Marseilleviridae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Marseilleviridae'' is a
''Marseilleviridae'' is a
 Additional species have since been recognized. The first member of this family recognized has been named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga marseillevirus''. A second member is ''Acanthamoeba castellanii lausannevirus''. Two additional viruses have been isolated but have yet to be named. Another member of this family has been isolated from blood donors. An isolate from insects—''Insectomime'' virus—has also been reported.
The viruses appear to fall into at least 3 lineages: (1) ''Marseillevirus'' and ''Cannes8virus'' (2) ''Insectomime'' and ''Tunisvirus'' and (3) ''Lausannevirus''. A sixth potential member of this family—''Melbournevirus''—appears to be related to the ''Marseillevirus''/''Cannes8virus'' clade.
A seventh virus—Brazilian Marseillevirus—has been reported. This virus appears to belong to a fourth lineage of virus in this family.
Another virus—Tokyovirus—has also been reported.
Another member of this family is Kurlavirus.
In 2017, it was proposed that the family contained the following five lineages:Fabre E, Jeudy S, Santini S, Legendre M, Trauchessec M, Claverie J-M, et al (2017). Noumeavirus replication relies on a transient remote control of the host nucleus. Nat Commun 8:15087
Lineage A
* Cannes 8 virus
* Marseillevirus marseillevirus
* Marseillevirus shanghai
* Melbournvirus
* Senegalvirus
* Tokyovirus
Lineage B
* Kurlavirus
* Lausannevirus
* Noumeavirus
* Port-miou virus
Lineage C
* Insectomime virus
* Tunisvirus
Lineage D
* Brazilian marseillevirus
Lineage E
* Golden marseillevirus
Another putative member of this family is Marseillevirus shanghai. If this virus is confirmed, it would belong to the A lineage.
Additional species have since been recognized. The first member of this family recognized has been named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga marseillevirus''. A second member is ''Acanthamoeba castellanii lausannevirus''. Two additional viruses have been isolated but have yet to be named. Another member of this family has been isolated from blood donors. An isolate from insects—''Insectomime'' virus—has also been reported.
The viruses appear to fall into at least 3 lineages: (1) ''Marseillevirus'' and ''Cannes8virus'' (2) ''Insectomime'' and ''Tunisvirus'' and (3) ''Lausannevirus''. A sixth potential member of this family—''Melbournevirus''—appears to be related to the ''Marseillevirus''/''Cannes8virus'' clade.
A seventh virus—Brazilian Marseillevirus—has been reported. This virus appears to belong to a fourth lineage of virus in this family.
Another virus—Tokyovirus—has also been reported.
Another member of this family is Kurlavirus.
In 2017, it was proposed that the family contained the following five lineages:Fabre E, Jeudy S, Santini S, Legendre M, Trauchessec M, Claverie J-M, et al (2017). Noumeavirus replication relies on a transient remote control of the host nucleus. Nat Commun 8:15087
Lineage A
* Cannes 8 virus
* Marseillevirus marseillevirus
* Marseillevirus shanghai
* Melbournvirus
* Senegalvirus
* Tokyovirus
Lineage B
* Kurlavirus
* Lausannevirus
* Noumeavirus
* Port-miou virus
Lineage C
* Insectomime virus
* Tunisvirus
Lineage D
* Brazilian marseillevirus
Lineage E
* Golden marseillevirus
Another putative member of this family is Marseillevirus shanghai. If this virus is confirmed, it would belong to the A lineage.
Viralzone: Marseilleviridae
ICTV
{{Taxonbar, from=Q6773274 Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses Virus families
 ''Marseilleviridae'' is a
''Marseilleviridae'' is a family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
of viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's ...
first named in 2012. The genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
s of these viruses are double-stranded DNA. Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudop ...
are often hosts
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
*Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
*Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
*Michel Host ( ...
, but there is evidence that they are found in humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
as well. The family contains one genus and four species, two of which are unassigned to a genus. It is a member of the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses
''Nucleocytoviricota'' is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix - for virus phylum. These viruses are refe ...
clade.
Taxonomy
The genus contains the following genera and species: *'' Marseillevirus'' **'' Marseillevirus marseillevirus'' **'' Senegalvirus marseillevirus'' *Species unassigned to a genus: **'' Lausannevirus'' **'' Tunisvirus''Related Viruses
 Additional species have since been recognized. The first member of this family recognized has been named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga marseillevirus''. A second member is ''Acanthamoeba castellanii lausannevirus''. Two additional viruses have been isolated but have yet to be named. Another member of this family has been isolated from blood donors. An isolate from insects—''Insectomime'' virus—has also been reported.
The viruses appear to fall into at least 3 lineages: (1) ''Marseillevirus'' and ''Cannes8virus'' (2) ''Insectomime'' and ''Tunisvirus'' and (3) ''Lausannevirus''. A sixth potential member of this family—''Melbournevirus''—appears to be related to the ''Marseillevirus''/''Cannes8virus'' clade.
A seventh virus—Brazilian Marseillevirus—has been reported. This virus appears to belong to a fourth lineage of virus in this family.
Another virus—Tokyovirus—has also been reported.
Another member of this family is Kurlavirus.
In 2017, it was proposed that the family contained the following five lineages:Fabre E, Jeudy S, Santini S, Legendre M, Trauchessec M, Claverie J-M, et al (2017). Noumeavirus replication relies on a transient remote control of the host nucleus. Nat Commun 8:15087
Lineage A
* Cannes 8 virus
* Marseillevirus marseillevirus
* Marseillevirus shanghai
* Melbournvirus
* Senegalvirus
* Tokyovirus
Lineage B
* Kurlavirus
* Lausannevirus
* Noumeavirus
* Port-miou virus
Lineage C
* Insectomime virus
* Tunisvirus
Lineage D
* Brazilian marseillevirus
Lineage E
* Golden marseillevirus
Another putative member of this family is Marseillevirus shanghai. If this virus is confirmed, it would belong to the A lineage.
Additional species have since been recognized. The first member of this family recognized has been named ''Acanthamoeba polyphaga marseillevirus''. A second member is ''Acanthamoeba castellanii lausannevirus''. Two additional viruses have been isolated but have yet to be named. Another member of this family has been isolated from blood donors. An isolate from insects—''Insectomime'' virus—has also been reported.
The viruses appear to fall into at least 3 lineages: (1) ''Marseillevirus'' and ''Cannes8virus'' (2) ''Insectomime'' and ''Tunisvirus'' and (3) ''Lausannevirus''. A sixth potential member of this family—''Melbournevirus''—appears to be related to the ''Marseillevirus''/''Cannes8virus'' clade.
A seventh virus—Brazilian Marseillevirus—has been reported. This virus appears to belong to a fourth lineage of virus in this family.
Another virus—Tokyovirus—has also been reported.
Another member of this family is Kurlavirus.
In 2017, it was proposed that the family contained the following five lineages:Fabre E, Jeudy S, Santini S, Legendre M, Trauchessec M, Claverie J-M, et al (2017). Noumeavirus replication relies on a transient remote control of the host nucleus. Nat Commun 8:15087
Lineage A
* Cannes 8 virus
* Marseillevirus marseillevirus
* Marseillevirus shanghai
* Melbournvirus
* Senegalvirus
* Tokyovirus
Lineage B
* Kurlavirus
* Lausannevirus
* Noumeavirus
* Port-miou virus
Lineage C
* Insectomime virus
* Tunisvirus
Lineage D
* Brazilian marseillevirus
Lineage E
* Golden marseillevirus
Another putative member of this family is Marseillevirus shanghai. If this virus is confirmed, it would belong to the A lineage.
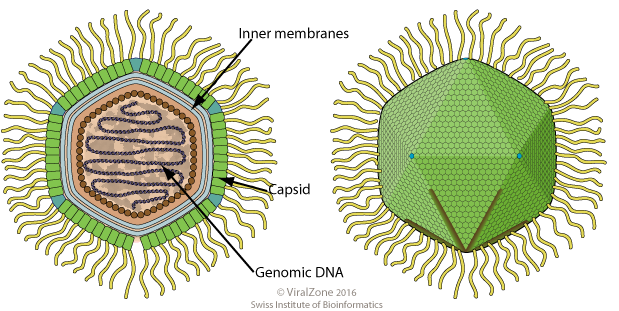
Structure
Viruses in ''Marseilleviridae'' have icosahedral geometries. The diameter is around 250 nm. Genomes are circular, around 372kb in length. The genome has 457 open reading frames.Life cycle
DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. Amoeba serve as the natural host.Genomics
A promoter sequence—AAATATTT—has been found associated with 55% of the identified genes in this virus. Most of these sequences occur in multiple copies.History
One of the first members of this family was described in 2009. Other members described around then (2007) and since then have been documented.References
External links
Viralzone: Marseilleviridae
ICTV
{{Taxonbar, from=Q6773274 Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses Virus families