Macintosh 128K on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Apple Macintosh—later rebranded as the Macintosh 128K—is the original
 In 1978 Apple began to organize the
In 1978 Apple began to organize the


 The original Macintosh was unusual in that it included the signatures of the Macintosh Division as of early 1982 molded on the inside of the case. The names were Peggy Alexio, Colette Askeland,
The original Macintosh was unusual in that it included the signatures of the Macintosh Division as of early 1982 molded on the inside of the case. The names were Peggy Alexio, Colette Askeland,
Macintosh 128K profile
Low End Mac.
at Mac512.com *
The 72PPI Web Resolution MythOnline attempt at simulating Macintosh System 1
Mac Essentials
Lost 1984 Videos *
Apple Macintosh before System 7
Macintosh 128K Hardware
Tips For the 128K
Support For 128K Diehard Users
The M0001 Registry
Owners of Vintage Macintosh
Inside the Macintosh 128K
The Original Macintosh, anecdotes and the people who made it
{{Authority control 128k 128k Computer-related introductions in 1984 32-bit computers
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
Macintosh
The Mac (known as Macintosh until 1999) is a family of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple Inc. Macs are known for their ease of use and minimalist designs, and are popular among students, creative professionals, and ...
personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
. It played a pivotal role in establishing desktop publishing
Desktop publishing (DTP) is the creation of documents using page layout software on a personal ("desktop") computer. It was first used almost exclusively for print publications, but now it also assists in the creation of various forms of online c ...
as a general office function. The motherboard, a CRT monitor, and a floppy drive were housed in a beige case with integrated carrying handle; it came with a keyboard and single-button mouse. It sold for . The Macintosh was introduced by a television commercial entitled "1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeast A ...
" shown during Super Bowl XVIII
Super Bowl XVIII was an American football game played on January 22, 1984, at Tampa Stadium between the National Football Conference (NFC) champion and defending Super Bowl XVII champion Washington Redskins and the American Football Conference ( ...
on January 22, 1984 and directed by Ridley Scott
Sir Ridley Scott (born 30 November 1937) is a British film director and producer. Directing, among others, science fiction films, his work is known for its atmospheric and highly concentrated visual style. Scott has received many accolades thr ...
. Sales of the Macintosh were strong from its initial release on January 24, 1984, and reached 70,000 units on May 3, 1984. Upon the release of its successor, the Macintosh 512K
The Macintosh 512K is a personal computer that was designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer from September 1984 to April 1986. It is the first update to the original Macintosh 128K. It was virtually identical to the previous Macint ...
, it was rebranded as the Macintosh 128K. The computer's model number was M0001.
Development
1978–1984: Development
 In 1978 Apple began to organize the
In 1978 Apple began to organize the Apple Lisa
Lisa is a desktop computer developed by Apple, released on January 19, 1983. It is one of the first personal computers to present a graphical user interface (GUI) in a machine aimed at individual business users. Its development began in 1978. ...
project, aiming to build a next-generation machine similar to an advanced Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-m ...
or the yet-to-be-introduced IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team ...
. In 1979, Apple co-founder Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
learned of the advanced work on graphical user interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, inste ...
s (GUI) taking place at Xerox PARC
PARC (Palo Alto Research Center; formerly Xerox PARC) is a research and development company in Palo Alto, California. Founded in 1969 by Jacob E. "Jack" Goldman, chief scientist of Xerox Corporation, the company was originally a division of Xero ...
. He arranged for Apple engineers to be allowed to visit PARC to see the systems in action. The Apple Lisa project was immediately redirected to use a GUI, which at that time was well beyond the state of the art
The state of the art (sometimes cutting edge or leading edge) refers to the highest level of general development, as of a device, technique, or scientific field achieved at a particular time. However, in some contexts it can also refer to a level ...
for microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
abilities; the Xerox Alto
The Xerox Alto is a computer designed from its inception to support an operating system based on a graphical user interface (GUI), later using the desktop metaphor. The first machines were introduced on 1 March 1973, a decade before mass-market ...
required a custom processor that spanned several circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in Electrical engineering, electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a L ...
s in a case which was the size of a small refrigerator. Things had changed dramatically with the introduction of the 16/32-bit Motorola 68k
The Motorola 68000 series (also known as 680x0, m68000, m68k, or 68k) is a family of 32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessors. During the 1980s and early 1990s, they were popular in personal computers and workstations and w ...
in 1979, which offered at least an order of magnitude
An order of magnitude is an approximation of the logarithm of a value relative to some contextually understood reference value, usually 10, interpreted as the base of the logarithm and the representative of values of magnitude one. Logarithmic dis ...
better performance than existing designs and made a software GUI machine a practical possibility. The basic layout of the Lisa was largely complete by 1982, at which point Jobs's continual suggestions for improvements led to him being kicked off the project.
At the same time that the Lisa was becoming a GUI machine in 1979, Jef Raskin
Jef Raskin (born Jeff Raskin; March 9, 1943 – February 26, 2005) was an American human–computer interface expert best known for conceiving and starting the Macintosh project at Apple in the late 1970s.
Early life and education
Jef Raskin ...
began the Macintosh project. The design at that time was for a low-cost, easy-to-use machine for the average consumer. Instead of a GUI, it intended to use a text-based user interface
In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI) (alternately terminal user interfaces, to reflect a dependence upon the properties of computer terminals and not just text), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an ear ...
that allowed multitasking, and special command keys on the keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Musi ...
that accessed standardized commands in the programs. Bud Tribble, a member of the Macintosh team, asked Burrell Smith to integrate the Apple Lisa's 68k microprocessor into the Macintosh so that it could run graphical programs. By December 1980, Smith had succeeded in designing a board that integrated an 8 MHz Motorola 68k. Smith's design used fewer RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* ...
than the Lisa, which made producing the board significantly more cost-efficient. The final Mac design was self-contained and had the complete QuickDraw
A quickdraw (also known as an extender) is a piece of climbing equipment used by rock and ice climbers to allow the climbing rope to run freely through protection such as a bolt anchors or other traditional gear while leading.
A quickdraw ...
picture language and interpreter in 64 KB of ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
– far more than most other computers which typically had around 4 to 8 KB of ROM; it had 128 kB of RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* ...
, in the form of sixteen 64-kilobit
The kilobit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix ''kilo-'' (symbol k) is defined in the International System of Units (SI) as a multiplier of 103 (1 thousand), and therefore,
:1 kilobit = = 1000& ...
(kb) RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* ...
solder
Solder (; NA: ) is a fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. Solder is melted in order to wet the parts of the joint, where it adheres to and connects the pieces after cooling. Metals or alloys suitable ...
ed to the logicboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
. The final product's screen was a , 512x342 pixel monochrome
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, monochrom ...
display.
Smith's innovative design, combining the low production cost of an Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-m ...
with the computing power of Lisa's Motorola 68k CPU, began to receive Jobs's attentions. Jobs took over the Macintosh project after deciding that the Macintosh was more marketable than the Lisa, which led former project leader Raskin to leave the team in 1981. Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak
Stephen Gary Wozniak (; born August 11, 1950), also known by his nickname "Woz", is an American electronics engineer, computer programmer, philanthropist, inventor, and technology entrepreneur. In 1976, with business partner Steve Jobs, he c ...
, who had been leading the project with Raskin, was on temporary leave from the company at this time due to an airplane crash he had experienced earlier that year, making it easier for Jobs to take over the program. After development had completed, team member and engineer Andy Hertzfeld
Andrew Jay Hertzfeld (born April 6, 1953) is an American software engineer and innovator who was a member of the original Apple Macintosh development team during the 1980s. After buying an Apple II in January 1978, he went to work for Apple ...
said that the final Macintosh design is closer to Jobs's ideas than Raskin's. ''InfoWorld
''InfoWorld'' (abbreviated IW) is an information technology media business. Founded in 1978, it began as a monthly magazine. In 2007, it transitioned to a web-only publication. Its parent company today is International Data Group, and its siste ...
'' in September 1981 reported on the existence of the secret Lisa and "McIntosh" projects at Apple.
1984: Debut
In 1982 Regis McKenna was brought in to shape the marketing and launch of the Macintosh. Later the Regis McKenna team grew to include Jane Anderson, Katie Cadigan and Andy Cunningham, who eventually led the Apple account for the agency. Cunningham and Anderson were the primary authors of the Macintosh launch plan. The launch of the Macintosh pioneered many different tactics that are used today in launching technology products, including the "multiple exclusive," event marketing (credited to John Sculley, who brought the concept over from Pepsi), creating a mystique about a product and giving an inside look into a product's creation. After the Lisa's announcement, John Dvorak discussed rumors of a mysterious "MacIntosh" project at Apple in February 1983. The company announced the Macintosh 128K—manufactured at an Apple factory inFremont, California
Fremont is a city in Alameda County, California, United States. Located in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area, Bay Area, Fremont has a population of 230,504 as of 2020, making it the fourth List of cities and towns in the San Fra ...
—in October 1983, followed by an 18-page brochure included with various magazines in December. The Macintosh was introduced by a US$1.5 million Ridley Scott
Sir Ridley Scott (born 30 November 1937) is a British film director and producer. Directing, among others, science fiction films, his work is known for its atmospheric and highly concentrated visual style. Scott has received many accolades thr ...
television commercial, "1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeast A ...
". It aired during the third quarter of Super Bowl XVIII
Super Bowl XVIII was an American football game played on January 22, 1984, at Tampa Stadium between the National Football Conference (NFC) champion and defending Super Bowl XVII champion Washington Redskins and the American Football Conference ( ...
on January 22, 1984, and is now considered a "watershed event" and a "masterpiece". McKenna called the ad "more successful than the Mac itself." "1984" used an unnamed heroine to represent the coming of the Macintosh (indicated by a Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
-style picture of the computer on her white tank top) as a means of saving humanity from the "conformity" of IBM's attempts to dominate the computer industry. The ad alludes to George Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950), better known by his pen name George Orwell, was an English novelist, essayist, journalist, and critic. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to totalitar ...
's novel ''Nineteen Eighty-Four
''Nineteen Eighty-Four'' (also stylised as ''1984'') is a dystopian social science fiction novel and cautionary tale written by the English writer George Orwell. It was published on 8 June 1949 by Secker & Warburg as Orwell's ninth and final ...
'' which described a dystopia
A dystopia (from Ancient Greek δυσ- "bad, hard" and τόπος "place"; alternatively cacotopiaCacotopia (from κακός ''kakos'' "bad") was the term used by Jeremy Bentham in his 1818 Plan of Parliamentary Reform (Works, vol. 3, p. 493). ...
n future ruled by a televised " Big Brother."
Two days after "1984" aired, the Macintosh went on sale, and came bundled with two applications designed to show off its interface: MacWrite
MacWrite is a WYSIWYG word processor application released along with the first Apple Macintosh systems in 1984. Together with MacPaint, it was one of the two original "killer applications" that propelled the adoption and popularity of the GUI i ...
and MacPaint
MacPaint is a raster graphics editor developed by Apple Computer and released with the original Macintosh personal computer on January 24, 1984. It was sold separately for US$195 with its word processing counterpart, MacWrite. MacPaint was nota ...
. The Macintosh was the first successful mass-market all-in-one desktop personal computer with a graphical user interface, built-in screen, and mouse. It was first demonstrated by Steve Jobs in the first of his famous Mac keynote speeches, and though the Mac garnered an immediate, enthusiastic following, some labeled it a mere "toy". Apple sold it alongside its popular Apple II series until the others were discontinued in the 1990s. Because the operating system was designed largely for the GUI, existing text-mode and command-driven applications had to be redesigned and the programming code rewritten. This was a time-consuming task that many software developer
Software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, Computer programming, programming, software documentation, documenting, software testing, testing, and Software bugs, bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applic ...
s chose not to undertake, and could be regarded as a reason for an initial lack of software for the new system. In April 1984, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washing ...
's MultiPlan
Multiplan is spreadsheet program developed by Microsoft and introduced in 1982 as a competitor to VisiCalc.
Multiplan was released first for computers running CP/M; it was developed using a Microsoft proprietary p-code C compiler as part of ...
migrated over from MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few ope ...
, with Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processing software developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name ''Multi-Tool Word'' for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms includin ...
following in January 1985. Apple introduced the Macintosh Office
The Macintosh Office was an effort by Apple Computer to design an office-wide computing environment consisting of Macintosh computers, a local area networking system, a file server, and a networked laser printer. Apple announced Macintosh Offic ...
suite the same year with the "Lemmings" ad; infamous for insulting its own potential customers, the ad was not successful.
Apple spent $2.5 million purchasing all 39 advertising pages in a special, post-election issue of ''Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly online news magazine co-owned 50 percent each by Dev Pragad, its president and CEO, and Johnathan Davis (businessman), Johnathan Davis, who has no operational role at ''Newsweek''. Founded as a weekly print m ...
'', and ran a "Test Drive a Macintosh" promotion, in which potential buyers with a credit card could take home a Macintosh for 24 hours and return it to a dealer afterwards. While 200,000 people participated, dealers disliked the promotion, the supply of computers was insufficient for demand, and many were returned in such a bad condition that they could no longer be sold. This marketing campaign caused CEO John Sculley to raise the price from $1,995 to $2,495 (). The computer sold well, nonetheless, reportedly outselling the IBM PCjr
The IBM PCjr (pronounced "PC junior") was a home computer produced and marketed by IBM from March 1984 to May 1985, intended as a lower-cost variant of the IBM PC with hardware capabilities better suited for video games, in order to compete mor ...
which also began shipping early that year; one dealer reported a backlog of more than 600 orders. By April 1984 the company sold 50,000 Macintoshes, and hoped for 70,000 by early May and almost 250,000 by the end of the year.
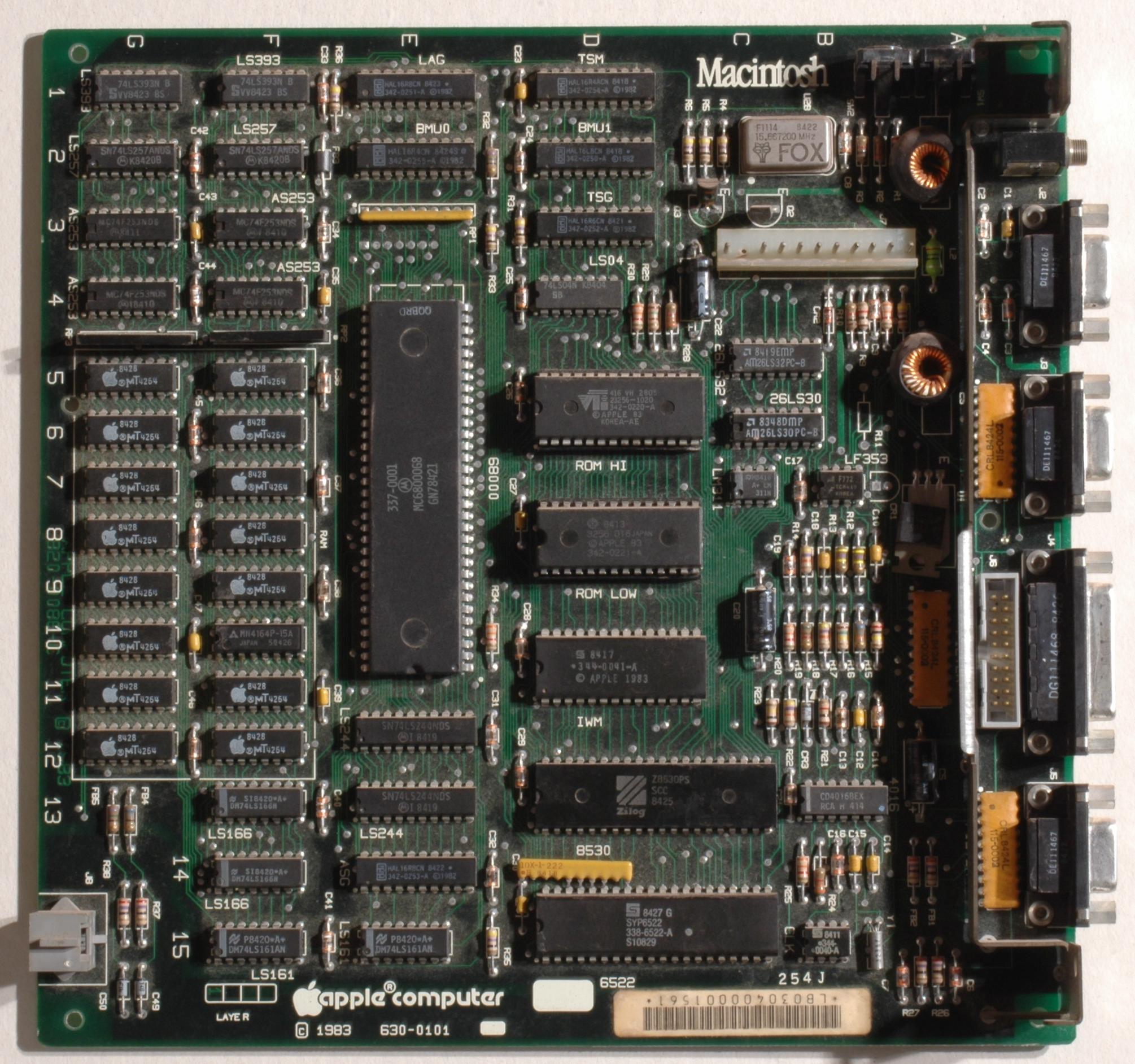
Processor and memory
The heart of the computer was aMotorola 68000
The Motorola 68000 (sometimes shortened to Motorola 68k or m68k and usually pronounced "sixty-eight-thousand") is a 16/32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessor, introduced in 1979 by Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector ...
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
running at , connected to 128 KB RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* ...
shared by the processor and the display controller. The boot procedure and some operating system routines were contained in an additional 64 KB ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
chip. Apple did not offer RAM upgrades. Unlike the Apple II, no source code listings of the Macintosh system ROMs were offered.
The RAM in the Macintosh consisted of sixteen 64k×1 DRAMs. The 68000 and video controller took turns accessing DRAM every four CPU cycles during display of the frame buffer, while the 68000 had unrestricted access to DRAM during vertical and horizontal blanking intervals. Such an arrangement reduced the overall performance of the CPU as much as 35% for most code as the display logic often blocked the CPU's access to RAM. Despite the nominally high clock rate, this caused the computer to run slower than several of its competitors and resulted in an effective clock rate of 6 MHz.

Peripherals
The built-in display was a one-bit per pixel,black-and-white
Black-and-white (B&W or B/W) images combine black and white in a continuous spectrum, producing a range of shades of grey.
Media
The history of various visual media began with black and white, and as technology improved, altered to color. ...
, 9 in/23 cm CRT with a fixed resolution of 512 × 342 pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the smal ...
s, using the Apple standard of 72 ppi (pixels per inch), a standard that was quickly abandoned once higher resolution screens became available. Expansion and networking were achieved using two non-standard RS-422
RS-422, also known as TIA/EIA-422, is a technical standard originated by the Electronic Industries Alliance that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit. It was meant to be the foundation of a suite of standards that ...
DE-9
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.
Description, n ...
serial ports named "printer" and "modem", which did not support hardware handshaking
A handshake is a globally widespread, brief greeting or parting tradition in which two people grasp one of each other's like hands, in most cases accompanied by a brief up-and-down movement of the grasped hands. Customs surrounding handshakes a ...
. An external floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined w ...
drive could be added using a proprietary connector (19-pin D-sub
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.
Description, no ...
). The keyboard and mouse used simple proprietary protocols, allowing some third-party upgrades. The original keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Musi ...
had no arrow keys
Arrow keys or cursor movement keys are buttons on a computer keyboard that are either programmed or designated to move the cursor (computers), cursor in a specified direction.
The term "cursor movement key" is distinct from "arrow key" in that ...
, numeric keypad or function key
A function key is a key on a computer or terminal keyboard that can be programmed so as to cause an operating system command interpreter or application program to perform certain actions, a form of soft key. On some keyboards/computers, function ...
s. This was an intentional decision by Apple, as these keys were common on older platforms and it was thought that the addition of these keys would encourage software developers to simply port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
their existing applications to the Mac, rather than design new ones around the GUI paradigm. Later, Apple made a numeric keypad
A numeric keypad, number pad, numpad, or ten key,
is the palm-sized, usually-17-key section of a standard computer keyboard, usually on the far right. It provides calculator-style efficiency for entering numbers. The idea of a 10-key nu ...
available for the Macintosh 128K. The keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Musi ...
sold with the newer Macintosh Plus
The Macintosh Plus computer is the third model in the Macintosh line, introduced on January 16, 1986, two years after the original Macintosh and a little more than a year after the Macintosh 512K, with a price tag of US$2,599. As an evolutiona ...
model included the numeric keypad and arrow keys, but still no function keys. As with the Apple Lisa
Lisa is a desktop computer developed by Apple, released on January 19, 1983. It is one of the first personal computers to present a graphical user interface (GUI) in a machine aimed at individual business users. Its development began in 1978. ...
before it, the mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
had a single button. Standard headphones could also be connected to a monaural jack. Apple also offered their 300 and 1200 baud modems originally released for the Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-m ...
line. Initially, the only printer available was the Apple ImageWriter
The ImageWriter is a product line of dot matrix printers formerly manufactured by Apple Computer, Inc., and designed then to be compatible with their entire line of computers. There were three different models introduced over time, which were p ...
, a dot matrix printer which was designed to produce 144 dpi WYSIWYG
In computing, WYSIWYG ( ), an acronym for What You See Is What You Get, is a system in which editing software allows content to be edited in a form that resembles its appearance when printed or displayed as a finished product, such as a printed d ...
output from the Mac's 72 dpi screen. Eventually, the LaserWriter
The LaserWriter is a laser printer with built-in PostScript interpreter sold by Apple, Inc. from 1985 to 1988. It was one of the first laser printers available to the mass market. In combination with WYSIWYG publishing software like PageMaker, ...
and other printers were capable of being connected using AppleTalk
AppleTalk is a discontinued proprietary suite of networking protocols developed by Apple Computer for their Macintosh computers. AppleTalk includes a number of features that allow local area networks to be connected with no prior setup or the n ...
, Apple's built-in networking system.
Storage
The Macintosh contained a single 400 KB, single-sided -inch
Measuring tape with inches
The inch (symbol: in or ″) is a unit of length in the British imperial and the United States customary systems of measurement. It is equal to yard or of a foot. Derived from the Roman uncia ("twelfth") ...
floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined w ...
drive, dedicating no space to other internal mechanical storage. The Mac OS was disk-based from the beginning, as RAM had to be conserved, but this "Startup Disk" could still be temporarily ejected. (Ejecting the root filesystem remained an unusual feature of the classic Mac OS
Mac OS (originally System Software; retronym: Classic Mac OS) is the series of operating systems developed for the Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Computer from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The ...
until System 7
System 7, codenamed "Big Bang", and also known as Mac OS 7, is a graphical user interface-based operating system for Macintosh computers and is part of the classic Mac OS series of operating systems. It was introduced on May 13, 1991, by Apple Co ...
.) One floppy disk was sufficient to store the System Software, an application and the data files created with the application. The 400 KB drive capacity was larger than the PC XT's 360 KB 5.25-inch drive, however, more sophisticated work environments of the time required separate disks for documents and the system installation. Due to the memory constraints (128 KB) of the original Macintosh, and the fact that the floppies could hold only 400 KB, users had to frequently swap disks in and out of the floppy drive, which caused external floppy drives to be utilized more frequently. The Macintosh External Disk Drive
The Macintosh External Disk Drive is the original model in a series of external -inch floppy disk drives manufactured and sold by Apple Computer exclusively for the Macintosh series of computers introduced in January 1984. Later, Apple would u ...
(mechanically identical to the internal one, piggybacking on the same controller) was a popular add-on that cost US$495. Third-party hard drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnet ...
s were considerably more expensive and usually connected to the slower serial port
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel. ...
(as specified by Apple), although a few manufacturers chose to utilize the faster non-standard floppy port. The 128K can only use the original Macintosh File System
Macintosh File System (MFS) is a volume format (or disk file system) created by Apple Computer for storing files on 400K floppy disks. MFS was introduced with the original Apple Macintosh computer in January 1984.
MFS is notable both for ...
released in 1984 for storage.

Cooling
The unit did not include a fan, relying instead onconvective heat transfer
Convection (or convective heat transfer) is the heat transfer, transfer of heat from one place to another due to the movement of fluid. Although often discussed as a distinct method of heat transfer, convective heat transfer involves the combin ...
, which made it quiet while in operation. Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
insisted that the Macintosh ship without a fan, which persisted until the introduction of the Macintosh SE
The Macintosh SE is a personal computer designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple Computer, from March 1987 to October 1990. It marked a significant improvement on the Macintosh Plus design and was introduced by Apple at the same time as the Mac ...
in 1987. Jobs believed that computers equipped with fans tend to distract the user from completing work. Unfortunately, this was allegedly a source of many common, costly component failures in the first four Macintosh models. This was enough of a problem to prompt the introduction of several third-party, external cooling fan solutions such as the MacFan, the Mac N Frost, the Fanny Mac and the Kensington
Kensington is a district in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in the West End of London, West of Central London.
The district's commercial heart is Kensington High Street, running on an east–west axis. The north-east is taken up b ...
System Saver. These units fitted inside the Macintosh's carrying-handle slot and produced a forced draft through the computer's existing ventilation holes.
Software
The Macintosh shipped with the very firstSystem
A system is a group of Interaction, interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment (systems), environment, is described by its boundaries, ...
and Finder application, known to the public as "System 1.0" (formally known as System 0.97 and Finder 1.0). The original Macintosh saw three upgrades to both before it was discontinued. Apple recommends System 2.0 and Finder 4.2, with System 3.2 and Finder 5.3 as the maximum. System 4.0 officially dropped support for the Macintosh 128K because it was distributed on 800 KB floppy disks, which could not be used by the 128K.
The applications MacPaint
MacPaint is a raster graphics editor developed by Apple Computer and released with the original Macintosh personal computer on January 24, 1984. It was sold separately for US$195 with its word processing counterpart, MacWrite. MacPaint was nota ...
and MacWrite
MacWrite is a WYSIWYG word processor application released along with the first Apple Macintosh systems in 1984. Together with MacPaint, it was one of the two original "killer applications" that propelled the adoption and popularity of the GUI i ...
were bundled with the Mac. Other programs available included MacProject
MacProject was a project management and scheduling business application released along with the first Apple Macintosh systems in 1984. MacProject was one of the first major business tools for the Macintosh which enabled users to calculate the ...
, MacTerminal and Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processing software developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name ''Multi-Tool Word'' for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms includin ...
. Programming languages available at the time included MacBASIC, MacPascal and the Macintosh 68000 Development System. The Macintosh also came with a manual and a unique guided tour cassette tape which worked together with the guided tour diskette as a tutorial for both the Macintosh itself and the bundled applications, since most new Macintosh users had never used a mouse before, much less manipulated a graphical user interface
The GUI ( "UI" by itself is still usually pronounced . or ), graphical user interface, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and audio indicator such as primary notation, inste ...
.
Models
The computer was released in January 1984 as simply the Apple Macintosh. Following the release of theMacintosh 512K
The Macintosh 512K is a personal computer that was designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer from September 1984 to April 1986. It is the first update to the original Macintosh 128K. It was virtually identical to the previous Macint ...
in September, which expanded the memory from 128 KB to 512 KB, the original Macintosh was re-branded Macintosh 128K and nicknamed the "thin Mac". The new 512K model was nicknamed the "fat Mac". While functionally the same, as closed systems, the ''Macintosh'' and ''Macintosh 128K'' were technically two different computers, with the re-badged ''128K'' containing a completely redesigned logic board to easily accommodate both 128 KB and 512 KB RAM configurations during manufacturing. Though the RAM was still permanently soldered to the logic board, the new design allowed for easier (though unsanctioned) third-party upgrades to 512 KB. In addition, most of the newer models contained the 1984 revision ''B'' of the ROM to accommodate changes in the 400 KB floppy disk drive. System software contains support for an unreleased Macintosh 256K.
The increased RAM of the 512K was vitally important for the Macintosh as it finally allowed for more powerful software applications, such as the then-popular Microsoft Multiplan. However, Apple continued to market the ''128K'' for over a year as an entry-level computer, the mid-level ''512K'' and high-end ''Lisa Lisa or LISA may refer to:
People
People with the mononym
* Lisa Lisa (born 1967), American actress and lead singer of the Cult Jam
* Lisa (Japanese musician, born 1974), stylized "LISA", Japanese singer and producer
* Lisa Komine (born 1978), J ...
'' (and claiming that it could be easily expanded should the user ever need more RAM).
Expansion
Jobs stated that because "customization really is mostly software now ... most of the options in other computers are in Mac", unlike the Apple II the Macintosh 128K did not need slots, which he described as costly and requiring larger size and more power. It was not officially upgradable by the user and only Apple service centers were permitted to open the case. There were third parties that did offer RAM upgrades and even memory and CPU upgrades, allowing the original 128 kB Macintosh to be expanded to a 4 MB 32-bit data path, 68020 CPU (16 MHz), 68881 FPU (16 MHz), 68851 MMU (16 MHz) with an external SCSI port (with a ribbon cable out the clock battery door, internal SCSI hard drive (20 MB Rodime) and a piezo-electric fan for cooling. This upgrade was featured on a ''Macworld'' magazine cover titled "Faster than a Vax" in August 1986. All accessories were external, such as theMacCharlie
The MacCharlie is a hardware add-on for the Apple Macintosh that was made by Dayna Communications. The name refers to an IBM PC advertising campaign of the time featuring Charlie Chaplin's "Little Tramp" character.
It allows users to run DO ...
that added IBM PC compatibility. There was no provision for adding internal storage, more RAM or any upgrade cards; however, some of the Macintosh engineers objected to Jobs's ideas and secretly developed workarounds for them. As an example, the Macintosh was supposed to have only 17 address lines on the motherboard, enough to support 128 KB of system RAM, but the design team added two address lines without Jobs's knowledge, making it possible to expand the computer to 512 KB, although the actual act of upgrading system RAM was difficult and required piggybacking additional RAM chips atop the onboard 4164 chips. In September 1984, after months of complaints over the Mac's inadequate RAM, Apple released an official 512 KB machine. Although this had always been planned from the beginning, Steve Jobs maintained if the user desired more RAM than the Mac 128 provided, he should simply pay extra money for a Mac 512 rather than upgrade the computer himself. When the Mac 512 was released, Apple rebranded the original model as "Macintosh 128k" and modified the motherboard to allow easier RAM upgrades. Improving on the hard-wired RAM thus required a motherboard replacement (which was priced similarly to a new computer), or a third-party chip replacement upgrade, which was not only expensive but would void Apple's warranty. The difficulty of fitting software into its limited free memory, coupled with the new interface and event-driven programming
In computer programming, event-driven programming is a programming paradigm in which the flow of the program is determined by events such as user actions ( mouse clicks, key presses), sensor outputs, or message passing from other programs or t ...
model, discouraged software vendors from supporting it, leaving the 128K with a relatively small software library. Whereas the Macintosh Plus
The Macintosh Plus computer is the third model in the Macintosh line, introduced on January 16, 1986, two years after the original Macintosh and a little more than a year after the Macintosh 512K, with a price tag of US$2,599. As an evolutiona ...
, and to a lesser extent the Macintosh 512K
The Macintosh 512K is a personal computer that was designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer from September 1984 to April 1986. It is the first update to the original Macintosh 128K. It was virtually identical to the previous Macint ...
, are compatible with much later software, the 128K is limited to specially crafted programs. A stock Mac 128K with the original 64K ROM is incompatible with either Apple's external 800 KB drive with HFS or Apple's Hard Disk 20
The Macintosh Hard Disk 20 was the first hard drive developed by Apple Computer specifically for use with the Macintosh 512K. Introduced on September 17, 1985, it was part of Apple's long-awaited solution toward completing the Macintosh Offi ...
. A Mac 128K that has been upgraded with the newer 128 KB ROM (called a Macintosh 128Ke) can use internal and external 800 KB drives with HFS, as well as the HD20. Both can print on an AppleShare network, but neither can do file sharing because of their limited RAM.
OEM upgrades
By early 1985 much Macintosh software required 512K of memory. Apple sold an official memory upgrade for the Macintosh 128K, which included a motherboard replacement effectively making it a Macintosh 512K, for the price of . Additionally, Apple offered an 800 KB floppy disk drive kit, including updated 128K ROMs. Finally, a Mac 128K could be upgraded to aMacintosh Plus
The Macintosh Plus computer is the third model in the Macintosh line, introduced on January 16, 1986, two years after the original Macintosh and a little more than a year after the Macintosh 512K, with a price tag of US$2,599. As an evolutiona ...
by swapping the logic board as well as the case back (to accommodate the slightly different port configuration) and optionally adding the Macintosh Plus
The Macintosh Plus computer is the third model in the Macintosh line, introduced on January 16, 1986, two years after the original Macintosh and a little more than a year after the Macintosh 512K, with a price tag of US$2,599. As an evolutiona ...
extended keyboard. Any of the kits could be purchased alone or together at any time, for a partial or full upgrade for the Macintosh 128K. All upgrades were required to be performed by professional Apple technicians, who reportedly refused to work on any Macintosh upgraded to 512K without Apple's official upgrade, which at was much more expensive than about for third-party versions.
Credits
 The original Macintosh was unusual in that it included the signatures of the Macintosh Division as of early 1982 molded on the inside of the case. The names were Peggy Alexio, Colette Askeland,
The original Macintosh was unusual in that it included the signatures of the Macintosh Division as of early 1982 molded on the inside of the case. The names were Peggy Alexio, Colette Askeland, Bill Atkinson
Bill Atkinson (born March 17, 1951) is an American computer engineer and photographer. Atkinson worked at Apple Computer from 1978 to 1990.
Atkinson was the principal designer and developer of the graphical user interface (GUI) of the Apple ...
, Steve Balog, Bob Belleville, Mike Boich
Mike Boich was a major figure at Apple Computer who was in charge of demonstrating the first Macintosh to software developers and potential customers. He is notable as a technology evangelist who persuaded developers to write computer software. ...
, Bill Bull, Matt Carter, Berry Cash, Debi Coleman, George Crow, Donn Denman, Christopher Espinosa, Bill Fernandez
Bill Fernandez is a user-interface architect and innovator who was Apple Computer's first full time employee when they incorporated in 1977 and was issued badge number 4. He is the son of Jeryy Fernandez and Bambi Fernandez (both Stanford Un ...
, Martin Haeberli, Andy Hertzfeld
Andrew Jay Hertzfeld (born April 6, 1953) is an American software engineer and innovator who was a member of the original Apple Macintosh development team during the 1980s. After buying an Apple II in January 1978, he went to work for Apple ...
, Joanna Hoffman
Joanna Karine Hoffman (born July 27, 1955) is a Polish-American marketing executive. She was one of the original members of both the Apple Computer Macintosh team and the NeXT team. At the time she began at Apple Computer, the Mac was "still a r ...
, Rod Holt, Bruce Horn
Bruce Lawrence Horn (born 1960) is a programmer and creator. He created the Macintosh Finder and the Macintosh Resource Manager for Apple Computer. His signature is amongst those molded to the case of the Macintosh 128K. He is a distinguished e ...
, Hap Horn, Brian Howard, Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
, Larry Kenyon, Patti King, Daniel Kottke
Daniel Kottke () is an American businessman known for being a college friend of Steve Jobs and one of the first employees of Apple Inc.
Early life and education
Kottke was born on April 4, 1954, in Bronxville, New York.
Kottke first met Steve ...
, Angeline Lo, Ivan Mach, Jerrold Manock, Mary Ellen McCammon, Vicki Milledge, Mike Murray, Ron Nicholson Jr., Terry Oyama, Benjamin Pang, Jef Raskin
Jef Raskin (born Jeff Raskin; March 9, 1943 – February 26, 2005) was an American human–computer interface expert best known for conceiving and starting the Macintosh project at Apple in the late 1970s.
Early life and education
Jef Raskin ...
, Ed Riddle, Brian Robertson, Dave Roots, Patricia Sharp, Burrell Smith
Burrell Carver Smith (born December 16, 1955) is an American engineer who, while working at Apple Computer, designed the motherboard (digital circuit board) for the original Macintosh. He was Apple employee #282, and was hired in February 1979, i ...
, Bryan Stearns, Lynn Takahashi, Guy "Bud" Tribble, Randy Wigginton
Randy Wigginton was one of Apple Computer's first employees (#6), creator of MacWrite, Full Impact, and numerous other Mac applications. He used to work in development at eBay, Quigo, Inc and Move.com. In November 2010, he left his position as ...
, Linda Wilkin, Steve Wozniak
Stephen Gary Wozniak (; born August 11, 1950), also known by his nickname "Woz", is an American electronics engineer, computer programmer, philanthropist, inventor, and technology entrepreneur. In 1976, with business partner Steve Jobs, he c ...
, Pamela Wyman and Laszlo Zidek.
The Macintosh 128/512K models also included Easter eggs
Easter eggs, also called Paschal eggs, are eggs that are decorated for the Christian feast of Easter, which celebrates the resurrection of Jesus. As such, Easter eggs are common during the season of Eastertide (Easter season). The oldest tra ...
in the OS ROM. If the user went to the system debugger and typed G 4188A4, a graphic reading "Stolen from Apple Computers" would appear in the upper left corner of the screen. This was designed to prevent unauthorized cloning of the Macintosh after numerous Apple II clones appeared, many of which simply stole Apple's copyrighted system ROMs. Steve Jobs allegedly planned that if a Macintosh clone appeared on the market and a court case happened, he could access this Easter egg on the computer to prove that it was using pirated Macintosh ROMs. The Macintosh SE later augmented this Easter Egg with a slideshow of 4 photos of the Apple design team when G 41D89A was entered.
Reception
Erik Sandberg-Diment of ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' in January 1984 stated that Macintosh "presages a revolution in personal computing". Although preferring larger screens and calling the lack of color a "mistake", he praised the "refreshingly crisp and clear" display and lack of fan noise. While unsure whether it would become "a second standard to Big Blue", Ronald Rosenberg of ''The Boston Globe
''The Boston Globe'' is an American daily newspaper founded and based in Boston, Massachusetts. The newspaper has won a total of 27 Pulitzer Prizes, and has a total circulation of close to 300,000 print and digital subscribers. ''The Boston Glob ...
'' wrote in February of "a euphoria that Macintosh will change how America computes. Anyone that tries the pint-size machine gets hooked by its features". The computer was indeed so compelling to buyers that one dealer in March described it as "the first $2,500 impulse item".
Gregg Williams of ''BYTE
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
'' in February found the hardware and software design (which it predicted would be "imitated but not copied") impressive, but criticized the lack of a standard second disk drive. He predicted that the computer would popularize the 3½ in floppy disk drive standard, that the Macintosh would improve Apple's reputation, and that it "will delay IBM's domination of the personal computer market." Williams concluded that the Macintosh was "the most important development in computers in the last five years. tbrings us one step closer to the ideal of computer as appliance." In the May 1984 issue Williams added, "Initial reaction to the Macintosh has been strongly, but not overpoweringly, favorable. A few traditional computer users see the mouse, the windows, and the desktop metaphor as silly, useless frills, and others are outraged at the lack of color graphics, but most users are impressed by the machine and its capabilities. Still, some people have expressed concern about the relatively small 128K-byte RAM size, the lack of any computer language sent as part of the basic unit, and the inconvenience of the single disk drive."
Jerry Pournelle
Jerry Eugene Pournelle (; August 7, 1933 – September 8, 2017) was an American scientist in the area of operations research and human factors research, a science fiction writer, essayist, journalist, and one of the first bloggers. In the 1960s ...
, also of BYTE, added that "The Macintosh is a bargain only if you can get it at the heavily discounted price offered to faculty and students of the favored 24 universities in the Macintosh consortium." He noted, however, that the Macintosh attracted people "who previously hated computers... There is, apparently, something about mice and pull-down menus and icons that appeal to people previously intimidated by A> and the like".
Timeline
See also
* Technical information on the Mac 128KReferences
External links
*Macintosh 128K profile
Low End Mac.
at Mac512.com *
The 72PPI Web Resolution Myth
Mac Essentials
Lost 1984 Videos *
Apple Macintosh before System 7
Macintosh 128K Hardware
Tips For the 128K
Support For 128K Diehard Users
The M0001 Registry
Owners of Vintage Macintosh
Inside the Macintosh 128K
The Original Macintosh, anecdotes and the people who made it
{{Authority control 128k 128k Computer-related introductions in 1984 32-bit computers