Maurice de Nassau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Maurice of Orange ( nl, Maurits van Oranje; 14 November 1567 – 23 April 1625) was ''
 Only 16 when his father was murdered in
Only 16 when his father was murdered in
 As part of his efforts to find allies against Spain, Maurice received Moroccan envoys such as Al-Hajari. They discussed the possibility of an alliance between Holland, the Ottoman Empire, Morocco and the Moriscos, against the common enemy Spain. Al-Hajari's journey chronicles, authored in 1637, mentions in detail the discussion for a combined offensive against Spain.
Maurice was known in his time and by historians as the first general of his age. His reputation rests not as much on his ability to win and exploit field battles as it does on his expertise as a siege commander, military organizer, and innovator. Of his two great adversaries,
As part of his efforts to find allies against Spain, Maurice received Moroccan envoys such as Al-Hajari. They discussed the possibility of an alliance between Holland, the Ottoman Empire, Morocco and the Moriscos, against the common enemy Spain. Al-Hajari's journey chronicles, authored in 1637, mentions in detail the discussion for a combined offensive against Spain.
Maurice was known in his time and by historians as the first general of his age. His reputation rests not as much on his ability to win and exploit field battles as it does on his expertise as a siege commander, military organizer, and innovator. Of his two great adversaries,

 :
:
 Maurice, besides being stadtholder of several provinces and Captain-General, both non-hereditary and appointive titles, was the hereditary
Maurice, besides being stadtholder of several provinces and Captain-General, both non-hereditary and appointive titles, was the hereditary
stadtholder
In the Low Countries, ''stadtholder'' ( nl, stadhouder ) was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and H ...
'' of all the provinces of the Dutch Republic except for Friesland from 1585 at the earliest until his death in 1625. Before he became Prince of Orange upon the death of his eldest half-brother Philip William in 1618, he was known as Maurice of Nassau.
Maurice spent his youth in Dillenburg in Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
, and studied in Heidelberg and Leiden. He succeeded his father William the Silent as stadtholder of Holland and Zeeland in 1585, and became stadtholder of Utrecht, Guelders and Overijssel in 1590, and of Groningen in 1620. As Captain-General and Admiral of the Union, Maurice organized the Dutch rebellion against Spain into a coherent, successful revolt and won fame as a military strategist. Under his leadership and in cooperation with the Land's Advocate of Holland Johan van Oldenbarnevelt, the Dutch States Army achieved many victories and drove the Spaniards out of the north and east of the Republic. Maurice set out to revive and revise the classical doctrines of Vegetius and pioneered the new European forms of armament and drill. During the Twelve Years' Truce, a religious dispute broke out in the Republic, and a conflict erupted between Maurice and Van Oldenbarnevelt, which ended with the latter's decapitation. After the Truce, Maurice failed to achieve more military victories. He died without legitimate children in The Hague in 1625 and was succeeded by his younger half-brother Frederick Henry.
Life
Maurice was the son of William the Silent andAnna of Saxony
Anna of Saxony (23 December 1544 – 18 December 1577) was the heiress of Maurice, Elector of Saxony, and Agnes, eldest daughter of Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse. Maurice's only son, Albert, died in infancy. Anna was the second wife of William th ...
and was born at the castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
of Dillenburg. He was named after his maternal grandfather, the Elector
Elector may refer to:
* Prince-elector or elector, a member of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Holy Roman Emperors
* Elector, a member of an electoral college
** Confederate elector, a member of ...
Maurice of Saxony
Maurice (21 March 1521 – 9 July 1553) was Duke (1541–47) and later Elector (1547–53) of Saxony. His clever manipulation of alliances and disputes gained the Albertine branch of the Wettin dynasty extensive lands and the electoral dignity.
...
, who was also a noted general.
Maurice never married but was the father of illegitimate children by Margaretha van Mechelen
Margaretha van Mechelen (c. 1580 in Lier – 17 May 1662 in The Hague) was a noblewoman of the Southern Netherlands and (from c.1600 to c.1610) the mistress of Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange, with whom she had 3 sons:
* Willem of Nassau, lor ...
(including Willem of Nassau, Lord of the Lek
Willem () is a Dutch and West FrisianRienk de Haan, ''Fryske Foarnammen'', Leeuwarden, 2002 (Friese Pers Boekerij), , p. 158. masculine given name. The name is Germanic, and can be seen as the Dutch equivalent of the name William in English, Gui ...
, and Louis of Nassau, Lord of De Lek and Beverweerd
Louis of Nassau, Lord of De Lek and Beverweerd (1602 – The Hague, 28 February 1665) was a Dutch soldier. He was the illegitimate son of Margaretha van Mechelen and Maurice, Prince of Orange, and so a collateral member of the House of Oran ...
) and Anna van de Kelder
Anna may refer to:
People Surname and given name
* Anna (name)
Mononym
* Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke
* Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773)
* Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century)
* Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 1221)
...
. He was raised in Dillenburg by his uncle Johan of Nassau
Count John VI of Nassau-Dillenburg (22 November 1536 – 8 October 1606) was the second son of William I, Count of Nassau-Siegen, William the Rich and the younger brother of William the Silent. He has a special place in the history of the Neth ...
(Jan the Old).
Together with his cousin Willem Lodewijk he studied in Heidelberg and later in Leiden where he met Simon Stevin
Simon Stevin (; 1548–1620), sometimes called Stevinus, was a Flemish mathematician, scientist and music theorist. He made various contributions in many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. He also translated vario ...
. The States of Holland and Zeeland paid for his studies, as their father had run into financial problems after spending his entire fortune in the early stages of the Dutch revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) (Historiography of the Eighty Years' War#Name and periodisation, c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and t ...
.
Delft
Delft () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, Netherlands. It is located between Rotterdam, to the southeast, ...
in 1584, he soon was appointed to his father's office of stadtholder
In the Low Countries, ''stadtholder'' ( nl, stadhouder ) was an office of steward, designated a medieval official and then a national leader. The ''stadtholder'' was the replacement of the duke or count of a province during the Burgundian and H ...
(''Stadhouder''). The monarchs of England and France had been requested to accept sovereignty but had refused. This had left Maurice as the only acceptable candidate for the position of Stadtholder. He became stadtholder of Holland and Zeeland in 1585, of Guelders
The Duchy of Guelders ( nl, Gelre, french: Gueldre, german: Geldern) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
Geography
The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in pr ...
, Overijssel
Overijssel (, ; nds, Oaveriessel ; german: Oberyssel) is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the eastern part of the country. The province's name translates to "across the IJssel", from the perspective of the ...
and Utrecht in 1590 and of Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
and Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nov ...
in 1620 (following the death of Willem Lodewijk, who had been stadtholder there and in Friesland).
Protestant Maurice was preceded as Prince of Orange (not a Dutch title) by his Roman Catholic eldest half-brother Philip William, Prince of Orange, deceased 1618. However, Philip William was in the custody of Spain, remaining so until 1596, and was thus unable to lead the Dutch independence cause.
Maria of Nassau Maria of Nassau may refer to:
* Maria of Nassau (1539–1599), daughter of William the Rich and Juliana of Stolberg
* Maria of Nassau (1553–1554), first daughter of William the Silent and Anna of Egmond
* Maria of Nassau (1556–1616), second daug ...
(1556–1616) was a full sister of Philip William from the first marriage of William I, Prince of Orange
William the Silent (24 April 153310 July 1584), also known as William the Taciturn (translated from nl, Willem de Zwijger), or, more commonly in the Netherlands, William of Orange ( nl, Willem van Oranje), was the main leader of the Dutch Rev ...
, (assassinated 1584), to wealthy and powerful aristocrat Anna van Egmont
Anna van Egmont (March 1533 – 24 March 1558), mainly known as Anna van Buren (or Anna van Bueren), was a Dutch heiress who became the first wife of William the Silent, Prince of Orange.
Biography
Anna was born in Grave, Netherlands in March ...
(1533–1558), and a contender to Maurice over the estate of their father.
He was appointed captain-general of the army in 1587, bypassing the Earl of Leicester, who returned to England on hearing this news.
Military career
Maurice organized therebellion
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
against Spain into a coherent, successful revolt. He reorganized the Dutch States Army together with Willem Lodewijk, studied military history
Military history is the study of armed conflict in the history of humanity, and its impact on the societies, cultures and economies thereof, as well as the resulting changes to local and international relationships.
Professional historians norma ...
, strategy and tactics, mathematics and astronomy, and proved himself to be among the best strategists of his age. The Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Refo ...
was a challenge to his style, so he could prove himself a good leader by taking several Spanish outposts. Paying special attention to the siege theories of Simon Stevin
Simon Stevin (; 1548–1620), sometimes called Stevinus, was a Flemish mathematician, scientist and music theorist. He made various contributions in many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. He also translated vario ...
, he took valuable key fortresses and towns during a period known as the ''Ten Glory Years'': Breda
Breda () is a city and municipality in the southern part of the Netherlands, located in the province of North Brabant. The name derived from ''brede Aa'' ('wide Aa' or 'broad Aa') and refers to the confluence of the rivers Mark and Aa. Breda has ...
in 1590, Zutphen, Knodsenburg in 1591, Steenwijk
Steenwijk (; Low German: ''Steenwiek'', ''Stienwiek'' English: ''Stenwick'') is a city in the Dutch province of Overijssel. It is located in the municipality of Steenwijkerland. It is the largest town of the municipality.
Steenwijk received city ...
and Coevorden in 1592, Geertruidenberg in 1593, and Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of t ...
in 1594. In 1597 he went on a further offensive and took Rheinberg, Meurs, Groenlo, Bredevoort, Enschede
Enschede (; known as in the local Twents dialect) is a municipality and city in the eastern Netherlands in the province of Overijssel and in the Twente region. The eastern parts of the urban area reaches the border of the German city of Gronau ...
, Ootmarsum, and Oldenzaal and closed off the year with the capture of Lingen. These victories rounded out the borders to the Dutch Republic, solidifying the revolt and allowing a national state to develop behind secure borders. They also established Maurice as the foremost general of his time. Many of the great generals of the succeeding generation, including his brother Frederick Henry and many of the commanders of the English Civil War, learned their trade under his command.
For a series of maps showing Maurice's campaigns to extend and consolidate the borders of the Republic, see Gallery of Maps of the 80 Years War (in Dutch).
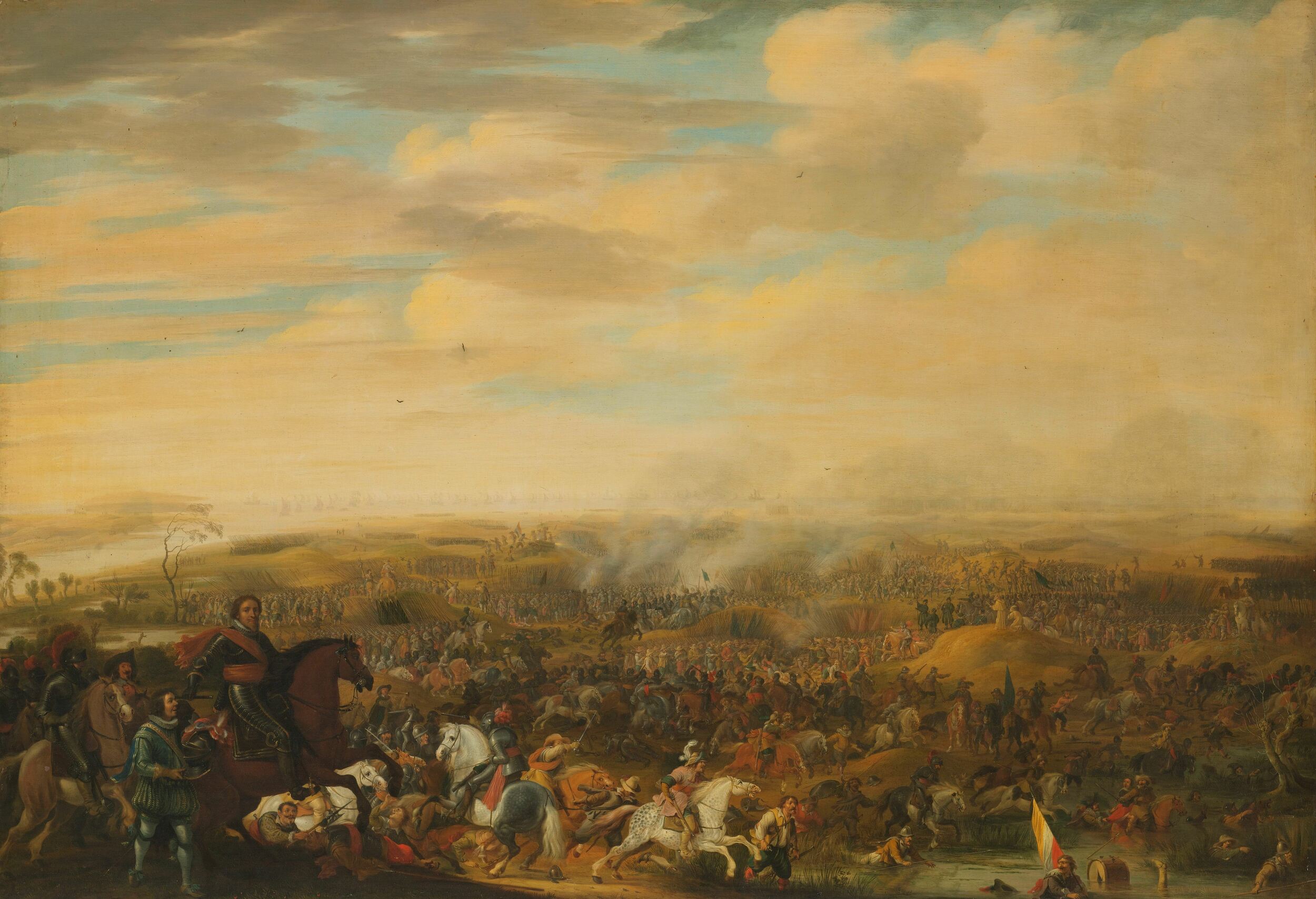
His victories in the pitched battles at Turnhout (1597) and at Nieuwpoort (1600) were dependent on his innovation of cooperation between arms, with his cavalry playing a major role. The victories earned him military fame and acknowledgement throughout Europe. Despite these successes, the House of Orange did not attain great respect among European royalty, as the Stadtholdership was not inheritable.
The training of his army was especially important to early modern warfare
Early modern warfare is the era of warfare following medieval warfare. It is associated with the start of the widespread use of gunpowder and the development of suitable weapons to use the explosive, including artillery and firearms; for this ...
and the Military Revolution
The Military Revolution is the theory that a series of radical changes in military strategy and tactics during the 16th and 17th centuries resulted in major lasting changes in governments and society. The theory was introduced by Michael Roberts i ...
of 1560–1650. Previous generals had made use of drill and exercise in order to instill discipline or to keep the men physically fit, but for Maurice, they "were the fundamental postulates of tactics." This change affected the entire conduct of warfare, since it required the officers to train men in addition to leading them, decreased the size of the basic infantry unit for functional purposes since more specific orders had to be given in battle, and the decrease in herd behavior required more initiative and intelligence from the average soldier. One major contribution was the introduction of volley fire, which enabled soldiers to compensate for the inaccuracy of their weapons by firing in a large group. It was first used in European combat at the battle of Nieuwpoort in 1600.
 As part of his efforts to find allies against Spain, Maurice received Moroccan envoys such as Al-Hajari. They discussed the possibility of an alliance between Holland, the Ottoman Empire, Morocco and the Moriscos, against the common enemy Spain. Al-Hajari's journey chronicles, authored in 1637, mentions in detail the discussion for a combined offensive against Spain.
Maurice was known in his time and by historians as the first general of his age. His reputation rests not as much on his ability to win and exploit field battles as it does on his expertise as a siege commander, military organizer, and innovator. Of his two great adversaries,
As part of his efforts to find allies against Spain, Maurice received Moroccan envoys such as Al-Hajari. They discussed the possibility of an alliance between Holland, the Ottoman Empire, Morocco and the Moriscos, against the common enemy Spain. Al-Hajari's journey chronicles, authored in 1637, mentions in detail the discussion for a combined offensive against Spain.
Maurice was known in his time and by historians as the first general of his age. His reputation rests not as much on his ability to win and exploit field battles as it does on his expertise as a siege commander, military organizer, and innovator. Of his two great adversaries, Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma
Alexander Farnese ( it, Alessandro Farnese, es, Alejandro Farnesio; 27 August 1545 – 3 December 1592) was an Italian noble and condottiero and later a general of the Spanish army, who was Duke of Parma, Piacenza and Castro from 1586 to 1592 ...
, and Ambrogio Spinola, he cautiously never allowed himself to be brought to battle with Parma and did not follow up chances to offer Spinola battle with forces in his favour on the Yssel in 1606. He was, however, dealt a defeat by the Spanish general at the battle of Mülheim
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
in October 1605. Based on his preference for sieges and small-scale actions, historian David Trim
David J.B. Trim is a historian, archivist, and educator whose specialties are in European military history and religious history. Currently, he is the director of Archives, Statistics, and Research at the World Headquarters of Seventh-day Adve ...
states that it is difficult to reach a verdict on his ability as a tactician. Jonathan Israel notes that on one of the rare occasions when he did have to fight a major battle in the open – the 1600 Battle of Nieuwpoort – it did end with a Dutch victory, but this outcome was highly risky, and Maurice took care to extricate his army and avoid a second such battle.
Maurice founded a whole new school of military professional practice. These pointed the way to the professional armies of the future by reapplying Roman tactics and innovating in the fields of logistics, training, and economics (e.g. paying troops regularly and on time). Many graduates of service under Maurice, such as his nephew, the Marshal Turenne
Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne (11 September 161127 July 1675), commonly known as Turenne , was a French general and one of only six Marshals to have been promoted Marshal General of France. The most illustrious member of the ...
, or his disciples such as Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden
Gustavus Adolphus (9 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates">N.S_19_December.html" ;"title="Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Old Style and New Style dates">N.S 19 December">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="/now ...
, applied the Mauritian reforms to great effect in the remainder of the 17th century.
Maurice and Oldenbarnevelt
Maurice started out as the protégé of Landsadvocaat ( Land's Advocate, i.e. secretary to the nobility of Holland and legal counsel to the States of Holland, but functioning as de facto chief minister of Holland and the States-General) Johan van Oldenbarnevelt, but gradually tensions rose between these two men. Against Maurice's advice, and despite his protests, Van Oldenbarnevelt decided to sign the Twelve Years' Truce with Spain, which lasted from 1609 to 1621. The required funds to maintain the army and navy and the general course of the war were other topics of constant struggle. With the religious troubles betweenGomarists
Franciscus Gomarus (François Gomaer; 30 January 1563 – 11 January 1641) was a Dutch theologian, a strict Calvinist and an opponent of the teaching of Jacobus Arminius (and his followers), whose theological disputes were addressed at the Synod ...
(strict Calvinists) and the Remonstrants
The Remonstrants (or the Remonstrant Brotherhood) is a Protestant movement that had split from the Dutch Reformed Church in the early 17th century. The early Remonstrants supported Jacobus Arminius, and after his death, continued to maintain his ...
( Arminians), the struggle between Van Oldenbarnevelt and Maurice reached a climax. Van Oldenbarnevelt was arrested, tried and decapitated despite numerous requests for mercy. From 1618 till his death Maurice now enjoyed uncontested power over the Republic. He expanded the Stadtholder's palace at the Binnenhof
The Binnenhof (; en, Inner Court) is a complex of buildings in the city centre of The Hague, Netherlands, next to the Hofvijver lake. It houses the meeting place of both houses of the States General of the Netherlands, as well as the Ministr ...
in the Hague. The Maurice Tower is now part of the building complex of the Senate of the Netherlands. In 1618, he also succeeded his elder half-brother Philip William as Prince of Orange, a title he seems rarely to have used.
Maurice urged his cadet half brother Frederick Henry to marry in order to preserve the dynasty.
Thirty Years' and Eighty Years' War
Historian Jonathan Israel places upon Maurice part of the responsibility for the outbreak of the Thirty Years' War in which Germany was devastated and a large part of its population killed. As noted by Israel, German Protestants were not eager for an all-out confrontation with the Catholics. Maurice significantly helped precipitate such a confrontation by persuading his nephew Frederick V, Elector Palatine, to accept the Bohemian Crown, as well as actively encouraging the Bohemians to confront Habsburg rule, providing them 50,000 guilders as well as sending Dutch troops to fight in the doomed Battle of the White Mountain. This ill-considered decision proved disastrous to the Bohemians, who were thereby plunged into prolonged oppression, and to Frederick who lost his ancestral lands. It also worsened the Dutch Republic's own strategic position. In 1621 the war with Spain resumed after a 12-year period of truces. The Spanish, led by Ambrogio Spinola, had notable successes, including the Siege of Breda, the old Nassau family residence, in 1625. Maurice died on 23 April 1625, with the siege still underway.Justin of Nassau
Justinus van Nassau (1559–1631) was the only extramarital child of William the Silent. He was a Dutch army commander known for his role in the defeat of the Spanish Armada, his leadership of the forces in Breda during the siege of 1624, ...
surrendered Breda in June 1625 after a costly eleven-month siege.

 :
:
List of battles
Maurice participated in these battles as principal commander of Dutch forces: * Axel * 1st Bergen op Zoom, 1588 * Medemblik, 1588 * 3rd Breda, 1590 * 2nd Steenbergen, 1590 * 3rd Zutphen, 1591 * 2nd Deventer, 1591 * Delfzijl, 1591 * Knodsenburg, 1591 * Hulst, 1591 * Nijmegen, 1591 * Steenwijk, 1592 * 1st Coevorden, 1592 * Gertrudenberg, 1593 * 2nd Coevorden, 1593 * Groningen, 1594 * 2nd Groenlo, 1595 * 1st Hulst, 1596 * Turnhout, 1597 * 2nd Venlo, 1597 * 2nd Rheinberg, 1597 * 1st Meurs, 1597 * 3rd Groenlo, 1597 * 1st Bredevoort, 1597 * Enschede, 1597 * Ootmarsum, 1597 * 1st Oldenzaal, 1597 * 1st Lingen, 1597 * 2nd Meurs, 1598 * 3rd Rheinberg, 1598 * Doetinchem * Rees, 1599 * Zaltbommel (1599) * San Andreas * Nieuwpoort, 1600 * Ostend, 1601 *Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1601)
The siege of 's-Hertogenbosch of 1601 ''(Sitio de Bolduque de 1601 in Spanish)'' was an unsuccessful Dutch attempt led by Prince Maurice of Nassau and William Louis of Nassau-Dillenburg to capture the city of 's-Hertogenbosch, North Brabant, Spani ...
* Siege of Sluis (1604)
* 2nd Oldenzaal, 1605
* 2nd Lingen, 1605
* Mülheim, 1605
* Wachtendonk
* Krakau Castle
* 2nd Bredevoort, 1606
* 4th Rheinberg, 1606
* 4th Groenlo, 1606
* 3rd Venlo, 1606
* Jülich, 1621–22
* 2nd Bergen op Zoom, 1622
* 3rd Steenbergen, 1622
* 4th Breda, 1624
Namesakes
* The island nation of Mauritius, located in the Indian Ocean, was named after him. The island was named in the prince's honour by Wybrant Warwijck in 1598 and Dutch emigrants first settled it in May 1638. * In 1611, the Dutch variously named what is now known as the Hudson River the Mauritius River or the Mauritz River, in honour of the prince. It was also similarly referred to as the Nassau River.Coat of arms and titles
sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
of the principality of Orange in what is today Provence in France. He also was the lord of many other estates, which formed his wealth:
* Marquis
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman wi ...
of Veere and Vlissingen
* Count of Nassau-Dillenburg
The House of Nassau is a diversified aristocratic dynasty in Europe. It is named after the lordship associated with Nassau Castle, located in present-day Nassau, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. The lords of Nassau were originally titled "Count ...
, Buren
Buren () is a town and municipality in the Betuwe region of the Netherlands.
Buren has 27,168 inhabitants as of 1 January 2022.
Geography
Buren is located in Gelderland, a province of the Netherlands. It is part of the landscape of Betuwe, a ve ...
, Leerdam, Katzenelnbogen
Katzenelnbogen () is the name of a castle and small town in the district of Rhein-Lahn-Kreis in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Katzenelnbogen is the seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Aar-Einrich.
History
Katzenelnboge ...
, and Vianden
* Viscount of Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
and Besançon
* Baron
Baron is a rank of nobility or title of honour, often hereditary, in various European countries, either current or historical. The female equivalent is baroness. Typically, the title denotes an aristocrat who ranks higher than a lord or knig ...
of Aggeris, Breda
Breda () is a city and municipality in the southern part of the Netherlands, located in the province of North Brabant. The name derived from ''brede Aa'' ('wide Aa' or 'broad Aa') and refers to the confluence of the rivers Mark and Aa. Breda has ...
, Cranendonck, Lands of Cuijk, Daesburg, Eindhoven
Eindhoven () is a city and municipality in the Netherlands, located in the southern province of North Brabant of which it is its largest. With a population of 238,326 on 1 January 2022,City of Grave,
Lek
Lek or LEK may refer to:
* Lek mating, mating in a lek, a type of animal territory in which males of a species gather
* Albanian lek, the currency of Albania
* Lek (magazine), a Norwegian softcore pornographic magazine
* Lek (pharmaceutical comp ...
, IJsselstein, Diest, Grimbergen
Grimbergen () is a municipality in the Belgian province of Flemish Brabant, 10 km north of the capital Brussels. It comprises the towns of Beigem, Grimbergen, Humbeek, and Strombeek-Bever. In 2017, it had a population of 37,030 and an are ...
, Herstal, Warneton
Warneton (; nl, Waasten) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. It is part of the Métropole Européenne de Lille.
Bounding communes and places
*Warneton, Belgium (part of Comines-Warneton)
* Comines, east
*Quesnoy-sur-Deûle ...
, , Bentheim-Lingen
Bentheim-Lingen was a county seated in Lingen in Germany. Bentheim-Lingen emerged as a partition of Bentheim-Tecklenburg in 1450, and was absorbed by Spain in 1555. Over the next century, ownership of Bentheim-Lingen passed between Spain and Nass ...
, Moers, Arlay
Arlay is a commune in the Jura department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. On 1 January 2016, the former commune of Saint-Germain-lès-Arlay was merged into Arlay.
History
Arlay's early importance lay in the fact ...
, and Nozeroy
Nozeroy () is a commune in the Jura department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France.
Population
See also
*Communes of the Jura department
The following is a list of the 494 communes of the Jura department of France.
The commu ...
; Lord of Dasburg
Dasburg is a municipality in the district of Bitburg-Prüm, in Rhineland-Palatinate, western Germany. Before the French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping ...
, Geertruidenberg, Hooge en Lage Zwaluwe
Hooge en Lage Zwaluwe was a municipality in the Dutch province of North Brabant. It included the villages of Lage Zwaluwe, and Hooge Zwaluwe.
Hooge en Lage Zwaluwe existed until 1997, when it merged with Made
Made or MADE may refer to:
Entertain ...
, Klundert
Klundert is a city in the Dutch province of North Brabant. It is located close to the Hollands Diep, about 3 km northwest of Zevenbergen. It received city rights in 1357.
History
The current name was first mentioned in 1537 as "die clunder ...
, Montfort, Naaldwijk, Niervaart, Polanen, Steenbergen
Steenbergen () is a municipality and a town in the province of North Brabant in the south of the Netherlands. The municipality had a population of in and covers an area of of which is water. The municipality is mainly agricultural including a ...
, Sint-Maartensdijk
Sint-Maartensdijk is a village in the Dutch province of Zeeland. It is a part of the municipality of Tholen, and lies about 16 km west of Bergen op Zoom.
History
Sint-Maartensdijk was founded as 'Haestinge', and renamed when it got a ch ...
, Willemstad, Bütgenbach
Bütgenbach (; french: Butgenbach, ) is a municipality located in the Belgian province of Liège. On January 1, 2006, Bütgenbach had a total population of 5,574. The total area is 97.31 km² which gives a population density of 57 inhabitants ...
, Sankt Vith, and Besançon.
During his lifetime he kept using the arms as during his father's life-time shown here, and never changed to the simpler arms used by his father and half brothers.
Descendants
Maurice never married but was the father of several illegitimate children: byMargaretha van Mechelen
Margaretha van Mechelen (c. 1580 in Lier – 17 May 1662 in The Hague) was a noblewoman of the Southern Netherlands and (from c.1600 to c.1610) the mistress of Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange, with whom she had 3 sons:
* Willem of Nassau, lor ...
:
* Willem of Nassau, Lord of the Lek
Willem () is a Dutch and West FrisianRienk de Haan, ''Fryske Foarnammen'', Leeuwarden, 2002 (Friese Pers Boekerij), , p. 158. masculine given name. The name is Germanic, and can be seen as the Dutch equivalent of the name William in English, Gui ...
(1601–1627)
* Louis of Nassau, Lord of De Lek and Beverweerd
Louis of Nassau, Lord of De Lek and Beverweerd (1602 – The Hague, 28 February 1665) was a Dutch soldier. He was the illegitimate son of Margaretha van Mechelen and Maurice, Prince of Orange, and so a collateral member of the House of Oran ...
(Lodewijk) (1604–1665)
* Maurice (Maurits) (1604–1617)
by Cornelia Jacobsdochter:
* Anna (?–1673)
by Ursula de Rijck:
* Elisabeth (1611–1679)
* Karl (Carel) (ca. 1612–1637)
by Anna van de Kelder:
* Karl (Carel) Maurice
by Deliana de Backer:
* Eleonora (?–1673)
See also
* Dutch Empire (begun during his reign, circa 1603–1605) *Dutch Revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) (Historiography of the Eighty Years' War#Name and periodisation, c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and t ...
References
Further reading
* * * John Lothrop Motley, "History of the United Netherlands from the Death of William the Silent to the Synod of Dort". London: John Murray, 1860. * John Lothrop Motley, "The Life and Death of John of Barenvelt". New York & London: Harper and Brothers Publishing, 1900. * Petrus Johannes Blok, "History of the people of the Netherlands". New York: G. P. Putnam's sons, 1898.External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Maurice of Nassau, Prince of Orange 1567 births Counts of Nassau 1625 deaths People from Dillenburg Dutch stadtholders Dutch military commanders Dutch people of the Eighty Years' War (United Provinces) 17th-century Dutch military personnel 17th-century Dutch politicians House of Orange-Nassau Princes of Orange Lords of Breda Knights of the Garter Burials in the Royal Crypt at Nieuwe Kerk, Delft Military strategists People of the Anglo-Spanish War (1625–1630)