Meteorological Season on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A season is a division of the year based on changes in 
 Seasons often hold special significance for agrarian societies, whose lives revolve around
Seasons often hold special significance for agrarian societies, whose lives revolve around
 The Earth's orbit exhibits approximate
The Earth's orbit exhibits approximate
 The seasons result from the Earth's
The seasons result from the Earth's
File:Earth-lighting-summer-solstice EN - corrected.png, Illumination of Earth by Sun at the northern solstice.
File:Earth-lighting-winter-solstice EN.png, Illumination of Earth by Sun at the southern solstice.
File:Earth seasons 2021-2022.jpg, Illumination of Earth at each change of astronomical season
File:Earth seen from the sun.ogv, Animation of Earth as seen daily from the Sun looking at UTC+02:00, showing the solstice and changing seasons.
File:ReflectedSolarRadiation Solstices.jpg, Two images showing the amount of reflected sunlight at southern and northern summer solstices respectively (watts / m2).
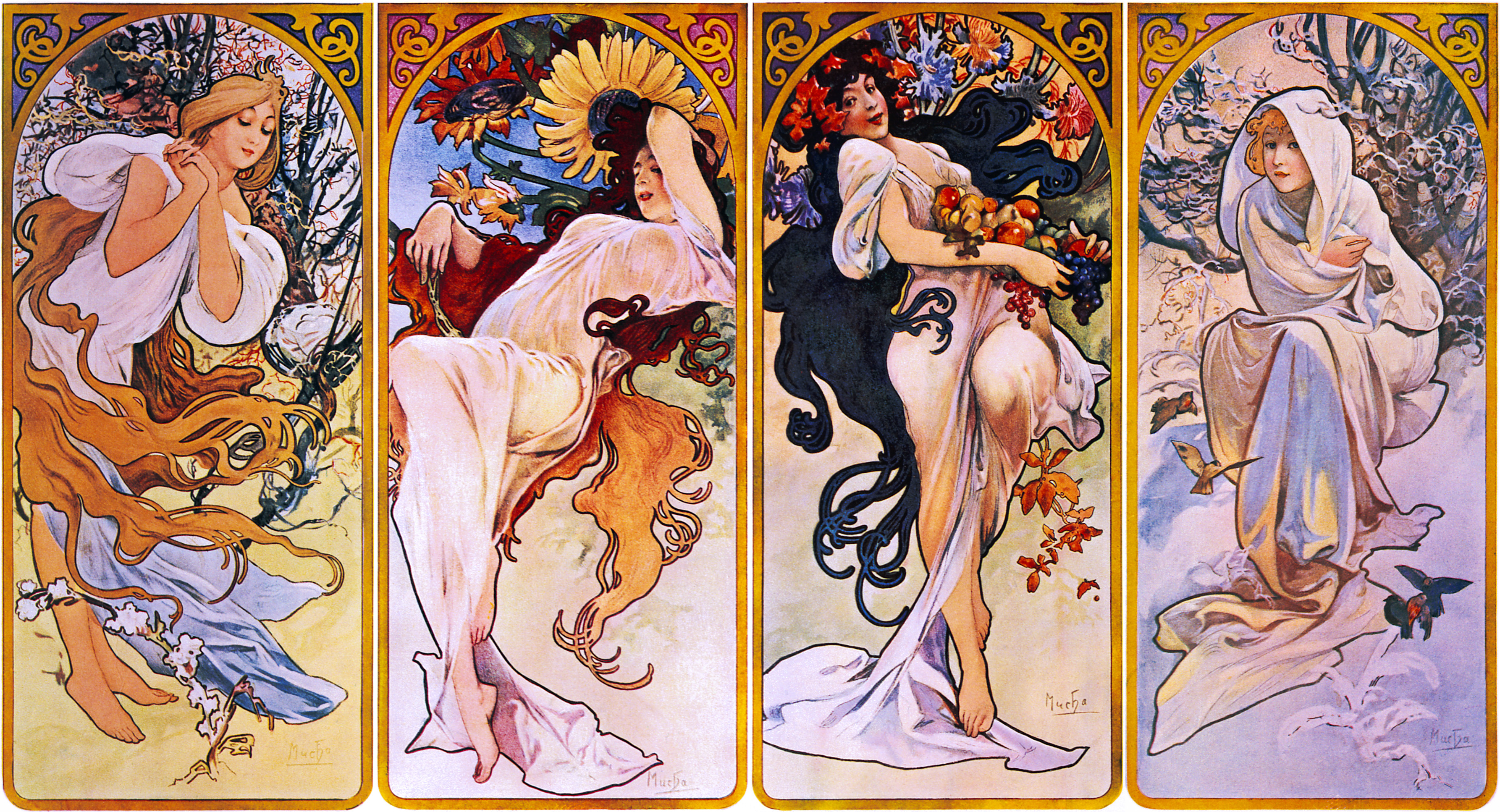 Most calendar-based partitions use a four-season model to demarcate the warmest and coldest seasons, which are further separated by two intermediate seasons. Calendar-based reckoning defines the seasons in relative rather than absolute terms, so the coldest quarter-year is considered winter even if floral activity is regularly observed during it, despite the traditional association of flowers with spring and summer. The major exception is in the tropics where, as already noted, the winter season is not observed.
The four seasons have been in use since at least Roman times, as in
Most calendar-based partitions use a four-season model to demarcate the warmest and coldest seasons, which are further separated by two intermediate seasons. Calendar-based reckoning defines the seasons in relative rather than absolute terms, so the coldest quarter-year is considered winter even if floral activity is regularly observed during it, despite the traditional association of flowers with spring and summer. The major exception is in the tropics where, as already noted, the winter season is not observed.
The four seasons have been in use since at least Roman times, as in
28
Varro says that spring, summer, autumn, and winter start on the 23rd day of the sun's passage through Aquarius, Taurus, Leo, and Scorpio, respectively. Nine years before he wrote,
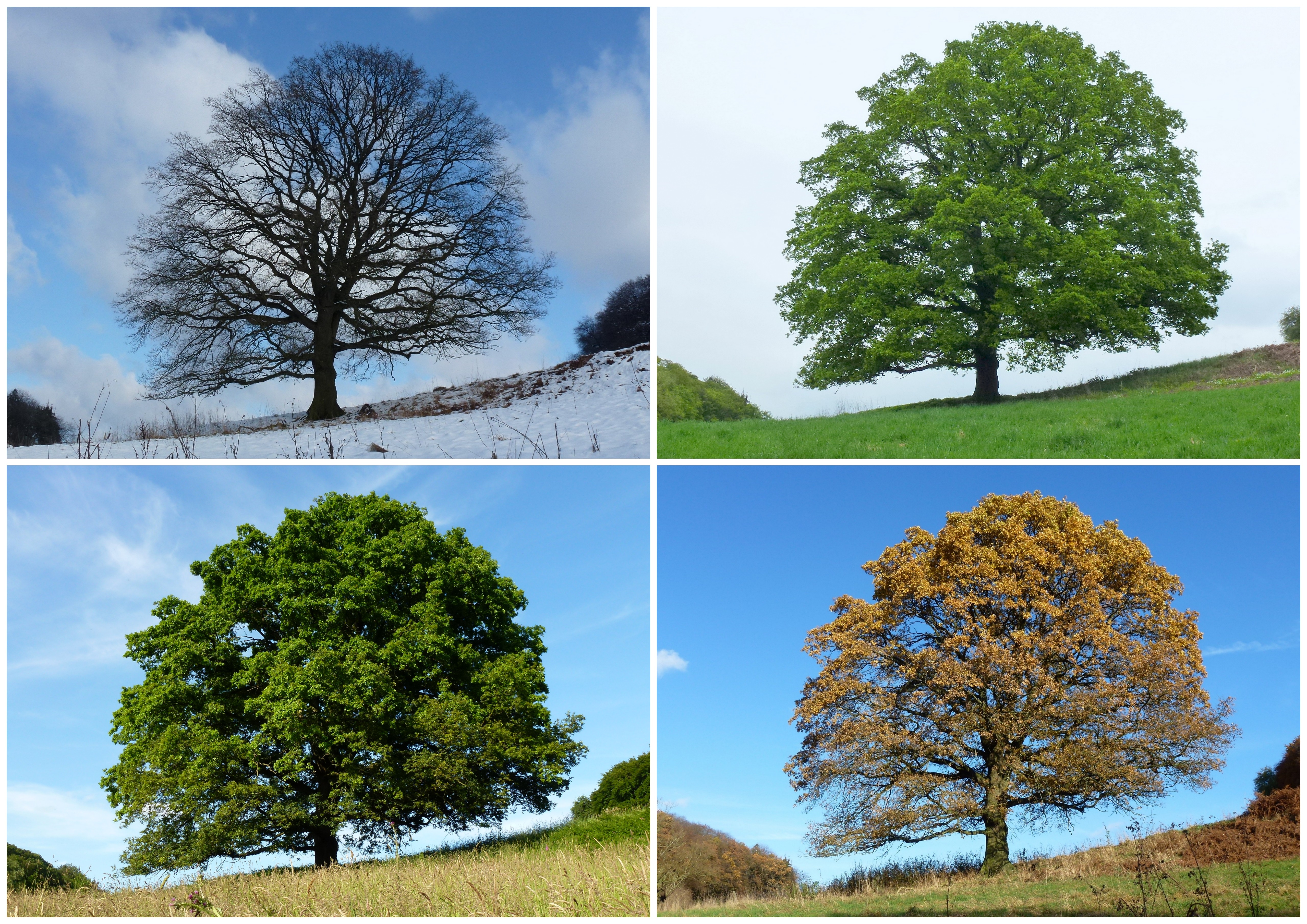 Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina (which became defunct in 1795), an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months as identified by the Gregorian calendar. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition.
Therefore, for temperate areas in the northern hemisphere, spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December. For the southern hemisphere temperate zone, spring begins on 1 September, summer on 1 December, autumn on 1 March, and winter on 1 June. In
Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina (which became defunct in 1795), an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months as identified by the Gregorian calendar. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition.
Therefore, for temperate areas in the northern hemisphere, spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December. For the southern hemisphere temperate zone, spring begins on 1 September, summer on 1 December, autumn on 1 March, and winter on 1 June. In
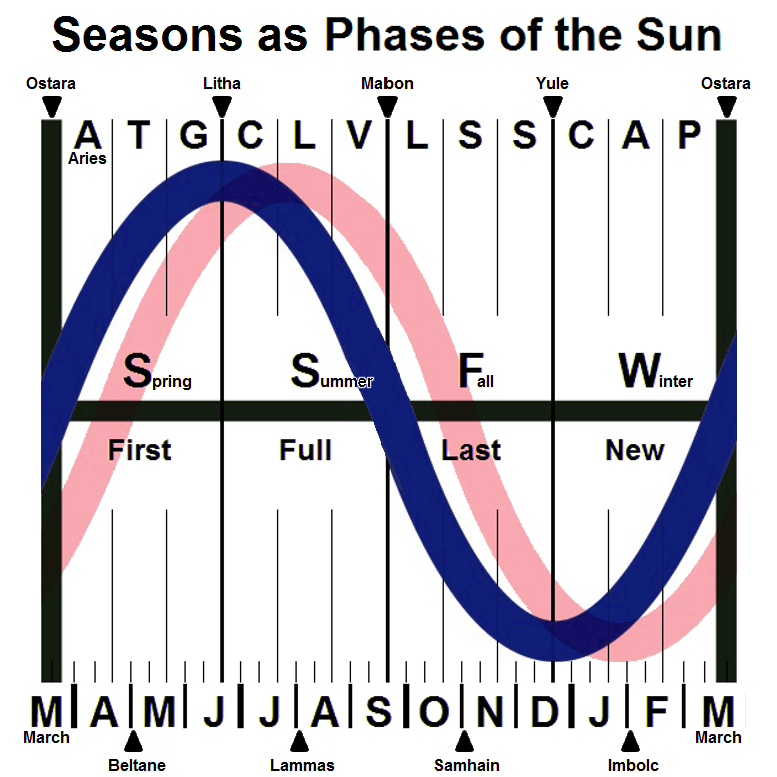 Solar timing is based on insolation in which the solstices and equinoxes are seen as the midpoints of the seasons. This was the case with the seasons described by the Roman scholar
Solar timing is based on insolation in which the solstices and equinoxes are seen as the midpoints of the seasons. This was the case with the seasons described by the Roman scholar
 Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral and animal events, the season is changing. In this sense, ecological seasons are defined in absolute terms, unlike calendar-based methods in which the seasons are relative. If specific conditions associated with a particular ecological season don't normally occur in a particular region, then that area cannot be said to experience that season on a regular basis.
In Great Britain, the onset of spring used to be defined as when the maximum daily temperature reached 50 °F (10 °C) in a defined sequence of days. This almost always occurred in March. However, with
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral and animal events, the season is changing. In this sense, ecological seasons are defined in absolute terms, unlike calendar-based methods in which the seasons are relative. If specific conditions associated with a particular ecological season don't normally occur in a particular region, then that area cannot be said to experience that season on a regular basis.
In Great Britain, the onset of spring used to be defined as when the maximum daily temperature reached 50 °F (10 °C) in a defined sequence of days. This almost always occurred in March. However, with

When do the Seasons Begin?
(from the Bad Astronomer)
Why the Earth has seasons
article on h2g2.
Aboriginal seasons of Kakadu
Indigenous seasons (Australian Bureau of Meteorology)
Mt Stirling Seasons
The Lost Seasons
Tutorial on Earth/Sun Relations and Seasons
Sunpreview Season Forecast Project
Satellite photo demonstrating seasons changes in 2004 on NASA website
{{Authority control Calendars Climate patterns Units of time Articles containing video clips
weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the ...
, ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
, and the number of daylight
Daylight is the combination of all direct and indirect sunlight during the daytime. This includes direct sunlight, diffuse sky radiation, and (often) both of these reflected by Earth and terrestrial objects, like landforms and buildings. Sunligh ...
hours in a given region. On Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism
Axial parallelism (also known as gyroscopic stiffness, inertia or rigidity, or "rigidity in space") is the characteristic of a spinning body in which the direction of the axis of rotation remains fixed as the object moves through space. In astrono ...
of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when t ...
that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most ...
or to migrate
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical cultures whose number of seasons varies.
The Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
experiences most direct sunlight during May, June, and July, as the hemisphere faces the Sun. The same is true of the Southern Hemisphere in November, December, and January. It is Earth's axial tilt that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the summer months, which increases the solar flux
Solar irradiance is the power (physics), power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per ...
. However, due to seasonal lag
Seasonal lag is the phenomenon whereby the date of maximum average air temperature at a geographical location on a planet is delayed until some time after the date of maximum insolation (i.e. the summer solstice). This also applies to the minimum ...
, June, July, and August are the warmest months in the Northern Hemisphere while December, January, and February are the warmest months in the Southern Hemisphere.
In temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
and sub-polar regions, four seasons based on the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years dif ...
are generally recognized: ''spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a ...
'', ''summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
'', ''autumn
Autumn, also known as fall in American English and Canadian English, is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September ( Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Sou ...
'' (or ''fall''), and ''winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures ...
''. Ecologists often use a six-season model for temperate climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
regions which are not tied to any fixed calendar dates: ''prevernal'', ''vernal'', ''estival'', ''serotinal'', ''autumnal'', and ''hibernal''. Many tropical regions have two seasons: the ''rainy
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water fo ...
'', '' wet'', or ''monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
season'' and the ''dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The te ...
''. Some have a third ''cool'', ''mild'', or ''harmattan
The Harmattan is a season in West Africa that occurs between the end of November and the middle of March. It is characterized by the dry and dusty northeasterly trade wind, of the same name, which blows from the Sahara over West Africa into the ...
season''. "Seasons" can also be dictated by the timing of important ecological events such as '' hurricane season'', ''tornado season
Tornadoes have been recorded on all continents except Antarctica. They are most common in the middle latitudes where conditions are often favorable for convective storm development. The United States has the most tornadoes of any country, as we ...
'', and ''wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire ...
season''. Some examples of historical importance are the ancient Egyptian seasons—''flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
'', ''growth
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
* Cell growth
* Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
* Human development (biology)
* Plant growth
* Secondary growth ...
'', and ''low water
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ca ...
''—which were previously defined by the former annual flooding of the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
.
 Seasons often hold special significance for agrarian societies, whose lives revolve around
Seasons often hold special significance for agrarian societies, whose lives revolve around planting
Sowing is the process of planting seeds. An area or object that has had seeds planted in it will be described as a sowed or sown area.
Plants which are usually sown
Among the major field crops, oats, wheat, and rye are sown, grasses and leg ...
and harvest
Harvesting is the process of gathering a ripe crop from the fields. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most labor-i ...
times, and the change of seasons is often attended by ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized, b ...
. The definition of seasons is also cultural. In India, from ancient times to the present day, six seasons or Ritu based on south Asian religious or cultural calendars are recognised and identified for purposes such as agriculture and trade.
Causes and effects
Axial parallelism
 The Earth's orbit exhibits approximate
The Earth's orbit exhibits approximate axial parallelism
Axial parallelism (also known as gyroscopic stiffness, inertia or rigidity, or "rigidity in space") is the characteristic of a spinning body in which the direction of the axis of rotation remains fixed as the object moves through space. In astrono ...
, maintaining its direction towards Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris ( Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an apparent magnitude that ...
(the "North Star") year-round. This is one of the primary reasons for the Earth's seasons, as illustrated by the diagram to the right. Minor variation in the direction of the axis, known as axial precession, takes place over the course of 26,000 years, and therefore is not noticeable to modern human civilization.
Axial tilt
axis of rotation
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rota ...
being tilted with respect to its orbital plane by an angle of approximately 23.4 degrees. (This tilt is also known as "obliquity of the ecliptic".)
Regardless of the time of year, the northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ra ...
and southern hemispheres always experience opposite seasons. This is because during summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
or winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures ...
, one part of the planet is more directly exposed to the rays of the Sun than the other, and this exposure alternates as the Earth revolves in its orbit. For approximately half of the year (from around March20 to around September22), the Northern Hemisphere tips toward the Sun, with the maximum amount occurring on about June21. For the other half of the year, the same happens, but in the Southern Hemisphere instead of the Northern, with the maximum around December21. The two instants when the Sun is directly overhead at the Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
are the equinoxes. Also at that moment, both the North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Mag ...
and the South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ...
of the Earth are just on the terminator, and hence day and night are equally divided between the two hemispheres. Around the March equinox
The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the verna ...
, the Northern Hemisphere will be experiencing spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a ...
as the hours of daylight
Daylight is the combination of all direct and indirect sunlight during the daytime. This includes direct sunlight, diffuse sky radiation, and (often) both of these reflected by Earth and terrestrial objects, like landforms and buildings. Sunligh ...
increase, and the Southern Hemisphere is experiencing autumn
Autumn, also known as fall in American English and Canadian English, is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September ( Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Sou ...
as daylight hours shorten.
The effect of axial tilt is observable as the change in day length and altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
of the Sun at solar noon (the Sun's culmination
In observational astronomy, culmination is the passage of a celestial object (such as the Sun, the Moon, a planet, a star, constellation or a deep-sky object) across the observer's local meridian. These events were also known as meridian transits ...
) during the year
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hou ...
. The low angle of Sun during the winter months means that incoming rays of solar radiation are spread over a larger area of the Earth's surface, so the light received is more indirect and of lower intensity. Between this effect and the shorter daylight hours, the axial tilt of the Earth accounts for most of the seasonal variation in climate in both hemispheres.
Elliptical Earth orbit
Compared to axial parallelism and axial tilt, other factors contribute little to seasonal temperature changes. The seasons are not the result of the variation in Earth's distance to the Sun because of its elliptical orbit. In fact, Earth reaches perihelion (the point in its orbit closest to the Sun) in January, and it reaches aphelion (the point farthest from the Sun) in July, so the slight contribution oforbital eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values betwee ...
opposes the temperature trends of the seasons in the Northern Hemisphere. In general, the effect of orbital eccentricity on Earth's seasons is a 7% variation in sunlight received.
Orbital eccentricity can influence temperatures, but on Earth, this effect is small and is more than counteracted by other factors; research shows that the Earth as a whole is actually slightly warmer when ''farther'' from the sun. This is because the Northern Hemisphere has more land than the Southern, and land warms more readily than sea.
Any noticeable intensification of southern winters and summers due to Earth's elliptical orbit is mitigated by the abundance of water in the Southern Hemisphere.
Maritime and hemispheric
Seasonal weather fluctuations (changes) also depend on factors such as proximity toocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
s or other large bodies of water, currents in those oceans, El Niño/ENSO and other oceanic cycles, and prevailing wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
s.
In the temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
and polar regions, seasons are marked by changes in the amount of sunlight
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when t ...
, which in turn often causes cycles of dormancy in plants and hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It most ...
in animals. These effects vary with latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and with proximity to bodies of water. For example, the South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ...
is in the middle of the continent of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
and therefore a considerable distance from the moderating influence of the southern oceans. The North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Mag ...
is in the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
, and thus its temperature extremes are buffered by the water. The result is that the South Pole is consistently colder during the southern winter than the North Pole during the northern winter.
The seasonal cycle in the polar and temperate zones of one hemisphere is opposite to that of the other. When it is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it is winter in the Southern, and vice versa.
Tropics
Thetropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
and subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical z ...
regions see little annual fluctuation of sunlight. However, seasonal shifts occur along a rainy, low-pressure belt called the Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
(ICZ). As a result, the amount of precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
tends to vary more dramatically than the average temperature. When the Zone is north of the Equator, the northern tropics experience their wet season while the southern tropics have their dry season. This pattern reverses when the Zone migrates to a position south of the Equator.
Mid-latitude thermal lag
In meteorological terms, thesolstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countr ...
s (the maximum and minimum insolation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m ...
) do not fall in the middles of summer and winter. The heights of these seasons occur up to 7 weeks later because of seasonal lag
Seasonal lag is the phenomenon whereby the date of maximum average air temperature at a geographical location on a planet is delayed until some time after the date of maximum insolation (i.e. the summer solstice). This also applies to the minimum ...
. Seasons, though, are not always defined in meteorological terms.
In astronomical reckoning by hours of daylight
Daylight is the combination of all direct and indirect sunlight during the daytime. This includes direct sunlight, diffuse sky radiation, and (often) both of these reflected by Earth and terrestrial objects, like landforms and buildings. Sunligh ...
alone, the solstices and equinoxes are in the ''middle'' of the respective seasons. Because of seasonal lag due to thermal absorption
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
and release by the oceans, regions with a continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
, which predominate in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
, often consider these four dates to be the ''start'' of the seasons as in the diagram, with the cross-quarter day
The Wheel of the Year is an annual cycle of seasonal festivals, observed by many modern pagans, consisting of the year's chief solar events (solstices and equinoxes) and the midpoints between them. While names for each festival vary among dive ...
s considered seasonal midpoints. The length of these seasons is not uniform because of Earth's elliptical orbit and its different speeds along that orbit.
Four-season reckoning
 Most calendar-based partitions use a four-season model to demarcate the warmest and coldest seasons, which are further separated by two intermediate seasons. Calendar-based reckoning defines the seasons in relative rather than absolute terms, so the coldest quarter-year is considered winter even if floral activity is regularly observed during it, despite the traditional association of flowers with spring and summer. The major exception is in the tropics where, as already noted, the winter season is not observed.
The four seasons have been in use since at least Roman times, as in
Most calendar-based partitions use a four-season model to demarcate the warmest and coldest seasons, which are further separated by two intermediate seasons. Calendar-based reckoning defines the seasons in relative rather than absolute terms, so the coldest quarter-year is considered winter even if floral activity is regularly observed during it, despite the traditional association of flowers with spring and summer. The major exception is in the tropics where, as already noted, the winter season is not observed.
The four seasons have been in use since at least Roman times, as in Rerum rusticarum Rerum may refer to :
*Lacrimae rerum is the Latin for tears for things.
*Rerum novarum is an encyclical issued by Pope Leo XIII on May 16, 1891.
*Rerum Moscoviticarum Commentarii was a Latin book by Baron Sigismund von Herberstein on the geography ...
of Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes calle ...
De Re Rustica28
Varro says that spring, summer, autumn, and winter start on the 23rd day of the sun's passage through Aquarius, Taurus, Leo, and Scorpio, respectively. Nine years before he wrote,
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
had reformed the calendar, so Varro was able to assign the dates of February 7, May 9, August 11, and November 10 to the start of spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
Official
As noted, a variety of dates and even exact times are used in different countries or regions to mark changes of the calendar seasons. These observances are often declared "official" within their respective areas by the local or national media, even when the weather or climate is contradictory. However, they are mainly a matter of custom only, and have not generally been proclaimed by governments north or south of the equator for civil purposes.Meteorological
 Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina (which became defunct in 1795), an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months as identified by the Gregorian calendar. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition.
Therefore, for temperate areas in the northern hemisphere, spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December. For the southern hemisphere temperate zone, spring begins on 1 September, summer on 1 December, autumn on 1 March, and winter on 1 June. In
Meteorological seasons are reckoned by temperature, with summer being the hottest quarter of the year and winter the coldest quarter of the year. In 1780 the Societas Meteorologica Palatina (which became defunct in 1795), an early international organization for meteorology, defined seasons as groupings of three whole months as identified by the Gregorian calendar. Ever since, professional meteorologists all over the world have used this definition.
Therefore, for temperate areas in the northern hemisphere, spring begins on 1 March, summer on 1 June, autumn on 1 September, and winter on 1 December. For the southern hemisphere temperate zone, spring begins on 1 September, summer on 1 December, autumn on 1 March, and winter on 1 June. In Australasia
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologica ...
the meteorological terms for seasons apply to the temperate zone that occupies all of New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, Victoria, Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
, the south-eastern corner of South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
and the south-west of Western Australia, and the south east Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
areas south of Brisbane
Brisbane ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the states and territories of Australia, Australian state of Queensland, and the list of cities in Australia by population, third-most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a populati ...
.
In Sweden and Finland, meteorologists and news outlets use the concept of thermal season
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
s, which are defined based on mean daily temperatures. The beginning of spring is defined as when the mean daily temperature permanently rises above 0 °C. The beginning of summer is defined as when the temperature permanently rises above +10 °C, autumn as when the temperature permanently falls below +10 °C, and winter as when the temperature permanently falls below 0 °C. In Finland, "permanently" is defined as when the mean daily averaged temperature remains above or below the defined limit for seven consecutive days. (In Sweden the number of days ranges from 5 to 7 depending on the season.) This implies two things:
* the seasons do not begin on fixed dates and must be determined by observation and are known only after the fact,
* the seasons begin on different dates in different parts of the country.
The India Meteorological Department
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India. It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology. IMD is headquarter ...
(IMD) designates four climatological seasons:
* Winter, occurring from December to February. The year's coldest months are December and January, when temperatures average around in the northwest; temperatures rise as one proceeds towards the equator, peaking around in mainland India's southeast.
* Summer or pre-monsoon season, lasting from March to May. In western and southern regions, the hottest month is April; for northern regions of India, May is the hottest month. Temperatures average around in most of the interior.
* Monsoon or rainy season, lasting from June to September. The season is dominated by the humid southwest summer monsoon, which slowly sweeps across the country beginning in late May or early June. Monsoon rains begin to recede from North India at the beginning of October. South India typically receives more rainfall.
* Post-monsoon or autumn season, lasting from October to November. In the northwest of India, October and November are usually cloudless. Tamil Nadu receives most of its annual precipitation in the northeast monsoon season.
Astronomical
Astronomical timing as the basis for designating the temperate seasons dates back at least to theJulian Calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
used by the ancient Romans. As mentioned above, Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes calle ...
wrote that spring, summer, autumn, and winter start on the 23rd day of the sun's passage through Aquarius, Taurus, Leo, and Scorpio, respectively, and that (in the Julian Calendar) these days were February 7, May 9, August 11, and November 10. He points out that the lengths are not equal, being 91 (in non-leap years), 94, 91, and 89 days for spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively. The midpoints of these seasons were March 24 or 25, June 25, September 25 or 26, and December 24 or 25, which are near to the equinoxes and solstices of his day.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
, in his '' Natural History'', mentions the two equinoxes and the two solstices and gives the lengths of the intervals (values which were fairly correct in his day but are no longer very correct because the perihelion has moved from December into January). He then defines the seasons of autumn, winter, spring, and summer as starting half-way through these intervals. He gives "the eighth day to the Kalends of January" (December 25) as the date of the winter solstice, though actually it occurred on the 22nd or 23rd at that time.
Nowadays the astronomical timing has winter starting at the winter solstice, spring at the spring equinox, and so on. This is used worldwide, although some countries like Australia, New Zealand, Pakistan and Russia prefer to use meteorological reckoning. The precise timing of the seasons is determined by the exact times of the sun reaching the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn for the solstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countr ...
s and the times of the sun's transit over the equator for the equinoxes, or a traditional date close to these times.
The following diagram shows the relation between the line of solstice and the line of apsides
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any ellip ...
of Earth's elliptical orbit. The orbital ellipse (with eccentricity exaggerated for effect) goes through each of the six Earth images, which are sequentially the perihelion (periapsis—nearest point to the sun) on anywhere from 2 January to 5 January, the point of March equinox on 19, 20 or 21 March, the point of June solstice on 20 or 21 June, the aphelion (apoapsis—farthest point from the sun) on anywhere from 3 July to 6 July, the September equinox on 22 or 23 September, and the December solstice on 21 or 22 December.
These "astronomical" seasons are not of equal length, because of the elliptical nature of the orbit of the Earth, as discovered by Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
. From the March equinox it currently takes 92.75 days until the June solstice, then 93.65 days until the September equinox, 89.85 days until the December solstice and finally 88.99 days until the March equinox. Thus the time from the March equinox to the September equinox is 7.56 days longer than from the September equinox to the March equinox.
Variation due to calendar misalignment
The times of the equinoxes and solstices are not fixed with respect to the modern Gregorian calendar, but fall about six hours later every year, amounting to one full day in four years. They are reset by the occurrence of a leap year. The Gregorian calendar is designed to keep the March equinox no later than 21 March as accurately as is practical. ''Also see: Gregorian calendar seasonal error.'' The calendar equinox (used in the calculation of Easter) is 21 March, the same date as in the Easter tables current at the time of the Council of Nicaea in AD 325. The calendar is therefore framed to prevent the astronomical equinox wandering onto 22 March. From Nicaea to the date of the reform, the years 500, 600, 700, 900, 1000, 1100, 1300, 1400, and 1500, which would not have been leap years in the Gregorian calendar, amount to nine extra days, but astronomers directed that ten days be removed. Because of this, the (proleptic
Proleptic may refer to:
* Prolepsis
Prolepsis may refer to:
* Prolepsis (rhetoric), a figure of speech in which the speaker raises an objection and then immediately answers it
*Prolepsis (literary), anticipating action, a flash forward, see For ...
) Gregorian calendar agrees with the Julian calendar in the third century
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 ( CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar..
In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander i ...
of the Christian era
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used to label or number years in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means 'in the year of the Lord', but is often presented using "our Lord" instead of "the Lord", ...
, rather than in the fourth.
Currently, the most common equinox and solstice dates are March 20, June 21, September 22 or 23, and December 21; the four-year average slowly shifts to earlier times as a century progresses. This shift is a full day in about 128 years (compensated mainly by the century "leap year" rules of the Gregorian calendar); as 2000 was a leap year, the current shift has been progressing since the beginning of the last century, when equinoxes and solstices were relatively late. This also means that in many years of the twentieth century, the dates March 21, June 22, September 23, and December 22 were much more common, so older books teach (and older people may still remember) these dates.
Note that all the times are given in UTC (roughly speaking, the time at Greenwich, ignoring British Summer Time
During British Summer Time (BST), civil time in the United Kingdom is advanced one hour forward of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), in effect changing the time zone from UTC±00:00 to UTC+01:00, so that mornings have one hour less daylight, and ev ...
). People living farther to the east (Asia and Australia), whose local times are in advance, see the astronomical seasons apparently start later; for example, in Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
(UTC+13), an equinox occurred on September 24, 1999, a date on which the equinox will not fall again until 2103. On the other hand, people living far to the west (America), whose clocks run behind UTC, may experience an equinox as early as March 19.
Change over time
Over thousands of years, the Earth'saxial tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbi ...
and orbital eccentricity vary (see Milankovitch cycles). The equinoxes and solstices move westward relative to the stars while the perihelion and aphelion move eastward. Thus, ten thousand years from now Earth's northern winter will occur at aphelion and northern summer at perihelion. The severity of seasonal change — the average temperature difference between summer and winter in location — will also change over time because the Earth's axial tilt fluctuates between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees.
Smaller irregularities in the times are caused by perturbations of the Moon and the other planets.
Solar
 Solar timing is based on insolation in which the solstices and equinoxes are seen as the midpoints of the seasons. This was the case with the seasons described by the Roman scholar
Solar timing is based on insolation in which the solstices and equinoxes are seen as the midpoints of the seasons. This was the case with the seasons described by the Roman scholar Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes calle ...
(see above). It was the method for reckoning seasons in medieval Europe, especially by the Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
, and is still ceremonially observed in Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
and some East Asian countries. Summer is defined as the quarter of the year with the greatest insolation and winter as the quarter with the least.
The solar seasons change at the cross-quarter days, which are about 3–4 weeks earlier than the meteorological seasons and 6–7 weeks earlier than seasons starting at equinoxes and solstices. Thus, the day of greatest insolation is designated "midsummer" as noted in William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
's play ''A Midsummer Night's Dream
''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' is a comedy written by William Shakespeare 1595 or 1596. The play is set in Athens, and consists of several subplots that revolve around the marriage of Theseus and Hippolyta. One subplot involves a conflict amon ...
'', which is set on the summer solstice. On the Celtic calendar, the start of the seasons corresponds to four Pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
agricultural festivals - the traditional first day of winter is 1 November ( Samhain, the Celtic origin of Halloween
Halloween or Hallowe'en (less commonly known as Allhalloween, All Hallows' Eve, or All Saints' Eve) is a celebration observed in many countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christian feast of All Saints' Day. It begins the observanc ...
); spring starts 1 February ( Imbolc, the Celtic origin of Groundhog Day
Groundhog Day ( pdc, Grund'sau dåk, , , ; Nova Scotia: Daks Day) is a popular North American tradition observed in the United States and Canada on February 2. It derives from the Pennsylvania Dutch superstition that if a groundhog emerges from ...
); summer begins 1 May ( Beltane, the Celtic origin of May Day); the first day of autumn is 1 August (Celtic Lughnasadh).
Solar terms
The traditional calendar in China has 4 seasons based on 24 periods known as solar terms. The four seasons ''chūn'' (), ''xià'' (), ''qiū'' (), and ''dōng'' ()—universally translated as "spring", "summer", "autumn", and "winter"—each center around the respective solstice or equinox. Astronomically, the seasons are said to begin on Lichun (, "the start of spring") on about 4 February, Lixia () on about 6 May, Liqiu () on about 8 August, and Lidong () on about 7 November. These dates were not part of the traditional lunar calendar, however, and moveable holidays such asChinese New Year
Chinese New Year is the festival that celebrates the beginning of a New Year, new year on the traditional lunisolar calendar, lunisolar and solar Chinese calendar. In Sinophone, Chinese and other East Asian cultures, the festival is commonly r ...
and the Mid-Autumn Festival
The Mid-Autumn Festival (Chinese: / ), also known as the Moon Festival or Mooncake Festival, is a traditional festival celebrated in Chinese culture. Similar holidays are celebrated in Japan (), Korea (), Vietnam (), and other countries in Eas ...
are more closely associated with the seasons. It forms the basis of other such systems in East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and ...
n lunisolar calendar
A lunisolar calendar is a calendar in many cultures, combining lunar calendars and solar calendars. The date of Lunisolar calendars therefore indicates both the Moon phase and the time of the solar year, that is the position of the Sun in the Ea ...
s.
Six-season reckoning
Some calendars in south Asia use a six-season partition where the number of seasons between summer and winter can number from one to three. The dates are fixed at even intervals of months. In theHindu calendar
The Hindu calendar, Panchanga () or Panjika is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a s ...
of tropical and subtropical India, there are six seasons or Ritu that are calendar-based in the sense of having fixed dates: Vasanta (spring), Greeshma (summer), Varsha (monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
), Sharad (autumn), Hemanta (early winter), and Shishira (prevernal or late winter). The six seasons are ascribed to two months each of the twelve months in the Hindu calendar. The rough correspondences are:
The Bengali Calendar is similar but differs in start and end times. It has the following seasons or ritu:
The Odia Calendar is similar but differs in start and end times.
The Tamil calendar follows a similar pattern of six seasons
Non-calendar-based reckoning
 Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral and animal events, the season is changing. In this sense, ecological seasons are defined in absolute terms, unlike calendar-based methods in which the seasons are relative. If specific conditions associated with a particular ecological season don't normally occur in a particular region, then that area cannot be said to experience that season on a regular basis.
In Great Britain, the onset of spring used to be defined as when the maximum daily temperature reached 50 °F (10 °C) in a defined sequence of days. This almost always occurred in March. However, with
Ecologically speaking, a season is a period of the year in which only certain types of floral and animal events happen (e.g.: flowers bloom—spring; hedgehogs hibernate—winter). So, if we can observe a change in daily floral and animal events, the season is changing. In this sense, ecological seasons are defined in absolute terms, unlike calendar-based methods in which the seasons are relative. If specific conditions associated with a particular ecological season don't normally occur in a particular region, then that area cannot be said to experience that season on a regular basis.
In Great Britain, the onset of spring used to be defined as when the maximum daily temperature reached 50 °F (10 °C) in a defined sequence of days. This almost always occurred in March. However, with global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
this temperature is now not uncommon in the winter.
Modern mid-latitude ecological
Six ecological seasons can be distinguished without fixed calendar-based dates like the meteorological and astronomical seasons.Oceanic
Oceanic may refer to:
*Of or relating to the ocean
*Of or relating to Oceania
**Oceanic climate
**Oceanic languages
**Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)"
Places
* Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, ...
regions tend to experience the beginning of the hibernal season up to a month later than continental climates. Conversely, prevernal and vernal seasons begin up to a month earlier near oceanic and coastal areas. For example, prevernal crocus
''Crocus'' (; plural: crocuses or croci) is a genus of seasonal flowering plants in the family Iridaceae (iris family) comprising about 100 species of perennials growing from corms. They are low growing plants, whose flower stems remain undergro ...
blooms typically appear as early as February in coastal areas of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
, but generally don't appear until March or April in locations like the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
USA or parts of eastern Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. The actual dates for each season vary by climate region and can shift from one year to the next. Average dates listed here are for mild and cool temperate climate zones in the Northern Hemisphere:
* Prevernal (early or pre-spring): Begins February (mild temperate), to March (cool temperate). Deciduous tree buds begin to swell. Some types of migrating birds fly from winter to summer habitats.
* Vernal (spring): Begins mid March (mild temperate), to late April (cool temperate). Tree buds burst into leaves. Birds establish territories and begin mating and nesting.
* Estival (high summer): Begins June in most temperate climates. Trees in full leaf. Birds hatch and raise offspring.
* Serotinal (late summer): Generally begins mid to late August. Deciduous leaves begin to change color in higher latitude locations (above 45 north). Young birds reach maturity and join other adult birds preparing for autumn migration. The traditional "harvest season" begins by early September.
* Autumnal (autumn): Generally begins mid to late September. Tree leaves in full color then turn brown and fall to the ground. Birds migrate back to wintering areas.
* Hibernal (winter): Begins December (mild temperate), November (cool temperate). Deciduous trees are bare and fallen leaves begin to decay. Migrating birds settled in winter habitats.
Indigenous ecological
Indigenous people in polar, temperate and tropical climates of northern Eurasia, the Americas, Africa, Oceania, and Australia have traditionally defined the seasons ecologically by observing the activity of the plants, animals and weather around them. Each separate tribal group traditionally observes different seasons determined according to local criteria that can vary from the hibernation of polar bears on the arctic tundras to thegrowing season
A season is a division of the year marked by changes in weather, ecology, and the amount of daylight. The growing season is that portion of the year in which local conditions (i.e. rainfall, temperature, daylight) permit normal plant growth. Whil ...
s of plants in the tropical rainforests. In Australia, some tribes have up to eight seasons in a year, as do the Sami people in Scandinavia. Many indigenous people who no longer live directly off the land in traditional often nomadic styles, now observe modern methods of seasonal reckoning according to what is customary in their particular country or region.
The North American Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada ...
and possibly other Algonquian speaking peoples used or still use a 6-season system. The extra two seasons denoting the freezing and breaking up of the ice on rivers and lakes.
The Noongar
The Noongar (, also spelt Noongah, Nyungar , Nyoongar, Nyoongah, Nyungah, Nyugah, and Yunga ) are Aboriginal Australian peoples who live in the south-west corner of Western Australia, from Geraldton on the west coast to Esperance on the so ...
people of South-West Western Australia recognise maar-keyen bonar, or six seasons. Each season's arrival is heralded not by a calendar date, but by environmental factors such as changing winds, flowering plants, temperature and migration patterns and lasts approximately two standard calendar months. The seasons also correlate to aspects of the human condition, intrinsically linking the lives of the people to the world that surrounds them and also dictating their movements, as with each season, various parts of country would be visited which were particularly abundant or safe from the elements.
Tropical

Two seasons
In the tropics, where seasonal dates also vary, it is more common to speak of therainy
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water fo ...
(or wet, or monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
) season versus the dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The te ...
. For example, in Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the cou ...
the dry season (November to April) is called "summer" and the rainy season (May to October) is called "winter", even though it is located in the northern hemisphere. There is no noticeable change in the amount of sunlight at different times of the year. However, many regions (such as the northern Indian ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
) are subject to monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
and wind cycles.
Floral and animal activity variation near the equator depends more on wet/dry cycles than seasonal temperature variations, with different species flowering (or emerging from cocoons) at specific times before, during, or after the monsoon season. Thus, the tropics are characterized by numerous "mini-seasons" within the larger seasonal blocks of time.
In the tropical parts of Australia in the northern parts of Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
, Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
, and the Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an states and territories of Australia, Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory ...
, wet and dry seasons are observed in addition to or in place of temperate season names.
Three seasons
The most historically important of these are the three seasons—''flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
'', ''growth
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
* Cell growth
* Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
* Human development (biology)
* Plant growth
* Secondary growth ...
'', and ''low water
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ca ...
''—which were previously defined by the former annual flooding of the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin language, Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
. In some tropical areas a three-way division into hot, rainy, and cool season is used. In Thailand three seasons are recognised
Polar
Any point north of theArctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at w ...
or south of the Antarctic Circle
The Antarctic Circle is the most southerly of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of Earth. The region south of this circle is known as the Antarctic, and the zone immediately to the north is called the Southern Temperate Zone. S ...
will have one period in the summer called "polar day" when the sun does not set, and one period in the winter called 'polar night' when the sun does not rise. At progressively higher latitudes, the maximum periods of "midnight sun
The midnight sun is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when the Sun remains visible at the local midnight. When the midnight sun is seen in the Arctic, t ...
" and " polar night" are progressively longer.
For example, at the military and weather station Alert located at 82°30′05″N and 62°20′20″W, on the northern tip of Ellesmere Island
Ellesmere Island ( iu, script=Latn, Umingmak Nuna, lit=land of muskoxen; french: île d'Ellesmere) is Canada's northernmost and List of Canadian islands by area, third largest island, and the List of islands by area, tenth largest in the world. ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
(about 450 nautical mile
A nautical mile is a unit of length used in air, marine, and space navigation, and for the definition of territorial waters. Historically, it was defined as the meridian arc length corresponding to one minute ( of a degree) of latitude. Today ...
s or 830 km from the North Pole), the sun begins to peek above the horizon for minutes per day at the end of February and each day it climbs higher and stays up longer; by 21 March, the sun is up for over 12 hours. On 6 April the sun rises at 0522 UTC and remains above the horizon until it sets below the horizon again on 6 September at 0335 UTC. By October 13 the sun is above the horizon for only 1 hour 30 minutes, and on October 14 it does not rise above the horizon at all and remains below the horizon until it rises again on 27 February.
First light comes in late January because the sky has twilight
Twilight is light produced by sunlight scattering in the upper atmosphere, when the Sun is below the horizon, which illuminates the lower atmosphere and the Earth's surface. The word twilight can also refer to the periods of time when this il ...
, being a glow on the horizon, for increasing hours each day, for more than a month before the sun first appears with its disc above the horizon. From mid-November to mid-January, there is no twilight.
In the weeks surrounding 21 June, in the northern polar region, the sun is at its highest elevation, appearing to circle the sky there without going below the horizon. Eventually, it does go below the horizon, for progressively longer periods each day until around the middle of October, when it disappears for the last time until the following February. For a few more weeks, "day" is marked by decreasing periods of twilight. Eventually, from mid-November to mid-January, there is no twilight and it is continuously dark. In mid January the first faint wash of twilight briefly touches the horizon (for just minutes per day), and then twilight increases in duration with increasing brightness each day until sunrise at end of February, then on 6 April the sun remains above the horizon until mid October.
Military campaigning seasons
Seasonal weather and climate conditions can become important in the context of military operations. Seasonal reckoning in the military of any country or region tends to be very fluid and based mainly on short to medium term weather conditions that are independent of the calendar. For navies, the presence of accessible ports and bases can allow naval operations during certain (variable) seasons of the year. The availability of ice-free or warm-water ports can make navies much more effective. ThusRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, historically navally constrained when confined to using Arkhangelsk (before the 18th century) and even Kronstadt, has particular interests in maintaining and in preserving access to Baltiysk, Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
, and Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
.
Storm seasons or polar winter-weather conditions can inhibit surface warships at sea.
Pre-modern armies, especially in Europe, tended to campaign in the summer months - peasant conscripts tended to melt away at harvest time
Harvesting is the process of gathering a ripe crop from the field (agriculture), fields. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse (legume), pulse for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechaniz ...
, nor did it make economic sense in an agricultural society to neglect the sowing
Sowing is the process of planting seeds. An area or object that has had seeds planted in it will be described as a sowed or sown area.
Plants which are usually sown
Among the major field crops, oats, wheat, and rye are sown, grasses and leg ...
season.
Any modern war of manoeuvre profits from firm ground - summer can provide dry conditions suitable for marching and transport, frozen snow in winter can also offer a reliable surface for a period, but spring thaws or autumn rains can inhibit campaigning. Rainy-season floods may make rivers temporarily impassable, and winter snow tends to block mountain passes. Taliban offensives are usually confined to the Afghanistan fighting season
The Afghanistan fighting season refers to the cyclical restarting of fighting every spring during the War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) due to weather and economic factors. It generally ran from April to October and saw more combat deaths than the ...
.
See also
* Horae, Greek goddesses of seasons * Indian summer *Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after ...
, Greek mythological figure associated with the rebirth of vegetation in the spring
* Sun path
* Vertumnus, Roman god of the seasons
References
* Maris, Mihaela, St. Luchian School, Bacau, Romania, ''Seasonal Variations of the Bird Species'', ref. ecological seasons pp. 195–196 incl. and pp. 207–209 incl.External links
When do the Seasons Begin?
(from the Bad Astronomer)
Why the Earth has seasons
article on h2g2.
Aboriginal seasons of Kakadu
Indigenous seasons (Australian Bureau of Meteorology)
Mt Stirling Seasons
The Lost Seasons
Tutorial on Earth/Sun Relations and Seasons
Sunpreview Season Forecast Project
Satellite photo demonstrating seasons changes in 2004 on NASA website
{{Authority control Calendars Climate patterns Units of time Articles containing video clips