MHWS on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
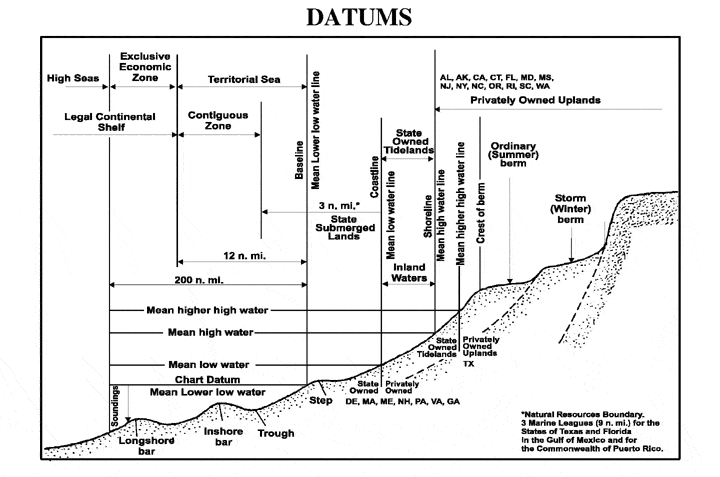 A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart. A chart datum is generally derived from some
A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart. A chart datum is generally derived from some
National Tide Centre Glossary
(retrieved 30 April 2013) and ''mean lower low water'' (MLLW). In non-tidal areas, e.g. the Baltic Sea, mean sea level (MSL) is used. A chart datum is a type of vertical datum and must not be confused with the
Australian Intergovernmental Committee on Surveying and Mapping, Permanent Committee on Tides and Mean Sea Level use the LAT to define chart datums. One advantage of using LAT for chart datums is that all predicted tidal heights must then be positive (or zero) avoiding possible ambiguity and the need to explicitly state sign. Calculation of the LAT only allows for gravitational effects so lower tides may occur in practice due to meteorological effects, such as high pressure systems.
Proudman Oceanographic Laboratory.
 A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart. A chart datum is generally derived from some
A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart. A chart datum is generally derived from some tidal phase
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables can ...
, in which case it is also known as a tidal datum. Common chart datums are ''lowest astronomical tide'' (LAT)Australian Bureau of MeteorologNational Tide Centre Glossary
(retrieved 30 April 2013) and ''mean lower low water'' (MLLW). In non-tidal areas, e.g. the Baltic Sea, mean sea level (MSL) is used. A chart datum is a type of vertical datum and must not be confused with the
horizontal datum
A geodetic datum or geodetic system (also: geodetic reference datum, geodetic reference system, or geodetic reference frame) is a global datum reference or reference frame for precisely representing the position of locations on Earth or other plan ...
for the chart.
Definitions
The followingtidal phase
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables can ...
s are commonly used in the definition of chart datums.
Lowest astronomical tide
''Lowest astronomical tide'' (LAT) is defined as the lowest tide level which can be predicted to occur under average meteorological conditions and under any combination of astronomical conditions. Many national charting agencies, including the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office and theAustralian Hydrographic Service
The Australian Hydrographic Service (formerly known as the Royal Australian Navy Hydrographic Service) is the Australian Commonwealth Government agency responsible for providing hydrographic services that meet Australia's obligations under the SO ...
,Australian Tides Manual SP9 V4.1Australian Intergovernmental Committee on Surveying and Mapping, Permanent Committee on Tides and Mean Sea Level use the LAT to define chart datums. One advantage of using LAT for chart datums is that all predicted tidal heights must then be positive (or zero) avoiding possible ambiguity and the need to explicitly state sign. Calculation of the LAT only allows for gravitational effects so lower tides may occur in practice due to meteorological effects, such as high pressure systems.
Mean high water
''Mean high water'' (MHW) is the average of all the daily tidal high water levels observed over a period of several years. In the United States this period spans 19 years and is referred to as the National Tidal Datum Epoch. InAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, the definition of the MHW is Ladder '...the line of the medium high tide between the highest tide of each
lunar month (the springs) and the lowest each lunar month (the Neaps) averaged over the year.'
Mean water
Mean lower low water
''Mean lower low water'' (MLLW) is the average height of the lowest tide recorded at a tide station each day during a 19-year recording period, known as the ''National Tidal Datum Epoch'' as used by the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. MLLW is only a mean, so some tidal levels may be negative relative to MLLW; see also #Mean low water springs. The 19-year recording period is the nearest full year count to the 18.6-year cycle of thelunar node
A lunar node is either of the two orbital nodes of the Moon, that is, the two points at which the orbit of the Moon intersects the ecliptic. The ''ascending'' (or ''north'') node is where the Moon moves into the northern ecliptic hemisphere, w ...
regression, which has an effect on tides.
Lower low water large tide
This is an average of lowest low waters taken over a fixed period of tidal predictions, as opposed to actual observations. This is the datum used for coastal charts published by the Canadian Hydrographic Service, with the average taken from 19 years of tidal predictions.Mean higher high water
Similarly, the ''mean higher high water'' (MHHW) is the average height of the highest tide recorded at a tide station each day during the recording period. It is used, among other things as a datum from which to measure the navigational clearance, or air draft, under bridges.Mean water spring
Spring tides are those when the moon is in a direct alignment with the sun (thus new or full) and in many extra-tropics places when itsdeclination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the ...
is 23.5°, its maximum. In equatorial, tropical seas, such as the Banda Sea such tides (bulges) occur when there is such an alignment and the declination of the moon is more towards its 0° average, thus more overhead or antiposed.
Mean low water springs
''Mean low water springs'' (MLWS) is the average of the water levels of each pair of successive low waters during that period of about 24 hours in each semi-lunation (approximately every 14 days), when the tidal range is greatest (spring range).Definitions of various tide related termsProudman Oceanographic Laboratory.
Mean high water springs
''Mean high water springs'' (MHWS) is the averaged highest level that spring tides reach over many years (often the last 19 years). Within this, to ensure anomalous levels are tempered, at least two successive high waters during the highest-tide 24 hours are taken. Such a local level is generally close to the " high water mark" where debris accumulates on a tidal shore on about two days six months apart (and nearby days) annually. The levels are local as some places are nearer to or form places of almost no tides in and around each ocean ( amphidromic points).Usage
Charts and tables
Charted depths and drying heights on nautical charts are given relative to chart datum. Some height values on charts, such as vertical clearances under bridges or overhead wires, may be referenced to a different vertical datum, such as mean high water springs or highest astronomical tide (HAT) (for "HAT" see tidal range). Tide tables give the height of the tide above a chart datum making it feasible to calculate the depth of water at a given point ''and'' at a given time by adding the charted depth to the height of the tide. One may calculate whether an area that dries is under water by subtracting the drying height from theiven
Iven is a municipality in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany.
Notable residents
*Georg Detlev von Flemming
Georg Detlev von Flemming (Polish: Jerzy Detloff Fleming) (3 March 1699 – 10 December 1771) was a ...
height calculated from the tide table.
Using charts and tables not based on the same geodetic datum can result in incorrect calculation of water depths.
Satellite navigation
In recent years national hydrographic agencies have spearheaded developments to establish chart datum with respect to the Geodetic Reference System 1980 (GRS 80) reference ellipsoid, thus enabling direct compatibility with satellite navigation (GNSS) positioning. Examples of this include Vertical Offshore Reference Frames (VORF) for the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office (UKHO) and Bathyelli for Naval Hydrographic and Oceanographic Service (SHOM).References
{{reflist Cartography Tide tables Vertical datums Nautical charts Zero-level elevation points