Macedonia Salutaris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Macedonia (; ) was a

 The Romans clashed with the Macedonian kingdom in three wars in the early third century BC. After defeating
The Romans clashed with the Macedonian kingdom in three wars in the early third century BC. After defeating
 Sometime after 146 BC, Gnaeus Egnatius initiated the construction of the Via Egnatia, a
Sometime after 146 BC, Gnaeus Egnatius initiated the construction of the Via Egnatia, a
 In the aftermath of the Mithridatic Wars, the Romans again launched a concerted military effort in the region. Before the war, governors had tended to be
In the aftermath of the Mithridatic Wars, the Romans again launched a concerted military effort in the region. Before the war, governors had tended to be
 Following Actium, Octavian entrusted Macedonia to the proconsul M. Licinius Crassus, grandson of Crassus the triumvir, who led a campaign into the north that lasted until 27 BC, finally subjugating the whole region south of the Danube, for which he was granted a triumph.
In the Augustan Settlement of 27 BC, provinces were divided into two categories: imperial provinces, which fell were governed by legates appointed by the Emperor, and senatorial provinces, which continued to be governed by senators who had previously served as consuls or praetors. Most of the provinces with a large military presence on the borders of the empire were Imperial provinces, but Macedonia was anomalous in being a senatorial province despite its military significance. The territories south of
Following Actium, Octavian entrusted Macedonia to the proconsul M. Licinius Crassus, grandson of Crassus the triumvir, who led a campaign into the north that lasted until 27 BC, finally subjugating the whole region south of the Danube, for which he was granted a triumph.
In the Augustan Settlement of 27 BC, provinces were divided into two categories: imperial provinces, which fell were governed by legates appointed by the Emperor, and senatorial provinces, which continued to be governed by senators who had previously served as consuls or praetors. Most of the provinces with a large military presence on the borders of the empire were Imperial provinces, but Macedonia was anomalous in being a senatorial province despite its military significance. The territories south of
 The cities of Macedonia were arranged into the League of the Macedonians (Greek: ''koinon ton Makedonon''), with its seat at Beroea. This league was a continuation of an institution first attested under Philip V. From 27 BC, they used their own "Macedonian era," in which the years were counted from the Battle of Actium in 31/30 BC. In the Imperial period, its main duties related to the Imperial cult, especially the organisation of games in honour of the emperors. It also hosted a local version of the
The cities of Macedonia were arranged into the League of the Macedonians (Greek: ''koinon ton Makedonon''), with its seat at Beroea. This league was a continuation of an institution first attested under Philip V. From 27 BC, they used their own "Macedonian era," in which the years were counted from the Battle of Actium in 31/30 BC. In the Imperial period, its main duties related to the Imperial cult, especially the organisation of games in honour of the emperors. It also hosted a local version of the
 The reforms of
The reforms of
 The reign of
The reign of
www.phl.uoc.gr/eulimene/eulimene03.pdf
/ref>
province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, encompassing the territory of the former Antigonid Kingdom of Macedonia, which had been conquered by the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
in 168 BC at the conclusion of the Third Macedonian War
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman fe ...
. The province was created in 146 BC, after the Roman general Quintus Caecilius Metellus defeated Andriscus of Macedon, the last self-styled King of Macedonia in the Fourth Macedonian War
The Fourth Macedonian War (150–148 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by the pretender Andriscus, and the Roman Republic. It was the last of the Macedonian Wars, and was the last war to seriously threaten Roman control of Greece until the First ...
. The province incorporated the former Kingdom of Macedonia with the addition of Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, and parts of Illyria
In classical and late antiquity, Illyria (; , ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; , ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.
The Ancient Gree ...
, Paeonia and Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
.
During the Republican period, the province was of great military significance, as the main bulwark protecting the Aegean region from attacks from the north. The Via Egnatia, which crossed the province from west to east was of great strategic importance, providing the main overland link between Rome and its domains in the Eastern Mediterranean. In this period, campaigns against the Dardani
The Dardani (; ; ) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Kingdom of Dardania, Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their society wa ...
and Scordisci
The Scordisci (; ) were an Iron Age cultural group who emerged after the Celtic settlement of Southeast Europe, and who were centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morav ...
to the north and the Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
to the east were nearly constant. By the first century BC, the province notionally extended to the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
.
Macedonia was a central theatre for several campaigns of the civil wars at the end of the Republic, including the Battles of Pharsalus and Philippi
Philippi (; , ''Phílippoi'') was a major Greek city northwest of the nearby island, Thasos. Its original name was Crenides (, ''Krēnĩdes'' "Fountains") after its establishment by Thasian colonists in 360/359 BC. The city was renamed by Phili ...
. During the Second Triumvirate
The Second Triumvirate was an extraordinary commission and magistracy created at the end of the Roman republic for Mark Antony, Lepidus, and Octavian to give them practically absolute power. It was formally constituted by law on 27 November ...
, it fell within Marc Antony's sphere. Several important Roman military colonies were established in Macedonia in this period. After the province came under the control of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
following the Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between Octavian's maritime fleet, led by Marcus Agrippa, and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, near the former R ...
in 30 BC, the northern sections were split off as the provinces of Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
, Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
and Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
, meaning that the province lost much of its military role in defending the Danube border, but it remained important for supply purposes and as a source of military manpower. Until AD 15 and again after AD 44, Macedonia was a senatorial province, governed by a proconsul
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a Roman consul, consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority.
In the Roman Republic, military ...
.
Throughout the Imperial period, Macedonia was a prosperous region with several thriving cities, notably Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
and Philippi
Philippi (; , ''Phílippoi'') was a major Greek city northwest of the nearby island, Thasos. Its original name was Crenides (, ''Krēnĩdes'' "Fountains") after its establishment by Thasian colonists in 360/359 BC. The city was renamed by Phili ...
. These communities were organised in a similar way to other cities of the Roman Empire and were largely self-governing. Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
was the main language of the region, but Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
was used for official purposes and in the Roman colonies. There were substantial Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
communities in the province by the mid-first century AD.
In late antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
, the province was split into several smaller units, but the old provincial capital, Thessalonica, became the regional centre for the Balkan region and was briefly an Imperial capital under Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Λικίνιος; c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign, he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan that ...
. The provincial system gradually faded away, until it was replaced altogether by the theme system in the mid-seventh century AD, but the region continued to form part of the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
until the end of the fourteenth century.
History
Macedonian Wars

 The Romans clashed with the Macedonian kingdom in three wars in the early third century BC. After defeating
The Romans clashed with the Macedonian kingdom in three wars in the early third century BC. After defeating Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (, ; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of ...
in the Third Macedonian War
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman fe ...
, Rome abolished the Macedonian monarchy and divided Macedon into four client republics, called , with capitals located at Amphipolis, Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
, Pella
Pella () is an ancient city located in Central Macedonia, Greece. It served as the capital of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. Currently, it is located 1 km outside the modern town of Pella ...
, and Pelagonia, which were members of a federal league, the League of the Macedonians. Numismatic evidence indicates that the cult of Roma was introduced at this time, being depicted on coins of Amphipolis, Pella
Pella () is an ancient city located in Central Macedonia, Greece. It served as the capital of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. Currently, it is located 1 km outside the modern town of Pella ...
, and Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
in this period. Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
had been separated from the Macedonian monarchy already, following the Second Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. ...
and a separate Thessalian League was created with Roman permission in 194 BC, with Zeus Eleutherius ('of Freedom') and Athena Itonia as its patron deities. Its coinage superseded that of the individual Thessalian cities and continued until the end of the first century BC.
The kingdom was briefly reunited in 150 BC by the pretender Andriscus
Andriscus (, ''Andrískos''; 154/153 BC – 146 BC), also often referenced as Pseudo-Philip, was a Greek pretender who became the last independent king of Macedon in 149 BC as Philip VI (, ''Philipos''), based on his claim of being Philip, a n ...
(or 'Pseudo-Philip'), leading to the Fourth Macedonian War
The Fourth Macedonian War (150–148 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by the pretender Andriscus, and the Roman Republic. It was the last of the Macedonian Wars, and was the last war to seriously threaten Roman control of Greece until the First ...
. After defeating Andriscus near Pydna in 148 BC, Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus (c. 188 BC – 116 BC/115 BC) was a statesman and general of the Roman Republic during the second century BC. He was praetor in 148 BC, consul in 143 BC, the Proconsul of Hispania Citerior in 142 BC an ...
made Macedonia into Rome's fifth provincia - the first new province since the creation of Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a Roman province located in Hispania (on the Iberian Peninsula) during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of moder ...
and Citerior in 197 BC. Surviving sources do not explicitly discuss how or why it was decided to convert the region into a permanent province. A number of factors may have been involved, including increased familiarity with territorial expansion, the proven failure of the previous system to maintain the peace, the desire for a new base from which further military expeditions could be undertaken in order to acquire booty and triumphs, and the desire for further tax revenue. The four republics continued to exist as subdivisions of the province, as did the federal league. The date of the establishment of the province in autumn 148 BC is indicated by the epoch date of the provincial era, but in practice it may have been a gradual process.
Republican province
At its creation, the province of Macedonia encompassedMacedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
itself, Paeonia and parts of Illyria
In classical and late antiquity, Illyria (; , ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; , ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.
The Ancient Gree ...
, Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
to the south, and Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
to the west. Notionally, the northern border ran from Lissus on the Adriatic coast, eastwards until it reached the Hebrus river, which formed the eastern border with Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
. These borders were only loosely defined and dependent on the military competence of the governors, with Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
claiming that "for the governors of Macedonia, the borders were always the same as those marked by swords and shields." The capital was Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
and the governor held proconsular status.
Two years after the foundation of the new province, in 146 BC, Romans defeated the Achaean League
The Achaean League () was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era confederation of polis, Greek city-states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea (ancient region), Achaea in the northwestern Pelopon ...
in the Achaean War
The Achaean War of 146 BC was fought between the Roman Republic and the Greek Achaean League, an alliance of Achaean and other Peloponnesian states in ancient Greece. It was the final stage of Rome's conquest of mainland Greece, taking place jus ...
and gained control of the rest of Mainland Greece
Greece is a country in Southeastern Europe, on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. It is bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cret ...
. Scholars disagree on whether or not Achaia was formally incorporated into the province of Macedonia following this defeat, but intermittent interventions in Achaian affairs by the governors are attested.
Via Egnatia
Roman road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Em ...
, which began at Dyrrhachium on the Adriatic coast opposite the terminus of the Via Appia
The Appian Way (Latin and Italian: Via Appia) is one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, in southeast Italy. Its importance is indicated by its common name, recor ...
in Italy, stretched across the Pindus mountains and continued through Macedonia to Thessalonica, and from there to Cypsela, on the east bank of the Hebrus river. This stretch was completed by 120 BC; it followed a pre-existing route, but was a more solid, level road than the previous road, with a width of between three and six metres. A second road from the Adriatic coast at Apollonia, which joined the main Via Egnatia somewhere inland was added shortly after 120 BC. Later in the second century BC, the eastern end of the road was extended all the way to the Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
. The road was important for military and economic purposes, providing the main overland link between Rome and its domains in the Eastern Mediterranean.
Northern and eastern campaigns
Macedonia was of central importance to Roman military strategy in this period as a bulwark against attacks from the north. TheDardani
The Dardani (; ; ) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Kingdom of Dardania, Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their society wa ...
to the northwest, had initially supported the Romans in their conquest of Macedonia, but after 148 BC, they increasingly came into conflict with the Romans. There were also occasional conflicts with the Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
to the east. However, the key enemy of the Romans in this period were the Scordisci
The Scordisci (; ) were an Iron Age cultural group who emerged after the Celtic settlement of Southeast Europe, and who were centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morav ...
, a Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
group that largely supplanted the Dardanians as the most powerful group in the central Balkans. They first invaded Macedonia in 149 BC during the Fourth Macedonian War and had to be driven out by Metellus.
In the first years of the province two pretenders attempted to restore the Macedonian kingdom. The first, Alexander, invaded from Thrace in 148 BC and was defeated by Metellus. The second, referred to in the sources as 'Pseudo-Philip' or 'Pseudo-Perseus' also invaded from the east, in 143 or 142, with an army of up to 16,000 men, but was defeated by the quaestor
A quaestor ( , ; ; "investigator") was a public official in ancient Rome. There were various types of quaestors, with the title used to describe greatly different offices at different times.
In the Roman Republic, quaestors were elected officia ...
Tremellus Scrofa. The Scordisci invaded in 141 BC and defeated a Roman army commanded by Decimus Junius Silanus Manlianus or, less likely, Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica. In belated response to this defeat, Marcus Cosconius launched an attack on the Scordisci in 135 BC, defeating them in Thrace. The delay may have been because Roman attention was focussed on the construction of the Via Egnatia.
In 119 BC, the Scordisci invaded again, ravaging the area near Stobi
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Ancient Rome, Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia ...
. The praetor Sextus Pompeius met the forces in battle and was killed, leaving his quaestor Marcus Annius to regroup and drive the Scordisci out, defeating a second invasion with the help of the Thracians. Following this set-back, a series of consuls were sent to Macedonia, apparently to settle the threat from the Scordisci decisively. The first of these, Quintus Fabius Maximus Eburnus arrived in 115 BC but his activities are not attested. In 114 BC, his successor, Gaius Porcius Cato launched a large-scale invasion, but he was defeated and nearly the whole army was killed. The Romans dispatched several further commanders, Gaius Caecilius Metellus Caprarius in 113 BC and Marcus Livius Drusus in 112, who inflicted defeats on the Thracians and the Scordisci respectively. From 110 to 107 BC, Marcus Minucius Rufus campaigned against the Scordisci and the Bessian tribe of Thracians to the east, bringing an end to their raids for about twenty years.
After this, the Romans turned their attention to the eastern border. The Romans defeated some Thracians under an unnamed commander in 104 BC. In 101 or 100 BC, Titus Didius conquered an area referred to as the "Caenic Chersonese" (exact location unknown, but some region of the Thracian coast). Another unnamed commander defeated the Maedian Thracians in the east and the Dardanians in the northwest in 97 BC. Gaius Sentius was defeated by the Maedi in 92 BC and was involved in a conflict with a Thracian king called Sordinus in 89 BC, only achieving victory after a struggle. From 87 BC onwards, Thracian forces allied with Mithridates VI attacked Macedonia, as part of the First Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War /ˌmɪθrəˈdædɪk/ (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule ...
. In that year, Gaius Sentius' legate Quintus Bruttius Sura repulsed an invasion from the Mithridatic general Archelaus. In 84 BC a force of Scordisci, Dardianians and Maedi penetrated all the way to Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
and sacked the sanctuary, before they were violently expelled by Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus (consul 83 BC).
praetor
''Praetor'' ( , ), also ''pretor'', was the title granted by the government of ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected ''magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to disch ...
s or propraetor
In ancient Rome, a promagistrate () was a person who was granted the power via '' prorogation'' to act in place of an ordinary magistrate in the field. This was normally ''pro consule'' or ''pro praetore'', that is, in place of a consul or praet ...
s, usually in office for a single year. Henceforth, they were consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states thro ...
s or proconsul
A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a Roman consul, consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority.
In the Roman Republic, military ...
s and often held command for several years. Appius Claudius Pulcher had some success in the Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; , ; , ''Rodopi''; ) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak ...
in 77 BC, but was replaced after his death from illness by C. Scribonius Curio, who was given a force of five legions. He campaigned from 75 to 74 BC, becoming the first Roman commander to lead an army to the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and reduced the Dardanians to submission. Between 73 and 71 BC, Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus led another force of five legions against the Bessi and entered Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
, bringing the Greek cities on the west coast of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
under Roman control and campaigning against the Getae
The Getae or Getai ( or , also Getans) were a large nation who inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania, throughout much of Classical Antiquity. The main source of informa ...
all the way to the mouth of the Danube. These campaigns were intended to secure the northern border so that Macedonia and Greece would no longer be threatened by raids and to put Rome in a better position to confront Mithridates VI in future conflicts. Efforts to consolidate these enormous conquests continued for decades, often meeting with rebuffs, most notably the two campaigns of Gaius Antonius Hybrida
Gaius Antonius Hybrida (flourished 1st century BC) was a politician of the Roman Republic. He was the second son of Marcus Antonius (orator), Marcus Antonius and brother of Marcus Antonius Creticus; his mother is unknown. He was also the uncle o ...
in the north ca. 62-61 BC, in which he was defeated disastrously by the Dardianians and at the Battle of Histria by the Bastarnae
The Bastarnae, Bastarni or Basternae, also known as the Peuci or Peucini, were an ancient people who are known from Greek and Roman records to have inhabited areas north and east of the Carpathian Mountains between about 300 BC and about 300 AD, ...
.
The governorship of Lucius Calpurnius Piso Caesoninus from 57 to 55 BC is the subject of Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
's '' In Pisonem'', in which Caesoninus is accused of corruption, abuse, and murder of the provincials on a grand scale, as well as shaving sparked another invasion by the Dardianians and Bessi that even placed Thessaloniki under siege, but the speech may not give an accurate picture of Caesoninus' conduct.
Civil wars
Macedonia was one of the main arenas of the civil wars at the end of the Roman Republic. WhenJulius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
crossed the Rubicon in 49 BC, starting Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected ret ...
, his opponents, led by Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. ...
abandoned Italy and retreated to Macedonia with five legions. Around two hundred Senators set themselves up in Thessalonica as a Senate in exile and raised a further legion from veterans in Macedonia and Crete. At the beginning of 48 BC, Caesar crossed the Adriatic and besieged Pompey at Dyrrhachium. During this period, one Menedemos came to Caesar as a delegate from "the part of the province that was called free" offering him support; he was subsequently captured by Pompey's forces and executed. After several months, Pompey broke out of Dyrrhachium and headed southeast toward Thessaly. On the march he was met by another Macedonian, Acornion of Dionysiopolis, who came offering an alliance with Burebista, the king of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus ro ...
. However, this offer had come too late to be of use to Pompey. Caesar decisively defeated him at the Battle of Pharsalus in August 48 BC and he fled for Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. On taking control of the province, Caesar separated it from Greece to the south for the first time. This division was reversed after his death in 44 BC, but would be revived in the Imperial period.
After the assassination of Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar, the Roman dictator, was assassinated on the Ides of March (15 March) 44 BC by a group of senators during a Roman Senate, Senate session at the Curia of Pompey, located within the Theatre of Pompey in Ancient Rome, Rome. The ...
in 44 BC, the assassins, led by Brutus and Cassius, also fled east. Caesar's former lieutenant, Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman people, Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the Crisis of the Roman Republic, transformation of the Roman Republic ...
passed a law requiring the governor, Quintus Hortensius Hortalus to hand the province over to Antony. Instead, he chose to place the province under Brutus' control - a move that was recognised by the Senate in 43 BC. This led Mark Antony to ally with Octavian
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in ...
in the Second Triumvirate
The Second Triumvirate was an extraordinary commission and magistracy created at the end of the Roman republic for Mark Antony, Lepidus, and Octavian to give them practically absolute power. It was formally constituted by law on 27 November ...
and invade Macedonia, defeating Brutus and his forces at the Battle of Philippi in 42 BC.
After Philippi, Macedonia fell within the territories assigned to Mark Antony and it was governed by his legates until war broke out between Octavian and Antony in 32 BC and Antony was defeated in 31 BC at the Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between Octavian's maritime fleet, led by Marcus Agrippa, and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, near the former R ...
, after which Macedonia and the rest of the Eastern Mediterranean came under Octavian's control, marking the beginning of the Principate
The Principate was the form of imperial government of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the Dominate. The principate was ch ...
.
Principate
 Following Actium, Octavian entrusted Macedonia to the proconsul M. Licinius Crassus, grandson of Crassus the triumvir, who led a campaign into the north that lasted until 27 BC, finally subjugating the whole region south of the Danube, for which he was granted a triumph.
In the Augustan Settlement of 27 BC, provinces were divided into two categories: imperial provinces, which fell were governed by legates appointed by the Emperor, and senatorial provinces, which continued to be governed by senators who had previously served as consuls or praetors. Most of the provinces with a large military presence on the borders of the empire were Imperial provinces, but Macedonia was anomalous in being a senatorial province despite its military significance. The territories south of
Following Actium, Octavian entrusted Macedonia to the proconsul M. Licinius Crassus, grandson of Crassus the triumvir, who led a campaign into the north that lasted until 27 BC, finally subjugating the whole region south of the Danube, for which he was granted a triumph.
In the Augustan Settlement of 27 BC, provinces were divided into two categories: imperial provinces, which fell were governed by legates appointed by the Emperor, and senatorial provinces, which continued to be governed by senators who had previously served as consuls or praetors. Most of the provinces with a large military presence on the borders of the empire were Imperial provinces, but Macedonia was anomalous in being a senatorial province despite its military significance. The territories south of Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; ; Ancient: , Katharevousa: ; ; "hot gates") is a narrow pass and modern town in Lamia (city), Lamia, Phthiotis, Greece. It derives its name from its Mineral spring, hot sulphur springs."Thermopylae" in: S. Hornblower & A. Spaw ...
and the Ceraunian Mountains now became the separate province of Achaia. This province included the territory which would become the province of Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
(later ''Epirus Vetus'') under Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
.
Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballi ...
was split off as a separate military command some time before 10 BC, and had become a separate province by AD 6. Territories to the northwest of Macedonia in Illyricum were separated off into the provinces of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
and Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
. In AD 15, complaints about the corruption of the governors led Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
to convert Macedonia and Achaia into imperial provinces, under the control of the governor of Moesia, but Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
made them both Senatorial provinces once more in AD 44 In the same year, the portion of Macedonia between the Hebrus and Nestus rivers in the east and the island of Thasos
Thasos or Thassos (, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of 380 km2 and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate regiona ...
were handed over to the newly created province of Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
.
The establishment of new provinces to the north and the consolidation of Roman control in the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
in general led to a decline in the military importance of Macedonia to Rome, as the legions defending the northern border were henceforth based in Dalmatia, Moesia, and Thrace. Nevertheless, the province continued to provide a vital role in the transport of supplies from Italy to the northern and eastern borders of the Empire, as well as serving as a source of manpower.
Organisation
The cities of the province had a range of different statuses. Six Roman colonies (''coloniae'') were established in the Triumviral period: Cassandrea, established in the late 40s BC by the proconsul Quintus Hortensius Hortalus, Philippi (''Colonia Iulia Augusta Philippensis'') founded by Antony's legate Quintus Paquius Rufus, Dium,Pella
Pella () is an ancient city located in Central Macedonia, Greece. It served as the capital of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. Currently, it is located 1 km outside the modern town of Pella ...
, Byllis, and Dyrrhachium. These communities were settled with veterans who became or remained Roman citizen
Citizenship in ancient Rome () was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cu ...
s. Local inhabitants of these communities were not expelled, but they did not receive citizenship of the new colonies or of Rome, except perhaps for some members of the local elite. Some scholars have suggested that these ''coloniae'' formed "double communities," with the old Greek city-state (''polis
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατ ...
'') and the new ''colonia'' existing side-by-side. This now seems unlikely, but has not been disproven. Stobi
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Ancient Rome, Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia ...
was a ''municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (: ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ('duty holders'), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the privileges ...
''. Amphipolis, Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
, Abdera, and Maroneia
Maroneia () is a village and a former municipality in Rhodope regional unit, East Macedonia and Thrace, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Maroneia-Sapes, of which it is a municipal unit. The munic ...
held the status of 'free cities' (''civitates liberae''), and Edessa
Edessa (; ) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, in what is now Urfa or Şanlıurfa, Turkey. It was founded during the Hellenistic period by Macedonian general and self proclaimed king Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Sel ...
was probably an 'allied city' (''civitas foederata'').
In the Republican period a cult of "the Roman Benefactors" (''Rhomaioi euergetai''), the goddess Roma, and Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
"Eleutherios" ("of freedom") developed in Macedonia. This cult is first attested in 95 or possibly 119 BC, but probably dates back to the establishment of the province. It endured in the Imperial period. The Roman Imperial cult
The Roman imperial cult () identified emperors and some members of their families with the divinely sanctioned authority ('' auctoritas'') of the Roman State. Its framework was based on Roman and Greek precedents, and was formulated during the ...
was introduced under Augustus, with numismatic and epigraphic evidence attesting to the worship of Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
as ''Divus Julius'' following Actium. Under Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
, cults of Augustus and of Livia
Livia Drusilla (30 January 59 BC
AD 29) was List of Roman and Byzantine empresses, Roman empress from 27 BC to AD 14 as the wife of Augustus, the first Roman emperor. She was known as Julia Augusta after her formal Adoption ...
are attested as well, while divine honours for Caligula
Gaius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), also called Gaius and Caligula (), was Roman emperor from AD 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the Roman general Germanicus and Augustus' granddaughter Ag ...
and subsequent emperors are attested during their own lifetimes.
 The cities of Macedonia were arranged into the League of the Macedonians (Greek: ''koinon ton Makedonon''), with its seat at Beroea. This league was a continuation of an institution first attested under Philip V. From 27 BC, they used their own "Macedonian era," in which the years were counted from the Battle of Actium in 31/30 BC. In the Imperial period, its main duties related to the Imperial cult, especially the organisation of games in honour of the emperors. It also hosted a local version of the
The cities of Macedonia were arranged into the League of the Macedonians (Greek: ''koinon ton Makedonon''), with its seat at Beroea. This league was a continuation of an institution first attested under Philip V. From 27 BC, they used their own "Macedonian era," in which the years were counted from the Battle of Actium in 31/30 BC. In the Imperial period, its main duties related to the Imperial cult, especially the organisation of games in honour of the emperors. It also hosted a local version of the Olympic games
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international Olympic sports, sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a Multi-s ...
, and from AD 229, games in honour of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
. From the time of the emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
until the end of the second century AD, the league minted its own coinage, with the thunderbolt, a traditional symbol of Macedon on the reverse. In the third century AD, the league continued to mint coinage, but with new types, relating to athletic competition. Through this institution, Macedonian identity and loyalty to the Roman emperor were closely aligned.
There was a separate civic league for the Thessalians.
Late Antiquity
 The reforms of
The reforms of Diocletian
Diocletian ( ; ; ; 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. As with other Illyri ...
around AD 293 saw provinces replaced by dioceses
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
and praetorian prefecture
The praetorian prefecture (; in Ancient Greek, Greek variously named ) was the largest administrative division of the Late Antiquity, late Roman Empire, above the mid-level Roman diocese, dioceses and the low-level Roman province, provinces. Praeto ...
s as the first order subdivision of the Roman Empire and provinces began to be split into smaller units. The province of Macedonia was initially part of the Diocese of Moesia, but subsequently became part of a new Diocese of Macedonia (administered from Thessaloniki), one of three dioceses comprising the praetorian prefecture of Illyricum
The praetorian prefecture of Illyricum (; , also termed simply the prefecture of Illyricum) was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Later Roman Empire, Late Roman Empire was divided.
The administrative centre of the prefecture wa ...
(administered from Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous province of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians ...
until 379, then from Thessaloniki). Meanwhile, the province of Macedonia was divided into a number of smaller provinces.
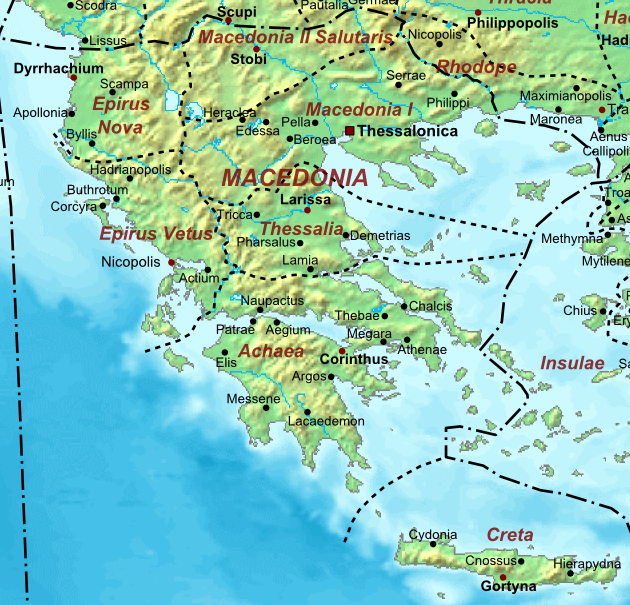
* '' Epirus Nova'' ("New Epirus") or ''Illyria Graeca'' or ''Illyris proper'', which was established by Diocletian, was the first province to be divided off. Dyrrachium (or Epidamnus) was the capital. The region of ''Epirus Nova'' corresponded to a portion of Illyria
In classical and late antiquity, Illyria (; , ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; , ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyrians.
The Ancient Gree ...
that was then "partly Hellenic and partly Hellenized".
*''Macedonia Prima'' ("First Macedonia"), encompassing most of the Kingdom of Macedonia, coinciding with most of the modern Greek region of Macedonia, and had Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
as its capital.
*''Macedonia Salutaris'' ("Wholesome Macedonia"), also known as ''Macedonia Secunda'' ("Second Macedonia"), partially encompassing both Pelagonia and Dardani
The Dardani (; ; ) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Kingdom of Dardania, Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their society wa ...
a and containing the whole of Paeonia. The province mostly coincides with the present-day North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
. The town of Stobi
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Ancient Rome, Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia ...
located to the junction of the Crna Reka and Vardar
The Vardar (; , , ) or Axios (, ) is the longest river in North Macedonia and a major river in Greece, where it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is long, out of which are in Greece, and drains an area of around . The maximum depth of ...
rivers, the former capital of Paeonia, became the provincial capital.
*''Thessalia'' encompassed the area of ancient Thessaly
Thessaly or Thessalia (Attic Greek: , ''Thessalía'' or , ''Thettalía'') was one of the traditional regions of Ancient Greece. During the Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean period, Thessaly was known as Aeolia, a name that continued to be used for one of ...
, in the south of ancient Macedonia
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
and was subdivided into Thessalia Prima and Thessalia Secunda.
When the Prefecture of Macedonia was divided between the Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Eastern Empires in 379, the Macedonian provinces were included in Eastern Illyricum
The praetorian prefecture of Illyricum (; , also termed simply the prefecture of Illyricum) was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided.
The administrative centre of the prefecture was Sirmium (375–379 ...
. With the permanent division of the Empire in 395, Macedonia passed to the Eastern Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
.
Jewish communities were present in the Balkans during this period of administrative reform. Koine Greek
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the koiné language, common supra-regional form of Greek language, Greek spoken and ...
-speaking Jews, part of the broader Hellenized diaspora, are attested in cities such as Stobi
Stobi or Stoboi (; ; ; ), was an ancient town of Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia, later conquered by Macedon, and finally turned into the capital of the Ancient Rome, Roman province of Macedonia Salutaris. It is located near Gradsko, North Macedonia ...
, Naissus, and Salona
Salona (, ) was an ancient city and the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia and near to Split, in Croatia. It was one of the largest cities of the late Roman empire with 60,000 inhabitants. It was the last residence of the final western ...
—all located within the reorganized provinces of Illyricum and Macedonia. These Jewish populations appear to have practiced Judaism aligned with Jerusalem-based traditions, independent from the Babylonian halakhic centers of the east. Archaeological evidence from Stobi, including a synagogue with Greek mosaic inscriptions, points to a well-integrated but culturally distinct Jewish presence. These communities were likely affected by the same urban reforms and diocesan realignments as other provincial groups, and their continued presence through Late Antiquity suggests a degree of local autonomy and adaptation within imperial religious frameworks.
Economy
 The reign of
The reign of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
(27 BC14 AD) began a long period of peace, prosperity and wealth for Macedonia, although its importance in the economic standing of the Roman world diminished when compared to its neighbor, Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
.
The economy was greatly stimulated by the construction of the Via Egnatia during 130s and 120s BC, the installation of Roman merchants in the cities, and the founding of Roman colonies. The Imperial government brought, along with its roads and administrative system, an economic boom, which benefited both the Roman ruling class and the lower classes. With vast arable and rich pastures, the great ruling families amassed huge fortunes in the society based on slave labor.
The improvement of the living conditions of the productive classes brought about an increase in the number artisans and craftspeople to the region. Stonemasons, miners, blacksmiths, etc. were employed in every kind of commercial activity and craft. Greek people were also widely employed as tutors, educators and doctors throughout the Roman world.
The export economy was based essentially on agriculture and livestock, while iron, copper, and gold along with such products as timber, resin, pitch, hemp, flax, and fish were also exported. Another source of wealth was the kingdom's ports, such as Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
and Cassandreia
Cassandreia or Cassandrea (, ''Kassándreia'') was once one of the most important cities in Ancient Macedonia, founded by and named after Cassander in 316 BC. It was located on the site of the earlier Ancient Greek city of Potidaea, at the isth ...
.
List of Roman governors
Republican
Imperial
*Marcus Licinius Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115–53 BC) was a ancient Rome, Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome".Wallechinsky, Da ...
(31-27 BC)
* Marcus Primus (c.24/23 BC)
* Lucius Tarius Rufus (18-16 BC)
* Publius Vinicius (AD 2/3)
* Publius Memmius Regulus (with Achaea, between AD 31 and 37)
* Marcus Helvius Geminus (before 54)
* Marcus Julius Romulus (between 54 and 68) Werner Eck, "Über die prätorischen Prokonsulate in der Kaiserzeit. Eine quellenkritische Überlegung", ''Zephyrus'' 23/24 (1972/73), pp. 240f
* Marcus Vettius Bolanus (before 66)
* Lucius Antonius Saturninus (76/77)
* P. Tullius Varro (between 70 and 79)
* Lucius Baebius Honoratus (before 83)
* Gaius Salvius Liberalis (84/85)
* L. Cocceius Justus (c. 100)
* Q. Annius Maximus (113/114)
* M. Arruntius Claudianus (between 96 and 118)
* Octavius Antoninus (119/120)
* Lucius Varius Ambibulus (124/125)
* Junius Rufinus (between 118 and 138)
* Q. Gellius Sentius Augurinus (between 118 and 139)
* ulus rgi (c. 138)
* Sextus Pedius Hirrutus Lucilius Pollio (c. 148)
* P. Antius Orestes (164/165)
* Publius Julius Geminius Marcianus (c. 166)
* .. Au inus (between 139 and 180)
* Cornelius Rufus (between 161 and 180)
* Ti. Claudius Gordianus (between 187 and 192)
* Junius Rufinus (192/193)
* Marcus Antius Crescens Calpurnianus (c. 200)
* (M. Ulipus ?) Tertullianus Aquila (212/213 or 213/214)
* P. Aelius Coeranus (c. 224)
* T. Clodius Pupienus Pulcher Maximus (c. 223)
* Q ? ''or'' C(L.)? Valerius Rufrius Justus (between 220 and 230)
* P. Julius Junianus Martialianus (''signo'' Leontius) (between 222 and 235)
* C. Caerellius (Fufidius Annius Ravus) Pollittianus (between 222 and 235)
* Dulcitius (c. 300)
* Calliopius of Antioch (362)
Notable individuals
Saints and clerics
*Agape, Chionia, and Irene
Agape, Chionia and Irene () were sisters and Christians, Christian saints from Aquileia, martyred at Thessalonica in 304 AD. Agape and Chionia were charged with refusing to eat sacrificial offerings, whilst Irene was killed for keeping Christian b ...
(died 304)
* Agathopous, deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions.
Major Christian denominations, such as the Cathol ...
* Aristarchus of Thessalonica, 1st century
* Demophilus of Constantinople
Demophilus of Constantinople (; died 386) was a bishop of Berea and an Archbishop of Constantinople from Early 370 until he was expelled on 27 November 380.
Biography
Born of good family in Thessalonica, he was elected by the Arians to t ...
(died 386), Bishop, born in Thessalonica
* Epaphroditus, first bishop of Philippi
* Gaius, first Bishop of Thessalonica
* Lydia of Thyatira
Lydia of Thyatira () is a woman mentioned in the New Testament who is regarded as the first documented convert to Christianity in Europe. Several Christian denominations have designated her a saint.
Lydia of Thyatira and Philippi
The name, "Lyd ...
, 1st century
* Matrona of Thessalonica
* Onesimus, first bishop of Beroea
* Saint Demetrius, patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, Eastern Orthodoxy or Oriental Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, fa ...
of the city of Salonika, martyred in 306
* Theodulus, Lector
Writers
* Craterus of Amphipolis (c. 100-30 BC) Rhapsode winner in Amphiarian games * Phaedrus of Pieria (c. 15 BC – c. AD 50), fabulist * Antipater of Thessalonica (late 1st century BC), epigrammatic poet and governor of the city *Philippus of Thessalonica Philippus of Thessalonica ( Greek: Φίλιππος ὁ Θεσσαλονικεύς) (1st century) or Philippus Epigrammaticus was the compiler of an Anthology of Epigrammatists subsequent to Meleager of Gadara and is himself the author of 72 epigr ...
(late 1st century AD), epigrammatic poet and compiler of the Greek Anthology
The ''Greek Anthology'' () is a collection of poems, mostly epigrams, that span the Classical Greece, Classical and Byzantine periods of Greek literature. Most of the material of the ''Greek Anthology'' comes from two manuscripts, the ''Palatine ...
* Archias, epigrammatist
* Antiphanes (late 1st century), epigrammatist
* Parmenio (late 1st century), epigrammatist
* Criton of Pieria, historian
* Polyaenus
Polyaenus or Polyenus ( ; see ae (æ) vs. e; , "much-praised") was a 2nd-century Roman Macedonian author and rhetorician, known best for his ''Stratagems in War'' (), which has been preserved. He was born in Bithynia, Asia Minor. The ''Suda'' c ...
, (2nd century), military writer
* Stobaeus
Joannes Stobaeus (; ; 5th-century AD), from Stobi in Macedonia (Roman province), Macedonia, was the compiler of a valuable series of extracts from Greek authors. The work was originally divided into two volumes containing two books each. The tw ...
(5th century), anthologist of Greek authors
* Macedonius of Thessalonica (6th century), epigrammatist of Greek Anthology
The ''Greek Anthology'' () is a collection of poems, mostly epigrams, that span the Classical Greece, Classical and Byzantine periods of Greek literature. Most of the material of the ''Greek Anthology'' comes from two manuscripts, the ''Palatine ...
Physicians
* Athryilatus ofThasos
Thasos or Thassos (, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of 380 km2 and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate regiona ...
* Alexander of Pella
Pella () is an ancient city located in Central Macedonia, Greece. It served as the capital of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. Currently, it is located 1 km outside the modern town of Pella ...
* Damian of Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
* Anthemius of Edessa
Edessa (; ) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, in what is now Urfa or Şanlıurfa, Turkey. It was founded during the Hellenistic period by Macedonian general and self proclaimed king Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Sel ...
* Paul of Philippi
Philippi (; , ''Phílippoi'') was a major Greek city northwest of the nearby island, Thasos. Its original name was Crenides (, ''Krēnĩdes'' "Fountains") after its establishment by Thasian colonists in 360/359 BC. The city was renamed by Phili ...
* Theodorus of Kato Kleines, Florina
* C. Iulius Nicetas of Lyke (Lyki) in Pella
Pella () is an ancient city located in Central Macedonia, Greece. It served as the capital of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. Currently, it is located 1 km outside the modern town of Pella ...
* Aurelius Isidorus of Thessalonica
* Sextus Iulius Chariton of Amphipolis
* Servia of Thessalonica
* Lalus and Publicius Hermias of Beroea
* Aelius Nicolaus of Edessa
* Aptus of Dion/ref>
See also
* Diocese of Macedonia *Macedon
Macedonia ( ; , ), also called Macedon ( ), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, which later became the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal ...
* Macedonia (region)
Macedonia ( ) is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid-19th century. ...
References
Bibliography
* Daubner, Frank (2018). ''Makedonien nach den Königen (168 v. Chr.–14 n. Chr.)'' acedonia after the kings, 168 BC–14 AD Historia Einzelschriften, vol. 251. Stuttgart: Franz Steiner, . * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Macedonia (Roman Province) Ancient Macedonia Roman Balkans . . . . States and territories established in the 2nd century BC States and territories disestablished in the 7th century 2nd-century BC establishments in Greece 7th-century disestablishments in the Byzantine Empire 7th-century disestablishments in Europe Romanization of Southeastern Europe 140s BC establishments