Manova Summit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 MANOVA's power is affected by the correlations of the dependent variables and by the effect sizes associated with those variables. For example, when there are two groups and two dependent variables, MANOVA's power is lowest when the correlation equals the ratio of the smaller to the larger standardized effect size.
MANOVA's power is affected by the correlations of the dependent variables and by the effect sizes associated with those variables. For example, when there are two groups and two dependent variables, MANOVA's power is lowest when the correlation equals the ratio of the smaller to the larger standardized effect size.
Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA) by Aaron French, Marcelo Macedo, John Poulsen, Tyler Waterson and Angela Yu, San Francisco State University
What is a MANOVA test used for?
{{Experimental design Analysis of variance Design of experiments
 In
In statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
, multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) is a procedure for comparing multivariate
Multivariate may refer to:
In mathematics
* Multivariable calculus
* Multivariate function
* Multivariate polynomial
In computing
* Multivariate cryptography
* Multivariate division algorithm
* Multivariate interpolation
* Multivariate optical c ...
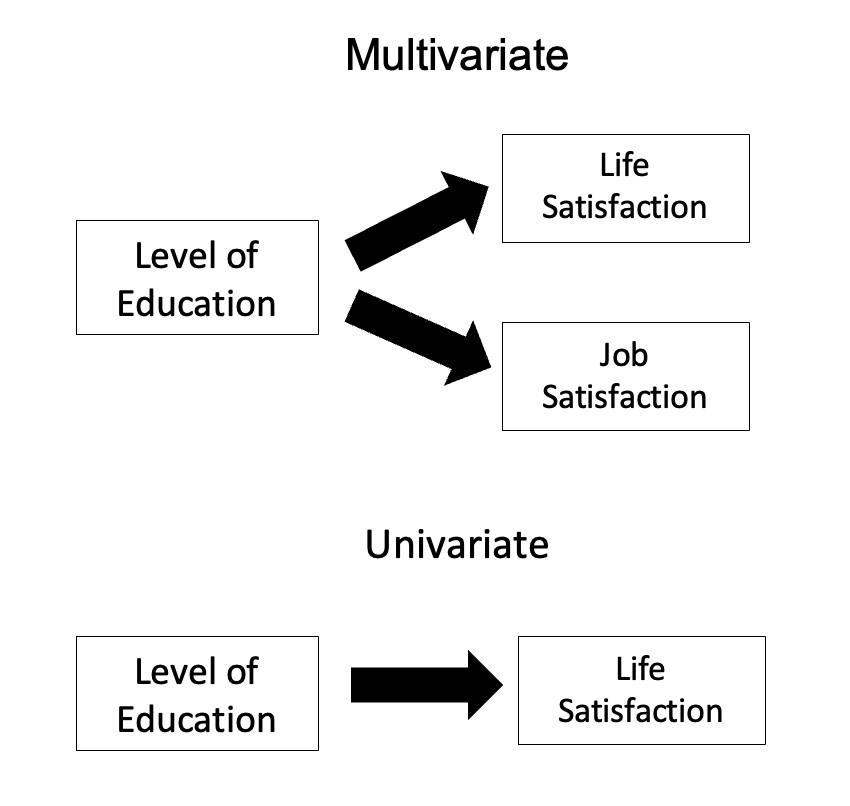
sample means. As a multivariate procedure, it is used when there are two or more dependent variables
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or demand ...
, and is often followed by significance tests involving individual dependent variables separately.
Without relation to the image, the dependent variables may be k life satisfactions scores measured at sequential time points and p job satisfaction scores measured at sequential time points. In this case there are k+p dependent variables whose linear combination follows a multivariate normal distribution, multivariate variance-covariance matrix homogeneity, and linear relationship, no multicollinearity, and each without outliers.
Relationship with ANOVA
MANOVA is a generalized form of univariateanalysis of variance
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation procedures (such as the "variation" among and between groups) used to analyze the differences among means. ANOVA was developed by the statisticia ...
(ANOVA), although, unlike univariate ANOVA, it uses the covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. If the greater values of one variable mainly correspond with the greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for the les ...
between outcome variables in testing the statistical significance of the mean differences.
Where sums of squares appear in univariate analysis of variance, in multivariate analysis of variance certain positive-definite matrices
In mathematics, a symmetric matrix M with real entries is positive-definite if the real number z^\textsfMz is positive for every nonzero real column vector z, where z^\textsf is the transpose of More generally, a Hermitian matrix (that is, a c ...
appear. The diagonal entries are the same kinds of sums of squares that appear in univariate ANOVA. The off-diagonal entries are corresponding sums of products. Under normality assumptions about error
An error (from the Latin ''error'', meaning "wandering") is an action which is inaccurate or incorrect. In some usages, an error is synonymous with a mistake. The etymology derives from the Latin term 'errare', meaning 'to stray'.
In statistics ...
distributions, the counterpart of the sum of squares due to error has a Wishart distribution
In statistics, the Wishart distribution is a generalization to multiple dimensions of the gamma distribution. It is named in honor of John Wishart, who first formulated the distribution in 1928.
It is a family of probability distributions define ...
.
MANOVA is based on the product of model variance matrix, and inverse of the error variance matrix, , or . The hypothesis that implies that the product . Invariance considerations imply the MANOVA statistic should be a measure of magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of the singular value decomposition
In linear algebra, the singular value decomposition (SVD) is a factorization of a real or complex matrix. It generalizes the eigendecomposition of a square normal matrix with an orthonormal eigenbasis to any \ m \times n\ matrix. It is related ...
of this matrix product, but there is no unique choice owing to the multi-dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a Space (mathematics), mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any Point (geometry), point within it. Thus, a Line (geometry), lin ...
al nature of the alternative hypothesis.
The most common statistics are summaries based on the roots (or eigenvalues
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted b ...
) of the matrix:
* Samuel Stanley Wilks
Samuel Stanley Wilks (June 17, 1906 – March 7, 1964) was an American mathematician and academic who played an important role in the development of mathematical statistics, especially in regard to practical applications.
Early life and edu ...
' distributed as lambda
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave rise ...
(Λ)
* the K. C. Sreedharan Pillai
K C Sreedharan Pillai (1920–1985) was an Demographics of India, Indian statistician who was known for his works on multivariate analysis and probability distributions.
Pillai studied at the University of Travancore in Trivandrum. He graduat ...
– M. S. Bartlett trace
Trace may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* Trace (Son Volt album), ''Trace'' (Son Volt album), 1995
* Trace (Died Pretty album), ''Trace'' (Died Pretty album), 1993
* Trace (band), a Dutch progressive rock band
* The Trace (album), ''The ...
,
* the Lawley– Hotelling trace,
* Roy's greatest root
Roy's is an upscale American restaurant that specializes in Hawaiian and Japanese fusion cuisine, with a focus on sushi, seafood and steak. The chain was founded by James Beard Foundation Award Winner, Roy Yamaguchi in 1988 in Honolulu, Hawaii. ...
(also called ''Roy's largest root''),
Discussion continues over the merits of each, although the greatest root leads only to a bound on significance which is not generally of practical interest. A further complication is that, except for the Roy's greatest root, the distribution of these statistics under the null hypothesis
In scientific research, the null hypothesis (often denoted ''H''0) is the claim that no difference or relationship exists between two sets of data or variables being analyzed. The null hypothesis is that any experimentally observed difference is d ...
is not straightforward and can only be approximated except in a few low-dimensional cases.
An algorithm for the distribution of the Roy's largest root under the null hypothesis
In scientific research, the null hypothesis (often denoted ''H''0) is the claim that no difference or relationship exists between two sets of data or variables being analyzed. The null hypothesis is that any experimentally observed difference is d ...
was derived in while the distribution under the alternative is studied in.
The best-known approximation
An approximation is anything that is intentionally similar but not exactly equality (mathematics), equal to something else.
Etymology and usage
The word ''approximation'' is derived from Latin ''approximatus'', from ''proximus'' meaning ''very ...
for Wilks' lambda was derived by C. R. Rao
Calyampudi Radhakrishna Rao FRS (born 10 September 1920), commonly known as C. R. Rao, is an Indian-American mathematician and statistician. He is currently professor emeritus at Pennsylvania State University and Research Professor at the Un ...
.
In the case of two groups, all the statistics are equivalent and the test reduces to Hotelling's T-square
In statistics, particularly in hypothesis testing, the Hotelling's ''T''-squared distribution (''T''2), proposed by Harold Hotelling, is a multivariate probability distribution that is tightly related to the ''F''-distribution and is most not ...
.
Correlation of dependent variables
 MANOVA's power is affected by the correlations of the dependent variables and by the effect sizes associated with those variables. For example, when there are two groups and two dependent variables, MANOVA's power is lowest when the correlation equals the ratio of the smaller to the larger standardized effect size.
MANOVA's power is affected by the correlations of the dependent variables and by the effect sizes associated with those variables. For example, when there are two groups and two dependent variables, MANOVA's power is lowest when the correlation equals the ratio of the smaller to the larger standardized effect size.
See also
*Discriminant function analysis
Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), normal discriminant analysis (NDA), or discriminant function analysis is a generalization of Fisher's linear discriminant, a method used in statistics and other fields, to find a linear combination of features ...
*Canonical correlation analysis
In statistics, canonical-correlation analysis (CCA), also called canonical variates analysis, is a way of inferring information from cross-covariance matrices. If we have two vectors ''X'' = (''X''1, ..., ''X'n'') and ''Y' ...
*Multivariate analysis of variance
In statistics, multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) is a procedure for comparing multivariate sample means. As a multivariate procedure, it is used when there are two or more dependent variables, and is often followed by significance tests i ...
(Wikiversity)
*Repeated measures design
Repeated measures design is a research design that involves multiple measures of the same variable taken on the same or matched subjects either under different conditions or over two or more time periods. For instance, repeated measurements are c ...
References
External links
Multivariate Analysis of Variance (MANOVA) by Aaron French, Marcelo Macedo, John Poulsen, Tyler Waterson and Angela Yu, San Francisco State University
What is a MANOVA test used for?
{{Experimental design Analysis of variance Design of experiments