Madagascar National Road 42 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: RГ©publique de Madagascar), is an
 Traditionally, archaeologists have estimated that the earliest settlers arrived in successive waves in
Traditionally, archaeologists have estimated that the earliest settlers arrived in successive waves in
 Madagascar was an important transoceanic trading hub connecting ports of the Indian Ocean in the early centuries following human settlement.
The
Madagascar was an important transoceanic trading hub connecting ports of the Indian Ocean in the early centuries following human settlement.
The
 Contacts continued from the 1550s. Several colonization and conversion missions were ordered by King
Contacts continued from the 1550s. Several colonization and conversion missions were ordered by King
 Upon its emergence in the early 17th century, the highland kingdom of Imerina was initially a minor power relative to the larger coastal kingdoms and grew even weaker in the early 18th century when King
Upon its emergence in the early 17th century, the highland kingdom of Imerina was initially a minor power relative to the larger coastal kingdoms and grew even weaker in the early 18th century when King
 Primarily on the basis that the Lambert Charter had not been respected, France invaded Madagascar in 1883 in what became known as the first
Primarily on the basis that the Lambert Charter had not been respected, France invaded Madagascar in 1883 in what became known as the first  Huge mining and forestry concessions were granted to large companies. Native chiefs loyal to the French administration were also granted part of the land. Forced labor was introduced in favor of the French companies and peasants were encouraged, through taxation, to work for wages (especially in the colonial concessions) to the detriment of small individual farms. However, the colonial period was accompanied by movements fighting for independence: the Menalamba, the Vy Vato Sakelika, the Democratic Movement for Malagasy Renovation (MDRM). In 1927, major demonstrations were organized in Antananarivo, notably on the initiative of the communist activist François Vittori, who was imprisoned as a result. The 1930s saw the Malagasy anti-colonial movement gain further momentum. Malagasy trade unionism began to appear underground and the Communist Party of the Madagascar region was formed. But in 1939, all the organizations were dissolved by the administration of the colony, which opted for the Vichy regime. The MDRM was accused by the colonial regime of being at the origin of the 1947 insurrection and was pursued by violent repression.
The Merina royal tradition of taxes paid in the form of labor was continued under the French and used to construct a railway and roads linking key coastal cities to Antananarivo. Malagasy troops fought for France in
Huge mining and forestry concessions were granted to large companies. Native chiefs loyal to the French administration were also granted part of the land. Forced labor was introduced in favor of the French companies and peasants were encouraged, through taxation, to work for wages (especially in the colonial concessions) to the detriment of small individual farms. However, the colonial period was accompanied by movements fighting for independence: the Menalamba, the Vy Vato Sakelika, the Democratic Movement for Malagasy Renovation (MDRM). In 1927, major demonstrations were organized in Antananarivo, notably on the initiative of the communist activist François Vittori, who was imprisoned as a result. The 1930s saw the Malagasy anti-colonial movement gain further momentum. Malagasy trade unionism began to appear underground and the Communist Party of the Madagascar region was formed. But in 1939, all the organizations were dissolved by the administration of the colony, which opted for the Vichy regime. The MDRM was accused by the colonial regime of being at the origin of the 1947 insurrection and was pursued by violent repression.
The Merina royal tradition of taxes paid in the form of labor was continued under the French and used to construct a railway and roads linking key coastal cities to Antananarivo. Malagasy troops fought for France in
 Since regaining independence, Madagascar has transitioned through four republics with corresponding revisions to its constitution. The First Republic (1960вҖ“72), under the leadership of French-appointed President
Since regaining independence, Madagascar has transitioned through four republics with corresponding revisions to its constitution. The First Republic (1960вҖ“72), under the leadership of French-appointed President
 The combination of southeastern
The combination of southeastern 
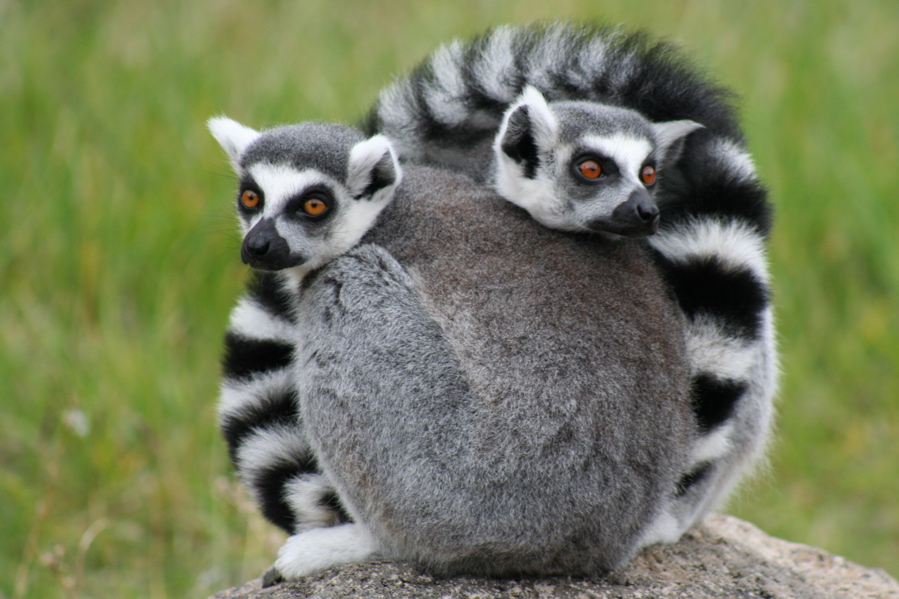 Like its flora, Madagascar's fauna is diverse and exhibits a high rate of endemism. Lemurs have been characterized as "Madagascar's flagship mammal species" by Conservation International. In the absence of monkeys and other competitors, these
Like its flora, Madagascar's fauna is diverse and exhibits a high rate of endemism. Lemurs have been characterized as "Madagascar's flagship mammal species" by Conservation International. In the absence of monkeys and other competitors, these
 Madagascar is a
Madagascar is a
 Since Madagascar gained independence from France in 1960, the island's political transitions have been marked by numerous popular protests, several disputed elections, an impeachment, two military coups and one assassination. The island's recurrent political crises are often prolonged, with detrimental effects on the local economy, international relations and Malagasy living standards. The eight-month standoff between incumbent Ratsiraka and challenger Marc Ravalomanana following the 2001 presidential elections cost Madagascar millions of dollars in lost tourism and trade revenue as well as damage to infrastructure, such as bombed bridges and buildings damaged by arson. A series of protests led by Andry Rajoelina against Ravalomanana in early 2009 became violent, with more than 170 people killed. Modern politics in Madagascar are colored by the history of Merina subjugation of coastal communities under their rule in the 19th century. The consequent tension between the highland and coastal populations has periodically flared up into isolated events of violence.
Madagascar has historically been perceived as being on the margin of mainstream African affairs despite being a founding member of the
Since Madagascar gained independence from France in 1960, the island's political transitions have been marked by numerous popular protests, several disputed elections, an impeachment, two military coups and one assassination. The island's recurrent political crises are often prolonged, with detrimental effects on the local economy, international relations and Malagasy living standards. The eight-month standoff between incumbent Ratsiraka and challenger Marc Ravalomanana following the 2001 presidential elections cost Madagascar millions of dollars in lost tourism and trade revenue as well as damage to infrastructure, such as bombed bridges and buildings damaged by arson. A series of protests led by Andry Rajoelina against Ravalomanana in early 2009 became violent, with more than 170 people killed. Modern politics in Madagascar are colored by the history of Merina subjugation of coastal communities under their rule in the 19th century. The consequent tension between the highland and coastal populations has periodically flared up into isolated events of violence.
Madagascar has historically been perceived as being on the margin of mainstream African affairs despite being a founding member of the
 Madagascar is subdivided into 22 regions (''faritra''). The regions are further subdivided into 119 districts, 1,579 communes, and 17,485 ''fokontany''.
Madagascar is subdivided into 22 regions (''faritra''). The regions are further subdivided into 119 districts, 1,579 communes, and 17,485 ''fokontany''.

 During the era of Madagascar's First Republic, France heavily influenced Madagascar's economic planning and policy and served as its key trading partner. Key products were cultivated and distributed nationally through producers' and consumers' cooperatives. Government initiatives such as a rural development program and state farms were established to boost production of commodities such as rice, coffee, cattle, silk and palm oil. Popular dissatisfaction over these policies was a key factor in launching the socialist-Marxist Second Republic, in which the formerly private bank and insurance industries were nationalized; state monopolies were established for such industries as textiles, cotton and power; and importвҖ“export trade and shipping were brought under state control. Madagascar's economy quickly deteriorated as exports fell, industrial production dropped by 75 percent, inflation spiked and government debt increased; the rural population was soon reduced to living at subsistence levels. Over 50 percent of the nation's export revenue was spent on debt servicing.
The IMF forced Madagascar's government to accept structural adjustment policies and liberalization of the economy when the state became bankrupt in 1982 and state-controlled industries were gradually privatized over the course of the 1980s. The political crisis of 1991 led to the suspension of IMF and World Bank assistance. Conditions for the resumption of aid were not met under Zafy, who tried unsuccessfully to attract other forms of revenue for the State before aid was once again resumed under the interim government established upon Zafy's impeachment. The IMF agreed to write off half Madagascar's debt in 2004 under the Ravalomanana administration. Having met a set of stringent economic, governance and human rights criteria, Madagascar became the first country to benefit from the
During the era of Madagascar's First Republic, France heavily influenced Madagascar's economic planning and policy and served as its key trading partner. Key products were cultivated and distributed nationally through producers' and consumers' cooperatives. Government initiatives such as a rural development program and state farms were established to boost production of commodities such as rice, coffee, cattle, silk and palm oil. Popular dissatisfaction over these policies was a key factor in launching the socialist-Marxist Second Republic, in which the formerly private bank and insurance industries were nationalized; state monopolies were established for such industries as textiles, cotton and power; and importвҖ“export trade and shipping were brought under state control. Madagascar's economy quickly deteriorated as exports fell, industrial production dropped by 75 percent, inflation spiked and government debt increased; the rural population was soon reduced to living at subsistence levels. Over 50 percent of the nation's export revenue was spent on debt servicing.
The IMF forced Madagascar's government to accept structural adjustment policies and liberalization of the economy when the state became bankrupt in 1982 and state-controlled industries were gradually privatized over the course of the 1980s. The political crisis of 1991 led to the suspension of IMF and World Bank assistance. Conditions for the resumption of aid were not met under Zafy, who tried unsuccessfully to attract other forms of revenue for the State before aid was once again resumed under the interim government established upon Zafy's impeachment. The IMF agreed to write off half Madagascar's debt in 2004 under the Ravalomanana administration. Having met a set of stringent economic, governance and human rights criteria, Madagascar became the first country to benefit from the  Madagascar's GDP in 2015 was estimated at US$9.98 billion, with a per capita GDP of $411.82. Approximately 69 percent of the population lives below the national poverty line threshold of one dollar per day. During 2011вҖ“15, the average growth rate was 2.6% but was expected to have reached 4.1% in 2016, due to public works programs and a growth of the service sector. The agriculture sector constituted 29 percent of Malagasy GDP in 2011, while manufacturing formed 15 percent of GDP. Madagascar's other sources of growth are tourism, agriculture and the extractive industries. Tourism focuses on the niche eco-tourism market, capitalizing on Madagascar's unique biodiversity, unspoiled natural habitats, national parks and lemur species. An estimated 365,000 tourists visited Madagascar in 2008, but the sector declined during the political crisis with 180,000 tourists visiting in 2010. However, the sector has been growing steadily for a few years; In 2016, 293,000 tourists landed in the African island with an increase of 20% compared to 2015; For 2017 the country has the goal of reaching 366,000 visitors, while for 2018 government estimates are expected to reach 500,000 annual tourists.
The island is still a very poor country in 2018; structural brakes remain in the development of the economy: corruption and the shackles of the public administration, lack of legal certainty, and backwardness of land legislation. The economy, however, has been growing since 2011, with GDP growth exceeding 4% per year; almost all economic indicators are growing, the GDP per capita was around $1600 (PPP) for 2017, one of the lowest in the world, although growing since 2012; unemployment was also cut, which in 2016 was equal to 2.1% with a work force of 13.4 million as of 2017. The main economic resources of Madagascar are
Madagascar's GDP in 2015 was estimated at US$9.98 billion, with a per capita GDP of $411.82. Approximately 69 percent of the population lives below the national poverty line threshold of one dollar per day. During 2011вҖ“15, the average growth rate was 2.6% but was expected to have reached 4.1% in 2016, due to public works programs and a growth of the service sector. The agriculture sector constituted 29 percent of Malagasy GDP in 2011, while manufacturing formed 15 percent of GDP. Madagascar's other sources of growth are tourism, agriculture and the extractive industries. Tourism focuses on the niche eco-tourism market, capitalizing on Madagascar's unique biodiversity, unspoiled natural habitats, national parks and lemur species. An estimated 365,000 tourists visited Madagascar in 2008, but the sector declined during the political crisis with 180,000 tourists visiting in 2010. However, the sector has been growing steadily for a few years; In 2016, 293,000 tourists landed in the African island with an increase of 20% compared to 2015; For 2017 the country has the goal of reaching 366,000 visitors, while for 2018 government estimates are expected to reach 500,000 annual tourists.
The island is still a very poor country in 2018; structural brakes remain in the development of the economy: corruption and the shackles of the public administration, lack of legal certainty, and backwardness of land legislation. The economy, however, has been growing since 2011, with GDP growth exceeding 4% per year; almost all economic indicators are growing, the GDP per capita was around $1600 (PPP) for 2017, one of the lowest in the world, although growing since 2012; unemployment was also cut, which in 2016 was equal to 2.1% with a work force of 13.4 million as of 2017. The main economic resources of Madagascar are
 Madagascar's natural resources include a variety of agricultural and mineral products. Agriculture (including the growing of
Madagascar's natural resources include a variety of agricultural and mineral products. Agriculture (including the growing of
 In 2010, Madagascar had approximately of paved roads, of railways and of navigable waterways. The majority of roads in Madagascar are unpaved, with many becoming impassable in the rainy season. Largely paved national routes connect the six largest regional towns to Antananarivo, with minor paved and unpaved routes providing access to other population centers in each district.
There are several rail lines. Antananarivo is connected to Toamasina, Ambatondrazaka and Antsirabe by rail, and another rail line connects Fianarantsoa to Manakara. The most important seaport in Madagascar is located on the east coast at Toamasina. Ports at Mahajanga and Antsiranana are significantly less used because of their remoteness. The island's newest port at Ehoala, constructed in 2008 and privately managed by Rio Tinto, will come under state control upon completion of the company's mining project near TГҙlanaro around 2038.
In 2010, Madagascar had approximately of paved roads, of railways and of navigable waterways. The majority of roads in Madagascar are unpaved, with many becoming impassable in the rainy season. Largely paved national routes connect the six largest regional towns to Antananarivo, with minor paved and unpaved routes providing access to other population centers in each district.
There are several rail lines. Antananarivo is connected to Toamasina, Ambatondrazaka and Antsirabe by rail, and another rail line connects Fianarantsoa to Manakara. The most important seaport in Madagascar is located on the east coast at Toamasina. Ports at Mahajanga and Antsiranana are significantly less used because of their remoteness. The island's newest port at Ehoala, constructed in 2008 and privately managed by Rio Tinto, will come under state control upon completion of the company's mining project near TГҙlanaro around 2038.
 Agriculture has long influenced settlement on the island. Only 15% of the nation's 24,894,551 population live in the 10 largest cities.
In , the population of Madagascar was estimated at million, up from 2.2 million in 1900. The annual population growth rate in Madagascar was approximately 2.9 percent in 2009.
Approximately 42.5 percent of the population is younger than 15 years of age, while 54.5 percent are between the ages of 15 and 64. Those aged 65 and older form 3 percent of the total population. Only two general censuses, in 1975 and 1993, have been carried out after independence. The most densely populated regions of the island are the eastern highlands and the eastern coast, contrasting most dramatically with the sparsely populated western plains.
Agriculture has long influenced settlement on the island. Only 15% of the nation's 24,894,551 population live in the 10 largest cities.
In , the population of Madagascar was estimated at million, up from 2.2 million in 1900. The annual population growth rate in Madagascar was approximately 2.9 percent in 2009.
Approximately 42.5 percent of the population is younger than 15 years of age, while 54.5 percent are between the ages of 15 and 64. Those aged 65 and older form 3 percent of the total population. Only two general censuses, in 1975 and 1993, have been carried out after independence. The most densely populated regions of the island are the eastern highlands and the eastern coast, contrasting most dramatically with the sparsely populated western plains.
 The Malagasy language is of
The Malagasy language is of

 According to the most recent national census available which was completed in 1993, 52% adhere to indigenous beliefs, 41 percent is Christian, and 7 percent is Muslim. It is common to alternate between religious identities or to mix traditions, and many individuals hold a combination of indigenous and Christian or Muslim beliefs. Muslim leaders and local scholars estimate Muslims currently constitute between 15 and 25 percent of the population. Muslims predominate in the northwestern coastal areas while Christians predominate in the highlands.
However, according to the
According to the most recent national census available which was completed in 1993, 52% adhere to indigenous beliefs, 41 percent is Christian, and 7 percent is Muslim. It is common to alternate between religious identities or to mix traditions, and many individuals hold a combination of indigenous and Christian or Muslim beliefs. Muslim leaders and local scholars estimate Muslims currently constitute between 15 and 25 percent of the population. Muslims predominate in the northwestern coastal areas while Christians predominate in the highlands.
However, according to the
 A wide variety of oral and written
A wide variety of oral and written
 A number of traditional pastimes have emerged in Madagascar. ''
A number of traditional pastimes have emerged in Madagascar. ''2015 FIBA Africa Under-16 Championship for Women
, FIBA.com, Retrieved 26 October 2015.
Country Profile
from
Madagascar
''
Madagascar
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Key Development Forecasts for Madagascar
from
Map of Madagascar, 1666
(in French). Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The
island country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
in the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
, approximately off the coast of East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
across the Mozambique Channel
The Mozambique Channel (french: Canal du Mozambique, mg, Lakandranon'i Mozambika, pt, Canal de Moçambique) is an arm of the Indian Ocean located between the Southeast African countries of Madagascar and Mozambique. The channel is about long ...
. At Madagascar is the world's second-largest island country, after Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. The nation is home to around 30 million inhabitants and consists of the island of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: RГ©publique de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
(the fourth-largest island in the world), along with numerous smaller peripheral islands. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
, Madagascar split from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
around 90 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation. Consequently, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot
A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human habitation. Norman Myers wrote about the concept in two articles in ''The Environmentalist'' in 1988 and 1990, after which the co ...
; over 90% of its wildlife is endemic.
Human settlement of Madagascar occurred during or before the mid first millennium AD by Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austro ...
, presumably arriving on outrigger canoes
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts ...
from present-day Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
. These were joined around the 9th century AD by Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the NigerвҖ“Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
migrants crossing the Mozambique Channel from East Africa. Other groups continued to settle on Madagascar over time, each one making lasting contributions to Malagasy cultural life. The Malagasy ethnic group is often divided into 18 or more subgroups
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, given a group ''G'' under a binary operation вҲ—, a subset ''H'' of ''G'' is called a subgroup of ''G'' if ''H'' also forms a group under the operation вҲ—. More precisely, ''H'' is a subgro ...
, of which the largest are the Merina
The Merina people (also known as the Imerina, Antimerina, or Hova) are the largest ethnic group in Madagascar.Merina ...
of the central highlands.
Until the late 18th century, the island of Madagascar was ruled by a fragmented assortment of shifting sociopolitical alliances. Beginning in the early 19th century, most of the island was united and ruled as the Kingdom of Madagascar
The Merina Kingdom, or Kingdom of Madagascar, officially the Kingdom of Imerina (вҖ“1897), was a pre-colonial state off the coast of Southeast Africa that, by the 19th century, dominated most of what is now Madagascar. It spread outward from I ...
by a series
Series may refer to:
People with the name
* Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series
* George Series (1920вҖ“1995), English physicist
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Series, the ordered sets used i ...
of Merina nobles
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristi ...
. The monarchy ended in 1897 when the island was absorbed into the French colonial empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas colonies, protectorates and mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French Colonial Empire", that exist ...
, from which the island gained independence in 1960. The autonomous state of Madagascar has since undergone four major constitutional periods, termed republics. Since 1992, the nation has officially been governed as a constitutional democracy from its capital at Antananarivo
Antananarivo ( French: ''Tananarive'', ), also known by its colonial shorthand form Tana, is the capital and largest city of Madagascar. The administrative area of the city, known as Antananarivo-Renivohitra ("Antananarivo-Mother Hill" or "An ...
. However, in a 2009 political crisis, president Marc Ravalomanana
Marc Ravalomanana (; born 12 December 1949) is a Malagasy politician who was the President of Madagascar from 2002 to 2009. Born into a farming Merina family in Imerinkasinina, near the capital city of Antananarivo, Ravalomanana first rose to ...
was made to resign and presidential power was transferred in March 2009 to Andry Rajoelina
Andry Nirina Rajoelina (Malagasy: ; born 30 May 1974) is a Malagasy politician and businessman who has been the president of Madagascar since 2019. He was previously president of a provisional government from 2009 to 2014 following a political ...
. Constitutional governance was restored in January 2014, when Hery Rajaonarimampianina
Hery Martial Rajaonarimampianina Rakotoarimanana (; ; born 6 November 1958) is a Malagasy politician who was President of Madagascar from January 2014 to September 2018, resigning to run for re-election. Previously he served as Minister of Fina ...
was named president following a 2013 election deemed fair and transparent by the international community. Madagascar is a member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
, the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
(AU), the Southern African Development Community
The Southern African Development Community (SADC) is an inter-governmental organization headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana.
Its goal is to further regional socio-economic cooperation and integration as well as political and security coopera ...
(SADC), and the Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie
The (OIF; sometimes shortened to the Francophonie, french: La Francophonie , but also called International Organisation of in English-language context) is an international organization representing countries and regions where French is a ...
.
Madagascar belongs to the group of least developed countries, according to the United Nations. Malagasy and French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
are both official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
s of the state. Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
is the predominant religion in the country, but a significant minority still practice traditional faiths. Ecotourism
Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving responsible travel (using sustainable transport) to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. Its purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide funds ...
and agriculture, paired with greater investments in education, health, and private enterprise, are key elements of Madagascar's development strategy. Under Ravalomanana, these investments produced substantial economic growth, but the benefits were not evenly spread throughout the population, producing tensions over the increasing cost of living and declining living standards among the poor and some segments of the middle class. The economy was weakened by the 2009 political crisis, and , quality of life remains low for the majority of the Malagasy population. Madagascar is experiencing an ongoing famine, which experts argue is the first to be caused entirely by climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warmingвҖ”the ongoing increase in global average temperatureвҖ”and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
.
Etymology
In theMalagasy language
Malagasy (; ) is an Austronesian language and the national language of Madagascar. Malagasy is the westernmost Malayo-Polynesian language, brought to Madagascar by the settlement of Austronesian peoples from the Sunda islands around the 5th ce ...
, the island of Madagascar is called ''Madagasikara'' () and its people are referred to as '' Malagasy''. The island's appellation "Madagascar" is not of local origin but rather was popularized in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
by Europeans.Cousins (1895), pp. 11вҖ“12 The name ''Madageiscar'' was first recorded in the memoirs of 13th-century Venetian explorer Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marv ...
as a corrupted transliteration of the name Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, Щ…ЩӮШҜЩҠШҙЩҲ ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and List of cities in Somalia by population, most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port ...
, the Somali port with which Marco Polo had confused the island.Room (2006), p. 230
On St. Laurence's Day in 1500, Portuguese explorer Diogo Dias
Diogo Dias, also known as Diogo Gomes, was a 15th-century Portugal, Portuguese explorer. He was the brother of Bartolomeu Dias and discovered some of the Cape Verde islands together with AntГіnio Noli.
Serving with da Gama
In 1497 on the first ...
landed on the island and named it ''São Lourenço''. Marco Polo's name was preferred and popularized on Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
maps. No single Malagasy-language name predating ''Madagasikara'' appears to have been used by the local population to refer to the island, although some communities had their own name for part or all of the land they inhabited.
History
Early period
 Traditionally, archaeologists have estimated that the earliest settlers arrived in successive waves in
Traditionally, archaeologists have estimated that the earliest settlers arrived in successive waves in outrigger canoe
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger ...
s from Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
, possibly throughout the period between 350 BCE and 550 CE, while others are cautious about dates earlier than 250 CE. In either case, these dates make Madagascar one of the latest major landmasses on Earth to be settled by humans, predating the settlement of Iceland
Iceland ( is, ГҚsland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is ReykjavГӯk, which (along with its s ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmassesвҖ”the North Island () and the South Island ()вҖ”and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
. It is proposed that Ma'anyan people
Ma'anyan (colonial spelling Maanjan or Meanjan), Dayak Maanyan or Eastern Barito Dayak people are a sub-ethnic group of the Dayak people indigenous to Borneo. They are also considered as part of the east Barito Dusun group with the name Dusun Ma ...
were brought as laborers and slaves by Javanese and Malays in their trading fleets to Madagascar. Dates earlier than the mid-first millennium AD are not strongly supported.
Upon arrival, early settlers practiced slash-and-burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a farming method that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. The downed vegeta ...
agriculture to clear the coastal rainforests for cultivation. The first settlers encountered Madagascar's abundance of megafauna
In terrestrial zoology, the megafauna (from Greek ОјОӯОіОұПӮ ''megas'' "large" and New Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") comprises the large or giant animals of an area, habitat, or geological period, extinct and/or extant. The most common threshold ...
, including giant lemurs
Subfossil lemurs are lemurs from Madagascar that are represented by recent (subfossil) remains dating from nearly 26,000 years ago to approximately 560 years ago (from the late Pleistocene until the Holocene). They include both extant ...
, elephant bird
Elephant birds are members of the extinct ratite family Aepyornithidae, made up of flightless birds that once lived on the island of Madagascar. They are thought to have become extinct around 1000-1200 CE, probably as a result of human activity. ...
s, giant fossa
''Cryptoprocta spelea'', also known as the giant fossa, is an extinct species of carnivore from Madagascar in the family Eupleridae which is most closely related to the mongooses and includes all Malagasy carnivorans. It was first described in 19 ...
, and the Malagasy hippopotamus, which have since become extinct because of hunting and habitat destruction. By 600 CE, groups of these early settlers had begun clearing the forests of the central highlands. Arab traders first reached the island between the 7th and 9th centuries.Wink (2004), p. 185 A wave of Bantu
Bantu may refer to:
*Bantu languages, constitute the largest sub-branch of the NigerвҖ“Congo languages
*Bantu peoples, over 400 peoples of Africa speaking a Bantu language
* Bantu knots, a type of African hairstyle
*Black Association for National ...
-speaking migrants from southeastern Africa arrived around 1000 CE. South Indian Tamil merchants arrived around 11th century. They introduced the zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus'' or ''Bos taurus indicus''), sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in the Indian sub-continent. Zebu are characterised by a fatty ...
, a type of long-horned humped cattle, which they kept in large herds. Irrigated paddy fields were developed in the central highland Betsileo
The Betsileo are a highland ethnic groups of Madagascar, ethnic group of Madagascar, the third largest in terms of population. They chose their name, meaning "The Many Invincible Ones", after a failed invasion by King Ramitraho of the Menabe king ...
Kingdom and were extended with terraced paddies throughout the neighboring Kingdom of Imerina
The Merina Kingdom, or Kingdom of Madagascar, officially the Kingdom of Imerina (вҖ“1897), was a pre-colonial state off the coast of Southeast Africa that, by the 19th century, dominated most of what is now Madagascar. It spread outward from I ...
a century later. The rising intensity of land cultivation and the ever-increasing demand for zebu pasturage had largely transformed the central highlands from a forest ecosystem to grassland by the 17th century. The oral histories of the Merina people, who may have arrived in the central highlands between 600 and 1,000 years ago, describe encountering an established population they called the Vazimba
The Vazimba (Malagasy ), according to popular belief, were the first inhabitants of Madagascar. While beliefs about the physical appearance of the Vazimba reflect regional variation, they are generally described as smaller in stature than the aver ...
. Probably the descendants of an earlier and less technologically advanced Austronesian settlement wave, the Vazimba were assimilated or expelled from the highlands by the Merina kings Andriamanelo
Andriamanelo (Floruit, ''fl.'' 1540–1575) was king of Twelve sacred hills of Imerina#Hill of Alasora, Alasora in the central highlands region of Madagascar. He is generally considered by historians to be the founder of the Kingdom of Imeri ...
, Ralambo
Ralambo was the ruler of the Kingdom of Imerina in the central Highlands region of Madagascar from 1575 to 1612. Ruling from Ambohidrabiby, Ralambo expanded the realm of his father, Andriamanelo, and was the first to assign the name of Imerina t ...
, and Andrianjaka
Andrianjaka reigned over the Kingdom of Imerina in the central highlands region of Madagascar from around 1612 to 1630. Despite being the younger of King Ralambo's two sons, Andrianjaka succeeded to the throne on the basis of his strength of char ...
in the 16th and early 17th centuries. Today, the spirits of the Vazimba are revered as ''tompontany'' (ancestral masters of the land) by many traditional Malagasy communities.
Arab and Portuguese contacts
 Madagascar was an important transoceanic trading hub connecting ports of the Indian Ocean in the early centuries following human settlement.
The
Madagascar was an important transoceanic trading hub connecting ports of the Indian Ocean in the early centuries following human settlement.
The written history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world hist ...
of Madagascar began with the Arabs, who established trading posts along the northwest coast by at least the 10th century and introduced Islam
Islam (; ar, ЫҳШ§Щ„ЩҗШҘШіЩ„ЩҺШ§Щ…, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, the Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used writing system in the world by number of countries using it or a script directly derived from it, and the ...
(used to transcribe the Malagasy language in a form of writing known as ''sorabe
Sorabe or Sora-be () is an alphabet based on Arabic, formerly used to transcribe the Malagasy language (belonging to the Malayo-Polynesian language family) and the Antemoro Malagasy dialect, dating from the 15th century.
History
Researchers ar ...
''), Arab astrology, and other cultural elements.
Portuguese
European contact began in 1500, when thePortuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
sea captain Diogo Dias
Diogo Dias, also known as Diogo Gomes, was a 15th-century Portugal, Portuguese explorer. He was the brother of Bartolomeu Dias and discovered some of the Cape Verde islands together with AntГіnio Noli.
Serving with da Gama
In 1497 on the first ...
sighted the island, while participating in the 2nd Armada of the Portuguese India Armadas
The Portuguese Indian Armadas ( pt, Armadas da ГҚndia) were the fleets of ships funded by the Crown of Portugal, and dispatched on an annual basis from Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal to Portuguese India, India. The principal destination was Por ...
.
Matatana was the first Portuguese settlement on the south coast, 10 km west of Fort Dauphin. In 1508, settlers there built a tower, a small village, and a stone column. This settlement was established in 1513 at the behest of the viceroy of Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da ГҚndia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado PortuguГӘs da ГҚndia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a se ...
, Jeronimo de Azevedo.
 Contacts continued from the 1550s. Several colonization and conversion missions were ordered by King
Contacts continued from the 1550s. Several colonization and conversion missions were ordered by King JoГЈo III
John III ( pt, JoГЈo III ; 7 June 1502 вҖ“ 11 June 1557), nicknamed The Pious ( Portuguese: ''o Piedoso''), was the King of Portugal and the Algarves from 1521 until his death in 1557. He was the son of King Manuel I and Maria of Aragon, the t ...
and by the Viceroy of India, including one in 1553 by Baltazar Lobo de Sousa. In that mission, according to detailed descriptions by chroniclers Diogo do Couto and JoГЈo de Barros, emissaries reached the inland via rivers and bays, exchanging goods and even converting one of the local kings.
French
The French established trading posts along the east coast in the late 17th century. From about 1774 to 1824, Madagascar gained prominence among pirates and European traders, particularly those involved in thetrans-Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
. The small island of Nosy Boroha off the northeastern coast of Madagascar has been proposed by some historians as the site of the legendary pirate utopia of Libertalia
Libertatia (also known as Libertalia) was a purported pirate colony founded in the late 17th century in Madagascar under the leadership of Captain James Misson (last name occasionally spelled "Mission", first name occasionally "Olivier"). The ma ...
. Many European sailors were shipwrecked on the coasts of the island, among them Robert Drury, whose journal is one of the few written depictions of life in southern Madagascar during the 18th century.
The wealth generated by maritime trade spurred the rise of organized kingdoms on the island, some of which had grown quite powerful by the 17th century. Among these were the Betsimisaraka alliance of the eastern coast and the Sakalava
The Sakalava are an ethnic groups of Madagascar, ethnic group of Madagascar. They are found on the western and northwest region of the island, in a band along the coast. The Sakalava are one of the smaller ethnic groups, constituting about 6.2 pe ...
chiefdoms of Menabe
Menabe is a Regions of Madagascar, region in western Madagascar, with its capital at Morondava. It covers an area of , and its population was 700,577 in 2018. The population mostly belongs to the Sakalava ethnic group. The region is named after th ...
and Boina on the west coast. The Kingdom of Imerina, located in the central highlands with its capital at the royal palace
This is a list of royal palaces, sorted by continent.
Africa
* Abdin Palace, Cairo
* Al-Gawhara Palace, Cairo
* Koubbeh Palace, Cairo
* Tahra Palace, Cairo
* Menelik Palace
* Jubilee Palace
* Guenete Leul Palace
* Imperial Palace- Massa ...
of Antananarivo, emerged at around the same time under the leadership of King Andriamanelo.Ogot (1992), p. 418
Kingdom of Madagascar
 Upon its emergence in the early 17th century, the highland kingdom of Imerina was initially a minor power relative to the larger coastal kingdoms and grew even weaker in the early 18th century when King
Upon its emergence in the early 17th century, the highland kingdom of Imerina was initially a minor power relative to the larger coastal kingdoms and grew even weaker in the early 18th century when King Andriamasinavalona
Andriamasinavalona (1675–1710), also known as Andrianjakanavalondambo, was a King of Imerina in the central highlands of Madagascar. He made significant and enduring contributions to the social, political and economic life of Imerina. Chief ...
divided it among his four sons. Following almost a century of warring and famine, Imerina was reunited in 1793 by King Andrianampoinimerina
Andrianampoinimerina () (1745вҖ“1810) ruled the Kingdom of Imerina on Madagascar from 1787 until his death. His reign was marked by the reunification of Imerina following 77 years of civil war, and the subsequent expansion of his kingdom into n ...
(1787вҖ“1810).Hodder (1982), p. 59 From his initial capital Ambohimanga
Ambohimanga is a hill and traditional fortified royal settlement (''rova'') in Madagascar, located approximately northeast of the capital city of Antananarivo. It is situated in the commune of Ambohimanga Rova.
The hill and the rova that sta ...
, and later from the Rova of Antananarivo
The Rova of Antananarivo ( mg, Rovan'i Manjakamiadana ) is a royal palace complex (''rova'') in Madagascar that served as the home of the sovereigns of the Kingdom of Imerina in the 17th and 18th centuries, as well as of the rulers of the King ...
, this Merina king rapidly expanded his rule over neighboring principalities. His ambition to bring the entire island under his control was largely achieved by his son and successor, King Radama I
Radama I "the Great" (1793вҖ“1828) was the first Malagasy sovereign to be recognized as King of Madagascar (1810вҖ“1828) by a European state. He came to power at the age of 18 following the death of his father, King Andrianampoinimerina. Under Ra ...
(1810вҖ“28), who was recognized by the British government as King of Madagascar. Radama concluded a treaty in 1817 with the British governor of Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It incl ...
to abolish the lucrative slave trade in return for British military and financial assistance. Artisan missionary envoys from the London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was an interdenominational evangelical missionary society formed in England in 1795 at the instigation of Welsh Congregationalist minister Edward Williams. It was largely Reformed in outlook, with Congregational miss ...
began arriving in 1818 and included such key figures as James Cameron
James Francis Cameron (born August 16, 1954) is a Canadian filmmaker. A major figure in the post-New Hollywood era, he is considered one of the industry's most innovative filmmakers, regularly pushing the boundaries of cinematic capability w ...
, David Jones and David Griffiths, who established schools, transcribed the Malagasy language
Malagasy (; ) is an Austronesian language and the national language of Madagascar. Malagasy is the westernmost Malayo-Polynesian language, brought to Madagascar by the settlement of Austronesian peoples from the Sunda islands around the 5th ce ...
using the Roman alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the o ...
, translated the Bible, and introduced a variety of new technologies to the island.Ade Ajayi (1998), pp. 413вҖ“422
Radama's successor, Queen Ranavalona I
Ranavalona I (born Rabodoandrianampoinimerina (also called Ramavo); 1778 вҖ“ 16 August 1861), also known as Ranavalo-Manjaka I and the вҖңMad Monarch of MadagascarвҖқ was sovereign of the Kingdom of Madagascar from 1828 to 1861. After pos ...
(1828вҖ“61), responded to increasing political and cultural encroachment on the part of Britain and France by issuing a royal edict prohibiting the practice of Christianity in Madagascar
Christianity in Madagascar is practiced by 85.3% of Madagascar's population according to the Pew Research Center in 2010, often in syncretic form with traditional religious practices. Protestantism was introduced by the first envoys of the Lon ...
and pressuring most foreigners to leave the territory. William Ellis of the London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was an interdenominational evangelical missionary society formed in England in 1795 at the instigation of Welsh Congregationalist minister Edward Williams. It was largely Reformed in outlook, with Congregational miss ...
described his visits made during her reign in his book ''Three Visits to Madagascar during the years 1853, 1854, and 1856''. The Queen made heavy use of the traditional practice of '' fanompoana'' (forced labor as tax payment) to complete public works projects and develop a standing army of between 20,000 and 30,000 Merina
The Merina people (also known as the Imerina, Antimerina, or Hova) are the largest ethnic group in Madagascar.Merina ...
soldiers, whom she deployed to pacify outlying regions of the island and further expand the Kingdom of Merina to encompass most of Madagascar. Residents of Madagascar could accuse one another of various crimes, including theft, Christianity and especially witchcraft, for which the ordeal of ''tangena
''Tangena'' is the indigenous name for the tree species ''Cerbera manghas'' (family Apocynaceae) of Madagascar, which produces seeds - containing the highly toxic cardiac glycoside cerberin - that were used historically on the island for trials b ...
'' was routinely obligatory. Between 1828 and 1861, the ''tangena'' ordeal caused about 3,000 deaths annually. In 1838, it was estimated that as many as 100,000 people in Imerina died as a result of the tangena ordeal, constituting roughly 20 percent of the population. The combination of regular warfare, disease, difficult forced labor, and harsh measures of justice resulted in a high mortality rate among soldiers and civilians alike during her 33-year reign; the population of Madagascar is estimated to have declined from around 5 million to 2.5 million between 1833 and 1839.
Among those who continued to reside in Imerina were Jean Laborde
Jean Laborde (16 October 1805 in Auch - 27 December 1878 in Mantasoa, Madagascar) was an adventurer and early industrialist in Madagascar. He became the chief engineer of the Merina monarchy, supervising the creation of a modern manufacturing cent ...
, an entrepreneur who developed munitions and other industries on behalf of the monarchy, and Joseph-François Lambert
Joseph-FranГ§ois Lambert, the "Duke of Imerina" (1824вҖ“1873) was a French adventurer, businessman, and diplomat who fathered the Lambert Charter.
Early years
Lambert was born in Redon, Ille-et-Vilaine in 1824. He traveled to Mauritius where, at ...
, a French adventurer and slave trader, with whom then-Prince Radama II
Radama II (September 23, 1829 вҖ“ May 12, 1863 'contested'' was the son and heir of Queen Ranavalona I and ruled from 1861 to 1863 over the Kingdom of Madagascar, which controlled virtually the entire island. Radama's rule, although brief, ...
signed a controversial trade agreement termed the Lambert Charter. Succeeding his mother, Radama II (1861вҖ“63) attempted to relax the queen's stringent policies, but was overthrown two years later by Prime Minister Rainivoninahitriniony
Rainivoninahitriniony (1824вҖ“1868), was Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Madagascar between 1852 and 1864. He was the chief engineer of the Aristocratic Revolution initialized upon the attempted assassination of King Radama II. His excesses and ...
(1852вҖ“1865) and an alliance of ''Andriana
Andriana refers to both the noble class and a title of nobility in Madagascar. Historically, many Malagasy ethnic groups lived in highly stratified caste-based social orders in which the ''andriana'' were the highest strata. They were above the ...
'' (noble) and '' Hova'' (commoner) courtiers, who sought to end the absolute power of the monarch.
Following the coup, the courtiers offered Radama's queen, Rasoherina
Rasoherina (1814 вҖ“ 1 April 1868) (also Rasoherina-Manjaka) was Queen regnant of Madagascar from 1863 to 1868, succeeding her husband Radama II following his presumed assassination.
Early years
Rasoherina, niece of Queen Ranavalona I, was born ...
(1863вҖ“68), the opportunity to rule, if she would accept a power sharing arrangement with the Prime Minister: a new social contract that would be sealed by a political marriage between them. Queen Rasoherina accepted, first marrying Rainivoninahitriniony, then later deposing him and marrying his brother, Prime Minister Rainilaiarivony
Rainilaiarivony (30 January 1828 вҖ“ 17 July 1896) was a Malagasy politician who served as the prime minister of Madagascar from 1864 to 1895, succeeding his older brother Rainivoninahitriniony, who had held the post for thirteen years. His ...
(1864вҖ“95), who would go on to marry Queen Ranavalona II
Ranavalona II (1829 вҖ“ 13 July 1883) was Queen regnant of Madagascar from 1868 to 1883, succeeding Queen Rasoherina, her first cousin. She is best remembered for Christianizing the royal court during her reign.
Early life
Ranavalona II was b ...
(1868вҖ“83) and Queen Ranavalona III
Ranavalona III (; 22 November 1861 вҖ“ 23 May 1917) was the last sovereign of the Kingdom of Madagascar. She ruled from 30 July 1883 to 28 February 1897 in a reign marked by ultimately futile efforts to resist the colonial designs of the go ...
(1883вҖ“97) in succession. Over the course of Rainilaiarivony's 31-year tenure as prime minister, numerous policies were adopted to modernize and consolidate the power of the central government. Schools were constructed throughout the island and attendance was made mandatory. Army organization was improved and British consultants were employed to train and professionalize soldiers.Fage, Flint & Oliver (1986), pp. 522вҖ“524 Polygamy
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is married ...
was outlawed and Christianity, declared the official religion of the court in 1869, was adopted alongside traditional beliefs among a growing portion of the populace.Thompson & Adloff (1965), pp. 9вҖ“10 Legal codes were reformed on the basis of British common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresen ...
and three European-style courts were established in the capital city. In his joint role as Commander-in-Chief, Rainilaiarivony also successfully ensured the defense of Madagascar against several French colonial incursions.
French colonization
 Primarily on the basis that the Lambert Charter had not been respected, France invaded Madagascar in 1883 in what became known as the first
Primarily on the basis that the Lambert Charter had not been respected, France invaded Madagascar in 1883 in what became known as the first Franco-Hova War
The Franco-Hova Wars, also known as the Franco-Malagasy Wars were two French military interventions in Madagascar between 1883 and 1896 that overthrew the ruling monarchy of the Merina Kingdom, and resulted in Madagascar becoming a French colon ...
.Van Den Boogaerde (2008), p. 7 At the end of the war, Madagascar ceded the northern port town of Antsiranana
Antsiranana ( mg, AntsiranМҲana ), named Diego-SuГЎrez prior to 1975, is a city in the far north of Madagascar. Antsiranana is the capital of Diana Region. It had an estimated population of 115,015 in 2013.
History
The bay and city originally u ...
(Diego Suarez) to France and paid 560,000 francs to Lambert's heirs.Randier (2006), p. 400 In 1890, the British accepted the full formal imposition of a French protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over m ...
on the island, but French authority was not acknowledged by the government of Madagascar. To force capitulation, the French bombarded and occupied the harbor of Toamasina
Toamasina (), meaning "like salt" or "salty", unofficially and in French Tamatave, is the capital of the Atsinanana region on the east coast of Madagascar on the Indian Ocean. The city is the chief seaport of the country, situated northeast of it ...
on the east coast, and Mahajanga
Mahajanga (French: Majunga) is a city and an administrative district on the northwest coast of Madagascar. The city of Mahajanga (Mahajanga I) is the capital of the Boeny Region. The district (identical to the city) had a population of 220,629 i ...
on the west coast, in December 1894 and January 1895 respectively.Curtin (1998), p. 186
A French military flying column
A flying column is a small, independent, military land unit capable of rapid mobility and usually composed of all arms. It is often an ''ad hoc'' unit, formed during the course of operations.
The term is usually, though not necessarily, appli ...
then marched toward Antananarivo, losing many men to malaria and other diseases. Reinforcements came from Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
and Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
. Upon reaching the city in September 1895, the column bombarded the royal palace with heavy artillery, causing heavy casualties and leading Queen Ranavalona III to surrender. France annexed Madagascar in 1896 and declared the island a colony the following year, dissolving the Merina monarchy and sending the royal family into exile on RГ©union Island
RГ©union (; french: La RГ©union, ; previously ''ГҺle Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La RГ©nyon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island o ...
and to Algeria. A two-year resistance movement
A resistance movement is an organized effort by some portion of the civil population of a country to withstand the legally established government or an occupying power and to disrupt civil order and stability. It may seek to achieve its objective ...
organized in response to the French capture of the royal palace was effectively put down at the end of 1897.
The conquest was followed by ten years of civil war, due to the Menalamba insurrection. The "pacification" carried out by the French administration lasted more than fifteen years, in response to the rural guerrillas scattered throughout the country. In total, the repression of this resistance to colonial conquest caused several tens of thousands of Malagasy victims.
Under colonial rule, plantations were established for the production of a variety of export crops. Slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slaveвҖ”someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
was abolished in 1896 and approximately 500,000 slaves were freed; many remained in their former masters' homes as servants or as sharecroppers; in many parts of the island strong discriminatory views against slave descendants are still held today. Wide paved boulevards and gathering places were constructed in the capital city of Antananarivo and the Rova palace compound was turned into a museum.FrГ©migacci (1999), pp. 421вҖ“444 Additional schools were built, particularly in rural and coastal areas where the schools of the Merina had not reached. Education became mandatory between the ages of 6 to 13 and focused primarily on French language and practical skills.
 Huge mining and forestry concessions were granted to large companies. Native chiefs loyal to the French administration were also granted part of the land. Forced labor was introduced in favor of the French companies and peasants were encouraged, through taxation, to work for wages (especially in the colonial concessions) to the detriment of small individual farms. However, the colonial period was accompanied by movements fighting for independence: the Menalamba, the Vy Vato Sakelika, the Democratic Movement for Malagasy Renovation (MDRM). In 1927, major demonstrations were organized in Antananarivo, notably on the initiative of the communist activist François Vittori, who was imprisoned as a result. The 1930s saw the Malagasy anti-colonial movement gain further momentum. Malagasy trade unionism began to appear underground and the Communist Party of the Madagascar region was formed. But in 1939, all the organizations were dissolved by the administration of the colony, which opted for the Vichy regime. The MDRM was accused by the colonial regime of being at the origin of the 1947 insurrection and was pursued by violent repression.
The Merina royal tradition of taxes paid in the form of labor was continued under the French and used to construct a railway and roads linking key coastal cities to Antananarivo. Malagasy troops fought for France in
Huge mining and forestry concessions were granted to large companies. Native chiefs loyal to the French administration were also granted part of the land. Forced labor was introduced in favor of the French companies and peasants were encouraged, through taxation, to work for wages (especially in the colonial concessions) to the detriment of small individual farms. However, the colonial period was accompanied by movements fighting for independence: the Menalamba, the Vy Vato Sakelika, the Democratic Movement for Malagasy Renovation (MDRM). In 1927, major demonstrations were organized in Antananarivo, notably on the initiative of the communist activist François Vittori, who was imprisoned as a result. The 1930s saw the Malagasy anti-colonial movement gain further momentum. Malagasy trade unionism began to appear underground and the Communist Party of the Madagascar region was formed. But in 1939, all the organizations were dissolved by the administration of the colony, which opted for the Vichy regime. The MDRM was accused by the colonial regime of being at the origin of the 1947 insurrection and was pursued by violent repression.
The Merina royal tradition of taxes paid in the form of labor was continued under the French and used to construct a railway and roads linking key coastal cities to Antananarivo. Malagasy troops fought for France in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. In the 1930s, Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
political thinkers developed the Madagascar Plan
The Madagascar Plan was a plan to forcibly relocate the Jewish population of Europe to the island of Madagascar which was proposed by the Nazi German government. Franz Rademacher, head of the Jewish Department of the German Foreign Office, pro ...
that had identified the island as a potential site for the deportation of Europe's Jews.Browning (2004), pp. 81вҖ“89 During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesвҖ”including all of the great powersвҖ”forming two opposin ...
, the island was the site of the Battle of Madagascar
The Battle of Madagascar (5 May вҖ“ 6 November 1942) was a British campaign to capture the Vichy French-controlled island Madagascar during World War II. The seizure of the island by the British was to deny Madagascar's ports to the Imperial ...
between the Vichy French
Vichy France (french: RГ©gime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 вҖ“ 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe PГ©tain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its terr ...
and an Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
expeditionary force.
The occupation of France during the Second World War tarnished the prestige of the colonial administration in Madagascar and galvanized the growing independence movement, leading to the Malagasy Uprising
The Malagasy Uprising (french: Insurrection malgache; mg, Tolom-bahoaka tamin' ny 1947) was a Malagasy nationalist rebellion against French colonial rule in Madagascar, lasting from March 1947 to February 1949. Starting in late 1945, Madagasca ...
of 1947. This movement led the French to establish reformed institutions in 1956 under the ''Loi Cadre
The ''loi-cadre'' (Reform Act) was a French legal reform passed by the French National Assembly on 23 June 1956, named after Overseas minister Gaston Defferre. It marked a turning point in relations between France and its overseas empire. Under p ...
'' (Overseas Reform Act), and Madagascar moved peacefully towards independence.Kitchen (1962), p. 256 The Malagasy Republic
The Malagasy Republic ( mg, Repoblika Malagasy, french: RГ©publique malgache) was a state situated in Southeast Africa. It was established in 1958 as an autonomous republic within the newly created French Community, became fully independent in ...
was proclaimed on 14 October 1958, as an autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from ОұбҪҗП„Оҝ- ''auto-'' "self" and ОҪПҢОјОҝПӮ ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ow ...
state within the French Community
The French Community (1958вҖ“1960; french: CommunautГ© franГ§aise) was the constitutional organization set up in 1958 between France and its remaining African colonies, then in the process of decolonization. It replaced the French Union, which ...
. A period of provisional government ended with the adoption of a constitution in 1959 and full independence on 26 June 1960.
Independent state
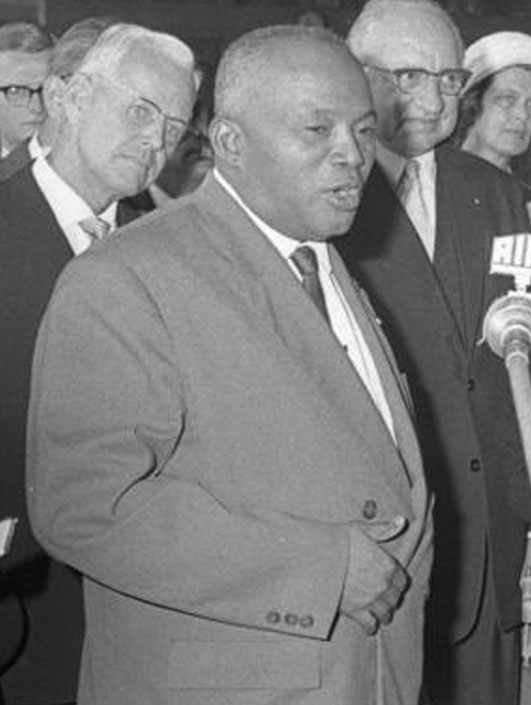
 Since regaining independence, Madagascar has transitioned through four republics with corresponding revisions to its constitution. The First Republic (1960вҖ“72), under the leadership of French-appointed President
Since regaining independence, Madagascar has transitioned through four republics with corresponding revisions to its constitution. The First Republic (1960вҖ“72), under the leadership of French-appointed President Philibert Tsiranana
Philibert Tsiranana (18 October 1912 вҖ“ 16 April 1978) was a Malagasy politician and leader, who served as the first President of Madagascar from 1959 to 1972.
During the twelve years of his administration, the Republic of Madagascar expe ...
, was characterized by a continuation of strong economic and political ties to France. Many high-level technical positions were filled by French expatriates, and French teachers, textbooks and curricula continued to be used in schools around the country. Popular resentment over Tsiranana's tolerance for this "neo-colonial" arrangement inspired a series of farmer and student protests that overturned his administration in 1972.
Gabriel Ramanantsoa
Gabriel Ramanantsoa (13 April 1906 Antananarivo вҖ“ 9 May 1979 Paris) was the President and Prime Minister of Madagascar from 1972 to 1975.
Ramanantsoa was a member of the Merina ethnic group, and came from a wealthy family. He graduated from Sai ...
, a major general in the army, was appointed interim president and prime minister that same year, but low public approval forced him to step down in 1975. Colonel Richard Ratsimandrava
Colonel Richard Ratsimandrava (March 21, 1931 Antananarivo – February 11, 1975 Antananarivo) was President of Madagascar for six days in February 1975 before his assassination in office.
Biography
Military career
He was born in 1931 an ...
, appointed to succeed him, was assassinated six days into his tenure. General Gilles Andriamahazo
General Gilles Andriamahazo (5 May 1919 вҖ“ 13 September 1989) was a Malagasy general and political figure. Originally he was a Merina and served as the military president of Madagascar (''Chairman of the National Military Leadership Committee' ...
ruled after Ratsimandrava for four months before being replaced by another military appointee: Vice Admiral Didier Ratsiraka
Didier Ignace Ratsiraka (; 4 November 1936 вҖ“ 28 March 2021) was a Malagasy people, Malagasy politician and Madagascar Navy, naval officer who was President of Madagascar from 1975 to 1993 and from 1997 to 2002. At the time of his death, he was ...
, who ushered in the Socialist-Marxist Second Republic that ran under his tenure from 1975 to 1993.
This period saw a political alignment with the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
countries and a shift toward economic insularity. These policies, coupled with economic pressures stemming from the 1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
, resulted in the rapid collapse of Madagascar's economy and a sharp decline in living standards, and the country had become completely bankrupt by 1979. The Ratsiraka administration accepted the conditions of transparency, anti-corruption measures and free market policies imposed by the International Monetary Fund, World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
and various bilateral donors in exchange for their bailout of the nation's broken economy.
Ratsiraka's dwindling popularity in the late 1980s reached a critical point in 1991 when presidential guards opened fire on unarmed protesters during a rally. Within two months, a transitional government had been established under the leadership of Albert Zafy
Albert Zafy (1 May 1927 вҖ“ 13 October 2017) was a Malagasy politician and educator who served as President of Madagascar from 27 March 1993 to 5 September 1996. In 1988, he founded the National Union for Democracy and Development (UNDD).
In ...
(1993вҖ“96), who went on to win the 1992 presidential elections and inaugurate the Third Republic (1992вҖ“2010). The new Madagascar constitution established a multi-party democracy and a separation of powers that placed significant control in the hands of the National Assembly. The new constitution also emphasized human rights, social and political freedoms, and free trade. Zafy's term, however, was marred by economic decline, allegations of corruption, and his introduction of legislation to give himself greater powers. He was consequently impeached in 1996, and an interim president, Norbert Ratsirahonana
Norbert Lala Ratsirahonana (born November 18, 1938) is a Malagasy politician.
Life and career
He was born in Antsiranana, Diana Region He founded and led the '' Asa Vita no Ifampitsarana'' (Judged By Your Work) Party, which opposed President Di ...
, was appointed for the three months prior to the next presidential election. Ratsiraka was then voted back into power on a platform of decentralization and economic reforms for a second term which lasted from 1996 to 2001.
The contested 2001 presidential elections in which then-mayor of Antananarivo, Marc Ravalomanana, eventually emerged victorious, caused a seven-month standoff in 2002 between supporters of Ravalomanana and Ratsiraka. The negative economic impact of the political crisis was gradually overcome by Ravalomanana's progressive economic and political policies, which encouraged investments in education and ecotourism, facilitated foreign direct investment, and cultivated trading partnerships both regionally and internationally. National GDP grew at an average rate of 7 percent per year under his administration. In the later half of his second term, Ravalomanana was criticised by domestic and international observers who accused him of increasing authoritarianism and corruption.
Opposition leader and then-mayor of Antananarivo, Andry Rajoelina, led a movement in early 2009 in which Ravalomanana was pushed from power in an unconstitutional process widely condemned as a ''coup d'Г©tat''. In March 2009, Rajoelina was declared by the Supreme Court as the President of the High Transitional Authority
The High Transitional Authority ( Malagasy: ''Fitondrana Avon'ny Tetezamita'' (FAT); french: Haute autoritГ© de transition or HAT) was a provisional executive body that came to power in Madagascar following the coup that forced Marc Ravalomanana t ...
, an interim governing body responsible for moving the country toward presidential elections. In 2010, a new constitution was adopted by referendum, establishing a Fourth Republic, which sustained the democratic, multi-party structure established in the previous constitution. Hery Rajaonarimampianina
Hery Martial Rajaonarimampianina Rakotoarimanana (; ; born 6 November 1958) is a Malagasy politician who was President of Madagascar from January 2014 to September 2018, resigning to run for re-election. Previously he served as Minister of Fina ...
was declared the winner of the 2013 presidential election, which the international community deemed fair and transparent.
In 2018 the first round of the presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pre ...
was held on 7 November and the second round was held on 10 December. Three former presidents and the most recent president were the main candidates of the elections. Former president Andry Rajoelina won the second round of the elections. He was previously president from 2009 to 2014. Former president Marc Ravalomana lost the second round and he did not accept the results because of allegations of fraud. Ravalomana was president from 2002 to 2009. The most recent president Hery Rajaonarimampianina received very modest support in the first round. In January 2019 the High Constitutional Court declared Rajoelina as the winner of the elections and the new president.
In June 2019 parliamentary elections
A general election is a political voting election where generally all or most members of a given political body are chosen. These are usually held for a nation, state, or territory's primary legislative body, and are different from by-elections ( ...
the party of president Andry Rajoelina won absolute majority of the seats of the National Assembly. It received 84 seats and the supporters of former president Ravalomana got only 16 seats of 151 seats of the National Assembly. 51 seats of deputies were independent or represented small parties. President Rajoelina could rule as a strongman
In the 19th century, the term strongman referred to an exhibitor of strength or similar circus performers who performed feats of strength. More recently, strength athletics, also known as strongman competitions, have grown in popularity. These ...
.
In 2020, on the 60th anniversary of Madagascar's independence, a national drive was marked with an inaugural gathering of volunteers to set out plantlings in the ground in an ambition to plant 60 million trees.
Geography
At , Madagascar is the world's 47th largest country, the 2nd largestisland country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
and the fourth-largest island. The country lies mostly between latitudes 12В°S and 26В°S, and longitudes 43В°E and 51В°E.Moriarty (1891), pp. 1вҖ“2 Neighboring islands include the French territory of RГ©union
RГ©union (; french: La RГ©union, ; previously ''ГҺle Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La RГ©nyon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island ...
and the country of Mauritius
Mauritius ( ; french: Maurice, link=no ; mfe, label=Mauritian Creole, Moris ), officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean about off the southeast coast of the African continent, east of Madagascar. It incl ...
to the east, as well as the state of Comoros
The Comoros,, ' officially the Union of the Comoros,; ar, Ш§Щ„Ш§ШӘШӯШ§ШҜ Ш§Щ„ЩӮЩ…ШұЩҠ ' is an independent country made up of three islands in southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. It ...
and the French territory of Mayotte
Mayotte (; french: Mayotte, ; Shimaore: ''Maore'', ; Kibushi: ''Maori'', ), officially the Department of Mayotte (french: DГ©partement de Mayotte), is an overseas department and region and single territorial collectivity of France. It is loc ...
to the north west. The nearest mainland state is Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
, located to the west.
The prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
resulted in the separation of East Gondwana (comprising Madagascar, Antarctica, Australia and the Indian subcontinent) and West Gondwana (AfricaвҖ“South America) during the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
period, around 185 million years ago. The Indo-Madagascar landmass separated from Antarctica and Australia around 125 million years ago and Madagascar separated from the Indian landmass about 84-92 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
. This long history of separation from other continents has allowed plants and animals on the island to evolve in relative isolation.Along the length of the eastern coast runs a narrow and steep escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escar ...
containing much of the island's remaining tropical lowland forest. To the west of this ridge lies a plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ha ...
in the center of the island ranging in altitude from above sea level. These central highlands, traditionally the homeland of the Merina people
The Merina people (also known as the Imerina, Antimerina, or Hova) are the largest ethnic group in Madagascar.Merina ...
and the location of their historic capital at Antananarivo
Antananarivo ( French: ''Tananarive'', ), also known by its colonial shorthand form Tana, is the capital and largest city of Madagascar. The administrative area of the city, known as Antananarivo-Renivohitra ("Antananarivo-Mother Hill" or "An ...
, are the most densely populated part of the island and are characterized by terraced, rice-growing valleys lying between grassy hills and patches of the subhumid forests that formerly covered the highland region. To the west of the highlands, the increasingly arid terrain gradually slopes down to the Mozambique Channel
The Mozambique Channel (french: Canal du Mozambique, mg, Lakandranon'i Mozambika, pt, Canal de Moçambique) is an arm of the Indian Ocean located between the Southeast African countries of Madagascar and Mozambique. The channel is about long ...
and mangrove swamps
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
along the coast.
Madagascar's highest peaks rise from three prominent highland massif
In geology, a massif ( or ) is a section of a planet's crust that is demarcated by faults or flexures. In the movement of the crust, a massif tends to retain its internal structure while being displaced as a whole. The term also refers to a ...
s: Maromokotro
Maromokotro or MaromokotraMadagascar National Parks
is the highest mountain on < ...
in the is the highest mountain on < ...
Tsaratanana Massif
Madagascar is a large island in the Indian Ocean off the eastern coast of southern Africa, east of Mozambique. It has a total area of with of land and of water. Madagascar is the fourth largest island and the 2nd largest island country in th ...
is the island's highest point, followed by Boby Peak in the Andringitra Massif
The Andringitra Massif ("desert of rocks") is a granite massif located within Andringitra National Park in Madagascar. The range is approximately long. In its central area, the range is almost wide, though it is much narrower on either end. Pic ...
, and Tsiafajavona in the Ankaratra
Ankaratra is a cinder cone volcano range located about southwest of Antananarivo, the capital city of Madagascar. It lies between the towns of Arivonimamo to the north, Ambatolampy to the east, Faratsiho to the west and Betafo to the south. It is ...
Massif. To the east, the ''Canal des Pangalanes
The Canal des Pangalanes is a canal that consists of a series of natural rivers, waterways and human-made lakes that extends for over and runs down the east coast of Madagascar from Mahavelona to Farafangana. It is used primarily for transport ...
'' is a chain of human-made and natural lakes connected by canals built by the French just inland from the east coast and running parallel to it for some .
The western and southern sides, which lie in the rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
of the central highlands, are home to dry deciduous forests, spiny forests, and deserts and xeric shrublands
Deserts and xeric shrublands are a biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Deserts and xeric (ancient Greek xД“rГіs, вҖңdry") shrublands form the largest terrestrial biome, covering 19% of Earth's land surface area. Ecoregions in this ...
. Due to their lower population densities, Madagascar's dry deciduous forests have been better preserved than the eastern rain forests or the original woodlands of the central plateau. The western coast features many protected harbors, but silting is a major problem caused by sediment from the high levels of inland erosion carried by rivers crossing the broad western plains.
Climate
trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
and northwestern monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
s produces a hot rainy season (NovemberвҖ“April) with frequently destructive cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anti ...
s, and a relatively cooler dry season (MayвҖ“October). Rain clouds originating over the Indian Ocean discharge much of their moisture over the island's eastern coast; the heavy precipitation supports the area's rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
ecosystem. The central highlands are both drier and cooler while the west is drier still, and a semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
prevails in the southwest and southern interior of the island.

Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s cause damage to infrastructure and local economies as well as loss of life. In 2004, Cyclone Gafilo
Very Intense Tropical Cyclone Gafilo was both the most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded in the South-West Indian Ocean and the most intense tropical cyclone worldwide in 2004. Being unusually large and intense, Gafilo was the deadliest a ...
became the strongest cyclone ever recorded to hit Madagascar. The storm killed 172 people, left 214,260 homeless and caused more than US$250 million in damage. In February 2022, Cyclone Batsirai
Intense Tropical Cyclone Batsirai was a deadly tropical cyclone which heavily impacted Madagascar in February 2022, becoming the strongest tropical cyclone to strike Madagascar since Cyclone Enawo in 2017. It made landfall two weeks after Trop ...
killed at least 10 people weeks after Cyclone Ana
Tropical Cyclone Ana was one of three tropical cyclones to impact the island nation of Fiji towards the end of January 2021. The fifth tropical disturbance, third tropical cyclone and second severe tropical cyclone of the 2020вҖ“21 South Pacif ...
killed 55 and displaced 130,000 people on the island.
Ecology
As a result of the island's long isolation from neighboring continents, Madagascar is home to variousendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsew ...
plants and animals found nowhere else on Earth. Approximately 90% of all plant and animal species found in Madagascar are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsew ...
. This distinctive ecology has led some ecologists to refer to Madagascar as the "eighth continent", and the island has been classified by Conservation International
Conservation International (CI) is an American nonprofit environmental organization headquartered in Crystal City, Arlington, Virginia.
CI's work focuses on science, policy and partnership with businesses, governments and communities. The organ ...
as a biodiversity hotspot. Madagascar is classed as one of 17 megadiverse countries. The country is home to seven terrestrial ecoregions: Madagascar lowland forests
The Madagascar lowland forests or Madagascar humid forests are a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion found on the eastern coast of the island of Madagascar, home to a plant and animal mix th ...
, Madagascar subhumid forests
The Madagascar subhumid forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion that covers most of the Central Highlands of the island of Madagascar. They are included in the WWF's Global 200 list of outstanding ecoregions. Most of the origin ...
, Madagascar dry deciduous forests
The Madagascar dry deciduous forests represent a tropical dry forest ecoregion situated in the western and northern part of Madagascar. The area has high numbers of endemic plant and animal species but has suffered large-scale clearance for agric ...
, Madagascar ericoid thickets
The Madagascar ericoid thickets is a montane shrubland ecoregion, found at higher altitudes on Madagascar's four major mountains.
Geography
The ecoregion covers the area above 1800 m elevation on (from north to south) Tsaratanana (2,876 m), Maro ...
, Madagascar spiny forests
The Madagascar spiny forests (also known as the Madagascar spiny thickets) is an ecoregion in the southwest of Madagascar. The vegetation type is found on poor substrates with low, erratic winter rainfall. The ecoregion contains an outstanding pr ...
, Madagascar succulent woodlands
The Madagascar succulent woodlands are a xeric shrublands ecoregion in southwestern and central western Madagascar. Native plants survive in the arid climate and long dry season with adaptations like succulent leaves, water storing trunks, photosy ...
, and Madagascar mangroves
Madagascar mangroves are a coastal ecoregion in the mangrove forest biome found on the west coast of Madagascar. They are included in the WWF's Global 200 list of most outstanding ecoregions.
Geography
Mangrove swamps are located in flat coast ...
.
More than 80 percent of Madagascar's 14,883 plant species
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora''.
Ety ...
are found nowhere else in the world, including five plant families. The family ''Didiereaceae
Didiereaceae is a family of flowering plants found in continental Africa and Madagascar.
It contains 20 species classified in three subfamilies and six genera. Species of the family are succulent plants, growing in sub-arid to arid habitats. Seve ...
'', composed of four genera and 11 species, is limited to the spiny forests of southwestern Madagascar. Four-fifths of the world's ''Pachypodium
''Pachypodium'' is a genus of succulent spine-bearing trees and shrubs, native to Madagascar and Africa. It belongs to the family Apocynaceae.
Genus characteristics
All ''Pachypodium'' are succulent plants that exhibit, to varying degrees, the ...
'' species are endemic to the island. Three-fourths of Madagascar's 860 orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant.
Along with the Asteraceae, they are one of the two largest families of flowering ...
species are found here alone, as are six of the world's nine baobab
''Adansonia'' is a genus made up of eight species of medium-to-large deciduous trees known as baobabs ( or ). They are placed in the Malvaceae family, subfamily Bombacoideae. They are native to Madagascar, mainland Africa, and Australia.Tropic ...
species. The island is home to around 170 palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
**List of Arecaceae genera
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music
* Palm (ba ...
species, three times as many as on all of mainland Africa; 165 of them are endemic.Bradt (2011), p. 38 Many native plant species are used as herbal remedies for a variety of afflictions. The drugs vinblastine
Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, bladder ca ...
and vincristine
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin's ...
are ''vinca'' alkaloids, used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated ReedвҖ“Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition wa ...
, leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ' ...
, and other cancers, were derived from the Madagascar periwinkle
''Catharanthus roseus'', commonly known as bright eyes, Cape periwinkle, graveyard plant, Madagascar periwinkle, old maid, pink periwinkle, rose periwinkle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native and endemic to M ...
. The traveler's palm
''Ravenala'' is a genus of monocotyledonous flowering plants. Classically, the genus was considered to include a single species, ''Ravenala madagascariensis'', commonly known as the traveller's tree, traveller's palm or East-West palm, from Mada ...
, known locally as ''ravinala'' and endemic to the eastern rain forests, is highly iconic of Madagascar and is featured in the national emblem as well as the Air Madagascar
''SociГ©tГ© Nationale Malgache de Transports AГ©riens S.A.'',REGLEMENT ...
logo.
 Like its flora, Madagascar's fauna is diverse and exhibits a high rate of endemism. Lemurs have been characterized as "Madagascar's flagship mammal species" by Conservation International. In the absence of monkeys and other competitors, these
Like its flora, Madagascar's fauna is diverse and exhibits a high rate of endemism. Lemurs have been characterized as "Madagascar's flagship mammal species" by Conservation International. In the absence of monkeys and other competitors, these primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
s have adapted to a wide range of habitats and diversified into numerous species. , there were officially 103 species and subspecies of lemur, 39 of which were described by zoologists between 2000 and 2008. They are almost all classified as rare, vulnerable, or endangered. At least 17 species of lemur have become extinct since humans arrived on Madagascar, all of which were larger than the surviving lemur species.
A number of other mammals, including the catlike fossa
Fossa may refer to:
Animals
* Fossa (animal), the common name of a carnivoran mammal of genus ''Cryptoprocta'' endemic to Madagascar
* ''Fossa'', the Latin genus name of the Malagasy civet, a related but smaller mammal endemic to Madagascar
Pla ...
, are endemic to Madagascar. Over 300 species of birds have been recorded on the island, of which over 60 percent (including four families and 42 genera) are endemic. The few families and genera of reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s that have reached Madagascar have diversified into more than 260 species, with over 90 percent of these being endemic (including one endemic family). The island is home to two-thirds of the world's chameleon
Chameleons or chamaeleons (family Chamaeleonidae) are a distinctive and highly specialized clade of Old World lizards with 202 species described as of June 2015. The members of this family are best known for their distinct range of colors, bein ...
species, including the smallest known, and researchers have proposed that Madagascar may be the origin of all chameleons.
Endemic fish of Madagascar include two families, 15 genera and over 100 species, primarily inhabiting the island's freshwater lakes and rivers. Although invertebrates remain poorly studied in Madagascar, researchers have found high rates of endemism among the known species. All 651 species of terrestrial snail are endemic, as are a majority of the island's butterflies, scarab beetles
The family Scarabaeidae, as currently defined, consists of over 30,000 species of beetles worldwide; they are often called scarabs or scarab beetles. The classification of this family has undergone significant change in recent years. Several sub ...
, lacewings
The insect order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order consists of some 6,000 species. Neuroptera can be grouped together with the Megaloptera and Raphidioptera in the ...
, spiders, and dragonflies.
Environmental issues
Madagascar's varied fauna and flora are endangered by human activity. Since the arrival of humans around 2,350 years ago, Madagascar has lost more than 90 percent of its original forest. This forest loss is largely fueled by ''tavy'' ("fat"), a traditionalslash-and-burn
Slash-and-burn agriculture is a farming method that involves the cutting and burning of plants in a forest or woodland to create a field called a swidden. The method begins by cutting down the trees and woody plants in an area. The downed vegeta ...
agricultural practice imported to Madagascar by the earliest settlers. Malagasy farmers embrace and perpetuate the practice not only for its practical benefits as an agricultural technique, but for its cultural associations with prosperity, health and venerated ancestral custom (''fomba malagasy''). As human population density rose on the island, deforestation accelerated beginning around 1,400 years ago. By the 16th century, the central highlands had been largely cleared of their original forests. More recent contributors to the loss of forest cover include the growth in cattle herd size since their introduction around 1,000 years ago, a continued reliance on charcoal as a fuel for cooking, and the increased prominence of coffee as a cash crop
A cash crop or profit crop is an Agriculture, agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate marketed crops from staple crop (or "subsistence crop") ...
over the past century.Emoff (2004), pp. 51вҖ“62 Madagascar had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 4.63/10, ranking it 119th globally out of 172 countries.
According to a conservative estimate, about 40 percent of the island's original forest cover was lost from the 1950s to 2000, with a thinning of remaining forest areas by 80 percent. In addition to traditional agricultural practice, wildlife conservation is challenged by the illicit harvesting of protected forests, as well as the state-sanctioned harvesting of precious woods within national parks. Although banned by then-President Marc Ravalomanana
Marc Ravalomanana (; born 12 December 1949) is a Malagasy politician who was the President of Madagascar from 2002 to 2009. Born into a farming Merina family in Imerinkasinina, near the capital city of Antananarivo, Ravalomanana first rose to ...
from 2000 to 2009, the collection of small quantities of precious timber from national parks was re-authorized in January 2009 and dramatically intensified under the administration of Andry Rajoelina
Andry Nirina Rajoelina (Malagasy: ; born 30 May 1974) is a Malagasy politician and businessman who has been the president of Madagascar since 2019. He was previously president of a provisional government from 2009 to 2014 following a political ...
as a key source of state revenues to offset cuts in donor support following Ravalomanana's ousting.
Invasive species have likewise been introduced by human populations. Following the 2014 discovery in Madagascar of the Asian common toad
''Duttaphrynus melanostictus'' is commonly called Asian common toad, Asian black-spined toad, Asian toad, black-spectacled toad, common Sunda toad, and Javanese toad. It is probably a complex of more than one true toad species that is widely d ...
, a relative of a toad species that has severely harmed wildlife in Australia since the 1930s, researchers warned the toad could "wreak havoc on the country's unique fauna." Habitat destruction and hunting have threatened many of Madagascar's endemic species or driven them to extinction. The island's elephant bird
Elephant birds are members of the extinct ratite family Aepyornithidae, made up of flightless birds that once lived on the island of Madagascar. They are thought to have become extinct around 1000-1200 CE, probably as a result of human activity. ...
s, a family of endemic giant ratite
A ratite () is any of a diverse group of flightless, large, long-necked, and long-legged birds of the infraclass Palaeognathae. Kiwi, the exception, are much smaller and shorter-legged and are the only nocturnal extant ratites.
The systematics ...
s, became extinct in the 17th century or earlier, most probably because of human hunting of adult birds and poaching of their large eggs for food.Davies (2003), pp. 99вҖ“101 Numerous giant lemur
Subfossil lemurs are lemurs from Madagascar that are represented by recent (subfossil) remains dating from nearly 26,000 years ago to approximately 560 years ago (from the late Pleistocene until the Holocene). They include both extant ...
species vanished with the arrival of human settlers to the island, while others became extinct over the course of the centuries as a growing human population put greater pressures on lemur habitats and, among some populations, increased the rate of lemur hunting for food. A July 2012 assessment found that the exploitation of natural resources since 2009 has had dire consequences for the island's wildlife: 90 percent of lemur species were found to be threatened with extinction, the highest proportion of any mammalian group. Of these, 23 species were classified as critically endangered. By contrast, a previous study in 2008 had found only 38 percent of lemur species were at risk of extinction.
In 2003, Ravalomanana announced the Durban Vision, an initiative to more than triple the island's protected natural areas to over or 10 percent of Madagascar's land surface. , areas protected by the state included five Strict Nature Reserves (''RГ©serves Naturelles IntГ©grales''), 21 Wildlife Reserves (''RГ©serves SpГ©ciales'') and 21 National Parks (''Parcs Nationaux''). In 2007 six of the national parks were declared a joint World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
under the name Rainforests of the Atsinanana
The Rainforests of the Atsinanana is a World Heritage Site that was inscribed in 2007 and consists of 13 specific areas in six national parks in the eastern part of Madagascar:
# Marojejy National Park
# Masoala National Park
# Zahamena National ...
. These parks are Marojejy
Marojejy National Park () is a national park in the Sava region of northeastern Madagascar. It covers and is centered on the Marojejy Massif, a mountain chain that rises to an elevation of . Access to the area around the massif was restricted ...
, Masoala
''Masoala'' is a genus of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. It contains the following species, both endemic to Madagascar:Jumelle, Henri Lucien. 1933. Annales du MusГ©e Colonial de Marseille, sГ©r. 5, 1(1): 8.
* ''Masoala kona'' Beentje ...
, Ranomafana, Zahamena, Andohahela and Andringitra. Local timber merchants are harvesting scarce species of rosewood trees from protected rainforests within Marojejy National Park and exporting the wood to China for the production of luxury furniture and musical instruments. To raise public awareness of Madagascar's environmental challenges, the Wildlife Conservation Society
The Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) is a non-governmental organization headquartered at the Bronx Zoo in New York City, that aims to conserve the world's largest wild places in 14 priority regions. Founded in 1895 as the New York Zoological ...
opened an exhibit entitled "''Madagascar!''" in June 2008 at the Bronx Zoo
The Bronx Zoo (also historically the Bronx Zoological Park and the Bronx Zoological Gardens) is a zoo within Bronx Park in the Bronx, New York. It is one of the largest zoos in the United States by area and is the largest metropolitan zoo in ...
in New York.
Mid-2021 marked the beginning of the 2021вҖ“2022 Madagascar famine
In mid-2021, a severe drought in southern Madagascar caused hundreds of thousands of people, with some estimating more than 1 million people, to suffer from food insecurity or famine. Some organizations have attributed the situation to the impac ...
which, due to a severe drought, caused hundreds of thousands of people to face food insecurity
Food security speaks to the availability of food in a country (or geography) and the ability of individuals within that country (geography) to access, afford, and source adequate foodstuffs. According to the United Nations' Committee on World F ...
and over one million people were on the verge of a famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
.
A 2022 analysis found that the expected costs for Madagascar, to adapt to and avert the environmental consequences of climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warmingвҖ”the ongoing increase in global average temperatureвҖ”and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
, are going to be high.
Government
Structure
 Madagascar is a
Madagascar is a semi-presidential
A semi-presidential republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has a ...
representative democratic
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
multi-party
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system in which multiple political parties across the political spectrum run for national elections, and all have the capacity to gain control of government offices, separately or in c ...
republic, wherein the popularly elected president is the head of state and selects a prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
, who recommends candidates to the president to form his cabinet of ministers. According to the constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
, executive power is exercised by the government while legislative power is vested in the ministerial cabinet, the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repre ...
, although in reality these two latter bodies have very little power or legislative role. The constitution establishes independent executive, legislative and judicial branches and mandates a popularly elected president limited to three five-year terms.
The public directly elects the president and the 127 members of the National Assembly to five-year terms. All 33 members of the Senate serve six-year terms, with 22 senators elected by local officials and 11 appointed by the president. The last National Assembly election was held on 20 December 2013 and the last Senate election was held on 30 December 2015.
At the local level, the island's 22 provinces are administered by a governor and provincial council. Provinces are further subdivided into regions and communes. The judiciary is modeled on the French system, with a High Constitutional Court, High Court of Justice, Supreme Court, Court of Appeals, criminal tribunals, and tribunals of first instance.Nalla (2010), pp. 122вҖ“128 The courts, which adhere to civil law, lack the capacity to quickly and transparently try the cases in the judicial system, often forcing defendants to pass lengthy pretrial detentions in unsanitary and overcrowded prisons.
Antananarivo is the administrative capital and largest city of Madagascar. It is located in the highlands region, near the geographic center of the island. King Andrianjaka founded Antananarivo as the capital of his Imerina Kingdom around 1610 or 1625 upon the site of a captured Vazimba capital on the hilltop of Analamanga Analamanga is a region in central Madagascar, containing the capital Antananarivo and its surrounding metropolitan area. The region has an area of , and had a population of 3,618,128 in 2018.
Administrative divisions
Analamanga Region is divided in ...
. As Merina dominance expanded over neighboring Malagasy peoples in the early 19th century to establish the Kingdom of Madagascar, Antananarivo became the center of administration for virtually the entire island. In 1896 the French colonizers of Madagascar adopted the Merina capital as their center of colonial administration. The city remained the capital of Madagascar after regaining independence in 1960. In 2017, the capital's population was estimated at 1,391,433 inhabitants. The next largest cities are Antsirabe
Antsirabe () is the third largest city in Madagascar and the capital of the Vakinankaratra region, with a population of 265,018 in 2014.
In Madagascar, Antsirabe is known for its relatively cool climate (like the rest of the central region), it ...
(500,000), Toamasina
Toamasina (), meaning "like salt" or "salty", unofficially and in French Tamatave, is the capital of the Atsinanana region on the east coast of Madagascar on the Indian Ocean. The city is the chief seaport of the country, situated northeast of it ...
(450,000) and Mahajanga
Mahajanga (French: Majunga) is a city and an administrative district on the northwest coast of Madagascar. The city of Mahajanga (Mahajanga I) is the capital of the Boeny Region. The district (identical to the city) had a population of 220,629 i ...
(400,000).
Politics
 Since Madagascar gained independence from France in 1960, the island's political transitions have been marked by numerous popular protests, several disputed elections, an impeachment, two military coups and one assassination. The island's recurrent political crises are often prolonged, with detrimental effects on the local economy, international relations and Malagasy living standards. The eight-month standoff between incumbent Ratsiraka and challenger Marc Ravalomanana following the 2001 presidential elections cost Madagascar millions of dollars in lost tourism and trade revenue as well as damage to infrastructure, such as bombed bridges and buildings damaged by arson. A series of protests led by Andry Rajoelina against Ravalomanana in early 2009 became violent, with more than 170 people killed. Modern politics in Madagascar are colored by the history of Merina subjugation of coastal communities under their rule in the 19th century. The consequent tension between the highland and coastal populations has periodically flared up into isolated events of violence.
Madagascar has historically been perceived as being on the margin of mainstream African affairs despite being a founding member of the
Since Madagascar gained independence from France in 1960, the island's political transitions have been marked by numerous popular protests, several disputed elections, an impeachment, two military coups and one assassination. The island's recurrent political crises are often prolonged, with detrimental effects on the local economy, international relations and Malagasy living standards. The eight-month standoff between incumbent Ratsiraka and challenger Marc Ravalomanana following the 2001 presidential elections cost Madagascar millions of dollars in lost tourism and trade revenue as well as damage to infrastructure, such as bombed bridges and buildings damaged by arson. A series of protests led by Andry Rajoelina against Ravalomanana in early 2009 became violent, with more than 170 people killed. Modern politics in Madagascar are colored by the history of Merina subjugation of coastal communities under their rule in the 19th century. The consequent tension between the highland and coastal populations has periodically flared up into isolated events of violence.
Madagascar has historically been perceived as being on the margin of mainstream African affairs despite being a founding member of the Organisation of African Unity
The Organisation of African Unity (OAU; french: Organisation de l'unitГ© africaine, OUA) was an intergovernmental organization established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, with 32 signatory governments. One of the main heads for OAU's ...
, which was established in 1963 and dissolved in 2002 to be replaced by the African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
. Madagascar was not permitted to attend the first African Union summit because of a dispute over the results of the 2001 presidential election, but rejoined the African Union in July 2003 after a 14-month hiatus. Madagascar was again suspended by the African Union in March 2009 following the unconstitutional transfer of executive power to Rajoelina. Madagascar is a member of the International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals ...
with a Bilateral Immunity Agreement of protection for the United States military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is the ...
. Eleven countries have established embassies in Madagascar, including France, the United Kingdom, the United States, China and India, while Madagascar has embassies in sixteen other countries.
Human rights in Madagascar are protected under the constitution and the state is a signatory to numerous international agreements including the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal De ...
and the Convention on the Rights of the Child
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (commonly abbreviated as the CRC or UNCRC) is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The Con ...
. Religious, ethnic and sexual minorities are protected under the law. Freedom of association and assembly are also guaranteed under the law, although in practice the denial of permits for public assembly has occasionally been used to impede political demonstrations. Torture by security forces is rare and state repression is low relative to other countries with comparably few legal safeguards, although arbitrary arrests and the corruption of military and police officers remain problems. Ravalomanana's 2004 creation of BIANCO, an anti-corruption bureau, resulted in reduced corruption among Antananarivo's lower-level bureaucrats in particular, although high-level officials have not been prosecuted by the bureau. Accusations of media censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments ...
have risen due to the alleged restrictions on the coverage of government opposition. Some journalists have been arrested for allegedly spreading fake news
Fake news is false or misleading information presented as news. Fake news often has the aim of damaging the reputation of a person or entity, or making money through advertising revenue.Schlesinger, Robert (April 14, 2017)"Fake news in reality ...
.
Military and law enforcement
The rise of centralized kingdoms among the Sakalava, Merina and other ethnic groups produced the island's first standing armies by the 16th century, initially equipped with spears but later with muskets, cannons and other firearms. By the early 19th century, the Merina sovereigns of the Kingdom of Madagascar had brought much of the island under their control by mobilizing an army of trained and armed soldiers numbering as high as 30,000.Freeman & Johns (1840), p. 25 French attacks on coastal towns in the later part of the century prompted then-Prime Minister Rainilaiarivony to solicit British assistance to provide training to the Merina monarchy's army. Despite the training and leadership provided by British military advisers, the Malagasy army was unable to withstand French weaponry and was forced to surrender following an attack on the royal palace at Antananarivo. Madagascar was declared a colony of France in 1897. The political independence and sovereignty of the Malagasy armed forces, which comprises an army, navy and air force, was restored with independence from France in 1960. Since this time the Malagasy military has never engaged in armed conflict with another state or within its own borders, but has occasionally intervened to restore order during periods of political unrest. Under the socialist Second Republic, Admiral Didier Ratsiraka instated mandatory national armed or civil service for all young citizens regardless of sex, a policy that remained in effect from 1976 to 1991. The armed forces are under the direction of the Minister of Defense and have remained largely neutral during times of political crisis, as during the protracted standoff between incumbent Ratsiraka and challenger Marc Ravalomanana in the disputed 2001 presidential elections, when the military refused to intervene in favor of either candidate. This tradition was broken in 2009, when a segment of the army defected to the side of Andry Rajoelina, then-mayor of Antananarivo, in support of his attempt to force President Ravalomanana from power. The Minister of Interior is responsible for the national police force, paramilitary force (''gendarmerie'') and the secret police. The police and gendarmerie are stationed and administered at the local level. However, in 2009 fewer than a third of all communes had access to the services of these security forces, with most lacking local-level headquarters for either corps. Traditional community tribunals, called ''dina'', are presided over by elders and other respected figures and remain a key means by which justice is served in rural areas where state presence is weak. Historically, security has been relatively high across the island. Violent crime rates are low, and criminal activities are predominantly crimes of opportunity such as pickpocketing and petty theft, although child prostitution, human trafficking and the production and sale of marijuana and other illegal drugs are increasing. Budget cuts since 2009 have severely impacted the national police force, producing a steep increase in criminal activity in recent years.Administrative divisions
United Nations involvement
Madagascar became a member state of the United Nations on 20 September 1960, shortly after gaining its independence on 26 June 1960. As of January 2017, 34 police officers from Madagascar are deployed in Haiti as part of theUnited Nations Stabilisation Mission in Haiti
)
, leader_title = Head
, leader_name = Sandra HonorГ© (Special Representative of the Secretary-General)
, status = Replaced by MINUJUSTH
, formation = 1 June 2004
, websiteUN Peacekeeping: MINUSTAH
. Starting in 2015, under the direction of and with assistance from the UN, the World Food Programme started the Madagascar Country Programme with the two main goals of long-term development and reconstruction efforts, and addressing the food insecurity issues in the southern regions of Madagascar. These goals plan to be accomplished by providing meals for specific schools in rural and urban priority areas and by developing national school feeding policies to increase consistency of nourishment throughout the country. Small and local farmers have also been assisted in increasing both the quantity and quality of their production, as well as improving their crop yield in unfavorable weather conditions. In 2017, Madagascar signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW), or the Nuclear Weapon Ban Treaty, is the first legally binding international agreement to comprehensively prohibit nuclear weapons with the ultimate goal being their total elimination. It ...
.
Economy
Millennium Challenge Account
The Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) is a bilateral United States foreign aid agency established by the U.S. Congress in 2004. It is an independent agency separate from the State Department and USAID. It provides grants to countries that ...
in 2005.
 Madagascar's GDP in 2015 was estimated at US$9.98 billion, with a per capita GDP of $411.82. Approximately 69 percent of the population lives below the national poverty line threshold of one dollar per day. During 2011вҖ“15, the average growth rate was 2.6% but was expected to have reached 4.1% in 2016, due to public works programs and a growth of the service sector. The agriculture sector constituted 29 percent of Malagasy GDP in 2011, while manufacturing formed 15 percent of GDP. Madagascar's other sources of growth are tourism, agriculture and the extractive industries. Tourism focuses on the niche eco-tourism market, capitalizing on Madagascar's unique biodiversity, unspoiled natural habitats, national parks and lemur species. An estimated 365,000 tourists visited Madagascar in 2008, but the sector declined during the political crisis with 180,000 tourists visiting in 2010. However, the sector has been growing steadily for a few years; In 2016, 293,000 tourists landed in the African island with an increase of 20% compared to 2015; For 2017 the country has the goal of reaching 366,000 visitors, while for 2018 government estimates are expected to reach 500,000 annual tourists.
The island is still a very poor country in 2018; structural brakes remain in the development of the economy: corruption and the shackles of the public administration, lack of legal certainty, and backwardness of land legislation. The economy, however, has been growing since 2011, with GDP growth exceeding 4% per year; almost all economic indicators are growing, the GDP per capita was around $1600 (PPP) for 2017, one of the lowest in the world, although growing since 2012; unemployment was also cut, which in 2016 was equal to 2.1% with a work force of 13.4 million as of 2017. The main economic resources of Madagascar are
Madagascar's GDP in 2015 was estimated at US$9.98 billion, with a per capita GDP of $411.82. Approximately 69 percent of the population lives below the national poverty line threshold of one dollar per day. During 2011вҖ“15, the average growth rate was 2.6% but was expected to have reached 4.1% in 2016, due to public works programs and a growth of the service sector. The agriculture sector constituted 29 percent of Malagasy GDP in 2011, while manufacturing formed 15 percent of GDP. Madagascar's other sources of growth are tourism, agriculture and the extractive industries. Tourism focuses on the niche eco-tourism market, capitalizing on Madagascar's unique biodiversity, unspoiled natural habitats, national parks and lemur species. An estimated 365,000 tourists visited Madagascar in 2008, but the sector declined during the political crisis with 180,000 tourists visiting in 2010. However, the sector has been growing steadily for a few years; In 2016, 293,000 tourists landed in the African island with an increase of 20% compared to 2015; For 2017 the country has the goal of reaching 366,000 visitors, while for 2018 government estimates are expected to reach 500,000 annual tourists.
The island is still a very poor country in 2018; structural brakes remain in the development of the economy: corruption and the shackles of the public administration, lack of legal certainty, and backwardness of land legislation. The economy, however, has been growing since 2011, with GDP growth exceeding 4% per year; almost all economic indicators are growing, the GDP per capita was around $1600 (PPP) for 2017, one of the lowest in the world, although growing since 2012; unemployment was also cut, which in 2016 was equal to 2.1% with a work force of 13.4 million as of 2017. The main economic resources of Madagascar are tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
, textiles
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, and mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
.
Poverty affects 92% of the population in 2017. The country ranks fourth in the world in terms of chronic malnutrition. Nearly one in two children under the age of five is stunted. In addition, Madagascar is among the five countries where access to water is the most difficult for the population. Twelve million people do not have access to clean water, according to the NGO WaterAid.
Natural resources and trade
 Madagascar's natural resources include a variety of agricultural and mineral products. Agriculture (including the growing of
Madagascar's natural resources include a variety of agricultural and mineral products. Agriculture (including the growing of raffia
Raffia palms (''Raphia'') are a genus of about twenty species of palms native to tropical regions of Africa, and especially Madagascar, with one species (''R. taedigera'') also occurring in Central and South America. ''R. taedigera'' is the sour ...
), mining, fishing and forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. Th ...
are mainstays of the economy. In 2017 the top exports were vanilla (US$894M), nickel metal (US$414M), cloves (US$288M), knitted sweaters (US$184M) and cobalt (US$143M).
Madagascar is the world's principal supplier of vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the p ...
, cloves and ylang-ylang
''Cananga odorata'', known as ylang-ylang ( ) or cananga tree, is a tropical tree that is native to the Philippines, Malaysia, Indonesia, New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, and Queensland, Australia. It is also native to parts of Thailand and Viet ...
. The island supplies 80% of the world's natural vanilla. Other key agricultural resources include coffee, lychee
Lychee (US: ; UK: ; ''Litchi chinensis''; ) is a Monotypic taxon, monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus ''Litchi'' in the Sapindus, soapberry family, ''Sapindaceae''.
It is a tropical tree native to Southeast and Southwest China (t ...
s and shrimp. Key mineral resources include various types of precious and semi-precious stones, and it currently provides half of the world's supply of sapphires, which were discovered near Ilakaka
Ilakaka is a small town in Ihorombe Region in the south western part of Madagascar. In the early 1990s there were only about 40 residents in the area. After the discovery of one of Earth's largest known alluvial sapphire deposits in the valley of ...
in the late 1990s.
Madagascar has one of the world's largest reserves of ilmenite
Ilmenite is a titanium-iron oxide mineral with the idealized formula . It is a weakly magnetic black or steel-gray solid. Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing ...
(titanium ore), as well as important reserves of chromite, coal, iron, cobalt, copper and nickel. Several major projects are underway in the mining, oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
and gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
sectors that are anticipated to give a significant boost to the Malagasy economy. These include such projects as ilmenite and zircon mining from heavy mineral sands near TГҙlanaro
Fort-Dauphin (Malagasy Tolagnaro or Taolagnaro) is a city (''commune urbaine'') on the southeast coast of Madagascar. It is the capital of the Anosy Region and of the Taolagnaro District. It has been a port of local importance since the early 1500 ...
by Rio Tinto Rio Tinto, meaning "red river", may refer to:
Businesses
* Rio Tinto (corporation), an Anglo-Australian multinational mining and resources corporation
** Rio Tinto Alcan, based in Canada
** Rio Tinto Borax in America
*** Rio Tinto Borax Mine, a ...
, extraction of nickel by the Ambatovy mine
The Ambatovy mine is large nickel and cobalt mine located in Madagascar, off the east coast of Africa. It is currently active, and the largest mine in the country.
Ownership and operations
Several exploration permits for the site were acquired ...
near Moramanga
Moramanga is a city (commune urbaine) in Madagascar. It is located in the region Alaotra-Mangoro and the Moramanga District.
It has a population of 57084 inhabitants (2018).
It is situated between the capital Antananarivo and the east coast on t ...
and its processing near Toamasina by Sherritt International
Sherritt International is a Canadian resource company, based in Toronto, Ontario. Sherritt is a world leader in the mining and refining of nickel and cobalt вҖ“ metals essential for the growing adoption of electric vehicles. Its Technologies Grou ...
, and the development of the giant onshore heavy oil deposits at Tsimiroro
Tsimiroro is a large oil field in the onshore Morondava Basin of Madagascar found south of the Bemolanga ultra heavy oil field and south of the town of Morafenobe. It is estimated to contain as many as of heavy oil with 14В° to 16В° API gravit ...
and Bemolanga
Bemolanga is a large oil sands deposit in the onshore Morondava Basin of Madagascar. The deposit was discovered in the early 1900s but was known to locals for centuries. The field is located north of the Tsimiroro heavy oil field and east of th ...
by Madagascar Oil
Madagascar Oil SA is an oil company operating in Madagascar. It is the principal onshore oil company in Madagascar in terms of oil resources and land.
Madagascar Oil's operational office is in Antananarivo, Madagascar and its administrative off ...
.
Exports formed 28 percent of GDP in 2009. Most of the country's export revenue is derived from the textiles industry, fish and shellfish, vanilla, cloves and other foodstuffs. France is the nation's main trading partner, although the United States, Japan and Germany also have strong economic ties. The Madagascar-U.S. Business Council was formed in May 2003, as a collaboration between USAID
The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $27 bi ...
and Malagasy artisan producers to support the export of local handicrafts to foreign markets. Imports of such items as foodstuffs, fuel, capital goods, vehicles, consumer goods and electronics consume an estimated 52 percent of GDP. The main sources of Madagascar's imports include China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, France, Iran, Mauritius and Hong Kong.
Infrastructure and media
Air Madagascar
''SociГ©tГ© Nationale Malgache de Transports AГ©riens S.A.'',REGLEMENT ...
services the island's many small regional airports, which offer the only practical means of access to many of the more remote regions during rainy season road washouts.
Running water and electricity are supplied at the national level by a government service provider, Jirama
Jirama ( ''Jiro sy rano malagasy'') is a state-owned electric utility and water services company in Madagascar.
History
The Jirama was established on 17 October 1975 when the SociГ©tГ© Malagasy des Eaux et ElectricitГ© and the SociГ©tГ© des En ...
, which is unable to service the entire population. , only 6.8 percent of Madagascar's ''fokontany'' had access to water provided by Jirama, while 9.5 percent had access to its electricity services. Fifty-six percent of Madagascar's power is provided by hydroelectric power plants, with the remaining 44% provided by diesel engine generators. Mobile telephone and internet access are widespread in urban areas but remain limited in rural parts of the island. Approximately 30% of the districts are able to access the nations' several private telecommunications networks via mobile telephones or land lines.
Radio broadcasts remain the principal means by which the Malagasy population access international, national, and local news. Only state radio broadcasts are transmitted across the entire island. Hundreds of public and private stations with local or regional range provide alternatives to state broadcasting. In addition to the state television channel, a variety of privately owned television stations broadcast local and international programming throughout Madagascar. Several media outlets are owned by political partisans or politicians themselves, including the media groups MBS (owned by Ravalomanana) and Viva (owned by Rajoelina), contributing to political polarization in reporting.
The media have historically come under varying degrees of pressure to censor their criticism of the government. Reporters are occasionally threatened or harassed, and media outlets are periodically forced to close. Accusations of media censorship have increased since 2009 because of the alleged intensification of restrictions on political criticism. Access to the internet has grown dramatically over the past decade, with an estimated 352,000 residents of Madagascar accessing the internet from home or in one of the nation's many internet cafГ©s in December 2011.
Health
Medical centers, dispensaries, and hospitals are found throughout the island, although they are concentrated in urban areas and particularly in Antananarivo. Access to medical care remains beyond the reach of many Malagasy, especially in the rural areas, and many recourse to traditional healers. In addition to the high expense of medical care relative to the average Malagasy income, the prevalence of trained medical professionals remains extremely low. In 2010, Madagascar had an average of three hospital beds per 10,000 people and a total of 3,150 doctors, 5,661 nurses, 385 community health workers, 175 pharmacists, and 57 dentists for a population of 22 million. Fifteen percent of government spending in 2008 was directed toward the health sector. Approximately 70 percent of spending on health was contributed by the government, while 30 percent originated with international donors and other private sources. The government provides at least one basic health center per commune. Private health centers are concentrated within urban areas and particularly those of the central highlands. Despite these barriers to access, health services have shown a trend toward improvement over the past twenty years. Child immunizations against such diseases ashepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the ''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. Fo ...
, diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and s ...
, and measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10вҖ“12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7вҖ“10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
increased an average of 60 percent in this period, indicating low but increasing availability of basic medical services and treatments. The Malagasy fertility rate in 2009 was 4.6 children per woman, declining from 6.3 in 1990. Teen pregnancy rates of 14.8 percent in 2011, much higher than the African average, are a contributing factor to rapid population growth. In 2010, the maternal mortality rate was 440 per 100,000 births, compared to 373.1 in 2008 and 484.4 in 1990, indicating a decline in perinatal care following the 2009 coup. The infant mortality rate in 2011 was 41 per 1,000 births, with an under-five mortality rate at 61 per 1,000 births. Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. The urinary tract or the intestines may be infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody s ...
, malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
, and sexually transmitted diseases are common in Madagascar, although infection rates of AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual m ...
remain low relative to many countries in mainland Africa, at 0.2 percent of the adult population. The malaria mortality rate is also among the lowest in Africa at 8.5 deaths per 100,000 people, in part because of the highest frequency use of insecticide treated nets in Africa. Adult life expectancy in 2009 was 63 years for men and 67 years for women.
Madagascar had outbreaks
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire ...
of the bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well a ...
and pneumonic plague
Pneumonic plague is a severe lung infection caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. Symptoms include fever, headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing. They typically start about three to seven days after exposure. It is one o ...
in 2017 (2575 cases, 221 deaths) and 2014 (263 confirmed cases, 71 deaths). In 2019, Madagascar had a measles outbreak, resulting in 118,000 cases and 1,688 deaths. In 2020, Madagascar was also affected by the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
. Undernourishment and hunger rates were at 42% in 2018. According to the United Nations, more than one million people in southern Madagascar are struggling to get enough to eat, due to what could become the first famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, Demographic trap, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. Th ...
caused by climate change.
Education
Prior to the 19th century, all education in Madagascar was informal and typically served to teach practical skills as well as social and cultural values, including respect for ancestors and elders. The first formal European-style school was established in 1818 atToamasina
Toamasina (), meaning "like salt" or "salty", unofficially and in French Tamatave, is the capital of the Atsinanana region on the east coast of Madagascar on the Indian Ocean. The city is the chief seaport of the country, situated northeast of it ...
by members of the London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was an interdenominational evangelical missionary society formed in England in 1795 at the instigation of Welsh Congregationalist minister Edward Williams. It was largely Reformed in outlook, with Congregational miss ...
(LMS). The LMS was invited by King Radama I to expand its schools throughout Imerina to teach basic literacy and numeracy to aristocratic children. The schools were closed by Ranavalona I in 1835,Ralibera (1993), p. 196 but reopened and expanded in the decades after her death.
By the end of the 19th century, Madagascar had the most developed and modern school system in pre-colonial Sub-Saharan Africa. Access to schooling was expanded in coastal areas during the colonial period, with French language and basic work skills becoming the focus of the curriculum. During the post-colonial First Republic, a continued reliance on French nationals as teachers, and French as the language of instruction, displeased those desiring a complete separation from the former colonial power. Consequently, under the socialist Second Republic, French instructors and other nationals were expelled, Malagasy was declared the language of instruction, and a large cadre of young Malagasy were rapidly trained to teach at remote rural schools under the mandatory two-year national service policy.
This policy, known as ''malgachization'', coincided with a severe economic downturn and a dramatic decline in the quality of education. Those schooled during this period generally failed to master the French language or many other subjects and struggled to find employment, forcing many to take low-paying jobs in the informal or black market that mired them in deepening poverty. Excepting the brief presidency of Albert Zafy, from 1992 to 1996, Ratsiraka remained in power from 1975 to 2001 and failed to achieve significant improvements in education throughout his tenure.
Education was prioritized under the Ravalomanana administration (2002вҖ“09), and is currently free and compulsory from ages 6 to 13. The primary schooling cycle is five years, followed by four years at the lower secondary level and three years at the upper secondary level. During Ravalomanana's first term, thousands of new primary schools and additional classrooms were constructed, older buildings were renovated, and tens of thousands of new primary teachers were recruited and trained. Primary school fees were eliminated, and kits containing basic school supplies were distributed to primary students.
Government school construction initiatives have ensured at least one primary school per ''fokontany'' and one lower secondary school within each commune. At least one upper secondary school is located in each of the larger urban centers. The three branches of the national public university are located at Antananarivo, Mahajanga, and Fianarantsoa. These are complemented by public teacher-training colleges and several private universities and technical colleges.
As a result of increased educational access, enrollment rates more than doubled between 1996 and 2006. However, education quality is weak, producing high rates of grade repetition and dropout. Education policy in Ravalomanana's second term focused on quality issues, including an increase in minimum education standards for the recruitment of primary teachers from a middle school leaving certificate (BEPC) to a high school leaving certificate (BAC), and a reformed teacher training program to support the transition from traditional didactic instruction to student-centered teaching methods to boost student learning and participation in the classroom. Public expenditure on education was 2.8 percent of GDP in 2014. The literacy rate is estimated at 64.7%.
Demographics
 Agriculture has long influenced settlement on the island. Only 15% of the nation's 24,894,551 population live in the 10 largest cities.
In , the population of Madagascar was estimated at million, up from 2.2 million in 1900. The annual population growth rate in Madagascar was approximately 2.9 percent in 2009.
Approximately 42.5 percent of the population is younger than 15 years of age, while 54.5 percent are between the ages of 15 and 64. Those aged 65 and older form 3 percent of the total population. Only two general censuses, in 1975 and 1993, have been carried out after independence. The most densely populated regions of the island are the eastern highlands and the eastern coast, contrasting most dramatically with the sparsely populated western plains.
Agriculture has long influenced settlement on the island. Only 15% of the nation's 24,894,551 population live in the 10 largest cities.
In , the population of Madagascar was estimated at million, up from 2.2 million in 1900. The annual population growth rate in Madagascar was approximately 2.9 percent in 2009.
Approximately 42.5 percent of the population is younger than 15 years of age, while 54.5 percent are between the ages of 15 and 64. Those aged 65 and older form 3 percent of the total population. Only two general censuses, in 1975 and 1993, have been carried out after independence. The most densely populated regions of the island are the eastern highlands and the eastern coast, contrasting most dramatically with the sparsely populated western plains.
Ethnic groups
The Malagasy ethnic group forms over 90 percent of Madagascar's population and is typically divided into 18 ethnic subgroups. Recent DNA research revealed that the genetic makeup of the average Malagasy person constitutes an approximately equal blend ofSoutheast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
n and East African genes, although the genetics of some communities show a predominance of Southeast Asian or East African origins or some Arab, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, or European ancestry.Adelaar (2006), pp. 205вҖ“235
Southeast Asian features вҖ“ specifically from the southern part of Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
вҖ“ are most predominant among the Merina
The Merina people (also known as the Imerina, Antimerina, or Hova) are the largest ethnic group in Madagascar.Merina ...
of the central highlands, who form the largest Malagasy ethnic subgroup at approximately 26 percent of the population, while certain communities among the coastal peoples (collectively called ''cГҙtiers'') have relatively stronger East African features. The largest coastal ethnic subgroups are the Betsimisaraka (14.9 percent) and the Tsimihety
The Tsimihety are a Malagasy ethnic group who are found in the north-central region of Madagascar.Tsimihety
E ...
and E ...
Sakalava
The Sakalava are an ethnic groups of Madagascar, ethnic group of Madagascar. They are found on the western and northwest region of the island, in a band along the coast. The Sakalava are one of the smaller ethnic groups, constituting about 6.2 pe ...
(6 percent each).
Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
and Comoran minorities are present in Madagascar, as well as a small European (primarily French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
) populace. Emigration in the late 20th century has reduced these minority populations, occasionally in abrupt waves, such as the exodus of Comorans in 1976, following anti-Comoran riots in Mahajanga. By comparison, there has been no significant emigration of Malagasy peoples. The number of Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (2004) ...
has declined since independence, reduced from 68,430 in 1958 to 17,000 three decades later. There were an estimated 25,000 Comorans, 18,000 Indians, and 9,000 Chinese living in Madagascar in the mid-1980s.
Largest cities
Languages
 The Malagasy language is of
The Malagasy language is of Malayo-Polynesian
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast ...
origin and is generally spoken throughout the island. The numerous dialects of Malagasy, which are generally mutually intelligible, can be clustered under one of two subgroups: eastern Malagasy, spoken along the eastern forests and highlands including the Merina dialect of Antananarivo, and western Malagasy, spoken across the western coastal plains. The Malagasy language
Malagasy (; ) is an Austronesian language and the national language of Madagascar. Malagasy is the westernmost Malayo-Polynesian language, brought to Madagascar by the settlement of Austronesian peoples from the Sunda islands around the 5th ce ...
derives from the Southeast Barito languages
The Barito languages are around twenty Austronesian languages of Indonesia (Borneo), Southern Philippines, plus Malagasy, the national language of Madagascar. They are named after the Barito River located in South Kalimantan, Indonesia.
The ...
, with the Ma'anyan language
Ma'anyan or Ma'anjan or Maanyak Dayak is an Austronesian language belonging to the East Barito languages. It is spoken by about 150,000 Ma'anyan people (subgroup of Dayak people) living in the province of Central Kalimantan and South Kalimant ...
being its closest relative, incorporating numerous Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
and Javanese loanwords. French became the official language during the colonial period, when Madagascar came under the authority of France. In the first national Constitution of 1958, Malagasy and French were named the official languages of the Malagasy Republic. Madagascar is a francophone
French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, by which time French was the l ...
country, and French is mostly spoken as a second language among the educated population and used for international communication.
No official languages were mentioned in the Constitution of 1992, although Malagasy was identified as the national language. Nonetheless, many sources still claimed that Malagasy and French were official languages, eventually leading a citizen to initiate a legal case against the state in April 2000, on the grounds that the publication of official documents only in the French language was unconstitutional. The High Constitutional Court observed in its decision that, in the absence of a language law, French still had the character of an official language.
In the Constitution of 2007, Malagasy remained the national language while official languages were reintroduced: Malagasy, French, and English. English was removed as an official language from the constitution approved by voters in the November 2010 referendum. The outcome of the referendum, and its consequences for official and national language policy, are not recognized by the political opposition, who cite lack of transparency and inclusiveness in the way the election was organized by the High Transitional Authority
The High Transitional Authority ( Malagasy: ''Fitondrana Avon'ny Tetezamita'' (FAT); french: Haute autoritГ© de transition or HAT) was a provisional executive body that came to power in Madagascar following the coup that forced Marc Ravalomanana t ...
.
Religion
 According to the most recent national census available which was completed in 1993, 52% adhere to indigenous beliefs, 41 percent is Christian, and 7 percent is Muslim. It is common to alternate between religious identities or to mix traditions, and many individuals hold a combination of indigenous and Christian or Muslim beliefs. Muslim leaders and local scholars estimate Muslims currently constitute between 15 and 25 percent of the population. Muslims predominate in the northwestern coastal areas while Christians predominate in the highlands.
However, according to the
According to the most recent national census available which was completed in 1993, 52% adhere to indigenous beliefs, 41 percent is Christian, and 7 percent is Muslim. It is common to alternate between religious identities or to mix traditions, and many individuals hold a combination of indigenous and Christian or Muslim beliefs. Muslim leaders and local scholars estimate Muslims currently constitute between 15 and 25 percent of the population. Muslims predominate in the northwestern coastal areas while Christians predominate in the highlands.
However, according to the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
in 2020, 85% of the population now practiced Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, while just 4.5% of Malagasys practiced folk religions; among Christians, practitioners of Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
outnumbered adherents of Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
. According to the Association of Religion Data Archives The Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) is a free source of online information related to American and international religion. One of the primary goals of the archive is to democratize access to academic information on religion by making th ...
, 58.1% of the population is Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''ChristГіs'' (О§ПҒО№ ...
, 2.1% is Muslim
Muslims ( ar, Ш§Щ„Щ…ШіЩ„Щ…ЩҲЩҶ, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, 39.2% practices traditional faiths, while 0.6% of the population is non-religious
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and anti ...
or adheres to other faiths as of 2020.
The veneration of ancestors
The veneration of the dead, including one's ancestors, is based on love and respect for the deceased. In some cultures, it is related to beliefs that the dead have a continued existence, and may possess the ability to influence the fortune of ...
has led to the widespread tradition of tomb building, as well as the highlands practice of the ''famadihana
Famadihana is a funerary tradition of the Malagasy people in Madagascar. During this ceremony, known as ''the turning of the bones'', people bring forth the bodies of their ancestors from the family crypts, rewrap the corpses in fresh cloth, and r ...
'', whereby a deceased family member's remains are exhumed and re-wrapped in fresh silk shrouds, before being replaced in the tomb. The ''famadihana'' is an occasion to celebrate the beloved ancestor's memory, reunite with family and community, and enjoy a festive atmosphere. Residents of surrounding villages are often invited to attend the party, where food and rum are typically served, and a ''hiragasy
Hiragasy or hira gasy (''hira'': song; ''gasy'': Malagasy) is a musical tradition in Madagascar, particularly among the Merina ethnic group of the Highland regions around the capital of Antananarivo. It is a day-long spectacle of music, dance, a ...
'' troupe or other musical entertainment is commonly present. Consideration for ancestors is also demonstrated through adherence to '' fady'', taboos that are respected during and after the lifetime of the person who establishes them. It is widely believed that by showing respect for ancestors in these ways, they may intervene on behalf of the living. Conversely, misfortunes are often attributed to ancestors whose memory or wishes have been neglected. The sacrifice of zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus'' or ''Bos taurus indicus''), sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in the Indian sub-continent. Zebu are characterised by a fatty ...
is a traditional method used to appease or honor the ancestors. In addition, the Malagasy traditionally believe in a creator god, called Zanahary
Zanahary is the personified sky of Malagasy mythology and folklore. He (usually male, but sometimes considered genderless) is considered a creator god, having collaborated with the earth god Ratovantany to create humanity; upon death, the soul mi ...
or Andriamanitra.Bradt (2011), pp. 13вҖ“20
Today, many Christians integrate and combine their religious beliefs with traditional ones related to honoring the ancestors. For instance, they may bless their dead at church before proceeding with traditional burial rites or invite a Christian minister
In Christianity, a minister is a person authorised by a church or other religious organization to perform functions such as teaching of beliefs; leading services such as weddings, baptisms or funerals; or otherwise providing spiritual guidanc ...
to consecrate a ''famadihana'' reburial. The Malagasy Council of Churches comprises the four oldest and most prominent Christian denominations of Madagascar (Roman Catholic, Church of Jesus Christ in Madagascar
The Church of Jesus Christ in Madagascar ( mg, Fiangonan'i Jesoa Kristy eto Madagasikara; FJKM) is the second-largest Christian denomination in Madagascar. The current officers include the Rev. Ammi Irako Andriamahazosoa, President; the Rev. Jean ...
, Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
, and Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
) and has been an influential force in Malagasy politics.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ЫҳШ§Щ„ЩҗШҘШіЩ„ЩҺШ§Щ…, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
is also practiced on the island. Islam was first brought to Madagascar in the Middle Ages by Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, Ш№ЩҺШұЩҺШЁЩҗЩҠЩҢЩ‘, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, Ш№ЩҺШұЩҺШЁ, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and Somali Muslim traders, who established several Islamic schools along the eastern coast. While the use of Arabic script and loan words and the adoption of Islamic astrology would spread across the island, the Islamic religion took hold in only a handful of southeastern coastal communities. Today, Muslims
Muslims ( ar, Ш§Щ„Щ…ШіЩ„Щ…ЩҲЩҶ, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
constitute 3вҖ“7 percent of the population of Madagascar and are largely concentrated in the northwestern provinces of Mahajanga
Mahajanga (French: Majunga) is a city and an administrative district on the northwest coast of Madagascar. The city of Mahajanga (Mahajanga I) is the capital of the Boeny Region. The district (identical to the city) had a population of 220,629 i ...
and Antsiranana
Antsiranana ( mg, AntsiranМҲana ), named Diego-SuГЎrez prior to 1975, is a city in the far north of Madagascar. Antsiranana is the capital of Diana Region. It had an estimated population of 115,015 in 2013.
History
The bay and city originally u ...
. However, Muslim leaders estimate Muslims currently constitute between 15 and 25 percent of the population. Muslims predominate in the northwestern coastal areas while Christians predominate in the highlands. The vast majority of Muslims are Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85вҖ“90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
, with a sizeable Ahmadiyya
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, Ш§Щ„Ш¬Щ…Ш§Ш№Ш© Ш§Щ„ШҘШіЩ„Ш§Щ…ЩҠШ© Ш§Щ„ШЈШӯЩ…ШҜЩҠШ©, al-JamДҒКҝah al-IslДҒmД«yah al-AбёҘmadД«yah; ur, , translit=JamДҒ'at AбёҘmadiyyah Musl ...
minority. Muslims are divided between those of Malagasy ethnicity, Indians, Pakistanis and Comorans.
More recently, Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2вҖ“1.35 billion followers, or 15вҖ“16% of the global p ...
was introduced to Madagascar through Gujarati people
The Gujarati people or Gujaratis, are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who reside in or can trace their ancestry or heritage to the present-day western Indian state of Gujarat. They primarily speak Gujarati, an Indo-Aryan language. While G ...
immigrating from the Saurashtra region of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
in the late 19th century. Most Hindus in Madagascar speak Gujarati
Gujarati may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India
* Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat
* Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them
* Gujarati languages, the Western Indo-Aryan sub- ...
or Hindi
Hindi (DevanДҒgarД«: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been de ...
at home.
Culture
Each of the many ethnic subgroups in Madagascar adhere to their own set of beliefs, practices and ways of life that have historically contributed to their unique identities. However, there are a number of core cultural features that are common throughout the island, creating a strongly unified Malagasy cultural identity. In addition to a common language and shared traditional religious beliefs around a creator god and veneration of the ancestors, the traditional Malagasy worldview is shaped by values that emphasize ''fihavanana'' (solidarity), ''vintana'' (destiny), ''tody'' (karma), and '' hasina'', a sacred life force that traditional communities believe imbues and thereby legitimates authority figures within the community or family. Other cultural elements commonly found throughout the island include the practice of male circumcision; strong kinship ties; a widespread belief in the power of magic, diviners, astrology and witch doctors; and a traditional division of social classes into nobles, commoners, and slaves. Although social castes are no longer legally recognized, ancestral caste affiliation often continues to affect social status, economic opportunity, and roles within the community. Malagasy people traditionally consult ''Mpanandro'' ("Makers of the Days") to identify the most auspicious days for important events such as weddings or ''famadihana'', according to a traditional astrological system introduced by Arabs. Similarly, the nobles of many Malagasy communities in the pre-colonial period would commonly employ advisers known as the ''ombiasy'' (from ''olona-be-hasina'', "man of much virtue") of the southeasternAntemoro
The Antemoro (or Antaimoro) are an ethnic group of Madagascar living on the southeastern coast, mostly between Manakara and Farafangana. Numbering around 500,000, this ethnic group mostly traces its origins back to East African Bantu and Indone ...
ethnic group, who trace their ancestry back to early Somali settlers.
The diverse origins of Malagasy culture are evident in its tangible expressions. The most emblematic instrument of Madagascar, the ''valiha
The valiha is a tube zither from Madagascar made from a species of local bamboo; it is considered the " national instrument" of Madagascar. The term is also used to describe a number of related zithers of differing shapes and materials.
Th ...
'', is a bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, bu ...
tube zither
The tube zither is a stringed musical instrument in which a tube functions both as an instrument's neck and its soundbox. As the neck, it holds strings taut and allows them to vibrate. As a soundbox or it modifies the sound and transfers it to ...
carried to Madagascar by early settlers from southern Borneo, and is very similar in form to those found in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, RepГәblica de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
today. Traditional houses in Madagascar are likewise similar to those of southern Borneo in terms of symbolism and construction, featuring a rectangular layout with a peaked roof and central support pillar. Reflecting a widespread veneration of the ancestors, tombs are culturally significant in many regions and tend to be built of more durable material, typically stone, and display more elaborate decoration than the houses of the living.Acquier (1997), pp. 143вҖ“175 The production and weaving of silk can be traced back to the island's earliest settlers, and Madagascar's national dress, the woven '' lamba'', has evolved into a varied and refined art.
The Southeast Asian cultural influence is also evident in Malagasy cuisine
Malagasy cuisine encompasses the many diverse culinary traditions of the Indian Ocean island of Madagascar. Foods eaten in Madagascar reflect the influence of Southeast Asian, African, Oceanian, Indian, Chinese and European migrants that have s ...
, in which rice is consumed at every meal, typically accompanied by one of a variety of flavorful vegetable or meat dishes. African influence is reflected in the sacred importance of zebu cattle and their embodiment of their owner's wealth, traditions originating on the African mainland. Cattle rustling
Cattle raiding is the act of stealing cattle. In Australia, such stealing is often referred to as duffing, and the perpetrator as a duffer.Baker, Sidney John (1945) ''The Australian language : an examination of the English language and English ...
, originally a rite of passage for young men in the plains areas of Madagascar where the largest herds of cattle are kept, has become a dangerous and sometimes deadly criminal enterprise as herdsmen in the southwest attempt to defend their cattle with traditional spears against increasingly armed professional rustlers.
Arts
 A wide variety of oral and written
A wide variety of oral and written literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
has developed in Madagascar. One of the island's foremost artistic traditions is its oratory, as expressed in the forms of ''hainteny
Hainteny (pronounced , Malagasy for "knowledge of words") is a traditional form of Malagasy oral literature and poetry, involving heavy use of metaphor. It is associated primarily with the Merina people of Madagascar. In its use of metaphor and ...
'' (poetry), ''kabary'' (public discourse) and ''ohabolana'' (proverbs). An epic poem exemplifying these traditions, the ''Ibonia
The Ibonia is an epic poem that has been told in various forms across the island of Madagascar for at least several hundred years. The Ibonia predates the introduction of the printing press in Madagascar in the early part of the 19th century and as ...
'', has been handed down over the centuries in several different forms across the island, and offers insight into the diverse mythologies and beliefs of traditional Malagasy communities. This tradition was continued in the 20th century by such artists as Jean-Joseph Rabearivelo
Jean-Joseph Rabearivelo (4 March 1901 or 1903 вҖ“ 22 June 1937), born Joseph-Casimir Rabearivelo, was a Malagasy poet who is widely considered to be Africa's first modern poet and the greatest literary artist of Madagascar. Part of the fi ...
, who is considered Africa's first modern poet, and Elie Rajaonarison
Elie Rajaonarison (November 15, 1951 - November 27, 2010) was a poet, artist, professor and civil servant from Madagascar. Considered the standard-bearer for modern Malagasy poetry,Auzias & Labourdette (2008), p. 142 Rajaonarison's published poet ...
, an exemplar of the new wave of Malagasy poetry. Madagascar has also developed a rich musical heritage, embodied in dozens of regional musical genres such as the coastal ''salegy
Salegy is a popular music genre from Madagascar. Originating as a Sub-Saharan African folk music style in the northwestern coastal areas of Madagascar, modern salegy is the genre of Malagasy music that has gained the widest recognition and comm ...
'' or highland ''hiragasy
Hiragasy or hira gasy (''hira'': song; ''gasy'': Malagasy) is a musical tradition in Madagascar, particularly among the Merina ethnic group of the Highland regions around the capital of Antananarivo. It is a day-long spectacle of music, dance, a ...
'' that enliven village gatherings, local dance floors and national airwaves.Randrianary (2001), pp. 109вҖ“137 Madagascar also has a growing culture of classical music fostered through youth academies, organizations and orchestras that promote youth involvement in classical music.
The plastic arts are also widespread throughout the island. In addition to the tradition of silk weaving and lamba production, the weaving of raffia
Raffia palms (''Raphia'') are a genus of about twenty species of palms native to tropical regions of Africa, and especially Madagascar, with one species (''R. taedigera'') also occurring in Central and South America. ''R. taedigera'' is the sour ...
and other local plant materials has been used to create a wide array of practical items such as floor mats, baskets, purses and hats. Wood carving is a highly developed art form, with distinct regional styles evident in the decoration of balcony railings and other architectural elements. Sculptors create a variety of furniture and household goods, ''aloalo'' funerary posts, and wooden sculptures, many of which are produced for the tourist market.Heale & Abdul Latif (2008), pp. 108вҖ“111 The decorative and functional woodworking traditions of the Zafimaniry
The Zafimaniry are a sub-group of the Betsileo people, Betsileo ethnic groups of Madagascar, ethnic group of Madagascar. They live in the forested mountains of the southern central highlands southeast of Ambositra, between the neighboring Betsile ...
people of the central highlands was inscribed on UNESCO's list of Intangible Cultural Heritage in 2008.
Among the Antaimoro people, the production of paper embedded with flowers and other decorative natural materials is a long-established tradition that the community has begun to market to eco-tourists. Embroidery and drawn thread work
Drawn thread work is one of the earliest forms of open work embroidery, and has been worked throughout Europe. Originally it was often used for ecclesiastical items and to ornament shrouds. It is a form of counted-thread embroidery based on remov ...
are done by hand to produce clothing, as well as tablecloths and other home textiles for sale in local crafts markets. A small but growing number of fine art galleries in Antananarivo, and several other urban areas, offer paintings by local artists, and annual art events, such as the Hosotra open-air exhibition in the capital, contribute to the continuing development of fine arts in Madagascar.
Sport
 A number of traditional pastimes have emerged in Madagascar. ''
A number of traditional pastimes have emerged in Madagascar. ''Moraingy
Moraingy (Malagasy) or Moringue (French) is a weaponless, bare-fisted striking style of traditional martial art that originated during the Maroseranana dynasty (1675вҖ“1896) of the Sakalava Kingdom of western coastal Madagascar. It has since beco ...
'', a type of hand-to-hand combat, is a popular spectator sport in coastal regions. It is traditionally practiced by men, but women have recently begun to participate. The wrestling of zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus'' or ''Bos taurus indicus''), sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in the Indian sub-continent. Zebu are characterised by a fatty ...
cattle, which is named savika or ''tolon-omby'', is also practiced in many regions.Kusimba, Odland & Bronson (2004), p. 87 In addition to sports, a wide variety of games are played. Among the most emblematic is ''fanorona
Fanorona () is a strategy board game for two players. The game is indigenous to Madagascar.
Rules
Fanorona has three standard versions: Fanoron-Telo, Fanoron-Dimy, and Fanoron-Tsivy. The difference between these variants is the size of board play ...
'', a board game widespread throughout the Highland regions. According to folk legend, the succession of King Andrianjaka
Andrianjaka reigned over the Kingdom of Imerina in the central highlands region of Madagascar from around 1612 to 1630. Despite being the younger of King Ralambo's two sons, Andrianjaka succeeded to the throne on the basis of his strength of char ...
after his father Ralambo
Ralambo was the ruler of the Kingdom of Imerina in the central Highlands region of Madagascar from 1575 to 1612. Ruling from Ambohidrabiby, Ralambo expanded the realm of his father, Andriamanelo, and was the first to assign the name of Imerina t ...
was partially the result of the obsession that Andrianjaka's older brother may have had with playing ''fanorona'' to the detriment of his other responsibilities.
Western recreational activities were introduced to Madagascar over the past two centuries. Rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In its m ...
is considered the national sport of Madagascar. Soccer
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
is also popular. Madagascar has produced a world champion in pГ©tanque
PГ©tanque (, ; oc, petanca, , also or ) is a sport that falls into the category of boules sports, along with raffa, bocce, boule lyonnaise, lawn bowls, and crown green bowling. In all of these sports, players or teams play their boules/balls ...
, a French game similar to lawn bowling
Bowls, also known as lawn bowls or lawn bowling, is a sport in which the objective is to roll biased balls so that they stop close to a smaller ball called a "jack" or "kitty". It is played on a bowling green, which may be flat (for "flat-gre ...
, which is widely played in urban areas and throughout the Highlands. School athletics programs typically include soccer, track and field, judo, boxing, women's basketball and women's tennis. Madagascar sent its first competitors to the Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
in 1964, and has also competed in the African Games
The African Games, formally known as the All-Africa Games or the Pan African Games, are a continental multi-sport event held every four years, organized by the African Union (AU) with the Association of National Olympic Committees of Africa (AN ...
. Scouting
Scouting, also known as the Scout Movement, is a worldwide youth movement employing the Scout method, a program of informal education with an emphasis on practical outdoor activities, including camping, woodcraft, aquatics, hiking, backpacking ...
is represented in Madagascar by its own local federation of three scouting clubs. Membership in 2011 was estimated at 14,905.
Because of its advanced sports facilities, Antananarivo gained the hosting rights for several of Africa's top international basketball events, including the 2011 FIBA Africa Championship
AfroBasket 2011 was the 26th FIBA Africa Championship, played under the auspices of the FГ©dГ©ration Internationale de Basketball, the basketball sport governing body, and the African zone thereof. At stake is the berth allocated to Africa in th ...
, the 2009 FIBA Africa Championship for Women
The 2009 FIBA Africa Championship for Women is the 19th continental championships held by FIBA Africa. The championship will serve as a qualifying tournament for the 2010 FIBA World Championship for Women in the Czech Republic. The tournament to ...
, the 2014 FIBA Africa Under-18 Championship
The 2014 FIBA Africa Under-18 Championship was the 19th FIBA Africa Under-18 Championship, played under the rules of FIBA, the world governing body for basketball, and the FIBA Africa thereof. The tournament was hosted by Madagascar from August 2 ...
, the 2013 FIBA Africa Under-16 Championship
The 2013 FIBA Africa Under-16 Championship for Men (alternatively the Afrobasket U16) was the 3rd U-16 FIBA Africa championship, organized by FIBA Africa and played under the auspices of the FГ©dГ©ration Internationale de Basketball, the basketb ...
, and the 2015 FIBA Africa Under-16 Championship for Women
The 2015 FIBA Africa Under-16 Championship for Women was the 4th FIBA Africa Under-16 Championship for Women, FIBA Africa U16 Championship for Women, played under the rules of FIBA, the world governing body for basketball, and the FIBA Africa ther ...
., FIBA.com, Retrieved 26 October 2015.
Madagascar's national 3x3 basketball team
The Madagascar men's national 3x3 team is a national basketball team of Madagascar, administered by the FГ©dГ©ration Malagasy de Basket-Ball.
It represents the country in international 3x3 (3 against 3) basketball competitions.
As of 2019, the h ...
won the gold medal at the 2019 African Games
The 12th African Games was held from 19 to 31 August 2019 in Rabat, Morocco. This was the first time that the African Games were hosted by Morocco following the country's readmission to the African Union in January 2017.
Bidding process
The 12th ...
.
Cuisine
Malagasy cuisine reflects the diverse influences ofSoutheast Asian
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, African
African or Africans may refer to:
* Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa:
** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa
*** Ethn ...
, Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, and European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
culinary traditions. The complexity of Malagasy meals can range from the simple, traditional preparations introduced by the earliest settlers, to the refined festival dishes prepared for the island's 19th-century monarchs. Throughout almost the entire island, the contemporary cuisine of Madagascar typically consists of a base of rice (''vary'') served with an accompaniment (''laoka''). The many varieties of ''laoka'' may be vegetarian
Vegetarianism is the practice of abstaining from the consumption of meat (red meat, poultry, seafood, insects, and the flesh of any other animal). It may also include abstaining from eating all by-products of animal slaughter.
Vegetarianism m ...
or include animal proteins, and typically feature a sauce flavored with such ingredients as ginger, onion, garlic, tomato, vanilla, coconut milk, salt, curry powder, green peppercorns or, less commonly, other spices or herbs. In parts of the arid south and west, pastoral families may replace rice with maize, cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively ...
, or curd
Curd is obtained by coagulating milk in a sequential process called curdling. It can be a final dairy product or the first stage in cheesemaking. The coagulation can be caused by adding rennet or any edible acidic substance such as lemon ...
s made from fermented zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus'' or ''Bos taurus indicus''), sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in the Indian sub-continent. Zebu are characterised by a fatty ...
milk. A wide variety of sweet and savory fritter
A fritter is a portion of meat, seafood, fruit, vegetables or other ingredients which have been Batter (cooking), battered or breading, breaded, or just a portion of dough without further ingredients, that is deep-frying, deep-fried. Fritters ar ...
s as well as other street foods are available across the island, as are diverse tropical and temperate-climate fruits. Locally produced beverages include fruit juices, coffee, herbal teas and teas, and alcoholic drinks such as rum
Rum is a liquor made by fermenting and then distilling sugarcane molasses or sugarcane juice. The distillate, a clear liquid, is usually aged in oak barrels. Rum is produced in nearly every sugar-producing region of the world, such as the Phili ...
, wine, and beer.Bradt (2011), p. 312 Three Horses Beer
Three Horses Beer (better known locally as THB) is a pale lager that has been brewed by Star Breweries of Madagascar since 1958. It is the highest selling beer in Madagascar and has been described as emblematic of the country. THB is sold nation ...
is the most popular beer on the island and is considered emblematic of Madagascar.
See also
*Index of Madagascar-related articles
Articles (arranged alphabetically) related to Madagascar include:
__NOTOC__
A
* Alaotra Mangoro Region
* Albert Camille Vital
* Albert Zafy
* Ambatovaky Special Reserve
* Amber Forest Reserve
* Amber Mountain National Park
* Ambohijanahary ...
* Outline of Madagascar
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Madagascar:
Madagascar – sovereign island nation located in the Indian Ocean off the southeastern coast of Africa. The Island of Madagascar is the fourth-large ...
* Telephone numbers in Madagascar
Telephone numbers in Madagascar are seven digits long, the first two digits being an area code.
Recent ITU documents suggest the area code is preceded by a two digit operator code, for example "20" for Telecom Malagasy.
International numbering ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Country Profile
from
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadca ...
Madagascar
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is available ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
*
Madagascar
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' *
Key Development Forecasts for Madagascar
from
International Futures
International Futures (IFs) is a global integrated assessment modelling, integrated assessment model designed to help with thinking strategically and systematically about key global systems (economic, demographic, education, health, environment, ...
* Map of Madagascar, 1666
(in French). Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The
National Library of Israel
The National Library of Israel (NLI; he, Ч”ЧЎЧӨЧЁЧҷЧҷЧ” Ч”ЧңЧҗЧ•ЧһЧҷЧӘ, translit=HaSifria HaLeumit; ar, Ш§Щ„Щ…ЩғШӘШЁШ© Ш§Щ„ЩҲШ·ЩҶЩҠШ© ЩҒЩҠ ШҘШіШұШ§ШҰЩҠЩ„), formerly Jewish National and University Library (JNUL; he, Ч‘ЧҷЧӘ Ч”ЧЎЧӨЧЁЧҷЧқ Ч”ЧңЧҗЧ ...
{{Authority control
Island countries of the Indian Ocean
Islands of Madagascar
East African countries
Southeast African countries
Former French colonies
French-speaking countries and territories
Least developed countries
Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
Member states of the African Union
Member states of the United Nations
States and territories established in 1960
1960 establishments in Madagascar
1960 establishments in Africa
Physiographic provinces
Republics
Countries in Africa
Former monarchies of Africa
Island countries