Medal of Honor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the

 During the first year of the
During the first year of the
File:US-MOH-1862.png, 1862–95 Army version
File:US-MOH-1896.png, 1896–1903 Army version
File:US-MOH-1904.png, 1904–44 Army version
File:Army Medal of Honor.jpg, Post 1944 Army version
File:US Navy Medal of Honor (1862 original).png, 1862–1912 Navy version
File:US Navy Medal of Honor (1913 to 1942).png, 1913–42 Navy version
File:Tiffany Cross Medal of Honor.jpg, 1919–42 Navy "Tiffany Cross" version
File:NavyMedalofHonor.jpg, Post 1942 Navy version

 Since 1944, the Medal of Honor has been attached to a light blue colored moiré silk neck ribbon that is in width and in length. The center of the ribbon displays thirteen white stars in the form of three chevron. Both the top and middle chevrons are made up of 5 stars, with the bottom chevron made of 3 stars. The Medal of Honor is one of only two United States military awards suspended from a neck ribbon. The other is the Commander's Degree of the
Since 1944, the Medal of Honor has been attached to a light blue colored moiré silk neck ribbon that is in width and in length. The center of the ribbon displays thirteen white stars in the form of three chevron. Both the top and middle chevrons are made up of 5 stars, with the bottom chevron made of 3 stars. The Medal of Honor is one of only two United States military awards suspended from a neck ribbon. The other is the Commander's Degree of the
 On October 23, 2002, was enacted, modifying , authorizing a Medal of Honor Flag to be presented to each person to whom a Medal of Honor is awarded. In the case of a posthumous award, the flag will be presented to whomever the Medal of Honor is presented to, which in most cases will be the primary
On October 23, 2002, was enacted, modifying , authorizing a Medal of Honor Flag to be presented to each person to whom a Medal of Honor is awarded. In the case of a posthumous award, the flag will be presented to whomever the Medal of Honor is presented to, which in most cases will be the primary
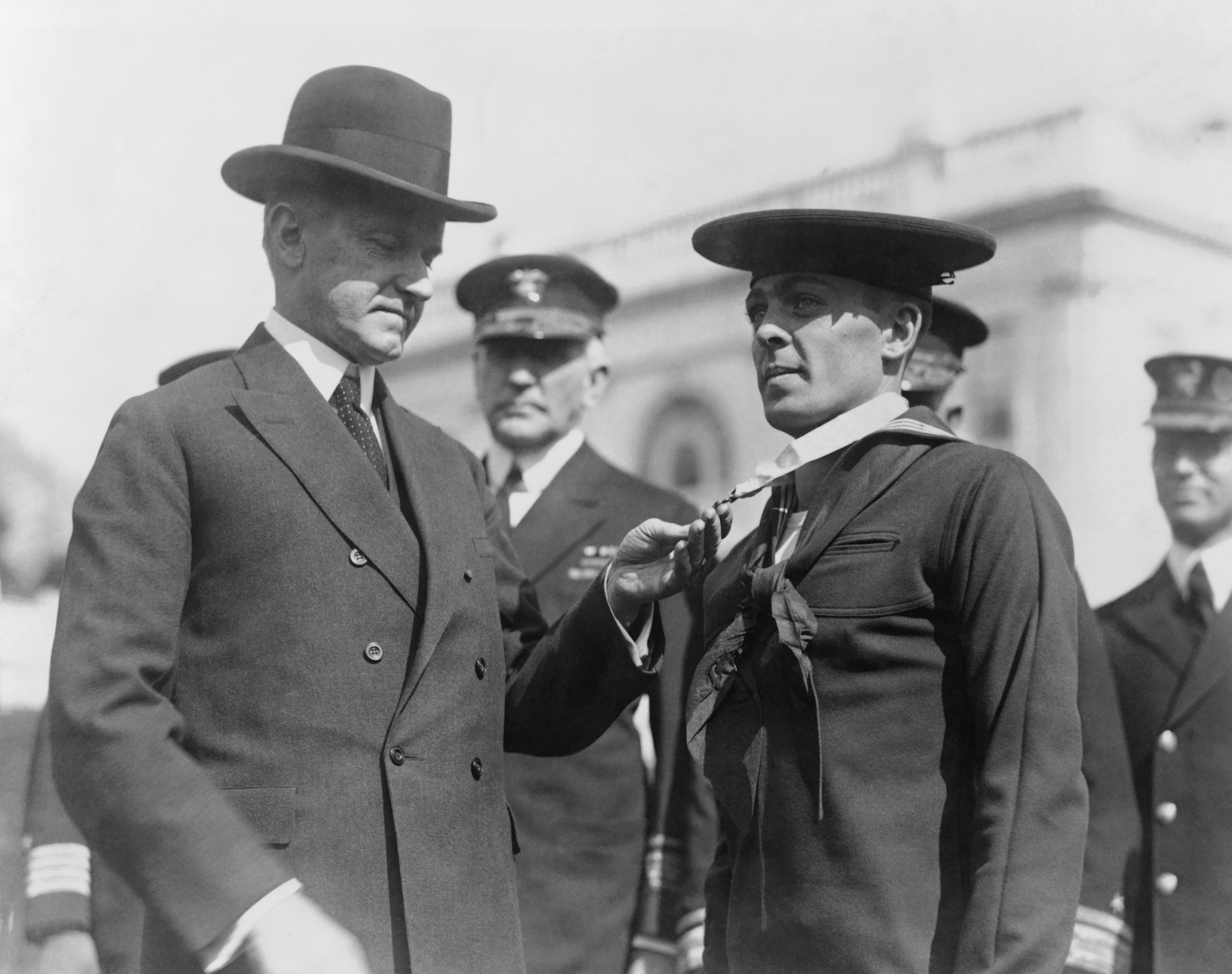 There are two distinct protocols for awarding the Medal of Honor. The first and most common is nomination and approval through the chain of command of the service member. The second method is nomination by a member of the U.S. Congress, generally at the request of a constituent. In both cases, if the proposal is outside the time limits for the recommendation, approval to waive the time limit requires a special Act of Congress. The Medal of Honor is presented by the President on behalf of, and in the name of, the Congress. Since 1980, nearly all Medal of Honor recipients—or in the case of posthumous awards, the next of kin—have been personally decorated by the president. Since 1941, more than half of the Medals of Honor have been awarded posthumously.
There are two distinct protocols for awarding the Medal of Honor. The first and most common is nomination and approval through the chain of command of the service member. The second method is nomination by a member of the U.S. Congress, generally at the request of a constituent. In both cases, if the proposal is outside the time limits for the recommendation, approval to waive the time limit requires a special Act of Congress. The Medal of Honor is presented by the President on behalf of, and in the name of, the Congress. Since 1980, nearly all Medal of Honor recipients—or in the case of posthumous awards, the next of kin—have been personally decorated by the president. Since 1941, more than half of the Medals of Honor have been awarded posthumously.

 The four specific statutory sections authorizing the medal, as last amended on August 13, 2018, are as follows:
* Army:
* Navy and Marine Corps:
* Air Force and Space Force:
* Coast Guard: A version is authorized but it has never been awarded.
The four specific statutory sections authorizing the medal, as last amended on August 13, 2018, are as follows:
* Army:
* Navy and Marine Corps:
* Air Force and Space Force:
* Coast Guard: A version is authorized but it has never been awarded.
 * Although not required by law or military regulation, members of the uniformed services are encouraged to render salutes to recipients of the Medal of Honor as a matter of respect and courtesy regardless of rank or status, whether or not they are in uniform. This is one of the few instances where a living member of the military will receive salutes from members of a higher rank. According to paragraph 1.6.1.1 of Air Force Instruction 1-1, the United States Air Force requires that salutes be rendered to Medal of Honor recipients.
* Although not required by law or military regulation, members of the uniformed services are encouraged to render salutes to recipients of the Medal of Honor as a matter of respect and courtesy regardless of rank or status, whether or not they are in uniform. This is one of the few instances where a living member of the military will receive salutes from members of a higher rank. According to paragraph 1.6.1.1 of Air Force Instruction 1-1, the United States Air Force requires that salutes be rendered to Medal of Honor recipients.
From the website of the Congressional Medal of Honor Society. Retrieved on July 1, 2012. To prevent the making of copies of the medal, Brigadier General George Gillespie, Jr., a Medal of Honor recipient from the Civil War, applied for and obtained a
 * The first black recipients of the Medal of Honor were sixteen Army soldiers and sixteen Navy sailors that fought during the Civil War. The first award was announced on April 6, 1865, to twelve black soldiers from the five regiments of
* The first black recipients of the Medal of Honor were sixteen Army soldiers and sixteen Navy sailors that fought during the Civil War. The first award was announced on April 6, 1865, to twelve black soldiers from the five regiments of
List of Recipients
On November 6, 2014, President Obama presented the Medal of Honor posthumously to First Lieutenant Alonzo Cushing for actions on July 3, 1863, during the
 During the Civil War, Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton promised a Medal of Honor to every man in the
During the Civil War, Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton promised a Medal of Honor to every man in the
Congressional Medal of Honor Society
U.S. Army Medal of Honor
Submarine Force Medal of Honor Recipients
Submarine Force Museum website
List of Native Americans who have received the Medal of Honor
(Medal of Honor recipients depicted on film)
National Medal of Honor Museum of Military History
in Chattanooga, Tennessee
American Valor
PBS/WETA.
Loubat, J. F. and Jacquemart, Jules, Illustrator, ''The Medallic History of the United States of America 1776–1876''.
U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry: Medal of Honor-Army
U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry: Medal of Honor-Navy
U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry: Medal of Honor-Air Force
Pritzker Military Museum & Library
{{DEFAULTSORT:Medal Of Honor 1862 establishments in the United States Awards established in 1862
United States Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is ...
' highest military decoration
Military awards and decorations are distinctions given as a mark of honor for military heroism, meritorious or outstanding service or achievement. DoD Manual 1348.33, 2010, Vol. 3 A decoration is often a medal consisting of a ribbon and a medal ...
and is awarded to recognize American soldiers
A soldier is a person who is a member of an army. A soldier can be a conscripted or volunteer enlisted person, a non-commissioned officer, or an officer.
Etymology
The word ''soldier'' derives from the Middle English word , from Old French ...
, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of valor. The medal is normally awarded by the president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal gove ...
, but as it is presented "in the name of the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washi ...
", it is sometimes erroneously referred to as the "Congressional Medal of Honor".
There are three distinct variants of the medal: one for the Department of the Army, awarded to soldiers, one for the Department of the Navy, awarded to sailors, marines, and coast guardsmen, and one for the Department of the Air Force, awarded to airmen and guardians. The Medal of Honor was introduced for the Department of the Navy in 1861, soon followed by the Department of the Army's version in 1862. The Department of the Air Force used the Department of the Army's version until they received their own distinctive version in 1965. The Medal of Honor is the oldest continuously issued combat decoration of the United States Armed Forces. The president typically presents the Medal of Honor at a formal ceremony intended to represent the gratitude of the American people, with posthumous presentations made to the primary next of kin.
According to the Medal of Honor Historical Society of the United States, there have been 3,530 Medals of Honor awarded to 3,511 individuals since the decoration's creation, with over 40% awarded for actions during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
. In 1990, Congress designated March 25 annually as "National Medal of Honor Day
Medal of Honor Day is a United States federal observance that is celebrated every year on March 25. It was created to honor the "heroism and sacrifice of Medal of Honor recipients for the United States." The holiday has been celebrated since 19 ...
".
History

 During the first year of the
During the first year of the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polic ...
(1861–1865), a proposal for a battlefield decoration for valor was submitted to Lieutenant General Winfield Scott, the Commanding General of the United States Army, by Lieutenant Colonel Edward D. Townsend, an assistant adjutant at the Department of War War Department may refer to:
* War Department (United Kingdom)
* United States Department of War (1789–1947)
See also
* War Office, a former department of the British Government
* Ministry of defence
* Ministry of War
* Ministry of Defence
* D ...
and Scott's chief of staff. Scott, however, was strictly against medals being awarded, which was the European tradition. After Scott retired in October 1861, Secretary of the Navy Gideon Welles adopted the idea of a decoration to recognize and honor distinguished naval service.
On December 9, 1861, Iowa
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wiscon ...
Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
James W. Grimes
James Wilson Grimes (October 20, 1816 – February 7, 1872) was an American politician, serving as the third Governor of Iowa and a United States Senator from Iowa.
Biography
Born in Deering, New Hampshire, Grimes graduated from Hampton Acad ...
, Chairman on the Committee on Naval Affairs, submitted Bill S. 82 (12 Stat. 329–330) during the Second Session of the 37th Congress
The 37th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1861, ...
, "''An Act to further promote the Efficiency of the Navy''". The bill included a provision (Chap. 1, Sec. 7) for 200 "medals of honor", "to be bestowed upon such petty officers, seamen, landsmen, and marines as shall most distinguish themselves by their gallantry in action and other seaman-like qualities during the present war, ..." On December 21, the bill was passed and signed into law by President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
. Secretary Welles directed the Philadelphia Mint to design the new military decoration. On May 15, 1862, the United States Department of the Navy ordered 175 medals ($1.85 each) from the U.S. Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bullion. It does not produce paper money; that ...
in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
with "Personal Valor" inscribed on the back of each one.
On February 15, 1862, Senator Henry Wilson, the chairman of the Senate Committee on Military Affairs and the Militia, introduced a resolution for a Medal of Honor for the Army. The resolution (37th Congress, Second Session; Resolution No. 52, 12 Stat. 623–624) was approved by Congress and signed into law on July 12, 1862 ("''A Resolution to provide for the Presentation of "Medals of Honor" to the Enlisted Men of the Army and Volunteer Forces who have distinguished, or may distinguish, themselves in Battle during the present Rebellion''"). This measure provided for awarding a medal of honor "to such non-commissioned officers and privates as shall most distinguish themselves by their gallantry in action and other soldier-like qualities during the present insurrection." During the war, Townsend would have some medals delivered to some recipients with a letter requesting acknowledgment of the "Medal of Honor". The letter, written and signed by Townsend on behalf of the Secretary of War, stated that the resolution was "to provide for the presentation of medals of honor to the enlisted men of the army and volunteer forces who have distinguished or may distinguish themselves in battle during the present rebellion." By mid-November the Department of War contracted with Philadelphia silversmith William Wilson and Son, who had been responsible for the Navy's design, to prepare 2,000 medals for the Army ($2.00 each) to be cast at the mint. The Army's version had "The Congress to" written on the back of the medal. Both versions were made of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish ...
and coated with bronze, which "gave them a reddish tint".
On March 3, 1863, Congress made the Medal of Honor a permanent decoration, and it was authorized for officers of the Army. On March 25, the Secretary of War presented the first Medals of Honor to six U.S. Army volunteers in his office.
In 1896, the ribbon of the Army's version of the Medal of Honor was redesigned with all stripes being vertical. Again, in 1904 the planchet of the Army's version of the Medal of Honor was redesigned by General George Lewis Gillespie. The purpose of the redesign was to help distinguish the Medal of Honor from other medals, particularly the membership insignia issued by the Grand Army of the Republic.
In 1917, based on the report of the Medal of Honor Review Board, established by Congress in 1916, 911 recipients were stricken off the Army's Medal of Honor list because the medal had been awarded inappropriately. Among them were William Frederick "Buffalo Bill" Cody and Mary Edwards Walker. In 1977, Congress began reviewing numerous cases; it reinstated the medals for Cody and four other civilian scouts on June 12, 1989. Walker's medal was restored in 1977.
A separate Coast Guard Medal of Honor was authorized in 1963, but not yet designed or awarded.
A separate design for a version of the medal for the Department of the Air Force was created in 1956, authorized in 1960, and officially adopted on April 14, 1965. Previously, airmen of the U.S. Air Force received the Army's version of the medal.
Appearance
There are three versions of the Medal of Honor, one for each of the military departments of the Department of Defense (DoD): the Department of the Army, Department of the Navy, and Department of the Air Force. Members of the Coast Guard (Department of Homeland Security) are eligible to receive the Department of the Navy's version. Each medal is constructed differently and the components are made from gilding metals and red brass alloys with some gold plating, enamel, and bronze pieces. The United States Congress considered a bill in 2004 which would require the Medal of Honor to be made with 90% gold, the same composition as the lesser-known Congressional Gold Medal, but the measure was dropped.Department of the Army variant
The Department of the Army's version is described by the Institute of Heraldry as "a gold five-pointed star, each point tipped with trefoils, wide, surrounded by a green laurel wreath and suspended from a gold bar inscribed ''VALOR'', surmounted by an eagle. In the center of the star, Minerva's head surrounded by the words ''UNITED STATES OF AMERICA''. On each ray of the star is a green oak leaf. On the reverse is a bar engraved ''THE CONGRESS TO'' with a space for engraving the name of the recipient." The pendant and suspension bar are made of gilding metal, with the eye, jump rings, and suspension ring made of red brass. The finish on the pendant and suspension bar is hard enameled, gold plated, and rose gold plated, with polished highlights.Department of the Navy variant
The Department of the Navy's version is described as "a five-pointed bronze star, tipped with trefoils containing a crown of laurel and oak. In the center is Minerva, personifying the United States, standing with her left hand resting on fasces and her right hand holding a shield emblazoned with the shield from the coat of arms of the United States. She repulses Discord, represented by snakes (originally, she was repulsing the snakes ofsecession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics l ...
). The medal is suspended from the flukes of an anchor. It is made of solid red brass, oxidized and buffed.
Department of the Air Force variant
The Department of the Air Force version is described as "within a wreath of green laurel, a gold five-pointed star, one point down, tipped with trefoils and each point containing a crown of laurel and oak on a green background. Centered on the star, an annulet of 34 stars is a representation of the head of theStatue of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty (''Liberty Enlightening the World''; French: ''La Liberté éclairant le monde'') is a colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor in New York City, in the United States. The copper statue, ...
. The star is suspended from a bar inscribed with the word ''VALOR'' above an adaptation of Jupiter's thunderbolt from the Department of the Air Force's seal. The pendant is made of gilding metal. The connecting bar, hinge, and pin are made of bronze. The finish on the pendant and suspension bar is hard enameled, gold plated, and rose gold plated, with buffed relief.
Historic versions
The Medal of Honor has evolved in appearance over time. The upside-down star design of the Department of the Navy version's pendant adopted in early 1862 has not changed since its inception. The Army's 1862 version followed and was identical to the Department of the Navy's version except an eagle perched atop cannons was used instead of an anchor to connect the pendant to the suspension ribbon. The medals featured a female allegory of the Union, with a shield in her right hand that she used to fend off a crouching attacker and serpents. In her left hand, she held a fasces. There are 34 stars surrounding the scene, representing the number of states in the union at the time. In 1896, the Army version changed the ribbon's design and colors due to misuse and imitation by nonmilitary organizations. In 1904, the Army " Gillespie" version introduced a smaller redesigned star and the ribbon was changed to the light blue pattern with white stars seen today. The 1904 Army version also introduced a bar with the word "Valor" above the star. In 1913, the Department of the Navy version adopted the same ribbon pattern. After World War I, the Department of the Navy decided to separate the Medal of Honor into two versions, one for combat and one for non-combat. This was an attempt to circumvent the requirement enacted in 1919 that recipients participate "in action involving actual conflict with the enemy," which would have foreclosed non-combat awards. By treating the 1919 Medal of Honor as a separate award from its Civil War counterpart, this allowed the Department of the Navy to claim that it was not literally in violation of the 1919 law. The original upside-down star was designated as the non-combat version and a new pattern of the medal pendant, in cross form, was designed by the Tiffany Company in 1919. Secretary of the Navy Josephus Daniels selected Tiffany after snubbing the Commission of Fine Arts, which had submitted drawings that Daniels criticized as "un-American". The "Tiffany Cross" was to be presented to a sailor or marine who "in action involving actual conflict with the enemy, distinguish shimself conspicuously by gallantry and intrepidity at the risk of his life above and beyond the call of duty". Despite the "actual conflict" guidelines, the ''Tiffany Cross'' was awarded to Navy CDR (later RADM) Richard E. Byrd and Floyd Bennett for their flight to the North Pole in 1926. The decision was controversial within the Navy's Bureau of Navigation (which handled personnel administration), and officials considered asking the attorney general of the United States for an advisory opinion on the matter. Byrd himself apparently disliked the "Tiffany Cross", and eventually requested the alternate version of the medal from President Herbert Hoover in 1930. The ''Tiffany Cross'' itself was not popular among recipients—one author reflected that it was "the most short-lived, legally contentious, and unpopular version of the Medal of Honor in American history." In 1942, in response to a lawsuit, the Department of the Navy requested an amendment to expressly allow noncombat awards of the Medal of Honor. When the amendment passed, the Department of the Navy returned to using only the original 1862 inverted 5-point star design. In 1944, the suspension ribbons for both versions were replaced with the now-familiar neck ribbon. When the Department of the Air Force's version was designed in 1956, it incorporated similar elements and design from the Department of the Army version. At the Department of the Air Force leadership's insistence, the new medal depicted the Statue of Liberty's image in place of Minerva on the medal and changed the connecting device from an eagle to Jupiter's thunderbolt flanked with wings as found on the Department of the Air Force's seal.Neck ribbon, service ribbon and lapel button
 Since 1944, the Medal of Honor has been attached to a light blue colored moiré silk neck ribbon that is in width and in length. The center of the ribbon displays thirteen white stars in the form of three chevron. Both the top and middle chevrons are made up of 5 stars, with the bottom chevron made of 3 stars. The Medal of Honor is one of only two United States military awards suspended from a neck ribbon. The other is the Commander's Degree of the
Since 1944, the Medal of Honor has been attached to a light blue colored moiré silk neck ribbon that is in width and in length. The center of the ribbon displays thirteen white stars in the form of three chevron. Both the top and middle chevrons are made up of 5 stars, with the bottom chevron made of 3 stars. The Medal of Honor is one of only two United States military awards suspended from a neck ribbon. The other is the Commander's Degree of the Legion of Merit
The Legion of Merit (LOM) is a military award of the United States Armed Forces that is given for exceptionally meritorious conduct in the performance of outstanding services and achievements. The decoration is issued to members of the eight ...
, and is usually awarded to individuals serving foreign governments.
On May 2, 1896, Congress authorized a "ribbon to be worn with the medal and rosette or knot
A knot is an intentional complication in Rope, cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including List of hitch knots, hitches, List of bend knots, bends, List of loop knots, loop knots, ...
to be worn in lieu of the medal." The service ribbon
A medal ribbon, service ribbon or ribbon bar is a small ribbon, mounted on a small metal bar equipped with an attaching device, which is generally issued for wear in place of a medal when it is not appropriate to wear the actual medal. Each co ...
is light blue with five white stars in the form of an "M". It is placed first in the top position in the order of precedence and is worn for situations other than full-dress military uniform. The lapel button is a , six-sided light blue bowknot rosette with thirteen white stars and may be worn on appropriate civilian clothing on the left lapel.
Devices
In 2011, Department of Defense instructions in regard to the Medal of Honor were amended to read "for each succeeding act that would otherwise justify award of the Medal of Honor, the individual receiving the subsequent award is authorized to wear an additional Medal of Honor ribbon and/or a 'V' device on the Medal of Honor suspension ribbon" (the "V" device is a bronze miniature letter "V" with serifs that denotes valor). The Medal of Honor was the only decoration authorized to use the "V" device (none were ever issued) to designate subsequent awards in such a fashion. Nineteen individuals, all now deceased, were double Medal of Honor recipients. In July 2014, DoD instructions were changed to read, "A separate MOH is presented to an individual for each succeeding act that justified award.", removing the authorization for the V device.Medal of Honor Flag
next of kin
A person's next of kin (NOK) are that person's closest living blood relatives. Some countries, such as the United States, have a legal definition of "next of kin". In other countries, such as the United Kingdom, "next of kin" may have no legal d ...
of the deceased awardee.
The flag was based on a concept by retired U.S. Army Special Forces First Sergeant Bill Kendall of Jefferson, Iowa, who in 2001, designed a flag to honor Medal of Honor recipient Army Air Forces Captain Darrell Lindsey
Darrell Robins Lindsey (December 30, 1919 – August 9, 1944) was a bomber pilot in the U.S. Army Air Forces during World War II and a posthumous recipient of the Medal of Honor.
Early life
Lindsey was born in Jefferson, Iowa, to Jesse Lyle ...
, a B-26 pilot from Jefferson who was killed in action during World War II. Kendall's design of a light blue field emblazoned with 13 white five-pointed stars was nearly identical to that of Sarah LeClerc's of the Institute of Heraldry. LeClerc's gold-fringed flag, ultimately accepted as the official flag, does not include the words "Medal of Honor" as written on Kendall's flag. The color of the field and the 13 white stars, arranged in the form of a three-bar chevron, consisting of two chevrons of five stars and one chevron of three stars, emulate the suspension ribbon of the Medal of Honor. The flag has no defined proportions.
The first Medal of Honor Flag recipient was U.S. Army Sergeant First Class Paul R. Smith
Paul Ray Smith (September 24, 1969 – April 4, 2003) was a United States Army soldier who was Posthumous recognition, posthumously awarded the Medal of Honor for his actions during the 2003 invasion of Iraq. While serving with B Company, 11th En ...
, whose flag was presented posthumously. President George W. Bush presented the Medal of Honor and Flag to the family of Smith during the award ceremony for him in the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest, Washington, D.C., NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. preside ...
on April 4, 2005.
A special Medal of Honor Flag presentation ceremony was held for over 60 living Medal of Honor recipients on board the in September 2006.
Presentation
 There are two distinct protocols for awarding the Medal of Honor. The first and most common is nomination and approval through the chain of command of the service member. The second method is nomination by a member of the U.S. Congress, generally at the request of a constituent. In both cases, if the proposal is outside the time limits for the recommendation, approval to waive the time limit requires a special Act of Congress. The Medal of Honor is presented by the President on behalf of, and in the name of, the Congress. Since 1980, nearly all Medal of Honor recipients—or in the case of posthumous awards, the next of kin—have been personally decorated by the president. Since 1941, more than half of the Medals of Honor have been awarded posthumously.
There are two distinct protocols for awarding the Medal of Honor. The first and most common is nomination and approval through the chain of command of the service member. The second method is nomination by a member of the U.S. Congress, generally at the request of a constituent. In both cases, if the proposal is outside the time limits for the recommendation, approval to waive the time limit requires a special Act of Congress. The Medal of Honor is presented by the President on behalf of, and in the name of, the Congress. Since 1980, nearly all Medal of Honor recipients—or in the case of posthumous awards, the next of kin—have been personally decorated by the president. Since 1941, more than half of the Medals of Honor have been awarded posthumously.
Evolution of criteria
* 19th century: Several months after President Abraham Lincoln signed Public Resolution 82 into law on December 21, 1861, for a Navy medal of honor, a similar resolution was passed in July 1862 for an Army version of the medal. Six U.S. Army soldiers who hijacked a Confederatelocomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, motor coach, railcar or power car; t ...
named ''The General'' in 1862 were the first Medal of Honor recipients; James J. Andrews
James J. Andrews (c. 1829 – June 7, 1862) was a Kentucky civilian who worked for the Union Army during the early years of the American Civil War. He led a daring raid behind enemy lines on the Western and Atlantic Railroad, known as ...
led the raid. He was caught and hanged as a U.S. spy, but as a civilian, he was not eligible to receive the medal. Many Medals of Honor awarded in the 19th century were associated with "saving the flag" (and country), not just for patriotic reasons, but because the U.S. flag was a primary means of battlefield communication at the time. Because no other military decoration was authorized during the Civil War, some seemingly less exceptional and notable actions were recognized by a Medal of Honor during that conflict.
* 20th century: Early in the twentieth century, the Department of the Navy awarded many Medals of Honor for peacetime bravery. For instance, in 1901, John Henry Helms
John Henry Helms (March 16, 1874 – February 17, 1919) was a United States Marine and a recipient of the United States military's highest decoration, the Medal of Honor, for saving a shipmate from drowning.
Biography
Helms was born on March 16, ...
aboard was awarded the medal for saving the ship's cook from drowning. Seven sailors aboard were awarded the medal after the ship's boiler exploded on January 25, 1904. Richard Byrd and Floyd Bennett were awarded the medal—combat ("Tiffany") version despite the existence then of a non-combat form of the Navy medal—for the 1926 flight they claim reached the North Pole. And Admiral Thomas J. Ryan was awarded the medal for saving a woman from the burning Grand Hotel in Yokohama, Japan, following the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake. Between 1919 and 1942, the Department of the Navy issued two separate versions of the Medal of Honor, one for acts related to combat and one for non-combat bravery. The criteria for the award tightened during World War I for the Army version of the Medal of Honor, while the Navy version retained a non-combat provision until 1963. In an Act of Congress of July 9, 1918, the War Department version of the medal required that the recipient "distinguish himself conspicuously by gallantry and intrepidity at the risk of his life above and beyond the call of duty", and also required that the act of valor be performed "in action involving actual conflict with an enemy".Act of July 9, 1918, 40 Stat. 870. This followed shortly after the results of the Army Medal of Honor Review Board, which struck 911 medals from the Medal of Honor list in February 1917 for lack of basic prerequisites. These included the members of the 27th Maine erroneously awarded the medal for reenlisting to guard the capital during the Civil War, 29 members of Abraham Lincoln's funeral detail, and six civilians, including Buffalo Bill Cody (restored along with four other scouts in 1989) and a female doctor, Mary Edwards Walker, who had cared for the sick (this last was restored posthumously in 1977).
* World War II: As a result of lawsuits, the Department of the Navy requested the Congress expressly authorize non-combat medals in the text of the authorizing statute, since the department had been awarding non-combat medals with questionable legal backing that had caused it much embarrassment. The last non-combat Navy Medal of Honor was awarded in 1945, although the Department of the Navy attempted to award a non-combat Medal of Honor as late as the Korean War. Official accounts vary, but generally, the Medal of Honor for combat was known as the "Tiffany Cross", after the company that designed the medal. The Tiffany Cross was first awarded in 1919, but was unpopular partly because of its design as well as a lower gratuity than the Navy's original medal. The Tiffany Cross Medal of Honor was awarded at least three times for non-combat. By a special authorized Act of Congress, the medal was presented to Byrd and Bennett (see above). In 1942, the Department of the Navy reverted to a single Medal of Honor, although the statute still contained a loophole allowing the award for both "action involving actual conflict with the enemy" or "in the line of his profession". Arising from these criteria, approximately 60 percent of the medals earned during and after World War II have been awarded posthumously.
* Public Law 88–77, July 25, 1963: The requirements for the Medal of Honor were standardized among all the services, requiring that a recipient had "distinguished himself conspicuously by gallantry and intrepidity at the risk of his life above and beyond the call of duty." Thus, the act removed the loophole allowing non-combat awards to Navy personnel. The act also clarified that the act of valor must occur during one of three circumstances:
# While engaged in action against an enemy of the United States
# While engaged in military operations involving conflict with an opposing foreign force.
# While serving with friendly foreign forces engaged in an armed conflict against an opposing armed force in which the United States is not a belligerent party."An Act to Amend Titles 10, 14, and 38, United States Code, with Respect to the Award of Certain Medals and the Medal of Honor Roll", July 25, 1963, HR 2998, Public Law 88–77, 77 Stat. 93.
Congress drew the three permutations of combat from President Kennedy's executive order of April 25, 1962, which previously added the same criteria to the Purple Heart. On August 24, Kennedy added similar criteria for the Bronze Star Medal."Subcommittee No.2 Consideration of HR2998, A Bill to Amend Titles 10, 14, and 38, United States Code, with Respect to the Award of Certain Medals and the Medal of Honor Roll", House of Representatives, Committee of Armed Services, June 6, 1963. The amendment was necessary because Cold War armed conflicts did not qualify for consideration under previous statutes such as the 1918 Army Medal of Honor Statute that required valor "in action involving actual conflict with an enemy", since the United States has not formally declared war since World War II as a result of the provisions of the United Nations Charter. According to congressional testimony by the Army's Deputy Chief of Staff for Personnel, the services were seeking authority to award the Medal of Honor and other valor awards retroactive to July 1, 1958, in areas such as Berlin, Lebanon, Quemoy and Matsu Islands, Taiwan Straits, Congo, Laos, Vietnam, and Cuba.
Authority and privileges

 The four specific statutory sections authorizing the medal, as last amended on August 13, 2018, are as follows:
* Army:
* Navy and Marine Corps:
* Air Force and Space Force:
* Coast Guard: A version is authorized but it has never been awarded.
The four specific statutory sections authorizing the medal, as last amended on August 13, 2018, are as follows:
* Army:
* Navy and Marine Corps:
* Air Force and Space Force:
* Coast Guard: A version is authorized but it has never been awarded.
Privileges and courtesies
The Medal of Honor confers special privileges on its recipients. By law, recipients have several benefits: * Each Medal of Honor recipient may have his or her name entered on the Medal of Honor Roll (). * Each person whose name is placed on the Medal of Honor Roll is certified to theUnited States Department of Veterans Affairs
The United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is a Cabinet-level executive branch department of the federal government charged with providing life-long healthcare services to eligible military veterans at the 170 VA medical centers ...
as being entitled to receive a monthly pension above and beyond any military pensions or other benefits for which they may be eligible. The pension is subject to cost-of-living increases; , it is $1,489.73 a month.
* Enlisted recipients of the Medal of Honor are entitled to a supplemental uniform allowance.
* Recipients receive special entitlements to air transportation under the provisions of DOD Regulation 4515.13-R. This benefit allows the recipient to travel as deemed fit, as well as allows the recipient's dependents to travel either overseas–overseas, overseas–continental U.S., or continental U.S.–overseas when accompanied by the recipient.
* Special identification cards and commissary and exchange privileges are provided for Medal of Honor recipients and their eligible dependents.
* Recipients are granted eligibility for interment at Arlington National Cemetery
Arlington National Cemetery is one of two national cemeteries run by the United States Army. Nearly 400,000 people are buried in its 639 acres (259 ha) in Arlington, Virginia. There are about 30 funerals conducted on weekdays and 7 held on Sa ...
, if not otherwise eligible.
* Fully qualified children of recipients automatically appointed to any of the United States service academies.
* Recipients receive a ten percent increase in retired pay.
* Those awarded the medal after October 23, 2002, receive a Medal of Honor Flag
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of valor ...
. The law specified that all 103 living prior recipients as of that date would receive a flag.
* Recipients receive an invitation to all future presidential inaugurations and inaugural balls.
* As with all medals, retired personnel may wear the Medal of Honor on "appropriate" civilian clothing. Regulations specify that recipients of the Medal of Honor are allowed to wear the uniform "at their pleasure" with standard restrictions on political, commercial, or extremist purposes (other former members of the armed forces may do so only at certain ceremonial occasions).
* Most states (40) offer a special license plate for certain types of vehicles to recipients at little or no cost to the recipient. The states that do not offer Medal of Honor specific license plate offer special license plates for veterans for which recipients may be eligible.
Saluting
 * Although not required by law or military regulation, members of the uniformed services are encouraged to render salutes to recipients of the Medal of Honor as a matter of respect and courtesy regardless of rank or status, whether or not they are in uniform. This is one of the few instances where a living member of the military will receive salutes from members of a higher rank. According to paragraph 1.6.1.1 of Air Force Instruction 1-1, the United States Air Force requires that salutes be rendered to Medal of Honor recipients.
* Although not required by law or military regulation, members of the uniformed services are encouraged to render salutes to recipients of the Medal of Honor as a matter of respect and courtesy regardless of rank or status, whether or not they are in uniform. This is one of the few instances where a living member of the military will receive salutes from members of a higher rank. According to paragraph 1.6.1.1 of Air Force Instruction 1-1, the United States Air Force requires that salutes be rendered to Medal of Honor recipients.
Legal protection
* 1904: The Army redesigned its Medal of Honor, largely a reaction to the copying of the Medal of Honor by various veterans organizations, such as the Grand Army of the Republic.Types of Medals of HonorFrom the website of the Congressional Medal of Honor Society. Retrieved on July 1, 2012. To prevent the making of copies of the medal, Brigadier General George Gillespie, Jr., a Medal of Honor recipient from the Civil War, applied for and obtained a
patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling disclo ...
for the new design. General Gillespie received the patent on November 22, 1904, and he transferred it the following month to the Secretary of War at the time, William Howard Taft.
* 1923: Congress passed a statute (the year before the 20-year term of the patent would expire)—which would later be codified at 18 U.S.C. §704—prohibiting the unauthorized wearing, manufacturing, or sale of military medals or decorations. In 1994, Congress amended the statute to permit an enhanced penalty if the offense involved the Medal of Honor.
* 2006: The Stolen Valor Act of 2005
The Stolen Valor Act of 2005, signed into law by President George W. Bush on December 20, 2006, was a U.S. law that broadened the provisions of previous U.S. law addressing the unauthorized wear, manufacture, or sale of any military decoration ...
was enacted. The law amended 18 U.S.C. § 704 to make it a federal criminal offense for a person to deliberately state falsely that he or she had been awarded a military decoration, service medal, or badge. The law also permitted an enhanced penalty for someone who falsely claimed to have been awarded the Medal of Honor.
* June 28, 2012: In the case of '' United States v. Alvarez'', the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
held that the Stolen Valor Act of 2005's criminalization of the making of false claims of having been awarded a military medal, decoration, or badge was an unconstitutional violation of the First Amendment's guarantee of free speech. The case involved an elected official in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
, Xavier Alvarez, who had falsely stated at a public meeting that he had been awarded the Medal of Honor, even though he had never served in any branch of the armed forces. The Supreme Court's decision did not specifically address the constitutionality of the older portion of the statute which prohibits the unauthorized wearing, manufacturing, or sale of military medals or decorations. Under the law, the unauthorized wearing, manufacturing, or sale of the Medal of Honor is punishable by a fine of up to $100,000 and imprisonment of up to one year.
* June 3, 2013: President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
signed into law a revised version of the Stolen Valor Act, making it a federal offense for someone to represent themselves as awardees of medals for valor in order to receive benefits or other privileges (such as grants, educational benefits, housing, etc.) that are set aside for veterans and other service members. As of 2017, there were only two reported arrests and prosecutions under the law, leading at least 22 states to enact their own legislation to criminalize stolen valor amid claims that the federal law was virtually unenforced.
Duplicate medals
Medal of Honor recipients may apply in writing to the headquarters of the service branch of the medal awarded for a replacement or display Medal of Honor, ribbon, and appurtenance (Medal of Honor flag) without charge. Primary next of kin may also do the same and have any questions answered in regard to the Medal of Honor that was awarded.Recipients
* The first Medals of Honor were awarded and presented to six U.S. Army soldiers ("Andrews Raiders
The Great Locomotive Chase (also known as Andrews' Raid or the Mitchel Raid) was a military raid that occurred April 12, 1862, in northern Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia during the American Civil War. Volunteers from the Union Army, led by civili ...
") on March 25, 1863, by Secretary of War Edwin Stanton, in his office of the War Department. Private Jacob Parrott, a U.S. Army volunteer from Ohio, became the first actual Medal of Honor recipient, awarded for his volunteering for and participation in a raid on a Confederate train in Big Shanty, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to t ...
, on April 12, 1862, during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
. After the medal presentations, the six decorated soldiers met with President Lincoln in the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest, Washington, D.C., NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. preside ...
.
* The first U.S. Navy sailors were awarded the Medal of Honor on April 3, 1863. 41 sailors received the award, with 17 awards for action during the Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip.
* The first marines awarded the Medal of Honor were John F. Mackie and Pinkerton R. Vaughn
Pinkerton Ross Vaughn, Sr. (1841 – August 22, 1866) was a United States Marine Corps sergeant during the American Civil War. He was awarded the nation's highest military decoration for valor—the Medal of Honor, for his actions aboard the duri ...
on July 10, 1863; Mackie for on May 15, 1862, and Vaughn for on March 14, 1863.
* The first, and so far only, Coast Guardsman to be awarded the Medal of Honor was Signalman First Class Douglas Munro. He was posthumously awarded it on May 27, 1943, for evacuating 500 marines under fire on September 27, 1942, during the Battle of Guadalcanal.
* The only woman awarded the Medal of Honor is Mary Edwards Walker, who was a civilian Army surgeon during the American Civil War. She received the award in 1865 after the Judge Advocate General of the Army determined that she could not be given a retroactive commission, and so President Andrew Johnson directed that "the usual medal of honor for meritorious services be given her."
 * The first black recipients of the Medal of Honor were sixteen Army soldiers and sixteen Navy sailors that fought during the Civil War. The first award was announced on April 6, 1865, to twelve black soldiers from the five regiments of
* The first black recipients of the Medal of Honor were sixteen Army soldiers and sixteen Navy sailors that fought during the Civil War. The first award was announced on April 6, 1865, to twelve black soldiers from the five regiments of U.S. Colored Troops
The United States Colored Troops (USCT) were regiments in the United States Army composed primarily of African-American (colored) soldiers, although members of other minority groups also served within the units. They were first recruited during ...
who fought at New Market Heights outside of Richmond on September 29, 1864. The first black man to earn the Medal of Honor was William Harvey Carney. He earned the Medal during the Battle of Ft Wagner, but was not presented with it until 1900.
The 1917 Medal of Honor Board deleted 911 awards, but only 910 names from the Army's Medal of Honor list, including awards to Mary Edwards Walker, William F. "Buffalo Bill" Cody and the first of two awards issued February 10, 1887, to George W. Mindil, who retained his award issued October 25, 1893. None of the 910 "deleted" recipients were ordered to return their medals, although on the question of whether the recipients could continue to wear their medals, the Judge Advocate General advised the Medal of Honor Board that the Army was not obligated to police the matter. Walker continued to wear her medal until her death. Although some sources claim that President Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 76th governor of Georgia from 19 ...
formally restored her medal posthumously in 1977, this action was actually taken unilaterally by the Army's Board for Correction of Military Records. The Army Board for Correction of Military Records also restored the Medals of Honor of Buffalo Bill and four other civilian scouts in 1989.
* Sixty-one Canadians
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
who served in the United States Armed Forces, mostly during the American Civil War. Since 1900, four Canadians have received the medal. The only Canadian-born, naturalized U.S. citizen to receive the medal for heroism during the Vietnam War was Peter C. Lemon.
While the governing statute for the Army's Medal of Honor (), beginning in 1918, explicitly stated that a recipient must be "an officer or enlisted man of the Army", "distinguish himself conspicuously by gallantry and intrepidity at the risk of his life above and beyond the call of duty", and perform an act of valor "in action involving actual conflict with an enemy", exceptions have been made:
* Charles Lindbergh, 1927, civilian pilot, and U.S. Army Air Corps reserve officer. Lindbergh's medal was authorized by a special act of Congress.
* Major General (Retired) Adolphus Greely was awarded the medal in 1935, on his 91st birthday, "for his life of splendid public service". The result of a special act of Congress similar to Lindbergh's, Greely's medal citation did not reference any acts of valor.
* Foreign unknown recipients include five WWI Unknowns: the Belgian Unknown Soldier, the British Unknown Warrior, the French Unknown Soldier, the Italian Unknown Soldier, and the Romanian Unknown Soldier.
* U.S. unknown recipients include one each from four wars: World War I, World War II, Korea, and Vietnam. The Vietnam Unknown was later identified as Air Force First Lieutenant Michael Blassie through the use of DNA identification. Blassie's family asked for his Medal of Honor, but the Department of Defense denied the request in 1998. According to Undersecretary of Defense Rudy de Leon, the medal was awarded symbolically to all Vietnam unknowns, not to Blassie specifically.
Note that the number of Air Force recipients does not count recipients from its pre-September 19, 1947, Army-related predecessor organizations.
Double recipients
Nineteen service members have been awarded the Medal of Honor twice. The first double Medal of Honor recipient was Thomas Custer (brother of George Armstrong Custer) for two separate actions that took place several days apart during the American Civil War. Five "double recipients" were awarded both the Army's and Navy's Medal of Honor for the same action, with all five of these occurrences taking place during World War I. No modern recipients have more than one medal because of laws passed for the Army in 1918, and for the Navy in 1919, which stipulated that "no more than one medal of honor . . . shall be issued to any one person," although subsequent awards were authorized by issuance of bars or other devices in lieu of the medal itself. The statutory bar was finally repealed in the FY2014 defense bill, at the request of the Office of the Secretary of Defense, meaning that recipients can now be issued more than one medal. However, no more than one medal may be issued for the same action. To date, the maximum number of Medals of Honor earned by any service member has been two. The last living individual to be awarded two Medals of Honor wasJohn J. Kelly
John Joseph Kelly (June 24, 1898 – November 20, 1957) was a United States Marine who was awarded both the Army and Navy Medals of Honor for his heroic actions on October 13, 1918, at the Battle of Blanc Mont Ridge, France, during World W ...
October 3, 1918; the last individual to receive two Medals of Honor for two different actions was Smedley Butler, in 1914 and 1915.
Related recipients
Arthur MacArthur, Jr. and Douglas MacArthur are the first father and son to be awarded the Medal of Honor. The only other such pairing is Theodore Roosevelt (awarded in 2001) andTheodore Roosevelt, Jr.
Theodore Roosevelt III ( ), often known as Theodore Jr.Morris, Edmund (1979). ''The Rise of Theodore Roosevelt''. index.While it was President Theodore Roosevelt who was legally named Theodore Roosevelt Jr., the President's fame made it simple ...
Five pairs of brothers have received the Medal of Honor:
* John and William Black
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conques ...
, in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
. The Blacks are the first brothers to be so honored.
* Charles and Henry Capehart, in the American Civil War, the latter for saving a drowning man while under fire.
* Antoine and Julien Gaujot. The Gaujots also have the unique distinction of receiving their medals for actions in separate conflicts, Antoine in the Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
and Julien when he crossed the Mexican border to rescue Mexicans and Americans in a Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution ( es, Revolución Mexicana) was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from approximately 1910 to 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction ...
skirmish.
* Harry and Willard Miller, during the same naval action in the Spanish–American War.
* Allen and James Thompson, in the same American Civil War action.
Another notable pair of related recipients are Admiral Frank Friday Fletcher
Frank Friday Fletcher (November 23, 1855 – November 28, 1928) was a United States Navy admiral who served in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He was awarded the U.S. military's highest decoration, the Medal of Honor, for his action ...
(rear admiral at the time of award) and his nephew, Admiral Frank Jack Fletcher (lieutenant at the time of award), both awarded for actions during the United States occupation of Veracruz.
Late awards
Since 1979, 86 late Medal of Honor awards have been presented for actions from the Civil War to the Vietnam War. In addition, five recipients whose names were not included on the Army's Medal of Honor Roll in 1917 had their awards restored. A 1993 study commissioned by the U.S. Army investigated "racial disparity" in the awarding of medals. At the time, no Medals of Honor had been awarded to U.S. soldiers of African descent who served in World War II. After an exhaustive review, the study recommended that ten Distinguished Service Cross recipients be awarded the Medal of Honor. On January 13, 1997, PresidentBill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (Birth name, né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 ...
presented the Medal of Honor to seven of these World War II veterans, six of them posthumously and one to former Second Lieutenant Vernon Baker
Vernon may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Vernon County, New South Wales
Canada
*Vernon, British Columbia, a city
*Vernon, Ontario
France
* Vernon, Ardèche
*Vernon, Eure
United States
* Vernon, Alabama
* Vernon, Arizona
* Vernon, California
* ...
.
In 1998, a similar study of Asian American
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian ancestry (including naturalized Americans who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). Although this term had historically been used for all the indigenous peopl ...
s resulted in President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (Birth name, né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 ...
presenting 22 Medals of Honor in 2000. Twenty of these medals went to U.S. soldiers of Japanese descent of the 442nd Regimental Combat Team (442nd RCT) who served in the European Theater of Operations during World War II. One of these Medal of Honor recipients was Senator Daniel Inouye, a former U.S. Army officer in the 442nd RCT.
In 2005, President George W. Bush presented the Medal of Honor to Tibor Rubin
Tibor "Ted" Rubin (June 18, 1929 – December 5, 2015) was a Hungarian-American Army Corporal. A Holocaust survivor who immigrated to the U.S. in 1948, he fought in the Korean War and was awarded the Medal of Honor for his actions during the ...
, a Hungarian-born American Jew
American Jews or Jewish Americans are American citizens who are Jewish, whether by religion, ethnicity, culture, or nationality. Today the Jewish community in the United States consists primarily of Ashkenazi Jews, who descend from diasp ...
who was a Holocaust survivor of World War II and enlisted U.S. infantryman and prisoner of war in the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
, whom many believed to have been overlooked because of his religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural ...
.
On April 11, 2013, President Obama presented the Medal of Honor posthumously to Army chaplain
A military chaplain ministers to military personnel and, in most cases, their families and civilians working for the military. In some cases they will also work with local civilians within a military area of operations.
Although the term '' ...
Captain Emil Kapaun
Emil Joseph Kapaun (April 20, 1916 – May 23, 1951) was a Roman Catholic priest and United States Army captain who served as a United States Army chaplain during World War II and the Korean War. Kapaun was a chaplain in the Burma Theater ...
for his actions as a prisoner of war during the Korean War. This follows other awards to Army Sergeant Leslie H. Sabo, Jr. for conspicuous gallantry in action on May 10, 1970, near Se San, Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
, during the Vietnam War and to Army Private First Class Henry Svehla and Army Private First Class Anthony T. Kahoʻohanohano
Anthony Thomas Kahoohanohano (July 22, 1930 – September 1, 1951) was an American soldier who was killed in action on September 1, 1951, during the Korean War. He became a recipient of the United States military's highest decoration for valor, th ...
for their heroic actions during the Korean War.
As a result of a congressionally mandated review to ensure brave acts were not overlooked due to prejudice or discrimination, on March 18, 2014, President Obama upgraded Distinguished Service Crosses to Medals of Honor for 24 Hispanic, Jewish, and black individuals—the "Valor 24"—for their actions in World War II, the Korean War and the Vietnam War. Three were still living at the time of the ceremony.• • List with basic details is at U.S. Army'List of Recipients
On November 6, 2014, President Obama presented the Medal of Honor posthumously to First Lieutenant Alonzo Cushing for actions on July 3, 1863, during the
Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of th ...
. Lieutenant Cushing's award is the last Medal of Honor to be presented to a soldier in the American Civil War, after 151 years since the date of the action.
27th Maine and other revoked awards
27th Maine Volunteer Infantry Regiment
The 27th Maine Infantry Regiment was a nine-month regiment raised for service in the Union Army during the American Civil War.
Service
One of eight regiments raised by Maine in the fall of 1862 under the call for men to serve nine-month terms, th ...
who extended his enlistment beyond their separation date. The Battle of Gettysburg was imminent, and 311 men of the regiment volunteered to serve until the battle was resolved. The remaining men returned to Maine, and with the Union victory at Gettysburg the 311 volunteers soon followed. They arrived back in Maine in time to be discharged with the men who had returned earlier. Since there seemed to be no official list of the 311 volunteers, the War Department exacerbated the situation by forwarding 864 medals to the commanding officer of the regiment. The commanding officer only issued the medals to the volunteers who stayed behind and retained the others on the grounds that, if he returned the remainder to the War Department, the War Department would try to reissue the medals.
In 1916, a board of five Army generals on the retired list convened under act of law to review every Army Medal of Honor awarded. The board was to report on any Medals of Honor awarded or issued "for any cause other than distinguished conduct by an officer or enlisted man in action involving actual conflict with an enemy." The commission, led by Nelson A. Miles, identified 911 awards for causes other than distinguished conduct. This included the 864 medals awarded to members of the 27th Maine regiment; 29 servicemen who served as Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
's funeral guard; six civilians, including Mary Edwards Walker and Buffalo Bill Cody; and 12 others. Walker's medal was restored by the Army Board for Correction of Military Records in 1977, an action that is often attributed to President Jimmy Carter in error. Cody and four other civilian scouts who rendered distinguished service in action, and who were therefore considered by the board to have fully earned their medals, also had their medals restored by the Army Board for Correction of Military Records in 1989. The report issued by the Medal of Honor review board in 1917 was reviewed by the Judge Advocate General, who also advised that the War Department should not seek the return of the revoked medals from the recipients identified by the board. In the case of recipients who continued to wear the medal, the War Department was advised to take no action to enforce the statute.66th Congress 1st Session, Document 58, General Staff and Medals of Honor, ordered to be printed July 23, 1919.
Similarly-named U.S. decorations
The following decorations, in one degree or another, bear similar names to the Medal of Honor, but are entirely separate awards with different criteria for issuance: * Cardenas Medal of Honor: decoration of the United States Revenue Cutter Service, which was later merged into the United States Coast Guard * Congressional Space Medal of Honor: the highest honor for NASA astronautsSee also
*African-American Medal of Honor Recipients Memorial
The African-American Medal of Honor Recipients Memorial is a monument dedicated to African-American recipients of the Medal of Honor since 1861.
History
The sculpture on top of the monument was created by Charles Parks. It depicts Sgt. William ...
* Distinguished Intelligence Cross
The Distinguished Intelligence Cross is the highest decoration awarded by the United States Central Intelligence Agency. It is given for "a voluntary act or acts of extraordinary heroism involving the acceptance of existing dangers with conspicuo ...
* Home of the Heroes, a recognition of Pueblo, Colorado, for being the hometown of four Medal of Honor recipients
* Kentucky Medal of Honor Memorial
The Kentucky Medal of Honor Memorial is located at the corner of Fifth and Jefferson Streets in downtown Louisville, Kentucky, on the grounds of the old Jefferson County Courthouse. The Memorial honors all recipients of the Medal of Honor from the ...
* List of Medal of Honor recipients
The Medal of Honor was created during the American Civil War and is the highest military decoration presented by the United States government to a member of its armed forces. The recipient must have distinguished themselves at the risk of their ...
* Medal of Honor Memorial (Indianapolis)
* Merchant Marine Distinguished Service Medal
* Military awards and decorations
* Texas Medal of Honor Memorial
The Texas Medal of Honor Memorial is a statue commemorating recipients of the Medal of Honor from the state of Texas. Sculpted by Doyle Glass and Scott Boyer, it was dedicated on Memorial Day of 2008 in Midland, Texas at the Commemorative Air Forc ...
References
Footnotes
Citations
Works cited
* * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * *External links
Congressional Medal of Honor Society
U.S. Army Medal of Honor
Submarine Force Medal of Honor Recipients
Submarine Force Museum website
List of Native Americans who have received the Medal of Honor
(Medal of Honor recipients depicted on film)
National Medal of Honor Museum of Military History
in Chattanooga, Tennessee
American Valor
PBS/WETA.
Loubat, J. F. and Jacquemart, Jules, Illustrator, ''The Medallic History of the United States of America 1776–1876''.
U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry: Medal of Honor-Army
U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry: Medal of Honor-Navy
U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry: Medal of Honor-Air Force
Pritzker Military Museum & Library
{{DEFAULTSORT:Medal Of Honor 1862 establishments in the United States Awards established in 1862