megaprojects on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
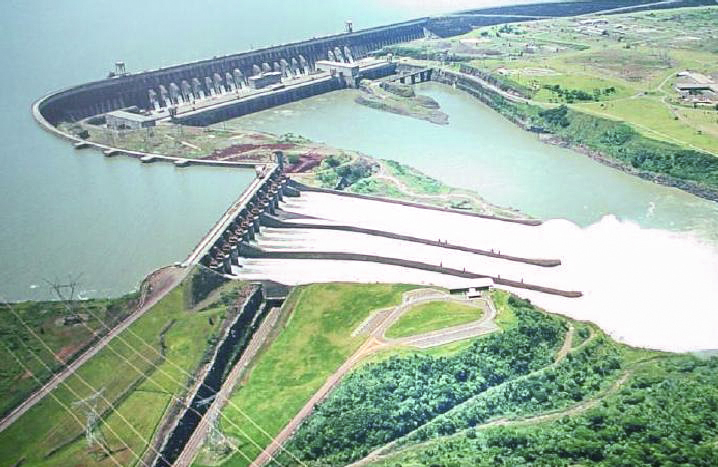

 A megaproject is an extremely large-scale
A megaproject is an extremely large-scale
Mega-project.eu, a website run by
Borovoye-Biocity
– megaproject of Bionic City for
Catalogue of Catastrophe
– list of troubled large projects {{Construction overview Engineering projects Risk management

 A megaproject is an extremely large-scale
A megaproject is an extremely large-scale investment
Investment is the dedication of money to purchase of an asset to attain an increase in value over a period of time. Investment requires a sacrifice of some present asset, such as time, money, or effort.
In finance, the purpose of investing i ...
project
A project is any undertaking, carried out individually or collaboratively and possibly involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular goal.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of even ...
.
According to the ''Oxford Handbook of Megaproject Management'', "Megaprojects are large-scale, complex ventures that typically cost $1 billion or more, take many years to develop and build, involve multiple public and private stakeholders, are transformational, and impact millions of people". However, $1 billion is not a constraint in defining megaprojects; in some contexts a relative approach is needed, such as in developing countries, where a much smaller project (such as one with a $100 million budget) could constitute a megaproject. Therefore, a more general definition is "Megaprojects are temporary endeavours (i.e. projects) characterized by: large investment commitment, vast complexity (especially in organizational terms), and long-lasting impact on the economy, the environment, and society".
Bent Flyvbjerg
Bent Flyvbjerg is a Danish economic geographer. He was the First BT Professor and Inaugural Chair of Major Programme Management at Oxford University's Saïd Business School (retiring from the post in 2021) and is the Villum Kann Rasmussen Profess ...
, a professor at the Saïd Business School
Saïd Business School (Oxford Saïd or SBS) is the business school of the University of Oxford. The School is a provider of management education and is consistently ranked as one of the world's top business schools.
Oxford School of Management ...
of the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
says that globally, megaprojects make up 8 percent of total global GDP. Megaprojects refer not only to construction projects but also decommissioning projects, which are projects that can reach multi-billion budgets, and have a high level of innovation and complexity, and are affected by a number of techno-socio-economic and organizational challenges.
Planning bias
Care in the project development process is required to reduce any possibleoptimism bias
Optimism bias (or the optimistic bias) is a cognitive bias that causes someone to believe that they themselves are less likely to experience a negative event. It is also known as unrealistic optimism or comparative optimism.
Optimism bias is commo ...
and strategic misrepresentation, as a curious paradox exists in which more and more megaprojects are being proposed despite their consistently poor performance against initial forecasts of budget, schedule, and benefits.
Downsides
Megaprojects are often affected by corruption, leading to higher cost and lower benefit. According to theEuropean Cooperation in Science and Technology
The European Cooperation in Science and Technology (COST Association) is running an EU-funded programme which enables researchers and innovators to set-up their own research networks in a wide range of scientific topics, called COST Actions. Whil ...
(COST), megaprojects are characterized both by "extreme complexity (both in technical and human terms) and by a long record of poor delivery". Megaprojects attract a lot of public attention because of substantial impacts on communities
A community is a Level of analysis, social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place (geography), place, Norm (social), norms, religion, values, Convention (norm), customs, or Identity (social science), identity. Communiti ...
, environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
, and budget
A budget is a calculation play, usually but not always financial, for a defined period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including time, costs and expenses, environmenta ...
s, and the high costs involved. Megaprojects can also be defined as "initiatives that are physical, very expensive, and public".
Examples
Megaprojects includespecial economic zone
A special economic zone (SEZ) is an area in which the business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are located within a country's national borders, and their aims include increasing trade balance, employment, increas ...
s, public building
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and fun ...
s, power plants
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.
Many pow ...
, dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
s, airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface ...
s, seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
s, bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
s, highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access ...
s, tunnel
A tunnel is an underground passageway, dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, and enclosed except for the entrance and exit, commonly at each end. A pipeline is not a tunnel, though some recent tunnels have used immersed tube cons ...
s, railways
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
, wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industr ...
projects, oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
extraction projects, aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astrona ...
projects, weapons system
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, s ...
s, information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information technology system (I ...
systems, large-scale sporting event
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, t ...
s and, more recently, mixed use waterfront redevelopments; however, the most common megaprojects are in the categories of hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
facilities, nuclear power plants, and large public transportation projects. Megaprojects can also include large-scale high-cost initiatives in scientific research and infrastructure, such as the sequencing of the human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the n ...
, a significant global advance in genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar wor ...
and biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
.
According to Bent Flyvbjerg
Bent Flyvbjerg is a Danish economic geographer. He was the First BT Professor and Inaugural Chair of Major Programme Management at Oxford University's Saïd Business School (retiring from the post in 2021) and is the Villum Kann Rasmussen Profess ...
, "As a general rule of thumb, 'megaprojects' are measured in billions of dollars, 'major projects' in hundreds of millions, and 'projects' in millions and tens of millions."
Rationale
The logic on which many of the typical megaprojects are built is collective benefits; for example electricity for everybody (who can pay), road access (for those that have cars), etc. They may also serve as a means to open frontiers. Megaprojects have been criticised for their top-down planning processes and their ill effects on certain communities. Large scale projects often advantage one group of people while disadvantaging another, for instance, theThree Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downstream of the Three Gorges. The Three Gorges Dam has been the world ...
in China, the largest hydroelectric project in the world, required the displacement of 1.2 million farmers. In the 1970s, the highway revolts
Highway revolts (also freeway revolts, expressway revolts, or road protests) are organized protests against the planning or construction of highways, freeways, expressways, and other civil engineering projects that favor vehicles.
Many freeway re ...
in some Western nations saw urban activists opposing government plans to demolish buildings for freeway route construction, on the basis that such demolitions would unfairly disadvantage the urban working class and benefit commuters. Anti-nuclear protests against proposed nuclear power plants in the United States and Germany prevented developments due to environmental and social concerns.
More recently, new types of megaprojects have been identified that no longer follow the old models of being singular and monolithic in their purposes, but have become quite flexible and diverse, such as waterfront redevelopment schemes that seem to offer something to everybody. However, just like the old megaprojects, the new ones also foreclose "upon a wide variety of social practices, reproducing rather than resolving urban inequality and disenfranchisement". Because of their plethora of land uses "these mega-projects inhibit the growth of oppositional and contestational practices". The collective benefits that are often the underlying logic of a mega-project, are here reduced to an individualized form of public benefit.
Flyvbjerg argues that policymakers are attracted to megaprojects for four reasons:
* Technological sublime: the rapture that engineers and technologists get from building large and innovative projects, pushing the boundaries for what technology can do.
* Political sublime: the rapture politicians get from building monuments to themselves and for their causes.
* Economic sublime: the delight business people and trade unions receive from the profits and jobs created by megaprojects.
* Aesthetic sublime: the pleasure designers and people who appreciate good design get from building, using, and looking at something very large that is also iconically beautiful.
Economics
Proponents ofinfrastructure-based development
Infrastructure-based economic development, also called infrastructure-driven development, combines key policy characteristics inherited from the Rooseveltian progressivist tradition and neo-Keynesian economics in the United States, France's Gaull ...
advocate for funding large-scale projects to create long-term economic benefits. Investing in megaprojects in order to stimulate the general economy has been a popular policy measure since the economic crisis of the 1930s. Recent examples are the 2008–2009 Chinese economic stimulus program
The 2008–09 Chinese economic stimulus plan () is a RMB¥ 4 trillion (US$586 billion) stimulus package announced by the State Council of the People's Republic of China on 9 November 2008 as an attempt to minimize the impact of the financial c ...
, the 2008 European Union stimulus plan, and the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) (), nicknamed the Recovery Act, was a stimulus package enacted by the 111th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama in February 2009. Developed in response to the Gr ...
.
Megaprojects often raise capital based on expected returns—though projects often go overbudget and over time, and market conditions like commodity prices can change. Concern at cost overruns is often expressed by critics of megaprojects during the planning phase. Bent Flyvbjerg has noted the existence of incentives to overstate income, underestimate costs, and exaggerate future social and economic benefits due to lack of accountability and risk-sharing mechanisms. If the megaproject is delivered in a country with relevant corruption the likelihood and magnitude of having overbudgets increases.
One of the most challenging aspects of megaprojects is obtaining sufficient funding. Alan Altshuler and David Luberoff have found that creative and politically adept political leadership is required to secure resources as well as generate public support, mollify critics, and manage conflict through many years of planning, authorization and implementation. Other challenges faced by those planning megaprojects include laws and regulations that empower community groups, contested information and methodologies, high levels of uncertainty, avoiding impacts on neighborhoods and the environment, and attempting to solve a wicked problem
In planning and policy, a wicked problem is a problem that is difficult or impossible to solve because of incomplete, contradictory, and changing requirements that are often difficult to recognize. It refers to an idea or problem that cannot be fix ...
.Plotch, Philip Mark. What’s Taking So Long? Identifying the Underlying Causes of Delays in Planning Transportation Megaprojects in the United States. Journal of Planning Literature. Available online January 8, 2015.
See also
*List of megaprojects
This is a list of megaprojects, which may be defined as:
* Projects that cost more than US$1 billion and attract a large amount of public attention because of substantial impacts on communities, the natural and built environment, and budgets.
* ...
* List of transport megaprojects
This is a list of megaprojects within the transport sector. Care should be taken in comparing the cost of projects from different times, even a few years apart due to inflation; comparing nominal costs without taking this into account can be hig ...
* Macro-engineering
In engineering, macro-engineering (alternatively known as macroengineering or macro engineering and as mega engineering) is the implementation of extremely large-scale design projects. It can be seen as a branch of civil engineering or structural ...
* Megastructure
A megastructure is a very large artificial object, although the limits of precisely how large vary considerably. Some apply the term to any especially large or tall building. Some sources define a megastructure as an enormous self-supporting a ...
* Reference class forecasting
Reference class forecasting or comparison class forecasting is a method of predicting the future by looking at similar past situations and their outcomes. The theories behind reference class forecasting were developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos T ...
* Optimism bias
Optimism bias (or the optimistic bias) is a cognitive bias that causes someone to believe that they themselves are less likely to experience a negative event. It is also known as unrealistic optimism or comparative optimism.
Optimism bias is commo ...
* ''Megaprojects and Risk
''Megaprojects and Risk: An Anatomy of Ambition'' is a 2003 book by Bent Flyvbjerg, Nils Bruzelius, and Werner Rothengatter, published by Cambridge University Press. According to chief economist and director of transportation policy at Infrastruc ...
''
* ''When Technology Fails
''When Technology Fails'', edited by Neil Schlager, is a collection of 103 case studies about significant technological disasters, accidents, and failures of the 20th century. It was published in 1994 by Gale Research, Inc. It was one of the top ...
''
References
External links
Mega-project.eu, a website run by
European Cooperation in Science and Technology
The European Cooperation in Science and Technology (COST Association) is running an EU-funded programme which enables researchers and innovators to set-up their own research networks in a wide range of scientific topics, called COST Actions. Whil ...
Borovoye-Biocity
– megaproject of Bionic City for
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
– S. Rastorguev, M. Kudryashov, 2008
Catalogue of Catastrophe
– list of troubled large projects {{Construction overview Engineering projects Risk management