MidSTAR I (USNA) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 MidSTAR-1 is an artificial
MidSTAR-1 is an artificial
 MidSTAR is a general-purpose satellite bus capable of supporting a variety of space missions by easily accommodating a wide range
of space experiments and instruments. The integration of the experiments with the satellite bus must be accomplished with minimal changes to the satellite bus design. MidSTAR is intended to be a relatively low-cost, quick response platform accommodating small payloads approved by the DoD Space Experiments Review Board (SERB) and awaiting launch through STP.
MidSTAR is designed for use on the
MidSTAR is a general-purpose satellite bus capable of supporting a variety of space missions by easily accommodating a wide range
of space experiments and instruments. The integration of the experiments with the satellite bus must be accomplished with minimal changes to the satellite bus design. MidSTAR is intended to be a relatively low-cost, quick response platform accommodating small payloads approved by the DoD Space Experiments Review Board (SERB) and awaiting launch through STP.
MidSTAR is designed for use on the
 The MidSTAR-1 frame is an
The MidSTAR-1 frame is an 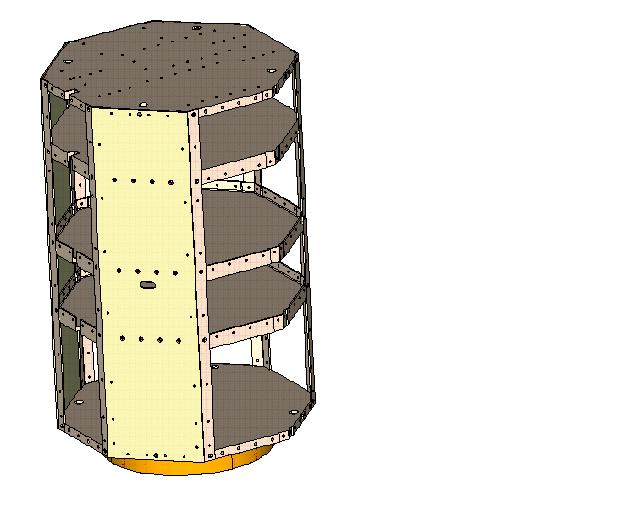 MidSTAR-1 has three interior shelves which provide area inside the satellite for mounting of components and payloads. Their locations are determined by the dimensions of the payloads and components. These can be varied in future implementations of the MidSTAR model, if necessary, as long as the structure remains within the
MidSTAR-1 has three interior shelves which provide area inside the satellite for mounting of components and payloads. Their locations are determined by the dimensions of the payloads and components. These can be varied in future implementations of the MidSTAR model, if necessary, as long as the structure remains within the
eoPortal describes MidSTAR-1
 MidSTAR-1 is an artificial
MidSTAR-1 is an artificial satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
produced by the United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (USNA, Navy, or Annapolis) is a United States Service academies, federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as United States Secre ...
Small Satellite Program. It was sponsored by the United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and superv ...
(DoD) Space Test Program (STP), and was launched on March 9, 2007 at 03:10 UTC, aboard an Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was developed by Lockheed Martin and has been operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2006. Primarily used to ...
expendable launch vehicle
An expendable launch system (or expendable launch vehicle/ELV) is a launch vehicle that can be launched only once, after which its components are destroyed during reentry or impact with Earth, or discarded in space. ELVs typically consist of s ...
from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the sta ...
. MidSTAR-1 flew along with FalconSat 3, STPSat 1, and CFESat as secondary payloads; the primary payload was Orbital Express
Orbital Express: ASTRO and NEXTSat
Orbital Express was a space mission managed by the United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and a team led by engineers at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Orbital Express p ...
.
MidSTAR-1 Mission (USNA-5)
 MidSTAR is a general-purpose satellite bus capable of supporting a variety of space missions by easily accommodating a wide range
of space experiments and instruments. The integration of the experiments with the satellite bus must be accomplished with minimal changes to the satellite bus design. MidSTAR is intended to be a relatively low-cost, quick response platform accommodating small payloads approved by the DoD Space Experiments Review Board (SERB) and awaiting launch through STP.
MidSTAR is designed for use on the
MidSTAR is a general-purpose satellite bus capable of supporting a variety of space missions by easily accommodating a wide range
of space experiments and instruments. The integration of the experiments with the satellite bus must be accomplished with minimal changes to the satellite bus design. MidSTAR is intended to be a relatively low-cost, quick response platform accommodating small payloads approved by the DoD Space Experiments Review Board (SERB) and awaiting launch through STP.
MidSTAR is designed for use on the EELV Secondary Payload Adapter
The EELV Secondary Payload Adapter (ESPA) is an adapter for launching secondary payloads on orbital launch vehicles.
Originally developed for US launch vehicles in the 2000s to launch secondary payloads on space missions of the United States Dep ...
(ESPA) Ring developed by Air Force Research Laboratory
The Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) is a scientific research and development detachment of the United States Air Force Air Force Materiel Command, Materiel Command dedicated to leading the discovery, development, and integration of direct- ...
(AFRL) for placement on Delta IV
Delta IV was a group of five expendable launch systems in the Delta rocket family. It flew 45 missions from 2002 to 2024. Originally designed by Boeing's Defense, Space and Security division for the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) p ...
or Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was developed by Lockheed Martin and has been operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2006. Primarily used to ...
expendable launch vehicles. MidSTAR is a Class D spacecraft, produced at minimum cost with a correspondingly higher technical risk in production and operation. It is intentionally simple in design and rugged in construction, using commercial off-the-shelf “plug-and-play” components to the greatest extent possible. Component development and circuit-board level design are accomplished only when necessary.
MidSTAR-1 is the first implementation of the design. It was commissioned by STP to carry the Internet Communications Satellite (ICSat) Experiment for SSP and the Configurable Fault Tolerant Processor (CFTP) Experiment for Naval Postgraduate School
Naval Postgraduate School (NPS) is a Naval command with a graduate university mission, operated by the United States Navy and located in Monterey, California.
The NPS mission is to provide "defense-focused graduate education, including clas ...
(NPS). In addition, MidSTAR-1 carries the Nano Chem Sensor Unit (NCSU) for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the United States's civil space program, aeronautics research and space research. Established in 1958, it su ...
(NASA) Ames Research Center
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laborat ...
; Eclipse, built by Eclipse Energy Systems, Inc. for NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C., in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959, as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC ...
(GSFC); and the Micro Dosimeter Instrument (MiDN), sponsored by the National Space Biomedical Research Institute (NSBRI) and built by the USNA Department of Aerospace Engineering. The mission is intended to last two years.
Mission architecture
The MidSTAR-1 mission includes a single spacecraft under the command and control of a single satellite ground station (SGS) located at theUnited States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (USNA, Navy, or Annapolis) is a United States Service academies, federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as United States Secre ...
, Annapolis, Maryland. The ground station forwards downlinked data files to the principal investigators via the Internet. The launch segment for MidSTAR-1 utilized an Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas launch vehicle family. It was developed by Lockheed Martin and has been operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA) since 2006. Primarily used to ...
launch vehicle through the Space Test Program, placing the satellite in a circular orbit
A circular orbit is an orbit with a fixed distance around the barycenter; that is, in the shape of a circle.
In this case, not only the distance, but also the speed, angular speed, Potential energy, potential and kinetic energy are constant. T ...
at 496 km altitude, 46 degrees inclination.
The satellite uses an uplink at 1.767 GHz with an intermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in Transmission (telecommunications), transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is ...
(IF) of 435 MHz, and a 2.20226 GHz downlink. By utilizing a Gaussian Mean Shift Key modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
, communications with the satellite are achieved at 68.4 kbit/s or higher data rate. The satellite also uses open source software
Open-source software (OSS) is Software, computer software that is released under a Open-source license, license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and Software distribution, distribute the software an ...
based on the Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
. MidSTAR-1 has no attitude control or determination and no active thermal control. The craft has a mass of 118 kg.
One hundred percent success would be the successful launch and operation of the satellite with full support for the two primary experiments for two years. Fifty percent success was the successful launch and operation of the satellite with: Full support of one primary experiment for two years; Full support of both primary experiments for one year; or, partial support of both primary experiments for two years. Thirty-three percent success was successful launch of the satellite and full operation of the satellite bus with partial support of any combination of primary and secondary payloads for any length of time.
Mission log
9 March 2007: MidSTAR-1 flew as part of the STP-1 mission on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V fromCape Canaveral
Cape Canaveral () is a cape (geography), cape in Brevard County, Florida, in the United States, near the center of the state's Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. Officially Cape Kennedy from 1963 to 1973, it lies east of Merritt Island, separated ...
Air Force Station. Liftoff occurred at 0310 UTC
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard globally used to regulate clocks and time. It establishes a reference for the current time, forming the basis for civil time and time zones. UTC facilitates international communica ...
; spacecraft separation occurred at 0332 UTC. USNA SGS successfully acquired communications with the spacecraft during the first pass over Annapolis MD at 0459 UTC. The spacecraft was operating nominally in safe mode
Safe mode is a diagnosis, diagnostic mode of a computer operating system (OS). It can also refer to a mode of operation by application software. ''Safe mode'' is intended to help fix most, if not all, problems within an operating system. It is a ...
.
21 March 2007: CFTP turned on at 2217 UTC to add 6 W continuous to the electrical power system load and thus lessen charging stress on the batteries.
28 March 2007: MiDN turned on at approximately 2400 UTC. Spacecraft stopped responding to all ground commands subsequent to this pass.
4 April 2007: First use of '' firecode reset'' of spacecraft at approximately 2130 UTC. This command toggles the reset switch on the MIP-405 processor and reboots the operating system. This reset returned the CFTP and MiDN experiments to ''off'' and cleared all command buffers. At 2324 UTC the spacecraft responded to a ''transmitter on'' command. Telemetry confirmed that the reboot was successful.
5 April 2007: CFTP and MiDN turned back on.
6 April 2007: Selective download of MiDN files retrieved 71 files of 92 byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable un ...
s each which were delivered to the Principal Investigator (PI). This was the first successful retrieval of science data from the spacecraft. With this milestone, MidSTAR-1 satisfied the criteria of 33% mission success.
26 May 2007: NCSU turned on at approximately 1900 Z.
29 May 2007: First data package delivered to NCSU PI. All four experiments are on and delivering data to the PIs.
18 June 2007: NASA press release announces success of NCSU.
5 September 2007: Spacecraft computer froze as a result of unknown influences, most likely radiation-induced upsets. This happened while the spacecraft was in full sun and with the power drains (30 W) on to prevent battery overcharging. Without the computer to cycle the drains off, the spacecraft remained in a continuous negative net power configuration which eventually drained the batteries. When the battery voltage dropped below 8 V, the electronic switches for the drains defaulted to off, returning the spacecraft to positive net power and allowing the batteries to recharge.
7 September 2007: Once the batteries recharged sufficiently, the computer restarted successfully. Restart occurred 48 hours after the initial event. No telemetry from the spacecraft or any experiment is available for that 48-hour period. Telemetry indicates that normal operation resumed, but all experiments were left off pending post-event analysis and the development of a plan to bring them back online.
12 September 2007: CFTP restarted.
21 September 2007: MiDN restarted.
April 2009: Contact with MidSTAR-1 lost. Spacecraft ceased transmitting and failed to respond to ground command. Anomaly attributed to failure of battery packs. MidSTAR-1 declared non-operational. MidSTAR-1 fully supported all onboard experiments for two full years, fulfilling the 100% success criteria.
17 August 2023: the satellite decayed from orbit.
Structure
 The MidSTAR-1 frame is an
The MidSTAR-1 frame is an octagon
In geometry, an octagon () is an eight-sided polygon or 8-gon.
A '' regular octagon'' has Schläfli symbol and can also be constructed as a quasiregular truncated square, t, which alternates two types of edges. A truncated octagon, t is a ...
al structure 32.5 " along the long axis, including separation system, and 21.2"x21.2" measured side-to-side in cross-section. The deployment mechanism is mounted on the negative x face. The positive x face is reserved for externally mounted experiments. Of the 38" along the x-axis allowed in the ESPA envelope, 2-4" are reserved for the deployment mechanism (15-in motorized lightband manufactured by Planetary Systems, Inc.), and 4-6" are reserved for external experiments. The frame length is 30". All eight sides of the spacecraft are covered with solar cells in order to maximize the power available. Eight dipole antennas are mounted on the four faces of the spacecraft which "cut the corners" of the ESPA envelope and are therefore positioned within the ESPA envelope rather than coincident with the envelope surface. The remaining sides are mounted with remove-before-flight eyeholes for lifting and transport during ground support.
 MidSTAR-1 has three interior shelves which provide area inside the satellite for mounting of components and payloads. Their locations are determined by the dimensions of the payloads and components. These can be varied in future implementations of the MidSTAR model, if necessary, as long as the structure remains within the
MidSTAR-1 has three interior shelves which provide area inside the satellite for mounting of components and payloads. Their locations are determined by the dimensions of the payloads and components. These can be varied in future implementations of the MidSTAR model, if necessary, as long as the structure remains within the center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. For ...
requirements.
The load-bearing structure of the octagon consists of the top and bottom decks, connected at the eight corners by stringers. The side panels of the spacecraft are 1/8" aluminum panels mounted to the stringers with #10 bolts.
Command and Data Handling (C&DH)
The mission of the Command and Data Handling System (C&DH) is to receive and execute commands; collect, store, and transmit house-keeping data; and support the onboard payloads. The flight computer is designed to control the satellite and manage telemetry and experiment data for a minimum of two years. The C&DH system consists of a custom-modified MIP405-3X single board computer which included (i) 133 MHz PowerPC processor; (ii) 128 MB ECC; (iii) 4 RS-232 asynchronous serial ports; (iv) 1 Ethernet Port; (v) a PC/104 bus; (vi) a PC/104+ bus; and, (vi) a 202-D384-X Disc on Chip providing 384 MB of secondary storage. The computer board is supported by an ESCC-104 Synchronous Serial Card with 2 synchronous serial ports, and an EMM-8M-XT Serial Expansion Card with 8RS-232
In telecommunications, RS-232 or Recommended Standard 232 is a standard introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a ''DTE'' (''data terminal equipment'') such as a compu ...
/422/485 asynchronous serial ports and 8 digital I/O channels. A modified I0485 data acquisition board provides 22 analog telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', 'far off', an ...
channels and 32 digital I/O channels.
The decision to use the PowerPC based MIP405 over an x86 based board was based solely on the low power consumption of the board combined with the feature set. The choice was limited to x86, PowerPC, and ARM processor architectures because of a program decision to use the Linux operating system. The MIP405 integrates Ethernet, serial ports, and Disk-on-Chip interface on a single board while providing 128 MB of ECC memory and a powerful processor for under 2 watts. The closest x86 based system with comparable features found consumed 5 watts of power.
The M-Systems Disk-on-Chip was chosen because it was the ''de facto'' standard flash memory harddisk replacement. Flash memory was chosen over a traditional hard disk to increase reliability and reduce power. The 384 MB version was chosen to provide the storage required for the operating system and still maintain adequate margin.
The Diamond Systems Emerald-MM-8 was chosen for the asynchronous serial board based on its innate flexibility with any of the 8 ports capable of being configured as RS-232, RS-422, RS-485.
RMV's IO485 data acquisition and control board was chosen for the distributed telemetry system because of built-in support for daisy chaining and handling a large number of boards. The integrated expandability is fundamental to addressing future telemetry issues in later versions of the MidSTAR line.
The C&DH uses the Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
operating system with a 2.4 series kernel. To create an open software architecture the IP protocol stack was chosen to provide inter process, intra-satellite, and satellite-ground communications. This allowed programs created at different facilities on different hardware to be integrated with minimum difficulty.
All internal and external communications use internet protocols. TCP is used for all internal satellite communications; UDP or MDP is used on the uplink and downlink.
See also
*USNA MidSTAR Program
MidSTAR, a project of the United States Naval Academy (USNA) Small Satellite Program (United States Naval Academy), Small Satellite Program (SSP), is a general-purpose satellite bus capable of supporting a variety of space missions by easily accomm ...
eoPortal describes MidSTAR-1
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Midstar-1 Satellite Internet access Satellites orbiting Earth Spacecraft launched in 2007 United States Naval Academy