Medieval somalia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Somalia ( so, Soomaaliya; ), officially the
 Somalia has been inhabited since at least the
Somalia has been inhabited since at least the
 In the classical period, the Somali city-states of
In the classical period, the Somali city-states of
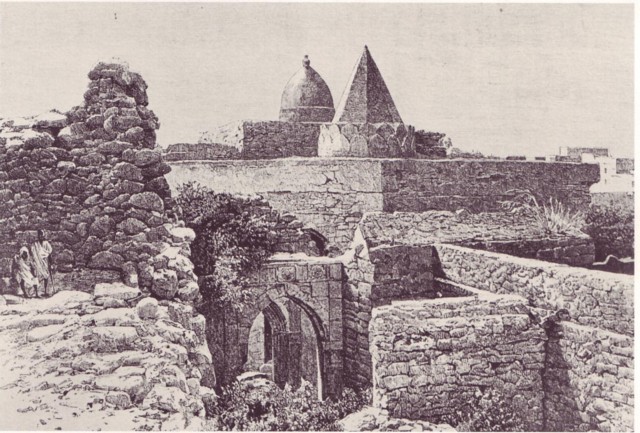
 The Sultanate of Mogadishu's first dynasty was established by Abubakr bin Fakhr ad-Din. This ruling house was succeeded by different dynasties like the Qahtani, Hilwaani and eventually the Muzaffar dynasty and remained a powerful regional trading city-state, being the first to make use of the gold mines in
The Sultanate of Mogadishu's first dynasty was established by Abubakr bin Fakhr ad-Din. This ruling house was succeeded by different dynasties like the Qahtani, Hilwaani and eventually the Muzaffar dynasty and remained a powerful regional trading city-state, being the first to make use of the gold mines in  The conquest of Shoa ignited a rivalry for supremacy between the Christian Solomonids and the Muslim Ifatites, which resulted in several devastating wars and ultimately ended in a Solomonic victory over the Kingdom of Ifat. Parts of northwestern Somalia came under the rule of the Solomonids in medieval times, especially during the reign of
The conquest of Shoa ignited a rivalry for supremacy between the Christian Solomonids and the Muslim Ifatites, which resulted in several devastating wars and ultimately ended in a Solomonic victory over the Kingdom of Ifat. Parts of northwestern Somalia came under the rule of the Solomonids in medieval times, especially during the reign of  Later on in the campaign, the Adalites were struck by a catastrophe when Sultan Mansur and his brother Muhammad were captured in battle by the Solomonids. Mansur was immediately succeeded by the youngest brother of the family
Later on in the campaign, the Adalites were struck by a catastrophe when Sultan Mansur and his brother Muhammad were captured in battle by the Solomonids. Mansur was immediately succeeded by the youngest brother of the family
 At the turn of the 16th century, Adal regrouped and, around 1527, under the charismatic leadership of Imam
At the turn of the 16th century, Adal regrouped and, around 1527, under the charismatic leadership of Imam  During the age of the Ajurans, the sultanates and republics of
During the age of the Ajurans, the sultanates and republics of 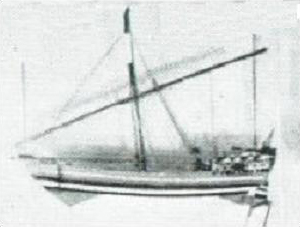 Mogadishu, the center of a thriving weaving industry known as ''toob benadir'' (specialized for the markets in Egypt and Syria), together with Merca and Barawa also served as transit stops for Swahili merchants from
Mogadishu, the center of a thriving weaving industry known as ''toob benadir'' (specialized for the markets in Egypt and Syria), together with Merca and Barawa also served as transit stops for Swahili merchants from  The 16th century Somali-Portuguese wars in East Africa meant that
The 16th century Somali-Portuguese wars in East Africa meant that
 In 1841, Haji
In 1841, Haji 
 In the late 19th century, after the
In the late 19th century, after the
 Governor De Vecchi's first plan was to disarm the sultanates. But, before the plan could be carried out, there had to be sufficient Italian troops in both sultanates. To make the enforcement of his plan more viable, he began to reconstitute the old Somali police corps, the ''Corpo Zaptié'', as a colonial force.
In preparation for the invasion plan of the sultanates, the Alula District, Alula Commissioner, E. Coronaro received orders in April 1924 to carry out a reconnaissance on the territories targeted for invasion. In spite of the 40-year Italian relationship with the sultanates, Italy did not have adequate knowledge of the geography. During this time, the Stefanini-Puccioni geological survey was scheduled to take place, so it was a good opportunity for the expedition of Coronaro to join with this.
Coronaro's survey concluded that the Majeerteen, Ismaan Sultanate (Majeerteen) depended on sea traffic, therefore, if this were blocked, any resistance that could be mounted after the invasion of the sultanate would be minimal. As the first stage of the invasion plan, Governor De Vecchi ordered the two Sultanates to disarm. The reaction of both sultanates was to object, as they felt the policy was in breach of the protectorate agreements. The pressure engendered by the new development forced the two rival sultanates to settle their differences over possession of Nugal, Somalia, Nugaal, and form a united front against their common enemy.
The
Governor De Vecchi's first plan was to disarm the sultanates. But, before the plan could be carried out, there had to be sufficient Italian troops in both sultanates. To make the enforcement of his plan more viable, he began to reconstitute the old Somali police corps, the ''Corpo Zaptié'', as a colonial force.
In preparation for the invasion plan of the sultanates, the Alula District, Alula Commissioner, E. Coronaro received orders in April 1924 to carry out a reconnaissance on the territories targeted for invasion. In spite of the 40-year Italian relationship with the sultanates, Italy did not have adequate knowledge of the geography. During this time, the Stefanini-Puccioni geological survey was scheduled to take place, so it was a good opportunity for the expedition of Coronaro to join with this.
Coronaro's survey concluded that the Majeerteen, Ismaan Sultanate (Majeerteen) depended on sea traffic, therefore, if this were blocked, any resistance that could be mounted after the invasion of the sultanate would be minimal. As the first stage of the invasion plan, Governor De Vecchi ordered the two Sultanates to disarm. The reaction of both sultanates was to object, as they felt the policy was in breach of the protectorate agreements. The pressure engendered by the new development forced the two rival sultanates to settle their differences over possession of Nugal, Somalia, Nugaal, and form a united front against their common enemy.
The  By 1 October, De Vecchi's plan was to go into action. The operation to invade Hobyo started in October 1925 . Columns of the new Zaptié began to move towards the sultanate. Hobyo, El Buur, Ceelbuur (El Buur), Galkayo, and the territory between were completely overrun within a month. Hobyo was transformed from a sultanate into an administrative region. Sultan Yusuf Ali surrendered. Nevertheless, soon suspicions were aroused as Trivulzio, the Hobyo commissioner, reported movement of armed men towards the borders of the sultanate before the takeover and after. Before the Italians could concentrate on the Majeerteen, they were diverted by new setbacks. On 9 November, the Italian fear was realized when a mutiny, led by one of the military chiefs of Sultan Ali Yusuf, Sultanate of Hobyo#Omar Samatar's Rebellion, Omar Samatar, recaptured El Buur. Soon the rebellion expanded to the local population. The region went into revolt as El-Dheere also came under the control of Omar Samatar. The Italian forces tried to recapture El Buur, but they were repulsed. On 15 November, the Italians retreated to Bud Bud and on the way they were ambushed and suffered heavy casualties.
While a third attempt was in the last stages of preparation, the operation's commander, Lieutenant-Colonel Splendorelli, was ambushed between Bud Bud and Buula Barde. He and some of his staff were killed. As a consequence of the death of the commander of the operations and the effect of two failed operations intended to overcome the El Buur mutiny, the spirit of Italian troops began to wane. The Governor took the situation seriously and, to prevent any more failure, he requested two battalions from Eritrea to reinforce his troops, and assumed lead of the operations. Meanwhile, the rebellion was gaining sympathy across the country, and as far afield as Ogaden, Western Somalia.
The fascist government was surprised by the setback in Hobyo. The whole policy of conquest was collapsing under its nose. The El-Buur episode drastically changed the strategy of Italy as it revived memories of the Battle of Adwa, Adwa fiasco when Italy had been defeated by Abyssinia. Furthermore, in the Colonial Ministry in Rome, senior officials distrusted the Governor's ability to deal with the matter. Rome instructed De Vecchi that he was to receive the reinforcement from Eritrea, but that the commander of the two battalions was to temporarily assume the military command of the operations and De Vecchi was to stay in Mogadishu and confine himself to other colonial matters. In the case of any military development, the military commander was to report directly to the Chief of Staff in Rome.
While the situation remained perplexing, De Vecchi moved the deposed sultan to Mogadishu. Fascist Italy was poised to re-conquer the sultanate by whatever means. To maneuver the situation within Hobyo, they even contemplated the idea of reinstating Ali Yusuf. However, the idea was dropped after they became pessimistic about the results.
To undermine the resistance, however, and before the Eritrean reinforcement could arrive, De Vecchi began to instill distrust among the local people by buying the loyalty of some of them. In fact, these tactics had better results than the military campaign had, and the resistance began gradually to wear down. Given the anarchy that would follow, the new policy was a success.
On the military front, Italian troops finally overran El Buur on 26 December 1925, and the forces of Omar Samatar were compelled to retreat to Western Somaliland.
By neutralising Hobyo, the fascists could concentrate on the Majeerteen. In early October 1924, E. Coronaro, the new Alula commissioner, presented Boqor (king) Osman Mahamuud with an ultimatum to disarm and surrender. Meanwhile, Italian troops began to pour into the sultanate in anticipation of this operation. While landing at Haafuun and Alula, the sultanate's troops opened fire on them. Fierce fighting ensued and to avoid escalating the conflict and to press the fascist government to revoke their policy, Boqor Osman tried to open a dialogue. However, he failed, and again fighting broke out between the two parties. Following this disturbance, on 7 October, the Governor instructed Coronaro to order the Sultan to surrender; to intimidate the people he ordered the seizure of all merchant boats in the Alula area. At Hafun, Arimondi bombarded and destroyed all the boats in the area.
By 1 October, De Vecchi's plan was to go into action. The operation to invade Hobyo started in October 1925 . Columns of the new Zaptié began to move towards the sultanate. Hobyo, El Buur, Ceelbuur (El Buur), Galkayo, and the territory between were completely overrun within a month. Hobyo was transformed from a sultanate into an administrative region. Sultan Yusuf Ali surrendered. Nevertheless, soon suspicions were aroused as Trivulzio, the Hobyo commissioner, reported movement of armed men towards the borders of the sultanate before the takeover and after. Before the Italians could concentrate on the Majeerteen, they were diverted by new setbacks. On 9 November, the Italian fear was realized when a mutiny, led by one of the military chiefs of Sultan Ali Yusuf, Sultanate of Hobyo#Omar Samatar's Rebellion, Omar Samatar, recaptured El Buur. Soon the rebellion expanded to the local population. The region went into revolt as El-Dheere also came under the control of Omar Samatar. The Italian forces tried to recapture El Buur, but they were repulsed. On 15 November, the Italians retreated to Bud Bud and on the way they were ambushed and suffered heavy casualties.
While a third attempt was in the last stages of preparation, the operation's commander, Lieutenant-Colonel Splendorelli, was ambushed between Bud Bud and Buula Barde. He and some of his staff were killed. As a consequence of the death of the commander of the operations and the effect of two failed operations intended to overcome the El Buur mutiny, the spirit of Italian troops began to wane. The Governor took the situation seriously and, to prevent any more failure, he requested two battalions from Eritrea to reinforce his troops, and assumed lead of the operations. Meanwhile, the rebellion was gaining sympathy across the country, and as far afield as Ogaden, Western Somalia.
The fascist government was surprised by the setback in Hobyo. The whole policy of conquest was collapsing under its nose. The El-Buur episode drastically changed the strategy of Italy as it revived memories of the Battle of Adwa, Adwa fiasco when Italy had been defeated by Abyssinia. Furthermore, in the Colonial Ministry in Rome, senior officials distrusted the Governor's ability to deal with the matter. Rome instructed De Vecchi that he was to receive the reinforcement from Eritrea, but that the commander of the two battalions was to temporarily assume the military command of the operations and De Vecchi was to stay in Mogadishu and confine himself to other colonial matters. In the case of any military development, the military commander was to report directly to the Chief of Staff in Rome.
While the situation remained perplexing, De Vecchi moved the deposed sultan to Mogadishu. Fascist Italy was poised to re-conquer the sultanate by whatever means. To maneuver the situation within Hobyo, they even contemplated the idea of reinstating Ali Yusuf. However, the idea was dropped after they became pessimistic about the results.
To undermine the resistance, however, and before the Eritrean reinforcement could arrive, De Vecchi began to instill distrust among the local people by buying the loyalty of some of them. In fact, these tactics had better results than the military campaign had, and the resistance began gradually to wear down. Given the anarchy that would follow, the new policy was a success.
On the military front, Italian troops finally overran El Buur on 26 December 1925, and the forces of Omar Samatar were compelled to retreat to Western Somaliland.
By neutralising Hobyo, the fascists could concentrate on the Majeerteen. In early October 1924, E. Coronaro, the new Alula commissioner, presented Boqor (king) Osman Mahamuud with an ultimatum to disarm and surrender. Meanwhile, Italian troops began to pour into the sultanate in anticipation of this operation. While landing at Haafuun and Alula, the sultanate's troops opened fire on them. Fierce fighting ensued and to avoid escalating the conflict and to press the fascist government to revoke their policy, Boqor Osman tried to open a dialogue. However, he failed, and again fighting broke out between the two parties. Following this disturbance, on 7 October, the Governor instructed Coronaro to order the Sultan to surrender; to intimidate the people he ordered the seizure of all merchant boats in the Alula area. At Hafun, Arimondi bombarded and destroyed all the boats in the area.
 On 13 October, Coronaro was to meet Boqor Osman at Bargal, Baargaal to press for his surrender. Under siege already, Boqor Osman was playing for time. However, on 23 October, Boqor Osman sent an angry response to the Governor defying his order. Following this a full-scale attack was ordered in November. Baargaal was bombarded and destroyed to the ground. This region was ethnically compact, and was out of range of direct action by the fascist government of Muqdisho. The attempt of the colonizers to suppress the region erupted into explosive confrontation. The Italians were meeting fierce resistance on many fronts. In December 1925, led by the charismatic leader Hersi Boqor, son of Boqor Osman, the sultanate forces drove the Italians out of Hurdia and Hafun, two strategic coastal towns. Another contingent attacked and destroyed an Italian communications centre at Cape Guardafui, at the tip of the Horn. In retaliation the ''Bernica'' and other warships were called on to bombard all main coastal towns of the Majeerteen. After a violent confrontation Italian forces captured Eyl (Eil), which until then had remained in the hands of Hersi Boqor. In response to the unyielding situation, Italy called for reinforcements from their other colonies, notably Eritrea. With their arrival at the closing of 1926, the Italians began to move into the interior where they had not been able to venture since their first seizure of the coastal towns. Their attempt to capture Dharoor Valley was resisted, and ended in failure.
De Vecchi had to reassess his plans as he was being humiliated on many fronts. After one year of exerting full force he could not yet manage to gain a result over the sultanate. In spite of the fact that the Italian navy sealed the sultanate's main coastal entrance, they could not succeed in stopping them from receiving arms and ammunition through it. It was only early 1927 when they finally succeeded in shutting the northern coast of the sultanate, thus cutting arms and ammunition supplies for the Majeerteen. By this time, the balance had tilted to the Italians' side, and in January 1927 they began to attack with a massive force, capturing Iskushuban, at the heart of the Majeerteen. Hersi Boqor unsuccessfully attacked and challenged the Italians at Iskushuban. To demoralise the resistance, ships were ordered to target and bombard the sultanate's coastal towns and villages. In the interior, the Italian troops confiscated livestock. By the end of the 1927, the Italians had taken full control of the sultanate. Hersi Boqor and his troops retreated to Ethiopia in order to rebuild their forces, but were unable to retake their territories, effectively ending the ''Campaign of the Sultanates''.
On 13 October, Coronaro was to meet Boqor Osman at Bargal, Baargaal to press for his surrender. Under siege already, Boqor Osman was playing for time. However, on 23 October, Boqor Osman sent an angry response to the Governor defying his order. Following this a full-scale attack was ordered in November. Baargaal was bombarded and destroyed to the ground. This region was ethnically compact, and was out of range of direct action by the fascist government of Muqdisho. The attempt of the colonizers to suppress the region erupted into explosive confrontation. The Italians were meeting fierce resistance on many fronts. In December 1925, led by the charismatic leader Hersi Boqor, son of Boqor Osman, the sultanate forces drove the Italians out of Hurdia and Hafun, two strategic coastal towns. Another contingent attacked and destroyed an Italian communications centre at Cape Guardafui, at the tip of the Horn. In retaliation the ''Bernica'' and other warships were called on to bombard all main coastal towns of the Majeerteen. After a violent confrontation Italian forces captured Eyl (Eil), which until then had remained in the hands of Hersi Boqor. In response to the unyielding situation, Italy called for reinforcements from their other colonies, notably Eritrea. With their arrival at the closing of 1926, the Italians began to move into the interior where they had not been able to venture since their first seizure of the coastal towns. Their attempt to capture Dharoor Valley was resisted, and ended in failure.
De Vecchi had to reassess his plans as he was being humiliated on many fronts. After one year of exerting full force he could not yet manage to gain a result over the sultanate. In spite of the fact that the Italian navy sealed the sultanate's main coastal entrance, they could not succeed in stopping them from receiving arms and ammunition through it. It was only early 1927 when they finally succeeded in shutting the northern coast of the sultanate, thus cutting arms and ammunition supplies for the Majeerteen. By this time, the balance had tilted to the Italians' side, and in January 1927 they began to attack with a massive force, capturing Iskushuban, at the heart of the Majeerteen. Hersi Boqor unsuccessfully attacked and challenged the Italians at Iskushuban. To demoralise the resistance, ships were ordered to target and bombard the sultanate's coastal towns and villages. In the interior, the Italian troops confiscated livestock. By the end of the 1927, the Italians had taken full control of the sultanate. Hersi Boqor and his troops retreated to Ethiopia in order to rebuild their forces, but were unable to retake their territories, effectively ending the ''Campaign of the Sultanates''.
 On 9 May 1936, Mussolini proclaimed the creation of the Italian Empire, calling it the ''Italian East Africa, Africa Orientale Italiana'' (A.O.I.) and formed by Italian Ethiopia, Ethiopia, Italian Eritrea, Eritrea and
On 9 May 1936, Mussolini proclaimed the creation of the Italian Empire, calling it the ''Italian East Africa, Africa Orientale Italiana'' (A.O.I.) and formed by Italian Ethiopia, Ethiopia, Italian Eritrea, Eritrea and
File:Somalia1911.png, Italian Somalia
File:Mogadischu Cathedral.jpg, Mogadiscio cathedral
File:CinemaitaliaMogadiscio.png, Cinema Italia in Mogadiscio, 1937
File:Fiatmogadiscio1940.png, Fiat building in Mogadiscio, 1940
File:ItaSomalia 1936 MiNr0237 pm Mogadishu B002.jpg, Italian stamp from Mogadiscio
File:1931-quaderno-Mogadiscio-palazzo-del-governatore.jpg, Governor's palace in Mogadiscio
 During World War II, Britain regained control of British Somaliland and conquered Italian Somaliland, administering both militarily as protectorates. In November 1945, during the Potsdam Conference, the United Nations granted Italy trusteeship of Italian Somaliland, but only under close supervision and on the condition—first proposed by the Somali Youth League (SYL) and other nascent Somali political organizations, such as Hizbia Digil Mirifle Somali (HDMS) and the Somali National League (SNL)—that Somalia achieve independence within ten years. British Somaliland remained a protectorate of Britain until 1960.
To the extent that Italy held the territory by UN mandate, the trusteeship provisions gave the Somalis the opportunity to gain experience in political education and self-government. These were advantages that British Somaliland, which was to be incorporated into the new Somali state, did not have. Although, in the 1950s, British colonial officials attempted, through various administrative development efforts, to make up for past neglect, the protectorate stagnated. The disparity between the two territories in economic development and political experience would cause serious difficulties when it came time to integrate the two parts.Helen Chapin Metz, ed. ''Somalia: A Country Study''. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1992
During World War II, Britain regained control of British Somaliland and conquered Italian Somaliland, administering both militarily as protectorates. In November 1945, during the Potsdam Conference, the United Nations granted Italy trusteeship of Italian Somaliland, but only under close supervision and on the condition—first proposed by the Somali Youth League (SYL) and other nascent Somali political organizations, such as Hizbia Digil Mirifle Somali (HDMS) and the Somali National League (SNL)—that Somalia achieve independence within ten years. British Somaliland remained a protectorate of Britain until 1960.
To the extent that Italy held the territory by UN mandate, the trusteeship provisions gave the Somalis the opportunity to gain experience in political education and self-government. These were advantages that British Somaliland, which was to be incorporated into the new Somali state, did not have. Although, in the 1950s, British colonial officials attempted, through various administrative development efforts, to make up for past neglect, the protectorate stagnated. The disparity between the two territories in economic development and political experience would cause serious difficulties when it came time to integrate the two parts.Helen Chapin Metz, ed. ''Somalia: A Country Study''. Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, 1992
countrystudies.us
/ref> Britain included the proviso that the Somali nomads would retain their autonomy, but Ethiopia immediately claimed sovereignty over them.Zolberg, Aristide R., et al., ''Escape from Violence: Conflict and the Refugee Crisis in the Developing World'', (Oxford University Press: 1992), p. 106 This prompted an unsuccessful bid by Britain in 1956 to buy back the Somali lands it had turned over. Britain also granted administration of the almost exclusively Somali-inhabited Northern Frontier District (NFD) to Kenyan nationalists despite an informal plebiscite demonstrating the overwhelming desire of the region's population to join the newly formed Somali Republic. A French Somaliland overseas territory referendum, 1958, referendum was held in neighboring Djibouti (then known as French Somaliland) in 1958, on the eve of Somalia's independence in 1960, to decide whether or not to join the Somali Republic or to remain with France. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, largely due to a combined yes vote by the sizable Afar people, Afar ethnic group and resident Europeans. There was also allegations of widespread vote rigging, with the French expelling thousands of Somalis before the referendum reached the polls.Kevin Shillington, ''Encyclopedia of African history'', (CRC Press: 2005), p. 360. The majority of those who voted "no" were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia, as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later.Barrington, Lowell, ''After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States'', (University of Michigan Press: 2006), p. 115 Djibouti finally gained its independence from France in 1977, and Hassan Gouled Aptidon, a Somali who had campaigned for a yes vote in the referendum of 1958, eventually wound up as Djibouti's first president (1977–1991).
On 1 July 1960, the two territories united to form the
A French Somaliland overseas territory referendum, 1958, referendum was held in neighboring Djibouti (then known as French Somaliland) in 1958, on the eve of Somalia's independence in 1960, to decide whether or not to join the Somali Republic or to remain with France. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, largely due to a combined yes vote by the sizable Afar people, Afar ethnic group and resident Europeans. There was also allegations of widespread vote rigging, with the French expelling thousands of Somalis before the referendum reached the polls.Kevin Shillington, ''Encyclopedia of African history'', (CRC Press: 2005), p. 360. The majority of those who voted "no" were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia, as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later.Barrington, Lowell, ''After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States'', (University of Michigan Press: 2006), p. 115 Djibouti finally gained its independence from France in 1977, and Hassan Gouled Aptidon, a Somali who had campaigned for a yes vote in the referendum of 1958, eventually wound up as Djibouti's first president (1977–1991).
On 1 July 1960, the two territories united to form the
The New Communist Third World: an essay in political economy
', (Taylor & Francis: 1982), p. 279 . The revolutionary army established large-scale public works programs and successfully implemented an urban and rural literacy campaign, which helped dramatically increase the literacy rate. In addition to a nationalization program of industry and land, the new regime's foreign policy placed an emphasis on Somalia's traditional and religious links with the Arab world, eventually joining the Arab League (AL) in 1974.Benjamin Frankel, ''The Cold War, 1945–1991: Leaders and other important figures in the Soviet Union, Eastern Europe, China, and the Third World'', (Gale Research: 1992), p. 306 . That same year, Barre also served as chairman of the Organization of African Unity (OAU), the predecessor of the African Union (AU).Oihe Yang, ''Africa South of the Sahara 2001'', 30th Ed., (Taylor and Francis: 2000), p. 1025 . In July 1976, Barre's SRC disbanded itself and established in its place the Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party (SRSP), a one-party government based on scientific socialism and Islamic tenets. The SRSP was an attempt to Revisionism (Marxism), reconcile the official state ideology with the official state religion by adapting Marxist precepts to local circumstances. Emphasis was placed on the Muslim principles of social progress, equality and justice, which the government argued formed the core of scientific socialism and its own accent on self-sufficiency, public participation and popular control, as well as direct ownership of the means of production. While the SRSP encouraged private investment on a limited scale, the administration's overall direction was essentially Communism, communist.
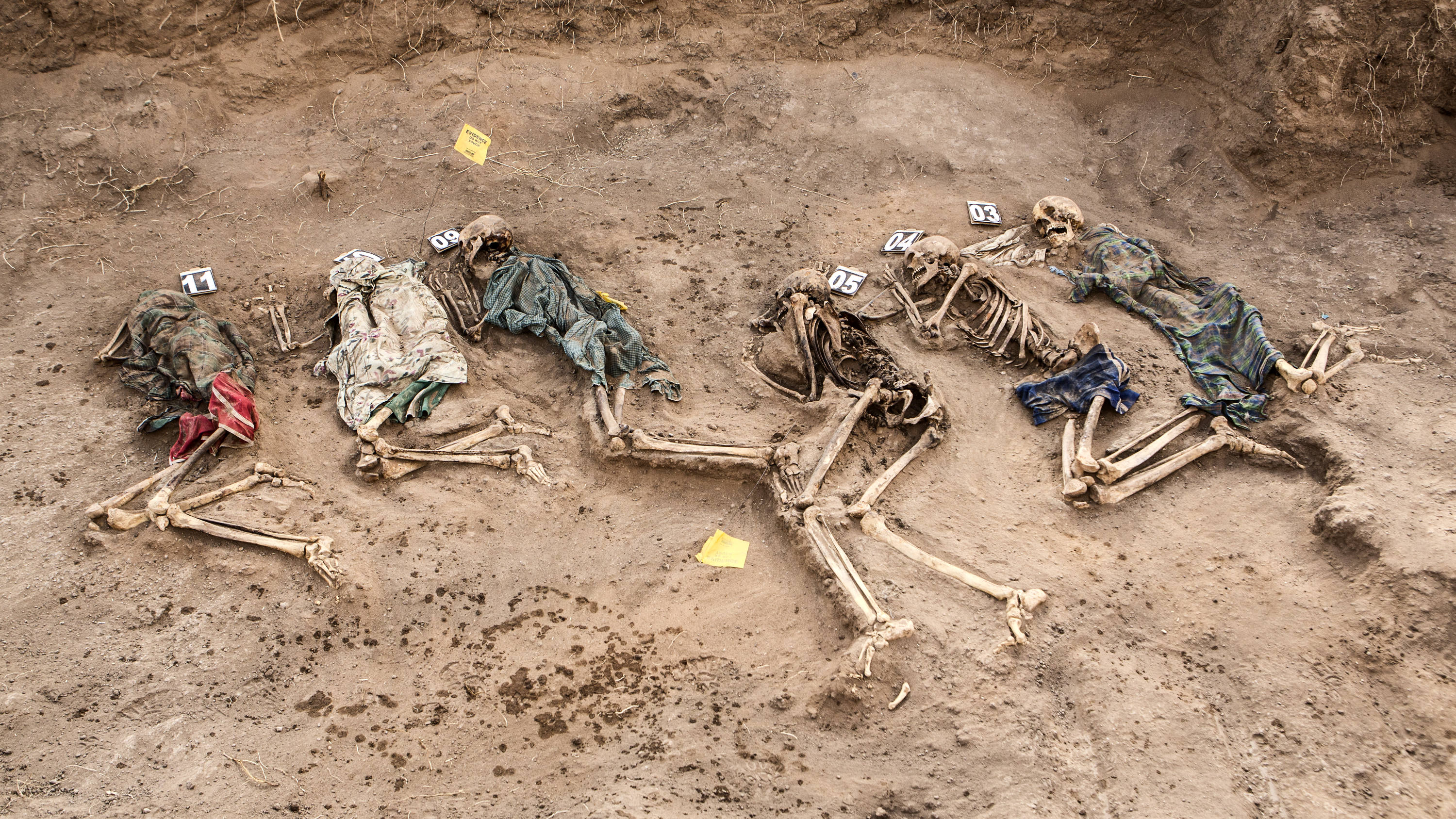 Isaaq genocide was the systematic, state-sponsored massacre of
Isaaq genocide was the systematic, state-sponsored massacre of
 A new constitution was promulgated in 1979 under which elections for a People's Assembly were held. However, Barre's Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party politburo continued to rule. In October 1980, the SRSP was disbanded, and the Supreme Revolutionary Council was re-established in its place.
A new constitution was promulgated in 1979 under which elections for a People's Assembly were held. However, Barre's Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party politburo continued to rule. In October 1980, the SRSP was disbanded, and the Supreme Revolutionary Council was re-established in its place.
 In May 1986, President Barre suffered serious injuries in a life-threatening automobile accident near Mogadishu, when the car that was transporting him smashed into the back of a bus during a heavy rainstorm.World of Information (Firm), ''Africa review'', (World of Information: 1987), p.213. He was treated in a hospital in Saudi Arabia for head injuries, broken ribs and shock over a period of a month.Arthur S. Banks, Thomas C. Muller, William Overstreet, ''Political Handbook of the World 2008'', (CQ Press: 2008), p.1198.National Academy of Sciences (U.S.). Committee on Human Rights, Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Committee on Health and Human Rights, ''Scientists and human rights in Somalia: report of a delegation'', (National Academies: 1988), p.9. Lieutenant General Mohamed Ali Samatar, then Vice President, subsequently served as de facto head of state for the next several months. Although Barre managed to recover enough to present himself as the sole presidential candidate for re-election over a term of seven years on 23 December 1986, his poor health and advanced age led to speculation about who would succeed him in power. Possible contenders included his son-in-law General Ahmed Suleiman Abdille, who was at the time the Minister of the Interior, in addition to Barre's Vice President Lt. Gen. Samatar.
By that time, Barre's government had become increasingly unpopular. Many Somalis had become disillusioned with life under military dictatorship. The regime was weakened further in the 1980s as the Cold War drew to a close and Somalia's strategic importance was diminished. The government became increasingly Totalitarianism, totalitarian, and resistance movements, encouraged by Ethiopia, sprang up across the country, eventually leading to the
In May 1986, President Barre suffered serious injuries in a life-threatening automobile accident near Mogadishu, when the car that was transporting him smashed into the back of a bus during a heavy rainstorm.World of Information (Firm), ''Africa review'', (World of Information: 1987), p.213. He was treated in a hospital in Saudi Arabia for head injuries, broken ribs and shock over a period of a month.Arthur S. Banks, Thomas C. Muller, William Overstreet, ''Political Handbook of the World 2008'', (CQ Press: 2008), p.1198.National Academy of Sciences (U.S.). Committee on Human Rights, Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Committee on Health and Human Rights, ''Scientists and human rights in Somalia: report of a delegation'', (National Academies: 1988), p.9. Lieutenant General Mohamed Ali Samatar, then Vice President, subsequently served as de facto head of state for the next several months. Although Barre managed to recover enough to present himself as the sole presidential candidate for re-election over a term of seven years on 23 December 1986, his poor health and advanced age led to speculation about who would succeed him in power. Possible contenders included his son-in-law General Ahmed Suleiman Abdille, who was at the time the Minister of the Interior, in addition to Barre's Vice President Lt. Gen. Samatar.
By that time, Barre's government had become increasingly unpopular. Many Somalis had become disillusioned with life under military dictatorship. The regime was weakened further in the 1980s as the Cold War drew to a close and Somalia's strategic importance was diminished. The government became increasingly Totalitarianism, totalitarian, and resistance movements, encouraged by Ethiopia, sprang up across the country, eventually leading to the
 With the political situation deteriorating, Barre's long-standing government in 1991 eventually collapsed under the pressure. The national army disbanded shortly afterwards.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 794 was unanimously passed on 3 December 1992, which approved a coalition of United Nations peacekeeping, United Nations peacekeepers led by the United States. Forming the Unified Task Force (UNITAF), the force was tasked with assuring security until humanitarian efforts aimed at stabilizing the situation were transferred to the UN. Landing in 1993, the UN peacekeeping coalition started the two-year United Nations Operation in Somalia II (UNOSOM II) primarily in the south to provide humanitarian relief.
Some militias that had seized power after the oust of Barre regime's interpreted the UN troops' presence as a threat to their hegemony. Consequently, several gun battles took place in Mogadishu between local gunmen and peacekeepers. Among these was the Battle of Mogadishu (1993), Battle of Mogadishu, an unsuccessful attempt by US troops to apprehend faction leader Mohamed Farah Aidid. The UN soldiers eventually withdrew altogether from the country on 3 March 1995, having incurred more significant casualties.
With the political situation deteriorating, Barre's long-standing government in 1991 eventually collapsed under the pressure. The national army disbanded shortly afterwards.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 794 was unanimously passed on 3 December 1992, which approved a coalition of United Nations peacekeeping, United Nations peacekeepers led by the United States. Forming the Unified Task Force (UNITAF), the force was tasked with assuring security until humanitarian efforts aimed at stabilizing the situation were transferred to the UN. Landing in 1993, the UN peacekeeping coalition started the two-year United Nations Operation in Somalia II (UNOSOM II) primarily in the south to provide humanitarian relief.
Some militias that had seized power after the oust of Barre regime's interpreted the UN troops' presence as a threat to their hegemony. Consequently, several gun battles took place in Mogadishu between local gunmen and peacekeepers. Among these was the Battle of Mogadishu (1993), Battle of Mogadishu, an unsuccessful attempt by US troops to apprehend faction leader Mohamed Farah Aidid. The UN soldiers eventually withdrew altogether from the country on 3 March 1995, having incurred more significant casualties.

BBC News, 29 December 2008. He also blamed the international community for its failure to support the government, and said that the speaker of parliament would succeed him in office per the Transitional Federal Charter of the Somali Republic, Charter of the Transitional Federal Government.
 Between May 31st and June 9th 2008, representatives of Somalia's federal government and the moderate Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia (ARS) group of Islamist rebels participated in peace talks in Djibouti brokered by the former United Nations Special Envoy to Somalia, Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah. The conference ended with a signed agreement calling for the withdrawal of Ethiopian troops in exchange for the cessation of armed confrontation. Parliament was subsequently expanded to 550 seats to accommodate ARS members, which then elected Sheikh Sharif Sheikh Ahmed, the former ARS chairman, to office. President Sharif shortly afterwards appointed Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke, the son of the assassinated former President Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke, as the nation's new Prime Minister.
With the help of a small team of African Union troops, the coalition government also began a Somali Civil War (2009–present), counteroffensive in February 2009 to assume full control of the southern half of the country. To solidify its rule, the TFG formed an alliance with the Islamic Courts Union, other members of the Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia, and Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a, a moderate Sufism, Sufi militia. Furthermore, Al-Shabaab and Hizbul Islam, the two main Islamist groups in opposition, began to fight amongst themselves in mid-2009.
As a truce, in March 2009, Somalia's coalition government announced that it would re-implement Shari'a as the nation's official judicial system.Shariah in Somalia
Between May 31st and June 9th 2008, representatives of Somalia's federal government and the moderate Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia (ARS) group of Islamist rebels participated in peace talks in Djibouti brokered by the former United Nations Special Envoy to Somalia, Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah. The conference ended with a signed agreement calling for the withdrawal of Ethiopian troops in exchange for the cessation of armed confrontation. Parliament was subsequently expanded to 550 seats to accommodate ARS members, which then elected Sheikh Sharif Sheikh Ahmed, the former ARS chairman, to office. President Sharif shortly afterwards appointed Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke, the son of the assassinated former President Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke, as the nation's new Prime Minister.
With the help of a small team of African Union troops, the coalition government also began a Somali Civil War (2009–present), counteroffensive in February 2009 to assume full control of the southern half of the country. To solidify its rule, the TFG formed an alliance with the Islamic Courts Union, other members of the Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia, and Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a, a moderate Sufism, Sufi militia. Furthermore, Al-Shabaab and Hizbul Islam, the two main Islamist groups in opposition, began to fight amongst themselves in mid-2009.
As a truce, in March 2009, Somalia's coalition government announced that it would re-implement Shari'a as the nation's official judicial system.Shariah in Somalia
– ''Arab News'' However, conflict continued in the southern and central parts of the country. Within months, the coalition government had gone from holding about 70% of south-central Somalia's conflict zones, territory which it had inherited from the previous Yusuf administration, to losing control of over 80% of the disputed territory to the Islamist insurgents. On 14 October 2010, diplomat Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed (Farmajo) was appointed the new Prime Minister of Somalia. The former Premier Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke resigned the month before following a protracted dispute with President Sharif over a proposed draft constitution. Per the Transitional Federal Government's (TFG) Transitional Federal Charter of the Somali Republic, Charter, Prime Minister Mohamed named a new Cabinet on 12 November 2010, which has been lauded by the international community. As had been expected, the allotted ministerial positions were significantly reduced in numbers, with only 18 administrative posts unveiled versus the previous government's bloated 39 portfolios. Only two Ministers from the previous Cabinet were reappointed: Hussein Abdi Halane, the former Minister of Finance and a well-regarded figure in the international community, was put in charge of a consolidated Ministry of Finance and Treasury; and Dr. Mohamud Abdi Ibrahim was reassigned to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a, a moderate Sufism, Sufi group and an important military ally of the TFG, was also accorded the key Interior and Labour ministries. The remaining ministerial positions were largely assigned to technocrats new to the Somali political arena.
In its first 50 days in office, Prime Minister Mohamed's new administration completed its first monthly payment of stipends to government soldiers, and initiated the implementation of a full biometric register for the security forces within a window of four months. Additional members of the Independent Constitutional Commission were also appointed to engage Somali constitutional lawyers, religious scholars and experts in Somali culture over the nation's upcoming new constitution, a key part of the government's Transitional Federal Tasks. In addition, high level federal delegations were dispatched to defuse clan-related tensions in several regions. According to the prime minister of Somalia, to improve transparency, Cabinet ministers fully disclosed their assets and signed a Ethical code, code of ethics.
An Anti-Corruption Commission with the power to carry out formal investigations and to review government decisions and protocols was also established so as to more closely monitor all activities by public officials. Furthermore, unnecessary trips abroad by members of government were prohibited, and all travel by ministers now require the Premier's consent. A budget outlining 2011's federal expenditures was also put before and approved by members of parliament, with the payment of civil service employees prioritized. In addition, a full audit of government property and vehicles is being put into place. On the war front, the new government and its AMISOM allies also managed to secure control of 60% of Mogadishu, where 80% of the capital's population now lives. According to the African Union and Prime Minister Mohamed, with increasing troop strength the pace of territorial gains is expected to greatly accelerate.
On 19 June 2011, Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed resigned from his position as Prime Minister of Somalia. Part of the controversial Kampala Accord's conditions, the agreement would also see the mandates of the President, the Parliament Speaker and Deputies extended until August 2012, after which point new elections are to be organized.Somalia: PM Mohamed Abdullahi Farmajo resigns
Per the Transitional Federal Government's (TFG) Transitional Federal Charter of the Somali Republic, Charter, Prime Minister Mohamed named a new Cabinet on 12 November 2010, which has been lauded by the international community. As had been expected, the allotted ministerial positions were significantly reduced in numbers, with only 18 administrative posts unveiled versus the previous government's bloated 39 portfolios. Only two Ministers from the previous Cabinet were reappointed: Hussein Abdi Halane, the former Minister of Finance and a well-regarded figure in the international community, was put in charge of a consolidated Ministry of Finance and Treasury; and Dr. Mohamud Abdi Ibrahim was reassigned to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a, a moderate Sufism, Sufi group and an important military ally of the TFG, was also accorded the key Interior and Labour ministries. The remaining ministerial positions were largely assigned to technocrats new to the Somali political arena.
In its first 50 days in office, Prime Minister Mohamed's new administration completed its first monthly payment of stipends to government soldiers, and initiated the implementation of a full biometric register for the security forces within a window of four months. Additional members of the Independent Constitutional Commission were also appointed to engage Somali constitutional lawyers, religious scholars and experts in Somali culture over the nation's upcoming new constitution, a key part of the government's Transitional Federal Tasks. In addition, high level federal delegations were dispatched to defuse clan-related tensions in several regions. According to the prime minister of Somalia, to improve transparency, Cabinet ministers fully disclosed their assets and signed a Ethical code, code of ethics.
An Anti-Corruption Commission with the power to carry out formal investigations and to review government decisions and protocols was also established so as to more closely monitor all activities by public officials. Furthermore, unnecessary trips abroad by members of government were prohibited, and all travel by ministers now require the Premier's consent. A budget outlining 2011's federal expenditures was also put before and approved by members of parliament, with the payment of civil service employees prioritized. In addition, a full audit of government property and vehicles is being put into place. On the war front, the new government and its AMISOM allies also managed to secure control of 60% of Mogadishu, where 80% of the capital's population now lives. According to the African Union and Prime Minister Mohamed, with increasing troop strength the pace of territorial gains is expected to greatly accelerate.
On 19 June 2011, Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed resigned from his position as Prime Minister of Somalia. Part of the controversial Kampala Accord's conditions, the agreement would also see the mandates of the President, the Parliament Speaker and Deputies extended until August 2012, after which point new elections are to be organized.Somalia: PM Mohamed Abdullahi Farmajo resigns
BBC.co.uk (19 June 2011). Retrieved 15 December 2011. Abdiweli Mohamed Ali, Mohamed's former Minister of Planning and International Cooperation, was later named permanent Prime Minister.
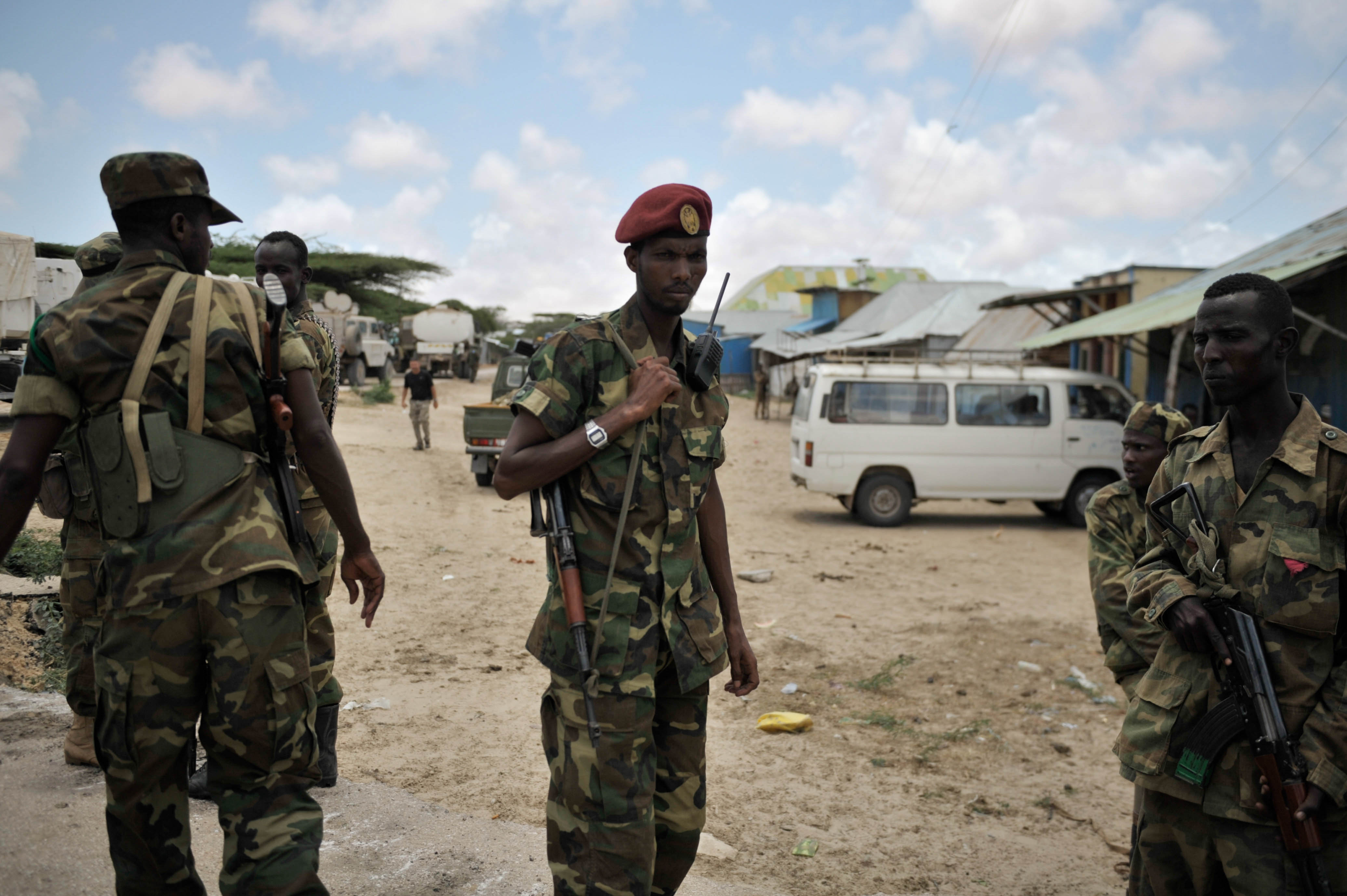
 In August 2013, the Somali federal government signed a national reconciliation agreement in Addis Ababa with the autonomous Jubaland administration based in southern Somalia. Endorsed by the federal State Minister for the Presidency Farah Abdulkadir on behalf of Hassan, the pact was brokered by the Foreign Ministry of Ethiopia and came after protracted bilateral talks. Under the terms of the agreement, Jubaland will be administered for a two-year period by a Juba Interim Administration and led by the region's incumbent president, Ahmed Mohamed Islam (Madobe). The regional president will serve as the chairperson of a new Executive Council, to which he will appoint three deputies. Management of Kismayo's seaport and airport will also be transferred to the Federal Government after a period of six months, and revenues and resources generated from these infrastructures will be earmarked for Jubaland's service delivery and security sectors as well as local institutional development. Additionally, the agreement includes the integration of Jubaland's military forces under the central command of the Somali National Army (SNA), and stipulates that the Juba Interim Administration will command the regional police. UN Special Envoy to Somalia Nicholas Kay hailed the pact as "a breakthrough that unlocks the door for a better future for Somalia,"
In August 2014, the Somali-government-led Operation Indian Ocean was launched against the Al-Shabaab (militant group), Al-Shabaab militant group to clean up the remaining insurgent-held pockets in the countryside.
On 17 December 2014, former Premier Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke was reappointed Prime Minister.
In February 2015, Hassan chaired a three-day consultation forum in
In August 2013, the Somali federal government signed a national reconciliation agreement in Addis Ababa with the autonomous Jubaland administration based in southern Somalia. Endorsed by the federal State Minister for the Presidency Farah Abdulkadir on behalf of Hassan, the pact was brokered by the Foreign Ministry of Ethiopia and came after protracted bilateral talks. Under the terms of the agreement, Jubaland will be administered for a two-year period by a Juba Interim Administration and led by the region's incumbent president, Ahmed Mohamed Islam (Madobe). The regional president will serve as the chairperson of a new Executive Council, to which he will appoint three deputies. Management of Kismayo's seaport and airport will also be transferred to the Federal Government after a period of six months, and revenues and resources generated from these infrastructures will be earmarked for Jubaland's service delivery and security sectors as well as local institutional development. Additionally, the agreement includes the integration of Jubaland's military forces under the central command of the Somali National Army (SNA), and stipulates that the Juba Interim Administration will command the regional police. UN Special Envoy to Somalia Nicholas Kay hailed the pact as "a breakthrough that unlocks the door for a better future for Somalia,"
In August 2014, the Somali-government-led Operation Indian Ocean was launched against the Al-Shabaab (militant group), Al-Shabaab militant group to clean up the remaining insurgent-held pockets in the countryside.
On 17 December 2014, former Premier Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke was reappointed Prime Minister.
In February 2015, Hassan chaired a three-day consultation forum in
CivicsWeb :*late 17th – late 19th century:
 :*20 July 1887 : British Somaliland protectorate (in the north) subordinated to
:*20 July 1887 : British Somaliland protectorate (in the north) subordinated to
Federal Republic of Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
( so, Jamhuuriyadda Federaalka Soomaaliya, ) and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Dimuqraadiya Soomaaliyeed; ar, الجمهورية الديمقراطية الصومالية, ; it, Repubblica Democratica Somala) was the name that the socialist military government gave to Som ...
, is a country located in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
. The country was an important centre for commerce with the rest of the ancient world, and according to most scholars, it is among the most probable locations of the fabled ancient Land of Punt
The Land of Punt ( Egyptian: '' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported gold, aromatic resins, blackwood, ebony, ivory an ...
.Christine El Mahdy, ''Egypt : 3000 Years of Civilization Brought to Life'', (Raincoast Books: 2005), p.297.Stefan Goodwin, ''Africa's legacies of urbanization: unfolding saga of a continent'', (Lexington Books: 2006), p. 48. During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, several powerful Somali states and port towns dominated the regional trade, the Mogadishu Sultanate
The Sultanate of Mogadishu ( so, Saldanadda Muqdisho, ar, سلطنة مقديشو) ( fl.9th- 13th centuries), also known as the Kingdom of Magadazo, was a medieval Somali sultanate centered in southern Somalia. It rose as one of the pre-eminent ...
and Ajuran Sultanate
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in the ...
both centered around the port town Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port ...
, but also the port towns of Barawe
Barawa ( so, Baraawe, Maay: ''Barawy'', ar, ﺑﺮﺍﻭة ''Barāwa''), also known as Barawe and Brava, is the capital of the South West State of Somalia.Pelizzari, Elisa. "Guerre civile et question de genre en Somalie. Les événements et l ...
and Merca
Merca ( so, Marka, Maay Maay, Maay: ''Marky'', ar, مركة) is a historic port city in the southern Lower Shebelle province of Somalia. It is located approximately to the southwest of the nation's capital Mogadishu. Merca is the traditional home ...
.
In the late 19th century, through a succession of treaties with these kingdoms, the Italian colonial empire
The Italian colonial empire ( it, Impero coloniale italiano), known as the Italian Empire (''Impero Italiano'') between 1936 and 1943, began in Africa in the 19th century and comprised the colonies, protectorates, concessions and dependencie ...
gained control of parts of the coast, and established the colony of Italian Somaliland
Italian Somalia ( it, Somalia Italiana; ar, الصومال الإيطالي, Al-Sumal Al-Italiy; so, Dhulka Talyaaniga ee Soomaalida), was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th centur ...
.. In southern parts of Somalia, the Italians fought a decades-long war, dubbed the Banadir Resistance
The Bimal Resistance also known as Bimal revolt, Bimal resistance or Merca revolt was a guerrilla war against the Italian Somaliland in southern Somalia. Named after the Bimal clan since they were the major element in the resistance. It was fough ...
, with the Somalis around the port town of Merca
Merca ( so, Marka, Maay Maay, Maay: ''Marky'', ar, مركة) is a historic port city in the southern Lower Shebelle province of Somalia. It is located approximately to the southwest of the nation's capital Mogadishu. Merca is the traditional home ...
. Italy acquired full control of the northeastern, central and southern parts of the territory after successfully waging a Campaign of the Sultanates against the ruling Majeerteen Sultanate
The Majeerteen Sultanate ( so, Suldanadda Majeerteen 𐒈𐒚𐒐𐒆𐒖𐒒𐒖𐒆𐒆𐒖 𐒑𐒖𐒃𐒜𐒇𐒂𐒜𐒒, lit=Boqortooyada Majerteen, ar, سلطنة مجرتين), also known as Majeerteen Kingdom or Majeerteenia and Migiu ...
and the Sultanate of Hobyo
The Sultanate of Hobyo ( so, Saldanadda Hobyo, ar, سلطنة هوبيو), also known as the Sultanate of Obbia,''New International Encyclopedia'', Volume 21, (Dodd, Mead: 1916), p.283. was a 19th-century Somali people, Somali kingdom in present ...
. This occupation lasted until 1941 when it was replaced by a British military administration
Military administration identifies both the techniques and systems used by military departments, agencies, and armed services involved in managing the armed forces. It describes the processes that take place within military organisations outsid ...
.
In 1950, the Trust Territory of Somaliland under Italian administration was established as a United Nations Trusteeship
Chapter XII of the United Nations Charter deals with the international trusteeship system. It reaffirms the twin goals mentioned in Chapter XI to "promote the political, economic, social, and educational advancement of the inhabitants of the tr ...
, with a promise of independence after 10 years. British Somaliland, nominally independent as the State of Somaliland
The State of Somaliland (, ) was a short-lived independent country in the territory of present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland. It existed on the territory of former British Somaliland for five days between 26 June 1960 and 1 ...
(now Somaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still conside ...
) for four days, merged as planned with the trust territory in 1960. Together, they formed the independent Somali Republic
The Somali Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Soomaaliyeed; it, Repubblica Somala; ar, الجمهورية الصومالية, Jumhūriyyat aṣ-Ṣūmālīyyah) was a sovereign state composed of Somalia and Somaliland, following the unification o ...
under a civilian government, the Somali National Assembly, headed by Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf
Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf ( so, Xaaji Bashiir Ismaaciil Yuusuf, ar, حاجي بشير اسماعيل يوسف) (b. 1912 in Hobyo, Somalia – d. 1984 in Cairo, Egypt), commonly referred to as Haji Bashir,SAMIULLAH, MUHAMMAD. DEVELOPMENT OF CREATI ...
. The administration lasted until 1969, when the Supreme Revolutionary Council led by Mohamed Siad Barre
Mohamed Siad Barre ( so, Maxamed Siyaad Barre, Osmanya script: ; ar, محمد سياد بري; c. 1910 – 2 January 1995) was a Somali head of state and general who served as the 3rd president of the Somali Democratic Republic from 1969 to 199 ...
, seized power in a bloodless coup and renamed the country the Somali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Dimuqraadiya Soomaaliyeed; ar, الجمهورية الديمقراطية الصومالية, ; it, Repubblica Democratica Somala) was the name that the socialist military government gave to Som ...
. In 1991, the Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War ( so, Dagaalkii Sokeeye ee Soomaaliya; ar, الحرب الأهلية الصومالية ) is an ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the Military dictatorship, military junta wh ...
divided the entire country. Despite the establishment of the Interim
An interim is a period of temporary pause or change in a sequence of events, or a temporary state, and is often applied to transitional political entities.
Interim may also refer to:
Temporary organizational arrangements (general concept)
*Provis ...
, Transitional, and Federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
s, Somalia remains divided with Somaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still conside ...
gaining ''de facto'' independence.
Prehistory
 Somalia has been inhabited since at least the
Somalia has been inhabited since at least the Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
, when the Doian and Hargeisan cultures flourished. The oldest evidence of burial customs in the Horn of Africa comes from cemeteries in Somalia dating back to the 4th millennium BC. The stone implements from the Jalelo site in the north (about halfway between Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
and Hargeisa
Hargeisa (; so, Hargeysa, ar, هرجيسا) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland. It is located in the Maroodi Jeex region of the Horn of Africa. It succeeded Burco as the capital of the British Somaliland Protector ...
) were also characterized in 1909 as important artefacts demonstrating the archaeological universality during the Paleolithic between the East and the West.
According to linguists, the first Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic su ...
-speaking populations arrived in the region during the ensuing Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period from the family's proposed urheimat
In historical linguistics, the homeland or ''Urheimat'' (, from German '' ur-'' "original" and ''Heimat'', home) of a proto-language is the region in which it was spoken before splitting into different daughter languages. A proto-language is the r ...
("original homeland") in the Nile Valley
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest rive ...
, or the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
. Other scholars propose that the Afro-Asiatic family developed in situ in the Horn, with its speakers subsequently dispersing from there.
The Laas Geel
Laas Geel ( so, Laas Geel), also spelled Laas Gaal, are cave formations on the rural outskirts of Hargeisa, Somaliland, situated in the Maroodi Jeex region of the country. They contain some of the earliest known cave paintings of domesticated Afr ...
cave complex on the outskirts of Hargeisa
Hargeisa (; so, Hargeysa, ar, هرجيسا) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland. It is located in the Maroodi Jeex region of the Horn of Africa. It succeeded Burco as the capital of the British Somaliland Protector ...
in northwestern Somalia has rock art
In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also ...
which dates back around 5,000 years and has depicting both wild animals and decorated cows. Other cave painting
In archaeology, Cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,000 ye ...
s are found in the northern Dhambalin
Dhambalin ("half, vertically cut mountain") is an archaeological site in the central Sahil province of Somaliland. The sandstone rock shelter contains rock art depicting various animals such as horned cattle and goats, as well as giraffes, an ani ...
region, which feature one of the earliest known depictions of a hunter on horseback. The rock art is in the distinctive Ethiopian-Arabian style, dated to 1000 to 3000 BCE. Additionally, between the towns of Las Khorey
Las Khorey ( so, Laasqoray, ar, لاسقُرَى ) is a historic coastal town in the Sanaag region of Somaliland.
History
The Las Khorey settlement is several centuries old. Between the town and El Ayo lies Karinhegane, a site containing numero ...
and El Ayo
El Ayo ( so, Ceelaayo, ar, عيلايو), also known as El Ayum, is a coastal town in the eastern Sanaag region of Somaliland, near the border with Somalia. There is a base of the Puntland Maritime Police Force, which is effectively controlled ...
in northern Somalia lies Karinhegane
Karinhegane is an archaeological site in the eastern Sanaag region of Somaliland. It contains some unique polychrome rock art.
Overview
Karinhegane is situated between the towns of Las Khorey and El Ayo. It is the site of numerous cave paintings ...
, the site of numerous cave paintings of real and mythical animals. Each painting has an inscription below it, which collectively have been estimated to be around 2,500 years old.
Ancient
Ancient Somalia domesticated the camel somewhere between the third millennium and second millennium BCE from where it spread to Ancient Egypt and North Africa.Land of Punt
Ancient pyramidical structures,mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be consid ...
s, ruined cities and stone wall
Stone walls are a kind of masonry construction that has been used for thousands of years. The first stone walls were constructed by farmers and primitive people by piling loose field stones into a dry stone wall. Later, mortar and plaster ...
s found in Somalia (such as the Wargaade Wall
Wargaade Wall is an ancient stone construction in Wargaade, Somalia. It enclosed a large historic settlement in the region.
Overview
Graves and unglazed sherds of pottery dating from antiquity have been found during excavations in the area. The ...
) are evidence of an old sophisticated civilization that once thrived in the Somali peninsula. The findings of archaeological excavations and research in Somalia show that this civilization enjoyed a lucrative trading relationship with Ancient Egypt and Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in ...
since the second millennium BCE. This supports the hypothesis of Somalia and/or the adjacent Horn territories corresponding with the ancient Land of Punt
The Land of Punt ( Egyptian: '' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported gold, aromatic resins, blackwood, ebony, ivory an ...
. The Puntites traded myrrh
Myrrh (; from Semitic, but see '' § Etymology'') is a gum-resin extracted from a number of small, thorny tree species of the genus ''Commiphora''. Myrrh resin has been used throughout history as a perfume, incense and medicine. Myrrh mi ...
, spices, gold, ebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus ''Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when pol ...
, short-horned cattle, ivory and frankincense
Frankincense (also known as olibanum) is an aromatic resin used in incense and perfumes, obtained from trees of the genus ''Boswellia'' in the family Burseraceae. The word is from Old French ('high-quality incense').
There are several species o ...
with the Ancient Egyptians, Phoenicians, Babylonians, Indians, Chinese and Romans through their commercial ports. An Ancient Egyptian expedition sent to Punt by the 18th dynasty Queen Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut (; also Hatchepsut; Egyptian: '' ḥꜣt- špswt'' "Foremost of Noble Ladies"; or Hatasu c. 1507–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the second historically confirmed female pharaoh, aft ...
is recorded on the temple reliefs at Deir el-Bahari
Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri ( ar, الدير البحري, al-Dayr al-Baḥrī, the Monastery of the North) is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part of ...
, during the reign of the Puntite King Parahu and Queen Ati. One of the main scholarly work on Punt, written from a native Somali standpoint, was by Somali historian Muxamed Ibraahim Muxamed, who wrote the work: ''Taariikhda Soomaaliya: dalkii filka weynaa ee punt''.
Somali City States
 In the classical period, the Somali city-states of
In the classical period, the Somali city-states of Mosylon
Mosylon ( grc, Μοσυλλόν and Μόσυλον), also known as Mosullon, was an ancient proto-Somali trading center on or near the site that later became the city of Bosaso.
History
Mosylon was the most prominent emporium on the Red Sea coas ...
, Opone
Opone ( grc, Οπώνη) was an ancient proto-Somali city situated in the Horn of Africa. It is primarily known for its trade with the Ancient Egyptians, Romans, Greeks, Persians, and the states of ancient India. Through archaeological remains, t ...
, Malao
Malao ( grc, Μαλαὼ) was an ancient proto-Somali port in present-day Somaliland. The town was situated on the site of what later became the city of Berbera. It was a key trading member involved in the Red Sea-Indian Ocean commerce in the ea ...
, Sarapion
Sarapion ( grc, Σαράπιον, also spelled Serapion) was an ancient proto-Somali port city in present-day Somalia. It was situated on a site that later became Mogadishu. Sarapion was briefly mentioned in Ptolemy's ''Geographia'' as one of the ...
, Mundus, Essina
Essina ( grc, Εσσίνα) was an ancient Proto-Somali emporium located on the southeastern coast of Somalia in the Horn of Africa.Ptolemy's Topography of Eastern Equatorial Africa, by Henry Schlichter Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Socie ...
and Tabae in Somalia developed a lucrative trade network
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
connecting with merchants from Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
, Ptolemic Egypt, Greece, Parthian Persia, Sheba
Sheba (; he, ''Šəḇāʾ''; ar, سبأ ''Sabaʾ''; Ge'ez: ሳባ ''Saba'') is a kingdom mentioned in the Hebrew Bible ( Old Testament) and the Quran. Sheba features in Jewish, Muslim, and Christian traditions, particularly the Ethiopian Ort ...
, Nabataea
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity.
The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, ...
and the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
. They used the ancient Somali maritime vessel known as the ''beden
The Beden, badan, or alternate type names Beden-seyed and Beden-safar, is a fast, ancient Somali single or double-masted maritime vessel and ship, typified by its towering stern-post and powerful rudder. It is also the longest surviving sewn boa ...
'' to transport their cargo.
After the Roman conquest of the Nabataean Empire and the Roman naval presence at Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 people. ...
to curb pillaging, Somali and Gulf Arab merchants by agreement barred Indian ships from trading in the free port cities of the Arabian peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
to protect the interests of Somali and Arab merchants in the extremely lucrative ancient Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
–Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
commerce.Eric Herbert Warmington, ''The Commerce Between the Roman Empire and India'', p. 229. However, Indian merchants continued to trade in the port cities of the Somali peninsula
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, which was free from Roman interference.
For centuries, the Indian merchants brought large quantities of cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, breakfa ...
from Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
to Somalia and Arabia. This is said to have been the best kept secret of the Somali and Gulf Arab merchants in their trade with the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
world. The Romans and Greeks believed the source of cinnamon to have been the Somali peninsula, but in reality, the highly valued product was brought to Somalia by way of Indian ships. Through collusive agreement by Somali and Gulf Arab traders, Indian/Chinese cinnamon was also exported for far higher prices to North Africa, the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
and Europe, which made the cinnamon trade a very profitable revenue generator, especially for the Somali merchants through whose hands large quantities were shipped across ancient sea and land routes.
Medieval

Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
was introduced to the northern Somali coast early on from the Arabian peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
, shortly after the hijra
Hijra, Hijrah, Hegira, Hejira, Hijrat or Hijri may refer to:
Islam
* Hijrah (often written as ''Hejira'' in older texts), the migration of Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE
* Migration to Abyssinia or First Hegira, of Muhammad's followers ...
. Zeila
Zeila ( so, Saylac, ar, زيلع, Zayla), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila (or Hawilah) with the Bibli ...
's two-mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla w ...
Masjid al-Qiblatayn
The Masjid al-Qiblatayn ( ar, مسجد القبلتين, lit=Mosque of the Two Qiblas), also spelt Masjid al-Qiblatain, is a mosque in Medina believed by Muslims to be the place where the final Islamic prophet, Muhammad, received the command to ...
dates to the 7th century, and is the oldest mosque in Africa. In the late 9th century, Al-Yaqubi
ʾAbū l-ʿAbbās ʾAḥmad bin ʾAbī Yaʿqūb bin Ǧaʿfar bin Wahb bin Waḍīḥ al-Yaʿqūbī (died 897/8), commonly referred to simply by his nisba al-Yaʿqūbī, was an Arab Muslim geographer and perhaps the first historian of world cultu ...
wrote that Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s were living along the northern Somali seaboard. He also mentioned that the Adal kingdom had its capital in the city, suggesting that the Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, or the Adal Empire or the ʿAdal or the Bar Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate, ''Adal ''Sultanate'') () was a medieval Sunni Muslim Empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din ...
with Zeila as its headquarters dates back to at least the 9th or 10th century. Adal's history from this founding period forth would be characterized by a succession of battles with neighbouring Abyssinia
The Ethiopian Empire (), also formerly known by the exonym Abyssinia, or just simply known as Ethiopia (; Amharic and Tigrinya: ኢትዮጵያ , , Oromo: Itoophiyaa, Somali: Itoobiya, Afar: ''Itiyoophiyaa''), was an empire that historica ...
.
Throughout the Middle Ages, Arab immigrants arrived in Somaliland, a historical experience which would later lead to the legendary stories about Muslim sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a ...
s such as Daarood
The Darod ( so, Daarood, ar, دارود) is a Somali clan. The forefather of this clan was Sheikh Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti, more commonly known as ''Darood''. The clan primarily settles the apex of the Horn of Africa and its peripherie ...
and Ishaaq bin Ahmed
Sheikh Ishaaq bin Ahmed bin Muhammad bin al-Hussein al-Hashimi, more commonly known as Sheikh Ishaaq or Sheikh Isaaq (, ) was the semi-legendary Arab forefather of the Somali Isaaq clan-family in the Horn of Africa, whose traditional territory i ...
(the purported ancestors of the Darod
The Darod ( so, Daarood, ar, دارود) is a Somali clan. The forefather of this clan was Sheikh Abdirahman bin Isma'il al-Jabarti, more commonly known as ''Darood''. The clan primarily settles the apex of the Horn of Africa and its peripherie ...
and Isaaq
The Isaaq (also Isaq, Ishaak, Isaac) ( so, Reer Sheekh Isxaaq, ar, بني إسحاق, Banī Isḥāq) is a Somali clan. It is one of the major Somali clans in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory. Per ...
clans, respectively) travelling from Arabia to Somalia and marrying into the local Dir clan.
 The Sultanate of Mogadishu's first dynasty was established by Abubakr bin Fakhr ad-Din. This ruling house was succeeded by different dynasties like the Qahtani, Hilwaani and eventually the Muzaffar dynasty and remained a powerful regional trading city-state, being the first to make use of the gold mines in
The Sultanate of Mogadishu's first dynasty was established by Abubakr bin Fakhr ad-Din. This ruling house was succeeded by different dynasties like the Qahtani, Hilwaani and eventually the Muzaffar dynasty and remained a powerful regional trading city-state, being the first to make use of the gold mines in Sofala
Sofala, at present known as Nova Sofala, used to be the chief seaport of the Mwenemutapa Kingdom, whose capital was at Mount Fura. It is located on the Sofala Bank in Sofala Province of Mozambique. It was founded by Somali merchants. This name wa ...
. Eventually at the end of the 16th century the Muzaffarid dynasty allied themselves to the Somali Ajuran Empire
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in the ...
For many years, Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port ...
stood as the pre-eminent city in the بلاد البربر, '' Bilad-al-Barbar'' ("Land of the Berbers"), which was the medieval Arab term for the Somali coast. Following his visit to the city, the 12th century Syrian historian Yaqut al-Hamawi
Yāqūt Shihāb al-Dīn ibn-ʿAbdullāh al-Rūmī al-Ḥamawī (1179–1229) ( ar, ياقوت الحموي الرومي) was a Muslim scholar of Byzantine Greek ancestry active during the late Abbasid period (12th-13th centuries). He is known fo ...
wrote that it was inhabited by "Berbers", the ancestors of the modern Somalis.
Amda Seyon I
Amda Seyon I ( gez, ዐምደ ፡ ጽዮን , am, አምደ ፅዮን , "Pillar of Zion"), throne name Gebre Mesqel (ገብረ መስቀል ) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1314 to 1344 and a member of the Solomonic dynasty.
He is best known ...
(r. 1314–1344). In 1403 or 1415 (under Emperor Dawit I
Dawit I ( gez, ዳዊት) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1382 to 6 October 1413, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. He was the younger son of Newaya Krestos.
Reign
Taddesse Tamrat discusses a tradition that early in his reign, Dawit campaigne ...
or Emperor Yeshaq I
Yeshaq I ( gez, ይሥሐቅ), throne name: Gabra Masqal II (Ge'ez: ገብረ መስቀል) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1414 to 1429/1430, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. He was the second son of Emperor Dawit I.
Ancestry
Of Amhara lin ...
, respectively), measures were taken against the Muslim Sultanate of Adal. The Emperor eventually captured King Sa'ad ad-Din II
Sa'ad ad-Din II ( ar, سعد الدين زنكي), reigned – c. 1403 or c. 1414, was a Sultan of the Ifat Sultanate. He was the brother of Haqq ad-Din II, and the father of Mansur ad-Din, Sabr ad-Din II and Badlay ibn Sa'ad ad-Din. The histori ...
of the Walashma dynasty
The Walashma dynasty was a medieval Muslim dynasty of the Horn of Africa. Founded in 1285, it was centered in Zeila, and established bases around the Horn of Africa. It governed the Sultanate of Ifat, Ifat and Adal Sultanate, Adal Sultanates in wh ...
in Zeila and had him executed. The Walashma Chronicle, however, records the date as 1415, which would make the Ethiopian victor Emperor Yeshaq I. After the war, the reigning king had his minstrels compose a song praising his victory, which contains the first written record of the word "Somali". Sa'ad ad-Din II's family was subsequently given safe haven at the court of the King of Yemen
The Imams of Yemen, later also titled the Kings of Yemen, were religiously consecrated leaders belonging to the Zaidiyyah branch of Shia Islam. They established a blend of religious and temporal-political rule in parts of Yemen from 897. Their i ...
, where his sons regrouped and planned their revenge on the Solomonids.
The oldest son Sabr ad-Din II
Sabr ad-Din III ( ar, الصبر الدين الثاني) (died 1422 or 1423) was a Sultan of Adal and the oldest son of Sa'ad ad-Din II. Sabr ad-Din returned to the Horn of Africa from Yemen to reclaim his father's realm. He defeated the Ethiop ...
built a new capital eastwards of Zeila known as Dakkar
Dakkar or Doggor, also known as Aw-Barkhadle () was a historical town located near Hargeisa in modern-day Somaliland. It was part of the Muslim empires in the Horn of Africa during the middle ages and served as the capital of the Adal Sultanate ...
and began referring to himself as the King of Adal. He continued the war against the Solomonic Empire. Despite his army's smaller size, he was able to defeat the Solomonids at the battles of Serjan and Zikr Amhara and consequently pillaged the surrounding areas. Many similar battles were fought between the Adalites and the Solomonids with both sides achieving victory and suffering defeat but ultimately Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
Sabr ad-Din II successfully managed to drive the Solomonic army out of Adal territory. He died a natural death and was succeeded by his brother Mansur ad-Din who invaded the capital and royal seat of the Solomonic Empire and drove Emperor Dawit II
Dawit II ( gez, ዳዊት; – 2 September 1540), also known by the macaronic name Wanag Segad (ወናግ ሰገድ, ''to whom the lions bow''), better known by his birth name Lebna Dengel ( am, ልብነ ድንግል, ''essence of the vi ...
to Yedaya where according to al-Maqrizi
Al-Maqrīzī or Maḳrīzī (Arabic: ), whose full name was Taqī al-Dīn Abū al-'Abbās Aḥmad ibn 'Alī ibn 'Abd al-Qādir ibn Muḥammad al-Maqrīzī (Arabic: ) (1364–1442) was a medieval Egyptian Arab historian during the Mamluk era, kn ...
, Sultan Mansur destroyed a Solomonic army and killed the Emperor. He then advanced to the mountains of Mokha, where he encountered a 30,000 strong Solomonic army. The Adalite soldiers surrounded their enemies and for two months besieged the trapped Solomonic soldiers until a truce was declared in Mansur's favour.
 Later on in the campaign, the Adalites were struck by a catastrophe when Sultan Mansur and his brother Muhammad were captured in battle by the Solomonids. Mansur was immediately succeeded by the youngest brother of the family
Later on in the campaign, the Adalites were struck by a catastrophe when Sultan Mansur and his brother Muhammad were captured in battle by the Solomonids. Mansur was immediately succeeded by the youngest brother of the family Jamal ad-Din II
Jamal ad-Din II ( ar, جمال اد الدين) (died 1433) was a Sultan of the Adal Sultanate. He was the youngest son of Sa'ad ad-Din II.Pankhurst, Richard. ''The Ethiopian Borderlands: Essays in Regional History from Ancient Times to the End ...
. Sultan Jamal reorganized the army into a formidable force and defeated the Solomonic armies at Bale, Yedeya and Jazja. Emperor Yeshaq I responded by gathering a large army and invaded the cities of Yedeya and Jazja but was repulsed by the soldiers of Jamal. Following this success, Jamal organized another successful attack against the Solomonic forces and inflicted heavy casualties in what was reportedly the largest Adalite army ever fielded. As a result, Yeshaq was forced to withdraw towards the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile (; ) is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the water ...
over the next five months, while Jamal ad Din's forces pursued them and looted much gold on the way, although no engagement ensued.
After returning home, Jamal sent his brother Ahmad with the Christian battle-expert Harb Jaush to successfully attack the province of Dawaro. Despite his losses, Emperor Yeshaq was still able to continue field armies against Jamal. Sultan Jamal continued to advance further into the Abyssinian heartland. However, Jamal on hearing of Yeshaq's plan to send several large armies to attack three different areas of Adal (including the capital), returned to Adal, where he fought the Solomonic forces at Harjai and, according to al-Maqrizi, this is where the Emperor Yeshaq died in battle. The young Sultan Jamal ad-Din II at the end of his reign had outperformed his brothers and forefathers in the war arena and became the most successful ruler of Adal to date. Within a few years, however, Jamal was assassinated by either disloyal friends or cousins around 1432 or 1433, and was succeeded by his brother Badlay ibn Sa'ad ad-Din
Badlay ibn Sa'ad ad-Din II ( ar, بادلاي بن سعد الدين) (also known as Sihab ad-Din Ahmad Badlay, Arwe Badlay – "Badlay the Beast" (died 1445) was a Sultan of the Sultanate of Adal and a son of Sa'ad ad-Din II. Brought numerous ...
. Sultan Badlay continued the campaigns of his younger brother and began several successful expeditions against the Christian empire. He recovered the Kingdom of Bali
The Kingdomship of Bali was a series of Hindu-Buddhist kingdoms that once ruled some parts of the volcanic island of Bali, in Lesser Sunda Islands, Indonesia. With a history of native Balinese kingship spanning from the early 10th to early 2 ...
and began preparations of a major Adalite offensive into the Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . ...
. He successfully collected funding from surrounding Muslim kingdoms as far away as the Kingdom of Mogadishu. However, these ambitious plans were thrown out the war chamber when King Badlay died during the invasion of Dawaro. He was succeeded by his son Muhammad ibn Badlay
Muhammad ibn Badlay ( ar, محمد بن بادلاي) (reigned 1445–1471) was a Sultan of the Sultanate of Adal. He was the son of Badlay ibn Sa'ad ad-Din. During his reign the Adalite ruler Muhammad and the Solomonic ruler Baeda Maryam agree ...
, who sent envoys to the Sultan of Mamluk Egypt
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16th ...
to gather support and arms in the continuing war against the Christian empire. The Adalite ruler Muhammad and the Solomonic ruler Baeda Maryam agreed to a truce and both states in the following decades saw an unprecedented period of peace and stability.
Early modern
Sultan Muhammad was succeeded by his son Shams ad Din, while Emperor Baeda Maryam was succeeded by his sonEskender
Eskender ( gez, እስክንድር, "Alexander"; 15 July 1471 – 7 May 1494) was Emperor of Ethiopia and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. His throne name was Kwestantinos II (Ge’ez: ቈስታንቲኖስ, "Constantine"). He was the son of Em ...
. During this time, period warfare broke out again between the two states and Emperor Eskender invaded Dakkar, where he was stopped by a large Adalite army, which destroyed the Solomonic army to such an extent that no further expeditions were carried out for the remainder of Eskender's reign. Adal, however, continued to raid the Christian empire unabated under the leadership of General Mahfuz
Mahfuz (or Mohammed) ( Harari: መሕፉዝ, ar, محفوظ; died July 1517) was a Harari Garad, Emir of Harar and Governor of Zeila in the Adal Sultanate.
Life and reign
Mahfuz led raids into the provinces of Abyssinia for a number of years. ...
, the leader of the Adalite war machine, who annually invaded the Christian territories. Eskender was succeeded by Emperor Na'od
Na'od ( gez, ናዖድ) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1494 to 31 July 1508, and a member of the Solomonic dynasty. His reign was marked by internal tension between territories with the assistance of Queen Eleni. He began construct an extravagant ch ...
, who tried to defend the Christians from General Mahfuz but he too was also killed in battle by the Adalite army in Ifat.
 At the turn of the 16th century, Adal regrouped and, around 1527, under the charismatic leadership of Imam
At the turn of the 16th century, Adal regrouped and, around 1527, under the charismatic leadership of Imam Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi
Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi ( so, Axmed Ibraahim al-Qaasi or Axmed Gurey, Harari: አሕመድ ኢብራሂም አል-ጋዚ, ar, أحمد بن إبراهيم الغازي ; 1506 – 21 February 1543) was an imam and general of the Adal Sultana ...
(Gurey in Somali, Gragn in Amharic
Amharic ( or ; (Amharic: ), ', ) is an Ethiopian Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is spoken as a first language by the Amharas, and also serves as a lingua franca for all oth ...
, both meaning "left-handed"), invaded Abyssinia. Adalite armies, with Ottoman arms and support, marched into Ethiopia and caused considerable damage on the highland state. Many historic churches, manuscripts and settlements were looted and burned during the campaigns. Adal's use of firearms, still only rarely used in Ethiopia, allowed the conquest of well over half of Ethiopia, reaching as far north as Tigray. The complete conquest of Ethiopia was averted by the timely arrival of a Portuguese expedition led by Cristóvão da Gama
Cristóvão da Gama ( 1516 – 29 August 1542), anglicised as Christopher da Gama, was a Portuguese military commander who led a Portuguese army of 400 musketeers on a crusade in Ethiopia (1541–1543) against the Adal Muslim army of Imam Ahmad ...
, son of the famed navigator Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira (; ; c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link E ...
. The Portuguese had been in the area earlier – in the early 16th century, in search of the legendary priest-king Prester John
Prester John ( la, Presbyter Ioannes) was a legendary Christian patriarch, presbyter, and king. Stories popular in Europe in the 12th to the 17th centuries told of a Nestorian patriarch and king who was said to rule over a Christian nation lost a ...
– and, although a diplomatic mission from Portugal, led by Rodrigo de Lima, had failed to improve relations between the countries, they responded to the Ethiopian pleas for help and sent a military expedition to their fellow Christians. A Portuguese fleet under the command of Estêvão da Gama was sent from Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a se ...
and arrived at Massawa
Massawa ( ; ti, ምጽዋዕ, məṣṣəwaʿ; gez, ምጽዋ; ar, مصوع; it, Massaua; pt, Maçuá) is a port city in the Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea, located on the Red Sea at the northern end of the Gulf of Zula beside the Dahlak ...
in February 1541. Here, he received an ambassador from the Emperor beseeching him to send help against the Muslims. In July, a force of 400 musketeer
A musketeer (french: mousquetaire) was a type of soldier equipped with a musket. Musketeers were an important part of early modern warfare particularly in Europe as they normally comprised the majority of their infantry. The musketeer was a pre ...
s, under the command of Cristóvão da Gama, younger brother of Estêvão, marched into the interior. Joined by Ethiopian troops, they were at first successful against the Muslims; but, they were subsequently defeated at the Battle of Wofla
The Battle of Wofla was fought on August 28, 1542 near Lake Ashenge in Wofla (Ofla) between the Portuguese under Cristóvão da Gama and the forces of Imam Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi. Reinforced with a superiority not only in numbers but in fir ...
(28 August 1542), and their commander captured and executed. On 21 February 1543, however, a joint Portuguese-Ethiopian force defeated the Muslim army at the Battle of Wayna Daga
The Battle of Wayna Daga was a large-scale battle between the Ethiopian forces assisted by Portuguese musketeers and cavalry and the forces of the Adal Sultanate and the Ottoman Empire in the east of Lake Tana in Ethiopia on 21 February 1543. ...
, in which Ahmed Gurey was killed and the war won. Ahmed Gurey's widow married his nephew Nur ibn Mujahid
Nur ibn Mujahid ibn ‘Ali ibn ‘Abdullah al Dhuhi Suha ( Harari: ኑር ኢብን ሙጃሂድ, so, Nuur ibn Mujaahid, ar, نور بن مجاهد; died 1567) was a Muslim Emir of Harar who ruled Sultanate of Harar. He was the primary reason fo ...
, in return for his promise to avenge Ahmed's death, who succeeded Ahmed Gurey, and continued hostilities against his northern adversaries until he killed the Ethiopian Emperor in his second invasion of Ethiopia.
 During the age of the Ajurans, the sultanates and republics of
During the age of the Ajurans, the sultanates and republics of Merca
Merca ( so, Marka, Maay Maay, Maay: ''Marky'', ar, مركة) is a historic port city in the southern Lower Shebelle province of Somalia. It is located approximately to the southwest of the nation's capital Mogadishu. Merca is the traditional home ...
, Mogadishu, Barawa
Barawa ( so, Baraawe, Maay Maay, Maay: ''Barawy'', ar, ﺑﺮﺍﻭة ''Barāwa''), also known as Barawe and Brava, is the capital city, capital of the South West State of Somalia, South West State of Somalia.Pelizzari, Elisa. "Guerre civile et ...
, Hobyo
Hobyo (; so, Hobyo), is an ancient port city in Galmudug state in the north-central Mudug region of Somalia.
Hobyo was founded as a coastal outpost by the Ajuran Empire during the 13th century.Lee V. Cassanelli, ''The shaping of Somali society: ...
and their respective ports flourished and had a lucrative foreign commerce with ships sailing to and coming from Arabia, India, Venetia, Persia, Egypt, Portugal and as far away as China. Vasco da Gama, who passed by Mogadishu in the 15th century, noted that it was a large city with houses of four or five storeys and big palaces in its centre and many mosques with cylindrical minaret
A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generall ...
s. In the 16th century, Duarte Barbosa
Duarte Barbosa (c. 14801 May 1521) was a Portuguese writer and officer from Portuguese India (between 1500 and 1516). He was a Christian pastor and scrivener in a ''feitoria'' in Kochi, and an interpreter of the local language, Malayalam. Barbosa ...
noted that many ships from the Kingdom of Cambaya in India sailed to Mogadishu with cloths and spices, for which they in return received gold, wax and ivory. Barbosa also highlighted the abundance of meat, wheat, barley, horses, and fruit on the coastal markets, which generated enormous wealth for the merchants.
Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town is ...
and Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban centre ...
and for the gold trade from Kilwa
Kilwa Kisiwani (English: ''Kilwa Island'') is an island, national historic site, and hamlet community located in the township of Kilwa Masoko, the district seat of Kilwa District in the Tanzanian region of Lindi Region in southern Tanzania. K ...
. Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
merchants from the Hormuz brought their Indian textile and fruit to the Somali coast in exchange for grain and wood. Trading relations were established with Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
in the 15th century with cloth, ambergris
Ambergris ( or , la, ambra grisea, fro, ambre gris), ''ambergrease'', or grey amber is a solid, waxy, flammable substance of a dull grey or blackish colour produced in the digestive system of sperm whales. Freshly produced ambergris has a mari ...
and porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises mainl ...
being the main commodities of the trade. Giraffes, zebras and incense were exported to the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
of China, which established Somali merchants as leaders in the commerce between the Asia and Africa. Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
merchants from Surat
Surat is a city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The word Surat literally means ''face'' in Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now ...
and Southeast African merchants from Pate, seeking to bypass both the Portuguese blockade and Omani meddling, used the Somali ports of Merca and Barawa (which were out of the two powers' jurisdiction) to conduct their trade in safety and without interference.
 The 16th century Somali-Portuguese wars in East Africa meant that
The 16th century Somali-Portuguese wars in East Africa meant that geopolitical
Geopolitics (from Greek γῆ ''gê'' "earth, land" and πολιτική ''politikḗ'' "politics") is the study of the effects of Earth's geography (human and physical) on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to ...
tensions would remain high and the increased contact between Somali sailors and Ottoman corsairs worried the Portuguese who actually sent multiple punitive expeditions against the Ajuran Empire
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in the ...
so that Portuguese could colonize the wealthy Somali port cities . Example, Barawa
Barawa ( so, Baraawe, Maay Maay, Maay: ''Barawy'', ar, ﺑﺮﺍﻭة ''Barāwa''), also known as Barawe and Brava, is the capital city, capital of the South West State of Somalia, South West State of Somalia.Pelizzari, Elisa. "Guerre civile et ...
under Tristão da Cunha
Tristão da Cunha (sometimes misspelled Tristão d'Acunha; ; c. 1460 – c. 1507) was a Portuguese explorer and naval commander. In 1499, he served as ambassador from King Manuel I of Portugal to Pope Leo X, leading a luxurious embassy presentin ...
was sacked in the Battle of Barawa
The Battle of Barawa was an armed military encounter between the Portuguese Empire and the Ajuran Sultanate, in the city of Barawa. The Portuguese staged a landing and achieved their objectives of sacking the city.
Battle
In February 1507, a ...
and the attack on Mogadishu by João de Sepúvelda was repelled, In the Battle of Benadir
The Battle of Benadir was an armed engagement between the Ajuran Sultanate and the Portuguese Empire.
Background
After the Portuguese conducted a large-scale naval expedition to Suez in 1541, the Ottoman Empire dedicated greater resources into ...
. Ottoman-Somali cooperation against the Portuguese in the Indian Ocean reached a high point in the 1580s when Ajuran clients of the Somali coastal cities began to sympathize with the Arabs and Swahilis under Portuguese rule
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas Colonialism, colonies, Factory ...
and sent an envoy to the Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
corsair Mir Ali Bey for a joint expedition against the Portuguese. He agreed and was joined by a Somali fleet, which began attacking Portuguese colonies in Southeast Africa
Southeast Africa or Southeastern Africa is an African region that is intermediate between East Africa and Southern Africa. It comprises the countries Botswana, Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, Tanzania ...
. The Somali-Ottoman offensive managed to drive out the Portuguese from several important cities such as Pate, Mombasa and Kilwa
Kilwa Kisiwani (English: ''Kilwa Island'') is an island, national historic site, and hamlet community located in the township of Kilwa Masoko, the district seat of Kilwa District in the Tanzanian region of Lindi Region in southern Tanzania. K ...
. However, the Portuguese governor sent envoys to India requesting a large Portuguese fleet. This request was answered and it reversed the previous offensive of the Muslims into one of defense. The Portuguese armada managed to re-take most of the lost cities and began punishing their leaders, but they refrained from attacking Mogadishu.
Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
, the main port of the Isaaq Sultanate
The Isaaq Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Isaaq, Wadaad: , ar, السلطنة الإسحاقية) was a Somali kingdom that ruled parts of the Horn of Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries. It spanned the territories of the Isaaq clan in modern ...
, was the most important port in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
between the 18th–19th centuries. For centuries, Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
had extensive trade relations with several historic ports in the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
. Additionally, the Somali and Ethiopian interiors were very dependent on Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
for trade, where most of the goods for export arrived from. During the 1833 trading season, the port town swelled to over 70,000 people, and upwards of 6,000 camels laden with goods arrived from the interior within a single day. Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
was the main marketplace in the entire Somali seaboard for various goods procured from the interior, such as livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals ...
, coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulant, stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
S ...
, frankincense
Frankincense (also known as olibanum) is an aromatic resin used in incense and perfumes, obtained from trees of the genus ''Boswellia'' in the family Burseraceae. The word is from Old French ('high-quality incense').
There are several species o ...
, myrrh
Myrrh (; from Semitic, but see '' § Etymology'') is a gum-resin extracted from a number of small, thorny tree species of the genus ''Commiphora''. Myrrh resin has been used throughout history as a perfume, incense and medicine. Myrrh mi ...
, acacia gum
Gum arabic, also known as gum sudani, acacia gum, Arabic gum, gum acacia, acacia, Senegal gum, Indian gum, and by other names, is a natural gum originally consisting of the hardened sap of two species of the '' Acacia'' tree, ''Senegalia sen ...
, saffron
Saffron () is a spice derived from the flower of ''Crocus sativus'', commonly known as the "saffron crocus". The vivid crimson stigma and styles, called threads, are collected and dried for use mainly as a seasoning and colouring agent i ...
, feathers
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier e ...
, ghee
Ghee is a type of clarified butter, originating from India. It is commonly used in India for cooking, as a traditional medicine, and for religious rituals.
Description
Ghee is typically prepared by simmering butter, which is churned from c ...
, hide (skin)
A hide or skin is an animal skin treated for human use.
The word "hide" is related to the German word "Haut" which means skin. The industry defines hides as "skins" of large animals ''e.g''. cow, buffalo; while skins refer to "skins" of smaller an ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
and ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals is ...
.
According to a trade journal published in 1856, Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
was described as "the freest port in the world, and the most important trading place on the whole Arabian Gulf".:
Historically, the port of Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
was controlled indigenously between the mercantile
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct exchan ...
Reer Ahmed Nuh and Reer Yunis Nuh sub-clans of the Habar Awal
The Habr Awal, also contemporarily known as the Subeer Awal, and alternately romanized as the Zubeyr Awal ( so, Habar Awal, ar, هبر أول, Full Name: '' Zubeyr ibn Abd al-Raḥmān ibn ash- Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad)'' is a major clan of ...
.
19th century
 In 1841, Haji
In 1841, Haji Sharmarke Ali Saleh
Sharmarke Ali Saleh ( so, Sharma'arke Cali Saalax ) was a leading 19th century Somali leader, captain, and merchant. He was known as "The African Rothschild " which indicates he was one of the richest man in Africa at that time and also the 'Polit ...
, a successful and ambitious Somali merchant, successfully invaded Zeila
Zeila ( so, Saylac, ar, زيلع, Zayla), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila (or Hawilah) with the Bibli ...
utilizing canons and Somali Musketeers. He deposed and imprisoned the port town's Arab ruler and succeeded him as the undisputed ruler of Zeila and its dependencies. Sharmarke's governorship had an instant effect on the city, as he maneuvered to monopolize as much of the regional trade as possible, with his sights set as far as Harar
Harar ( amh, ሐረር; Harari: ሀረር; om, Adare Biyyo; so, Herer; ar, هرر) known historically by the indigenous as Gey (Harari: ጌይ ''Gēy'', ) is a walled city in eastern Ethiopia. It is also known in Arabic as the City of Saint ...
and the Ogaden
Ogaden (pronounced and often spelled ''Ogadēn''; so, Ogaadeen, am, ውጋዴ/ውጋዴን) is one of the historical names given to the modern Somali Region, the territory comprising the eastern portion of Ethiopia formerly part of the Harargh ...
. In 1845, Sharmarke deployed a few matchlock men to wrest control of neighboring Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
from that town's then-feuding Somali authorities.
Sharmarke's influence was not limited to the coast as he had many allies in the interior of the Somali country and even further in Abyssinia. Among his allies were the Sultans of Shewa
Shewa ( am, ሸዋ; , om, Shawaa), formerly romanized as Shua, Shoa, Showa, Shuwa (''Scioà'' in Italian language, Italian), is a historical region of Ethiopia which was formerly an autonomous monarchy, kingdom within the Ethiopian Empire. The ...
. After the Amir of Harar Abu Bakr II ibn `Abd al-Munan arrested one of Sharmarke's agents in Harar
Harar ( amh, ሐረር; Harari: ሀረር; om, Adare Biyyo; so, Herer; ar, هرر) known historically by the indigenous as Gey (Harari: ጌይ ''Gēy'', ) is a walled city in eastern Ethiopia. It is also known in Arabic as the City of Saint ...
, there was tension between the two rulers. Sharmarke persuaded the son of Sahle Selassie
Sahle Selassie (Amharic: ሣህለ ሥላሴ, 1795 – 22 October 1847) was a ruler and later King of Shewa from 1813 to 1847. An important Amhara noble of Ethiopia, he was a younger son of Wossen Seged. Sahle Selassie was the father of numerou ...
, ruler of Shewa
Shewa ( am, ሸዋ; , om, Shawaa), formerly romanized as Shua, Shoa, Showa, Shuwa (''Scioà'' in Italian language, Italian), is a historical region of Ethiopia which was formerly an autonomous monarchy, kingdom within the Ethiopian Empire. The ...
, to imprison on his behalf about 300 citizens of Harar then resident in Shewa, for a length of two years.Burton, ''First Footsteps'', pp. 176 and note
Sultan Yusuf Mahamud Ibrahim
Yusuf Mahamud Ibrahim ( so, Yuusuf Maxamuud Ibrahiim, ar, يوسف محمود ابراهيم) was a Somali ruler. He was the third and most powerful Sultan of the Geledi sultanate, reigning from 1798 to 1848. Under the reign of Sultan Yusuf, his ...
, the third Sultan of the House of Gobroon, began the Golden age of the Gobroon dynasty. In 1843, his army came out victorious during the Bardheere
Bardera ( ar, بارديرا, so, Bardhere) is a city in Jubaland State of Somalia. It is the second largest and most populous city in Jubaland with Kismayo being the largest and most densely populated city in the region. Bardera sits on the Ju ...
''jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with Go ...
'', which restored stability in the region and revitalized the East African ivory trade
The ivory trade is the commercial, often illegal trade in the ivory tusks of the hippopotamus, walrus, narwhal, mammoth, and most commonly, African and Asian elephants.
Ivory has been traded for hundreds of years by people in Africa and Asia, ...
. He also received presents and had cordial relations with the leaders of neighbouring and distant kingdoms such as the Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
i, Wituland
Wituland (also Witu, Vitu, Witu Protectorate or Swahililand) was a territory of approximately in East Africa centered on the town of Witu just inland from Indian Ocean port of Lamu north of the mouth of the Tana River in what is now Kenya.
Hist ...
and Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
i sultans.
Sultan Ibrahim's son Ahmed Yusuf succeeded him and was one of the most important figures in 19th-century East Africa. He managed to gather 20 thousand Somali troops, invaded and captured the island of Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islands ...
, defeating the enemy troops and freeing the Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
slaves. Through his military dominance, Sultan Yusuf managed to exact tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
from the Omani king in the coastal town of Lamu
Lamu or Lamu Town is a small town on Lamu Island, which in turn is a part of the Lamu Archipelago in Kenya. Situated by road northeast of Mombasa that ends at Mokowe Jetty, from where the sea channel has to be crossed to reach Lamu Island. ...
.
In northern and southern Somalia, the Gerad Dynasty conducted trade with Yemen and Persia and competed with the merchants of the Bari Dynasty. The Gerads and the Bari Sultans built impressive palaces, castles and fortresses and had close relations with many different empires in the Near East.

 In the late 19th century, after the
In the late 19th century, after the Berlin Conference
The Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, also known as the Congo Conference (, ) or West Africa Conference (, ), regulated European colonisation and trade in Africa during the New Imperialism period and coincided with Germany's sudden emergence ...
, European powers began the Scramble for Africa, which inspired the Dervish leaders in the north like Mohammed Abdullah Hassan and Nur Ahmed Aman, Sultan Nur Ahmed Aman to rally support from across the Horn of Africa, but also Sheikh Abikar Gafle to start a resistance around Merca called the Banadir Resistance
The Bimal Resistance also known as Bimal revolt, Bimal resistance or Merca revolt was a guerrilla war against the Italian Somaliland in southern Somalia. Named after the Bimal clan since they were the major element in the resistance. It was fough ...
. Both the Banadir Resistance
The Bimal Resistance also known as Bimal revolt, Bimal resistance or Merca revolt was a guerrilla war against the Italian Somaliland in southern Somalia. Named after the Bimal clan since they were the major element in the resistance. It was fough ...
and Dervish Movement sparked the beginning one of the longest anti-colonial struggles on the continent.
Mohammed Abdullah Hassan's Dervish movement (Somali), Dervish movement spread into Somalia and successfully repulsed the British Empire four times, forcing them to retreat to the coastal region, but the Dervishes were finally defeated in 1920 by British airpower.
Banadir Resistance
In the 1890s, the Italian occupation of Marka sparked the beginning and outrage among the Bimaal, Bimal clan, many of them joined the Bimaal, Bimal resistance against Italy. An Italian resident of the city, Giacomo Trevis, was assassinated in 1904. In response Italy occupied the port town of Jazira about 30 miles south ofMogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port ...
. In response Bimal leaders called for a grand conference mobilizing the Banadiri clans, thus it came to eventually be known as the Banadir Resistance
The Bimal Resistance also known as Bimal revolt, Bimal resistance or Merca revolt was a guerrilla war against the Italian Somaliland in southern Somalia. Named after the Bimal clan since they were the major element in the resistance. It was fough ...
. The resistance was spearheaded by Sheikh Abdi Gafle and Ma’alin Mursal Abdi Yusuf; two prominent local Islamic teachers in Marka from the Bimal clan. The resistance, albeit clan-based initially transformed into one with a religious fervour, mainly Bimal, (but also later on some of the Wa’dan, Hintire and other clans of the Geledi confederation joined).
Dervish Movement
News of the incident that sparked the Dervish rebellion and the 21 years disturbance according to the consul-general James Hayes Sadler (colonial administrator), James Hayes Sadler was spread by Sultan Nur of the Habr Yunis. The incident in question was that of a group of Somali children that were converted to Christianity and adopted by the French Catholic missions, Catholic Mission atBerbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
in 1899. Whether Sultan Nur experienced the incident first hand or whether he was told of it is not clear but what is known is that he propagated the incident in the Tariqa at Kob Fardod in June 1899, precipitating the religious rebellion that later morphed into the Somali Dervish. In one of his letters to Deria Hassan, Sultan Deria in 1899, Hassan said that the British "''have destroyed our religion and made our children their children''" alluding to Sultan Nur's incident with the Roman French Mission at Berbera. The Dervish soon emerged as an opposition of the Christian activities, defending their version of Islam against the Christian mission. In several of his poems and speeches, Hassan insisted that the British and the Christian People of Ethiopia, Ethiopians in league with the British were bent upon plundering the political and religious freedom of the Somali nation. He soon emerged as "a champion of his country's political and religious freedom, defending it against all Christian invaders." Hassan issued a religious ordinance that any Somali national who did not accept the goal of unity of Somalia and would not fight under his leadership would be considered as ''kafir'' or ''gaal''. He soon acquired weapons from the Ottoman Empire, Sudan, and other sympathetic Muslim countries, and appointed ministers and advisers to administer different areas or sectors of Somalia. In addition, Hassan gave a clarion call for Somali unity and independence, in the process organizing his follower-warriors. His Dervish movement had an essentially military character, and the Dervish movement (Somali), Dervish movement was fashioned on the model of a Salihiya brotherhood. It was characterized by a rigid hierarchy and centralization. Hassan threatened to drive the Christians into the sea; he committed the first attack by launching his first major military offensive with his 1,500 Dervish equipped with 20 modern rifles on the British soldiers stationed in the region.
He repulsed the British in four expeditions and had favorable diplomatic relations with the Central Powers of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and German Empire, German Empires.
20th century
In 1920, the Dervish movement collapsed after intensive British aerial bombardments, and Dervish territories were subsequently turned into a protectorate. The dawn of fascism in the early 1920s heralded a change of strategy for Italy, as the north-eastern sultanates were soon to be forced within the boundaries of ''La Grande Somalia'' according to the plan of Italian Fascism, Fascist Italy. With the arrival of Governor Cesare Maria De Vecchi on 15 December 1923, things began to change for that part of History of Somaliland, Somaliland. Italy had access to these areas under the successive protection treaties, but not direct rule. The Fascist government had direct rule only over the Benadir territory Given the defeat of the Dervish movement in the early 1920s and the rise of fascism in Europe, on 10 July 1925, Benito Mussolini, Mussolini gave the green light to De Vecchi to start the takeover of the north-eastern sultanates. Everything was to be changed and the treaties abrogated. Governor De Vecchi's first plan was to disarm the sultanates. But, before the plan could be carried out, there had to be sufficient Italian troops in both sultanates. To make the enforcement of his plan more viable, he began to reconstitute the old Somali police corps, the ''Corpo Zaptié'', as a colonial force.
In preparation for the invasion plan of the sultanates, the Alula District, Alula Commissioner, E. Coronaro received orders in April 1924 to carry out a reconnaissance on the territories targeted for invasion. In spite of the 40-year Italian relationship with the sultanates, Italy did not have adequate knowledge of the geography. During this time, the Stefanini-Puccioni geological survey was scheduled to take place, so it was a good opportunity for the expedition of Coronaro to join with this.
Coronaro's survey concluded that the Majeerteen, Ismaan Sultanate (Majeerteen) depended on sea traffic, therefore, if this were blocked, any resistance that could be mounted after the invasion of the sultanate would be minimal. As the first stage of the invasion plan, Governor De Vecchi ordered the two Sultanates to disarm. The reaction of both sultanates was to object, as they felt the policy was in breach of the protectorate agreements. The pressure engendered by the new development forced the two rival sultanates to settle their differences over possession of Nugal, Somalia, Nugaal, and form a united front against their common enemy.
The
Governor De Vecchi's first plan was to disarm the sultanates. But, before the plan could be carried out, there had to be sufficient Italian troops in both sultanates. To make the enforcement of his plan more viable, he began to reconstitute the old Somali police corps, the ''Corpo Zaptié'', as a colonial force.
In preparation for the invasion plan of the sultanates, the Alula District, Alula Commissioner, E. Coronaro received orders in April 1924 to carry out a reconnaissance on the territories targeted for invasion. In spite of the 40-year Italian relationship with the sultanates, Italy did not have adequate knowledge of the geography. During this time, the Stefanini-Puccioni geological survey was scheduled to take place, so it was a good opportunity for the expedition of Coronaro to join with this.
Coronaro's survey concluded that the Majeerteen, Ismaan Sultanate (Majeerteen) depended on sea traffic, therefore, if this were blocked, any resistance that could be mounted after the invasion of the sultanate would be minimal. As the first stage of the invasion plan, Governor De Vecchi ordered the two Sultanates to disarm. The reaction of both sultanates was to object, as they felt the policy was in breach of the protectorate agreements. The pressure engendered by the new development forced the two rival sultanates to settle their differences over possession of Nugal, Somalia, Nugaal, and form a united front against their common enemy.
The Sultanate of Hobyo
The Sultanate of Hobyo ( so, Saldanadda Hobyo, ar, سلطنة هوبيو), also known as the Sultanate of Obbia,''New International Encyclopedia'', Volume 21, (Dodd, Mead: 1916), p.283. was a 19th-century Somali people, Somali kingdom in present ...
was different from that of the Majeerteen in terms of its geography and the pattern of the territory. It was founded by Yusuf Ali Kenadid in the middle of the 19th century in central Somalia. Its jurisdiction stretched from El Dher District, Ceeldheer (El Dher) through to Dhusamareb in the south-west, from Galladi to Galkayo in the west, from Jariban to Garaad in the north-east, and the Indian Ocean in the east.
 By 1 October, De Vecchi's plan was to go into action. The operation to invade Hobyo started in October 1925 . Columns of the new Zaptié began to move towards the sultanate. Hobyo, El Buur, Ceelbuur (El Buur), Galkayo, and the territory between were completely overrun within a month. Hobyo was transformed from a sultanate into an administrative region. Sultan Yusuf Ali surrendered. Nevertheless, soon suspicions were aroused as Trivulzio, the Hobyo commissioner, reported movement of armed men towards the borders of the sultanate before the takeover and after. Before the Italians could concentrate on the Majeerteen, they were diverted by new setbacks. On 9 November, the Italian fear was realized when a mutiny, led by one of the military chiefs of Sultan Ali Yusuf, Sultanate of Hobyo#Omar Samatar's Rebellion, Omar Samatar, recaptured El Buur. Soon the rebellion expanded to the local population. The region went into revolt as El-Dheere also came under the control of Omar Samatar. The Italian forces tried to recapture El Buur, but they were repulsed. On 15 November, the Italians retreated to Bud Bud and on the way they were ambushed and suffered heavy casualties.
While a third attempt was in the last stages of preparation, the operation's commander, Lieutenant-Colonel Splendorelli, was ambushed between Bud Bud and Buula Barde. He and some of his staff were killed. As a consequence of the death of the commander of the operations and the effect of two failed operations intended to overcome the El Buur mutiny, the spirit of Italian troops began to wane. The Governor took the situation seriously and, to prevent any more failure, he requested two battalions from Eritrea to reinforce his troops, and assumed lead of the operations. Meanwhile, the rebellion was gaining sympathy across the country, and as far afield as Ogaden, Western Somalia.
The fascist government was surprised by the setback in Hobyo. The whole policy of conquest was collapsing under its nose. The El-Buur episode drastically changed the strategy of Italy as it revived memories of the Battle of Adwa, Adwa fiasco when Italy had been defeated by Abyssinia. Furthermore, in the Colonial Ministry in Rome, senior officials distrusted the Governor's ability to deal with the matter. Rome instructed De Vecchi that he was to receive the reinforcement from Eritrea, but that the commander of the two battalions was to temporarily assume the military command of the operations and De Vecchi was to stay in Mogadishu and confine himself to other colonial matters. In the case of any military development, the military commander was to report directly to the Chief of Staff in Rome.
While the situation remained perplexing, De Vecchi moved the deposed sultan to Mogadishu. Fascist Italy was poised to re-conquer the sultanate by whatever means. To maneuver the situation within Hobyo, they even contemplated the idea of reinstating Ali Yusuf. However, the idea was dropped after they became pessimistic about the results.
To undermine the resistance, however, and before the Eritrean reinforcement could arrive, De Vecchi began to instill distrust among the local people by buying the loyalty of some of them. In fact, these tactics had better results than the military campaign had, and the resistance began gradually to wear down. Given the anarchy that would follow, the new policy was a success.
On the military front, Italian troops finally overran El Buur on 26 December 1925, and the forces of Omar Samatar were compelled to retreat to Western Somaliland.
By neutralising Hobyo, the fascists could concentrate on the Majeerteen. In early October 1924, E. Coronaro, the new Alula commissioner, presented Boqor (king) Osman Mahamuud with an ultimatum to disarm and surrender. Meanwhile, Italian troops began to pour into the sultanate in anticipation of this operation. While landing at Haafuun and Alula, the sultanate's troops opened fire on them. Fierce fighting ensued and to avoid escalating the conflict and to press the fascist government to revoke their policy, Boqor Osman tried to open a dialogue. However, he failed, and again fighting broke out between the two parties. Following this disturbance, on 7 October, the Governor instructed Coronaro to order the Sultan to surrender; to intimidate the people he ordered the seizure of all merchant boats in the Alula area. At Hafun, Arimondi bombarded and destroyed all the boats in the area.
By 1 October, De Vecchi's plan was to go into action. The operation to invade Hobyo started in October 1925 . Columns of the new Zaptié began to move towards the sultanate. Hobyo, El Buur, Ceelbuur (El Buur), Galkayo, and the territory between were completely overrun within a month. Hobyo was transformed from a sultanate into an administrative region. Sultan Yusuf Ali surrendered. Nevertheless, soon suspicions were aroused as Trivulzio, the Hobyo commissioner, reported movement of armed men towards the borders of the sultanate before the takeover and after. Before the Italians could concentrate on the Majeerteen, they were diverted by new setbacks. On 9 November, the Italian fear was realized when a mutiny, led by one of the military chiefs of Sultan Ali Yusuf, Sultanate of Hobyo#Omar Samatar's Rebellion, Omar Samatar, recaptured El Buur. Soon the rebellion expanded to the local population. The region went into revolt as El-Dheere also came under the control of Omar Samatar. The Italian forces tried to recapture El Buur, but they were repulsed. On 15 November, the Italians retreated to Bud Bud and on the way they were ambushed and suffered heavy casualties.
While a third attempt was in the last stages of preparation, the operation's commander, Lieutenant-Colonel Splendorelli, was ambushed between Bud Bud and Buula Barde. He and some of his staff were killed. As a consequence of the death of the commander of the operations and the effect of two failed operations intended to overcome the El Buur mutiny, the spirit of Italian troops began to wane. The Governor took the situation seriously and, to prevent any more failure, he requested two battalions from Eritrea to reinforce his troops, and assumed lead of the operations. Meanwhile, the rebellion was gaining sympathy across the country, and as far afield as Ogaden, Western Somalia.
The fascist government was surprised by the setback in Hobyo. The whole policy of conquest was collapsing under its nose. The El-Buur episode drastically changed the strategy of Italy as it revived memories of the Battle of Adwa, Adwa fiasco when Italy had been defeated by Abyssinia. Furthermore, in the Colonial Ministry in Rome, senior officials distrusted the Governor's ability to deal with the matter. Rome instructed De Vecchi that he was to receive the reinforcement from Eritrea, but that the commander of the two battalions was to temporarily assume the military command of the operations and De Vecchi was to stay in Mogadishu and confine himself to other colonial matters. In the case of any military development, the military commander was to report directly to the Chief of Staff in Rome.
While the situation remained perplexing, De Vecchi moved the deposed sultan to Mogadishu. Fascist Italy was poised to re-conquer the sultanate by whatever means. To maneuver the situation within Hobyo, they even contemplated the idea of reinstating Ali Yusuf. However, the idea was dropped after they became pessimistic about the results.
To undermine the resistance, however, and before the Eritrean reinforcement could arrive, De Vecchi began to instill distrust among the local people by buying the loyalty of some of them. In fact, these tactics had better results than the military campaign had, and the resistance began gradually to wear down. Given the anarchy that would follow, the new policy was a success.
On the military front, Italian troops finally overran El Buur on 26 December 1925, and the forces of Omar Samatar were compelled to retreat to Western Somaliland.
By neutralising Hobyo, the fascists could concentrate on the Majeerteen. In early October 1924, E. Coronaro, the new Alula commissioner, presented Boqor (king) Osman Mahamuud with an ultimatum to disarm and surrender. Meanwhile, Italian troops began to pour into the sultanate in anticipation of this operation. While landing at Haafuun and Alula, the sultanate's troops opened fire on them. Fierce fighting ensued and to avoid escalating the conflict and to press the fascist government to revoke their policy, Boqor Osman tried to open a dialogue. However, he failed, and again fighting broke out between the two parties. Following this disturbance, on 7 October, the Governor instructed Coronaro to order the Sultan to surrender; to intimidate the people he ordered the seizure of all merchant boats in the Alula area. At Hafun, Arimondi bombarded and destroyed all the boats in the area.
 On 13 October, Coronaro was to meet Boqor Osman at Bargal, Baargaal to press for his surrender. Under siege already, Boqor Osman was playing for time. However, on 23 October, Boqor Osman sent an angry response to the Governor defying his order. Following this a full-scale attack was ordered in November. Baargaal was bombarded and destroyed to the ground. This region was ethnically compact, and was out of range of direct action by the fascist government of Muqdisho. The attempt of the colonizers to suppress the region erupted into explosive confrontation. The Italians were meeting fierce resistance on many fronts. In December 1925, led by the charismatic leader Hersi Boqor, son of Boqor Osman, the sultanate forces drove the Italians out of Hurdia and Hafun, two strategic coastal towns. Another contingent attacked and destroyed an Italian communications centre at Cape Guardafui, at the tip of the Horn. In retaliation the ''Bernica'' and other warships were called on to bombard all main coastal towns of the Majeerteen. After a violent confrontation Italian forces captured Eyl (Eil), which until then had remained in the hands of Hersi Boqor. In response to the unyielding situation, Italy called for reinforcements from their other colonies, notably Eritrea. With their arrival at the closing of 1926, the Italians began to move into the interior where they had not been able to venture since their first seizure of the coastal towns. Their attempt to capture Dharoor Valley was resisted, and ended in failure.
De Vecchi had to reassess his plans as he was being humiliated on many fronts. After one year of exerting full force he could not yet manage to gain a result over the sultanate. In spite of the fact that the Italian navy sealed the sultanate's main coastal entrance, they could not succeed in stopping them from receiving arms and ammunition through it. It was only early 1927 when they finally succeeded in shutting the northern coast of the sultanate, thus cutting arms and ammunition supplies for the Majeerteen. By this time, the balance had tilted to the Italians' side, and in January 1927 they began to attack with a massive force, capturing Iskushuban, at the heart of the Majeerteen. Hersi Boqor unsuccessfully attacked and challenged the Italians at Iskushuban. To demoralise the resistance, ships were ordered to target and bombard the sultanate's coastal towns and villages. In the interior, the Italian troops confiscated livestock. By the end of the 1927, the Italians had taken full control of the sultanate. Hersi Boqor and his troops retreated to Ethiopia in order to rebuild their forces, but were unable to retake their territories, effectively ending the ''Campaign of the Sultanates''.
On 13 October, Coronaro was to meet Boqor Osman at Bargal, Baargaal to press for his surrender. Under siege already, Boqor Osman was playing for time. However, on 23 October, Boqor Osman sent an angry response to the Governor defying his order. Following this a full-scale attack was ordered in November. Baargaal was bombarded and destroyed to the ground. This region was ethnically compact, and was out of range of direct action by the fascist government of Muqdisho. The attempt of the colonizers to suppress the region erupted into explosive confrontation. The Italians were meeting fierce resistance on many fronts. In December 1925, led by the charismatic leader Hersi Boqor, son of Boqor Osman, the sultanate forces drove the Italians out of Hurdia and Hafun, two strategic coastal towns. Another contingent attacked and destroyed an Italian communications centre at Cape Guardafui, at the tip of the Horn. In retaliation the ''Bernica'' and other warships were called on to bombard all main coastal towns of the Majeerteen. After a violent confrontation Italian forces captured Eyl (Eil), which until then had remained in the hands of Hersi Boqor. In response to the unyielding situation, Italy called for reinforcements from their other colonies, notably Eritrea. With their arrival at the closing of 1926, the Italians began to move into the interior where they had not been able to venture since their first seizure of the coastal towns. Their attempt to capture Dharoor Valley was resisted, and ended in failure.
De Vecchi had to reassess his plans as he was being humiliated on many fronts. After one year of exerting full force he could not yet manage to gain a result over the sultanate. In spite of the fact that the Italian navy sealed the sultanate's main coastal entrance, they could not succeed in stopping them from receiving arms and ammunition through it. It was only early 1927 when they finally succeeded in shutting the northern coast of the sultanate, thus cutting arms and ammunition supplies for the Majeerteen. By this time, the balance had tilted to the Italians' side, and in January 1927 they began to attack with a massive force, capturing Iskushuban, at the heart of the Majeerteen. Hersi Boqor unsuccessfully attacked and challenged the Italians at Iskushuban. To demoralise the resistance, ships were ordered to target and bombard the sultanate's coastal towns and villages. In the interior, the Italian troops confiscated livestock. By the end of the 1927, the Italians had taken full control of the sultanate. Hersi Boqor and his troops retreated to Ethiopia in order to rebuild their forces, but were unable to retake their territories, effectively ending the ''Campaign of the Sultanates''.
"Somalia Italiana" and World War II
 On 9 May 1936, Mussolini proclaimed the creation of the Italian Empire, calling it the ''Italian East Africa, Africa Orientale Italiana'' (A.O.I.) and formed by Italian Ethiopia, Ethiopia, Italian Eritrea, Eritrea and
On 9 May 1936, Mussolini proclaimed the creation of the Italian Empire, calling it the ''Italian East Africa, Africa Orientale Italiana'' (A.O.I.) and formed by Italian Ethiopia, Ethiopia, Italian Eritrea, Eritrea and Italian Somaliland
Italian Somalia ( it, Somalia Italiana; ar, الصومال الإيطالي, Al-Sumal Al-Italiy; so, Dhulka Talyaaniga ee Soomaalida), was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th centur ...
(called officially "Somalia italiana"). The Italians made many new investments in infrastructure in the region, such as the ''Strada Imperiale'' ("imperial road") between Addis Ababa and Mogadishu and the railway Mogadishu-Villabruzzi of 114 km.
Over the course of Italian Somaliland's existence, many Somali troops fought in the so-called ''Regio Corpo Truppe Coloniali''. The soldiers were enrolled as Dubats, Zaptié and Bands (Italian Army irregulars), Bande irregolari. During World War II, these troops were regarded as a wing of the Italian Army's Infantry Division, as was the case in Italian Libyan Colonial Division, Libya and Italian 1st Eritrean Division, Eritrea. The Zaptié provided a ceremonial escort for the Italian Viceroy (Governor) as well as the territorial police. There were already more than one thousand such soldiers in 1922. In 1941, in Italian Somaliland and Ethiopia, 2,186 Zaptié plus an additional 500 recruits under training officially constituted a part of the Carabinieri. They were organised into a battalion commanded by Major Alfredo Serranti that defended Battle of Culqualber, Culqualber (Ethiopia) for three months until this military unit was destroyed by the Allies of World War II, Allies. After heavy fighting, the Somali troops and the Italian Carabinieri received full military honors from the British.
In the first half of 1940, there were 22,000 Italians living in Somalia and the colony was one of the most developed in East Africa in terms of the standard of living of the colonists and of the Somalis, mainly in the urban areas. More than 10,000 Italians were living in Mogadishu under Italian rule, Mogadishu, the administrative capital of the ''Africa Orientale Italiana'', and new buildings were erected in the Italian architectural tradition. By 1940, the Villaggio Duca degli Abruzzi (now Jowhar) had a population of 12,000 people, of whom nearly 3,000 were Italian Somalis, and enjoyed a notable level of development with a small manufacturing area with agricultural industries (sugar mills, etc.).
In the second half of 1940, Italian troops invaded British Somaliland and ejected the British. The Italians also occupied parts of the British East Africa Protectorate bordering Jubaland around the towns of Moyale and Buna, Kenya, Buna.
Benito Mussolini, Mussolini boasted in front of a group of Somalis leaders -in late summer 1940- that he had created the "''Greater Somalia''" (dreamed by the Somali population) after the union of British Somaliland to his Somalia Governorate.
Independence
countrystudies.us
/ref> Britain included the proviso that the Somali nomads would retain their autonomy, but Ethiopia immediately claimed sovereignty over them.Zolberg, Aristide R., et al., ''Escape from Violence: Conflict and the Refugee Crisis in the Developing World'', (Oxford University Press: 1992), p. 106 This prompted an unsuccessful bid by Britain in 1956 to buy back the Somali lands it had turned over. Britain also granted administration of the almost exclusively Somali-inhabited Northern Frontier District (NFD) to Kenyan nationalists despite an informal plebiscite demonstrating the overwhelming desire of the region's population to join the newly formed Somali Republic.
 A French Somaliland overseas territory referendum, 1958, referendum was held in neighboring Djibouti (then known as French Somaliland) in 1958, on the eve of Somalia's independence in 1960, to decide whether or not to join the Somali Republic or to remain with France. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, largely due to a combined yes vote by the sizable Afar people, Afar ethnic group and resident Europeans. There was also allegations of widespread vote rigging, with the French expelling thousands of Somalis before the referendum reached the polls.Kevin Shillington, ''Encyclopedia of African history'', (CRC Press: 2005), p. 360. The majority of those who voted "no" were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia, as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later.Barrington, Lowell, ''After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States'', (University of Michigan Press: 2006), p. 115 Djibouti finally gained its independence from France in 1977, and Hassan Gouled Aptidon, a Somali who had campaigned for a yes vote in the referendum of 1958, eventually wound up as Djibouti's first president (1977–1991).
On 1 July 1960, the two territories united to form the
A French Somaliland overseas territory referendum, 1958, referendum was held in neighboring Djibouti (then known as French Somaliland) in 1958, on the eve of Somalia's independence in 1960, to decide whether or not to join the Somali Republic or to remain with France. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, largely due to a combined yes vote by the sizable Afar people, Afar ethnic group and resident Europeans. There was also allegations of widespread vote rigging, with the French expelling thousands of Somalis before the referendum reached the polls.Kevin Shillington, ''Encyclopedia of African history'', (CRC Press: 2005), p. 360. The majority of those who voted "no" were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia, as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later.Barrington, Lowell, ''After Independence: Making and Protecting the Nation in Postcolonial and Postcommunist States'', (University of Michigan Press: 2006), p. 115 Djibouti finally gained its independence from France in 1977, and Hassan Gouled Aptidon, a Somali who had campaigned for a yes vote in the referendum of 1958, eventually wound up as Djibouti's first president (1977–1991).
On 1 July 1960, the two territories united to form the Somali Republic
The Somali Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Soomaaliyeed; it, Repubblica Somala; ar, الجمهورية الصومالية, Jumhūriyyat aṣ-Ṣūmālīyyah) was a sovereign state composed of Somalia and Somaliland, following the unification o ...
, albeit within boundaries drawn up by Italy and Britain. A government was formed by Abdullahi Issa Mohamud and Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal and other members of the trusteeship and protectorate governments, with the Speaker of the Somali Union Act Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf
Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf ( so, Xaaji Bashiir Ismaaciil Yuusuf, ar, حاجي بشير اسماعيل يوسف) (b. 1912 in Hobyo, Somalia – d. 1984 in Cairo, Egypt), commonly referred to as Haji Bashir,SAMIULLAH, MUHAMMAD. DEVELOPMENT OF CREATI ...
as President of the Parliament of Somalia, Somali National Assembly, Aden Abdullah Osman Daar as List of Presidents of Somalia, President of Somali Republic, and Abdirashid Ali Shermarke as Prime Minister of Somalia, Prime Minister (later to become president from 1967 to 1969). On 20 July 1961 and through a Somali constitutional referendum, 1961, popular referendum, the people of Somalia ratified a new Constitution of Somalia, constitution, which was first drafted in 1960. In 1967, Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal became Prime Minister, a position to which he was appointed by Shermarke. Egal would later become the President of the autonomous Somaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still conside ...
region in northwestern Somalia.
On 15 October 1969, while paying a visit to the northern town of Las Anod, Somalia's then President Abdirashid Ali Shermarke was shot dead by a policeman. His assassination was quickly followed by a 1969 Somali coup d'état, military coup d'état on 21 October 1969 (the day after his funeral), in which the Military of Somalia, Somali Army seized power without encountering armed opposition – essentially a bloodless takeover. The putsch was spearheaded by Major General Mohamed Siad Barre
Mohamed Siad Barre ( so, Maxamed Siyaad Barre, Osmanya script: ; ar, محمد سياد بري; c. 1910 – 2 January 1995) was a Somali head of state and general who served as the 3rd president of the Somali Democratic Republic from 1969 to 199 ...
, who at the time commanded the army.Moshe Y. Sachs, ''Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations'', Volume 2, (Worldmark Press: 1988), p. 290.
Somali Democratic Republic
Supreme Revolutionary Council
Alongside Barre, the Supreme Revolutionary Council (SRC) that assumed power after President Sharmarke's assassination was led by Lieutenant Colonel Salaad Gabeyre Kediye and Chief of Police Jama Korshel. Kediye officially held the title of "Father of the Revolution," and Barre shortly afterwards became the head of the SRC. The SRC subsequently renamed the country theSomali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Dimuqraadiya Soomaaliyeed; ar, الجمهورية الديمقراطية الصومالية, ; it, Repubblica Democratica Somala) was the name that the socialist military government gave to Som ...
,''The Encyclopedia Americana: complete in thirty volumes. Skin to Sumac'', Volume 25, (Grolier: 1995), p. 214. dissolved the parliament and the Supreme Court, and suspended the constitution.Peter John de la Fosse Wiles, The New Communist Third World: an essay in political economy
', (Taylor & Francis: 1982), p. 279 . The revolutionary army established large-scale public works programs and successfully implemented an urban and rural literacy campaign, which helped dramatically increase the literacy rate. In addition to a nationalization program of industry and land, the new regime's foreign policy placed an emphasis on Somalia's traditional and religious links with the Arab world, eventually joining the Arab League (AL) in 1974.Benjamin Frankel, ''The Cold War, 1945–1991: Leaders and other important figures in the Soviet Union, Eastern Europe, China, and the Third World'', (Gale Research: 1992), p. 306 . That same year, Barre also served as chairman of the Organization of African Unity (OAU), the predecessor of the African Union (AU).Oihe Yang, ''Africa South of the Sahara 2001'', 30th Ed., (Taylor and Francis: 2000), p. 1025 . In July 1976, Barre's SRC disbanded itself and established in its place the Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party (SRSP), a one-party government based on scientific socialism and Islamic tenets. The SRSP was an attempt to Revisionism (Marxism), reconcile the official state ideology with the official state religion by adapting Marxist precepts to local circumstances. Emphasis was placed on the Muslim principles of social progress, equality and justice, which the government argued formed the core of scientific socialism and its own accent on self-sufficiency, public participation and popular control, as well as direct ownership of the means of production. While the SRSP encouraged private investment on a limited scale, the administration's overall direction was essentially Communism, communist.
Ogaden War
In July 1977, the Ogaden War broke out after Barre's government sought to incorporate the predominantly Somali-inhabitedOgaden
Ogaden (pronounced and often spelled ''Ogadēn''; so, Ogaadeen, am, ውጋዴ/ውጋዴን) is one of the historical names given to the modern Somali Region, the territory comprising the eastern portion of Ethiopia formerly part of the Harargh ...
region of Ethiopia into a Pan-Somali Greater Somalia. In the first week of the conflict, Somali armed forces seized the southern and central parts of the Ogaden. The units in the Godey Front were led by Colonel Abdullahi Ahmed Irro. For most of the war, the Somali army scored continuous victories on the Ethiopian army, following it as far as Sidamo Province, Sidamo. By September 1977, Somalia controlled 90% of the Ogaden and captured strategic cities such as Jijiga and put heavy pressure on Dire Dawa, threatening the train route from the latter city to Djibouti. After the siege of Harar
Harar ( amh, ሐረር; Harari: ሀረር; om, Adare Biyyo; so, Herer; ar, هرر) known historically by the indigenous as Gey (Harari: ጌይ ''Gēy'', ) is a walled city in eastern Ethiopia. It is also known in Arabic as the City of Saint ...
, a massive unprecedented Soviet intervention consisting of 20,000 Cuban forces and several thousand Soviet experts came to the aid of Ethiopia's communist Derg regime. By 1978, the Somali troops were ultimately pushed out of the Ogaden. This shift in support by the Soviet Union motivated the Barre government to seek allies elsewhere. It eventually settled on the Soviets' Cold War arch-rival, the United States, which had been courting the Somali government for some time. All in all, Somalia's initial friendship with the Soviet Union and later partnership with the United States enabled it to build the largest army in Africa.Oliver Ramsbotham, Tom Woodhouse, ''Encyclopedia of international peacekeeping operations'', (ABC-CLIO: 1999), p. 222 .
Isaaq genocide
 Isaaq genocide was the systematic, state-sponsored massacre of
Isaaq genocide was the systematic, state-sponsored massacre of Isaaq
The Isaaq (also Isaq, Ishaak, Isaac) ( so, Reer Sheekh Isxaaq, ar, بني إسحاق, Banī Isḥāq) is a Somali clan. It is one of the major Somali clans in the Horn of Africa, with a large and densely populated traditional territory. Per ...
civilians between 1987 and 1989 by the Somali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Dimuqraadiya Soomaaliyeed; ar, الجمهورية الديمقراطية الصومالية, ; it, Repubblica Democratica Somala) was the name that the socialist military government gave to Som ...
under the dictatorship of Siad Barre. The number of civilian deaths in this massacre is estimated to be between 50,000 and 100,000 according to various sources, whilst local reports estimate the total civilian deaths to be upwards of 200,000 Isaaq civilians. This genocide also included the levelling and complete destruction of the second and third largest cities in Somalia, Hargeisa
Hargeisa (; so, Hargeysa, ar, هرجيسا) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Somaliland. It is located in the Maroodi Jeex region of the Horn of Africa. It succeeded Burco as the capital of the British Somaliland Protector ...
(which was 90 percent destroyed) and Burao (70 per cent destroyed) respectively, and had caused up to 500,000 Somalis (primarily of the Isaaq clan) to flee their land and cross the border to Hartasheikh in Ethiopia as refugees, in what was described as "one of the fastest and largest forced movements of people recorded in Africa", and resulted in the creation of the world's largest refugee camp then (1988), with another 400,000 being displaced. The scale of destruction led to Hargeisa being known as the 'Dresden of Africa'. The killings happened during the Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War ( so, Dagaalkii Sokeeye ee Soomaaliya; ar, الحرب الأهلية الصومالية ) is an ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the Military dictatorship, military junta wh ...
and have been referred to as a "forgotten genocide".
Rebellion
 A new constitution was promulgated in 1979 under which elections for a People's Assembly were held. However, Barre's Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party politburo continued to rule. In October 1980, the SRSP was disbanded, and the Supreme Revolutionary Council was re-established in its place.
A new constitution was promulgated in 1979 under which elections for a People's Assembly were held. However, Barre's Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party politburo continued to rule. In October 1980, the SRSP was disbanded, and the Supreme Revolutionary Council was re-established in its place.
 In May 1986, President Barre suffered serious injuries in a life-threatening automobile accident near Mogadishu, when the car that was transporting him smashed into the back of a bus during a heavy rainstorm.World of Information (Firm), ''Africa review'', (World of Information: 1987), p.213. He was treated in a hospital in Saudi Arabia for head injuries, broken ribs and shock over a period of a month.Arthur S. Banks, Thomas C. Muller, William Overstreet, ''Political Handbook of the World 2008'', (CQ Press: 2008), p.1198.National Academy of Sciences (U.S.). Committee on Human Rights, Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Committee on Health and Human Rights, ''Scientists and human rights in Somalia: report of a delegation'', (National Academies: 1988), p.9. Lieutenant General Mohamed Ali Samatar, then Vice President, subsequently served as de facto head of state for the next several months. Although Barre managed to recover enough to present himself as the sole presidential candidate for re-election over a term of seven years on 23 December 1986, his poor health and advanced age led to speculation about who would succeed him in power. Possible contenders included his son-in-law General Ahmed Suleiman Abdille, who was at the time the Minister of the Interior, in addition to Barre's Vice President Lt. Gen. Samatar.
By that time, Barre's government had become increasingly unpopular. Many Somalis had become disillusioned with life under military dictatorship. The regime was weakened further in the 1980s as the Cold War drew to a close and Somalia's strategic importance was diminished. The government became increasingly Totalitarianism, totalitarian, and resistance movements, encouraged by Ethiopia, sprang up across the country, eventually leading to the
In May 1986, President Barre suffered serious injuries in a life-threatening automobile accident near Mogadishu, when the car that was transporting him smashed into the back of a bus during a heavy rainstorm.World of Information (Firm), ''Africa review'', (World of Information: 1987), p.213. He was treated in a hospital in Saudi Arabia for head injuries, broken ribs and shock over a period of a month.Arthur S. Banks, Thomas C. Muller, William Overstreet, ''Political Handbook of the World 2008'', (CQ Press: 2008), p.1198.National Academy of Sciences (U.S.). Committee on Human Rights, Institute of Medicine (U.S.). Committee on Health and Human Rights, ''Scientists and human rights in Somalia: report of a delegation'', (National Academies: 1988), p.9. Lieutenant General Mohamed Ali Samatar, then Vice President, subsequently served as de facto head of state for the next several months. Although Barre managed to recover enough to present himself as the sole presidential candidate for re-election over a term of seven years on 23 December 1986, his poor health and advanced age led to speculation about who would succeed him in power. Possible contenders included his son-in-law General Ahmed Suleiman Abdille, who was at the time the Minister of the Interior, in addition to Barre's Vice President Lt. Gen. Samatar.
By that time, Barre's government had become increasingly unpopular. Many Somalis had become disillusioned with life under military dictatorship. The regime was weakened further in the 1980s as the Cold War drew to a close and Somalia's strategic importance was diminished. The government became increasingly Totalitarianism, totalitarian, and resistance movements, encouraged by Ethiopia, sprang up across the country, eventually leading to the Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War ( so, Dagaalkii Sokeeye ee Soomaaliya; ar, الحرب الأهلية الصومالية ) is an ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the Military dictatorship, military junta wh ...
. Among the militia groups were the Somali Salvation Democratic Front (SSDF), United Somali Congress (USC), Somali National Movement (SNM) and the Somali Patriotic Movement (SPM), together with the non-violent political oppositions of the Somali Democratic Movement (SDM), the Factions in the Somali Civil War#Somali Democratic Alliance (SDA), Somali Democratic Alliance (SDA) and the Somali Manifesto Group (SMG).
Somali Civil War
 With the political situation deteriorating, Barre's long-standing government in 1991 eventually collapsed under the pressure. The national army disbanded shortly afterwards.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 794 was unanimously passed on 3 December 1992, which approved a coalition of United Nations peacekeeping, United Nations peacekeepers led by the United States. Forming the Unified Task Force (UNITAF), the force was tasked with assuring security until humanitarian efforts aimed at stabilizing the situation were transferred to the UN. Landing in 1993, the UN peacekeeping coalition started the two-year United Nations Operation in Somalia II (UNOSOM II) primarily in the south to provide humanitarian relief.
Some militias that had seized power after the oust of Barre regime's interpreted the UN troops' presence as a threat to their hegemony. Consequently, several gun battles took place in Mogadishu between local gunmen and peacekeepers. Among these was the Battle of Mogadishu (1993), Battle of Mogadishu, an unsuccessful attempt by US troops to apprehend faction leader Mohamed Farah Aidid. The UN soldiers eventually withdrew altogether from the country on 3 March 1995, having incurred more significant casualties.
With the political situation deteriorating, Barre's long-standing government in 1991 eventually collapsed under the pressure. The national army disbanded shortly afterwards.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 794 was unanimously passed on 3 December 1992, which approved a coalition of United Nations peacekeeping, United Nations peacekeepers led by the United States. Forming the Unified Task Force (UNITAF), the force was tasked with assuring security until humanitarian efforts aimed at stabilizing the situation were transferred to the UN. Landing in 1993, the UN peacekeeping coalition started the two-year United Nations Operation in Somalia II (UNOSOM II) primarily in the south to provide humanitarian relief.
Some militias that had seized power after the oust of Barre regime's interpreted the UN troops' presence as a threat to their hegemony. Consequently, several gun battles took place in Mogadishu between local gunmen and peacekeepers. Among these was the Battle of Mogadishu (1993), Battle of Mogadishu, an unsuccessful attempt by US troops to apprehend faction leader Mohamed Farah Aidid. The UN soldiers eventually withdrew altogether from the country on 3 March 1995, having incurred more significant casualties.
Decentralization
Following the outbreak of the civil war and the ensuing collapse of the central government, Somalia's residents reverted to local forms of conflict resolution, either secular, traditional or Islamic law, with a provision for appeal of all sentences. The legal structure in Somalia is thus divided along three lines: Civil law (legal system), civil law, religious law and Custom (law), customary law.Civil law
While Somalia's formal judicial system was largely destroyed after the fall of the Siad Barre regime, it was later gradually rebuilt and administered under different regional governments, such as the autonomous Puntland andSomaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still conside ...
macro-regions. In the case of the later Transitional Federal Government, a new interim judicial structure was formed through various international conferences.
Despite some significant political differences between them, all of these administrations share similar legal structures, much of which are predicated on the judicial systems of previous Somali administrations. These similarities in civil law include: a) a charter which affirms the primacy of Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
shari'a or religious law, although in practice shari'a is applied mainly to matters such as marriage, divorce, inheritance, and civil issues. The charter guarantees respect for universal standards of human rights to all subjects of the law. It also assures the independence of the judiciary, which in turn is protected by a judicial committee; b) a three-tier judicial system including a supreme court, a court of appeals, and courts of first instance (either divided between district and regional courts, or a single court per region); and c) the laws of the civilian government which were in effect prior to the military coup d'état that saw the Barre regime into power remain in force until the laws are amended.
Shari'a
Islamic shari'a has traditionally played a significant part in Somali society. In theory, it has served as the basis for all national legislation in every Somali constitution. In practice, however, it only applied to common civil cases such as marriage, divorce, inheritance and family matters. This changed after the start of the civil war when a number of new shari'a courts began to spring up in many different cities and towns across the country. These new shari'a courts serve three functions; namely, to pass rulings in both criminal and civil cases, to organize a militia capable of arresting criminals, and to keep convicted prisoners incarcerated. The shari'a courts, though structured along simple lines, feature a conventional hierarchy of a chairman, vice-chairman and four judges. A police force that reports to the court enforces the judges' rulings, but also helps settle community disputes and apprehend suspected criminals. In addition, the courts manage detention centers where criminals are kept. An independent finance committee is also assigned the task of collecting and managing tax revenue levied on regional merchants by the local authorities.Xeer
Somalis have for centuries practiced a form of customary law, called Xeer (pronounced /ħeːr/). Xeer is a polycentric law, polycentric legal system where there is no monopolistic institution or agent that determines what the law should be or how it should be interpreted. The Xeer legal system is assumed to have developed exclusively in the Horn of Africa since approximately the 7th century. There is no evidence that it developed elsewhere or was greatly influenced by any foreign legal system. Its legal terminology is practically devoid of Loanword, loan words from foreign languages, suggesting that it is truly indigenous. The Xeer legal system also requires a certain amount of division of labour, specialization of different functions within the legal framework. Thus, one can find ''odayaal'' (judges), ''xeerbogeyaal'' (jurists), ''guurtiyaal'' (detectives), ''garxajiyaal'' (Lawyer, attorneys), ''markhaatiyal'' (witnesses) and ''waranle'' (police officers) to enforce the law. Xeer is defined by a few fundamental tenets that are immutable and which closely approximate the principle of ''jus cogens'' in international law: These precepts include: a) payment of Blood money (term), blood money (locally referred to as ''Diyya, diya'') for libel, theft, physical harm, rape and death, as well as supplying assistance to relatives; b) assuring good inter-clan relations by treating women justly, negotiating with "peace emissaries" in good faith, and sparing the lives of socially protected groups "Birr Magaydo," (e.g. children, women, the pious, poets, messengers, sheikhs, and guests); c) family obligations such as the payment of dowry, and sanctions for eloping; d) rules pertaining to the management of resources such as the use of pasture land, water, and other natural resources; e) providing financial support to married female relatives and newlyweds; f) donating livestock and other assets to the poor.Recent history

Transitional National Government
In 2000, Abdiqasim Salad Hassan was selected as the President of the nation's new Transitional National Government (TNG), an interim administration formed to guide Somalia to its third permanent republican government. On 10 October 2004, in a session held by the Transitional Federal Parliament (TFP), Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed was elected as President of the succeeding Transitional Federal Government (TFG), an interim federal administrative body that he had helped establish earlier in the year. He received 189 votes from the TFG Parliament, while the closest contender, erstwhile Somali ambassador to Washington Abdullahi Ahmed Addou, got 79 votes in the third round of voting. The then incumbent President of Somalia, Abdiqasim Salad Hassan, peacefully withdrew his candidature. Ahmed was sworn in a few days later on 14 October 2004.Transitional Federal Institutions
The Transitional Federal Government (TFG) was the internationally recognised government of Somalia until 20 August 2012, when its tenure officially ended. It was established as one of the Transitional Federal Institutions (TFIs) of government as defined in the Transitional Federal Charter (TFC) adopted in November 2004 by the Transitional Federal Parliament (TFP). The Transitional Federal Government officially comprised the executive branch of government, with the TFP serving as the Legislature, legislative branch. The government was headed by the President of Somalia, to whom the cabinet reported through the Prime Minister of Somalia, Prime Minister. However, it was also used as a general term to refer to all three branches collectively.Islamic Courts Union and Ethiopian intervention
In 2006, the Islamic Courts Union (ICU), an Islamism, Islamist organization, assumed control of much of the southern part of the country and promptly imposed Shari'a law. The Transitional Federal Government sought to reestablish its authority, and, with the assistance of Ethiopian National Defense Force, Ethiopian troops, African Union peacekeepers and air support by the United States, managed to drive out the rival ICU and solidify its rule. On 8 January 2007, as the Battle of Ras Kamboni raged, TFG President and founder Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed, a former colonel in the Somali Army and decorated war hero, entered Mogadishu for the first time since being elected to office. The government then relocated to Villa Somalia in the capital from its interim location in Baidoa. This marked the first time since the fall of the Siad Barre regime in 1991 that the federal government controlled most of the country. Following this defeat, the Islamic Courts Union splintered into several different factions. Some of the more radical elements, including Al-Shabaab (Somalia), Al-Shabaab, regrouped to continue their insurgency against the TFG and oppose the Ethiopian military's presence in Somalia. Throughout 2007 and 2008, Al-Shabaab scored military victories, seizing control of key towns and ports in both central and southern Somalia. At the end of 2008, the group had captured Baidoa but not Mogadishu. By January 2009, Al-Shabaab and other militias had managed to force the Ethiopian troops to retreat, leaving behind an under-equipped African Union peacekeeping force to assist the Transitional Federal Government's troops. Owing to a lack of funding and human resources, an arms embargo that made it difficult to re-establish a national security force, and general indifference on the part of the international community, President Yusuf found himself obliged to deploy thousands of troops from Puntland to Mogadishu to sustain the battle against insurgent elements in the southern part of the country. Financial support for this effort was provided by the autonomous region's government. This left little revenue for Puntland's own security forces and civil service employees, leaving the territory vulnerable to piracy and terrorist attacks. On 29 December 2008, Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed announced before a united parliament in Baidoa his resignation as President of Somalia. In his speech, which was broadcast on national radio, Yusuf expressed regret at failing to end the country's seventeen-year conflict as his government had mandated to do."Somalia's president quits office"BBC News, 29 December 2008. He also blamed the international community for its failure to support the government, and said that the speaker of parliament would succeed him in office per the Transitional Federal Charter of the Somali Republic, Charter of the Transitional Federal Government.
Coalition government
– ''Arab News'' However, conflict continued in the southern and central parts of the country. Within months, the coalition government had gone from holding about 70% of south-central Somalia's conflict zones, territory which it had inherited from the previous Yusuf administration, to losing control of over 80% of the disputed territory to the Islamist insurgents. On 14 October 2010, diplomat Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed (Farmajo) was appointed the new Prime Minister of Somalia. The former Premier Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke resigned the month before following a protracted dispute with President Sharif over a proposed draft constitution.
 Per the Transitional Federal Government's (TFG) Transitional Federal Charter of the Somali Republic, Charter, Prime Minister Mohamed named a new Cabinet on 12 November 2010, which has been lauded by the international community. As had been expected, the allotted ministerial positions were significantly reduced in numbers, with only 18 administrative posts unveiled versus the previous government's bloated 39 portfolios. Only two Ministers from the previous Cabinet were reappointed: Hussein Abdi Halane, the former Minister of Finance and a well-regarded figure in the international community, was put in charge of a consolidated Ministry of Finance and Treasury; and Dr. Mohamud Abdi Ibrahim was reassigned to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a, a moderate Sufism, Sufi group and an important military ally of the TFG, was also accorded the key Interior and Labour ministries. The remaining ministerial positions were largely assigned to technocrats new to the Somali political arena.
In its first 50 days in office, Prime Minister Mohamed's new administration completed its first monthly payment of stipends to government soldiers, and initiated the implementation of a full biometric register for the security forces within a window of four months. Additional members of the Independent Constitutional Commission were also appointed to engage Somali constitutional lawyers, religious scholars and experts in Somali culture over the nation's upcoming new constitution, a key part of the government's Transitional Federal Tasks. In addition, high level federal delegations were dispatched to defuse clan-related tensions in several regions. According to the prime minister of Somalia, to improve transparency, Cabinet ministers fully disclosed their assets and signed a Ethical code, code of ethics.
An Anti-Corruption Commission with the power to carry out formal investigations and to review government decisions and protocols was also established so as to more closely monitor all activities by public officials. Furthermore, unnecessary trips abroad by members of government were prohibited, and all travel by ministers now require the Premier's consent. A budget outlining 2011's federal expenditures was also put before and approved by members of parliament, with the payment of civil service employees prioritized. In addition, a full audit of government property and vehicles is being put into place. On the war front, the new government and its AMISOM allies also managed to secure control of 60% of Mogadishu, where 80% of the capital's population now lives. According to the African Union and Prime Minister Mohamed, with increasing troop strength the pace of territorial gains is expected to greatly accelerate.
On 19 June 2011, Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed resigned from his position as Prime Minister of Somalia. Part of the controversial Kampala Accord's conditions, the agreement would also see the mandates of the President, the Parliament Speaker and Deputies extended until August 2012, after which point new elections are to be organized.Somalia: PM Mohamed Abdullahi Farmajo resigns
Per the Transitional Federal Government's (TFG) Transitional Federal Charter of the Somali Republic, Charter, Prime Minister Mohamed named a new Cabinet on 12 November 2010, which has been lauded by the international community. As had been expected, the allotted ministerial positions were significantly reduced in numbers, with only 18 administrative posts unveiled versus the previous government's bloated 39 portfolios. Only two Ministers from the previous Cabinet were reappointed: Hussein Abdi Halane, the former Minister of Finance and a well-regarded figure in the international community, was put in charge of a consolidated Ministry of Finance and Treasury; and Dr. Mohamud Abdi Ibrahim was reassigned to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a, a moderate Sufism, Sufi group and an important military ally of the TFG, was also accorded the key Interior and Labour ministries. The remaining ministerial positions were largely assigned to technocrats new to the Somali political arena.
In its first 50 days in office, Prime Minister Mohamed's new administration completed its first monthly payment of stipends to government soldiers, and initiated the implementation of a full biometric register for the security forces within a window of four months. Additional members of the Independent Constitutional Commission were also appointed to engage Somali constitutional lawyers, religious scholars and experts in Somali culture over the nation's upcoming new constitution, a key part of the government's Transitional Federal Tasks. In addition, high level federal delegations were dispatched to defuse clan-related tensions in several regions. According to the prime minister of Somalia, to improve transparency, Cabinet ministers fully disclosed their assets and signed a Ethical code, code of ethics.
An Anti-Corruption Commission with the power to carry out formal investigations and to review government decisions and protocols was also established so as to more closely monitor all activities by public officials. Furthermore, unnecessary trips abroad by members of government were prohibited, and all travel by ministers now require the Premier's consent. A budget outlining 2011's federal expenditures was also put before and approved by members of parliament, with the payment of civil service employees prioritized. In addition, a full audit of government property and vehicles is being put into place. On the war front, the new government and its AMISOM allies also managed to secure control of 60% of Mogadishu, where 80% of the capital's population now lives. According to the African Union and Prime Minister Mohamed, with increasing troop strength the pace of territorial gains is expected to greatly accelerate.
On 19 June 2011, Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed resigned from his position as Prime Minister of Somalia. Part of the controversial Kampala Accord's conditions, the agreement would also see the mandates of the President, the Parliament Speaker and Deputies extended until August 2012, after which point new elections are to be organized.Somalia: PM Mohamed Abdullahi Farmajo resignsBBC.co.uk (19 June 2011). Retrieved 15 December 2011. Abdiweli Mohamed Ali, Mohamed's former Minister of Planning and International Cooperation, was later named permanent Prime Minister.
Federal government
As part of the official "Roadmap for the End of Transition", a political process which provided clear benchmarks leading toward the formation of permanent democratic institutions in Somalia, the Transitional Federal Government's interim mandate ended on 20 August 2012. The Federal Parliament of Somalia was concurrently inaugurated, ushering in the Federal Government of Somalia, the first permanent central government in the country since the start of the civil war. On 10 September 2012, parliament elected Hassan Sheikh Mohamud as the new President of Somalia. President Mohamud later appointed Abdi Farah Shirdon as the new Prime Minister on 6 October 2012, who was succeeded in office by Abdiweli Sheikh Ahmed on 21 December 2013. In April 2013, Hassan resumed national reconciliation talks between the central government inMogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port ...
and the secessionist Somaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still conside ...
authorities. Organized by the government of Turkey in Ankara, the meeting ended with a signed agreement between Hassan and Ahmed Mahamoud Silanyo, President of Somaliland, agreeing to allocate fairly to the Somaliland its portion of the development aid earmarked for Somalia as a whole and to cooperate on security.

 In August 2013, the Somali federal government signed a national reconciliation agreement in Addis Ababa with the autonomous Jubaland administration based in southern Somalia. Endorsed by the federal State Minister for the Presidency Farah Abdulkadir on behalf of Hassan, the pact was brokered by the Foreign Ministry of Ethiopia and came after protracted bilateral talks. Under the terms of the agreement, Jubaland will be administered for a two-year period by a Juba Interim Administration and led by the region's incumbent president, Ahmed Mohamed Islam (Madobe). The regional president will serve as the chairperson of a new Executive Council, to which he will appoint three deputies. Management of Kismayo's seaport and airport will also be transferred to the Federal Government after a period of six months, and revenues and resources generated from these infrastructures will be earmarked for Jubaland's service delivery and security sectors as well as local institutional development. Additionally, the agreement includes the integration of Jubaland's military forces under the central command of the Somali National Army (SNA), and stipulates that the Juba Interim Administration will command the regional police. UN Special Envoy to Somalia Nicholas Kay hailed the pact as "a breakthrough that unlocks the door for a better future for Somalia,"
In August 2014, the Somali-government-led Operation Indian Ocean was launched against the Al-Shabaab (militant group), Al-Shabaab militant group to clean up the remaining insurgent-held pockets in the countryside.
On 17 December 2014, former Premier Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke was reappointed Prime Minister.
In February 2015, Hassan chaired a three-day consultation forum in
In August 2013, the Somali federal government signed a national reconciliation agreement in Addis Ababa with the autonomous Jubaland administration based in southern Somalia. Endorsed by the federal State Minister for the Presidency Farah Abdulkadir on behalf of Hassan, the pact was brokered by the Foreign Ministry of Ethiopia and came after protracted bilateral talks. Under the terms of the agreement, Jubaland will be administered for a two-year period by a Juba Interim Administration and led by the region's incumbent president, Ahmed Mohamed Islam (Madobe). The regional president will serve as the chairperson of a new Executive Council, to which he will appoint three deputies. Management of Kismayo's seaport and airport will also be transferred to the Federal Government after a period of six months, and revenues and resources generated from these infrastructures will be earmarked for Jubaland's service delivery and security sectors as well as local institutional development. Additionally, the agreement includes the integration of Jubaland's military forces under the central command of the Somali National Army (SNA), and stipulates that the Juba Interim Administration will command the regional police. UN Special Envoy to Somalia Nicholas Kay hailed the pact as "a breakthrough that unlocks the door for a better future for Somalia,"
In August 2014, the Somali-government-led Operation Indian Ocean was launched against the Al-Shabaab (militant group), Al-Shabaab militant group to clean up the remaining insurgent-held pockets in the countryside.
On 17 December 2014, former Premier Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke was reappointed Prime Minister.
In February 2015, Hassan chaired a three-day consultation forum in Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port ...
with presidents Abdiweli Mohamed Ali, Ahmed Mohamed Islam and Sharif Hassan Sheikh Adan of the Puntland, Jubaland and South West State regional administrations, respectively. Under the rubric of the New Deal for Somalia, Hassan held additional national reconciliation talks with the regional leaders in Garowe in April and May of the year. The officials therein signed a seven-point agreement in Garowe authorizing the immediate deployment of the 3,000 troops from Puntland toward the Somali National Army. They also agreed to integrate soldiers from the other regional states into the SNA.
On 8 February 2017, Somali MPs elected Ex-Prime Minister Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed, Mohamed Abdullahi "Farmajo" Mohamed in a surprise result. On 23 February 2017, President Mohamed appointed former humanitarian worker and businessman Hassan Ali Khaire, Hassan Khaire as his Prime Minister.
When President Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed's term expired in February 2021, dates had not been set for the election of a successor, and fighting subsequently broke out in Mogadishu. This fighting continued until May 2021, when the government and opposition agreed to hold elections within 60 days; after further negotiation, the presidential election was scheduled for October 10.
In December 2021, Mohamed revoked the authority of prime minister Mohamed Hussein Roble to organize upcoming elections and suggested that a new committee should be formed to oversee them. This prompted Roble to accuse Mohamed of sabotaging the electoral process on 26 December 2021. On 27 December, Mohamed announced that he was suspending Roble over alleged obstruction of corruption allegations.
On 15 May 2022, Hassan Sheikh Mohamud was again 2022 Somali presidential election, elected as President of Somalia.
Timelines
Ancient
:*c. 2350 BC: TheLand of Punt
The Land of Punt ( Egyptian: '' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported gold, aromatic resins, blackwood, ebony, ivory an ...
establishes trade with the Ancient Egyptians.
:*1st century AD: City states on the Somali coast are active in commerce trading with Ancient Greeks, Greek, and later Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
merchants.
Muslim era
:*700–900: Somali people, Somalis adoptIslam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
.
:*9th century – 13th century: Adal Kingdom.
:*10th century – 16th century: Sultanate of Mogadishu.
:*1285–1415: The rise and fall of the Sultanate of Ifat.
:*1200s – late 1600s: The rise and fall of the Ajuran Sultanate
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in the ...
.
:*1300–1400: Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port ...
, Zeila
Zeila ( so, Saylac, ar, زيلع, Zayla), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila (or Hawilah) with the Bibli ...
and Barawe are visited by Ibn Battuta and Zheng He.
:*1415–1559: The rise and fall of the Adal Sultanate
The Adal Sultanate, or the Adal Empire or the ʿAdal or the Bar Saʿad dīn (alt. spelling ''Adel Sultanate, ''Adal ''Sultanate'') () was a medieval Sunni Muslim Empire which was located in the Horn of Africa. It was founded by Sabr ad-Din ...
.
:*1528–1535: Ethiopian-Adal War, Jihad against Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia led by Ahmad ibn Ibrihim al-Ghazi (also called Ahmed Gurey and Ahmed Gran; "the Left-handed").''Somalia: From The Dawn of Civilization To The Modern Times'' Chapter 5: Puntland: Ancient Somali Contacts With Other CountriesCivicsWeb :*late 17th – late 19th century:
Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
's domination in Gulf of Aden trade, Haji Sharmarke Ali Saleh, governor of Zeila
Zeila ( so, Saylac, ar, زيلع, Zayla), also known as Zaila or Zayla, is a historical port town in the western Awdal region of Somaliland.
In the Middle Ages, the Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela identified Zeila (or Hawilah) with the Bibli ...
, Berbera
Berbera (; so, Barbara, ar, بربرة) is the capital of the Sahil region of Somaliland and is the main sea port of the country. Berbera is a coastal city and was the former capital of the British Somaliland protectorate before Hargeisa. It ...
and Tadjourah, and Sultanate of the Geledi.
:*mid-18th century – 1929: Majeerteen Sultanate
The Majeerteen Sultanate ( so, Suldanadda Majeerteen 𐒈𐒚𐒐𐒆𐒖𐒒𐒖𐒆𐒆𐒖 𐒑𐒖𐒃𐒜𐒇𐒂𐒜𐒒, lit=Boqortooyada Majerteen, ar, سلطنة مجرتين), also known as Majeerteen Kingdom or Majeerteenia and Migiu ...
also known as Migiurtinia/Majeerteenia.
:*1878–1927: Sultanate of Hobyo
The Sultanate of Hobyo ( so, Saldanadda Hobyo, ar, سلطنة هوبيو), also known as the Sultanate of Obbia,''New International Encyclopedia'', Volume 21, (Dodd, Mead: 1916), p.283. was a 19th-century Somali people, Somali kingdom in present ...
.
Modern era
 :*20 July 1887 : British Somaliland protectorate (in the north) subordinated to
:*20 July 1887 : British Somaliland protectorate (in the north) subordinated to Aden
Aden ( ar, عدن ' Yemeni: ) is a city, and since 2015, the temporary capital of Yemen, near the eastern approach to the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aden), some east of the strait Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000 people. ...
to 1905.
:*3 August 1889: Benadir Coast Italian Protectorate (in the northeast), (unoccupied until May 1893).
:*1895–1920: Dervish movement (Nugaal), Darawiish
:*16 March 1905: Italian Somaliland
Italian Somalia ( it, Somalia Italiana; ar, الصومال الإيطالي, Al-Sumal Al-Italiy; so, Dhulka Talyaaniga ee Soomaalida), was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th centur ...
colony (in the northeast, central and south).
:*July 1910: Italian Somaliland a crown colony
:*1920: The Dervish leader Mohammed Abdullah Hassan dies in Imey and the longest and bloodiest colonial resistance war in Africa ends.
:*15 January 1935: Italian Somaliland, part of Italian East Africa along with Italian Eritrea (and from 1936 Ethiopia).
:*1 June 1936: The Somalia Governorate is established as one of the six governorates of Italian East Africa.
World War II
:*18 August 1940: Italian occupation of British Somaliland. :*February 1941: British administration of Italian Somaliland.Independence and Cold War
:*1 April 1950: Italian Somaliland becomes a United Nations trust territory administration, the Trust Territory of Somalia, which is promised independence within 10 years. :*26 June 1960: British Somaliland is granted independence as theState of Somaliland
The State of Somaliland (, ) was a short-lived independent country in the territory of present-day unilaterally declared Republic of Somaliland. It existed on the territory of former British Somaliland for five days between 26 June 1960 and 1 ...
, with the understanding that it is to reunite with Italian Somaliland.
:*1 July 1960: Reunification of British Somaliland with Italian Somaliland to form the Somali Republic
The Somali Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Soomaaliyeed; it, Repubblica Somala; ar, الجمهورية الصومالية, Jumhūriyyat aṣ-Ṣūmālīyyah) was a sovereign state composed of Somalia and Somaliland, following the unification o ...
.
:*1 July 1960: First president of Somali National Assembly, Speaker of the Somali Union Act. Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf
Haji Bashir Ismail Yusuf ( so, Xaaji Bashiir Ismaaciil Yuusuf, ar, حاجي بشير اسماعيل يوسف) (b. 1912 in Hobyo, Somalia – d. 1984 in Cairo, Egypt), commonly referred to as Haji Bashir,SAMIULLAH, MUHAMMAD. DEVELOPMENT OF CREATI ...
.
:*1 July 1960 – 1967: Presidency of Aden Abdullah Osman Daar
:*1967–1969: Presidency of Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke; assassinated by one of the policemen assigned to his protection.
:*21 October 1969: Somali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic ( so, Jamhuuriyadda Dimuqraadiya Soomaaliyeed; ar, الجمهورية الديمقراطية الصومالية, ; it, Repubblica Democratica Somala) was the name that the socialist military government gave to Som ...
.
:*1969–1991: Siad Barre, leader of the Supreme Revolutionary Council, rises to power.
:*23 July 1977 – 15 March 1978: Ogaden War.
:*1982: 1982 Ethiopian–Somali Border War.
:*1986: Fall of Barre government.
:*1991: Somaliland Declaration of Independence, Somaliland declares independence from Somalia.
See also
*Economic history of Somalia *Federal Parliament of Somalia *History of Africa *List of colonial governors of British Somaliland *List of colonial governors of Italian Somaliland *Military history of Somalia *Political history of Somalia *President of Somalia *Prime Minister of Somalia *XeerNotes
References
* * * *External links
* {{History of Africa History of Somalia, ja:ソマリア#歴史