to the pipe. As the four Marines got into position to raise the flagstaff, Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block called out to two nearby Marines to help them raise the heavy flagstaff. Then, under Lt. Schrier's orders, the second flag was raised at approximately 1 p.m. by Sgt. Strank, Cpl. Block, Pfc. Hayes, Pfc. Sousley, Pfc. Harold Schultz, and Pfc. Harold Keller,USMC Statement on Marine Corps Flag RaisersOffice of U.S. Marine Corps Communication, 23 June 2016 as the original flag came down. Pfc. Schultz and Pfc. Keller were members of Lt. Schrier's patrol. In order to keep the second flagstaff in a vertical position in the high winds on the summit, rocks were immediately added to the base of the flagstaff by Pfc. Schultz and Pfc. Keller, and another Marine. Three guy-ropes were then tied to the flagstaff to stabilize it. The six Marine flag-raisers were photographed in action by Associated Press photographer
Joe Rosenthal
Joseph John Rosenthal (October 9, 1911 – August 20, 2006) was an American photographer who received the Pulitzer Prize for his iconic World War II photograph '' Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima'', taken during the 1945 Battle of Iwo Jima.
H ...
and by Marine motion picture cameraman Sergeant William (Bill) Genaust (later killed in action) in color. After the second flag-raising, Rosenthal photographed sixteen Marines including Sgt. Strank and two Navy corpsmen around the base of the flagstaff. Rosenthal's black-and-white flag-raising picture, which appeared in newspapers on February 25, 1945, was later titled Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima. It became the most copied photograph in Marine Corps history.
On March 14, another American flag was officially raised up a flagpole by two Marines under the orders of Lt. Gen. Holland Smith during a ceremony at the V Amphibious Corps command post on the other side of Mount Suribachi where the 3rd Marine Division
The 3rd Marine Division is a division of the United States Marine Corps based at Camp Courtney, Marine Corps Base Camp Smedley D. Butler in Okinawa, Japan. It is one of three active duty infantry divisions in the Marine Corps and together with th ...
troops were located. The flag flying on the summit of Mount Suribachi since February 23 was taken down. On March 26, 1945, the island was considered secure and the battle of Iwo Jima was officially ended. The 28th Marines left Iwo Jima on March 27 and returned to Hawaii to the 5th Marine Division training camp. Lt. Col. Johnson was killed in action on March 2, Sgt. Genaust was killed on March 4, Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block were killed on March 1, and Pfc. Sousley was killed on March 21.
On March 20, President Roosevelt ordered all the men in Rosenthal's photograph be sent to Washington D.C. after the battle was over. Pfc. Gagnon arrived alone on April 7 and was questioned at Marine Headquarters by a public information officer about the identities of the six flag raisers. Pfc. Gagnon identified Navy corpsman John Bradley and Pfc. Ira Hayes as flag raisers in the photograph and they were sent for and arrived on April 19 and, they were separately questioned that day (Sgt. Strank, Cpl. Block, and Pfc. Sousley were killed on Iwo Jima). All three said they were in the photograph and raised the flag; on April 8, they had been named publicly by the Marine Corps as the surviving flag raisers. Over time it was discovered that all of the second flag-raisers were Marines and that three of the six Marines in Rosenthal's photograph were not correctly identified: Cpl. Block was not recognized until January 1947, Pfc. Schultz was not recognized until June 2016, and Pfc. Keller was not recognized until October 2019. Cpl. Block was incorrectly identified in the photograph as Henry Hansen. Pfc. Schultz was identified as Pfc. Sousley in the photograph. In turn, Pfc. Sousley was identified as PhM2c. Bradley in the photograph. Pfc. Keller was incorrectly identified as Pfc. Gagnon in the photograph. Rosenthal did not take the names of any of the flag raisers in his photograph. Pfc. Schultz and Pfc. Keller did not ever claim publicly to be in Rosenthal's photograph or that they were flag-raisers.
Death and burial
On February 28, Sgt. Strank and E Company moved northward. Fighting was heavy, and both the Japanese and the American forces were taking heavy casualties. On March 1, Sgt. Strank's rifle squad came under heavy fire and took cover. While forming a plan of attack, he was killed by friendly artillery fire. The shell that killed him was almost certainly fired from offshore by an American ship. Cpl. Harlon Block, Sgt. Strank's assistant squad leader, took command of the squad. Cpl. Block was killed later on the same day by a Japanese mortar shell. However, former Marine Ralph Griffiths of Second Platoon, Easy Company, said that Sgt. Strank and Cpl. Block were on both sides of him on March 1 and were killed by the same shell which wounded him. Sgt. Strank and the other Marines killed in action of the 28th Regiment were buried in the 5th Marine Division Cemetery on the island with the last rites of the Roman Catholic Church. Sgt. Strank (and possibly Cpl. Block) was the first person in Rosenthal's flag raising photograph to be killed. On January 13, 1949, his remains were reinterred in Grave 7179, Section 12, Arlington National Cemetery. Sgt. Strank's brother, Peter Strank, was serving aboard the aircraft carrier ''USS Franklin'' in theSouth Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
when Sgt. Strank was killed.
Marine Corps War Memorial
 The
The Marine Corps War Memorial
The United States Marine Corps War Memorial (Iwo Jima Memorial) is a national memorial located in Arlington County, Virginia. The memorial was dedicated in 1954 to all Marines who have given their lives in defense of the United States since 177 ...
in Arlington, Virginia, was dedicated on November 10, 1954. Sculptor Felix de Weldon was inspired to make the memorial after seeing Rosenthal's photograph of the second flag raising. De Weldon duplicated the flag raisers images and positions on the memorial from the photograph. Strank is depicted as the fourth bronze figure from the base of the flagstaff on the memorial with the 32-foot (9.8 M) bronze figures of the other five flag raisers depicted on the memorial. The Marine Corps announced on June 23, 2016, that Harold Schultz is now in back of Strank instead of Franklin Sousley, who is now in front of Strank instead of John Bradley, who is no longer in the photograph. The Memorial was turned over to the National Park Service in 1955.
During the dedication, President Dwight D. Eisenhower sat upfront with Vice President Richard Nixon, Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
Charles E. Wilson, Deputy Secretary of Defense Robert Anderson, Assistant Secretary of the Interior
Assistant may refer to:
* Assistant (by Speaktoit), a virtual assistant app for smartphones
* Assistant (software), a software tool to assist in computer configuration
* Google Assistant, a virtual assistant by Google
* ''The Assistant'' (TV seri ...
Orme Lewis, and General Lemuel C. Shepherd
Lemuel Cornick Shepherd Jr. (February 10, 1896 – August 6, 1990) was a four-star general of the United States Marine Corps. A veteran of World War I, World War II, and the Korean War, he was the 20th Commandant of the Marine Corps. As Co ...
, the 20th Commandant of the Marine Corps
The commandant of the Marine Corps (CMC) is normally the highest-ranking officer in the United States Marine Corps and is a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. Joint Chiefs of Staff: composition; functions. The CMC reports directly to the secr ...
.
Ira Hayes, one of the three surviving flag-raisers depicted on the monument, was seated together with John Bradley, Rene Gagnon Mrs. Martha Strank, Ada Belle Block, and Mrs. Goldie Price (mother of Franklin Sousley). Those giving remarks at the dedication included Robert Anderson, Chairman of Day; Colonel J.W. Moreau, U.S. Marine Corps (Retired), President, Marine Corps War Memorial Foundation; General Shepherd, who presented the memorial to the American people; Felix de Weldon, sculptor; and Richard Nixon, who gave the dedication address. Inscribed on the memorial are the following words:
:In Honor And Memory Of The Men of The United States Marine Corps Who Have Given Their Lives To Their Country Since 10 November 1775
Military awards
Strank's military decorations and awards include:Legacy
 Strank was born on November 10, the Marine Corps birthday. The members of Strank's rifle squad idolized him (Cpl. Harlon Block for one followed his every instruction without question), and many men since who served with and alongside him have stated he had a way of setting them at ease, making them feel that ''he'' could help them survive the war. Of the men photographed raising the second flag on Mount Suribachi, Strank at age 25, was the oldest, and Harold Keller and him the most experienced in combat.
In interviews of former Marines conducted years later, many documented in the book ''
Strank was born on November 10, the Marine Corps birthday. The members of Strank's rifle squad idolized him (Cpl. Harlon Block for one followed his every instruction without question), and many men since who served with and alongside him have stated he had a way of setting them at ease, making them feel that ''he'' could help them survive the war. Of the men photographed raising the second flag on Mount Suribachi, Strank at age 25, was the oldest, and Harold Keller and him the most experienced in combat.
In interviews of former Marines conducted years later, many documented in the book ''Flags of Our Fathers
''Flags of Our Fathers'' (2000) is a book by James Bradley with Ron Powers about his father, Navy corpsman John Bradley, and five United States Marines, who were made famous by Joe Rosenthal’s '' Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima'' photograph. Th ...
'' written by James Bradley (son of corpsman John Bradley), he is described by men who served with him as "a Marine's Marine", a true warrior and leader, who led his men by example. Strank often told his men, "Follow me, and I'll try to bring you all safely home to your mothers." One former Marine who served with Strank stated, "He was the kind of Marine you read about, the kind they make movies about." Former Paramarine Lowell B. Holly, who served in Strank's squad on Iwo Jima and who was with Strank when he died, stated, "He was the best Marine I ever knew."
U.S. citizenship
In 2008, Gunnery Sergeant Matt Blais, who was a Marine security guard in the American Embassy in Slovakia, discovered that Strank was not a natural-born U.S. citizen. Strank had become a U.S. citizen after his father's naturalization in 1935, but had never received official documentation. GySgt. Blais petitioned the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services on Strank's behalf and on July 29, 2008, Strank's youngest sister, Mary Pero, was presented with his certificate of citizenship in a ceremony at theMarine Corps War Memorial
The United States Marine Corps War Memorial (Iwo Jima Memorial) is a national memorial located in Arlington County, Virginia. The memorial was dedicated in 1954 to all Marines who have given their lives in defense of the United States since 177 ...
.
Monuments and memorials
Strank's public recognitions include: * Sgt. Michael Strank statue:Marine Corps War Memorial
The United States Marine Corps War Memorial (Iwo Jima Memorial) is a national memorial located in Arlington County, Virginia. The memorial was dedicated in 1954 to all Marines who have given their lives in defense of the United States since 177 ...
, Arlington, Virginia
* Sgt. Michael Strank - Pennsylvania Historical Marker: Franklin Borough, Cambria County, Pennsylvania.
* Sgt. Michael Strank Marine Corps Reserve Center (NMCRC), Ebensburg, Pennsylvania. This building was opened in 1987 and later decommissioned in 2019.
* Sergeant Michael Strank Memorial Bridge: crosses Little Conemaugh River on PA 271 in East Conemaugh
* Michael Strank mini-sculpture ( English spelling name and surname): located near school #4 in Uzhhorod, Ukraine (installed on February 16, 2015, the 70th anniversary of liberation of the city at the end of World War II).
* Stará Ľubovňa, Slovakia
Portrayal in film
Strank is prominently featured in the 2006 movie ''Flags of Our Fathers
''Flags of Our Fathers'' (2000) is a book by James Bradley with Ron Powers about his father, Navy corpsman John Bradley, and five United States Marines, who were made famous by Joe Rosenthal’s '' Raising the Flag on Iwo Jima'' photograph. Th ...
''. In the movie, Sgt. Strank is played by Canadian actor Barry Pepper
Barry Robert Pepper (born April 4, 1970) is a Canadian actor. He played Private Daniel Jackson in ''Saving Private Ryan'' (1998), Corrections Officer Dean Stanton in '' The Green Mile'' (1999), Roger Maris in '' 61*'' (2001), Joseph L. Galloway ...
. The movie is based on the 2000 book of the same title.
In 2016, Radio and Television of Slovakia
Radio and Television of Slovakia ( sk, Rozhlas a televízia Slovenska ) or RTVS is a nationwide public broadcasting, state-funded organisation in Slovakia. It is headquartered in Bratislava and led by Ľuboš Machaj.
History
The organization i ...
filmed a documentary about Sgt. Strank called "Chlapec, ktorý chcel byť prezidentom" ("The boy who wanted to be a president"). It was aired for the first time on May 2, 2017.
In 2019, an English version of the documentary "Chlapec, ktorý chcel byť prezidentom" will be premiered in the United States under the title, "The Oath".
See also
* Meliton Kantaria – Soviet flag raiser over the Reichstag in Berlin, 1945 *Mikhail Yegorov
Mikhail Alekseyevich Yegorov (russian: Михаил Алексеевич Егоров; May 5, 1923 – June 20, 1975), along with Meliton Kantaria and Alexei Berest, was one of the three soldiers credited with raising the Soviet flag over the Re ...
– Soviet flag raiser over the Reichstag in Berlin, 1945
Notes
References
External links
The Flag-raisers on Iwojima.com
eFilmCritic.com interview with Barry Pepper on playing Michael Strank in "Flags of Our Fathers"
The story continues: Transcarpathian Michael Strank goes to Washington
Arlington National Cemetery
{{DEFAULTSORT:Strank, Michael 1919 births 1945 deaths American Eastern Catholics People from Stará Ľubovňa District People from Cambria County, Pennsylvania Military personnel from Pennsylvania Czechoslovak emigrants to the United States American people of Rusyn descent American people of Lemko descent American people of Ukrainian descent Ruthenian Greek Catholics United States Marine Corps personnel killed in World War II Burials at Arlington National Cemetery Civilian Conservation Corps people United States Marine Corps non-commissioned officers Battle of Iwo Jima People notable for being the subject of a specific photograph Bethlehem Steel people Articles containing video clips Marine Raiders Military personnel killed by friendly fire Friendly fire incidents of World War II