Mesopotamic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran,
 Mesopotamia encompasses the land between the
Mesopotamia encompasses the land between the
 The prehistory of the Ancient Near East begins in the
The prehistory of the Ancient Near East begins in the
 * Pre- and protohistory
**
* Pre- and protohistory
**
 The earliest language written in Mesopotamia was
The earliest language written in Mesopotamia was
but Sumerian continued to be used as a sacred, ceremonial, literary, and scientific language in Mesopotamia until the 1st century AD.
 The Ancient Mesopotamian religion was the first recorded. Mesopotamians believed that the world was a flat disc, surrounded by a huge, holed space, and above that,
The Ancient Mesopotamian religion was the first recorded. Mesopotamians believed that the world was a flat disc, surrounded by a huge, holed space, and above that,
 Mesopotamia, as shown by successive law codes, those of Urukagina,
Mesopotamia, as shown by successive law codes, those of Urukagina,
 Sumerian temples functioned as banks and developed the first large-scale system of loans and credit, but the Babylonians developed the earliest system of commercial banking. It was comparable in some ways to modern post-Keynesian economics, but with a more "anything goes" approach.
Sumerian temples functioned as banks and developed the first large-scale system of loans and credit, but the Babylonians developed the earliest system of commercial banking. It was comparable in some ways to modern post-Keynesian economics, but with a more "anything goes" approach.
 With the end of the Uruk phase, walled cities grew and many isolated Ubaid villages were abandoned indicating a rise in communal violence. An early king Lugalbanda was supposed to have built the white walls around the city. As city-states began to grow, their spheres of influence overlapped, creating arguments between other city-states, especially over land and canals. These arguments were recorded in tablets several hundreds of years before any major war—the first recording of a war occurred around 3200 BC but was not common until about 2500 BC. An
With the end of the Uruk phase, walled cities grew and many isolated Ubaid villages were abandoned indicating a rise in communal violence. An early king Lugalbanda was supposed to have built the white walls around the city. As city-states began to grow, their spheres of influence overlapped, creating arguments between other city-states, especially over land and canals. These arguments were recorded in tablets several hundreds of years before any major war—the first recording of a war occurred around 3200 BC but was not common until about 2500 BC. An
File:Mask of Sargon of Akkad.jpg, Bronze head of an Akkadian ruler, discovered in
File:Ishtar Gate.gif, The Ishtar gate was constructed in about 575 BCE by order of King
Ancient Mesopotamia
– timeline, definition, and articles at World History Encyclopedia
Mesopotamia
nbsp;– introduction to Mesopotamia from the British Museum
''By Nile and Tigris, a narrative of journeys in Egypt and Mesopotamia on behalf of the British museum between the years 1886 and 1913''
by Sir E. A. Wallis Budge, 1920 (a searchable facsimile at the University of Georgia Libraries;
layered PDF
format)
''Mesopotamian Archaeology''
by Percy S. P. Handcock, 1912 (a searchable facsimile at the University of Georgia Libraries;
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Turkey.
The Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ians and Akkadians (including Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
and Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
ns) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history () to the fall of Babylon
The Fall of Babylon denotes the end of the Neo-Babylonian Empire after it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire in 539 BCE.
Nabonidus (Nabû-na'id, 556–539 BCE), son of the Assyrian priestess Adda-Guppi, came to the throne in 556 BCE, afte ...
in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
. Later the Arameans
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean ...
dominated major parts of Mesopotamia ().
Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
from around 10,000 BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction wi ...
, the planting of the first cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantit ...
crops, and the development of cursive
Cursive (also known as script, among other names) is any style of penmanship in which characters are written joined in a flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing faster, in contrast to block letters. It varies in functionalit ...
script, mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, astronomy, and agriculture". It is recognised as the cradle of some of the world's earliest civilizations.
Around 150 BC, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. It became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with western parts of the region coming under ephemeral Roman control. In 226 AD, the eastern regions of Mesopotamia fell to the Sassanid Persians. The division of the region between Roman (Byzantine from 395 AD) and Sassanid Empires lasted until the 7th century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
and Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant ( ar, فَتْحُ الشَّام, translit=Feth eş-Şâm), also known as the Rashidun conquest of Syria, occurred in the first half of the 7th century, shortly after the rise of Islam."Syria." Encyclopædia Br ...
from Byzantines. A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BC and 3rd century AD, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra.
Regions of Asia
Etymology
The regional toponym ''Mesopotamia'' (, grc, Μεσοποταμία ' andbetween rivers'; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; fa, میانرودان ; syr, ܒܝܬ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ "(land) between the (two) rivers") comes from the ancient Greek root words (, 'middle') and (, 'river') and translates to '(land) between rivers', likely being a calque of the older Aramaic term, with the Aramaic term itself likely being a calque of the Akkadian ''birit narim''. It is used throughout the Greek Septuagint () to translate the Hebrew and Aramaic equivalent ''Naharaim''. An even earlier Greek usage of the name ''Mesopotamia'' is evident from '' The Anabasis of Alexander'', which was written in the late 2nd century AD but specifically refers to sources from the time of Alexander the Great. In the ''Anabasis'', Mesopotamia was used to designate the land east of theEuphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
in north Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. The term ''Ārām Nahrīn'' ( syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, links=no) ( he, ארם נהריים, ) was used multiple times in the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
of the Bible to describe "Aram between the (two) rivers".
The Akkadian term corresponded to a similar geographical concept. Later, the term ''Mesopotamia'' was more generally applied to all the lands between the Euphrates and the Tigris, thereby incorporating not only parts of Syria but also almost all of Iraq and southeastern Turkey. The neighbouring steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
s to the west of the Euphrates and the western part of the Zagros Mountains are also often included under the wider term ''Mesopotami''a.
A further distinction is usually made between ''Northern'' or '' Upper Mesopotamia'' and ''Southern'' or ''Lower Mesopotamia
Lower Mesopotamia is a historical region of Mesopotamia. It's located in the alluvial plain of Iraq from the Hamrin Mountains to the Faw Peninsula near the Persian Gulf.
In the Middle Ages it was also known as the ''Sawad'' and al-Jazira al-sfli ...
''. Upper Mesopotamia, also known as the ''Jazira'', is the area between the Euphrates and the Tigris from their sources down to Baghdad. Lower Mesopotamia is the area from Baghdad to the Persian Gulf and includes Kuwait and parts of western Iran.
In modern academic usage, the term ''Mesopotamia'' often also has a chronological connotation. It is usually used to designate the area until the Muslim conquests, with names like ''Syria'', ''Jazira'', and ''Iraq'' being used to describe the region after that date. It has been argued that these later euphemisms are Eurocentric terms attributed to the region in the midst of various 19th-century Western encroachments.
Geography
 Mesopotamia encompasses the land between the
Mesopotamia encompasses the land between the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
and Tigris rivers, both of which have their headwaters in the neighboring Armenian highlands. Both rivers are fed by numerous tributaries, and the entire river system drains a vast mountainous region. Overland routes in Mesopotamia usually follow the Euphrates because the banks of the Tigris are frequently steep and difficult. The climate of the region is semi-arid with a vast desert expanse in the north which gives way to a region of marshes, lagoons, mudflats, and reed banks in the south. In the extreme south, the Euphrates and the Tigris unite and empty into the Persian Gulf.
The arid environment ranges from the northern areas of rain-fed agriculture to the south where irrigation of agriculture is essential if a surplus energy returned on energy invested (EROEI) is to be obtained. This irrigation is aided by a high water table and by melting snows from the high peaks of the northern Zagros Mountains and from the Armenian Highlands, the source of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers that give the region its name. The usefulness of irrigation depends upon the ability to mobilize sufficient labor for the construction and maintenance of canals, and this, from the earliest period, has assisted the development of urban settlements and centralized systems of political authority.
Agriculture throughout the region has been supplemented by nomadic pastoralism, where tent-dwelling nomads herded sheep and goats (and later camels) from the river pastures in the dry summer months, out into seasonal grazing lands on the desert fringe in the wet winter season. The area is generally lacking in building stone, precious metals, and timber, and so historically has relied upon long-distance trade of agricultural products to secure these items from outlying areas. In the marshlands to the south of the area, a complex water-borne fishing culture has existed since prehistoric times and has added to the cultural mix.
Periodic breakdowns in the cultural system have occurred for a number of reasons. The demands for labor has from time to time led to population increases that push the limits of the ecological carrying capacity, and should a period of climatic instability ensue, collapsing central government and declining populations can occur. Alternatively, military vulnerability to invasion from marginal hill tribes or nomadic pastoralists has led to periods of trade collapse and neglect of irrigation systems. Equally, centripetal tendencies amongst city-states have meant that central authority over the whole region, when imposed, has tended to be ephemeral, and localism has fragmented power into tribal or smaller regional units. These trends have continued to the present day in Iraq.
History
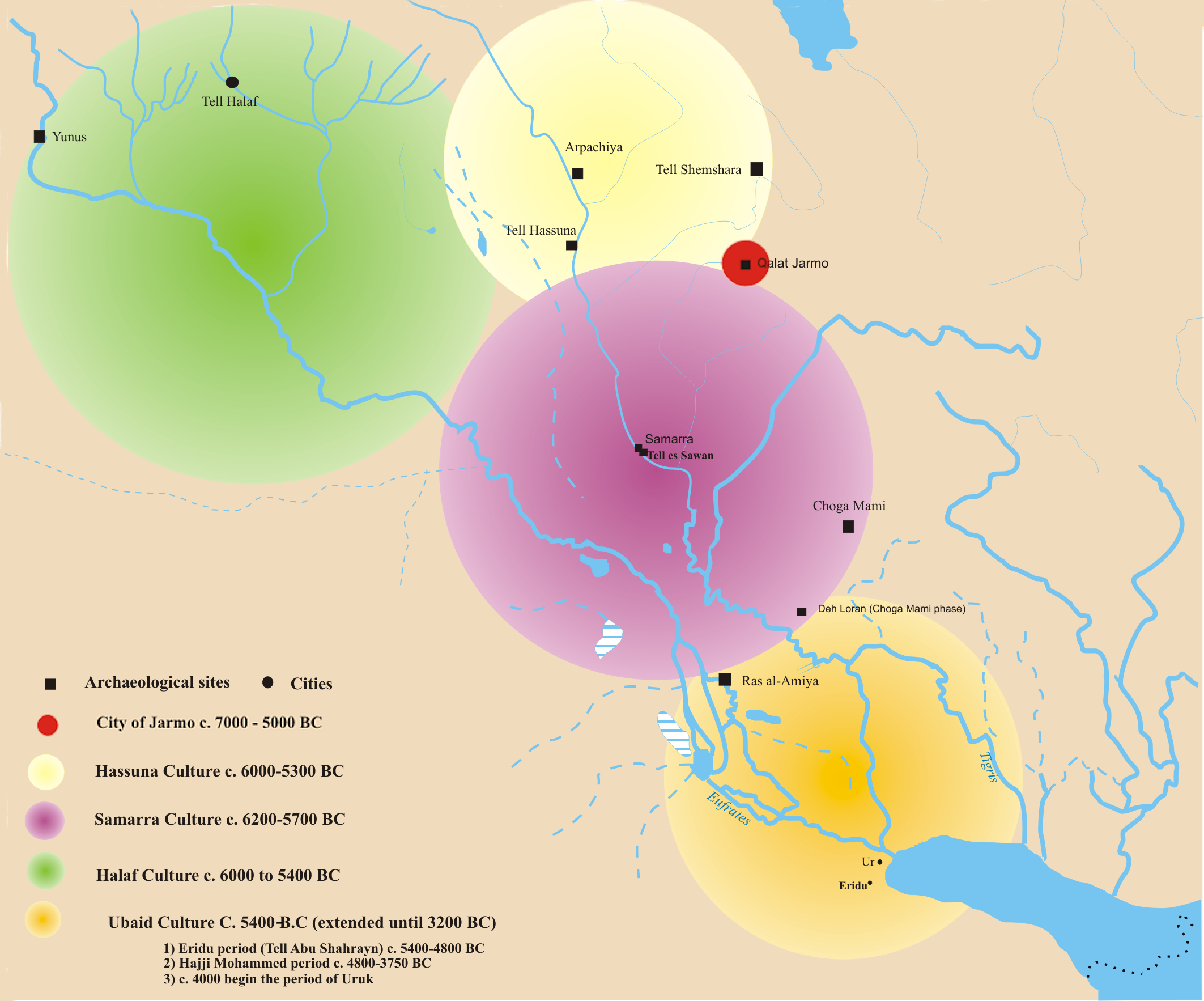
 The prehistory of the Ancient Near East begins in the
The prehistory of the Ancient Near East begins in the Lower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in ...
period. Therein, writing emerged with a pictographic script, Proto-cuneiform, in the Uruk IV period (). The documented record of actual historical events — and the ancient history of lower Mesopotamia — commenced in the early-third millennium BC with cuneiform records of early dynastic kings. This entire history ends with either the arrival of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
in the late 6th century BC or with the Muslim conquest and the establishment of the Caliphate in the late 7th century AD, from which point the region came to be known as Iraq. In the long span of this period, Mesopotamia housed some of the world's most ancient highly developed, and socially complex states.
The region was one of the four riverine civilizations where writing was invented, along with the Nile valley in Ancient Egypt, the Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
in the Indian subcontinent, and the Yellow River in Ancient China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
. Mesopotamia housed historically important cities such as Uruk, Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory': Vol. 1, Part 1. Accessed 15 Dec 2010. Akkadian language, Akkadian: '' ...
, Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
, Assur and Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
, as well as major territorial states such as the city of Eridu, the Akkadian kingdoms, the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the various Assyrian empires. Some of the important historical Mesopotamian leaders were Ur-Nammu (king of Ur), Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; akk, ''Šarrugi''), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highl ...
(who established the Akkadian Empire), Hammurabi (who established the Old Babylonian state), Ashur-uballit I and Tiglath-Pileser I (who established the Assyrian Empire).
Scientists analysed DNA from the 8,000-year-old remains of early farmers found at an ancient graveyard in Germany. They compared the genetic signatures to those of modern populations and found similarities with the DNA of people living in today's Turkey and Iraq.
Periodization
 * Pre- and protohistory
**
* Pre- and protohistory
** Pre-Pottery Neolithic A
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) denotes the first stage of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, in early Levantine and Anatolian Neolithic culture, dating to years ago, that is, 10,000–8,800 BCE. Archaeological remains are located in the Levantine and Up ...
(10,000–8700 BC)
** Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (8700–6800 BC)
** Jarmo
Jarmo (Qal'at Jarmo) ( ku, Çermo) is a prehistoric archeological site located in modern Iraq on the foothills of the Zagros Mountains. It lies at an altitude of 800 m above sea-level in a belt of oak and pistachio woodlands in the Adhai ...
(7500–5000 BC)
** Hassuna (~6000 BC)
** Samarra
Samarra ( ar, سَامَرَّاء, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The city of Samarra was founded by Abbasid Caliph Al-Mutasim for his Turkish professional army ...
(~5700–4900 BC)
** Halaf cultures (~6000–5300 BC)
** Ubaid period (~6500–4000 BC)
** Uruk period (~4000–3100 BC)
** Jemdet Nasr period (~3100–2900 BC)
* Early Bronze Age
** Early Dynastic period (~2900–2350 BC)
** Akkadian Empire (~2350–2100 BC)
** Third Dynasty of Ur (2112–2004 BC)
* Middle Bronze Age
** Isin-Larsa period (19th to 18th century BC)
** First Babylonian dynasty (18th to 17th century BC)
** Minoan eruption
The Minoan eruption was a catastrophic Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruption that devastated the Aegean Islands, Aegean island of Thera (also called Santorini) circa 1600 BCE. It destroyed the Minoan civilization, Minoan settlement at ...
()
* Late Bronze Age
** Old Assyrian period (16th to 11th century BC)
** Middle Assyrian period
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
()
** Kassites
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon ...
in Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
, ()
** Late Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near East ...
(12th to 11th century BC)
* Iron Age
** Syro-Hittite states (11th to 7th century BC)
** Neo-Assyrian Empire (10th to 7th century BC)
** Neo-Babylonian Empire (7th to 6th century BC)
* Classical antiquity
** Fall of Babylon
The Fall of Babylon denotes the end of the Neo-Babylonian Empire after it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire in 539 BCE.
Nabonidus (Nabû-na'id, 556–539 BCE), son of the Assyrian priestess Adda-Guppi, came to the throne in 556 BCE, afte ...
(6th century BC)
** Achaemenid Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1 ...
, Achaemenid Assyria (6th to 4th century BC)
** Seleucid Mesopotamia (4th to 3rd century BC)
** Parthian Babylonia (3rd century BC to 3rd century AD)
** Osroene (2nd century BC to 3rd century AD)
** Adiabene (1st to 2nd century AD)
** Hatra (1st to 2nd century AD)
** Roman Mesopotamia (2nd to 7th centuries AD), Roman Assyria (2nd century AD)
* Late Antiquity
** Asōristān (3rd to 7th century AD)
** Muslim conquest (mid-7th century AD)
Language and writing
Sumerian
Sumerian or Sumerians may refer to:
*Sumer, an ancient civilization
**Sumerian language
**Sumerian art
**Sumerian architecture
**Sumerian literature
**Cuneiform script, used in Sumerian writing
*Sumerian Records, an American record label based in ...
, an agglutinative language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The num ...
. Along with Sumerian, Semitic languages were also spoken in early Mesopotamia. Subartuan, a language of the Zagros possibly related to the Hurro-Urartuan language family, is attested in personal names, rivers and mountains and in various crafts. Akkadian came to be the dominant language during the Akkadian Empire and the Assyrian empires, but Sumerian was retained for administrative, religious, literary and scientific purposes. Different varieties of Akkadian were used until the end of the Neo-Babylonian period. Old Aramaic, which had already become common in Mesopotamia, then became the official provincial administration language of first the Neo-Assyrian Empire, and then the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
: the official lect is called Imperial Aramaic. Akkadian fell into disuse, but both it and Sumerian were still used in temples for some centuries. The last Akkadian texts date from the late 1st century AD.
Early in Mesopotamia's history (around the mid-4th millennium BC) cuneiform was invented for the Sumerian language. Cuneiform literally means "wedge-shaped", due to the triangular tip of the stylus used for impressing signs on wet clay. The standardized form of each cuneiform sign appears to have been developed from pictograms. The earliest texts (7 archaic tablets) come from the É, a temple dedicated to the goddess Inanna at Uruk, from a building labeled as Temple C by its excavators.
The early logographic system of cuneiform script took many years to master. Thus, only a limited number of individuals were hired as scribe
A scribe is a person who serves as a professional copyist, especially one who made copies of manuscripts before the invention of automatic printing.
The profession of the scribe, previously widespread across cultures, lost most of its promi ...
s to be trained in its use. It was not until the widespread use of a syllabic script was adopted under Sargon's rule that significant portions of the Mesopotamian population became literate. Massive archives of texts were recovered from the archaeological contexts of Old Babylonian scribal schools, through which literacy was disseminated.
Akkadian gradually replaced Sumerian as the spoken language of Mesopotamia somewhere around the turn of the 3rd and the 2nd millennium BC (the exact dating being a matter of debate),Woods C. 2006 "Bilingualism, Scribal Learning, and the Death of Sumerian". In S.L. Sanders (ed) ''Margins of Writing, Origins of Culture'': 91–120 Chicagbut Sumerian continued to be used as a sacred, ceremonial, literary, and scientific language in Mesopotamia until the 1st century AD.
Literature
Libraries were extant in towns and temples during the Babylonian Empire. An old Sumerian proverb averred that "he who would excel in the school of the scribes must rise with the dawn." Women as well as men learned to read and write, and for the Semitic languages, Semitic Babylonians, this involved knowledge of the extinct Sumerian language, and a complicated and extensive syllabary. A considerable amount of Babylonian literature was translated from Sumerian originals, and the language of religion and law long continued to be the old agglutinative language of Sumer. Vocabularies, grammars, and interlinear translations were compiled for the use of students, as well as commentaries on the older texts and explanations of obscure words and phrases. The characters of the syllabary were all arranged and named, and elaborate lists were drawn up. Many Babylonian literary works are still studied today. One of the most famous of these was the Epic of Gilgamesh, in twelve books, translated from the original Sumerian by a certainSîn-lēqi-unninni
Sîn-lēqi-unninni ( akk, ) was a '' mašmaššu'' who lived in Mesopotamia, probably in the period between 1300 BC and 1000 BC. He is traditionally thought to have compiled the best-preserved version of the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. ...
, and arranged upon an astronomical principle. Each division contains the story of a single adventure in the career of Gilgamesh. The whole story is a composite product, although it is probable that some of the stories are artificially attached to the central figure.
Science and technology
Mathematics
Mesopotamian mathematics and science was based on a sexagesimal (base 60) numeral system. This is the source of the 60-minute hour, the 24-hour day, and the 360-degree
Degree may refer to:
As a unit of measurement
* Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement
** Degree of geographical latitude
** Degree of geographical longitude
* Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathematics
...
circle. The Sumerian calendar was lunisolar, with three seven-day weeks of a lunar month. This form of mathematics was instrumental in early map-making. The Babylonians also had theorems on how to measure the area of several shapes and solids. They measured the circumference of a circle as three times the diameter and the area as one-twelfth the square of the circumference, which would be correct if were fixed at 3. The volume of a cylinder was taken as the product of the area of the base and the height; however, the volume of the frustum of a cone or a square pyramid
In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid having a square base. If the apex is perpendicularly above the center of the square, it is a right square pyramid, and has symmetry. If all edge lengths are equal, it is an equilateral square pyramid, ...
was incorrectly taken as the product of the height and half the sum of the bases. Also, there was a recent discovery in which a tablet used as 25/8 (3.125 instead of 3.14159~). The Babylonians are also known for the Babylonian mile, which was a measure of distance equal to about seven modern miles (11 km). This measurement for distances eventually was converted to a time-mile used for measuring the travel of the Sun, therefore, representing time.
Algebra
The roots of algebra can be traced to the ancient Babylonia who developed an advanced arithmetical system with which they were able to do calculations in an algorithmic fashion. The Babylonian clay tablet YBC 7289 (c. 1800–1600 BC) gives an approximation of in four sexagesimal figures, , which is accurate to about sixdecimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers of the Hindu–Arabic numeral ...
digits, and is the closest possible three-place sexagesimal representation of :
:
The Babylonians were not interested in exact solutions, but rather approximations, and so they would commonly use linear interpolation to approximate intermediate values.: "Babylonian mathematicians did not hesitate to interpolate by proportional parts to approximate intermediate values. Linear interpolation seems to have been a commonplace procedure in ancient Mesopotamia, and the positional notation lent itself conveniently to the rile of three. ..a table essential in Babylonian algebra; this subject reached a considerably higher level in Mesopotamia than in Egypt. Many problem texts from the Old Babylonian period show that the solution of the complete three-term quadratic equation afforded the Babylonians no serious difficulty, for flexible algebraic operations had been developed. They could transpose terms in an equations by adding equals to equals, and they could multiply both sides by like quantities to remove fractions or to eliminate factors. By adding to they could obtain for they were familiar with many simple forms of factoring. ..gyptian algebra had been much concerned with linear equations, but the Babylonians evidently found these too elementary for much attention. ..In another problem in an Old Babylonian text we find two simultaneous linear equations in two unknown quantities, called respectively the "first silver ring" and the "second silver ring."" One of the most famous tablets is the Plimpton 322 tablet, created around 1900–1600 BC, which gives a table of Pythagorean triples and represents some of the most advanced mathematics prior to Greek mathematics.
Astronomy
FromSumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ian times, temple priesthoods had attempted to associate current events with certain positions of the planets and stars. This continued to Assyrian times, when Limmu lists were created as a year by year association of events with planetary positions, which, when they have survived to the present day, allow accurate associations of relative with absolute dating for establishing the history of Mesopotamia.
The Babylonian astronomers were very adept at mathematics and could predict eclipses and solstices. Scholars thought that everything had some purpose in astronomy. Most of these related to religion and omens. Mesopotamian astronomers worked out a 12-month calendar based on the cycles of the moon. They divided the year into two seasons: summer and winter. The origins of astronomy as well as astrology date from this time.
During the 8th and 7th centuries BC, Babylonian astronomers developed a new approach to astronomy. They began studying philosophy dealing with the ideal nature of the early universe and began employing an internal logic within their predictive planetary systems. This was an important contribution to astronomy and the philosophy of science and some scholars have thus referred to this new approach as the first scientific revolution.D. Brown (2000), ''Mesopotamian Planetary Astronomy-Astrology'', Styx Publications, . This new approach to astronomy was adopted and further developed in Greek and Hellenistic astronomy.
In Seleucid and Parthian times, the astronomical reports were thoroughly scientific; how much earlier their advanced knowledge and methods were developed is uncertain. The Babylonian development of methods for predicting the motions of the planets is considered to be a major episode in the history of astronomy
Astronomy is the oldest of the natural sciences, dating back to antiquity, with its origins in the religious, mythological, cosmological, calendrical, and astrological beliefs and practices of prehistory: vestiges of these are still found in ...
.
The only Greek-Babylonian astronomer known to have supported a heliocentric
Heliocentrism (also known as the Heliocentric model) is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at ...
model of planetary motion was Seleucus of Seleucia (b. 190 BC). Seleucus is known from the writings of Plutarch. He supported Aristarchus of Samos' heliocentric theory where the Earth rotated around its own axis which in turn revolved around the Sun. According to Plutarch, Seleucus even proved the heliocentric system, but it is not known what arguments he used (except that he correctly theorized on tides as a result of Moon's attraction).
Babylonian astronomy served as the basis for much of Greek, classical Indian, Sassanian, Byzantine, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
n, medieval Islamic, Central Asian, and Western European astronomy.
Medicine
The oldest Babylonian texts on medicine date back to the Old Babylonian period in the first half of the2nd millennium BC
The 2nd millennium BC spanned the years 2000 BC to 1001 BC.
In the Ancient Near East, it marks the transition from the Middle to the Late Bronze Age.
The Ancient Near Eastern cultures are well within the historical era:
The first half of the mil ...
. The most extensive Babylonian medical text, however, is the ''Diagnostic Handbook'' written by the ''ummânū'', or chief scholar, Esagil-kin-apli of Borsippa
Borsippa ( Sumerian: BAD.SI.(A).AB.BAKI; Akkadian: ''Barsip'' and ''Til-Barsip'')The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory': Vol. 1, Part 1. Accessed 15 Dec 2010. or Birs Nimrud (having been identified with Nimrod) is an archeologi ...
, during the reign of the Babylonian king Adad-apla-iddina
Adad-apla-iddina, typically inscribed in cuneiform mdIM- DUMU.UŠ-SUM''-na'', mdIM-A-SUM''-na'' or dIM''-ap-lam-i-din-'' 'nam''meaning the storm god “Adad has given me an heir”, was the 8th king of the 2nd Dynasty of Isin and the 4th Dynasty ...
(1069-1046 BC).
Along with contemporary Egyptian medicine
The medicine of the ancient Egyptians is some of the oldest documented. From the beginnings of the civilization in the late fourth millennium BC until the Persian invasion of 525 BC, Egyptian medical practice went largely unchanged and includ ...
, the Babylonians introduced the concepts of diagnosis, prognosis
Prognosis (Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing") is a medical term for predicting the likely or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stabl ...
, physical examination, enemas, and prescriptions. In addition, the ''Diagnostic Handbook'' introduced the methods of therapy and aetiology and the use of empiricism
In philosophy, empiricism is an epistemological theory that holds that knowledge or justification comes only or primarily from sensory experience. It is one of several views within epistemology, along with rationalism and skepticism. Empir ...
, logic, and rationality
Rationality is the quality of being guided by or based on reasons. In this regard, a person acts rationally if they have a good reason for what they do or a belief is rational if it is based on strong evidence. This quality can apply to an abil ...
in diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. The text contains a list of medical symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
s and often detailed empirical observation
Observation is the active acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the perception and recording of data via the use of scientific instruments. The ...
s along with logical rules used in combining observed symptoms on the body of a patient with its diagnosis and prognosis.
The symptoms and diseases of a patient were treated through therapeutic means such as bandages, creams
Cream is a dairy product composed of the higher-fat layer skimmed from the top of milk before homogenization. In un-homogenized milk, the fat, which is less dense, eventually rises to the top. In the industrial production of cream, this process ...
and pills. If a patient could not be cured physically, the Babylonian physicians often relied on exorcism to cleanse the patient from any curses. Esagil-kin-apli's ''Diagnostic Handbook'' was based on a logical set of axiom
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or f ...
s and assumptions, including the modern view that through the examination and inspection
An inspection is, most generally, an organized examination or formal evaluation exercise. In engineering activities inspection involves the measurements, tests, and gauges applied to certain characteristics in regard to an object or activity. ...
of the symptoms of a patient, it is possible to determine the patient's disease, its aetiology, its future development, and the chances of the patient's recovery.H.F.J. Horstmanshoff, Marten Stol, Cornelis Tilburg (2004), ''Magic and Rationality in Ancient Near Eastern and Graeco-Roman Medicine'', p. 99, Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers (known as E. J. Brill, Koninklijke Brill, Brill ()) is a Dutch international academic publisher founded in 1683 in Leiden, Netherlands. With offices in Leiden, Boston, Paderborn and Singapore, Brill today publishes 27 ...
, .
Esagil-kin-apli discovered a variety of illnesses and diseases and described their symptoms in his ''Diagnostic Handbook''. These include the symptoms for many varieties of epilepsy and related ailments along with their diagnosis and prognosis.
Technology
Mesopotamian people invented many technologies including metal and copper-working, glass and lamp making, textile weaving, flood control, water storage, and irrigation. They were also one of the first Bronze Age societies in the world. They developed from copper, bronze, and gold on to iron. Palaces were decorated with hundreds of kilograms of these very expensive metals. Also, copper, bronze, and iron were used for armor as well as for different weapons such as swords, daggers, spears, andmaces
Mace may refer to:
Spices
* Mace (spice), a spice derived from the aril of nutmeg
* '' Achillea ageratum'', known as English mace, a flowering plant once used as a herb
Weapons
* Mace (bludgeon), a weapon with a heavy head on a solid shaft used ...
.
According to a recent hypothesis, the Archimedes' screw may have been used by Sennacherib, King of Assyria, for the water systems at the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World listed by Hellenic culture. They were described as a remarkable feat of engineering with an ascending series of tiered gardens containing a wide variety of tre ...
and Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
in the 7th century BC, although mainstream scholarship holds it to be a Greek invention of later times. Later, during the Parthian or Sasanian periods, the Baghdad Battery, which may have been the world's first battery, was created in Mesopotamia.
Religion and philosophy
heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
. They also believed that water was everywhere, the top, bottom and sides, and that the universe was born from this enormous sea. In addition, Mesopotamian religion was polytheistic. Although the beliefs described above were held in common among Mesopotamians, there were also regional variations. The Sumerian word for universe is an-ki, which refers to the god An and the goddess Ki. Their son was Enlil, the air god. They believed that Enlil was the most powerful god. He was the chief god of the pantheon.
Philosophy
The numerous civilizations of the area influenced the Abrahamic religions, especially the Hebrew Bible; its cultural values and literary influence are especially evident in the Book of Genesis. Giorgio Buccellati believes that the origins ofphilosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
can be traced back to early Mesopotamian wisdom, which embodied certain philosophies of life, particularly ethics, in the forms of dialectic
Dialectic ( grc-gre, διαλεκτική, ''dialektikḗ''; related to dialogue; german: Dialektik), also known as the dialectical method, is a discourse between two or more people holding different points of view about a subject but wishing ...
, dialogue
Dialogue (sometimes spelled dialog in American English) is a written or spoken conversational exchange between two or more people, and a literary and theatrical form that depicts such an exchange. As a philosophical or didactic device, it is c ...
s, epic poetry, folklore, hymns, lyrics, prose works, and proverbs. Babylonian reason and rationality
Rationality is the quality of being guided by or based on reasons. In this regard, a person acts rationally if they have a good reason for what they do or a belief is rational if it is based on strong evidence. This quality can apply to an abil ...
developed beyond empirical
Empirical evidence for a proposition is evidence, i.e. what supports or counters this proposition, that is constituted by or accessible to sense experience or experimental procedure. Empirical evidence is of central importance to the sciences and ...
observation.
The earliest form of logic was developed by the Babylonians, notably in the rigorous nonergodic nature of their social systems. Babylonian thought was axiom
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or f ...
atic and is comparable to the "ordinary logic" described by John Maynard Keynes. Babylonian thought was also based on an open-systems ontology which is compatible with ergodic
In mathematics, ergodicity expresses the idea that a point of a moving system, either a dynamical system or a stochastic process, will eventually visit all parts of the space that the system moves in, in a uniform and random sense. This implies tha ...
axioms. Logic was employed to some extent in Babylonian astronomy and medicine.
Babylonian thought had a considerable influence on early Ancient Greek and Hellenistic philosophy
Hellenistic philosophy is a time-frame for Western philosophy and Ancient Greek philosophy corresponding to the Hellenistic period. It is purely external and encompasses disparate intellectual content. There is no single philosophical school or cu ...
. In particular, the Babylonian text ''Dialogue of Pessimism The Dialogue of Pessimism is an ancient Mesopotamian literary composition in the form of a dialogue between a master and his slave. Its interpretations have varied, but it is generally considered an unusual text which thematises the futility of huma ...
'' contains similarities to the agonistic thought of the Sophists, the Heraclitean doctrine of dialectic
Dialectic ( grc-gre, διαλεκτική, ''dialektikḗ''; related to dialogue; german: Dialektik), also known as the dialectical method, is a discourse between two or more people holding different points of view about a subject but wishing ...
, and the dialogs of Plato, as well as a precursor to the Socratic method. The Ionian
Ionic or Ionian may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Ionic meter, a poetic metre in ancient Greek and Latin poetry
* Ionian mode, a musical mode or a diatonic scale
Places and peoples
* Ionian, of or from Ionia, an ancient region in western ...
philosopher Thales was influenced by Babylonian cosmological ideas.
Culture

Festivals
Ancient Mesopotamians had ceremonies each month. The theme of the rituals and festivals for each month was determined by at least six important factors: # TheLunar phase
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the t ...
(a waxing moon meant abundance and growth, while a waning moon was associated with decline, conservation, and festivals of the Underworld)
# The phase of the annual agricultural cycle
# Equinoxes and solstices
# The local mythos and its divine Patrons
# The success of the reigning Monarch
# The Akitu
Akitu or Akitum is a spring festival held on the first day of Nisan in ancient Mesopotamia, to celebrate the sowing of barley. The Assyrian and Babylonian Akitu festival has played a pivotal role in the development of theories of religion, myth ...
, or New Year Festival (first full moon after spring equinox)
# Commemoration of specific historical events (founding, military victories, temple holidays, etc.)
Music
Some songs were written for the gods but many were written to describe important events. Although music and songs amusedkings
Kings or King's may refer to:
*Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings
*One of several works known as the "Book of Kings":
**The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts
**The ''Shahnameh'' ...
, they were also enjoyed by ordinary people who liked to sing and dance in their homes or in the marketplaces.
Songs were sung to children who passed them on to their children. Thus songs were passed on through many generations as an oral tradition until writing was more universal. These songs provided a means of passing on through the centuries highly important information about historical events.
Games
Hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
was popular among Assyrian kings. Boxing and wrestling feature frequently in art, and some form of polo
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small hard ...
was probably popular, with men sitting on the shoulders of other men rather than on horses.
They also played ''majore'', a game similar to the sport rugby, but played with a ball made of wood. They also played a board game similar to senet and backgammon, now known as the " Royal Game of Ur".
Family life
 Mesopotamia, as shown by successive law codes, those of Urukagina,
Mesopotamia, as shown by successive law codes, those of Urukagina, Lipit Ishtar
Lipit-Ishtar (Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''Lipit-Ištar''; ''Floruit, fl.'' ''c.'' 1870 BC – ''c.'' 1860 BC by the short chronology, short chronology of the ancient near east) was the 5th king of the First Dynasty of Isin, according to the ''Su ...
and Hammurabi, across its history became more and more a patriarchal society, one in which the men were far more powerful than the women. For example, during the earliest Sumerian period, the ''"en"'', or high priest of male gods was originally a woman, that of female goddesses. Thorkild Jacobsen, as well as others, have suggested that early Mesopotamian society was ruled by a "council of elders" in which men and women were equally represented, but that over time, as the status of women fell, that of men increased. As for schooling, only royal offspring and sons of the rich and professionals, such as scribes, physicians, temple administrators, went to school. Most boys were taught their father's trade or were apprenticed out to learn a trade. Girls had to stay home with their mothers to learn housekeeping and cooking
Cooking, cookery, or culinary arts is the art, science and craft of using heat to Outline of food preparation, prepare food for consumption. Cooking techniques and ingredients vary widely, from grilling food over an open fire to using electric ...
, and to look after the younger children. Some children would help with crushing grain or cleaning birds. Unusually for that time in history, women in Mesopotamia had rights. They could own property and, if they had good reason, get a divorce.
Burials
Hundreds of graves have been excavated in parts of Mesopotamia, revealing information about Mesopotamianburial
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
habits. In the city of Ur, most people were buried in family graves under their houses, along with some possessions. A few have been found wrapped in mats and carpets
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, nylon, or polyester have ...
. Deceased children were put in big "jars" which were placed in the family chapel. Other remains have been found buried in common city graveyards. 17 graves have been found with very precious objects in them. It is assumed that these were royal graves. Rich of various periods, have been discovered to have sought burial in Bahrein, identified with Sumerian Dilmun.
Economy
Agriculture
Irrigated agriculture spread southwards from the Zagros foothills with the Samara and Hadji Muhammed culture, from about 5,000 BC. In the early period down to Ur III temples owned up to one third of the available land, declining over time as royal and other private holdings increased in frequency. The word ''Ensi'' was used to describe the official who organized the work of all facets of temple agriculture. Villeins are known to have worked most frequently within agriculture, especially in the grounds of temples or palaces. The geography of southern Mesopotamia is such that agriculture is possible only with irrigation and with good drainage, a fact which had a profound effect on the evolution of early Mesopotamian civilization. The need for irrigation led the Sumerians, and later the Akkadians, to build their cities along the Tigris and Euphrates and the branches of these rivers. Major cities, such as Ur and Uruk, took root on tributaries of the Euphrates, while others, notably Lagash, were built on branches of the Tigris. The rivers provided the further benefits of fish (used both for food and fertilizer), reeds, and clay (for building materials). With irrigation, the food supply in Mesopotamia was comparable to that of the Canadian prairies. The Tigris and Euphrates River valleys form the northeastern portion of the Fertile Crescent, which also included the Jordan River valley and that of the Nile. Although land nearer to the rivers was fertile and good forcrops
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydroponics ...
, portions of land farther from the water were dry and largely uninhabitable. Thus the development of irrigation became very important for settlers of Mesopotamia. Other Mesopotamian innovations include the control of water by dams and the use of aqueducts. Early settlers of fertile land in Mesopotamia used wooden plow
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
s to soften the soil before planting crops such as barley, onions, grapes, turnips, and apples. Mesopotamian settlers were some of the first people to make beer and wine. As a result of the skill involved in farming in the Mesopotamian region, farmers did not generally depend on slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
to complete farm work for them, but there were some exceptions. There were too many risks involved to make slavery practical (i.e. the escape/mutiny of the slaves). Although the rivers sustained life, they also destroyed it by frequent floods that ravaged entire cities. The unpredictable Mesopotamian weather was often hard on farmers; crops were often ruined so backup sources of food such as cows and lambs were also kept. Over time the southernmost parts of Sumerian Mesopotamia suffered from increased salinity of the soils, leading to a slow urban decline and a centring of power in Akkad, further north.
Trade
Mesopotamian trade with the Indus Valley civilisation flourished as early as the third millennium BC. Starting in the 4th millennium BC, Mesopotamian civilizations also traded with ancient Egypt (seeEgypt–Mesopotamia relations
Egypt–Mesopotamia relations were the relations between the civilisations of ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, in the Middle East. They seem to have developed from the 4th millennium BCE, starting in the Uruk period for Mesopotamia (circa 4000–31 ...
).Shaw, Ian. & Nicholson, Paul, ''The Dictionary of Ancient Egypt,'' (London: British Museum Press, 1995), p. 109.
For much of history, Mesopotamia served as a trade nexus - east-west between Central Asia and the Mediterranean world
(part of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
), as well as north–south between the Eastern Europe and Baghdad ( Volga trade route). Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira (; ; c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link E ...
's pioneering (1497-1499) of the sea route between India and Europe and the opening of the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
in 1869 impacted on this nexus.
Government
The geography of Mesopotamia had a profound impact on the political development of the region. Among the rivers and streams, the Sumerian people built the first cities along with irrigation canals which were separated by vast stretches of open desert or swamp where nomadic tribes roamed. Communication among the isolated cities was difficult and, at times, dangerous. Thus, each Sumerian city became a city-state, independent of the others and protective of its independence. At times one city would try to conquer and unify the region, but such efforts were resisted and failed for centuries. As a result, the political history of Sumer is one of almost constant warfare. Eventually Sumer was unified by Eannatum, but the unification was tenuous and failed to last as the Akkadians conquered Sumer in 2331 BC only a generation later. The Akkadian Empire was the first successful empire to last beyond a generation and see the peaceful succession of kings. The empire was relatively short-lived, as the Babylonians conquered them within only a few generations.Kings
The Mesopotamians believed their kings and queens were descended from the city gods, but, unlike the ancient Egyptians, they never believed their kings were real gods. Most kings named themselves "king of the universe" or "great king". Another common name was "shepherd
A shepherd or sheepherder is a person who tends, herds, feeds, or guards flocks of sheep. ''Shepherd'' derives from Old English ''sceaphierde (''sceap'' 'sheep' + ''hierde'' 'herder'). ''Shepherding is one of the world's oldest occupations, i ...
", as kings had to look after their people.
Power
When Assyria grew into an empire, it was divided into smaller parts, called provinces. Each of these were named after their main cities, likeNineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
, Samaria, Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, and Arpad. They all had their own governor who had to make sure everyone paid their taxes. Governors also had to call up soldiers to war and supply workers when a temple was built. He was also responsible for enforcing the laws. In this way, it was easier to keep control of a large empire. Although Babylon was quite a small state in Sumer, it grew tremendously throughout the time of Hammurabi's rule. He was known as "the lawmaker" and created the Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organised, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian, purportedly by Hamm ...
, and soon Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
became one of the main cities in Mesopotamia. It was later called Babylonia, which meant "the gateway of the gods." It also became one of history's greatest centers of learning.
Warfare
 With the end of the Uruk phase, walled cities grew and many isolated Ubaid villages were abandoned indicating a rise in communal violence. An early king Lugalbanda was supposed to have built the white walls around the city. As city-states began to grow, their spheres of influence overlapped, creating arguments between other city-states, especially over land and canals. These arguments were recorded in tablets several hundreds of years before any major war—the first recording of a war occurred around 3200 BC but was not common until about 2500 BC. An
With the end of the Uruk phase, walled cities grew and many isolated Ubaid villages were abandoned indicating a rise in communal violence. An early king Lugalbanda was supposed to have built the white walls around the city. As city-states began to grow, their spheres of influence overlapped, creating arguments between other city-states, especially over land and canals. These arguments were recorded in tablets several hundreds of years before any major war—the first recording of a war occurred around 3200 BC but was not common until about 2500 BC. An Early Dynastic II
The Early Dynastic period (abbreviated ED period or ED) is an archaeological culture in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) that is generally dated to c. 2900–2350 BC and was preceded by the Uruk and Jemdet Nasr periods. It saw the development of w ...
king (Ensi) of Uruk in Sumer, Gilgamesh (c. 2600 BC), was commended for military exploits against Humbaba guardian of the Cedar Mountain, and was later celebrated in many later poems and songs in which he was claimed to be two-thirds god and only one-third human. The later Stele of the Vultures
The Stele of the Vultures is a monument from the Early Dynastic IIIb period (2600–2350 BC) in Mesopotamia celebrating a victory of the city-state of Lagash over its neighbour Umma. It shows various battle and religious scenes and is named after ...
at the end of the Early Dynastic III period (2600–2350 BC), commemorating the victory of Eannatum of Lagash over the neighbouring rival city of Umma is the oldest monument in the world that celebrates a massacre. From this point forwards, warfare was incorporated into the Mesopotamian political system. At times a neutral city may act as an arbitrator for the two rival cities. This helped to form unions between cities, leading to regional states. When empires were created, they went to war more with foreign countries. King Sargon, for example, conquered all the cities of Sumer, some cities in Mari, and then went to war with cities in modern-day Syria. Many Assyrian and Babylonian palace walls were decorated with the pictures of the successful fights and the enemy either desperately escaping or hiding amongst reeds.
The Neo-Babylonian kings used deportation as a means of control, like their predecessors, the Assyrians. For the Neo-Babylonian kings, war was a means to obtain tribute, plunder, sought after materials such as various metals and quality wood) and prisoners of war which could be put to work as slaves in the temples which they built. The Assyrians had displaced populations throughout their vast empire, however, this particular practice under the Babylonian kings would appear to have been more limited, only being used to establish new populations in Babylonia itself. Though royal inscriptions from the Neo-Babylonian period don't speak of acts of destruction and deportation in the same boastful way royal inscriptions from the Neo-Assyrian period do, this however, does not prove that the practice ceased or that the Babylonians were less brutal than the Assyrians, since there is evidence that the city Ashkelon was destroyed by Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
in 604 BC.
Laws
City-states of Mesopotamia created the first law codes, drawn from legal precedence and decisions made by kings. The codes of Urukagina andLipit Ishtar
Lipit-Ishtar (Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''Lipit-Ištar''; ''Floruit, fl.'' ''c.'' 1870 BC – ''c.'' 1860 BC by the short chronology, short chronology of the ancient near east) was the 5th king of the First Dynasty of Isin, according to the ''Su ...
have been found. The most renowned of these was that of Hammurabi, as mentioned above, who was posthumously famous for his set of laws, the Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organised, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian, purportedly by Hamm ...
(created c. 1780 BC), which is one of the earliest sets of laws found and one of the best preserved examples of this type of document from ancient Mesopotamia. He codified over 200 laws for Mesopotamia. Examination of the laws show a progressive weakening of the rights of women, and increasing severity in the treatment of slaves.
Art
The art of Mesopotamia rivalled that of Ancient Egypt as the most grand, sophisticated and elaborate in western Eurasia from the 4th millennium BC until the Persian Achaemenid Empire conquered the region in the 6th century BC. The main emphasis was on various, very durable, forms of sculpture in stone and clay; little painting has survived, but what has suggests that painting was mainly used for geometrical and plant-based decorative schemes, though most sculpture was also painted. TheProtoliterate period
The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BC; also known as Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after ...
, dominated by Uruk, saw the production of sophisticated works like the Warka Vase and cylinder seals. The Guennol Lioness is an outstanding small limestone figure from Elam
Elam (; Linear Elamite: ''hatamti''; Cuneiform Elamite: ; Sumerian: ; Akkadian: ; he, עֵילָם ''ʿēlām''; peo, 𐎢𐎺𐎩 ''hūja'') was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of modern-day Iran, stretc ...
of about 3000–2800 BC, part man and part lion. A little later there are a number of figures of large-eyed priests and worshippers, mostly in alabaster and up to a foot high, who attended temple cult image
In the practice of religion, a cult image is a human-made object that is venerated or worshipped for the deity, spirit or daemon that it embodies or represents. In several traditions, including the ancient religions of Egypt, Greece and Rome ...
s of the deity, but very few of these have survived. Sculptures from the Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ian and Akkadian period generally had large, staring eyes, and long beards on the men. Many masterpieces have also been found at the Royal Cemetery at Ur (c. 2650 BC), including the two figures of a ''Ram in a Thicket
The ''Ram in a Thicket'' is a pair of figures excavated at Ur, in southern Iraq, which date from about 2600–2400 BC. One is in the Mesopotamia Gallery in Room 56 of the British Museum in London; the other is in the University of Pennsylvania ...
'', the '' Copper Bull'' and a bull's head on one of the Lyres of Ur
The Lyres of Ur or Harps of Ur are a group of four stringed instruments excavated in a fragmentary condition at the Royal Cemetery of Ur in modern Iraq from 1922 onwards. They date back to the Early Dynastic III Period of Mesopotamia, between a ...
.
From the many subsequent periods before the ascendency of the Neo-Assyrian Empire Mesopotamian art survives in a number of forms: cylinder seals, relatively small figures in the round, and reliefs of various sizes, including cheap plaques of moulded pottery for the home, some religious and some apparently not. The Burney Relief is an unusual elaborate and relatively large (20 x 15 inches) terracotta plaque of a naked winged goddess with the feet of a bird of prey, and attendant owls and lions. It comes from the 18th or 19th century BC, and may also be moulded. Stone stelae, votive offerings, or ones probably commemorating victories and showing feasts, are also found from temples, which unlike more official ones lack inscriptions that would explain them; the fragmentary Stele of the Vultures
The Stele of the Vultures is a monument from the Early Dynastic IIIb period (2600–2350 BC) in Mesopotamia celebrating a victory of the city-state of Lagash over its neighbour Umma. It shows various battle and religious scenes and is named after ...
is an early example of the inscribed type, and the Assyrian Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III a large and solid late one.
The conquest of the whole of Mesopotamia and much surrounding territory by the Assyrians created a larger and wealthier state than the region had known before, and very grandiose art in palaces and public places, no doubt partly intended to match the splendour of the art of the neighbouring Egyptian empire. The Assyrians developed a style of extremely large schemes of very finely detailed narrative low reliefs in stone for palaces, with scenes of war or hunting; the British Museum has an outstanding collection. They produced very little sculpture in the round, except for colossal guardian figures, often the human-headed lamassu, which are sculpted in high relief on two sides of a rectangular block, with the heads effectively in the round (and also five legs, so that both views seem complete). Even before dominating the region they had continued the cylinder seal tradition with designs which are often exceptionally energetic and refined.Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
in 1931, presumably depicting either Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; akk, ''Šarrugi''), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highl ...
or Sargon's grandson Naram-Sin.
File:Striding lions - Processional Way of Babylon - Pergamonmuseum - Berlin - Germany 2017.jpg, Striding lions from the Processional Street of Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
.
File:Assyrian Winged Bull.jpg, Lamassu, initially depicted as a goddess in Sumerian times, when it was called ''Lamma'', it was later depicted from Assyrian times as a hybrid of a human, bird, and either a bull or lion—specifically having a human head, the body of a bull or a lion, and bird wings, under the name ''Lamassu''.
File:Ancient Egyptian, Assyrian, and Persian costumes and decorations (1920) (14741970056).jpg, Assyrian ornaments and patterns, illustrated in a book from 1920
File:Detail, Nebuchadnezzar II's Building Inscription plaque of the Ishtar Gate, from Babylon, Iraq. 6th century BCE. Pergamon Museum.jpg, alt=, Detail of Nebuchadnezzar II's Building Inscription plaque of the Ishtar Gate, from Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
File:Artist’s impression of a hall in an Assyrian palace from The Monuments of Nineveh by Sir Austen Henry Layard, 1853.jpg, alt=, Artist's impression of a hall in an Assyrian palace from ''The Monuments of Nineveh'' by Austen Henry Layard
Sir Austen Henry Layard (; 5 March 18175 July 1894) was an English Assyriologist, traveller, cuneiformist, art historian, draughtsman, collector, politician and diplomat. He was born to a mostly English family in Paris and largely raised in It ...
, 1853
File:Ashur god.jpg, alt=, A Neo-Assyrian relief of Ashur as a feather robed archer holding a bow instead of a ring (9th-8th century BC)
File:The Assyrian king Shalmaneser III receives tribute from Sua, king of Gilzanu, The Black Obelisk..JPG, alt=, The Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III. The king, surrounded by his royal attendants and a high-ranking official, receives a tribute from Sua, king of Gilzanu (north-west Iran), who bows and prostrates before the king. From Nimrud
File:History of babylon.jpg, alt=, Contemporary artwork depicting Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
at the height of its stature.
File:Genien, Nimrud 870 v. Chr. Aegyptisches Museum, Muenchen-4.jpg, alt=, " Winged genie", Nimrud c. 870 BC, with inscription running across his midriff.
Architecture
The study of ancient Mesopotamian architecture is based on availablearchaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
evidence, pictorial representation of buildings, and texts on building practices. Scholarly literature usually concentrates on temples, palaces, city walls and gates, and other monumental buildings, but occasionally one finds works on residential architecture as well. Archaeological surface surveys also allowed for the study of urban form in early Mesopotamian cities.
Brick is the dominant material, as the material was freely available locally, whereas building stone had to be brought a considerable distance to most cities. The ziggurat is the most distinctive form, and cities often had large gateways, of which the Ishtar Gate from Neo-Babylonian Babylon, decorated with beasts in polychrome brick, is the most famous, now largely in the Pergamon Museum in Berlin.
The most notable architectural remains from early Mesopotamia are the temple complexes at Uruk from the 4th millennium BC, temples and palaces from the Early Dynastic period sites in the Diyala River
The Diyala River (Arabic: ; ku, Sîrwan; Farsi: , ) is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of Sirwan river and Tanjaro river in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total ...
valley such as Khafajah and Tell Asmar, the Third Dynasty of Ur remains at Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory': Vol. 1, Part 1. Accessed 15 Dec 2010. Akkadian language, Akkadian: '' ...
(Sanctuary of Enlil
Enlil, , "Lord f theWind" later known as Elil, is an ancient Mesopotamian god associated with wind, air, earth, and storms. He is first attested as the chief deity of the Sumerian pantheon, but he was later worshipped by the Akkadians, Bab ...
) and Ur (Sanctuary of Nanna
Nanna may refer to:
*Grandmother
Mythology
* Sin (mythology), god of the moon in Sumerian mythology, also called Suen
* Nanna (Norse deity), goddess associated with the god Baldr in Norse mythology
* Nana Buluku, Fon/Dahomey androgynous deity cre ...
), Middle Bronze Age remains at Syrian-Turkish sites of Ebla, Mari, Alalakh, Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
and Kultepe, Late Bronze Age palaces at Hattusa, Ugarit, Ashur Ashur, Assur, or Asur may refer to:
Places
* Assur, an Assyrian city and first capital of ancient Assyria
* Ashur, Iran, a village in Iran
* Asur, Thanjavur district, a village in the Kumbakonam taluk of Thanjavur district, Tamil Nadu, India
* Assu ...
and Nuzi, Iron Age palaces and temples at Assyrian ( Kalhu/Nimrud, Khorsabad, Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern ban ...
), Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
n (Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
), Urartian ( Tushpa/Van, Kalesi, Cavustepe, Ayanis, Armavir, Erebuni, Bastam) and Neo-Hittite
The states that are called Syro-Hittite, Neo-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works), were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern ...
sites ( Karkamis, Tell Halaf, Karatepe). Houses are mostly known from Old Babylonian remains at Nippur and Ur. Among the textual sources on building construction and associated rituals are Gudea's cylinders from the late 3rd millennium are notable, as well as the Assyrian and Babylonian royal inscriptions from the Iron Age.Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
. Pergamon Museum, Berlin
File:Street in Babylon.jpg, The walls of Babylon, in Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
File:Zig front right side.JPG, Ziggurat of Ur
File:The ziggurat at Aqar Quf.jpg, Ziggurat of Dur-kuriagalzu in 2010
File:SumerianZiggurat.jpg, A suggested reconstruction of the appearance of a Sumerian ziggurat
File:20160105-Abraham house in Ur Iraq.jpg, alt=, The alleged Abraham house in Ur
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * *Further reading
* Algaze, Guillermo, 2008 '' Ancient Mesopotamia at the Dawn of Civilization: the Evolution of an Urban Landscape''. University of Chicago Press. * ''Atlas de la Mésopotamie et du Proche-Orient ancien'', Brepols, 1996 . * Bottéro, Jean; 1987. ''Mésopotamie. L'écriture, la raison et les dieux'', Gallimard, coll. « Folio Histoire », . * * Edzard, Dietz Otto; 2004. ''Geschichte Mesopotamiens. Von den Sumerern bis zu Alexander dem Großen'', München, * Hrouda, Barthel and Rene Pfeilschifter; 2005. ''Mesopotamien. Die antiken Kulturen zwischen Euphrat und Tigris.'' München 2005 (4. Aufl.), * Joannès, Francis; 2001. ''Dictionnaire de la civilisation mésopotamienne'', Robert Laffont. * Korn, Wolfgang; 2004. ''Mesopotamien – Wiege der Zivilisation. 6000 Jahre Hochkulturen an Euphrat und Tigris'', Stuttgart, * Matthews, Roger; 2005. ''The early prehistory of Mesopotamia – 500,000 to 4,500 BC'', Turnhout 2005, * Oppenheim, A. Leo; 1964. ''Ancient Mesopotamia: Portrait of a dead civilization''. The University of Chicago Press: Chicago and London. Revised edition completed by Erica Reiner, 1977. * Pollock, Susan; 1999.'' Ancient Mesopotamia: the Eden that never was''. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge. * Postgate, J. Nicholas; 1992. ''Early Mesopotamia: Society and Economy at the dawn of history''. Routledge: London and New York. * Roux, Georges; 1964. ''Ancient Iraq'', Penguin Books. * Silver, Morris; 2007. ''Redistribution and Markets in the Economy of Ancient Mesopotamia: Updating Polanyi'', Antiguo Oriente 5: 89–112.External links
Ancient Mesopotamia
– timeline, definition, and articles at World History Encyclopedia
Mesopotamia
nbsp;– introduction to Mesopotamia from the British Museum
''By Nile and Tigris, a narrative of journeys in Egypt and Mesopotamia on behalf of the British museum between the years 1886 and 1913''
by Sir E. A. Wallis Budge, 1920 (a searchable facsimile at the University of Georgia Libraries;
DjVu
DjVu ( , like French "déjà vu") is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, indexed color images, and photographs. It uses technologies such as ima ...
layered PDF
format)
''Mesopotamian Archaeology''
by Percy S. P. Handcock, 1912 (a searchable facsimile at the University of Georgia Libraries;
DjVu
DjVu ( , like French "déjà vu") is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, indexed color images, and photographs. It uses technologies such as ima ...
& )
{{Authority control
Ancient history of Iraq
Ancient Near East
Ancient Syria
Eastern Mediterranean
Geography of Iran
Geography of Iraq
Geography of Kuwait
Geography of Syria
Geography of the Middle East
Geography of Turkey
Geography of Western Asia
Historical regions
History of the Middle East
History of Western Asia
Levant
Near East
Persian Gulf