Michał Tokarzewski-Karaszewicz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 General Michał Tadeusz Tokarzewski-Karaszewicz, Coat of arms of Trąby pseudonym Doktor, Stolarski, TorwidJozef Garlinski ''Poland in the Second World War'', Page 40 (b. 5 January 1893 in
General Michał Tadeusz Tokarzewski-Karaszewicz, Coat of arms of Trąby pseudonym Doktor, Stolarski, TorwidJozef Garlinski ''Poland in the Second World War'', Page 40 (b. 5 January 1893 in
 During the Polish Defensive War of 1939, he was commanding the Operation Group (grupa operacyjna) of the "
During the Polish Defensive War of 1939, he was commanding the Operation Group (grupa operacyjna) of the "
 Porucznik (
Porucznik ( Kapitan (
Kapitan ( Pułkownik (
Pułkownik ( Generał brygady ( Brigadier general) – 1 December 1924
*
Generał brygady ( Brigadier general) – 1 December 1924
*  Generał dywizji ( Major general) – 1 January 1943
*
Generał dywizji ( Major general) – 1 January 1943
*  Generał broni (
Generał broni (
 Commander of the
Commander of the  Commander of the
Commander of the  Officer of the
Officer of the  Commemorative Medal for War 1918-1921
* Medal of the 10th Anniversary of Regained Independence
* Wound Decoration
*
Commemorative Medal for War 1918-1921
* Medal of the 10th Anniversary of Regained Independence
* Wound Decoration
*  Grand Cross of
Grand Cross of  Commander's Cross of Order of the White Eagle (Yugoslavia)
*
Commander's Cross of Order of the White Eagle (Yugoslavia)
* 
 Chevalier of
Chevalier of  Victory Medal
Victory Medal

 General Michał Tadeusz Tokarzewski-Karaszewicz, Coat of arms of Trąby pseudonym Doktor, Stolarski, TorwidJozef Garlinski ''Poland in the Second World War'', Page 40 (b. 5 January 1893 in
General Michał Tadeusz Tokarzewski-Karaszewicz, Coat of arms of Trąby pseudonym Doktor, Stolarski, TorwidJozef Garlinski ''Poland in the Second World War'', Page 40 (b. 5 January 1893 in Lemberg
Lviv ( or ; ; ; see #Names and symbols, below for other names) is the largest city in western Ukraine, as well as the List of cities in Ukraine, fifth-largest city in Ukraine, with a population of It serves as the administrative centre of ...
– 22 May 1964 in Casablanca
Casablanca (, ) is the largest city in Morocco and the country's economic and business centre. Located on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Chaouia (Morocco), Chaouia plain in the central-western part of Morocco, the city has a populatio ...
, Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
) was a Polish general and founder of the resistance movement
A resistance movement is an organized group of people that tries to resist or try to overthrow a government or an occupying power, causing disruption and unrest in civil order and stability. Such a movement may seek to achieve its goals through ei ...
Polish Victory Service.
Early life
He was born on January 5, 1893, inLviv
Lviv ( or ; ; ; see #Names and symbols, below for other names) is the largest city in western Ukraine, as well as the List of cities in Ukraine, fifth-largest city in Ukraine, with a population of It serves as the administrative centre of ...
as the son of Bolesław Wincenty Tokarzewski-Karaszewicz and Helena Lerch de Lechensfeld. Tokarzewski served in the Polish Legions from 1914 until 1917, then in the POW
POW is "prisoner of war", a person, whether civilian or combatant, who is held in custody by an enemy power during or immediately after an armed conflict.
POW or pow may also refer to:
Music
* P.O.W (Bullet for My Valentine song), "P.O.W" (Bull ...
(Polish Military Organization). He was a commanding officer of the "5th Infantry Legion Regiment" during the Polish-Ukrainian War, which fought in Lwów.Rosa Bailly ''A city fights for freedom'' Leopolis 1956 Pages 276-310
During the November–December 1918 pogroms
A pogrom is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe late 19th- and early 20th-century attacks on Jews i ...
in Poland, Tokarzewski was removed from his post by the Polish Government as District Commander of Przemysl for posting a notice in which he fined the Jewish population 3,000,000 crowns as punishment for allegedly fighting against the Polish army, despite their assertion of neutrality. This charge was never proven.
The poster read: "An appeal to the population of Przemysl of Mosaic Confession. (ie, the Jewish population)
"In view of a well-known fact that in the course of the struggle of recapturing Przemysl, the Jews, notwithstanding their repeated assertion of neutrality, took part in the fight with the Ukrainian forces and fired on the attacking police detachment.
"I order the Jewish community to deposit at the district headquarters of the Polish troops of Przemysl a sum of 3,000,000 crowns.""A Record of Pogroms in Poland," page 1, section 4, The New York Times, June 1, 1919.
After Poland regained independence in 1918, Tokarzewski served in the Polish Army
The Land Forces () are the Army, land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 110,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military histor ...
. In April 1919 he participated in the Polish-Soviet War when Wilno
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
was seized by Poland. From 1924 until 1926 he was commanding the 19th Infantry Division in Wilno, from 1928 until 1932 a commanding officer of the 25th Infantry Division in Kalisz
Kalisz () is a city in central Poland, and the second-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship, with 97,905 residents (December 2021). It is the capital city of the Kalisz Region. Situated on the Prosna river in the southeastern part of Gr ...
and from 1932 until 1939 a commanding officer of the Corps area (okreg korpusu) in Grodno
Grodno, or Hrodna, is a city in western Belarus. It is one of the oldest cities in Belarus. The city is located on the Neman, Neman River, from Minsk, about from the Belarus–Poland border, border with Poland, and from the Belarus–Lithua ...
, Lwów and Toruń
Toruń is a city on the Vistula River in north-central Poland and a World Heritage Sites of Poland, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Its population was 196,935 as of December 2021. Previously, it was the capital of the Toruń Voivodeship (1975–199 ...
.
World War II
 During the Polish Defensive War of 1939, he was commanding the Operation Group (grupa operacyjna) of the "
During the Polish Defensive War of 1939, he was commanding the Operation Group (grupa operacyjna) of the "Armia Pomorze
The Pomeranian Army () was one of the Polish armies defending against the 1939 Invasion of Poland. It was officially created on 23 March 1939. Led by General dywizji Władysław Bortnowski, it consisted of 5 infantry divisions, 2 National Defen ...
" (Pomeranian Army). He fought in the Battle of Bzura
The Battle of the Bzura (or the Battle of Kutno) was both the largest battle and Polish counter-attack of the German invasion of Poland and was fought from 9 to 19 September.''The Second World War: An Illustrated History '', Putnam, 1975, Goog ...
and was the second-in-command of " Armia Warszawa" (Army Warsaw) which was commanded by general Juliusz Rómmel
Juliusz Karol Wilhelm Józef Rómmel (; 3 June 1881 – 8 September 1967) was a Polish military commander, a general of the Polish Armed Forces.
He graduated from the Corps of Cadets in Pskov and later from Кonstantin Artillery School at St. Pe ...
, during the defence of Warsaw.
In occupied Poland, on 27 September 1939 he founded the resistance movement
A resistance movement is an organized group of people that tries to resist or try to overthrow a government or an occupying power, causing disruption and unrest in civil order and stability. Such a movement may seek to achieve its goals through ei ...
"Służba Zwycięstwu Polski
Service for Poland's Victory (; SZP), also translated as the Polish Victory Service, was the first Polish resistance movement in World War II. It was created by the order of general Juliusz Rómmel on 27 September 1939, when the siege of Warsaw, ...
" (Polish Victory Service)Norman Davies ''God's Playground VolumeII'' Clarendon, 1986 Page 464 and was its commander-in-chief until December 1939, when he became the commanding officer of the "3rd Lwów area ( ZWZ)"Jozef Garlinski ''Poland in the Second World War'', Page 50 under Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
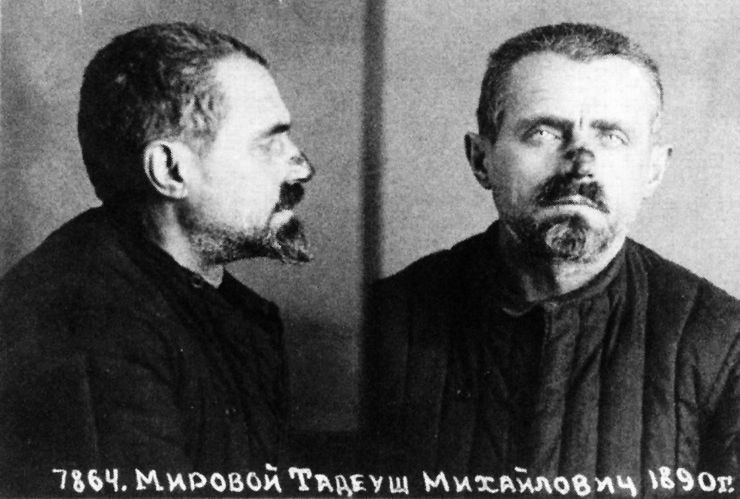
occupation. Crossing the new German–Soviet border, in March 1940 he was arrested and imprisoned by the NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (, ), abbreviated as NKVD (; ), was the interior ministry and secret police of the Soviet Union from 1934 to 1946. The agency was formed to succeed the Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU) se ...
.Jozef Garlinski ''Poland in the Second World War'', Page 51
After being released from prison, Tokarzewski was appointed a commanding officer of the "6th Infantry Division" of the Polish Army in the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(Anders Army
Anders' Army was the informal yet common name of the Polish Armed Forces in the East in the 1941–42 period, in recognition of its commander Władysław Anders. The army was created in the Soviet Union but, in March 1942, based on an understand ...
) in August 1941. From March 1943 until 1944 he served as the second-in-command of the Polish Army in the East. In 1944 he became a commander of the 3rd Polish Corps which was formed in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
.
After World War II
After the war he stayed in exile inEngland
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and settled in London. From 1954 on he was the General Inspector of the Armed Forces
General Inspector of the Armed Forces () was an office created in the Second Polish Republic in 1926, after the May Coup.
The General Inspector reported directly to the President, and was not responsible to the ''Sejm'' (parliament) or the gov ...
of the Polish forces in exile. He died on 22 May 1964 in Casablanca, Morocco
Casablanca (, ) is the largest city in Morocco and the country's economic and business centre. Located on the Atlantic coast of the Chaouia plain in the central-western part of Morocco, the city has a population of about 3.22 million in the urb ...
. In September 1992 the urn with his ashes was transferred from Brompton Cemetery
Brompton Cemetery (originally the West of London and Westminster Cemetery) is since 1852 the first (and only) London cemetery to be Crown Estate, Crown property, managed by The Royal Parks, in West Brompton in the Royal Borough of Kensington a ...
in London to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and buried at the Powązki Cemetery
Powązki Cemetery (; ), also known as Stare Powązki (), is a historic necropolis located in Wola district, in the western part of Warsaw, Poland. It is the most famous cemetery in the city and one of the oldest, having been established in 179 ...
in Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
.
In 2006, General Tokarzewski's medals and battledress came up for public auction. Two Canadians
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
, who were aware of the unfortunate history of Poland during World War II, were successful in their bid and brought the items to Canada. The two then donated the entire collection to "Poland and the Polish people" during a ceremony at the Polish Combatants' Association, Branch#20, in Toronto, Ontario
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a p ...
, Canada. The collection was displayed at the Branch #20 museum until March, 2007, when it was shipped to Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
to be displayed in the Warsaw Military Museum
A military museum or war museum is an institution dedicated to the preservation and education of the significance of wars, conflicts, and military actions. These museums serve as repositories of artifacts (not least weapons), documents, photographs ...
in that city.
Promotions
*Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a Junior officer, junior commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations, as well as fire services, emergency medical services, Security agency, security services ...
) – 29 September 1914
* Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader or highest rank officer of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police depa ...
) – 5 March 1915
* Colonel
Colonel ( ; abbreviated as Col., Col, or COL) is a senior military Officer (armed forces), officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries, a colon ...
) – 22 May 1920
* Lieutenant general
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was norma ...
) – 19 March 1964 (by the Polish authorities in exile)
Awards
* Order of the White Eagle (posthumously in 1964 by the Polish authorities in exile) *Virtuti Militari
The War Order of Virtuti Militari (Latin: ''"For Military Virtue"'', ) is Poland's highest military decoration for heroism and courage in the face of the enemy at war. It was established in 1792 by the last King of Poland Stanislaus II of Poland, ...
Order
* Order of Polonia Restituta
The Order of Polonia Restituta (, ) is a Polish state decoration, state Order (decoration), order established 4 February 1921. It is conferred on both military and civilians as well as on alien (law), foreigners for outstanding achievements in ...
* Order of Polonia Restituta
The Order of Polonia Restituta (, ) is a Polish state decoration, state Order (decoration), order established 4 February 1921. It is conferred on both military and civilians as well as on alien (law), foreigners for outstanding achievements in ...
* Cross of Independence
Cross of Independence () was the second highest Polish military decoration between World Wars I and II. It was awarded to individuals who had fought actively for the independence of Poland, and was released in three classes.
History
The Cr ...
, with Swords
* Cross of Valour, 4 times
* Cross of Merit with Swords
The Cross of Merit with Swords () is a Polish military award established October 19, 1942, by the Polish Government in Exile.
Criteria
The Cross of Merit with Swords is awarded for deeds of bravery and valor during time of war not connected with ...
, twice
* Golden Cross of Merit
*  Commemorative Medal for War 1918-1921
* Medal of the 10th Anniversary of Regained Independence
* Wound Decoration
*
Commemorative Medal for War 1918-1921
* Medal of the 10th Anniversary of Regained Independence
* Wound Decoration
* Order of the Crown of Romania
The Order of the Crown of Romania is a chivalric order set up on 14 March 1881 by King Carol I of Romania to commemorate the establishment of the Kingdom of Romania. It was awarded as a state order until the end of the Romanian monarchy in 1947. ...
(Romania)
* Grand Officer of Order of the Three Stars
Order of the Three Stars () is the highest civilian order awarded for meritorious service to Latvia. It was established in 1924 in remembrance of the founding of Latvia. Its motto is ''Per aspera ad astra'', meaning "Through hardships towards the ...
(Latvia)
* Medal of the 10th Anniversary of the War of Independence (Latvia)
* Order of the Bath
The Most Honourable Order of the Bath is a British order of chivalry founded by King George I of Great Britain, George I on 18 May 1725. Recipients of the Order are usually senior British Armed Forces, military officers or senior Civil Service ...
(United Kingdom)
* Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and Civil society, civil. Currently consisting of five cl ...
(France)
*  Victory Medal
Victory Medal

See also
*Armia Krajowa
The Home Army (, ; abbreviated AK) was the dominant resistance movement in German-occupied Poland during World War II. The Home Army was formed in February 1942 from the earlier Związek Walki Zbrojnej (Armed Resistance) established in the ...
* 2nd Polish Corps
The 2nd Polish Corps (), 1943–1947, was a major tactical and operational unit of the Polish Armed Forces in the West during World War II. It was commanded by Lieutenant General Władysław Anders and fought with distinction in the Italian Ca ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Karaszewicz-Tokarzewski, Michal 1893 births 1964 deaths Antisemitism in Poland Writers from Lviv Clergy from the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria Clan of Trąby Polish Socialist Party politicians Polish generals Polish Military Organisation members Polish Theosophists Polish legionnaires (World War I) Polish people of the Polish–Ukrainian War Polish people of the Polish–Soviet War People of the Polish May Coup (pro-Piłsudski side) Polish military personnel of World War II Polish resistance members of World War II Polish people detained by the NKVD Commanders of the Virtuti Militari Recipients of the Cross of Independence with Swords Commanders of the Order of Polonia Restituta Recipients of the Cross of Valour (Poland) Recipients of the Gold Cross of Merit (Poland) Burials at Brompton Cemetery Burials at Powązki Cemetery Polish emigrants to the United Kingdom Recipients of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland)