Malaysia Penang License Plate Front on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in
 The name "
The name "
 Evidence of modern human habitation in Malaysia dates back 40,000 years. In the Malay Peninsula, the first inhabitants are thought to be
Evidence of modern human habitation in Malaysia dates back 40,000 years. In the Malay Peninsula, the first inhabitants are thought to be  During this time, the mostly ethnically Chinese rebels under the leadership of the Malayan Communist Party launched guerrilla operations designed to force the British out of Malaya. The Malayan Emergency, Malayan Emergency (1948–1960) involved a long anti-insurgency campaign by
During this time, the mostly ethnically Chinese rebels under the leadership of the Malayan Communist Party launched guerrilla operations designed to force the British out of Malaya. The Malayan Emergency, Malayan Emergency (1948–1960) involved a long anti-insurgency campaign by
 Malaysia is a
Malaysia is a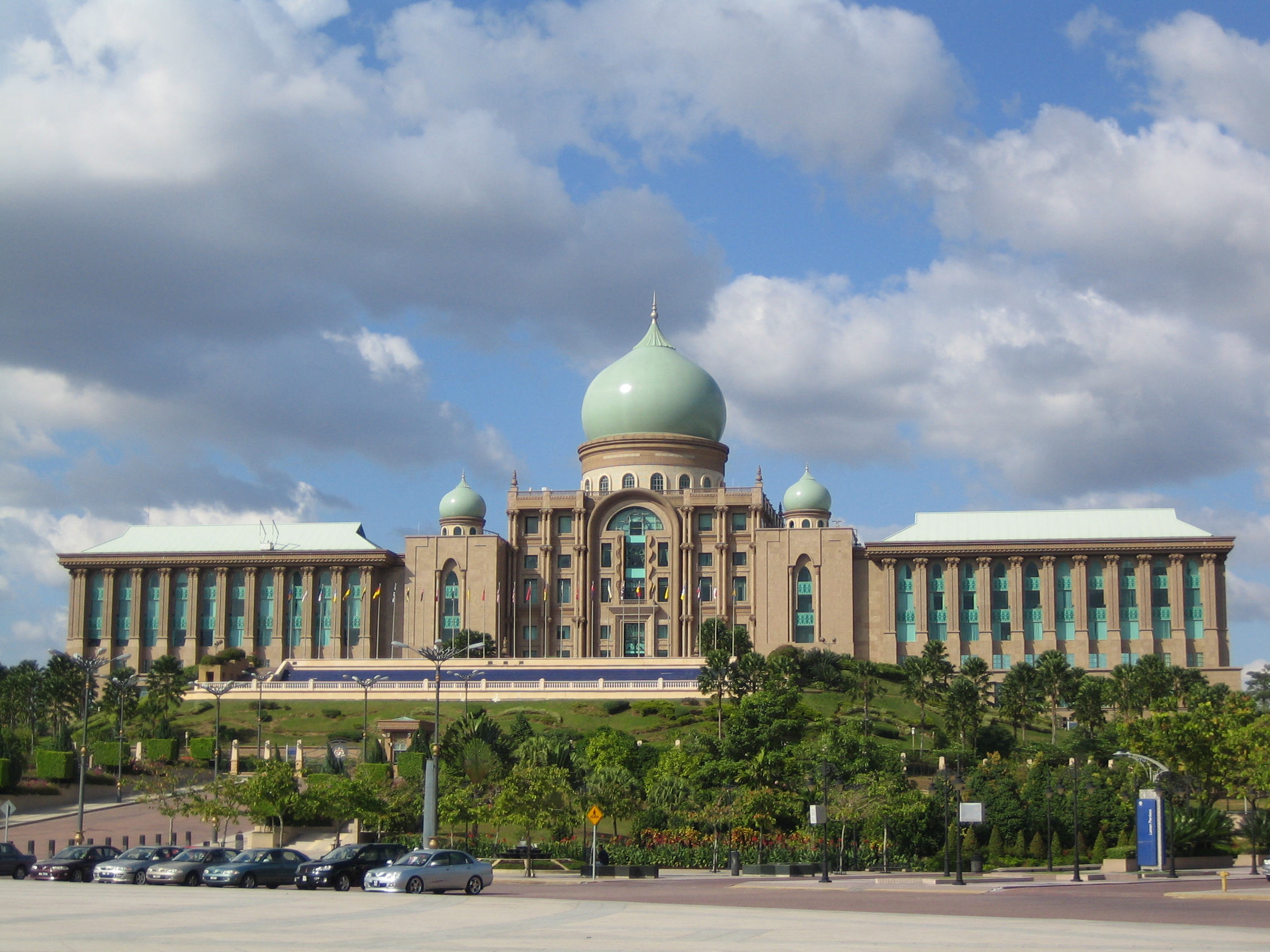  Executive branch, Executive power is vested in the
Executive branch, Executive power is vested in the
 Malaysia is the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 66th largest country by total land area, with a land area of . It has land Borders of Malaysia, borders with Thailand in West Malaysia, and
Malaysia is the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 66th largest country by total land area, with a land area of . It has land Borders of Malaysia, borders with Thailand in West Malaysia, and
 About two thirds of Malaysia was covered in forest as of 2007, with some forests believed to be 130 million years old. The forests are dominated by Dipterocarpaceae, dipterocarps. Lowland forest covers areas below , and formerly East Malaysia was covered in Borneo lowland rain forests, such rainforest, which is supported by its hot wet climate. There are around 14,500 species of flowering plants and trees. Besides rainforests, there are over of mangroves in Malaysia, and a large amount of peat forest. At higher altitudes, oaks, chestnuts, and rhododendrons replace dipterocarps. There are an estimated 8,500 species of vascular plants in Peninsular Malaysia, with another 15,000 in the East. The forests of East Malaysia are estimated to be the habitat of around 2,000 tree species, and are one of the most biodiverse areas in the world, with 240 different species of trees every hectare. These forests host many members of the Rafflesia genus, the largest flowers in the world, with a maximum diameter of .
Logging, along with cultivation practices has devastated tree cover, causing severe environmental degradation in the country. Over 80 per cent of Sarawak's rainforest has been logged. Floods in East Malaysia have been worsened by the loss of trees, and over 60 per cent of the Peninsula's forest have been cleared. With current rates of Social and environmental impact of palm oil#Deforestation, deforestation, mainly for the Palm oil production in Malaysia, palm oil industry, the forests are predicted to be extinct by 2020. Deforestation in Malaysia, Deforestation is a major problem for animals, fungi and plants, having caused species such as ''Begonia eiromischa'' to go extinct. Most remaining forest is found inside reserves and national parks. Habitat destruction has proved a threat for marine life. Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing, Illegal fishing is another major threat, with fishing methods such as dynamite fishing and poisoning depleting marine ecosystems. Leatherback turtle numbers have dropped 98 per cent since the 1950s. Hunting has also been an issue for some animals, with overconsumption and the use of animal parts for profit endangering many animals, from marine life to tigers. Marine life is also detrimentally affected by uncontrolled tourism.
The Malaysian government aims to balance economic growth with environmental protection, but has been accused of favouring big business over the environment. Some state governments are now trying to counter the environmental impact and pollution created by deforestation; and the federal government is trying to cut logging by 10 per cent each year. A total of List of national parks of Malaysia, 28 national parks have been established, 23 in East Malaysia and five in the Peninsula. Tourism has been limited in biodiverse areas such as Sipadan island. Wildlife smuggling, Wildlife trafficking is a large issue, and the Malaysian government has held talks with the governments of Brunei and Indonesia to standardise anti-trafficking laws.
About two thirds of Malaysia was covered in forest as of 2007, with some forests believed to be 130 million years old. The forests are dominated by Dipterocarpaceae, dipterocarps. Lowland forest covers areas below , and formerly East Malaysia was covered in Borneo lowland rain forests, such rainforest, which is supported by its hot wet climate. There are around 14,500 species of flowering plants and trees. Besides rainforests, there are over of mangroves in Malaysia, and a large amount of peat forest. At higher altitudes, oaks, chestnuts, and rhododendrons replace dipterocarps. There are an estimated 8,500 species of vascular plants in Peninsular Malaysia, with another 15,000 in the East. The forests of East Malaysia are estimated to be the habitat of around 2,000 tree species, and are one of the most biodiverse areas in the world, with 240 different species of trees every hectare. These forests host many members of the Rafflesia genus, the largest flowers in the world, with a maximum diameter of .
Logging, along with cultivation practices has devastated tree cover, causing severe environmental degradation in the country. Over 80 per cent of Sarawak's rainforest has been logged. Floods in East Malaysia have been worsened by the loss of trees, and over 60 per cent of the Peninsula's forest have been cleared. With current rates of Social and environmental impact of palm oil#Deforestation, deforestation, mainly for the Palm oil production in Malaysia, palm oil industry, the forests are predicted to be extinct by 2020. Deforestation in Malaysia, Deforestation is a major problem for animals, fungi and plants, having caused species such as ''Begonia eiromischa'' to go extinct. Most remaining forest is found inside reserves and national parks. Habitat destruction has proved a threat for marine life. Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing, Illegal fishing is another major threat, with fishing methods such as dynamite fishing and poisoning depleting marine ecosystems. Leatherback turtle numbers have dropped 98 per cent since the 1950s. Hunting has also been an issue for some animals, with overconsumption and the use of animal parts for profit endangering many animals, from marine life to tigers. Marine life is also detrimentally affected by uncontrolled tourism.
The Malaysian government aims to balance economic growth with environmental protection, but has been accused of favouring big business over the environment. Some state governments are now trying to counter the environmental impact and pollution created by deforestation; and the federal government is trying to cut logging by 10 per cent each year. A total of List of national parks of Malaysia, 28 national parks have been established, 23 in East Malaysia and five in the Peninsula. Tourism has been limited in biodiverse areas such as Sipadan island. Wildlife smuggling, Wildlife trafficking is a large issue, and the Malaysian government has held talks with the governments of Brunei and Indonesia to standardise anti-trafficking laws.
 Malaysia is a relatively open economy, open state-oriented and newly industrialised
Malaysia is a relatively open economy, open state-oriented and newly industrialised
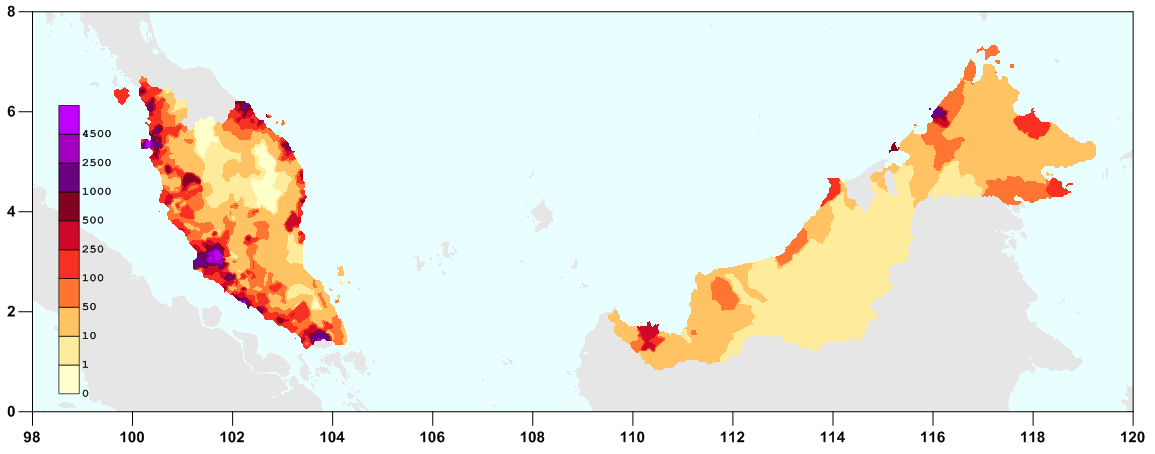 According to the Malaysian Department of Statistics, the country's population was 32,447,385 in 2020, making it the List of countries by population in 2010, 42nd most populated country. According to a 2012 estimate, the population is increasing by 1.54 percent per year. Malaysia has an average population density of 96 people per km2, ranking it List of countries and territories by population density, 116th in the world for population density. People within the 15–64 age group constitute 69.5 percent of the total population; the 0–14 age group corresponds to 24.5 percent; while senior citizens aged 65 years or older make up 6.0 percent. In 1960, when the first official census was recorded in Malaysia, the population was 8.11 million. 91.8 per cent of the population are Malaysian citizens.
Malaysian citizens are divided along local ethnic lines, with 69.7 per cent considered ''Bumiputera (Malaysia), bumiputera''. The largest group of bumiputera are Malays (ethnic group), Malays, who are defined in the constitution as Muslims who practise Malay customs and culture. They play a dominant role politically. Bumiputera status is also accorded to the non-Malay indigenous groups of Sabah and Sarawak: which includes Dayak people, Dayaks (Iban people, Iban, Bidayuh, Orang Ulu), Kadazan-Dusun, Melanau people, Melanau, Sama-Bajau, Bajau and others. Non-Malay bumiputeras make up more than half of Sarawak's population and over two thirds of Sabah's population. There are also indigenous or aboriginal groups in much smaller numbers on the peninsular, where they are collectively known as the Orang Asli. Laws over who gets bumiputera status vary between states.
There are also two other non-Bumiputera local ethnic groups. 22.5 per cent of the population are Malaysian Chinese, while 6.8 per cent are Malaysian Indians, Malaysian Indian. The local Chinese have historically been more dominant in the business community. Local Indians are mostly of Tamil people, Tamil descent. Malaysian citizenship is not automatically granted to those born in Malaysia, but is granted to a child born of two Malaysian parents outside Malaysia. Dual citizenship is not permitted. Citizenship in the states of Sabah and Sarawak in Malaysian Borneo are distinct from citizenship in Peninsular Malaysia for immigration purposes. Every citizen is issued a biometric smart chip identity document, identity card known as ''MyKad'' at the age of 12, and must carry the card at all times.
The population is concentrated on Peninsular Malaysia, where 20 million out of approximately 28 million Malaysians live. 70 per cent of the population is urban. Due to the rise in labour-intensive industries, the country is estimated to have over 3 million migrant workers; about 10 per cent of the population. Sabah-based NGOs estimate that out of the 3 million that make up the population of Sabah, 2 million are illegal immigrants. Malaysia hosts a population of refugees and asylum seekers numbering approximately 171,500. Of this population, approximately 79,000 are from Burma, 72,400 from the Philippines, and 17,700 from Indonesia. Malaysian officials are reported to have turned deportees directly over to human smugglers in 2007, and Malaysia employs RELA Corps, RELA, a volunteer militia with a history of controversies, to enforce its immigration law.
According to the Malaysian Department of Statistics, the country's population was 32,447,385 in 2020, making it the List of countries by population in 2010, 42nd most populated country. According to a 2012 estimate, the population is increasing by 1.54 percent per year. Malaysia has an average population density of 96 people per km2, ranking it List of countries and territories by population density, 116th in the world for population density. People within the 15–64 age group constitute 69.5 percent of the total population; the 0–14 age group corresponds to 24.5 percent; while senior citizens aged 65 years or older make up 6.0 percent. In 1960, when the first official census was recorded in Malaysia, the population was 8.11 million. 91.8 per cent of the population are Malaysian citizens.
Malaysian citizens are divided along local ethnic lines, with 69.7 per cent considered ''Bumiputera (Malaysia), bumiputera''. The largest group of bumiputera are Malays (ethnic group), Malays, who are defined in the constitution as Muslims who practise Malay customs and culture. They play a dominant role politically. Bumiputera status is also accorded to the non-Malay indigenous groups of Sabah and Sarawak: which includes Dayak people, Dayaks (Iban people, Iban, Bidayuh, Orang Ulu), Kadazan-Dusun, Melanau people, Melanau, Sama-Bajau, Bajau and others. Non-Malay bumiputeras make up more than half of Sarawak's population and over two thirds of Sabah's population. There are also indigenous or aboriginal groups in much smaller numbers on the peninsular, where they are collectively known as the Orang Asli. Laws over who gets bumiputera status vary between states.
There are also two other non-Bumiputera local ethnic groups. 22.5 per cent of the population are Malaysian Chinese, while 6.8 per cent are Malaysian Indians, Malaysian Indian. The local Chinese have historically been more dominant in the business community. Local Indians are mostly of Tamil people, Tamil descent. Malaysian citizenship is not automatically granted to those born in Malaysia, but is granted to a child born of two Malaysian parents outside Malaysia. Dual citizenship is not permitted. Citizenship in the states of Sabah and Sarawak in Malaysian Borneo are distinct from citizenship in Peninsular Malaysia for immigration purposes. Every citizen is issued a biometric smart chip identity document, identity card known as ''MyKad'' at the age of 12, and must carry the card at all times.
The population is concentrated on Peninsular Malaysia, where 20 million out of approximately 28 million Malaysians live. 70 per cent of the population is urban. Due to the rise in labour-intensive industries, the country is estimated to have over 3 million migrant workers; about 10 per cent of the population. Sabah-based NGOs estimate that out of the 3 million that make up the population of Sabah, 2 million are illegal immigrants. Malaysia hosts a population of refugees and asylum seekers numbering approximately 171,500. Of this population, approximately 79,000 are from Burma, 72,400 from the Philippines, and 17,700 from Indonesia. Malaysian officials are reported to have turned deportees directly over to human smugglers in 2007, and Malaysia employs RELA Corps, RELA, a volunteer militia with a history of controversies, to enforce its immigration law.
 The constitution grants freedom of religion and makes Malaysia an officially secular state, while establishing Islam as the "religion of the Federation". According to the Population and Housing Census 2020 figures, ethnicity and religious beliefs correlate highly. Approximately 63.5% of the population practise Islam in Malaysia, Islam, 18.7% practise Buddhism in Malaysia, Buddhism, 9.1% Christianity in Malaysia, Christianity, 6.1% Hinduism in Malaysia, Hinduism and 1.3% practise Confucianism, Taoism and other traditional Chinese folk religion, Chinese religions. 2.7% declared no religion or practised other religions or did not provide any information. The states of Sarawak, Penang and the federal territory of
The constitution grants freedom of religion and makes Malaysia an officially secular state, while establishing Islam as the "religion of the Federation". According to the Population and Housing Census 2020 figures, ethnicity and religious beliefs correlate highly. Approximately 63.5% of the population practise Islam in Malaysia, Islam, 18.7% practise Buddhism in Malaysia, Buddhism, 9.1% Christianity in Malaysia, Christianity, 6.1% Hinduism in Malaysia, Hinduism and 1.3% practise Confucianism, Taoism and other traditional Chinese folk religion, Chinese religions. 2.7% declared no religion or practised other religions or did not provide any information. The states of Sarawak, Penang and the federal territory of
 The official and national language of Malaysia is
The official and national language of Malaysia is
 The education system of Malaysia features a non-compulsory kindergarten education followed by six years of compulsory primary education, and five years of optional secondary education. Schools in the primary education system are divided into two categories: national primary schools, which teach in Malay, and vernacular schools, which teach in Chinese or Tamil. Secondary education is conducted for five years. In the final year of secondary education, students sit for the Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia, Malaysian Certificate of Education examination. Since the introduction of the Malaysian Matriculation Programme, matriculation programme in 1999, students who completed the 12-month programme in matriculation colleges can enroll in local universities. However, in the matriculation system, only 10 per cent of places are open to non-''bumiputera'' students.
The education system of Malaysia features a non-compulsory kindergarten education followed by six years of compulsory primary education, and five years of optional secondary education. Schools in the primary education system are divided into two categories: national primary schools, which teach in Malay, and vernacular schools, which teach in Chinese or Tamil. Secondary education is conducted for five years. In the final year of secondary education, students sit for the Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia, Malaysian Certificate of Education examination. Since the introduction of the Malaysian Matriculation Programme, matriculation programme in 1999, students who completed the 12-month programme in matriculation colleges can enroll in local universities. However, in the matriculation system, only 10 per cent of places are open to non-''bumiputera'' students.
 Malaysia has a multi-ethnic, multicultural, and multilingual society. The original culture of the area stemmed from indigenous tribes that inhabited it, along with the Malay people, Malays who later moved there. Substantial influence exists from Chinese culture, Chinese and Indian Culture, Indian culture, dating back to when foreign trade began. Other cultural influences include the Persian culture, Persian, Arabic culture, Arabic, and British culture, British cultures. Due to the structure of the government, coupled with the social contract (Malaysia), social contract theory, there has been minimal cultural assimilation of ethnic minorities. Some cultural disputes exist between Malaysia and neighbouring countries, notably
Malaysia has a multi-ethnic, multicultural, and multilingual society. The original culture of the area stemmed from indigenous tribes that inhabited it, along with the Malay people, Malays who later moved there. Substantial influence exists from Chinese culture, Chinese and Indian Culture, Indian culture, dating back to when foreign trade began. Other cultural influences include the Persian culture, Persian, Arabic culture, Arabic, and British culture, British cultures. Due to the structure of the government, coupled with the social contract (Malaysia), social contract theory, there has been minimal cultural assimilation of ethnic minorities. Some cultural disputes exist between Malaysia and neighbouring countries, notably
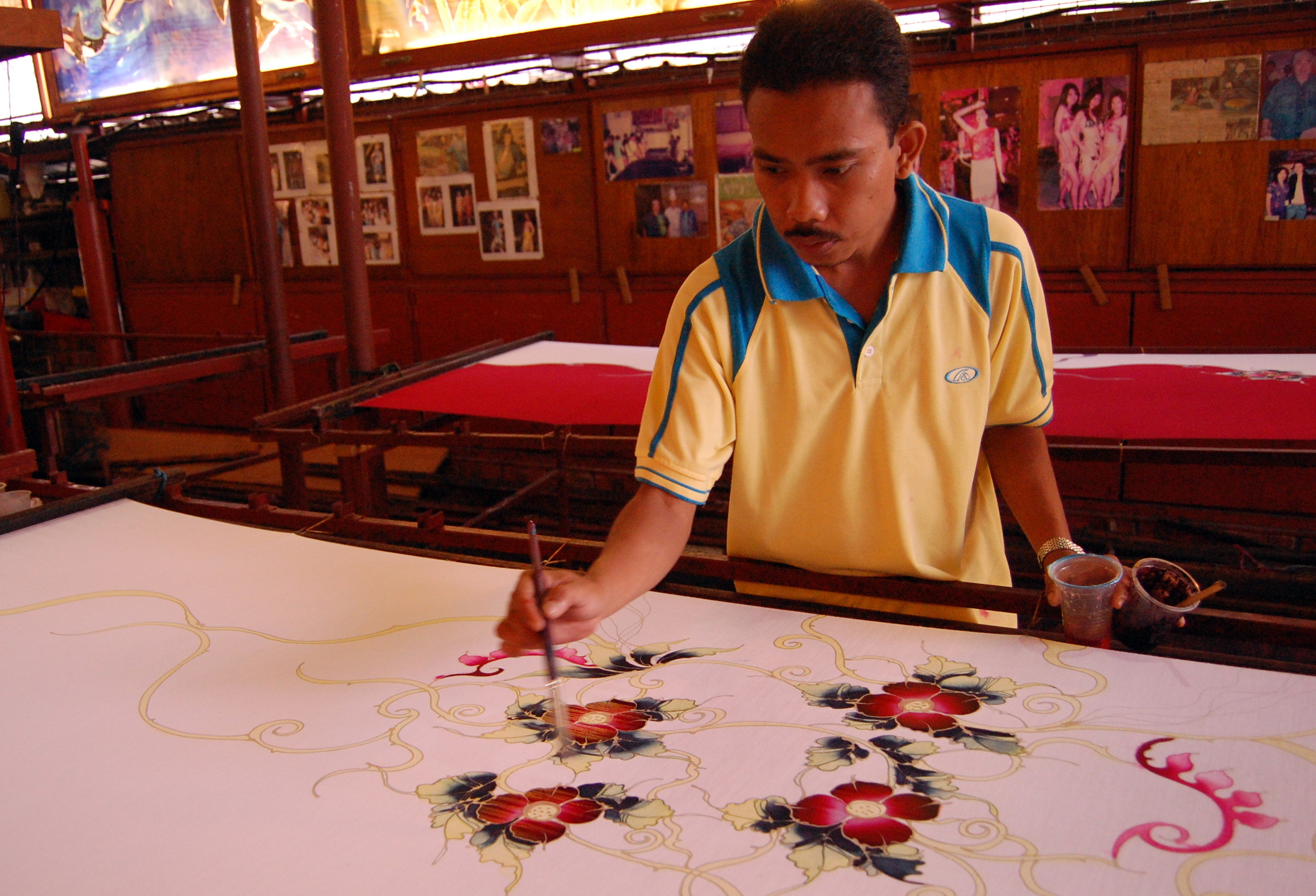 Traditional Malaysian art was mainly centred on the areas of carving, weaving, and silversmithing. Traditional art ranges from handwoven baskets from rural areas to the silverwork of the Malay courts. Common artworks included ornamental kris, beetle nut sets, and woven batik and songket fabrics. Indigenous East Malaysians are known for their wooden masks. Each ethnic group have distinct performing arts, with little overlap between them. However, Malay art does show some North Indian influence due to the historical influence of India.
Traditional Malay music and performing arts appear to have originated in the Kelantan-Pattani region with influences from India, China, Thailand, and Indonesia. The music is based around percussion instruments, the most important of which is the gendang (drum). There are at least 14 types of traditional drums. Drums and other traditional percussion instruments and are often made from natural materials. Music is traditionally used for storytelling, celebrating life-cycle events, and occasions such as a harvest. It was once used as a form of long-distance communication. In East Malaysia, gong-based musical ensembles such as agung and kulintang are commonly used in ceremonies such as funerals and weddings. These ensembles are also common in neighbouring regions such as in Mindanao in the Philippines, Kalimantan in Indonesia, and Brunei.
Malaysia has a strong oral tradition that has existed since before the arrival of writing, and continues today. Each of the Malay Sultanates created their own literary tradition, influenced by pre-existing oral stories and by the stories that came with Islam. The first Malay literature was in the Arabic script. The earliest known Malay writing is on the Terengganu Inscription Stone, Terengganu stone, made in 1303. Chinese and Indian literature became common as the numbers of speakers increased in Malaysia, and locally produced works based in languages from those areas began to be produced in the 19th century. English has also become a common literary language. In 1971, the government took the step of defining the literature of different languages. Literature written in Malay was called "the national literature of Malaysia", literature in other ''bumiputera'' languages was called "regional literature", while literature in other languages was called "sectional literature". Malay poetry is highly developed, and uses many forms. The ''Hikayat'' form is popular, and the ''pantun'' has spread from Malay to other languages.
Traditional Malaysian art was mainly centred on the areas of carving, weaving, and silversmithing. Traditional art ranges from handwoven baskets from rural areas to the silverwork of the Malay courts. Common artworks included ornamental kris, beetle nut sets, and woven batik and songket fabrics. Indigenous East Malaysians are known for their wooden masks. Each ethnic group have distinct performing arts, with little overlap between them. However, Malay art does show some North Indian influence due to the historical influence of India.
Traditional Malay music and performing arts appear to have originated in the Kelantan-Pattani region with influences from India, China, Thailand, and Indonesia. The music is based around percussion instruments, the most important of which is the gendang (drum). There are at least 14 types of traditional drums. Drums and other traditional percussion instruments and are often made from natural materials. Music is traditionally used for storytelling, celebrating life-cycle events, and occasions such as a harvest. It was once used as a form of long-distance communication. In East Malaysia, gong-based musical ensembles such as agung and kulintang are commonly used in ceremonies such as funerals and weddings. These ensembles are also common in neighbouring regions such as in Mindanao in the Philippines, Kalimantan in Indonesia, and Brunei.
Malaysia has a strong oral tradition that has existed since before the arrival of writing, and continues today. Each of the Malay Sultanates created their own literary tradition, influenced by pre-existing oral stories and by the stories that came with Islam. The first Malay literature was in the Arabic script. The earliest known Malay writing is on the Terengganu Inscription Stone, Terengganu stone, made in 1303. Chinese and Indian literature became common as the numbers of speakers increased in Malaysia, and locally produced works based in languages from those areas began to be produced in the 19th century. English has also become a common literary language. In 1971, the government took the step of defining the literature of different languages. Literature written in Malay was called "the national literature of Malaysia", literature in other ''bumiputera'' languages was called "regional literature", while literature in other languages was called "sectional literature". Malay poetry is highly developed, and uses many forms. The ''Hikayat'' form is popular, and the ''pantun'' has spread from Malay to other languages.
 Malaysia's main newspapers are owned by the government and political parties in the ruling coalition, although some major opposition parties also have their own, which are openly sold alongside regular newspapers. A divide exists between the media in the two halves of the country. Peninsular-based media gives low priority to news from the East, and often treats the eastern states as colonies of the Peninsula. As a result of this, East Malaysia region of Sarawak launched TVS (TV channel), TV Sarawak as internet streaming beginning in 2014, and as TV station on 10 October 2020 to overcome the low priority and coverage of Peninsular-based media and to solidify the representation of East Malaysia. The media have been blamed for increasing tension between Indonesia and Malaysia, and giving Malaysians a bad image of Indonesians. The country has Malay, English, Chinese, and Tamil dailies. Kadazandusun and Bajau news only available via TV broadcast Berita RTM. Written Kadazan news was once included in publications such as The Borneo Post, the Borneo Mail, the Daily Express (Malaysia), Daily Express, and the New Sabah Times, but publication has ceased with the newspaper or as a section.
Freedom of the press is limited, with numerous restrictions on publishing rights and information dissemination. The government has previously tried to crack down on opposition papers before elections. In 2007, a government agency issued a directive to all private television and radio stations to refrain from broadcasting speeches made by opposition leaders, a move condemned by politicians from the opposition Democratic Action Party (Malaysia), Democratic Action Party. Sabah, where all tabloids but one are independent of government control, has the freest press in Malaysia. Laws such as the Printing Presses and Publications Act have also been cited as curtailing freedom of expression.
Malaysia's main newspapers are owned by the government and political parties in the ruling coalition, although some major opposition parties also have their own, which are openly sold alongside regular newspapers. A divide exists between the media in the two halves of the country. Peninsular-based media gives low priority to news from the East, and often treats the eastern states as colonies of the Peninsula. As a result of this, East Malaysia region of Sarawak launched TVS (TV channel), TV Sarawak as internet streaming beginning in 2014, and as TV station on 10 October 2020 to overcome the low priority and coverage of Peninsular-based media and to solidify the representation of East Malaysia. The media have been blamed for increasing tension between Indonesia and Malaysia, and giving Malaysians a bad image of Indonesians. The country has Malay, English, Chinese, and Tamil dailies. Kadazandusun and Bajau news only available via TV broadcast Berita RTM. Written Kadazan news was once included in publications such as The Borneo Post, the Borneo Mail, the Daily Express (Malaysia), Daily Express, and the New Sabah Times, but publication has ceased with the newspaper or as a section.
Freedom of the press is limited, with numerous restrictions on publishing rights and information dissemination. The government has previously tried to crack down on opposition papers before elections. In 2007, a government agency issued a directive to all private television and radio stations to refrain from broadcasting speeches made by opposition leaders, a move condemned by politicians from the opposition Democratic Action Party (Malaysia), Democratic Action Party. Sabah, where all tabloids but one are independent of government control, has the freest press in Malaysia. Laws such as the Printing Presses and Publications Act have also been cited as curtailing freedom of expression.
 Malaysians observe a number of holidays and festivities throughout the year. Some are federally gazetted public holidays and some are observed by individual states. Other festivals are observed by particular ethnic or religion groups, and the main holiday of each major group has been declared a public holiday. The most observed national holiday is ''Independence Day (Malaysia), Hari Merdeka'' (Independence Day) on 31 August, commemorating the independence of the Federation of Malaya in 1957. Malaysia Day on 16 September commemorates federation in 1963. Other notable national holidays are Labour Day (1 May) and the King's birthday (first week of June).
Muslim holidays are prominent as Islam is the state religion; ''Hari Raya Puasa'' (also called ''Hari Raya Aidilfitri'', Malay for Eid al-Fitr), ''Hari Raya Haji'' (also called ''Hari Raya Aidiladha'', Malay for Eid ul-Adha), ''Mawlid, Maulidur Rasul'' (birthday of the Prophet), and others being observed. Malaysian Chinese celebrate festivals such as Chinese New Year and others relating to traditional Chinese beliefs. Wesak Day is observed and celebrated by Buddhists. Hindus in Malaysia celebrate ''Deepavali'', the festival of lights, while ''Thaipusam'' is a religious rite which sees pilgrims from all over the country converge at the Batu Caves. Malaysia's Christian community celebrates most of the holidays observed by Christians elsewhere, most notably Christmas and Easter. In addition to this, the Dayak community in Sarawak celebrate a harvest festival known as ''Gawai Dayak, Gawai'', and the Kadazandusun community celebrate ''Kaamatan''. Despite most festivals being identified with a particular ethnic or religious group, celebrations are universal. In a custom known as "open house" Malaysians participate in the celebrations of others, often visiting the houses of those who identify with the festival.
Malaysians observe a number of holidays and festivities throughout the year. Some are federally gazetted public holidays and some are observed by individual states. Other festivals are observed by particular ethnic or religion groups, and the main holiday of each major group has been declared a public holiday. The most observed national holiday is ''Independence Day (Malaysia), Hari Merdeka'' (Independence Day) on 31 August, commemorating the independence of the Federation of Malaya in 1957. Malaysia Day on 16 September commemorates federation in 1963. Other notable national holidays are Labour Day (1 May) and the King's birthday (first week of June).
Muslim holidays are prominent as Islam is the state religion; ''Hari Raya Puasa'' (also called ''Hari Raya Aidilfitri'', Malay for Eid al-Fitr), ''Hari Raya Haji'' (also called ''Hari Raya Aidiladha'', Malay for Eid ul-Adha), ''Mawlid, Maulidur Rasul'' (birthday of the Prophet), and others being observed. Malaysian Chinese celebrate festivals such as Chinese New Year and others relating to traditional Chinese beliefs. Wesak Day is observed and celebrated by Buddhists. Hindus in Malaysia celebrate ''Deepavali'', the festival of lights, while ''Thaipusam'' is a religious rite which sees pilgrims from all over the country converge at the Batu Caves. Malaysia's Christian community celebrates most of the holidays observed by Christians elsewhere, most notably Christmas and Easter. In addition to this, the Dayak community in Sarawak celebrate a harvest festival known as ''Gawai Dayak, Gawai'', and the Kadazandusun community celebrate ''Kaamatan''. Despite most festivals being identified with a particular ethnic or religious group, celebrations are universal. In a custom known as "open house" Malaysians participate in the celebrations of others, often visiting the houses of those who identify with the festival.
 Popular sports in Malaysia include association football, badminton, field hockey, bowls, tennis, squash (sport), squash, martial arts, horse riding, sailing, and skate boarding. Football is the most popular sport in Malaysia. Badminton matches also attract thousands of spectators, and since 1948 Malaysia has been one of four countries to hold the Thomas Cup, the world team championship trophy of men's badminton. The Malaysian Lawn Bowls Federation was registered in 1997. Squash was brought to the country by members of the British army, with the first competition being held in 1939. The Squash Racquets Association Of Malaysia was created on 25 June 1972. The men's Malaysia men's national field hockey team, national field hockey team ranked FIH World Rankings, 10th in the world . The 3rd Hockey World Cup was hosted at Merdeka Stadium in Kuala Lumpur, as well as the 10th cup. The country also has its own Formula One track – the Sepang International Circuit, with the first Malaysian Grand Prix held in 1999. Traditional sports include Silat Melayu, the most common style of martial arts practised by ethnic Malays.
The Federation of Malaya Olympic Council was formed in 1953, and received recognition by the IOC in 1954. It first participated in the 1956 Summer Olympics, 1956 Melbourne Olympic Games. The council was renamed the Olympic Council of Malaysia in 1964, and Malaysia at the Olympics, has participated in all but one Olympic games since its inception. The largest number of athletes ever sent to the Olympics was 57 to the 1972 Munich Olympic Games. Besides the Olympic Games, Malaysia also participates in the Paralympic Games. Malaysia has competed at the Commonwealth Games since 1950 as Malaya, and 1966 as Malaysia, and the games were hosted in Kuala Lumpur in 1998.
Popular sports in Malaysia include association football, badminton, field hockey, bowls, tennis, squash (sport), squash, martial arts, horse riding, sailing, and skate boarding. Football is the most popular sport in Malaysia. Badminton matches also attract thousands of spectators, and since 1948 Malaysia has been one of four countries to hold the Thomas Cup, the world team championship trophy of men's badminton. The Malaysian Lawn Bowls Federation was registered in 1997. Squash was brought to the country by members of the British army, with the first competition being held in 1939. The Squash Racquets Association Of Malaysia was created on 25 June 1972. The men's Malaysia men's national field hockey team, national field hockey team ranked FIH World Rankings, 10th in the world . The 3rd Hockey World Cup was hosted at Merdeka Stadium in Kuala Lumpur, as well as the 10th cup. The country also has its own Formula One track – the Sepang International Circuit, with the first Malaysian Grand Prix held in 1999. Traditional sports include Silat Melayu, the most common style of martial arts practised by ethnic Malays.
The Federation of Malaya Olympic Council was formed in 1953, and received recognition by the IOC in 1954. It first participated in the 1956 Summer Olympics, 1956 Melbourne Olympic Games. The council was renamed the Olympic Council of Malaysia in 1964, and Malaysia at the Olympics, has participated in all but one Olympic games since its inception. The largest number of athletes ever sent to the Olympics was 57 to the 1972 Munich Olympic Games. Besides the Olympic Games, Malaysia also participates in the Paralympic Games. Malaysia has competed at the Commonwealth Games since 1950 as Malaya, and 1966 as Malaysia, and the games were hosted in Kuala Lumpur in 1998.
Malaysia
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Malaysia
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Malaysia profile
from the BBC News * {{Coord, 2, N, 112, E, type:country_region:MY, display=title Malaysia, Commonwealth monarchies Developing 8 Countries member states Federal monarchies G15 nations Malay-speaking countries and territories Member states of ASEAN Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Southeast Asian countries States and territories established in 1963 World War II sites 1963 establishments in Malaysia Countries in Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
. The federal
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia ( ms, Semenanjung Malaysia; Jawi: سمننجڠ مليسيا), or the States of Malaya ( ms, Negeri-negeri Tanah Melayu; Jawi: نڬري-نڬري تانه ملايو), also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, ...
and Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
's East Malaysia
East Malaysia (), or the Borneo States, also known as Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia on and near the island of Borneo, the world's third-largest island. Near the coast of Sabah is a small archipelago called Labuan. East Malaysia li ...
. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
with Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
and maritime border
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of the Earth's water surface areas using physiographic or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Bound ...
s with Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
, and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, and a maritime border with the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
. Kuala Lumpur
, anthem = '' Maju dan Sejahtera''
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Malaysia#Southeast Asia#Asia
, pushpin_map_caption =
, coordinates =
, su ...
is the national capital, the country's largest city, and the seat of the legislative branch
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as ...
of the federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
. The nearby planned capital
A planned community, planned city, planned town, or planned settlement is any community that was carefully planned from its inception and is typically constructed on previously undeveloped land. This contrasts with settlements that evolve ...
of Putrajaya
Putrajaya (), officially the Federal Territory of Putrajaya ( ms, Wilayah Persekutuan Putrajaya), is a planned capital city which functions as the administrative capital and the judicial capital of Malaysia. The seat of the federal government ...
is the administrative capital, which represents the seat of both the executive branch
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a State (polity), state.
In poli ...
(the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, federal ministries, and agencies) and the judicial branch
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
of the federal government. With a population of over 32 million, Malaysia is the world's 45th-most populous country. The southernmost point of continental Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
is in Tanjung Piai
Tanjung Piai ( Jawi: تنجوڠ ڤياي) is a cape in Pontian District, Johor, Malaysia. It is the southernmost point of Peninsular Malaysia and thus the most southern point of mainland Eurasia. The skyline of Singapore is visible across the ...
. In the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
, Malaysia is one of 17 megadiverse countries, home to numerous endemic species
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsew ...
.
Malaysia has its origins in the Malay kingdoms, which, from the 18th century on, became subject to the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, along with the British Straits Settlements
The Straits Settlements were a group of British territories located in Southeast Asia. Headquartered in Singapore for more than a century, it was originally established in 1826 as part of the territories controlled by the British East India Comp ...
protectorate. Peninsular Malaysia was unified as the Malayan Union
The Malayan Union was a union of the Malay states and the Straits Settlements of Penang and Malacca. It was the successor to British Malaya and was conceived to unify the Malay Peninsula under a single government to simplify administratio ...
in 1946. Malaya was restructured as the Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya ( ms, Persekutuan Tanah Melayu; Jawi script, Jawi: ) was a federation of what previously had been British Malaya comprising eleven states (nine Malay states and two of the British Empire, British Straits Settlements, P ...
in 1948 and achieved independence on 31 August 1957. The independent Malaya united with the then British crown colonies of North Borneo
North Borneo (usually known as British North Borneo, also known as the State of North Borneo) was a British Protectorate, British protectorate in the northern part of the island of Borneo, which is present day Sabah. The territory of North Borneo ...
, Sarawak
Sarawak (; ) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia. The largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia, Sarawak is located in northwest Borneo Island, and is bordered by the M ...
, and Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
on 16 September 1963 to become Malaysia. In August 1965, Singapore was expelled from the federation and became a separate independent country.
The country is multiethnic
A multinational state or a multinational union is a sovereign entity that comprises two or more nations or states. This contrasts with a nation state, where a single nation accounts for the bulk of the population. Depending on the definition of " ...
and multicultural
The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for "Pluralism (political theory), ethnic pluralism", with the tw ...
, which has a significant effect on its politics. About half the population is ethnically Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, with minorities of Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Indians, and indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
. The country's official language is Malaysian Malay
Malaysian Malay ( ms, Bahasa Melayu Malaysia), also known as Standard Malay (Malay: ''Bahasa Melayu Standard''), ( English translation: Malaysian language), or simply Malay, is a standardized form of the Malay language used in Malaysia (as o ...
, a standard form of the Malay language
Malay (; ms, Bahasa Melayu, links=no, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , Rejang script, Rencong: ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, and that is also spo ...
. English remains an active second language. While recognising Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
as the country's established religion
A state religion (also called religious state or official religion) is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion (also known as confessional state), while not secular, is not necessarily a ...
, the constitution grants freedom of religion
Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freedom ...
to non-Muslims. The government is modelled on the Westminster parliamentary system, and the legal system is based on common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...
. The head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
is an elected monarch
An elective monarchy is a monarchy ruled by an elected monarch, in contrast to a hereditary monarchy in which the office is automatically passed down as a family inheritance. The manner of election, the nature of candidate qualifications, and the ...
, chosen from among the nine state sultans every five years. The head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a gro ...
is the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
.
After independence, the Malaysian GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
grew at an average rate of 6.5% per annum for almost 50 years. The economy has traditionally been fuelled by its natural resources but is expanding in the sectors of science, tourism, commerce and medical tourism
Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable a ...
. Malaysia has a newly industrialised market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
, ranked third-largest in Southeast Asia and 36th-largest in the world. It is a founding member of ASEAN
ASEAN ( , ), officially the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, is a political and economic union of 10 member states in Southeast Asia, which promotes intergovernmental cooperation and facilitates economic, political, security, militar ...
, EAS, and OIC and a member of APEC
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC ) is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region.
, the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
, and the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
.
Etymology
 The name "
The name "Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
" is a combination of the word " Malays" and the Latin-Greek suffix " -ia"/" -ία" which can be translated as "land of the Malays". The origin of the word 'Melayu' is subject to various theories. It may derive from the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
"Himalaya", referring to areas high in the mountains, or "Malaiyur-pura", meaning mountain town. Another similar theory claims its origin lies in the Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
words "''malai''" and "''ur''" meaning "mountain" and "city, land", respectively. Another suggestion is that it derives from the Pamalayu
The Pamalayu campaign was a diplomatic and military expeditionary force sent by the Javanese King Kertanegara of Singhasari to conquer the Sumatran Melayu Kingdom. It was decreed in 1275, though perhaps not undertaken until later.
Little is kno ...
campaign. A final suggestion is that it comes from a Javanese word meaning "to run", from which a river, the ''Sungai Melayu'' ('Melayu river'), was named due to its strong current. Similar-sounding variants have also appeared in accounts older than the 11th century, as toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s for areas in Sumatra or referring to a larger region around the Strait of Malacca. The Sanskrit text Vayu Purana
The ''Vayu Purana'' ( sa, वायुपुराण, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas of Hinduism.
''Vayu Purana'' is mentioned in the manuscripts of the Mahabharata and other Hindu texts, which has led scholars to pr ...
, thought to have been in existence since the first millennium CE, mentioned a land named 'Malayadvipa' which was identified by certain scholars as the modern Malay peninsula
The Malay Peninsula (Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area ...
. Other notable accounts are by the 2nd century Ptolemy's Geographia
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, com ...
that used the name ''Malayu Kulon'' for the west coast of Golden Chersonese, and the 7th century Yijing
The ''I Ching'' or ''Yi Jing'' (, ), usually translated ''Book of Changes'' or ''Classic of Changes'', is an ancient Chinese divination text that is among the oldest of the Chinese classics. Originally a divination manual in the Western Zhou ...
's account of ''Malayu''.
At some point, the Melayu Kingdom
The Melayu Kingdom (also known as Malayu, Dharmasraya Kingdom or the Jambi Kingdom; , reconstructed Middle Chinese pronunciation ''mat-la-yu kwok'')Muljana, Slamet , (2006), ''Sriwijaya'', Yogyakarta: LKIS, . was a classical Buddhist kingdom l ...
took its name from the ''Sungai Melayu''. 'Melayu' then became associated with Srivijaya
Srivijaya ( id, Sriwijaya) was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia), which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th t ...
, and remained associated with various parts of Sumatra, especially Palembang, where the founder of the Malacca Sultanate
The Malacca Sultanate ( ms, Kesultanan Melaka; Jawi script: ) was a Malay sultanate based in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Conventional historical thesis marks as the founding year of the sultanate by King of Singapura, Parameswa ...
is thought to have come from. It is only thought to have developed into an ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
as Malacca became a regional power in the 15th century. Islamisation
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occurre ...
established an ethnoreligious identity in Malacca, with the term 'Melayu' beginning to appear as interchangeable with 'Melakans'. It may have specifically referred to local Malays speakers thought loyal to the Malaccan Sultan. The initial Portuguese use of ''Malayos'' reflected this, referring only to the ruling people of Malacca. The prominence of traders from Malacca led 'Melayu' to be associated with Muslim traders, and from there became associated with the wider cultural and linguistic group. Malacca and later Johor
Johor (; ), also spelled as Johore, is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia in the south of the Malay Peninsula. Johor has land borders with the Malaysian states of Pahang to the north and Malacca and Negeri Sembilan ...
claimed they were the centre of Malay culture, a position supported by the British which led to the term 'Malay' becoming more usually linked to the Malay peninsula rather than Sumatra.
Before the onset of European colonisation, the Malay Peninsula was known natively as "'' Tanah Melayu''" ("Malay Land"). Under a racial classification created by a German scholar Johann Friedrich Blumenbach
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (11 May 1752 – 22 January 1840) was a German physician, naturalist, physiologist, and anthropologist. He is considered to be a main founder of zoology and anthropology as comparative, scientific disciplines. He wa ...
, the natives of maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Sout ...
were grouped into a single category, the Malay race
The concept of a Malay race was originally proposed by the Germany, German physician Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (1752–1840), and classified as a brown (racial classification), brown race. ''Malay'' is a loose term used in the late 19th century ...
. Following the expedition of French navigator Jules Dumont d'Urville
Jules Sébastien César Dumont d'Urville (; 23 May 1790 – 8 May 1842) was a French explorer and naval officer who explored the south and western Pacific, Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica. As a botanist and cartographer, he gave his nam ...
to Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
in 1826, he later proposed the terms of "Malaysia", "Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and ...
" and "Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
" to the ''Société de Géographie
The Société de Géographie (; ), is the world's oldest geographical society. It was founded in 1821 as the first Geographic Society. Since 1878, its headquarters have been at 184 Boulevard Saint-Germain, Paris. The entrance is marked by two gig ...
'' in 1831, distinguishing these Pacific cultures and island groups from the existing term "Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
". Dumont d'Urville described Malaysia as "an area commonly known as the East Indies". In 1850, the English ethnologist George Samuel Windsor Earl
George Windsor Earl (1813–1865), was an English navigator and author of works on the Indian Archipelago. He coined the term 'Indu-nesian', later adopted as the name for Indonesia.
Biography
Earl was born in London around 1813. He travelled to ...
, writing in the ''Journal of the Indian Archipelago and Eastern Asia'', proposed naming the islands of Southeast Asia as "Melayunesia" or "Indunesia", favouring the former. The name Malaysia gained some use to label what is now the Malay Archipelago. In modern terminology, "Malay" remains the name of an ethnoreligious group
An ethnoreligious group (or an ethno-religious group) is a grouping of people who are unified by a common religious and ethnic background.
Furthermore, the term ethno-religious group, along with ethno-regional and ethno-linguistic groups, is a s ...
of Austronesian people
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrones ...
predominantly inhabiting the Malay Peninsula and portions of the adjacent islands of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
, including the east coast of Sumatra, the coast of Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
, and smaller islands that lie between these areas.
The state that gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1957 took the name the "Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya ( ms, Persekutuan Tanah Melayu; Jawi script, Jawi: ) was a federation of what previously had been British Malaya comprising eleven states (nine Malay states and two of the British Empire, British Straits Settlements, P ...
", chosen in preference to other potential names such as "Langkasuka
Langkasuka was an ancient Hindu-Buddhist kingdom located in the Malay Peninsula. The name is Sanskrit in origin; it is thought to be a combination of ''langkha'' for "resplendent land" -'' sukkha'' for "bliss". The kingdom, along with Old Ke ...
", after the historic kingdom located at the upper section of the Malay Peninsula in the first millennium CE. The name "Malaysia" was adopted in 1963 when the existing states of the Federation of Malaya, plus Singapore, North Borneo and Sarawak formed a new federation. One theory posits the name was chosen so that "si" represented the inclusion of Singapore, North Borneo, and Sarawak to Malaya in 1963. Politicians in the Philippines contemplated renaming their state "Malaysia" before the modern country took the name.
History
Negritos
The term Negrito () refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese
The Gr ...
. Traders and settlers from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
arrived as early as the first century AD, establishing trading ports and coastal towns in the second and third centuries. Their presence resulted in strong India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
n and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
influences on the local cultures, and the people of the Malay Peninsula adopted the religions of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
. Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
inscriptions appear as early as the fourth or fifth century. The Kingdom of Langkasuka
Langkasuka was an ancient Hindu-Buddhist kingdom located in the Malay Peninsula. The name is Sanskrit in origin; it is thought to be a combination of ''langkha'' for "resplendent land" -'' sukkha'' for "bliss". The kingdom, along with Old Ke ...
arose around the second century in the northern area of the Malay Peninsula, lasting until about the 15th century. Between the 7th and 13th centuries, much of the southern Malay Peninsula was part of the maritime Srivijaya
Srivijaya ( id, Sriwijaya) was a Buddhist thalassocratic empire based on the island of Sumatra (in modern-day Indonesia), which influenced much of Southeast Asia. Srivijaya was an important centre for the expansion of Buddhism from the 7th t ...
n empire. By the 13th and the 14th century, the Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
empire had successfully wrested control over most of the peninsula and the Malay Archipelago from Srivijaya. In the early 15th century, Parameswara, a runaway king of the former Kingdom of Singapura
The Kingdom of Singapura ( Malay: ''Kerajaan Singapura'') was an Indianised Malay Hindu-Buddhist kingdom thought to have been established during the early history of Singapore upon its main island Pulau Ujong, then also known as Temasek, fr ...
linked to the old Srivijayan court, founded the Malacca Sultanate
The Malacca Sultanate ( ms, Kesultanan Melaka; Jawi script: ) was a Malay sultanate based in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Conventional historical thesis marks as the founding year of the sultanate by King of Singapura, Parameswa ...
. The spread of Islam increased following Parameswara's conversion to that religion. Malacca was an important commercial centre during this time, attracting trade from around the region.
In 1511, Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
was conquered by Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, after which it was taken by the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
in 1641. In 1786, the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
established a presence in Malaya, when the Sultan of Kedah leased Penang Island
Penang Island ( ms, Pulau Pinang; zh, 檳榔嶼; ta, பினாங்கு தீவு) is part of the state of Penang, on the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. It was named Prince of Wales Island when it was occupied by the British Ea ...
to the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
. The British obtained the town of Singapore in 1819, and in 1824 took control of Malacca following the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, Anglo-Dutch Treaty. By 1826, the British directly controlled Penang, Malacca, Singapore, and the island of Crown Colony of Labuan, Labuan, which they established as the crown colony of the Straits Settlements
The Straits Settlements were a group of British territories located in Southeast Asia. Headquartered in Singapore for more than a century, it was originally established in 1826 as part of the territories controlled by the British East India Comp ...
. By the 20th century, the states of Pahang, Selangor, Perak, and Negeri Sembilan, known together as the Federated Malay States, had British resident (title), residents appointed to advise the Malay rulers, to whom the rulers were bound to defer by treaty. The remaining five states in the peninsula, known as the Unfederated Malay States, while not directly under British rule, also accepted British advisers around the turn of the 20th century. Development on the peninsula and Borneo were generally separate until the 19th century. Under British rule the immigration of Chinese and Indians to serve as labourers was encouraged. The area that is now Sabah came under British control as North Borneo when both the Sultanate of Brunei, Sultan of Brunei and the Sultanate of Sulu, Sultan of Sulu transferred their respective territorial rights of ownership, between 1877 and 1878. In 1842, Sarawak was ceded by the Sultan of Brunei to James Brooke, whose successors ruled as the White Rajahs over an independent Raj of Sarawak, kingdom until 1946, when it became a Crown Colony of Sarawak, crown colony.
In the Second World War, the Japanese Army Japanese invasion of Malaya, invaded and occupied Japanese occupation of Malaya, Malaya, Japanese occupation of British Borneo, North Borneo, Sarawak, and Japanese occupation of Singapore, Singapore for over three years. During this time, ethnic tensions were raised and nationalism grew. Popular support for independence increased after Malaya was reconquered by Allied forces. Post-war British plans to unite the administration of Malaya under a single crown colony called the "Malayan Union
The Malayan Union was a union of the Malay states and the Straits Settlements of Penang and Malacca. It was the successor to British Malaya and was conceived to unify the Malay Peninsula under a single government to simplify administratio ...
" met with strong opposition from the Malays (ethnic group), Malays, who opposed the weakening of the Malay rulers and the granting of citizenship to the Malaysian Chinese, ethnic Chinese. The Malayan Union, established in 1946, and consisting of all the British possessions in the Malay Peninsula with the exception of Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
, was quickly dissolved and replaced on 1 February 1948 by the Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya ( ms, Persekutuan Tanah Melayu; Jawi script, Jawi: ) was a federation of what previously had been British Malaya comprising eleven states (nine Malay states and two of the British Empire, British Straits Settlements, P ...
, which restored the autonomy of the rulers of the Malay states under British protection.
Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
troops in Malaya. On 31 August 1957, Malaya became an independent member of the Commonwealth of Nations. After this a plan was put in place to federate Malaya with the crown colonies of North Borneo (which joined as Sabah), Sarawak, and Singapore. The date of federation was planned to be 31 August 1963 so as to coincide with the anniversary of Malayan independence; however, federation was delayed until 16 September 1963 in order for a United Nations survey of support for federation in Sabah and Sarawak, called for by parties opposed to federation including Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
's Sukarno and the Sarawak United Peoples' Party, to be completed.
Federation brought heightened tensions including a Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation, conflict with Indonesia as well continuous conflicts against the Communists in Borneo and the Malayan Peninsula which escalates to the Communist insurgency in Sarawak, Sarawak Communist Insurgency and Communist insurgency in Malaysia (1968–89), Second Malayan Emergency together with several other issues such as the Cross border attacks in Sabah, cross border attacks into North Borneo by Piracy in the Sulu Sea, Moro pirates from the southern islands of the Philippines, Singapore Singapore in Malaysia#Expulsion, being expelled from the Federation in 1965, and racial strife. This strife culminated in the 13 May Incident, 13 May race riots in 1969. After the riots, the controversial Malaysian New Economic Policy, New Economic Policy was launched by Prime Minister Tun Abdul Razak, trying to increase the share of the economy held by the ''Bumiputera (Malaysia), bumiputera''. Under Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad there was a period of rapid economic growth and urbanization beginning in the 1980s. The economy shifted from being agriculturally based to one based on manufacturing and industry. Numerous mega-projects were completed, such as the Petronas Towers, the North–South Expressway (Malaysia), North–South Expressway, the MSC Malaysia, Multimedia Super Corridor, and the new federal administrative capital of Putrajaya
Putrajaya (), officially the Federal Territory of Putrajaya ( ms, Wilayah Persekutuan Putrajaya), is a planned capital city which functions as the administrative capital and the judicial capital of Malaysia. The seat of the federal government ...
. However, in the late 1990s, the 1997 Asian Financial Crisis, Asian financial crisis almost caused the collapse of the currency and the stock and property markets, although they later recovered. The 1MDB scandal was a major global Corruption in Malaysia, corruption scandal that implicated then-Prime Minister Najib Razak in 2015. The scandal contributed to the first change in the ruling political party since independence in the 2018 Malaysian general election, 2018 general election. In the 2020s, the country was gripped by 2020–21 Malaysian political crisis, a political crisis that coincided with health and Economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in Malaysia, economic crises caused by the COVID-19 pandemic in Malaysia, COVID-19 pandemic. This was then followed by an earlier 2022 Malaysian general election, general election in November 2022, which resulted in the first hung parliament in the nation's history. Opposition leader Anwar Ibrahim’s Pakatan Harapan (PH) coalition won 82 seats and former Prime Minister Muhyiddin Yassin’s Perikatan Nasional (PN) gained 73 seats. Prime Minister Ismail Sabri Yaakob’s ruling Barisan Nasional (BN) coalition was the biggest loser securing just 30 seats in the 222-member parliament. On 24 November 2022, Anwar Ibrahim was sworn in as the 10th Prime Minister of Malaysia.
Government and politics
 Malaysia is a
Malaysia is a federal
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
constitutional monarchy, constitutional elective monarchy; the only federal country in Southeast Asia. The system of government is closely modelled on the Westminster system, Westminster parliamentary system, a legacy of British Empire, British rule. The head of state is the King, whose official title is the Yang di-Pertuan Agong. The King is elected to a five-year term by and from among the nine hereditary Monarchies of Malaysia, rulers of the Malay states. The other four states, which have titular Yang di-Pertua Negeri, Governors, do not participate in the selection. By informal agreement the position is rotated among the nine, and has been held by Abdullah of Pahang since 31 January 2019. The King's role has been largely ceremonial since changes to the Constitution of Malaysia, constitution in 1993 amendments to the Constitution of Malaysia, 1994, picking ministers and members of the upper house.
Legislative power is divided between federal and state legislatures. The bicameral federal Parliament of Malaysia, parliament consists of the lower house, the House of Representatives of Malaysia, House of Representatives and the upper house, the Senate of Malaysia, Senate. The 222-member House of Representatives is elected for a maximum term of five years from single-member constituencies. All 70 senators sit for three-year terms; 26 are elected by the 13 state assemblies, and the remaining 44 are appointed by the King upon the Prime Minister's recommendation. The parliament follows a multi-party system and the government is elected through a first-past-the-post voting, first-past-the-post system. Parliamentary Elections in Malaysia, elections are held at least once every five years, the most recent of which took place in May 2018. Before 2018, registered voters aged 21 and above could vote for the members of the House of Representatives and, in most of the states, for the state legislative chamber. Voting is not mandatory. In July 2019, a bill to lower the voting age to 18 years old was officially passed.
 Executive branch, Executive power is vested in the
Executive branch, Executive power is vested in the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, led by the Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
. The prime minister must be a member of the House of Representatives, who in the opinion of His Majesty the King, commands the support of a majority of members. The Cabinet is chosen from members of both houses of Parliament. The Prime Minister is both the Cabinet of Malaysia, head of cabinet and the head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a gro ...
. As a result of the 2018 Malaysian general election, 2018 general election Malaysia was governed by the Pakatan Harapan political alliance, although Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad resigned amid a 2020–21 Malaysian political crisis, political crisis in 2020. In March 2020, the Perikatan Nasional coalition formed under Prime Minister Muhyiddin Yassin, before Muhyiddin lost majority support and was replaced by deputy Prime Minister Ismail Sabri Yaakob, a veteran politician from UMNO, in August 2021.As a result of the 2022 Malaysian general election, a hung parliament was elected. Anwar Ibrahim of the PH coalition was appointed as the new Prime Minister to lead the coalition government of PH, BN, Gabungan Parti Sarawak (GPS), Gabungan Rakyat Sabah (GRS) and several other political parties and independents. Meanwhile PN, the only political coalition not in the coalition government became the Opposition. Law of Malaysia, Malaysia's legal system is based on English law, English Common Law. Although Judiciary of Malaysia, the judiciary is theoretically independent, its independence has been called into question and the appointment of judges lacks accountability and transparency. The highest court in the judicial system is the Federal Court of Malaysia, Federal Court, followed by the Court of Appeal of Malaysia, Court of Appeal and two High Courts of Malaysia, high courts, one for Peninsular Malaysia and one for East Malaysia. Malaysia also has a special court to hear cases brought by or against royalty.
Demographics of Malaysia, Race is a significant force in politics. Affirmative action#Malaysia, Affirmative actions such as the Malaysian New Economic Policy, New Economic Policy and the National Development Policy which superseded it, were implemented to advance the standing of the ''bumiputera'', consisting of Malays and the indigenous tribes who are considered the original inhabitants of Malaysia, over non-''bumiputera'' such as Malaysian Chinese and Malaysian Indians. These policies provide preferential treatment to ''bumiputera'' in employment, education, scholarships, business, and access to cheaper housing and assisted savings. However, it has generated greater interethnic resentment. There is ongoing Religion in Malaysia#Secularism, debate over whether the laws and society of Malaysia should reflect Islamism or secularism. Islamic criminal laws passed by the Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party with the support of United Malays National Organisation (UMNO) state assemblymen in the state legislative assembly of Kelantan have been blocked by the federal government on the basis that criminal laws are the responsibility of the federal government.
After the United Malays National Organisation (UMNO) lost power at the 2018 Malaysian general election, Malaysia's ranking increased by 9 places in the 2019 Democracy Index to 43th compared to the previous year, and is classified as a 'flawed democracy'. Malaysia's ranking in the 2020 Press Freedom Index increased by 22 places to 101st compared to the previous year, making it one of two countries in Southeast Asia without a 'Difficult situation' or 'Very Serious situation' with regards to press freedom. However, it fell 18 places the following year due to the policies of the Perikatan Nasional government.
Malaysia is marked at 48 and 62nd place according to the 2021 Corruption Perceptions Index, indicating above average levels of Corruption in Malaysia, corruption. Freedom House noted Malaysia as "partly free" in its 2018 survey. A lawsuit filed by United States Department of Justice, Department of Justice (DOJ), alleged that at least $3.5 billion involving former prime minister Najib Razak had been stolen from Malaysia's 1Malaysia Development Berhad, 1MDB state-owned fund, known as the 1Malaysia Development Berhad scandal.
Administrative divisions
Malaysia is a federation of 13 states and three federal territories. These are divided between two regions, with 11 states and two federal territories onPeninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia ( ms, Semenanjung Malaysia; Jawi: سمننجڠ مليسيا), or the States of Malaya ( ms, Negeri-negeri Tanah Melayu; Jawi: نڬري-نڬري تانه ملايو), also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, ...
and the other two states and one federal territory in East Malaysia
East Malaysia (), or the Borneo States, also known as Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia on and near the island of Borneo, the world's third-largest island. Near the coast of Sabah is a small archipelago called Labuan. East Malaysia li ...
. Each state is divided into Districts of Malaysia, districts, which are then divided into mukim. In Sabah and Sarawak districts are grouped into divisions.
Governance of the states is divided between the federal and the state governments, with different powers reserved for each, and the Federal government has direct administration of the federal territories. Each state has a unicameral State legislative assemblies of Malaysia, State Legislative Assembly whose members are elected from single-member constituencies. State governments are led by Chief Ministers in Malaysia, Chief Ministers, who are state assembly members from the majority party in the assembly. In each of the states with a hereditary ruler, the Chief Minister is normally required to be a Malays (ethnic group), Malay, appointed by the ruler upon the recommendation of the Prime Minister. Except for state elections in Sarawak, by constitutional convention (political custom), convention state elections are held concurrently with the federal election.
Lower-level administration is carried out by local authorities, which include city councils, district councils, and municipal councils, although autonomous statutory bodies can be created by the federal and state governments to deal with certain tasks. The federal constitution puts local authorities outside of the federal territories under the exclusive jurisdictions of the state government, although in practice the federal government has intervened in the affairs of state local governments. There are 154 local authorities, consisting of 14 city councils, 38 municipal councils and 97 district councils.
The 13 states are based on historical Malay kingdoms, and 9 of the 11 Peninsular states, known as the Malay states, retain their royal families. The King is elected by and from Conference of Rulers, the nine rulers to serve a five-year term. This King appoints governors serving a four-year term for the states without monarchies, after consultations with the chief minister of that state. Each state has its own written constitution. Sabah and Sarawak have considerably more autonomy than the other states, most notably having separate immigration policies and controls, and a unique residency status. Federal intervention in state affairs, lack of development, and disputes over oil royalties have occasionally led to statements about secession from leaders in several states such as Penang, Johor, Kelantan, Sabah and Sarawak, although these have not been followed up and no serious independence movements exist.
;States
A list of thirteen states and each state capital (in brackets):
# Johor (Johor Bahru)
# Kedah (Alor Setar)
# Kelantan (Kota Bharu)
# Malacca
Malacca ( ms, Melaka) is a state in Malaysia located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, next to the Strait of Malacca. Its capital is Malacca City, dubbed the Historic City, which has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site si ...
(Malacca City)
# Negeri Sembilan (Seremban)
# Pahang (Kuantan)
# Penang (George Town, Penang, George Town)
# Perak (Ipoh)
# Perlis (Kangar)
# Selangor (Shah Alam)
# Sabah (Kota Kinabalu)
# Sarawak (Kuching)
# Terengganu (Kuala Terengganu)
;Federal territories
# Kuala Lumpur, Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur
# Labuan, Federal Territory of Labuan
# Putrajaya, Federal Territory of Putrajaya
Foreign relations and military
A founding member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), the country participates in many international organisations such as the United Nations, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, the Developing 8 Countries, and theNon-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
(NAM). It has chaired ASEAN, the OIC, and the NAM in the past. A former British colony, it is also a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. Kuala Lumpur was the site of the first East Asia Summit in 2005.
Malaysia's foreign policy is officially based on the principle of neutrality and maintaining peaceful relations with all countries, regardless of their political system. The government attaches a high priority to the security and stability of Southeast Asia, and seeks to further develop relations with other countries in the region. Historically the government has tried to portray Malaysia as a progressive Islamic nation while strengthening relations with other Islamic states. A strong tenet of Malaysia's policy is national sovereignty and the right of a country to control its domestic affairs. Malaysia signed the UN treaty on the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
The Spratly Islands are disputed by many states in the area, and Territorial disputes in the South China Sea, a large portion of the South China Sea is claimed by China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Unlike its neighbours of Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Malaysia historically avoided conflicts with China. However, after the encroachment of Chinese ships in Malaysian territorial waters, and breach of airspace by their military aircraft, Malaysia has become active in condemning China. Brunei and Malaysia in 2009 announced an end to claims of each other's land, and committed to resolve issues related to their maritime borders. The Philippines has a North Borneo dispute, dormant claim to the eastern part of Sabah. Singapore's land reclamation has caused tensions, and minor maritime and land border disputes exist with Indonesia.
The Malaysian Armed Forces have three branches: the Malaysian Army, Royal Malaysian Navy and the Royal Malaysian Air Force. There is no conscription, and the required age for voluntary military service is 18. The military uses 1.5% of the country's GDP, and employs 1.23% of Malaysia's manpower. Malaysian peacekeeping forces have contributed to many UN peacekeeping missions, such as in United Nations Operation in the Congo, Congo, United Nations Iran–Iraq Military Observer Group, Iran–Iraq, United Nations Transition Assistance Group, Namibia, United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia, Cambodia, United Nations Protection Force, Bosnia and Herzegovina, United Nations Operation in Somalia II, Somalia, United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo, Kosovo, United Nations Integrated Mission in East Timor, East Timor and United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, Lebanon.
The Five Power Defence Arrangements is a regional security initiative which has been in place for almost 40 years. It involves joint military exercises held among Malaysia, Singapore, Australia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. Joint exercises and war games have also been held with Brunei, China, India, Indonesia, Japan, and the United States. Malaysia, Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam have agreed to host joint security force exercises to secure their maritime border and tackle issues such as illegal immigration, piracy, and smuggling. Previously there were fears that extremist militants activities in the Muslim areas of the Moro conflict in the Philippines, southern Philippines and South Thailand insurgency, southern Thailand would spill over into Malaysia. Because of this, Malaysia began to increase its border security.
Human rights
Homosexuality is LGBT rights in Malaysia, illegal in Malaysia, and the authorities has imposed punishments such as Caning in Malaysia, caning and imprisonment. Human trafficking and sex trafficking in Malaysia are significant problems. There has also been cases of vigilante executions and beatings against LGBT individuals in Malaysia. The illegality of homosexuality in Malaysia has also been the forefront of Anwar Ibrahim's Anwar Ibrahim sodomy trials, sodomy trials, which Anwar has responded to it being politically motivated, a response supported by the United Nations' (UN) Working Group on Arbitrary Detention along with Amnesty International and the Human Rights Watch. The Capital punishment in Malaysia, death penalty is in use for serious crimes such as murder, terrorism, drug trafficking, and kidnapping, but in June 2022, Malaysian law minister Wan Junaidi pledged to abolish the capital punishment and replace it with other punishments at the discretion of the court.Geography
 Malaysia is the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 66th largest country by total land area, with a land area of . It has land Borders of Malaysia, borders with Thailand in West Malaysia, and
Malaysia is the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 66th largest country by total land area, with a land area of . It has land Borders of Malaysia, borders with Thailand in West Malaysia, and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and Brunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely sur ...
in East Malaysia. It is linked to Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, borde ...
by a narrow causeway and a Malaysia–Singapore Second Link, bridge. The country also has maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and the Philippines. The land borders are defined in large part by geological features such as the Perlis River, the Golok River and the Pagalayan Canal, whilst some of the maritime boundaries are the subject of ongoing contention. Brunei forms what is almost an enclave in Malaysia, with the state of Sarawak dividing it into two parts. Malaysia is the only country with territory on both the Asian mainland and the Malay archipelago. The Strait of Malacca, lying between Sumatra and Peninsular Malaysia, is one of the most important thoroughfares in global commerce, carrying 40 per cent of the world's trade.
The two parts of Malaysia, separated from each other by the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
, share a largely similar landscape in that both Peninsular and East Malaysia feature coastal plains rising to hills and mountains. Peninsular Malaysia, containing 40 per cent of Malaysia's land area, extends from north to south, and its maximum width is . It is divided between its east and west coasts by the Titiwangsa Mountains, rising to a peak elevation of at Mount Korbu, part of a series of mountain ranges running down the centre of the peninsula. These mountains are heavily forested, and mainly composed of granite and other igneous rocks. Much of it has been eroded, creating a karst landscape. The range is the origin of some of Peninsular Malaysia's river systems. The coastal plains surrounding the peninsula reach a maximum width of , and the peninsula's coastline is nearly long, although harbours are only available on the western side.
East Malaysia, on the island of Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
, has a coastline of . It is divided between coastal regions, hills and valleys, and a mountainous interior. The Crocker Range extends northwards from Sarawak, dividing the state of Sabah. It is the location of the high Mount Kinabalu, the tallest mountain in Malaysia. Mount Kinabalu is located in the Kinabalu National Park, which is protected as one of the four UNESCO World Heritage Sites List of World Heritage Sites in Malaysia, in Malaysia. The highest mountain ranges form the border between Malaysia and Indonesia. Sarawak contains the Mulu Caves, the largest cave system in the world, in the Gunung Mulu National Park which is also a World Heritage Site. The largest river in Malaysia is the Rajang River, Rajang.
Around these two halves of Malaysia are List of islands of Malaysia, numerous islands, the largest of which is Banggi Island, Banggi. The local climate is Tropical climate, equatorial and characterised by the annual southwest (April to October) and northeast (October to February) monsoons. The temperature is moderated by the presence of the surrounding oceans. Humidity is usually high, and the average annual rainfall is . The climates of the Peninsula and the East differ, as the climate on the peninsula is directly affected by wind from the mainland, as opposed to the more maritime weather of the East. Local climates can be divided into three regions, highland, lowland, and coastal. Climate change is likely to affect sea levels and rainfall, increasing flood risks and leading to droughts.
Biodiversity and conservation
Malaysia signed the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity on 12 June 1993, and became a party to the convention on 24 June 1994. It has subsequently produced a Biodiversity action plan, National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan, which was received by the convention on 16 April 1998. The country is megadiverse countries, megadiverse with a high number of species and high levels of endemism. It is estimated to contain 20 per cent of the world's animal species. High levels of endemism are found on the diverse forests of Borneo's mountains, as species are isolated from each other by lowland forest. There are about 210 mammal species in the country. Over 620 species of birds have been recorded in Peninsular Malaysia, with many endemic to the mountains there. A high number of endemic bird species are also found in Malaysian Borneo. 250 reptile species have been recorded in the country, with about 150 species of snakes and 80 species of lizards. There are about 150 species of frogs, and thousands of insect species. The Exclusive economic zone of Malaysia is and 1.5 times larger than its land area. It is mainly in theSouth China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Phil ...
. Some of its waters are in the Coral Triangle, a biodiversity hotspot. The waters around Sipadan island are the most biodiverse in the world. Bordering East Malaysia, the Sulu Sea is a biodiversity hotspot, with around 600 coral species and 1200 fish species. The unique biodiversity of Malaysian Caves always attracts lovers of ecotourism from all over the world.
Nearly 4,000 species of fungi, including lichen-forming species have been recorded from Malaysia. Of the two fungal groups with the largest number of species in Malaysia, the Ascomycota and their asexual states have been surveyed in some habitats (decaying wood, marine and freshwater ecosystems, as parasites of some plants, and as agents of biodegradation), but have not been or have been only poorly surveyed in other habitats (as endobionts, in soils, on dung, as human and animal pathogens); the Basidiomycota are only partly surveyed: bracket fungi, and mushrooms and toadstools have been studied, but Malaysian rust and smut fungi remain very poorly known. Without doubt, many more fungal species in Malaysia have not yet been recorded, and it is likely that many of those, when found, will be new to science.
 About two thirds of Malaysia was covered in forest as of 2007, with some forests believed to be 130 million years old. The forests are dominated by Dipterocarpaceae, dipterocarps. Lowland forest covers areas below , and formerly East Malaysia was covered in Borneo lowland rain forests, such rainforest, which is supported by its hot wet climate. There are around 14,500 species of flowering plants and trees. Besides rainforests, there are over of mangroves in Malaysia, and a large amount of peat forest. At higher altitudes, oaks, chestnuts, and rhododendrons replace dipterocarps. There are an estimated 8,500 species of vascular plants in Peninsular Malaysia, with another 15,000 in the East. The forests of East Malaysia are estimated to be the habitat of around 2,000 tree species, and are one of the most biodiverse areas in the world, with 240 different species of trees every hectare. These forests host many members of the Rafflesia genus, the largest flowers in the world, with a maximum diameter of .
Logging, along with cultivation practices has devastated tree cover, causing severe environmental degradation in the country. Over 80 per cent of Sarawak's rainforest has been logged. Floods in East Malaysia have been worsened by the loss of trees, and over 60 per cent of the Peninsula's forest have been cleared. With current rates of Social and environmental impact of palm oil#Deforestation, deforestation, mainly for the Palm oil production in Malaysia, palm oil industry, the forests are predicted to be extinct by 2020. Deforestation in Malaysia, Deforestation is a major problem for animals, fungi and plants, having caused species such as ''Begonia eiromischa'' to go extinct. Most remaining forest is found inside reserves and national parks. Habitat destruction has proved a threat for marine life. Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing, Illegal fishing is another major threat, with fishing methods such as dynamite fishing and poisoning depleting marine ecosystems. Leatherback turtle numbers have dropped 98 per cent since the 1950s. Hunting has also been an issue for some animals, with overconsumption and the use of animal parts for profit endangering many animals, from marine life to tigers. Marine life is also detrimentally affected by uncontrolled tourism.
The Malaysian government aims to balance economic growth with environmental protection, but has been accused of favouring big business over the environment. Some state governments are now trying to counter the environmental impact and pollution created by deforestation; and the federal government is trying to cut logging by 10 per cent each year. A total of List of national parks of Malaysia, 28 national parks have been established, 23 in East Malaysia and five in the Peninsula. Tourism has been limited in biodiverse areas such as Sipadan island. Wildlife smuggling, Wildlife trafficking is a large issue, and the Malaysian government has held talks with the governments of Brunei and Indonesia to standardise anti-trafficking laws.
About two thirds of Malaysia was covered in forest as of 2007, with some forests believed to be 130 million years old. The forests are dominated by Dipterocarpaceae, dipterocarps. Lowland forest covers areas below , and formerly East Malaysia was covered in Borneo lowland rain forests, such rainforest, which is supported by its hot wet climate. There are around 14,500 species of flowering plants and trees. Besides rainforests, there are over of mangroves in Malaysia, and a large amount of peat forest. At higher altitudes, oaks, chestnuts, and rhododendrons replace dipterocarps. There are an estimated 8,500 species of vascular plants in Peninsular Malaysia, with another 15,000 in the East. The forests of East Malaysia are estimated to be the habitat of around 2,000 tree species, and are one of the most biodiverse areas in the world, with 240 different species of trees every hectare. These forests host many members of the Rafflesia genus, the largest flowers in the world, with a maximum diameter of .
Logging, along with cultivation practices has devastated tree cover, causing severe environmental degradation in the country. Over 80 per cent of Sarawak's rainforest has been logged. Floods in East Malaysia have been worsened by the loss of trees, and over 60 per cent of the Peninsula's forest have been cleared. With current rates of Social and environmental impact of palm oil#Deforestation, deforestation, mainly for the Palm oil production in Malaysia, palm oil industry, the forests are predicted to be extinct by 2020. Deforestation in Malaysia, Deforestation is a major problem for animals, fungi and plants, having caused species such as ''Begonia eiromischa'' to go extinct. Most remaining forest is found inside reserves and national parks. Habitat destruction has proved a threat for marine life. Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing, Illegal fishing is another major threat, with fishing methods such as dynamite fishing and poisoning depleting marine ecosystems. Leatherback turtle numbers have dropped 98 per cent since the 1950s. Hunting has also been an issue for some animals, with overconsumption and the use of animal parts for profit endangering many animals, from marine life to tigers. Marine life is also detrimentally affected by uncontrolled tourism.
The Malaysian government aims to balance economic growth with environmental protection, but has been accused of favouring big business over the environment. Some state governments are now trying to counter the environmental impact and pollution created by deforestation; and the federal government is trying to cut logging by 10 per cent each year. A total of List of national parks of Malaysia, 28 national parks have been established, 23 in East Malaysia and five in the Peninsula. Tourism has been limited in biodiverse areas such as Sipadan island. Wildlife smuggling, Wildlife trafficking is a large issue, and the Malaysian government has held talks with the governments of Brunei and Indonesia to standardise anti-trafficking laws.
Economy
market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
. It has the world's List of countries by GDP (nominal), 36th-largest economy by nominal GDP and the List of countries by GDP (PPP), 31st-largest by purchasing power parity, PPP. In 2017, the large Tertiary sector of the economy, service sector contributed to 53.6% of total GDP, the industrial sector 37.6%, and the small agricultural sector roughly 8.8%. Malaysia has a low official List of countries by unemployment rate, unemployment rate of 3.9%. Its foreign exchange reserves are the world's List of countries by foreign-exchange reserves, 24th-largest. It has a labour force of about 15 million, which is the world's List of countries by labour force, 34th-largest. Malaysia's large Automotive industry in Malaysia, automotive industry ranks as the world's List of countries by motor vehicle production, 22nd-largest by production.
Malaysia is the world's 23th-largest List of countries by exports, exporter and 25th-largest List of countries by imports, importer. However, economic inequalities exist between different ethnic groups. The Chinese make up about one-quarter of the population, but accounts for 70 per cent of the country's market capitalisation. Chinese businesses in Malaysia are part of the larger bamboo network, a network of overseas Chinese businesses in the Southeast Asian market sharing common family and cultural ties.
International trade, facilitated by the shipping route in adjacent Strait of Malacca, and manufacturing are the key sectors. Malaysia is an exporter of natural and agricultural resources, and petroleum is a major export. Malaysia has once been the largest producer of tin, rubber and palm oil in the world. Manufacturing has a large influence in the country's economy, although Malaysia's economic structure has been moving away from it. Malaysia remains one of the world's largest producers of palm oil.
Tourism in Malaysia, Tourism is the third-largest contributor to Malaysia's GDP, after the manufacturing and commodities sectors. In 2019, the sector contributed about 15.9 per cent to the total GDP. According to the World Tourism Organization, Malaysia was the fourteenth-most visited country in the world, and the fourth-most visited country in Asia in 2019, with over 26.1 million visits. Malaysia was ranked 38th in the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019. Its international tourism receipts in 2019 amounted to $19.8 billion.
The country has developed into a centre of Islamic banking, and has the highest numbers of female workers in that industry. Knowledge-based services are also expanding. In 2020, Malaysian exported high-tech products worth $92.1 billion, the second-highest in the ASEAN, after Singapore. Malaysia was ranked 36th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, and 32nd in the Global Competitiveness Report in 2022.
Infrastructure
Rail transport in Malaysia, Railway transport in Malaysia is state-run, and spans some . , Malaysia has the world's List of countries by road network size, 26th-largest road network, with some of roads. Malaysia's inland waterways are the world's List of countries by waterways length, 22nd-longest, and total . Among List of airports in Malaysia, Malaysia's 114 airports, among which the List of the busiest airports in Malaysia, busiest is Kuala Lumpur International Airport in Kuala Lumpur, which is also the List of the busiest airports in Asia, twelfth-busiest airport in Asia. Among the 7 federal ports, the major one is Port Klang, which is the List of busiest container ports, thirteenth-busiest container port. Malaysia's flag carrier is Malaysia Airlines, providing international and domestic air services. Malaysia's telecommunications network is second only to Singapore's in Southeast Asia, with 4.7 million fixed-line subscribers and more than 30 million cellular subscribers. There are 200 industrial parks along with specialised parks such as Technology Park Malaysia and Kulim Hi-Tech Park. Fresh water is available to over 95% of the population, with ground water accounting for 90% of the freshwater resources. Although rural areas have been the focus of great development, they still lag behind areas such as the West Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. The telecommunication network, although strong in urban areas, is less available to the rural population. Energy policy of Malaysia, Malaysia's energy infrastructure sector is largely dominated by Tenaga Nasional, the largest electric utility company in Southeast Asia. Customers are connected to electricity through the National Grid (Malaysia), National Grid. The other two electric utility companies in the country are Sarawak Energy and Sabah Electricity. In 2013, Malaysia's total power generation capacity was over 29,728 megawatts. Total electricity generation was 140,985.01 GWh and total electricity consumption was 116,087.51 GWh. List of power stations in Malaysia, Energy production in Malaysia is largely based on oil and natural gas, owing to Malaysia's oil reserves and natural gas reserves, which is the fourth largest in Asia-Pacific region.Demographics
 According to the Malaysian Department of Statistics, the country's population was 32,447,385 in 2020, making it the List of countries by population in 2010, 42nd most populated country. According to a 2012 estimate, the population is increasing by 1.54 percent per year. Malaysia has an average population density of 96 people per km2, ranking it List of countries and territories by population density, 116th in the world for population density. People within the 15–64 age group constitute 69.5 percent of the total population; the 0–14 age group corresponds to 24.5 percent; while senior citizens aged 65 years or older make up 6.0 percent. In 1960, when the first official census was recorded in Malaysia, the population was 8.11 million. 91.8 per cent of the population are Malaysian citizens.
Malaysian citizens are divided along local ethnic lines, with 69.7 per cent considered ''Bumiputera (Malaysia), bumiputera''. The largest group of bumiputera are Malays (ethnic group), Malays, who are defined in the constitution as Muslims who practise Malay customs and culture. They play a dominant role politically. Bumiputera status is also accorded to the non-Malay indigenous groups of Sabah and Sarawak: which includes Dayak people, Dayaks (Iban people, Iban, Bidayuh, Orang Ulu), Kadazan-Dusun, Melanau people, Melanau, Sama-Bajau, Bajau and others. Non-Malay bumiputeras make up more than half of Sarawak's population and over two thirds of Sabah's population. There are also indigenous or aboriginal groups in much smaller numbers on the peninsular, where they are collectively known as the Orang Asli. Laws over who gets bumiputera status vary between states.
There are also two other non-Bumiputera local ethnic groups. 22.5 per cent of the population are Malaysian Chinese, while 6.8 per cent are Malaysian Indians, Malaysian Indian. The local Chinese have historically been more dominant in the business community. Local Indians are mostly of Tamil people, Tamil descent. Malaysian citizenship is not automatically granted to those born in Malaysia, but is granted to a child born of two Malaysian parents outside Malaysia. Dual citizenship is not permitted. Citizenship in the states of Sabah and Sarawak in Malaysian Borneo are distinct from citizenship in Peninsular Malaysia for immigration purposes. Every citizen is issued a biometric smart chip identity document, identity card known as ''MyKad'' at the age of 12, and must carry the card at all times.
The population is concentrated on Peninsular Malaysia, where 20 million out of approximately 28 million Malaysians live. 70 per cent of the population is urban. Due to the rise in labour-intensive industries, the country is estimated to have over 3 million migrant workers; about 10 per cent of the population. Sabah-based NGOs estimate that out of the 3 million that make up the population of Sabah, 2 million are illegal immigrants. Malaysia hosts a population of refugees and asylum seekers numbering approximately 171,500. Of this population, approximately 79,000 are from Burma, 72,400 from the Philippines, and 17,700 from Indonesia. Malaysian officials are reported to have turned deportees directly over to human smugglers in 2007, and Malaysia employs RELA Corps, RELA, a volunteer militia with a history of controversies, to enforce its immigration law.
According to the Malaysian Department of Statistics, the country's population was 32,447,385 in 2020, making it the List of countries by population in 2010, 42nd most populated country. According to a 2012 estimate, the population is increasing by 1.54 percent per year. Malaysia has an average population density of 96 people per km2, ranking it List of countries and territories by population density, 116th in the world for population density. People within the 15–64 age group constitute 69.5 percent of the total population; the 0–14 age group corresponds to 24.5 percent; while senior citizens aged 65 years or older make up 6.0 percent. In 1960, when the first official census was recorded in Malaysia, the population was 8.11 million. 91.8 per cent of the population are Malaysian citizens.
Malaysian citizens are divided along local ethnic lines, with 69.7 per cent considered ''Bumiputera (Malaysia), bumiputera''. The largest group of bumiputera are Malays (ethnic group), Malays, who are defined in the constitution as Muslims who practise Malay customs and culture. They play a dominant role politically. Bumiputera status is also accorded to the non-Malay indigenous groups of Sabah and Sarawak: which includes Dayak people, Dayaks (Iban people, Iban, Bidayuh, Orang Ulu), Kadazan-Dusun, Melanau people, Melanau, Sama-Bajau, Bajau and others. Non-Malay bumiputeras make up more than half of Sarawak's population and over two thirds of Sabah's population. There are also indigenous or aboriginal groups in much smaller numbers on the peninsular, where they are collectively known as the Orang Asli. Laws over who gets bumiputera status vary between states.
There are also two other non-Bumiputera local ethnic groups. 22.5 per cent of the population are Malaysian Chinese, while 6.8 per cent are Malaysian Indians, Malaysian Indian. The local Chinese have historically been more dominant in the business community. Local Indians are mostly of Tamil people, Tamil descent. Malaysian citizenship is not automatically granted to those born in Malaysia, but is granted to a child born of two Malaysian parents outside Malaysia. Dual citizenship is not permitted. Citizenship in the states of Sabah and Sarawak in Malaysian Borneo are distinct from citizenship in Peninsular Malaysia for immigration purposes. Every citizen is issued a biometric smart chip identity document, identity card known as ''MyKad'' at the age of 12, and must carry the card at all times.
The population is concentrated on Peninsular Malaysia, where 20 million out of approximately 28 million Malaysians live. 70 per cent of the population is urban. Due to the rise in labour-intensive industries, the country is estimated to have over 3 million migrant workers; about 10 per cent of the population. Sabah-based NGOs estimate that out of the 3 million that make up the population of Sabah, 2 million are illegal immigrants. Malaysia hosts a population of refugees and asylum seekers numbering approximately 171,500. Of this population, approximately 79,000 are from Burma, 72,400 from the Philippines, and 17,700 from Indonesia. Malaysian officials are reported to have turned deportees directly over to human smugglers in 2007, and Malaysia employs RELA Corps, RELA, a volunteer militia with a history of controversies, to enforce its immigration law.
Religion
 The constitution grants freedom of religion and makes Malaysia an officially secular state, while establishing Islam as the "religion of the Federation". According to the Population and Housing Census 2020 figures, ethnicity and religious beliefs correlate highly. Approximately 63.5% of the population practise Islam in Malaysia, Islam, 18.7% practise Buddhism in Malaysia, Buddhism, 9.1% Christianity in Malaysia, Christianity, 6.1% Hinduism in Malaysia, Hinduism and 1.3% practise Confucianism, Taoism and other traditional Chinese folk religion, Chinese religions. 2.7% declared no religion or practised other religions or did not provide any information. The states of Sarawak, Penang and the federal territory of
The constitution grants freedom of religion and makes Malaysia an officially secular state, while establishing Islam as the "religion of the Federation". According to the Population and Housing Census 2020 figures, ethnicity and religious beliefs correlate highly. Approximately 63.5% of the population practise Islam in Malaysia, Islam, 18.7% practise Buddhism in Malaysia, Buddhism, 9.1% Christianity in Malaysia, Christianity, 6.1% Hinduism in Malaysia, Hinduism and 1.3% practise Confucianism, Taoism and other traditional Chinese folk religion, Chinese religions. 2.7% declared no religion or practised other religions or did not provide any information. The states of Sarawak, Penang and the federal territory of Kuala Lumpur
, anthem = '' Maju dan Sejahtera''
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Malaysia#Southeast Asia#Asia
, pushpin_map_caption =
, coordinates =
, su ...
have non-Muslim majorities.
Sunni Islam of Shafi'i school of jurisprudence is the dominant branch of Islam in Malaysia, while 18% are nondenominational Muslims. The Malaysian constitution strictly defines what makes a "Malay", considering Malays those who are Muslim, speak Malay regularly, practise Malay customs, and lived in or have ancestors from Brunei, Malaysia and Singapore. Statistics from the 2010 Census indicate that 83.6% of the Chinese population identify as Buddhist, with significant numbers of adherents following Taoism (3.4%) and Christianity (11.1%), along with small Muslim populations in areas like Penang. The majority of the Indian population follow Hinduism (86.2%), with a significant minority identifying as Christians (6.0%) or Muslims (4.1%). Christianity is the predominant religion of the non-Malay ''bumiputera'' community (46.5%) with an additional 40.4% identifying as Muslims.
Muslims are obliged to follow the decisions of Syariah Courts (i.e. Shariah courts) in matters concerning their religion. The Islamic judges are expected to follow the Shafi'i legal school of Islam, which is the main ''madh'hab'' of Malaysia. The jurisdiction of Syariah courts is limited to Muslims in matters such as marriage, inheritance, divorce, apostasy, religious conversion, and custody among others. No other criminal or civil offences are under the jurisdiction of the Syariah courts, which have a similar hierarchy to the Courts of Malaysia, Civil Courts. The Civil Courts do not hear matters related to Islamic practices.
Languages
 The official and national language of Malaysia is
The official and national language of Malaysia is Malaysian Malay
Malaysian Malay ( ms, Bahasa Melayu Malaysia), also known as Standard Malay (Malay: ''Bahasa Melayu Standard''), ( English translation: Malaysian language), or simply Malay, is a standardized form of the Malay language used in Malaysia (as o ...
, a standardised form of the Malay language
Malay (; ms, Bahasa Melayu, links=no, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , Rejang script, Rencong: ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, and that is also spo ...
. The terminology as per government policy is ("Malaysian language") but legislation continues to refer to the official language as () and both terms remain in use. The National Language Act 1967 specifies the Malay alphabet, Latin (Rumi) script as the official writing system, script of the national language, but does not prohibit the use of the traditional Jawi alphabet, Jawi script.
English remains an active second language, with its use allowed for some official purposes under the National Language Act of 1967. In Sarawak, English is an official state language alongside Malaysian. Historically, English was the de facto administrative language; Malay became predominant after the 1969 race riots (13 May incident). Malaysian English, also known as Malaysian Standard English, is a form of English derived from British English. Malaysian English is widely used in business, along with Manglish, which is a colloquial form of English with heavy Malay, Chinese, and Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
influences. The government discourages the use of non-standard Malay but has no power to issue compounds or fines to those who use what is perceived as improper Malay on their advertisements.
Many other languages are used in Malaysia, which contains speakers of 137 living languages. Peninsular Malaysia contains speakers of 41 of these languages. The native tribes of East Malaysia have their own languages which are related to, but easily distinguishable from, Malay. Iban language, Iban is the main tribal language in Sarawak while Dusunic languages, Dusunic and Coastal Kadazan language, Kadazan languages are spoken by the natives in Sabah. Chinese Malaysians predominantly speak Chinese dialects from the South China, southern part of China. The more common varieties of Chinese, Chinese varieties in the country are Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin, Cantonese, Hokkien, and so on. The Tamil language is used predominantly by the majority of Malaysian Indians. A small number of Malaysians have Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry and speak creole languages, such as the Portuguese-based Portuguese-based creole languages#Southeast Asia, Malaccan Creoles, and the Spanish-based Chavacano language.
Health
Malaysia operates an efficient and widespread two-tier healthcare system, consisting of a universal healthcare system and a co-existing private healthcare system; provided by highly subsidized healthcare through its extensive network of public hospitals and clinics. The Ministry of Health (Malaysia), Ministry of Health (MOH) is the main provider of healthcare services to the country's population. Malaysia's healthcare system is considered to be among the most developed in Asia, which contributes to its thriving Medical tourism in Malaysia, medical tourism industry. Malaysia spent 3.83% of its GDP on healthcare in 2019. In 2020, the overall life expectancy in Malaysia at birth was 76 years (74 years for males and 78 years for females), and it had an infant mortality rate of 7 deaths per 1000 births. Malaysia had a total fertility rate of 2.0 in 2020, which is just below the Sub-replacement fertility, replacement level of 2.1. In 2020, the country's crude birth rate was 16 per 1000 people, and the crude Mortality rate, death rate was 5 per 1000 people. In 2021, the principal cause of death among Malaysian adults was coronary artery disease, representing 17% of the medically certified deaths in 2020—being followed by pneumonia; which accounted for 11% of the deaths. Transport accidents are considered a major health hazard, as Malaysia, relative to its population, has one of the List of countries by traffic-related death rate, highest traffic fatality rates in the world. Smoking in Malaysia, Smoking is also considered a major health issue across the country.Education
 The education system of Malaysia features a non-compulsory kindergarten education followed by six years of compulsory primary education, and five years of optional secondary education. Schools in the primary education system are divided into two categories: national primary schools, which teach in Malay, and vernacular schools, which teach in Chinese or Tamil. Secondary education is conducted for five years. In the final year of secondary education, students sit for the Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia, Malaysian Certificate of Education examination. Since the introduction of the Malaysian Matriculation Programme, matriculation programme in 1999, students who completed the 12-month programme in matriculation colleges can enroll in local universities. However, in the matriculation system, only 10 per cent of places are open to non-''bumiputera'' students.
The education system of Malaysia features a non-compulsory kindergarten education followed by six years of compulsory primary education, and five years of optional secondary education. Schools in the primary education system are divided into two categories: national primary schools, which teach in Malay, and vernacular schools, which teach in Chinese or Tamil. Secondary education is conducted for five years. In the final year of secondary education, students sit for the Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia, Malaysian Certificate of Education examination. Since the introduction of the Malaysian Matriculation Programme, matriculation programme in 1999, students who completed the 12-month programme in matriculation colleges can enroll in local universities. However, in the matriculation system, only 10 per cent of places are open to non-''bumiputera'' students.
Culture
 Malaysia has a multi-ethnic, multicultural, and multilingual society. The original culture of the area stemmed from indigenous tribes that inhabited it, along with the Malay people, Malays who later moved there. Substantial influence exists from Chinese culture, Chinese and Indian Culture, Indian culture, dating back to when foreign trade began. Other cultural influences include the Persian culture, Persian, Arabic culture, Arabic, and British culture, British cultures. Due to the structure of the government, coupled with the social contract (Malaysia), social contract theory, there has been minimal cultural assimilation of ethnic minorities. Some cultural disputes exist between Malaysia and neighbouring countries, notably
Malaysia has a multi-ethnic, multicultural, and multilingual society. The original culture of the area stemmed from indigenous tribes that inhabited it, along with the Malay people, Malays who later moved there. Substantial influence exists from Chinese culture, Chinese and Indian Culture, Indian culture, dating back to when foreign trade began. Other cultural influences include the Persian culture, Persian, Arabic culture, Arabic, and British culture, British cultures. Due to the structure of the government, coupled with the social contract (Malaysia), social contract theory, there has been minimal cultural assimilation of ethnic minorities. Some cultural disputes exist between Malaysia and neighbouring countries, notably Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
.
In 1971, the government created a "National Cultural Policy", defining Malaysian culture. It stated that Malaysian culture must be based on the culture of the indigenous peoples of Malaysia, that it may incorporate suitable elements from other cultures, and that Islam must play a part in it. It also promoted the Malay language above others. This government intervention into culture has caused resentment among non-Malays who feel their cultural freedom was lessened. Both Chinese and Indian associations have submitted memorandums to the government, accusing it of formulating an undemocratic culture policy.
Fine arts
 Traditional Malaysian art was mainly centred on the areas of carving, weaving, and silversmithing. Traditional art ranges from handwoven baskets from rural areas to the silverwork of the Malay courts. Common artworks included ornamental kris, beetle nut sets, and woven batik and songket fabrics. Indigenous East Malaysians are known for their wooden masks. Each ethnic group have distinct performing arts, with little overlap between them. However, Malay art does show some North Indian influence due to the historical influence of India.
Traditional Malay music and performing arts appear to have originated in the Kelantan-Pattani region with influences from India, China, Thailand, and Indonesia. The music is based around percussion instruments, the most important of which is the gendang (drum). There are at least 14 types of traditional drums. Drums and other traditional percussion instruments and are often made from natural materials. Music is traditionally used for storytelling, celebrating life-cycle events, and occasions such as a harvest. It was once used as a form of long-distance communication. In East Malaysia, gong-based musical ensembles such as agung and kulintang are commonly used in ceremonies such as funerals and weddings. These ensembles are also common in neighbouring regions such as in Mindanao in the Philippines, Kalimantan in Indonesia, and Brunei.
Malaysia has a strong oral tradition that has existed since before the arrival of writing, and continues today. Each of the Malay Sultanates created their own literary tradition, influenced by pre-existing oral stories and by the stories that came with Islam. The first Malay literature was in the Arabic script. The earliest known Malay writing is on the Terengganu Inscription Stone, Terengganu stone, made in 1303. Chinese and Indian literature became common as the numbers of speakers increased in Malaysia, and locally produced works based in languages from those areas began to be produced in the 19th century. English has also become a common literary language. In 1971, the government took the step of defining the literature of different languages. Literature written in Malay was called "the national literature of Malaysia", literature in other ''bumiputera'' languages was called "regional literature", while literature in other languages was called "sectional literature". Malay poetry is highly developed, and uses many forms. The ''Hikayat'' form is popular, and the ''pantun'' has spread from Malay to other languages.
Traditional Malaysian art was mainly centred on the areas of carving, weaving, and silversmithing. Traditional art ranges from handwoven baskets from rural areas to the silverwork of the Malay courts. Common artworks included ornamental kris, beetle nut sets, and woven batik and songket fabrics. Indigenous East Malaysians are known for their wooden masks. Each ethnic group have distinct performing arts, with little overlap between them. However, Malay art does show some North Indian influence due to the historical influence of India.
Traditional Malay music and performing arts appear to have originated in the Kelantan-Pattani region with influences from India, China, Thailand, and Indonesia. The music is based around percussion instruments, the most important of which is the gendang (drum). There are at least 14 types of traditional drums. Drums and other traditional percussion instruments and are often made from natural materials. Music is traditionally used for storytelling, celebrating life-cycle events, and occasions such as a harvest. It was once used as a form of long-distance communication. In East Malaysia, gong-based musical ensembles such as agung and kulintang are commonly used in ceremonies such as funerals and weddings. These ensembles are also common in neighbouring regions such as in Mindanao in the Philippines, Kalimantan in Indonesia, and Brunei.
Malaysia has a strong oral tradition that has existed since before the arrival of writing, and continues today. Each of the Malay Sultanates created their own literary tradition, influenced by pre-existing oral stories and by the stories that came with Islam. The first Malay literature was in the Arabic script. The earliest known Malay writing is on the Terengganu Inscription Stone, Terengganu stone, made in 1303. Chinese and Indian literature became common as the numbers of speakers increased in Malaysia, and locally produced works based in languages from those areas began to be produced in the 19th century. English has also become a common literary language. In 1971, the government took the step of defining the literature of different languages. Literature written in Malay was called "the national literature of Malaysia", literature in other ''bumiputera'' languages was called "regional literature", while literature in other languages was called "sectional literature". Malay poetry is highly developed, and uses many forms. The ''Hikayat'' form is popular, and the ''pantun'' has spread from Malay to other languages.
Cuisine
Malaysia's cuisine reflects the multi-ethnic makeup of its population. Many cultures from within the country and from surrounding regions have greatly influenced the cuisine. Much of the influence comes from the Malay, Chinese, Indian, Thai, Javanese, and Sumatran cultures, largely due to the country being part of the ancient spice route. The cuisine is very similar to that of Singapore and Brunei, and also bears resemblance to Filipino cuisine. The different states have varied dishes, and often the food in Malaysia is different from the original dishes. Sometimes food not found in its original culture is assimilated into another; for example, Chinese restaurants in Malaysia often serve Malay dishes. Food from one culture is sometimes also cooked using styles taken from another culture, For example, ''sambal belacan'' (shrimp paste) are commonly used as ingredients by Chinese restaurants to create the stir fried water spinach (''kangkung belacan''). This means that although much of Malaysian food can be traced back to a certain culture, they have their own identity. Rice is a staple food, and an important constituent of the country's culture. Chili is commonly found in local cuisine, although this does not necessarily make them spicy.Media
 Malaysia's main newspapers are owned by the government and political parties in the ruling coalition, although some major opposition parties also have their own, which are openly sold alongside regular newspapers. A divide exists between the media in the two halves of the country. Peninsular-based media gives low priority to news from the East, and often treats the eastern states as colonies of the Peninsula. As a result of this, East Malaysia region of Sarawak launched TVS (TV channel), TV Sarawak as internet streaming beginning in 2014, and as TV station on 10 October 2020 to overcome the low priority and coverage of Peninsular-based media and to solidify the representation of East Malaysia. The media have been blamed for increasing tension between Indonesia and Malaysia, and giving Malaysians a bad image of Indonesians. The country has Malay, English, Chinese, and Tamil dailies. Kadazandusun and Bajau news only available via TV broadcast Berita RTM. Written Kadazan news was once included in publications such as The Borneo Post, the Borneo Mail, the Daily Express (Malaysia), Daily Express, and the New Sabah Times, but publication has ceased with the newspaper or as a section.
Freedom of the press is limited, with numerous restrictions on publishing rights and information dissemination. The government has previously tried to crack down on opposition papers before elections. In 2007, a government agency issued a directive to all private television and radio stations to refrain from broadcasting speeches made by opposition leaders, a move condemned by politicians from the opposition Democratic Action Party (Malaysia), Democratic Action Party. Sabah, where all tabloids but one are independent of government control, has the freest press in Malaysia. Laws such as the Printing Presses and Publications Act have also been cited as curtailing freedom of expression.
Malaysia's main newspapers are owned by the government and political parties in the ruling coalition, although some major opposition parties also have their own, which are openly sold alongside regular newspapers. A divide exists between the media in the two halves of the country. Peninsular-based media gives low priority to news from the East, and often treats the eastern states as colonies of the Peninsula. As a result of this, East Malaysia region of Sarawak launched TVS (TV channel), TV Sarawak as internet streaming beginning in 2014, and as TV station on 10 October 2020 to overcome the low priority and coverage of Peninsular-based media and to solidify the representation of East Malaysia. The media have been blamed for increasing tension between Indonesia and Malaysia, and giving Malaysians a bad image of Indonesians. The country has Malay, English, Chinese, and Tamil dailies. Kadazandusun and Bajau news only available via TV broadcast Berita RTM. Written Kadazan news was once included in publications such as The Borneo Post, the Borneo Mail, the Daily Express (Malaysia), Daily Express, and the New Sabah Times, but publication has ceased with the newspaper or as a section.
Freedom of the press is limited, with numerous restrictions on publishing rights and information dissemination. The government has previously tried to crack down on opposition papers before elections. In 2007, a government agency issued a directive to all private television and radio stations to refrain from broadcasting speeches made by opposition leaders, a move condemned by politicians from the opposition Democratic Action Party (Malaysia), Democratic Action Party. Sabah, where all tabloids but one are independent of government control, has the freest press in Malaysia. Laws such as the Printing Presses and Publications Act have also been cited as curtailing freedom of expression.
Holidays and festivals
Sports
 Popular sports in Malaysia include association football, badminton, field hockey, bowls, tennis, squash (sport), squash, martial arts, horse riding, sailing, and skate boarding. Football is the most popular sport in Malaysia. Badminton matches also attract thousands of spectators, and since 1948 Malaysia has been one of four countries to hold the Thomas Cup, the world team championship trophy of men's badminton. The Malaysian Lawn Bowls Federation was registered in 1997. Squash was brought to the country by members of the British army, with the first competition being held in 1939. The Squash Racquets Association Of Malaysia was created on 25 June 1972. The men's Malaysia men's national field hockey team, national field hockey team ranked FIH World Rankings, 10th in the world . The 3rd Hockey World Cup was hosted at Merdeka Stadium in Kuala Lumpur, as well as the 10th cup. The country also has its own Formula One track – the Sepang International Circuit, with the first Malaysian Grand Prix held in 1999. Traditional sports include Silat Melayu, the most common style of martial arts practised by ethnic Malays.
The Federation of Malaya Olympic Council was formed in 1953, and received recognition by the IOC in 1954. It first participated in the 1956 Summer Olympics, 1956 Melbourne Olympic Games. The council was renamed the Olympic Council of Malaysia in 1964, and Malaysia at the Olympics, has participated in all but one Olympic games since its inception. The largest number of athletes ever sent to the Olympics was 57 to the 1972 Munich Olympic Games. Besides the Olympic Games, Malaysia also participates in the Paralympic Games. Malaysia has competed at the Commonwealth Games since 1950 as Malaya, and 1966 as Malaysia, and the games were hosted in Kuala Lumpur in 1998.
Popular sports in Malaysia include association football, badminton, field hockey, bowls, tennis, squash (sport), squash, martial arts, horse riding, sailing, and skate boarding. Football is the most popular sport in Malaysia. Badminton matches also attract thousands of spectators, and since 1948 Malaysia has been one of four countries to hold the Thomas Cup, the world team championship trophy of men's badminton. The Malaysian Lawn Bowls Federation was registered in 1997. Squash was brought to the country by members of the British army, with the first competition being held in 1939. The Squash Racquets Association Of Malaysia was created on 25 June 1972. The men's Malaysia men's national field hockey team, national field hockey team ranked FIH World Rankings, 10th in the world . The 3rd Hockey World Cup was hosted at Merdeka Stadium in Kuala Lumpur, as well as the 10th cup. The country also has its own Formula One track – the Sepang International Circuit, with the first Malaysian Grand Prix held in 1999. Traditional sports include Silat Melayu, the most common style of martial arts practised by ethnic Malays.
The Federation of Malaya Olympic Council was formed in 1953, and received recognition by the IOC in 1954. It first participated in the 1956 Summer Olympics, 1956 Melbourne Olympic Games. The council was renamed the Olympic Council of Malaysia in 1964, and Malaysia at the Olympics, has participated in all but one Olympic games since its inception. The largest number of athletes ever sent to the Olympics was 57 to the 1972 Munich Olympic Games. Besides the Olympic Games, Malaysia also participates in the Paralympic Games. Malaysia has competed at the Commonwealth Games since 1950 as Malaya, and 1966 as Malaysia, and the games were hosted in Kuala Lumpur in 1998.
See also
* List of Malaysia-related topics * Outline of Malaysia * List of countries with multiple capitalsNotes
References
External links
* * * *Malaysia
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Malaysia
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Malaysia profile
from the BBC News * {{Coord, 2, N, 112, E, type:country_region:MY, display=title Malaysia, Commonwealth monarchies Developing 8 Countries member states Federal monarchies G15 nations Malay-speaking countries and territories Member states of ASEAN Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Southeast Asian countries States and territories established in 1963 World War II sites 1963 establishments in Malaysia Countries in Asia